Drive Successful Sourcing Outcomes With a Robust RFP Process

- Most IT organizations do not have standard RFP templates and tools.
- Many RFPs lack sufficient requirements.
- Most RFP team members are not adequately trained on RFP best practices.
- Most IT departments underestimate the amount of time that is required to perform an effective RFP.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Vendors generally do not like RFPs
Vendors view RFPs as time consuming and costly to respond to and believe that the decision is already made. - Don’t ignore the benefits of an RFI
An RFI is too often overlooked as a tool for collecting information from vendors about their product offerings and services. - Leverage a pre-proposal conference to maintain an equal and level playing field
Pre-proposal conference is a convenient and effective way to respond to vendors’ questions ensuring all vendors have the same information to provide a quality response.
Impact and Result
- A bad or incomplete RFP results in confusing and incomplete vendor RFP responses which consume time and resources.
- Incomplete or misunderstood requirements add cost to your project due to the change orders required to complete the project.
Drive Successful Sourcing Outcomes With a Robust RFP Process Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Storyboard – Leverage your vendor sourcing process to get better results
Discover a proven process for your RFPs. Review Info-Tech’s process and understand how you can prevent your organization from leaking negotiation leverage while preventing vendors from taking control of your RFP. Our 7-phase process prevents a bad RFP from taking your time, money, and resources.
- Drive Successful Sourcing Outcomes With a Robust RFP Process Storyboard
2. Define your RFP Requirements Tool – A convenient tool to gather your requirements and align them to your negotiation strategy.
Use this tool to assist you and your team in documenting the requirements for your RFP. Use the results of this tool to populate the requirements section of your RFP.
- RFP Requirements Worksheet
3. RFP Development Suite of Tools – Use Info-Tech’s RFP, pricing, and vendor response tools and templates to increase your efficiency in your RFP process.
Configure this time-saving suite of tools to your organizational culture, needs, and most importantly the desired outcome of your RFP initiative. This suite contains four unique RFP templates. Evaluate which template is appropriate for your RFP. Also included in this suite are a response evaluation guidebook and several evaluation scoring tools along with a template to report the RFP results to stakeholders.
- RFP Calendar and Key Date Tool
- Vendor Pricing Tool
- Lean RFP Template
- Short-Form RFP Template
- Long-Form RFP Template
- Excel Form RFP Tool
- RFP Evaluation Guidebook
- RFP Evaluation Tool
- Vendor TCO Tool
- Consolidated Vendor RFP Response Evaluation Summary
- Vendor Recommendation Presentation
Infographic
Workshop: Drive Successful Sourcing Outcomes With a Robust RFP Process
Workshops offer an easy way to accelerate your project. If you are unable to do the project yourself, and a Guided Implementation isn't enough, we offer low-cost delivery of our project workshops. We take you through every phase of your project and ensure that you have a roadmap in place to complete your project successfully.
1 Foundation for Creating Requirements
The Purpose
Problem Identification
Key Benefits Achieved
Current process mapped and requirements template configured
Activities
1.1 Overview and level-setting
1.2 Identify needs and drivers
1.3 Define and prioritize requirements
1.4 Gain business authorization and ensure internal alignment
Outputs
Map Your Process With Gap Identification
Requirements Template
Map Your Process With Gap Identification
Requirements Template
Map Your Process With Gap Identification
Requirements Template
Map Your Process With Gap Identification
Requirements Template
2 Creating a Sourcing Process
The Purpose
Define Success Target
Key Benefits Achieved
Baseline RFP and evaluation templates
Activities
2.1 Create and issue RFP
2.2 Evaluate responses/proposals and negotiate the agreement
2.3 Purchase goods and services
Outputs
RFP Calendar Tool
RFP Evaluation Guidebook
RFP Respondent Evaluation Tool
3 Configure Templates
The Purpose
Configure Templates
Key Benefits Achieved
Configured Templates
Activities
3.1 Assess and measure
3.2 Review templates
Outputs
Long-Form RFP Template
Short-Form RFP Template
Excel-Based RFP Template
Further reading
Drive Successful Sourcing Outcomes With a Robust RFP Process
Leverage your vendor sourcing process to get better results.
EXECUTIVE BRIEF
Drive Successful Sourcing Outcomes with a Robust RFP Process
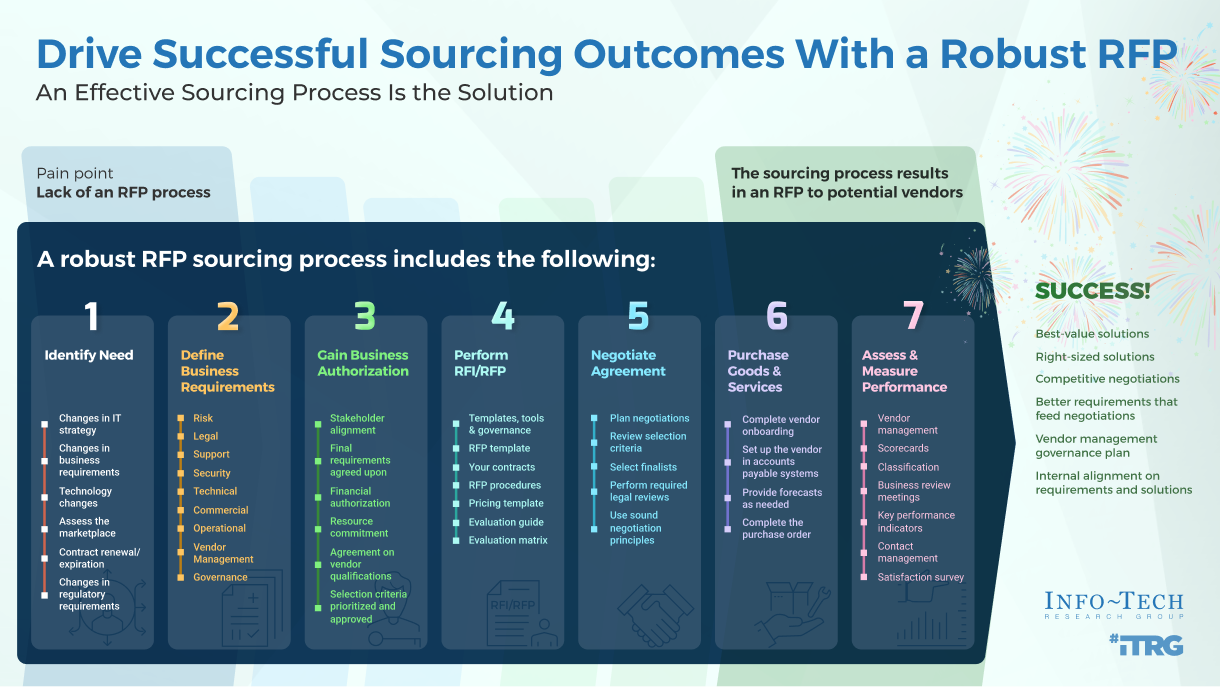
Lack of RFP Process Causes...
|
Solution: RFP Process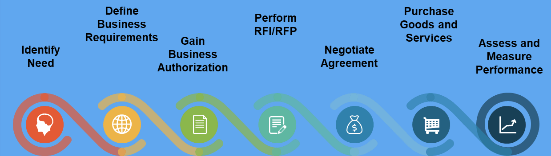
|
|
||
Requirements
|
Templates, Tools, Governance
|
Vendor Management
|
||
Analyst Perspective
Consequences of a bad RFP

“A bad request for proposal (RFP) is the gift that keeps on taking – your time, your resources, your energy, and your ability to accomplish your goal. A bad RFP is ineffective and incomplete, it creates more questions than it answers, and, perhaps most importantly, it does not meet your organization’s expectations.”
Steven Jeffery
Principal Research Director, Vendor Management
Co-Author: The Art of Creating a Quality RFP
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
- Most IT organizations are absent of standard RFP templates, tools, and processes.
- Many RFPs lack sufficient requirements from across the business (Legal, Finance, Security, Risk, Procurement, VMO).
- Most RFP team members are not adequately trained on RFP best practices.
- Most IT departments underestimate the amount of time required to perform an effective RFP.
- An ad hoc sourcing process is a common recipe for vendor performance failure.
Common Obstacles
- Lack of time
- Lack of resources
- Right team members not engaged
- Poorly defined requirements
- Too difficult to change supplier
- Lack of a process
- Lack of adequate tools/processes
- Lack of a vendor communications plan that includes all business stakeholders.
- Lack of consensus as to what the ideal result should look like.
Info-Tech’s Approach
- Establish a repeatable, consistent RFP process that maintains negotiation leverage and includes all key components.
- Create reusable templates to expedite the RFP evaluation and selection process.
- Maximize the competition by creating an equal and level playing field that encourages all the vendors to respond to your RFP.
- Create a process that is clear and understandable for both the business unit and the vendor to follow.
- Include Vendor Management concepts in the process.
Info-Tech Insight
A well planned and executed sourcing strategy that focuses on solid requirements, evaluation criteria, and vendor management will improve vendor performance.
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
Your challenge is to determine the best sourcing tool to obtain vendor information on capabilities, solution(s), pricing and contracting: RFI, RFP, eRFX.
Depending on your organization’s knowledge of the market, your available funding, and where you are in the sourcing process, there are several approaches to getting the information you need.
An additional challenge is to answer the question “What is the purpose of our RFX?”
If you do not have in-depth knowledge of the market, available solutions, and viable vendors, you may want to perform an RFI to provide available market information to guide your RFP strategy.
If you have defined requirements, approved funding, and enough time, you can issue a detailed, concise RFP.
If you have “the basics” about the solution to be acquired and are on a tight timeframe, an “enhanced RFI” may fit your needs.
This blueprint will provide you with the tools and processes and insights to affect the best possible outcome.
Executive Summary
Common Obstacles
- Lack of process/tools
- Lack of input from stakeholders
- Stakeholders circumventing the process to vendors
- Vendors circumventing the process to key stakeholders
- Lack of clear, concise, and thoroughly articulated requirements
- Waiting until the vendor is selected to start contract negotiations
- Waiting until the RFP responses are back to consider vendor management requirements
- Lack of clear communication strategy to the vendor community that the team adheres to
Many organizations underestimate the time commitment for an RFP
|
70 Days is the average duration of an IT RFP. The average number of evaluators is 5-6 4 Is the average number of vendor submissions, each requiring an average of two to three hours to review. (Source: Bonfire, 2019. Note: The 2019 Bonfire report on the “State of the RFP” is the most recent published.) |
“IT RFPs take the longest from posting to award and have the most evaluators. This may be because IT is regarded as a complex subject requiring complex evaluation. Certainly, of all categories, IT offers the most alternative solutions. The technology is also changing rapidly, as are the requirements of IT users – the half-life of an IT requirement is less than six months (half the requirements specified now will be invalid six months from now). And when the RFP process takes up two of those months, vendors may be unable to meet changed requirements when the time to implement arrives. This is why IT RFPs should specify the problem to be resolved rather than the solution to be provided. If the problem resolution is the goal, vendors are free to implement the latest technologies to meet that need.” (Bonfire, “2019 State of the RFP”) |
Why Vendors Don’t Like RFPs
Vendors’ win rate
44%Vendors only win an average of 44% of the RFPs they respond to (Loopio, 2022). |
High cost to respond
3-5%Vendors budget 3-5% of the anticipated contract value to respond (LinkedIn, 2017, Note: LinkedIn source is the latest information available). |
Time spent writing response
23.8 hoursVendors spend on average 23.8 hours to write or respond to your RFP (Marketingprofs, 2021). |
Negative effects on your organization from a lack of RFP process
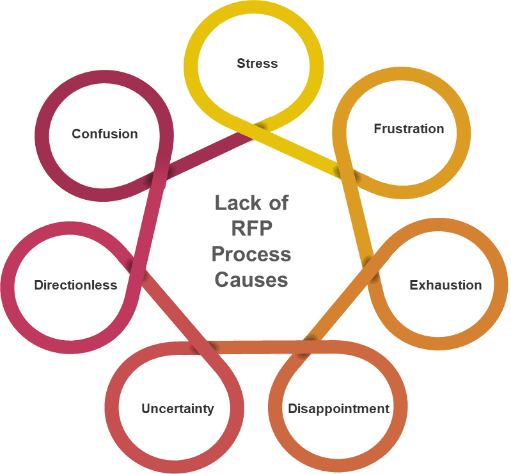
|
Stress, because roles and responsibilities aren’t clearly defined and communication is haphazard, resulting in strained relationships. Confusion, because you don’t know what the expected or desired results are. Directionless, because you don’t know where the team is going. Uncertainty, with many questions of your own and many more from other team members. Frustration, because of all the questions the vendors ask as a result of unclear or incomplete requirements. Exhaustion, because reviewing RFP responses of insufficient quality is tedious. Disappointment in the results your company realizes. (Source: The Art of Creating a Quality RFP) |
Info-Tech’s approach
Develop an inclusive and thorough approach to the RFP Process
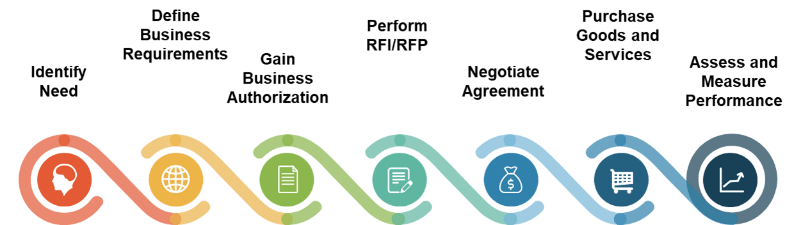
The Info-Tech difference:
- The secret to managing an RFP is to make it as manageable and as thorough as possible. The RFP process should be like any other aspect of business – by developing a standard process. With a process in place, you are better able to handle whatever comes your way, because you know the steps you need to follow to produce a top-notch RFP.
- The business then identifies the need for more information about a product/service or determines that a purchase is required.
- A team of stakeholders from each area impacted gather all business, technical, legal, and risk requirements. What are the expectations of the vendor relationship post-RFP? How will the vendors be evaluated?
- Based on the predetermined requirements, either an RFI or an RFP is issued to vendors with a predetermined due date.
Insight Summary
Overarching insight
Without a well defined, consistent RFP process, with input from all key stakeholders, the organization will not achieve the best possible results from its sourcing efforts.
Phase 1 insight
Vendors are choosing to not respond to RFPs due to their length and lack of complete requirements.
Phase 2 insight
Be clear and concise in stating your requirements and include, in addition to IT requirements, procurement, security, legal, and risk requirements.
Phase 3 insight
Consider adding vendor management requirements to manage the ongoing relationship post contract.
Tactical insight
Consider the RFP Evaluation Process as you draft the RFP, including weighting the RFP components. Don’t underestimate the level of effort required to effectively evaluate responses – write the RFP with this in mind.
Tactical insight
Provide strict, prescriptive instructions detailing how the vendor should submit their responses. Controlling vendor responses will increase your team’s efficiency in evaluations while providing ease of reference responses across multiple vendors.
Key deliverables
Each step of this blueprint is accompanied by supporting deliverables to help you accomplish your goals:
| Key deliverables:
Info-Tech provides you with the tools you need to go to market in the most efficient manner possible, with guidance on how to achieve your goals.
|
Long-Form RFP Template
For when you have complete requirements and time to develop a thorough RFP. |

|
Short-Form RFP Template
When the requirements are not as extensive, time is short, and you are familiar with the market. |
|
| Lean RFP Template
When you have limited time and some knowledge of the market and wish to include only a few vendors. |

|
Excel-Form RFP Template
When there are many requirements, many options, multiple vendors, and a broad evaluation team. |

|
Blueprint benefits
IT Benefits
|
Mutual IT and Business Benefits
|
Business Benefits
|
Info-Tech offers various levels of support to best suit your needs
DIY Toolkit |
Guided Implementation |
Workshop |
Consulting |
| "Our team has already made this critical project a priority, and we have the time and capability, but some guidance along the way would be helpful." | "Our team knows that we need to fix a process, but we need assistance to determine where to focus. Some check-ins along the way would help keep us on track." | "We need to hit the ground running and get this project kicked off immediately. Our team has the ability to take this over once we get a framework and strategy in place." | "Our team does not have the time or the knowledge to take this project on. We need assistance through the entirety of this project." |
Diagnostics and consistent frameworks used throughout all four options
Guided Implementation
A Guided Implementation (GI) is a series of calls with an Info-Tech analyst to help implement our best practices in your organization.
A typical GI is seven to twelve calls over the course of four to six months.
What does a typical GI on this topic look like?
Phase 1 |
Phase 2 |
Phase 3 |
Phase 4 |
Phase 5 |
Phase 6 |
Phase 7 |
| Call #1: Identify the need | Call #3: Gain business authorization | Call #5: Negotiate agreement strategy | Call #7: Assess and measure performance | |||
| Call #2: Define business requirements | Call #4: Review and perform the RFX or RFP | Call #6: Purchase goods and services |
Workshop Overview
Contact your account representative for more information.
workshops@infotech.com1-888-670-8889
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | |
| Activities |
Answer “What problem do we need to solve?”1.1 Overview and level-setting 1.2 Identify needs and drivers 1.3 Define and prioritize requirements 1.4 Gain business authorization and ensure internal alignment |
Define what success looks like?2.1 Create and issue RFP 2.2 Evaluate responses/ proposals and negotiate the agreement. 2.3 Purchase goods and services |
Configure Templates3.1 Assess and measure 3.2 Review tools |
| Deliverables |
|
|
|
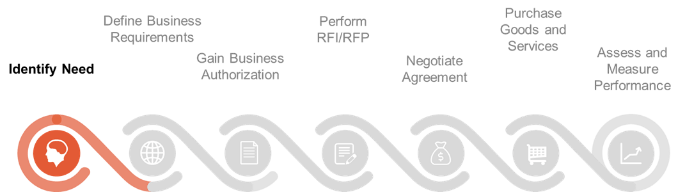
Phase 1
Identify Need
| Steps
1.1 Establish the need to either purchase goods/services (RFP) or acquire additional information from the market (RFI). |
|
This phase involves the following participants:
- Business stakeholders
- IT
- Sourcing/Procurement
- Finance
Identify the need based on business requirements, changing technology, increasing vendor costs, expiring contracts, and changing regulatory requirements.
Outcomes of this phase
Agreement on the need to go to market to make a purchase (RFP) or to acquire additional information (RFI) along with a high-level agreement on requirements, rough schedule (is there time to do a full blown RFP or are you time constrained, which may result in an eRFP) and the RFP team is identified.
Identify Need| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 | Phase 5 | Phase 6 | Phase 7 |
Identify the Need for Your RFP
|

|
Phase 2
Define Your RFP Requirements
| Steps
2.1 Define and classify the technical, business, financial, legal, and support and security requirements for your business. |
|
This phase involves the following participants:
- IT
- Legal
- Finance
- Risk management
- Sourcing/Procurement
- Business stakeholders
Outcomes of this phase
A detailed list of required business, technical, legal and procurement requirements classified as to absolute need(s), bargaining and concession need(s), and “nice to haves.”
Define Business Requirements
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 | Phase 5 | Phase 6 | Phase 7 |
Define RFP Requirements
Key things to consider when defining requirements
- Must be inclusive of the needs of all stakeholders: business, technical, financial, and legal
- Strive for clarity and completeness in each area of consideration.
- Begin defining your “absolute,” “bargaining,” “concession,” and ‘”dropped/out of scope” requirements to streamline the evaluation process.
- Keep the requirements identified as “absolute” to a minimum, because vendors that do not meet absolute requirements will be removed from consideration.
- Do you have a standard contract that can be included or do you want to review the vendor’s contract?
- Don’t forget Data Security!
- Begin defining your vendor selection criteria.
- What do you want the end result to look like?
- How will you manage the selected vendor after the contract? Include key VM requirements.
- Defining requirements can’t be rushed or you’ll find yourself answering many questions, which may create confusion.
- Collect all your current spend and budget considerations regarding the needed product(s) and service(s).
“Concentrate on the needs of the organization and not the wants of the individuals when creating requirements to avoid scope creep.” (Donna Glidden, ITRG Research Director)
Leverage the “ABCD” approach found in our Prepare for Negotiations More Effectively blueprint:
https://tymansgrpup.com/research/ss/prepare-for-negotiations-more-effectively
2.1 Prioritize your requirements
1 hr to several daysInput: List of all requirements from IT and IT Security, Business, Sourcing/Procurement, Risk Management, and Legal
Output: Prioritized list of RFP requirements approved by the stakeholder team
Materials: The RFP Requirements Worksheet
Participants: All stakeholders impacted by the RFP: IT, IT Security, the Business, Sourcing/ Procurement, Risk Management, Legal
- Use this tool to assist you and your team in documenting the requirements for your RFP. Leverage it to collect and categorize your requirements in preparation for negotiations. Use the results of this tool to populate the requirements section of your RFP.
- As a group, review each of the requirements and determine their priority as they will ultimately relate to the negotiations.
- Prioritizing your requirements will set up your negotiation strategy and streamline the process.
- By establishing the priority of each requirement upfront, you will save time and effort in the selection process.
- Review RFP requirements with stakeholders for approval.
Download the RFP Requirements Worksheet
Phase 3
Gain Business Authorization
| Steps
3.1 Obtain business authorization from the business, technology, finance and Sourcing/Procurement |
|
This phase involves the following participants:
- Business stakeholders
- Technology and finance (depending upon the business)
- Sourcing/Procurement
Outcomes of this phase
Approval by all key stakeholders to proceed with the issuing of the RFP and to make a purchase as a result.
Gain Business Authorization
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 | Phase 5 | Phase 6 | Phase 7 |
Gain Business Authorization
Gain authorization for your RFP from all relevant stakeholders
Obtaining cross-function alignment will clear the way for contract, SOW, and budget approvals and not waste any of your and your vendor’s resources in performing an RFP that your organization is not ready to implement or invest financial and human resources in. |

|
Phase 4
Create and Issue
| Steps
4.1 Build your RFP 4.2 Decide RFI or not 4.3 Create your RFP 4.4 Receive & answer questions 4.5 Perform Pre-Proposal Conference 4.6 Evaluate responses |
|
This phase involves the following participants:
- The RFP owner
- IT
- Business SMEs/stakeholders
Outcomes of this phase
RFP package is issued to vendors and includes the date of the Pre-Proposal Conference, which should be held shortly after RFP release and includes all parties.
SME’s/stakeholders participate in providing answers to RFP contact for response to vendors.
Create and Issue Your RFP/RFI
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 | Phase 5 | Phase 6 | Phase 7 |
Six Steps to Perform RFI/RFP
Step 1
|
Step 2
|
Step 3
|
Step 4
|
Step 5
|
Step 6
|
Build your RFP with evaluation in mind
Easing evaluation frustrations
At the beginning of your RFP creation process consider how your requirements will impact the vendor’s response. Concentrate on the instructions you provide the vendors and how you wish to receive their responses. View the RFP through the lens of the vendors and envision how they are going to respond to the proposal.
Limiting the number of requirements included in the RFP will increase the evaluation team’s speed when reviewing vendors’ responses. This is accomplished by not asking questions for common features and functionality that all vendors provide. Don’t ask multiple questions within a question. Avoid “lifting” vendor-specific language to copy into the RFP as this will signal to vendors who their competition might be and may deter their participation. Concentrate your requirement questions to those areas that are unique to your solution to reduce the amount of time required to evaluate the vendors’ response.
Things to Consider When Creating Your RFP:
- Consistency is the foundation for ease of evaluation.
- Provide templates, such as an Excel worksheet, for the vendor’s pricing submissions and for its responses to close-ended questions.
- Give detailed instructions on how the vendor should organize their response.
- Limit the number of open-ended questions requiring a long narrative response to must-have requirements.
- Organize your requirements and objectives in a numerical outline and have the vendor respond in the same manner, such as the following:
- 1
- 1.1
- 1.1.1
Increase your response quality
Inconsistent formatting of vendor responses prevents an apples-to-apples evaluation between vendor responses. Evaluation teams are frequently challenged and are unable to evaluate vendors’ responses equally against each other for the following reasons:
Challenges
|
Prevention
|
Six Steps to Perform RFI/RFP
Step 1
| Step 2
| Step 3
| Step 4
| Step 5
| Step 6
|
Perform Request for Information
Don’t underestimate the importance of the RFI
As the name implies, a request for information (RFI) is a tool for collecting information from vendors about the companies, their products, and their services. We find RFIs useful when faced with a lot of vendors that we don’t know much about, when we want to benchmark the marketplace for products and services, including budgetary information, and when we have identified more potential vendors than we care to commit a full RFP to.
RFIs are simpler and less time-consuming than RFPs to prepare and evaluate, so it can make a lot of sense to start with an RFI. Eliminating unqualified vendors from further consideration will save your team from weeding through RFP responses that do not meet your objectives. For their part, your vendors will appreciate your efforts to determine up-front which of them are the best bets before asking them to spend resources and money producing a costly proposal.
While many organizations rarely use RFIs, they can be an effective tool in the vendor manager’s toolbox when used at the right time in the right way. RFIs can be deployed in competitive targeted negotiations.
A Lean RFP is a two-stage strategy that speeds up the typical RFP process. The first stage is like an RFI on steroids, and the second stage is targeted competitive negotiation.
Don’t rely solely on the internet to qualify vendors; use an RFI to acquire additional information before finalizing an RFP.
4.2.1 In a hurry? Consider a Lean RFP instead of an RFP
Several days- Create an RFI with all of the normal and customary components. Next, add a few additional RFP-like requirements (e.g. operational, technical, and legal requirements). Make sure you include a request for budgetary pricing and provide any significant features and functionality requirements so that the vendors have enough information to propose solutions. In addition, allow the vendors to ask questions through your single point of coordination and share answers with all of the vendors. Finally, notify the vendors that you will not be doing an RFP.
- Review the vendors’ proposals and evaluate their proposals against your requirements along with their notional or budgetary pricing.
- Have the evaluators utilize the Lean RFP Template to record their scores accordingly.
- After collecting the scores from the evaluators, consolidate the scores together to discuss which vendors – we recommend two or three – you want to present demos.
- Based on the vendors’ demos, the team selects at least two vendors to negotiate contract and pricing terms with intent of selecting the best-value vendor.
- The Lean RFP shortens the typical RFP process, maintains leverage for your organization, and works great with low- to medium-spend items (however your organization defines them). You’ll get clarification on vendors’ competencies and capabilities, obtain a fair market price, and meet your internal clients’ aggressive timelines while still taking steps to protect your organization.
Download the Lean RFP Template
Download the RFP Evaluation Tool
4.2.1 In a hurry? Consider a Lean RFP instead of an RFP continued
Input
|
Output
|
Materials
|
Participants
|
Case StudyA Lean RFP saves time |
INDUSTRY: Pharmaceutical
|
|
Challenge
|
Solution
|
Results
|
Six Steps to Perform RFI/RFP
Step 1
| Step 2
| Step 3
| Step 4
| Step 5
| Step 6
|
4.3.1 RFP Calendar
1 hourInput: List duration in days of key activities, RFP Calendar and Key Date Tool, For all vendor-inclusive meetings, include the dates on your RFP calendar and reference them in the RFP
Output: A timeline to complete the RFP that has the support of each stakeholder involved in the process and that allows for a complete and thorough vendor response.
Materials: RFP Calendar and Key Date Tool
Participants: IT management, Business stakeholder(s), Legal (as required), Risk management (as required), Sourcing/Procurement, Vendor management
- As a group, identify the key activities to be accomplished and the amount of time estimated to complete each task:
- Identify who is ultimately accountable for the completion of each task
- Determine the length of time required to complete each task
- Use the RFP Calendar and Key Date Tool to build the calendar specific to your needs.
- Include vendor-related dates in the RFP, i.e., Pre-Proposal Conference, deadline for RFP questions as well as response.
Download the RFP Calendar and Key Date Tool
Draft your RFP
Create and issue your RFP, which should contain at least the following:
|
|
Create a template for the vendors’ response
Dictating to the vendors the format of their response will increase your evaluation efficiency
Narrative Response:Create either a Word or Excel document that provides the vendor with an easy vehicle for their response. This template should include the question identifier that ties the response back to the requirement in the RFP. Instruct vendors to include the question number on any ancillary materials they wish to include. Pricing Response:Create a separate Excel template that the vendors must use to provide their financial offer. This template should include pricing for hardware, software, training, implementation, and professional services, as well as placeholders for any additional fees. Always be flexible in accepting alternative proposals after the vendor has responded with the information you requested in the format you require. |

|
4.3.2 Vendor Pricing Tool
1 hourInput: Identify pricing components for hardware, software, training, consulting/services, support, and additional licenses (if needed)
Output: Vendor Pricing Tool
Materials: RFP Requirements Worksheet, Pricing template
Participants: IT, Finance, Business stakeholders, Sourcing/Procurement, Vendor management
- Using a good pricing template will prevent vendors from providing pricing offers that create a strategic advantage designed to prevent you from performing an apples-to-apples comparison.
- Provide specific instructions as to how the vendor is to organize their pricing response, which should be submitted separate from the RFP response.
- Configure and tailor pricing templates that are specific to the product and/or services.
- Upon receipt of all the vendor’s responses, simply cut and paste their total response to your base template for an easy side-by-side pricing comparison.
- Do not allow vendors to submit financial proposals outside of your template.
Download the Vendor Pricing Tool
Three RFP Templates
Choose the right template for the right sourcing initiative
- Short-Form
- Long-Form
- Excel-Form
Use the Short-Form RFP Template for simple, non-complex solutions that are medium to low dollar amounts that do not require numerous requirements.
We recommend the Long-Form RFP Template for highly technical and complex solutions that are high dollar and have long implementation duration.
Leverage the Excel-Form RFP Tool for requirements that are more specific in nature to evaluate a vendor’s capability for their solution. This template is designed to be complete and inclusive of the RFP process, e.g., requirements, vendor response, and vendor response evaluation scoring.
Like tools in a carpenters’ tool box or truck, there is no right or wrong template for any job. Take into account your organization culture, resources available, time frame, policies, and procedures to pick the right tool for the job. (Steve Jeffery, Principal Research Director, Vendor Management, Co-Author: The Art of Creating a Quality RFP, Info-Tech Research Group)
4.3.3 Short-Form RFP Template
1-2 hours
Input: List of technical, legal, business, and data security requirements
Output: Full set of requirements, prioritized, that all participants agree to
Materials: Short-Form RFP Template, Vendor Pricing Tool, Supporting exhibits
Participants: IT management, Business stakeholder(s), Legal (as required), Risk management (as required), Sourcing/Procurement, Vendor management
- This is a less complex RFP that has relatively basic requirements and perhaps a small window in which the vendors can respond. As with the long-form RFP, exhibits are placed at the end of the RFP, an arrangement that saves both your team and the vendors time. Of course, the short-form RFP contains less-specific instructions, guidelines, and rules for vendors’ proposal submissions.
- We find that short-form RFPs are a good choice when you need to use something more than a request for quote (RFQ) but less than an RFP running 20 or more pages. It’s ideal, for example, when you want to send an RFP to only one vendor or to acquire items such as office supplies, contingent labor, or commodity items that don’t require significant vendor risk assessment.
Download the Short-Form RFP Template
4.3.4 Long-Form RFP Template
1-3 hours
Input: List of technical, legal, business, and data security requirements
Output: Full set of requirements, prioritized, that all stakeholders agree to
Materials: Long-Form RFP Template, Vendor Pricing Tool, Supporting exhibits
Participants: IT management, Business stakeholder(s), Legal (as required), Risk management (as required), Sourcing/Procurement, Vendor management
- A long-form or major RFP is an excellent tool for more complex and complicated requirements. This template is for a baseline RFP.
- It starts with best-in-class RFP terms and conditions that are essential to maintaining your control throughout the RFP process. The specific requirements for the business, functional, technical, legal, and pricing areas should be included in the exhibits at the end of the template. That makes it easier to tailor the RFP for each deal, since you and your team can quickly identify specific areas that need modification. Grouping the exhibits together also makes it convenient for both your team to review and the vendors to respond.
- You can use this sample RFP as the basis for your template RFP, taking it all as is or picking and choosing the sections that best meet the mission and objectives of the RFP and your organization.
Download the Long-Form RFP Template
4.3.5 Excel-Form RFP Tool
Several weeks
Input: List of technical, legal, business, and data security requirements
Output: Full set of requirements, prioritized, that all stakeholders agree to
Materials: Excel-Form RFP Template, Vendor Pricing Tool, Supporting exhibits
Participants: IT management, Business stakeholder(s), Legal (as required), Risk management (as required), Sourcing/Procurement, Vendor management
- The Excel-Form RFP Tool is used as an alternative to the other RFP toolsets if you have multiple requirements and have multiple vendors to choose from.
- Requirements are written as a “statement” and the vendor can select from five answers as to their ability to meet the requirements, with the ability to provide additional context and materials to augment their answers, as needed.
- Requirements are listed separately in each tab, for example, Business, Legal, Technical, Security, Support, Professional Services, etc.
Download the Excel-Form RFP Template
Six Steps to Perform RFI/RFP
Step 1
| Step 2
| Step 3
| Step 4
| Step 5
| Step 6
|
Answer Vendor Questions
Maintaining your equal and level playing field among vendors
|

|
|
Six Steps to Perform RFI/RFP
Step 1
| Step 2
| Step 3
| Step 4
| Step 5
| Step 6
|
Conduct Pre-Proposal Conference
Maintain an equal and level playing field
- Consolidate all Q&A to be presented to all vendors during the Pre-Proposal Conference.
- If the Pre-Proposal Conference is conducted via conference call, be sure to record the session and advise all participants at the beginning of the call.
- Be sure to have key stakeholders present on the call to answer questions.
- Read each question and answer, after which ask if there are any follow up questions. Be sure to capture them and then add them to the Q&A document.
- Remind respondents that no further questions will be entertained during the remainder of the RFP response period.
- Send the updated and completed document to all vendors (even if circumstances prevented their attending the Pre-Proposal Conference). Use the same process as when you sent out the initial answers: via email, blind copy the respondents and request read/receipt.
“Using a Pre-Proposal Conference allows you to reinforce that there is a level playing field for all of the vendors…that each vendor has an equal chance to earn your business. This encourages and maximizes competition, and when that happens, the customer wins.” (Phil Bode, Principal Research Director, Co-Author: The Art of Creating a Quality RFP, Info-Tech Research Group)
Pre-Proposal Conference Agenda
| Modify this agenda for your specific organization’s culture | |
(Source: The Art of Creating a Quality RFP, Jeffery et al., 2019) |
|
Allow your executive or leadership sponsor to leave the Pre-Proposal Conference after they provide their comments to allow them to continue their day while demonstrating to the vendors the importance of the project.
Six Steps to Perform RFI/RFP
Step 1
| Step 2
| Step 3
| Step 4
| Step 5
| Step 6
|
Evaluate Responses
Other important information
|

|
Use a proven evaluation method
Two proven methods to reviewing vendors’ proposals are by response and by objective
The first, by response, is when the evaluator reviews each vendor’s response in its entirety.
The second, reviewing by objective, is when the evaluator reviews each vendor’s response to a single objective before moving on to the next.
| By Response
|
By Objective
|
||
|
|
|
|
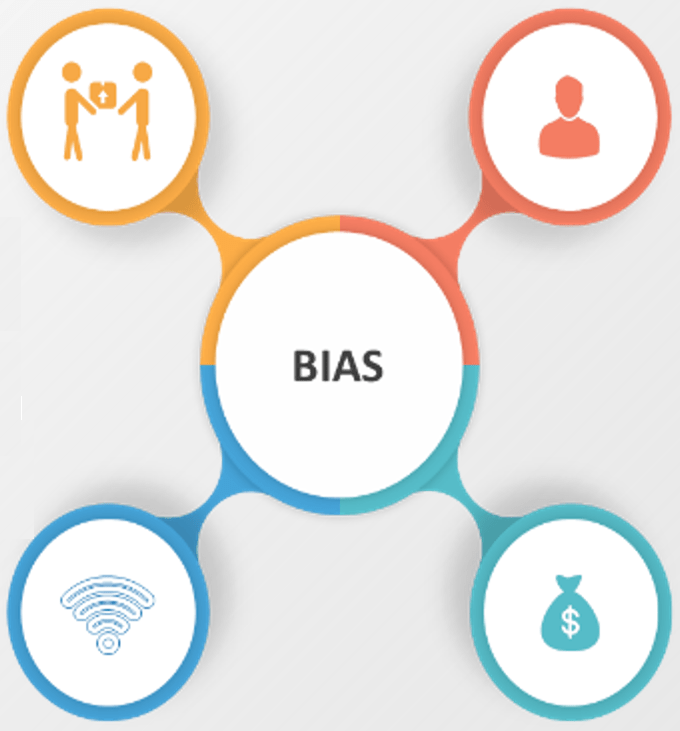
Maintain evaluation objectivity by reducing response evaluation biases
Evaluation teams can be naturally biased during their review of the vendors’ responses.
You cannot eliminate bias completely – the best you can do is manage it by identifying these biases with the team and mitigating their influence in the evaluation process.
VendorThe evaluator only trusts a certain vendor and is uncomfortable with any other vendor.
|
|
Account RepresentativesRelationships extend beyond business, and an evaluator doesn't want to jeopardize them.
|
TechnicalA vendor is the only technical solution the evaluator is looking for, and they will not consider anything else.
|
PriceAs humans, we can justify anything at a good price.
|
Additional insights when evaluating RFPs
| When your evaluation team includes a member of the C-suite or senior leadership, ensure you give them extra time to sufficiently review the vendor's responses. | When your questions require a definitive “Yes”/“True” or “No”/“False” responses, we recommend giving the maximum score for “Yes”/“True” and the minimum score for “No”/“False”. | |
| Increase your efficiency and speed of evaluation by evaluating the mandatory requirements first. If a vendor's response doesn't meet the minimum requirements, save time by not reviewing the remainder of the response. | Group your RFP questions with a high-level qualifying question, then the supporting detailed requirements. The evaluation team can save time by not evaluating a response that does not meet a high-level qualifying requirement. |
Establish your evaluation scoring scale
Define your ranking scale to ensure consistency in ratingsWithin each section of your RFP are objectives, each of which should be given its own score. Our recommended approach is to award on a scale of 0 to 5. With such a scale, you need to define every level. Below are the recommended definitions for a 0 to 5 scoring scale.
|

|
Weigh the sections of your RFP on how important or critical they are to the RFP
Obtain Alignment on Weighting the Scores of Each Section
|
Example RFP Section Weights
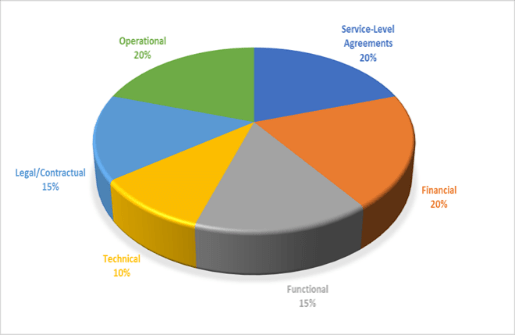
(Source: The Art of Creating a Quality RFP, Jeffery et al., 2019) |
Protect your negotiation leverage with these best practices
Protect your organization's reputation within the vendor community with a fair and balanced process.
|

|
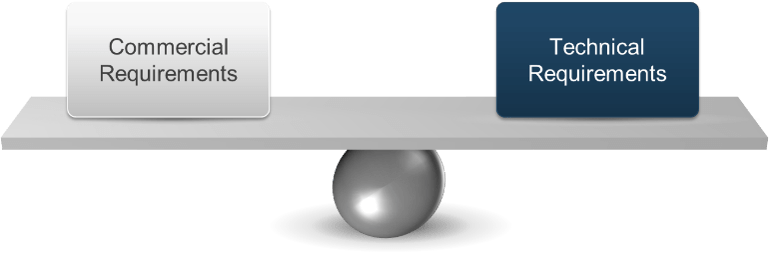
Evaluation teams must balance commercial vs. technical requirements
Do not alter the evaluation weights after responses are submitted.
|
|
4.6.1 Evaluation Guidebook
1 hour
Input: RFP responses, Weighted Scoring Matrix, Vendor Response Scorecard
Output: One or two finalists for which negotiations will proceed
Materials: RFP Evaluation Guidebook
Participants: IT, Finance, Business stakeholders, Sourcing/Procurement, Vendor management
- Info-Tech provides an excellent resource for your evaluation team to better understand the process of evaluating vendor response. The guidebook is designed to be configured to the specifics of your RFP, with guidance and instructions to the team.
- Use this guidebook to provide instruction to the evaluation team as to how best to score and rate the RFP responses.
- Specific definitions are provided for applying the numerical scores to the RFP objectives will ensure consistency among the appropriate numerical score.
Download the RFP Evaluation Guidebook
4.6.2 RFP Vendor Proposal Scoring Tool
1-4 hours
Input: Each vendor’s RFP response, A copy of the RFP (less pricing), A list of the weighted criteria incorporated into a vendor response scorecard
Output: A consolidated ranked and weighted comparison of the vendor responses with pricing
Materials: Vendor responses, RFP Evaluation Tool
Participants: Sourcing/Procurement, Vendor management
- Using the RFP outline as a base, develop a scorecard to evaluate and rate each section of the vendor response, based on the criteria predetermined by the team.
- Provide each stakeholder with the scorecard when you provide the vendor responses for them to review and provide the team with adequate time to review each response thoroughly and completely.
- Do not, at this stage, provide the pricing. Allow stakeholders to review the responses based on the technical, business, operational criteria without prejudice as to pricing.
- Evaluators should always be reminded that they are evaluating each vendor’s response against the objectives and requirements of the RFP. The evaluators should not be evaluating each vendor’s response against one another.
- While the team is reviewing and scoring responses, review and consolidate the vendor pricing submissions into one document for a side-by-side comparison.
Download the RFP Evaluation Tool
4.6.3 Total Cost of Owners (TCO)
1-2 hoursInput: Consolidated vendor pricing responses, Consolidated vendor RFP responses, Current spend within your organization for the product/service, if available, Budget
Output: A completed TCO model summarizing the financial results of the RFP showing the anticipated costs over the term of the agreement, taking into consideration the impact of renewals.
Materials: Vendor TCO Tool, Vendor pricing responses
Participants: IT, Finance, Business stakeholders, Sourcing/Procurement
- Use Info-Tech’s Vendor TCO Tool to normalize each vendor’s pricing proposal and account for the lifetime cost of the product.
- Fill in pricing information (the total of all annual costs) from each vendor's returned Pricing Proposal.
- The tool will summarize the net present value of the TCO for each vendor proposal.
- The tool will also provide the rank of each pricing proposal.
Download the Vendor TCO Tool
Conduct an evaluation team results meeting
Follow the checklist below to ensure an effective evaluation results meeting
- Schedule the evaluation team’s review meeting well in advance to ensure there are no scheduling conflicts.
- Collect the evaluation team’s scores in advance.
- Collate scores and provide an initial ranking.
- Do not reveal the pricing evaluation results until after initial discussions and review of the scoring results.
- Examine both high and low scores to understand why the team members scored the response as they did.
- Allow the team to discuss, debate, and arrive at consensus on the ranking.
- After consensus, reveal the pricing to examine if or how it changes the ranking.
- Align the team on the next steps with the applicable vendors.
4.6.4 Consolidated RFP Response Scoring
1-2 hours
Input: Vendor Response Scorecard from each stakeholder, Consolidated RFP responses and pricing, Any follow up questions or items requiring further vendor clarification.
Output: An RFP Response Evaluation Summary that identifies the finalists based on pre-determined criteria.
Materials: RFP Evaluation Tool from each stakeholder, Consolidated RFP responses and pricing.
Participants: IT, Finance, Business stakeholders, Sourcing/Procurement, Vendor management
- Collect from the evaluation team all scorecards and any associated questions requiring further clarification from the vendor(s). Consolidate the scorecards into one for presentation to the team and key decision makers.
- Present the final scores to the team, with the pricing evaluation, to determine, based on your needs, two or three finalists that will move forward to the next steps of negotiations.
- Discuss any scores that are have large gaps, e.g., a requirement with a score of one from one evaluator and the same requirement with a score five from different evaluator.
- Arrive at a consensus of your top one or two potential vendors.
- Determine any required follow-up actions with the vendors and include them in the Evaluation Summary.
Download the Consolidated Vender RFP Response Evaluation Summary
4.6.5 Vendor Recommendation Presentation
1-3 hours- Use the Vendor Recommendation Presentation to present your finalist and obtain final approval to negotiate and execute any agreements.
- The Vendor Recommendation Presentation provides leadership with:
- An overview of the RFP, its primary goals, and key requirements
- A summary of the vendors invited to participate and why
- A summary of each component of the RFP
- A side-by-side comparison of key vendor responses to each of the key/primary requirements, with ranking/weighting results
- A summary of the vendor’s responses to key legal terms
- A consolidated summary of the vendors’ pricing, augmented by the TCO calculations for the finalist(s).
- The RFP team’s vendor recommendations based on its findings
- A summary of next steps with dates
- Request approval to proceed to next steps of negotiations with the primary and secondary vendor
Download the Vendor Recommendation Presentation
4.6.5 Vendor Recommendation Presentation
Input
| Output
| Materials
| Participants
|
Caution: Configure templates and tools to align with RFP objectives
Templates and tools are invaluable assets to any RFP process
|
Templates/ToolsRFP templates and tools are found in a variety of places, such as previous projects, your favorite search engine, or by asking a colleague. |
SourcingRegardless of the source of these documents, you must take great care and consideration to sanitize any reference to another vendor, company, or name of the deal. |
ReviewThen you must carefully examine the components of the deal before creating your final documents.Popular RFP templates include:
|
Phase 5
Negotiate Agreement(s)
| Steps
5.1 Perform negotiation process |
|
This phase involves the following participants:
- Procurement
- Vendor management
- Legal
- IT stakeholders
- Finance
Outcomes of this phase
A negotiated agreement or agreements that are a result of competitive negotiations.
Negotiate Agreement(s)
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 | Phase 5 | Phase 6 | Phase 7 |
Negotiate Agreement
| You should evaluate your RFP responses first to see if they are complete and the vendor followed your instructions.
Info-Tech InsightBe certain to include any commitments made in the RFP, presentations, and proposals in the agreement – dovetails to underperforming vendor. |  Leverage Info-Tech's negotiation process research for additional information | Negotiate before you select your vendor:
Info-Tech InsightProviding contract terms in an RFP can dramatically reduce time for this step by understanding the vendor’s initial contractual position for negotiation. |
Phase 6
Purchase Goods and Services
| Steps
6.1 Purchase Goods & Services |
|
This phase involves the following participants:
- Procurement
- Vendor management
- IT stakeholders
Outcomes of this phase
A purchase order that completes the RFP process.
The beginning of the vendor management process.
Purchase Goods and Services
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 | Phase 5 | Phase 6 | Phase 7 |
Purchase Goods and Services
Prepare to purchase goods and services
Prepare to purchase goods and services by completing all items on your organization’s onboarding checklist.
|

|
Info-Tech Insight
As a customer, honoring your contractual obligations and commitments will ensure that your organization is not only well respected but considered a customer of choice.
Phase 7
Assess and Measure Performance
| Steps
7.1 Assess and measure performance against the agreement |
|
This phase involves the following participants:
- Vendor management
- Business stakeholders
- Senior leadership (as needed)
- IT stakeholders
- Vendor representatives & senior management
Outcomes of this phase
A list of what went well during the period – it’s important to recognize successes
A list of areas needing improvement that includes:
- A timeline for each item to be completed
- The team member(s) responsible
Purchase Goods and Services
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 | Phase 5 | Phase 6 | Phase 7 |
Assess and Measure Performance
Measure to manage: the job doesn’t end when the contract is signed.
- Classify vendor
- Assess vendor performance
- Manage improvement
- Conduct periodic vendor performance reviews or quarterly business reviews
- Ensure contract compliance for both the vendor and your organization
- Build knowledgebase for future
- Re-evaluate and improve appropriately your RFP processes
Info-Tech Insight
To be an objective vendor manager, you should also assess and measure your company’s performance along with the vendor’s performance.
Summary of Accomplishment
Problem Solved
Upon completion of this blueprint, guided implementation, or workshop, your team should have a comprehensive, well-defined end-to-end approach to performing a quality sourcing event. Leverage Info-Tech’s industry-proven tools and templates to provide your organization with an effective approach to maintain your negotiation leverage, improve the ease with which you evaluate vendor proposals, and reduce your risk while obtaining the best market value for your goods and services.
Additionally, your team will have a foundation to execute your vendor management principles. These principles will assist your organization in ensuring you receive the perceived value from the vendor as a result of your competitive negotiations.
If you would like additional support, have our analysts guide you through other phases as part of an Info-Tech workshop.
Contact your account representative for more information.
workshops@infotech.com 1-888-670-8889
Final Thoughts: RFP Do’s and Don’ts
DO
|
DON'T
|
Bibliography
“2022 RFP Response Trends & Benchmarks.” Loopio, 2022. Web.
Corrigan, Tony. “How Much Does it Cost to Respond to an RFP?” LinkedIn, March 2017. Accessed 10 Dec. 2019
“Death by RFP:7 Reasons Not to Respond.” Inc. Magazine, 2013. Web.
Jeffery, Steven, George Bordon, and Phil Bode. The Art of Creating a Quality RFP, 3rd ed. Info-Tech Research Group, 2019.
“RFP Benchmarks: How Much Time and Staff Firms Devote to Proposals.” MarketingProfs, 2020. Web.
“State of the RFP 2019.” Bonfire, 2019. Web.
“What Vendors Want (in RFPs).” Vendorful, 2020. Web.
Related Info-Tech Research

|
Prepare for Negotiations More Effectively
|

|
Understand Common IT Contract Provisions to Negotiate More Effectively
|

|
Jump Start Your Vendor Management Initiative
|
Buying Options
Drive Successful Sourcing Outcomes With a Robust RFP Process
Client rating
Cost Savings
Days Saved
IT Risk Management · IT Leadership & Strategy implementation · Operational Management · Service Delivery · Organizational Management · Process Improvements · ITIL, CORM, Agile · Cost Control · Business Process Analysis · Technology Development · Project Implementation · International Coordination · In & Outsourcing · Customer Care · Multilingual: Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese · Entrepreneur
Tymans Group is a brand by Gert Taeymans BV
Gert Taeymans bv
Europe: Koning Albertstraat 136, 2070 Burcht, Belgium — VAT No: BE0685.974.694 — phone: +32 (0) 468.142.754
USA: 4023 KENNETT PIKE, SUITE 751, GREENVILLE, DE 19807 — Phone: 1-917-473-8669
Copyright 2017-2022 Gert Taeymans BV