Secure Your Hybrid Workforce

- Many IT and security leaders struggle to cope with the challenges associated with an hybrid workforce and how best to secure it.
- Understanding the main principles of zero trust: never trust, always verify, assume breach, and verify explicitly.
- How to go about achieving a zero trust framework.
- Understanding the premise of SASE as it pertains to a hybrid workforce.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
Securing your hybrid workforce should be an opportunity to get started on the zero trust journey. Realizing the core features needed to achieve this will assist you determine which of the options is a good fit for your organization.
Impact and Result
Every organization's strategy to secure their hybrid workforce should include introducing zero trust principles in certain areas. Our unique approach:
- Assess the suitability of SASE/SSE and zero trust.
- Present capabilities and feature benefits.
- Procure SASE product and/or build a zero trust roadmap.
Secure Your Hybrid Workforce Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Secure Your Hybrid Workforce Deck – The purpose of the storyboard is to provide a detailed description of the steps involved in securing your hybrid workforce with zero trust.
The storyboard contains two easy-to-follow steps on securing your hybrid workforce with zero trust, from assessing the suitability of SASE/SSE to taking a step in building a zero trust roadmap.
- Secure Your Hybrid Workforce – Phases 1-2
2. Suitability Assessment Tool – A tool to identify whether SASE/SSE or a zero trust roadmap is a better fit for your organization.
Use this tool to identify your next line of action in securing your hybrid workforce by assessing key components that conforms to the ideals and principles of Zero Trust.
- Zero Trust - SASE Suitability Assessment Tool
3. RFP Template – A document to guide you through requesting proposals from vendors.
Use this document to request proposals from select vendors.
- Request for Proposal (RFP) Template
Further reading
Secure Your Hybrid Workforce
SASE as a driver to zero trust.
Analyst Perspective
Consolidate your security and network.
Remote connections like VPNs were not designed to be security tools or to have the capacity to handle a large hybrid workforce; hence, organizations are burdened with implementing controls that are perceived to be "security solutions." The COVID-19 pandemic forced a wave of remote work for employees that were not taken into consideration for most VPN implementations, and as a result, the understanding of the traditional network perimeter as we always knew it has shifted to include devices, applications, edges, and the internet. Additionally, remote work is here to stay as recruiting talent in the current market means you must make yourself attractive to potential hires.
The shift in the network perimeter increases the risks associated with traditional VPN solutions as well as exposing the limitations of the solution. This is where zero trust as a principle introduces a more security-focused strategy that not only mitigates most (if not all) of the risks, but also eliminates limitations, which would enhance the business and improve customer/employee experience.
There are several ways of achieving zero trust maturity, and one of those is SASE, which consolidates security and networking to better secure your hybrid workforce as implied trust is thrown out of the window and verification of everything becomes the new normal to defend the business.

Victor Okorie
Senior Research Analyst, Security and Privacy
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
CISOs are looking to zero trust to fill the gaps associated with their traditional remote setup as well as to build an adaptable security strategy. Some challenges faced include:
- Understanding the main principles of zero trust: never trust, always verify, assume breach, and verify explicitly.
- Understanding how to achieve a zero trust framework.
- Understanding the premise of SASE as it pertains to a hybrid workforce.
Common Obstacles
The zero trust journey may seem tedious because of a few obstacles like:
- Knowing what the principle is all about and the components that align with it.
- Knowing where to start. Due to the lack of a standardized path for the zero trust journey, going about the journey can be confusing.
- Not having a uniform definition of what makes up a SASE solution as it is heavily dependent on vendors.
Info-Tech's Approach
Info-Tech provides a three-service approach to helping organizations better secure their hybrid workforce.
- Understand your current, existing technological capabilities and challenges with your hybrid infrastructure, and prioritize those challenges.
- Gain insight into zero trust and SASE as a mitigation/control/tool to those challenges.
- Identify the SASE features that are relevant to your needs and a source guide for a SASE vendor.
Info-Tech Insight
Securing your hybrid workforce should be an opportunity to get started on the zero trust journey. Realizing the core features needed to achieve this will assist you in determining which of the options is a good fit for your organization.
Turn your challenges into opportunities
Hybrid workforce is the new normal
The pandemic has shown there is no going back to full on-prem work, and as such, security should be looked at differently with various considerations in mind.
Understand that current hybrid solutions are susceptible to various forms of attack as the threat attack surface area has now expanded with users, devices, applications, locations, and data. The traditional perimeter as we know it has expanded beyond just the corporate network, and as such, it needs a more mature security strategy.
Onboarding and offboarding have been done remotely, and with some growth recorded, the size of companies has also increased, leading to a scaling issue.
Employees are now demanding remote work capabilities as part of contract negotiation before accepting a job.
Attacks have increased far more quickly during the pandemic, and all indications point to them increasing even more.
Scarce available security personnel in the job market for hire.
Reality Today
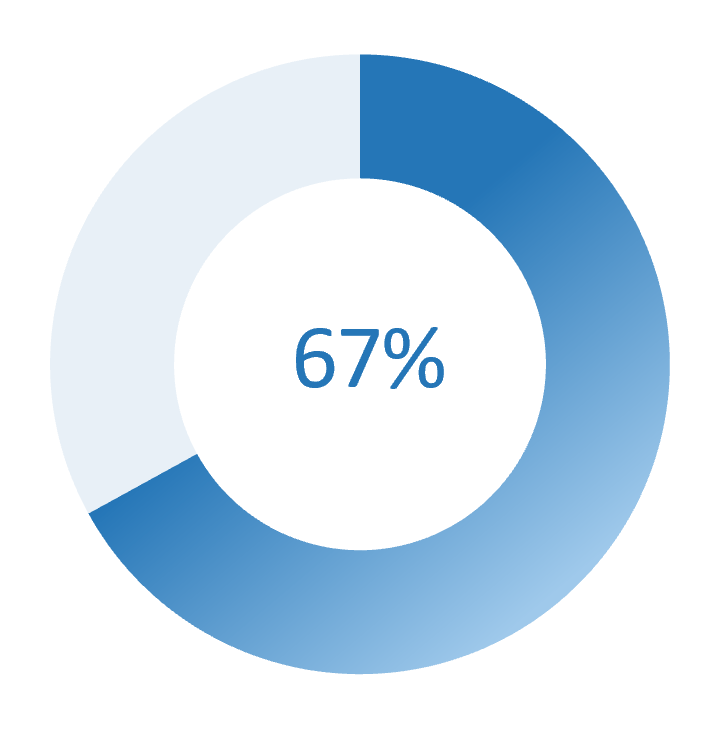
The number of breach incidents by identity theft.
Source: Security Magazine, 2022.
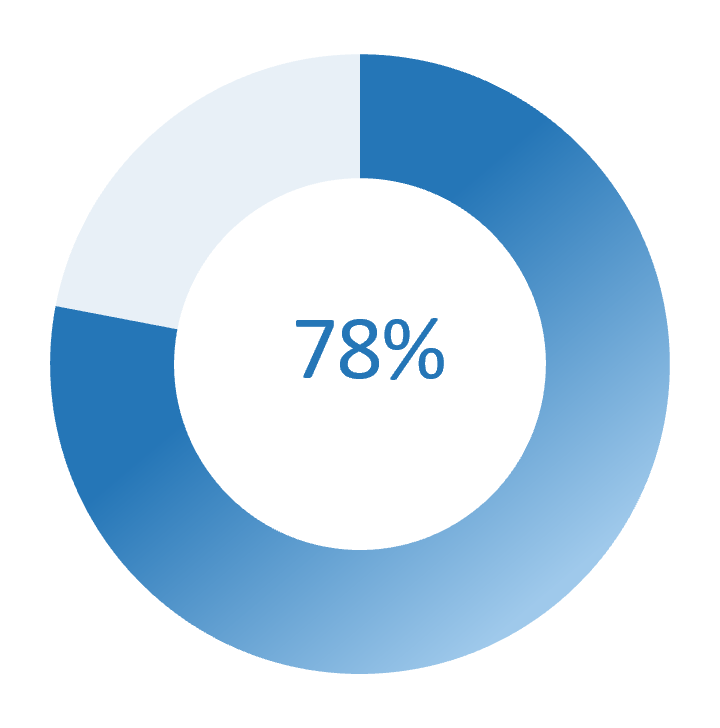
IT security teams want to adopt zero trust.
Source: Cybersecurity Insiders, 2019.
Reduce the risks of remote work by using zero trust
$1.07m |
$1.76m |
235 |
|---|---|---|
|
Increase in breaches related to remote work |
Cost difference in a breach where zero trust is deployed |
Days to identify a breach |
|
The average cost of a data breach where remote work was a factor rose by $1.07 million in 2021. COVID-19 brought about rapid changes in organizations, and digital transformation changes curbed some of its excesses. Organizations that did not make any digital transformation changes reported a $750,000 higher costs compared to global average. |
The average cost of a breach in an organization with no zero trust deployed was $5.04 million in 2021 compared to the average cost of a breach in an organization with zero trust deployed of $3.28 million. With a difference of $1.76 million, zero trust makes a significant difference. |
Organizations with a remote work adoption rate of 50% took 235 days to identify a breach and 81 days to contain that breach – this is in comparison to the average of 212 days to identify a breach and 75 days to contain that breach. |
Source: IBM, 2021.
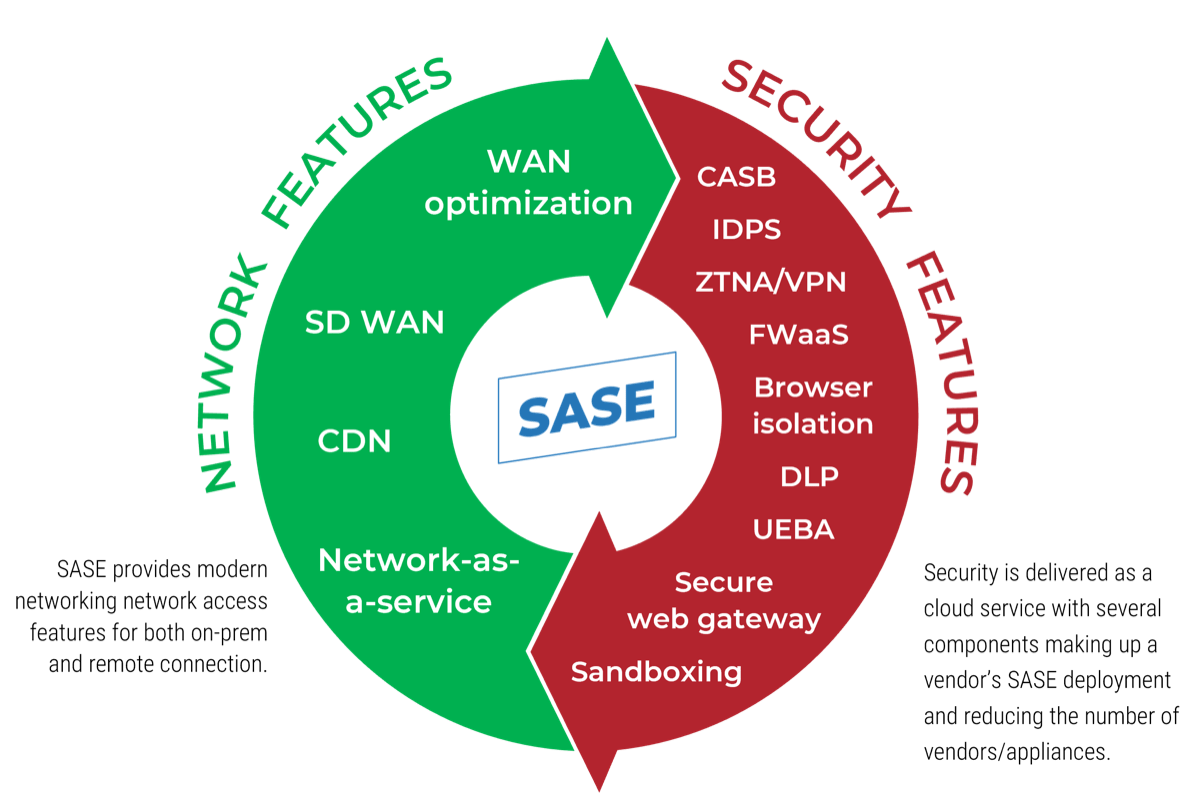
Network + Security = SASE
What exactly is a SASE product?
The convergence and consolidation of security and network brought about the formation of secure access service edge (SASE – pronounced like "sassy"). Digital transformation, hybrid workforce, high demand of availability, uninterrupted access for employees, and a host of other factors influenced the need for this convergence that is delivered as a cloud service.
The capabilities of a SASE solution being delivered are based on certain criteria, such as the identity of the entity (users, devices, applications, data, services, location), real-time context, continuous assessment and verification of risk and "trust" throughout the lifetime of a session, and the security and compliance policies of the organization.
SASE continuously identifies users and devices, applies security based on policy, and provides secure access to the appropriate and requested application or data regardless of location.
Current Approach
The traditional perimeter security using the castle and moat approach is depicted in the image here. The security shields valuable resources from external attack; however, it isn't foolproof for all kinds of external attacks. Furthermore, it does not protect those valuable resources from insider threat.
This security perimeter also allows for lateral movement when it has been breached. Access to these resources is now considered "trusted" solely because it is now behind the wall/perimeter.
This approach is no longer feasible in our world today where both external and internal threats pose continuous risk and need to be contained.
Determine the suitability of SASE and zero trust
The Challenge:
Complications facing traditional infrastructure
- Increased hybrid workforce
- Regulatory compliance
- Limited Infosec personnel
- Poor threat detection
- Increased attack surface
Common vulnerabilities in traditional infrastructure
- MITM attack
- XSS attack
- Session hijacking
- Trust-based model
- IP spoofing
- Brute force attack
- Distributed denial of service
- DNS hijacking
- Latency issues
- Lateral movement once connection is established
|
TRADITIONAL INFRASTRUCTURE |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NETWORK |
SECURITY |
AUTHENTICATION |
IDENTITY |
ACCESS |
|
|
|
|
|
Candidate Solutions
Proposed benefits of SASE
- Access is only granted to the requested resource
- Consolidated network and security as a service
- Micro-segmentation on application and gateway
- Adopts a zero trust security posture for all access
- Managed detection and response
- Uniform enforcement of policy
- Distributed denial of service shield
SASE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
NETWORK | SECURITY | AUTHENTICATION | IDENTITY | ACCESS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ZERO TRUST |
|
|---|---|
|
TENETS OF ZERO TRUST |
ZERO TRUST PILLARS |
|
|
Proposed benefits of zero trust
- Identify and protect critical and non-critical resources in accordance with business objectives.
- Produce initiatives that conform to the ideals of zero trust and are aligned with the corresponding pillars above.
- Formulate policies to protect resources and aid segmentation.
Info-Tech Insight
Securing your hybrid workforce should be an opportunity to get started on the zero trust journey. Realizing the core features needed to achieve this will help you determine which of the options is a good fit for your organization.
Measure the value of using Info-Tech's approach
IT and business value
PHASE 1
|
PHASE 2 Assess the benefits of adopting SASE or zero trust |
Vendors will try to control the narrative in terms of what they can do for you, but it's time for you to control the narrative and identify pain points to IT and the business, and with that, to understand and define what the vendor solution can do for you. |
|---|---|
|
PHASE 2 Assess the benefits of adopting SASE or zero trust |
Vendors will try to control the narrative in terms of what they can do for you, but it's time for you to control the narrative and identify pain points to IT and the business, and with that, to understand and define what the vendor solution can do for you. |
Short-term benefits
- Gain awareness of your zero trust readiness.
- Embed a zero trust mindset across your architecture.
- Control the narrative of what SASE brings to your organization.
Long-term benefits
- Identified controls to mitigate risks with current architecture while on a zero trust journey.
- Improved security posture that reduces risk by increasing visibility into threats and user connections.
- Reduced CapEx and OpEx due to the scalability, low staffing requirements, and improved time to respond to threats using a SASE or SSE solution.
Determine SASE cost factors
IT and business value
Info-Tech Insight
IT leaders need to examine different areas of their budget and determine how the adoption of a SASE solution could influence several areas of their budget breakdown.
Determining the SASE cost factors early could accelerate the justification the business needs to move forward in making an informed decision.
|
01- Infrastructure |
|
|---|---|
|
02- Administration |
|
|
03- Inbound |
|
|
04- Outbound |
|
|
04- Data Protection |
|
|
06- Monitoring |
|
Info-Tech's methodology for securing your hybrid workforce
|
1. Current state and future mitigation |
2. Assess the benefits of moving to SASE/zero trust |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Phase Steps |
1.1 Limitations of legacy infrastructure 1.2 Zero trust principle as a control 1.3 SASE as a driver of zero trust |
2.1 Sourcing out a SASE/SSE vendor 2.2 Build a zero trust roadmap |
|
Phase Outcomes |
Identify and prioritize risks of current infrastructure and several ways to mitigate them. |
RFP template and build a zero trust roadmap. |
Consider several factors needed to protect your growing hybrid workforce and assess your current resource capabilities, solutions, and desire for a more mature security program. The outcome should either address a quick pain point or a long-term roadmap.
The internet is the new corporate network
The internet is the new corporate network, which opens the organization up to more risks not protected by the current security stack. Using Info-Tech's methodology of zero trust adoption is a sure way to reduce the attack surface, and SASE is one useful tool to take you on the zero trust journey.
Current-state risks and future mitigation
Securing your hybrid workforce via zero trust will inevitably include (but is not limited to) technological products/solutions.
SASE and SSE features sit as an overlay here as technological solutions that will help on the zero trust journey by aggregating all the disparate solutions required for you to meet zero trust requirements into a single interface. The knowledge and implementation of this helps put things into perspective of where and what our target state is.
The right solution for the right problem
It is critical to choose a solution that addresses the security problems you are actually trying to solve.
Don't allow the solution provider to tell you what you need – rather, start by understanding your capability gaps and then go to market to find the right partner.
Take advantage of the RFP template to source a SASE or SSE vendor. Additionally, build a zero trust roadmap to develop and strategize initiatives and tasks.
Blueprint deliverables
Each step of this blueprint is accompanied by supporting deliverables to help you accomplish your goals:
Zero Trust and SASE Suitability Tool
Identify critical and vulnerable DAAS elements to protect and align them to business goals.
Zero Trust Program Gap Analysis Tool
Perform a gap analysis between current and target states to build a zero trust roadmap.
Key deliverable:
Secure Your Hybrid Workforce With Zero Trust Communication deck
Present your zero trust strategy in a prepopulated document that summarizes the work you have completed as a part of this blueprint.
Phase 1
Current state and future mitigation
Phase 1 | Phase 2 |
|---|---|
1.1 Limitations of legacy infrastructure 1.2 Zero trust principle as a control 1.3 SASE as a driver of zero trust | 2.1 Sourcing out a SASE/SSE vendor 2.2 Build a zero trust roadmap |
This phase will walk you through the following activities:
- Introduction to the tool, how to use the input tabs to identify current challenges, technologies being used, and to prioritize the challenges. The prioritized list will highlight existing gaps and eventually be mapped to recommended mitigations in the following phase.
This phase involves the following participants:
- CIO
- CISO
- CSO
- IT security team
- IT network team
Secure Your Hybrid Workforce
1.1 Limitations of legacy infrastructure
Traditional security & remote access solutions must be modernized
Info-Tech Insight
Traditional security is architected with a perimeter in mind and is poorly suited to the threats in hybrid or distributed environments.
Ensure you minimize or eliminate weak points on all layers.
- SECURITY
- DDoS
- DNS hijacking
- Weak VPN protocols
- IDENTITY
- One-time verification allowing lateral movement
- NETWORK
- Risk perimeter stops at corporate network edge
- Split tunneling
- AUTHENTICATION
- Weak authentication
- Weak passwords
- ACCESS
- Man-in-the-middle attack
- Cross-site scripting
- Session hijacking
1.1.1 For example: traditional VPNs are poorly suited to a hybrid workforce
There are many limitations that make it difficult for traditional VPNs to adapt to an ever-growing hybrid workforce.
The listed limitations are tied to associated risks of legacy infrastructure as well as security components that are almost non-existent in a VPN implementation today.
Scaling
VPNs were designed for small-scale remote access to corporate network. An increase in the remote workforce will require expensive hardware investment.
Visibility
Users and attackers are not restricted to specific network resources, and with an absence of activity logs, they can go undetected.
Managed detection & response
Due to the reduction in or lack of visibility, threat detections are poorly managed, and responses are already too late.
Hardware
Limited number of locations for VPN hardware to be situated as it can be expensive.
Hybrid workforce
The increase in the hybrid workforce requires the risk perimeter to be expanded from the corporate network to devices and applications. VPNs are built for privacy, not security.
Info-Tech Insight
Hybrid workforces are here to stay, and adopting a strategy that is adaptable, flexible, simple, and cost-effective is a recommended road to take on the journey to bettering your security and network.
1.1 Identify risk from legacy infrastructure
Estimated Time: 1-2 hours
- Ensure all vulnerabilities described on slide 17 are removed.
- Note any forecasted challenge you think you might have down the line with your current hybrid setup.
- Identify any trend that may be of interest to you with regards to your hybrid setup.
Download the Zero Trust - SASE Suitability Assessment Tool
Input
- List of key pain points and challenges
- List of forecasted challenges and trends of interest
Output
- Prioritized list of pain points and/or challenges
Materials
- Excel tool
- Whiteboard
Participants
- CISO
- InfoSec team
- IT manager
- CIO
- Infrastructure team
1.2 Zero trust principle as a control
A zero trust implementation comes with benefits/initiatives that mitigate the challenges identified in earlier activities.
Info-Tech Insight
Zero trust/"always verify" is applied to identity, workloads, devices, networks, and data to provide a greater control for risks associated with traditional network architecture.
Improve IAM maturity
Zero trust identity and access will lead to a mature IAM process in an organization with the removal of implicit trust.
Secure your remote access
With a zero trust network architecture (ZTNA), both the remote and on-prem network access are more secure than the traditional network deployment. The software-defined parameter ensures security on each network access.
Reduce threat surface area
With zero trust principle applied on identity, workload, devices, network, and data, the threat surface area which births some of the risks identified earlier will be significantly reduced.
Improve hybrid workforce
Scaling, visibility, network throughput, secure connection from anywhere, micro-segmentation, and a host of other benefits to improve your hybrid workforce.
1.2 SASE as an overlay to zero trust
Security and network initiatives of a zero trust roadmap converged into a single pane of glass.
Info-Tech Insight
Security and network converged into a single pane of glass giving you some of the benefits and initiatives of a zero trust implemented architecture in one package.
Improve IAM maturity
The identity-centric nature of SASE solutions helps to improve your IAM maturity as it applies the principle of least privilege. The removal of implicit trust and continuous verification helps foster this more.
Secure your remote access
With ZTNA, both the remote and on-prem network access are more secure than the traditional network deployment. The software defined parameter ensures security on each network access.
Reduce threat surface area
Secure web gateway, cloud access security broker, domain name system, next-generation firewall, data loss prevention, and ZTNA protect against data leaks, prevent lateral movement, and prevent malicious actors from coming in.
Improve hybrid workforce
Reduced costs and complexity of IT, faster user experience, and reduced risk as a result of the scalability, visibility, ease of IT administration, network throughput, secure connection from anywhere, micro-segmentation, and a host of other benefits will surely improve your hybrid workforce.
Align SASE features to zero trust core capabilities
Verify Identity
- Authentication & verification are enforced for each app request or session.
- Use of multifactor authentication.
- RBAC/ABAC and principle of least privilege are applied on the identity regardless of user, device, or location.
Verify Device
- Device health is checked to ensure device is not compromised or vulnerable.
- No admin permissions on user devices.
- Device-based risk assessment is enforced as part of UEBA.
Verify Access
- Micro-segmentation built around network, user, device, location and roles.
- Use of context and content-based policy enforced to the user, application, and device identity.
- Network access only granted to specified application request and not to the entire network.
Verify Services
- Applications and services are checked before access is granted.
- Connections to the application and services are inspected with the security controls built into the SASE solution.
Info-Tech Insight
These features of SASE and zero trust mitigate the risks associated with a traditional VPN and reduce the threat surface area. With security at the core, network optimization is not compromised.
Security components of SASE
Otherwise known as security service edge (SSE)
Security service edge is the convergence of all security services typically found in SASE. At its core, SSE consists of three services which include:
- Secure web gateway – secure access to the internet and web.
- Cloud access security broker – secure access to SaaS and cloud applications.
- Zero trust network access – secure remote access to private applications.
SSE components are also mitigations or initiatives that make up a zero trust roadmap as they comply with the zero trust principle, and as a result, they sit up there with SASE as an overlay/driver of a zero trust implementation. SSE's benefits are identical to SASE's in that it provides zero trust access, risk reduction, low costs and complexity, and a better user experience. The difference is SSE's sole focus on security services and not the network component.
|
SASE |
|
|---|---|
|
NETWORK FEATURES |
SECURITY FEATURES |
|
|
1.3 Pros & cons of zero trust and SASE
|
Zero Trust |
SASE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Pros |
Cons |
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
|
|
Understand SASE and zero trust suitability for your needs
Estimated Time: 1 hour
Use the dashboard to understand the value assessment of adopting a SASE product or building a zero trust roadmap.
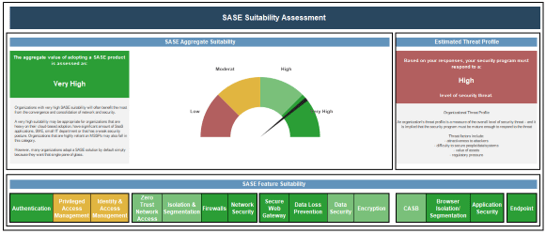
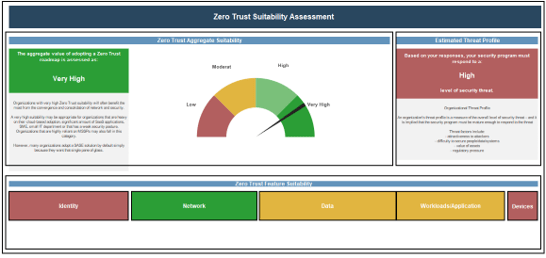
Info-Tech Insight
This tool will help steer you on a path to take as a form of mitigation/control to some or all the identified challenges.
Phase 2
Make a decision and next steps
Phase 1 | Phase 2 |
|---|---|
1.1 Limitations of legacy infrastructure 1.2 Zero trust principle as a control 1.3 SASE as a driver of zero trust | 2.1 Sourcing out a SASE/SSE vendor 2.2 Build a zero trust roadmap |
This phase will walk you through the following activities:
- Introduction to the tool activity, how to use the input tabs and considerations to generate an output that could help understand the current state of your hybrid infrastructure and what direction is to be followed next to improve.
This phase involves the following participants:
- CIO
- CISO
- CSO
- IT security
- IT network team
Secure Your Hybrid Workforce
Step 2.1
Sourcing out a SASE/SSE vendor
Activities
2.1.1 Use the RFP template to request proposal from vendors
2.1.2 Use SoftwareReviews to compare vendors
This step involves the following participants:
- CIO, CISO, IT manager, Infosec team, executives.
Outcomes of this step
- Zero Trust Roadmap
2.1.1 Use the RFP template to request proposal from vendors
Estimated Time: 1-3 hours
- As a group, use the RFP Template to include technical capabilities of your desired SASE product and to request proposals from vendors.
- The features that are most important to your organization generated from phase one should be highlighted in the RFP.
Input
- List of SASE features
- Technical capabilities
Output
- RFP
Materials
- RFP Template
Participants
- Security team
- IT leadership
Download the RFP Template
2.1.2 Use SoftwareReviews to compare vendors
SoftwareReviews
- The Data Quadrant is a thorough evaluation and ranking of all software in an individual category to compare platforms across multiple dimensions.
- Vendors are ranked by their Composite Score, based on individual feature evaluations, user satisfaction rankings, vendor capability comparisons, and likeliness to recommend the platform.
- The Emotional Footprint is a powerful indicator of overall user sentiment toward the relationship with the vendor, capturing data across five dimensions.
- Vendors are ranked by their Customer Experience (CX) Score, which combines the overall Emotional Footprint rating with a measure of the value delivered by the solution.
Step 2.2
Zero trust readiness and roadmap
Activities
2.2.1 Assess the maturity of your current zero trust implementation
2.2.2 Understand business needs and current security projects
2.2.3 Set target maturity state with timeframe
This step involves the following participants:
CIO, CISO, IT manager, Infosec team, executives.
Outcomes of this step
Zero Trust Roadmap
2.2.1 Assess the maturity of your current zero trust implementation
Estimated Time: 1-3 hours
- Realizing that zero trust is a journey helps create a better roadmap and implementation. Identify the current controls or solutions in your organization that align with the principle of zero trust.
- Break down these controls or solutions into different silos (e.g. identity, security, network, data, device, applications, etc.).
- Determine your zero trust readiness.
Input
- List of zero trust controls/solutions
- Siloed list of zero trust controls/solutions
- Current state of zero trust maturity
Output
- Zero trust readiness and current maturity state
Materials
- Zero Trust Security Benefit Assessment tool
Participants
- Security team
- IT leadership
Download the Zero Trust Security Benefit Assessment tool
2.2.2 Understand business needs and current security projects
Estimated Time: 1-3 hours
- Identify the business and IT executives, application owners, and board members whose vision aligns with the zero trust journey.
- Identify existing projects within security, IT, and the business and highlight interdependencies or how they fit with the zero trust journey.
- Build a rough sketch of the roadmap that fits the business needs, current projects and the zero trust journey.
Input
- Meetings with stakeholders
- List of current and future projects
Output
- Sketch of zero trust roadmap
Materials
- Whiteboard activity
Participants
- Security team
- IT leadership
- IT ops team
- Business executives
- Board members
2.2.3 Set target maturity state with a given timeframe
Estimated Time: 1-3 hours
- With the zero trust readiness, current business, IT and security projects, current maturity state, and sketch of the roadmap, setting a target maturity state within some timeframe is at the top of the list. The target maturity state will include a list of initiatives that could be siloed and confined to a timeframe.
- A Gantt chart or graph could be used to complete this task.
Input
- Results from previous activity slides
Output
- Current state and target state assessment for gap analysis
- List of initiatives and timeframe
Materials
- Zero Trust Program Gap Analysis Tool
Participants
- Security team
- IT leadership
- IT ops team
- Business executives
- Board members
Download the Zero Trust Program Gap Analysis Tool
Summary of Accomplishment
Insights Gained
- Difference between zero trust as a principle and SASE as a framework
- Difference between SASE and SSE platforms.
- Assessment of which path to take in securing your hybrid workforce
Deliverables Completed
- Zero Trust – SASE Suitability Assessment Tool
- Secure Your Hybrid Workforce Communication Deck
If you would like additional support, have our analysts guide you through other phases as part of an Info-Tech workshop
Contact your account representative for more information
workshops@infotech.com
1-888-670-8889
Additional Support
If you would like additional support, have our analysts guide you through other phases as part of an Info-Tech workshop
To accelerate this project, engage your IT team in an Info-Tech workshop with an Info-Tech analyst team.
Info-Tech analysts will join you and your team at your location or welcome you to Info-Tech's historic Toronto office to participate in an innovative onsite workshop.
Contact your account representative for more information.
workshops@infotech.com 1-888-670-8889
The following are sample activities that will be conducted by Info-Tech analysts with your team:
Zero Trust - SASE Suitability Assessment Tool
Assess current security capabilities and build a roadmap of tasks and initiatives that close maturity gaps.
Research Contributors
- Aaron Shum, Vice President, Security & Privacy
- Cameron Smith, Research Lead, Security & Privacy
- Brad Mateski, Zones, Solutions Architect for CyberSecurity
- Bob Smock, Info-Tech Research Group, Vice President of Consulting
- Dr. Chase Cunningham, Ericom Software, Chief Strategy Officer
- John Kindervag, ON2IT Cybersecurity, Senior Vice President, Cybersecurity Strategy and ON2IT Group Fellow
- John Zhao, Fonterra, Enterprise Security Architect
- Rongxing Lu, University of New Brunswick, Associate Professor
- Sumanta Sarkar, University of Warwick, Assistant Professor
- Tim Malone, J.B. Hunt Transport, Senior Director Information Security
- Vana Matte, J.B. Hunt Transport, Senior Vice President of Technology Services
Related Info-Tech Research
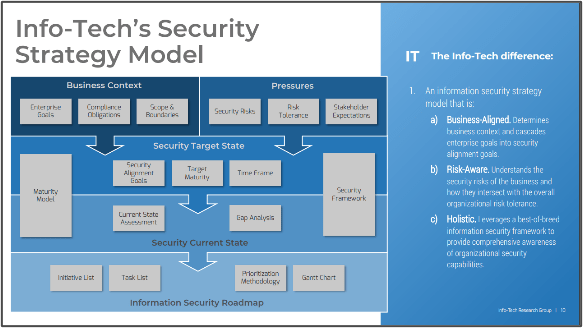
Build an Information Security Strategy
Info-Tech has developed a highly effective approach to building an information security strategy – an approach that has been successfully tested and refined for over seven years with hundreds of organizations. This unique approach includes tools for ensuring alignment with business objectives, assessing organizational risk and stakeholder expectations, enabling a comprehensive current state assessment, prioritizing initiatives, and building out a security roadmap.
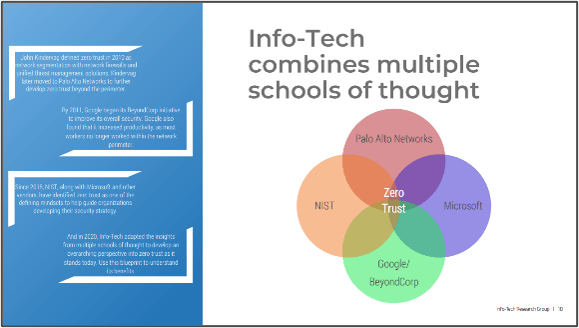
Determine Your Zero Trust Readiness
IT security was typified by perimeter security. However, the way the world does business has mandated a change to IT security. In response, zero trust is a set of principles that can add flexibility to planning your IT security strategy.
Use this blueprint to determine your zero trust readiness and understand how zero trust can benefit both security and the business.
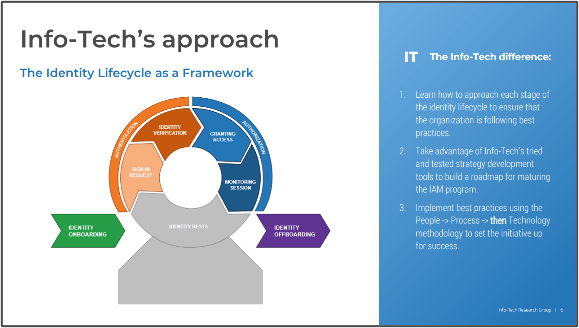
Mature Your Identity and Access Management Program
Many organizations are looking to improve their identity and access management (IAM) practices but struggle with where to start and whether all areas of IAM have been considered. This blueprint will help you improve the organization's IAM practices by following our three-phase methodology:
- Assess identity and access requirements.
- Identify initiatives using the identity lifecycle.
- Prioritize initiatives and build a roadmap.
Bibliography
"2021 Data Breach Investigations Report." Verizon, 2021. Web.
"Fortinet Brings Networking and Security to the Cloud" Fortinet, 2 Mar. 2021. Web.
"A Zero Trust Strategy Has 3 Needs – Identify, Authenticate, and Monitor Users and Devices on and off the Network." Fortinet, 15 July 2021. Web.
"Applying Zero Trust Principles to Enterprise Mobility." CISA, Mar. 2022. Web.
"CISA Zero Trust Maturity Model." CISA, Cybersecurity Division, June 2021. Web.
"Continuous Diagnostics and Mitigation Program Overview." CISA, Jan. 2022. Web.
"Cost of a Data Breach Report 2021 | IBM." IBM, July 2021. Web.
English, Melanie. "5 Stats That Show The Cost Saving Effect of Zero Trust." Teramind, 29 Sept. 2021. Web.
Hunter, Steve. "The Five Business Benefits of a Zero Trust Approach to Security." Security Brief - Australia, 19 Aug. 2020. Web.
"Improve Application Access and Security With Fortinet Zero Trust Network Access." Fortinet, 2 Mar. 2021. Web.
"Incorporating zero trust Strategies for Secure Network and Application Access." Fortinet, 21 Jul. 2021. Web.
Jakkal, Vasu. "Zero Trust Adoption Report: How Does Your Organization Compare?" Microsoft, 28 July 2021. Web.
"Jericho Forum™ Commandments." The Open Group, Jericho Forum, May 2007. Web.
Schulze, Holger. "2019 Zero Trust Adoption Report." Cybersecurity Insiders, 2019. Web.
"67% of Organizations Had Identity-Related Data Breaches Last Year." Security Magazine, 22 Aug. 2022. Web.
United States, Executive Office of the President Joseph R. Biden, Jr. "Executive Order on Improving the Nation's Cybersecurity." The White House, 12 May 2021. Web.
Buying Options
Secure Your Hybrid Workforce
IT Risk Management · IT Leadership & Strategy implementation · Operational Management · Service Delivery · Organizational Management · Process Improvements · ITIL, CORM, Agile · Cost Control · Business Process Analysis · Technology Development · Project Implementation · International Coordination · In & Outsourcing · Customer Care · Multilingual: Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese · Entrepreneur
Tymans Group is a brand by Gert Taeymans BV
Gert Taeymans bv
Europe: Koning Albertstraat 136, 2070 Burcht, Belgium — VAT No: BE0685.974.694 — phone: +32 (0) 468.142.754
USA: 4023 KENNETT PIKE, SUITE 751, GREENVILLE, DE 19807 — Phone: 1-917-473-8669
Copyright 2017-2022 Gert Taeymans BV