Develop and Deploy Security Policies

- Employees are not paying attention to policies. Awareness and understanding of what the security policy’s purpose is, how it benefits the organization, and the importance of compliance are overlooked when policies are distributed.
- Informal, un-rationalized, ad hoc policies do not explicitly outline responsibilities, are rarely comprehensive, and are difficult to implement, revise, and maintain.
- Data breaches are still on the rise and security policies are not shaping good employee behavior or security-conscious practices.
- Adhering to security policies is rarely a priority to users as compliance often feels like an interference to daily workflow. For a lot of organizations, security policies are not having the desired effect.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
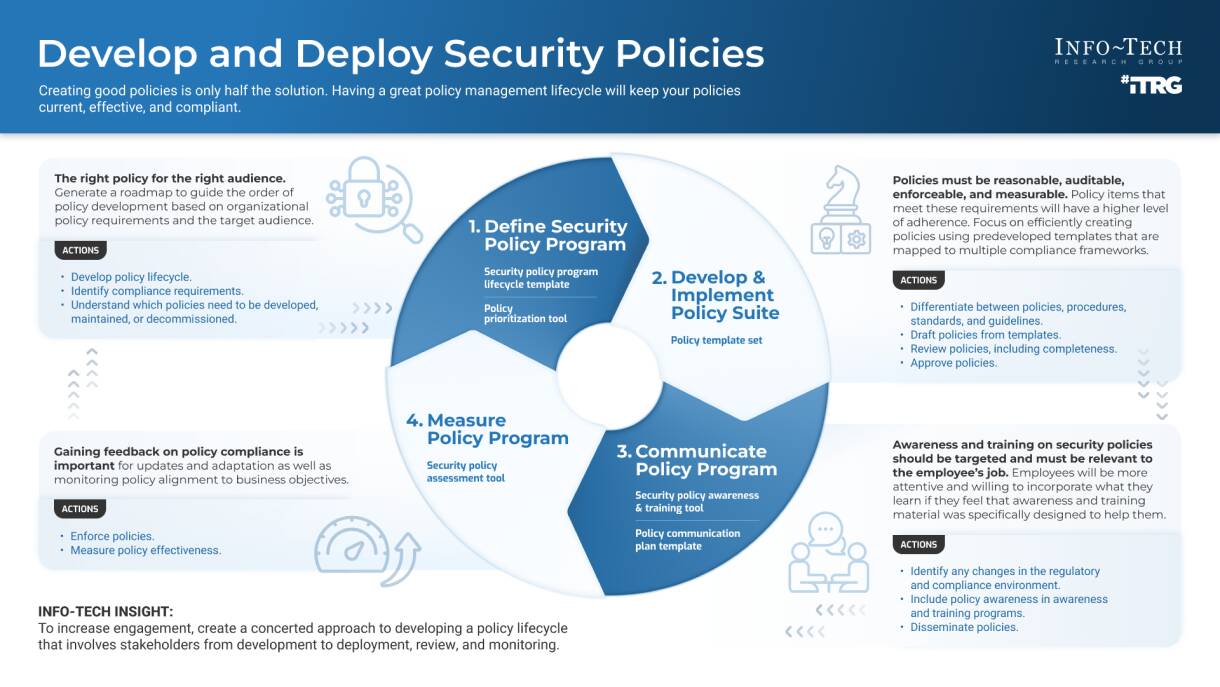
- Creating good policies is only half the solution. Having a great policy management lifecycle will keep your policies current, effective, and compliant.
- Policies must be reasonable, auditable, enforceable, and measurable. If the policy items don’t meet these requirements, users can’t be expected to adhere to them. Focus on developing policies to be quantified and qualified for them to be relevant.
Impact and Result
- Save time and money using the templates provided to create your own customized security policies mapped to the Info-Tech framework, which incorporates multiple industry best-practice frameworks (NIST, ISO, SOC2SEC, CIS, PCI, HIPAA).
Develop and Deploy Security Policies Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Develop and Deploy Security Policies Deck – A step-by-step guide to help you build, implement, and assess your security policy program.
Our systematic approach will ensure that all identified areas of security have an associated policy.
- Develop and Deploy Security Policies – Phases 1-4
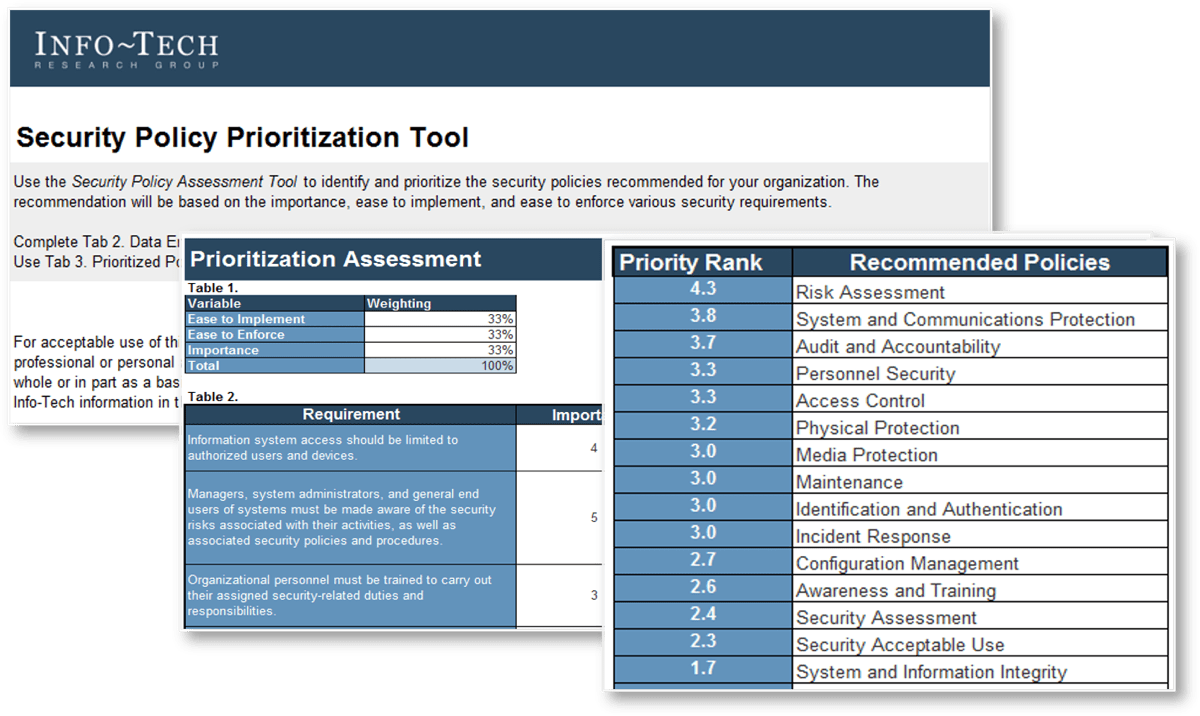
2. Security Policy Prioritization Tool – A structured tool to help your organization prioritize your policy suite to ensure that you are addressing the most important policies first.
The Security Policy Prioritization Tool assesses the policy suite on policy importance, ease to implement, and ease to enforce. The output of this tool is your prioritized list of policies based on our policy framework.
- Security Policy Prioritization Tool
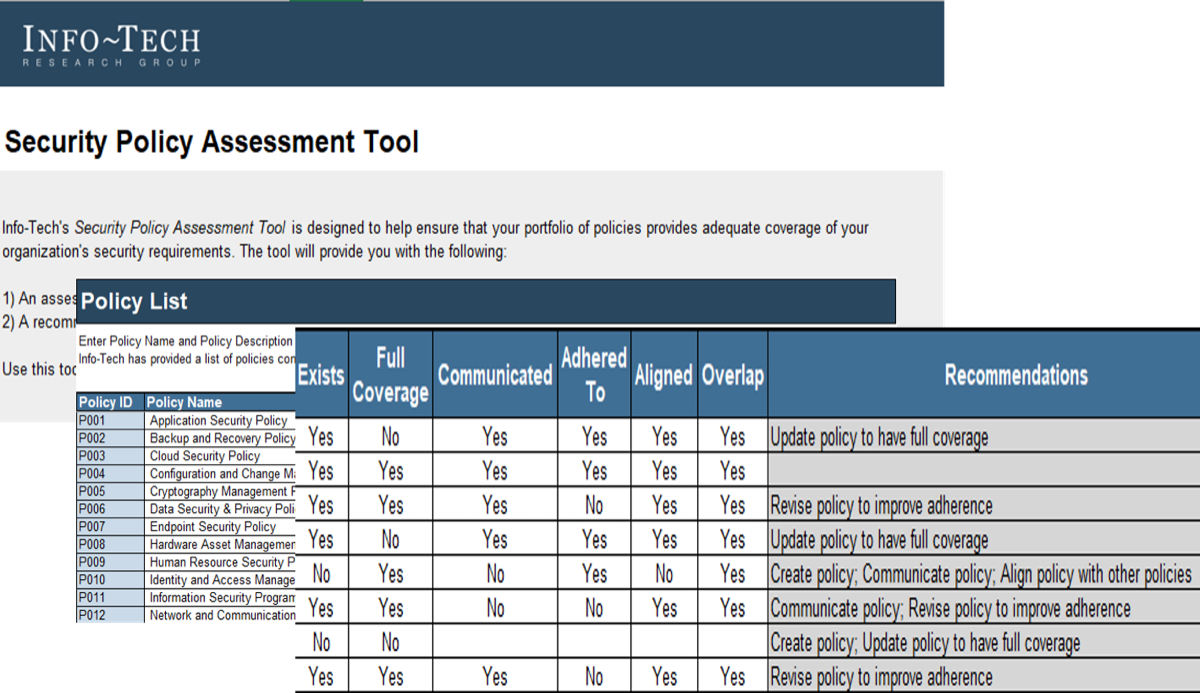
3. Security Policy Assessment Tool – A structured tool to assess the effectiveness of policies within your organization and determine recommended actions for remediation.
The Security Policy Assessment Tool assesses the policy suite on policy coverage, communication, adherence, alignment, and overlap. The output of this tool is a checklist of remediation actions for each individual policy.
- Security Policy Assessment Tool
4. Security Policy Lifecycle Template – A customizable lifecycle template to manage your security policy initiatives.
The Lifecycle Template includes sections on security vision, security mission, strategic security and policy objectives, policy design, roles and responsibilities for developing security policies, and organizational responsibilities.
- Security Policy Lifecycle Template
5. Policy Suite Templates – A best-of-breed templates suite mapped to the Info-Tech framework you can customize to reflect your organizational requirements and acquire approval.
Use Info-Tech's security policy templates, which incorporate multiple industry best-practice frameworks (NIST, ISO, SOC2SEC, CIS, PCI, HIPAA), to ensure that your policies are clear, concise, and consistent.
- Acceptable Use of Technology Policy Template
- Application Security Policy Template
- Asset Management Policy Template
- Backup and Recovery Policy Template
- Cloud Security Policy Template
- Compliance and Audit Management Policy Template
- Data Security Policy Template
- Endpoint Security Policy Template
- Human Resource Security Policy Template
- Identity and Access Management Policy Template
- Information Security Policy Template
- Network and Communications Security Policy Template
- Physical and Environmental Security Policy Template
- Security Awareness and Training Policy Template
- Security Incident Management Policy Template
- Security Risk Management Policy Template
- Security Threat Detection Policy Template
- System Configuration and Change Management Policy Template
- Vulnerability Management Policy Template
6. Policy Communication Plan Template – A template to help you plan your approach for publishing and communicating your policy updates across the entire organization.
This template helps you consider the budget time for communications, identify all stakeholders, and avoid scheduling communications in competition with one another.
- Policy Communication Plan Template
7. Security Awareness and Training Program Development Tool – A tool to help you identify initiatives to develop your security awareness and training program.
Use this tool to first identify the initiatives that can grow your program, then as a roadmap tool for tracking progress of completion for those initiatives.
- Security Awareness and Training Program Development Tool
Infographic
Workshop: Develop and Deploy Security Policies
Workshops offer an easy way to accelerate your project. If you are unable to do the project yourself, and a Guided Implementation isn't enough, we offer low-cost delivery of our project workshops. We take you through every phase of your project and ensure that you have a roadmap in place to complete your project successfully.
1 Define the Security Policy Program
The Purpose
Define the security policy development program.
Formalize a governing security policy lifecycle.
Key Benefits Achieved
Understanding the current state of policies within your organization.
Prioritizing list of security policies for your organization.
Being able to defend policies written based on business requirements and overarching security needs.
Leveraging an executive champion to help policy adoption across the organization.
Formalizing the roles, responsibilities, and overall mission of the program.
Activities
1.1 Understand the current state of policies.
1.2 Align your security policies to the Info-Tech framework for compliance.
1.3 Understand the relationship between policies and other documents.
1.4 Prioritize the development of security policies.
1.5 Discuss strategies to leverage stakeholder support.
1.6 Plan to communicate with all stakeholders.
1.7 Develop the security policy lifecycle.
Outputs
Security Policy Prioritization Tool
Security Policy Prioritization Tool
Security Policy Lifecycle Template
2 Develop the Security Policy Suite
The Purpose
Develop a comprehensive suite of security policies that are relevant to the needs of the organization.
Key Benefits Achieved
Time, effort, and money saved by developing formally documented security policies with input from Info-Tech’s subject-matter experts.
Activities
2.1 Discuss the risks and drivers your organization faces that must be addressed by policies.
2.2 Develop and customize security policies.
2.3 Develop a plan to gather feedback from users.
2.4 Discuss a plan to submit policies for approval.
Outputs
Understanding of the risks and drivers that will influence policy development.
Up to 14 customized security policies (dependent on need and time).
3 Implement Security Policy Program
The Purpose
Ensure policies and requirements are communicated with end users, along with steps to comply with the new security policies.
Improve compliance and accountability with security policies.
Plan for regular review and maintenance of the security policy program.
Key Benefits Achieved
Streamlined communication of the policies to users.
Improved end user compliance with policy guidelines and be better prepared for audits.
Incorporate security policies into daily schedule, eliminating disturbances to productivity and efficiency.
Activities
3.1 Plan the communication strategy of new policies.
3.2 Discuss myPolicies to automate management and implementation.
3.3 Incorporate policies and processes into your security awareness and training program.
3.4 Assess the effectiveness of security policies.
3.5 Understand the need for regular review and update.
Outputs
Policy Communication Plan Template
Understanding of how myPolicies can help policy management and implementation.
Security Awareness and Training Program Development Tool
Security Policy Assessment Tool
Action plan to regularly review and update the policies.
Further reading
Develop and Deploy Security Policies
Enhance your overall security posture with a defensible and prescriptive policy suite.
Analyst Perspective
A policy lifecycle can be the secret sauce to managing your policies.
A policy for policy’s sake is useless if it isn’t being used to ensure proper processes are followed. A policy should exist for more than just checking a requirement box. Policies need to be quantified, qualified, and enforced for them to be relevant.
Policies should be developed based on the use cases that enable the business to run securely and smoothly. Ensure they are aligned with the corporate culture. Rather than introducing hindrances to daily operations, policies should reflect security practices that support business goals and protection.
No published framework is going to be a perfect fit for any organization, so take the time to compare business operations and culture with security requirements to determine which ones apply to keep your organization secure.
 |
Danny Hammond
Research Analyst Security, Risk, Privacy & Compliance Practice Info-Tech Research Group |
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
|
Common Obstacles
InfoSec leaders will struggle to craft the right set of policies without knowing what the organization actually needs, such as:
|
Info-Tech’s Approach
Info-Tech’s Develop and Deploy Security Policies takes a multi-faceted approach to the problem that incorporates foundational technical elements, compliance considerations, and supporting processes:
|
Info-Tech Insight
Creating good policies is only half the solution. Having a great policy management lifecycle will keep your policies current, effective, and compliant.
Your ChallengeThis research is designed to help organizations design a program to develop and deploy security policies
|
The problem with security policies29% Of IT workers say it's just too hard and time consuming to track and enforce. 25% Of IT workers say they don’t enforce security policies universally. 20% Of workers don’t follow company security policies all the time. (Source: Security Magazine, 2020) |
Common obstaclesThe problem with security policies isn’t development; rather, it’s the communication, enforcement, and maintenance of them.
|
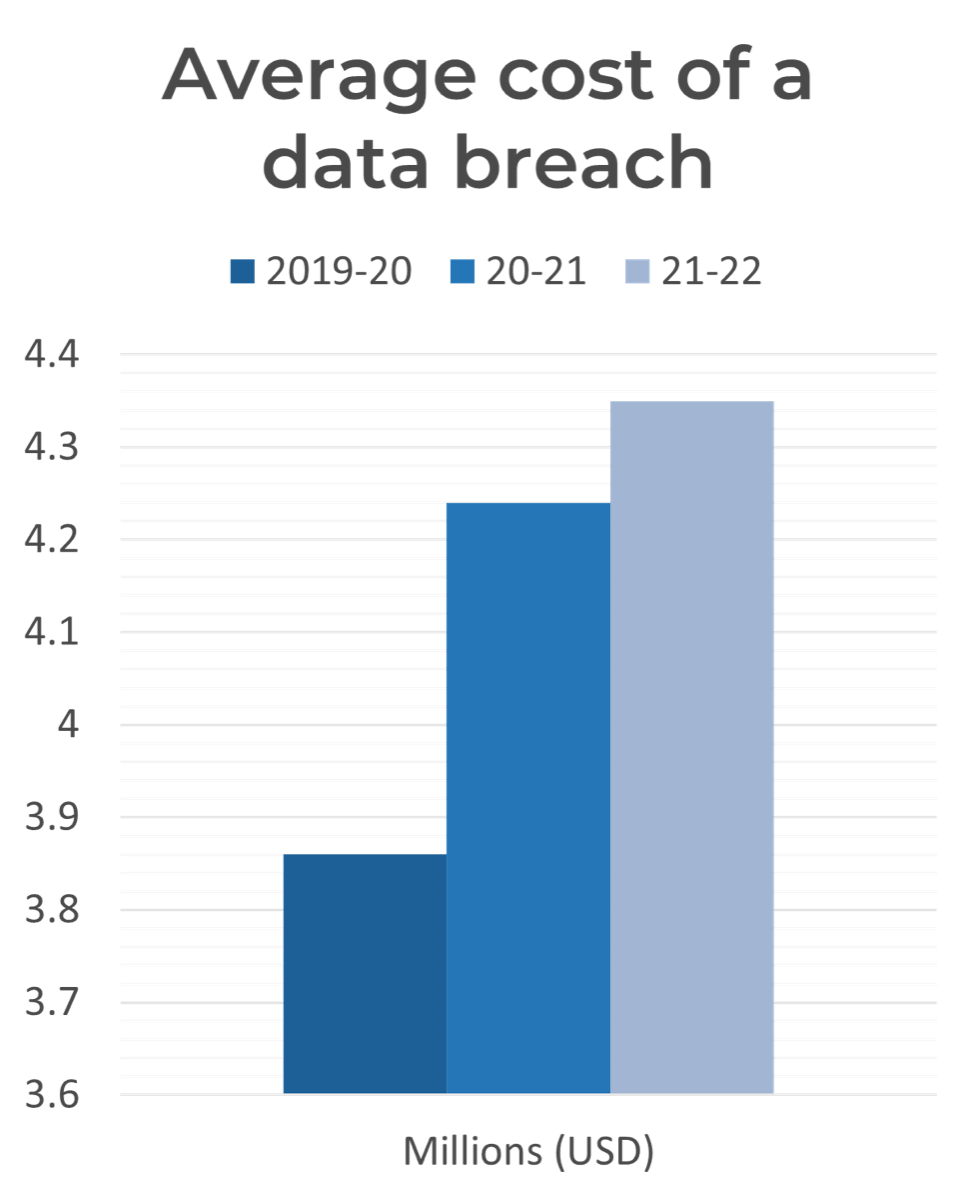
(Source: IBM, 2022 Cost of a Data Breach; n=537) Reaching an all-time high, the cost of a data breach averaged US$4.35 million in 2022. This figure represents a 2.6% increase from last year, when the average cost of a breach was US$4.24 million. The average cost has climbed 12.7% since 2020. |
Info-Tech’s approach
| The right policy for the right audience. Generate a roadmap to guide the order of policy development based on organizational policy requirements and the target audience.
Actions
|
I. Define Security Policy Program
a) Security policy program lifecycle template b) Policy prioritization tool |
 |
II. Develop & Implement Policy Suite
a) Policy template set |
Policies must be reasonable, auditable, enforceable, and measurable. Policy items that meet these requirements will have a higher level of adherence. Focus on efficiently creating policies using pre-developed templates that are mapped to multiple compliance frameworks.
Actions
|
| Gaining feedback on policy compliance is important for updates and adaptation, where necessary, as well as monitoring policy alignment to business objectives.
Actions
|
IV. Measure Policy Program
a) Security policy tracking tool |
III. Communicate Policy Program
a) Security policy awareness & training tool b) Policy communication plan template |
Awareness and training on security policies should be targeted and must be relevant to the employees’ jobs. Employees will be more attentive and willing to incorporate what they learn if they feel that awareness and training material was specifically designed to help them.
Actions
|
|
| Build trust in your policy program by involving stakeholder participation through the entire policy lifecycle. | ||||
Blueprint benefits
IT/InfoSec Benefits
|
Business Benefits
|
Key deliverable:Security Policy TemplatesTemplates for policies that can be used to map policy statements to multiple compliance frameworks. 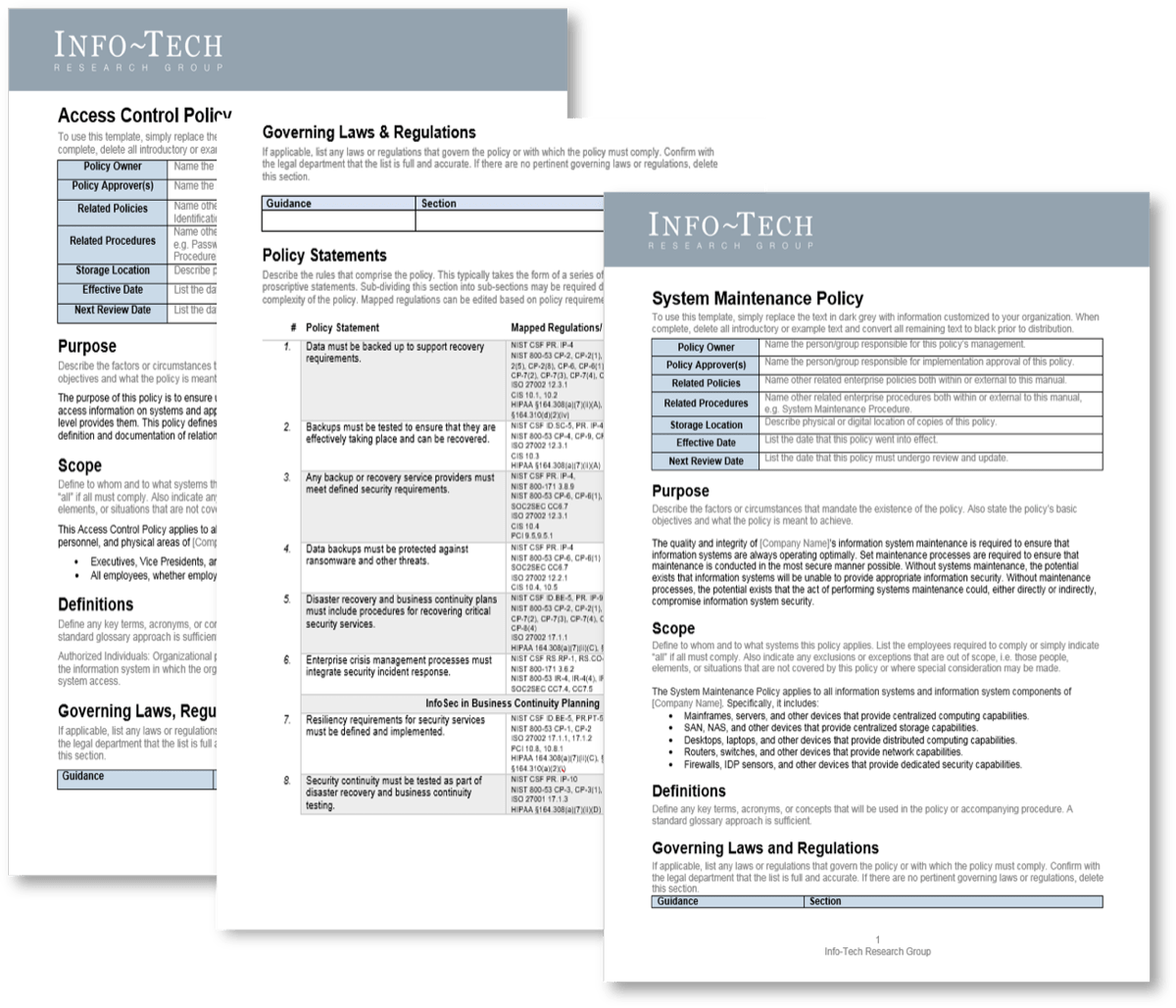 |
|
||||||
Measure the value of this blueprint
|
After each Info-Tech experience, we ask our members to quantify the real-time savings, monetary impact, and project improvements our research helped them achieve. Overall Impact9.5 /10Overall Average $ Saved$29,015Overall Average Days Saved25 |
Info-Tech offers various levels of support to best suit your needs
DIY Toolkit |
Guided Implementation |
Workshop |
Consulting |
| "Our team has already made this critical project a priority, and we have the time and capability, but some guidance along the way would be helpful." | "Our team knows that we need to fix a process, but we need assistance to determine where to focus. Some check-ins along the way would help keep us on track." | "We need to hit the ground running and get this project kicked off immediately. Our team has the ability to take this over once we get a framework and strategy in place." | "Our team does not have the time or the knowledge to take this project on. We need assistance through the entirety of this project." |
Diagnostics and consistent frameworks used throughout all four options |
|||
Guided Implementation
A Guided Implementation (GI) is series of calls with an Info-Tech analyst to help implement our best practices in your organization.
A typical GI is six to ten calls over the course of two to four months.
What does a typical GI on this topic look like?Phase 1 |
Phase 2 |
Phase 3 |
Phase 4 |
| Call #1: Scope security policy requirements, objectives, and any specific challenges.
Call #2: Review policy lifecycle; prioritize policy development. |
Call #3: Customize the policy templates.
Call #4: Gather feedback on policies and get approval. |
Call #5: Communicate the security policy program.
Call #6: Develop policy training and awareness programs. |
Call #7: Track policies and exceptions. |
Workshop Overview |
Contact your account representative for more information.
|
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | |
Define the security policy program |
Develop the security policy suite |
Develop the security policy suite |
Implement security policy program |
Finalize deliverables and next steps |
|
| Activities | 1.1 Understand the current state of policies. 1.2 Align your security policies to the Info-Tech framework for compliance. 1.3 Understand the relationship between policies and other documents. 1.4 Prioritize the development of security policies. 1.5 Discuss strategies to leverage stakeholder support. 1.6 Plan to communicate with all stakeholders. 1.7 Develop the security policy lifecycle. |
2.1 Discuss the risks and drivers your organization faces that must be addressed by policies. 2.2 Develop and customize security policies. |
2.1 Discuss the risks and drivers your organization faces that must be addressed by policies (continued). 2.2 Develop and customize security policies (continued). 2.3 Develop a plan to gather feedback from users. 2.4 Discuss a plan to submit policies for approval. |
3.1 Plan the communication strategy for new policies. 3.2 Discuss myPolicies to automate management and implementation. 3.3 Incorporate policies into your security awareness and training program. 3.4 Assess the effectiveness of policies. 3.5 Understand the need for regular review and update. |
4.1 Review customized lifecycle and policy templates. 4.2 Discuss the plan for policy roll out. 4.3 Schedule follow-up Guided Implementation calls. |
| Deliverables |
|
|
|
|
|
Develop and Deploy Security Policies
Phase 1
Define the Security Policy Program
| Phase 1
1.1 Understand the current state 1.2 Align your security policies to the Info-Tech framework 1.3 Document your policy hierarchy 1.4 Prioritize development of security policies 1.5 Leverage stakeholders 1.6 Develop the policy lifecycle |
Phase 2
2.1 Customize policy templates 2.2 Gather feedback from users on policy feasibility 2.3 Submit policies to upper management for approval |
Phase 3
3.1 Understand the need for communicating policies 3.2 Use myPolicies to automate the management of your security policies 3.3 Design, build, and implement your communications plan 3.4 Incorporate policies and processes into your training and awareness programs |
Phase 4
4.1 Assess the state of security policies 4.2 Identify triggers for regular policy review and update 4.3 Develop an action plan to update policies |
This phase will walk you through the following activities:
- Understand the current state of your organization’s security policies.
- Align your security policies to the Info-Tech framework for compliance.
- Prioritize the development of your security policies.
- Leverage key stakeholders to champion the policy initiative.
- Inform all relevant stakeholders of the upcoming policy program.
- Develop the security policy lifecycle.
1.1 Understand the current state of policies
Scenario 1: You have existing policies
|
Scenario 2: You are starting from scratch
|
Policies are living, evolving documents that require regular review and update, so even if you have policies already written, you’re not done with them.
1.2 Align your security policies to the Info-Tech framework for compliance
| You have an opportunity to improve your employee alignment and satisfaction, improve organizational agility, and obtain high policy adherence. This is achieved by translating your corporate culture into a policy-based compliance culture.
Align your security policies to the Info-Tech Security Framework by using Info-Tech’s policy templates. Info-Tech’s security framework uses a best-of-breed approach to leverage and align with most major security standards, including:
|
Info-Tech Security Framework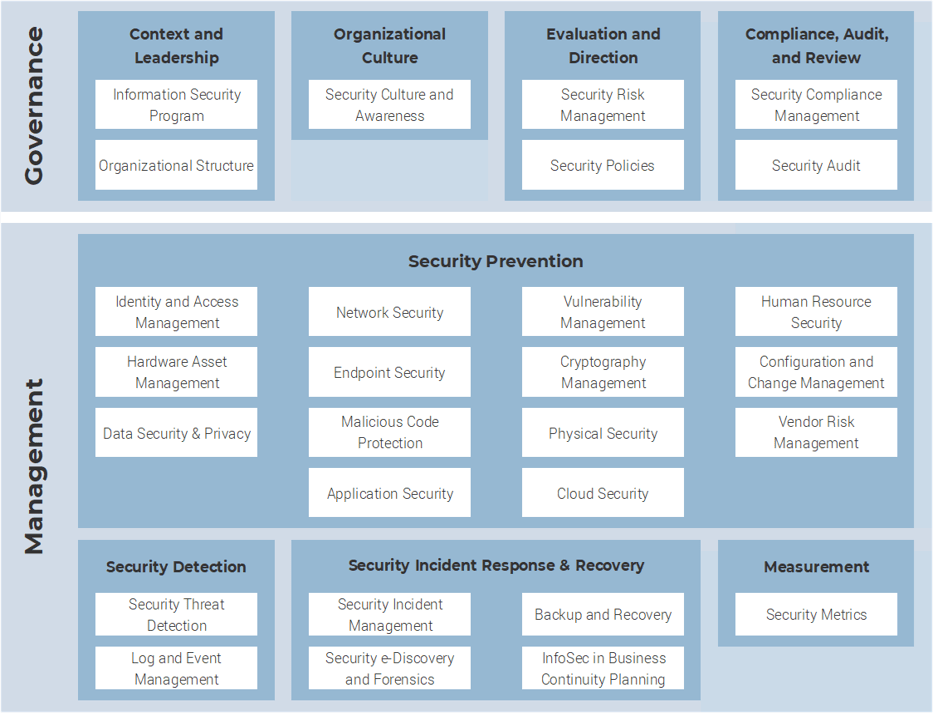 |
1.3 Document your policy hierarchy
Structuring policy components at different levels allows for efficient changes and direct communication depending on what information is needed.
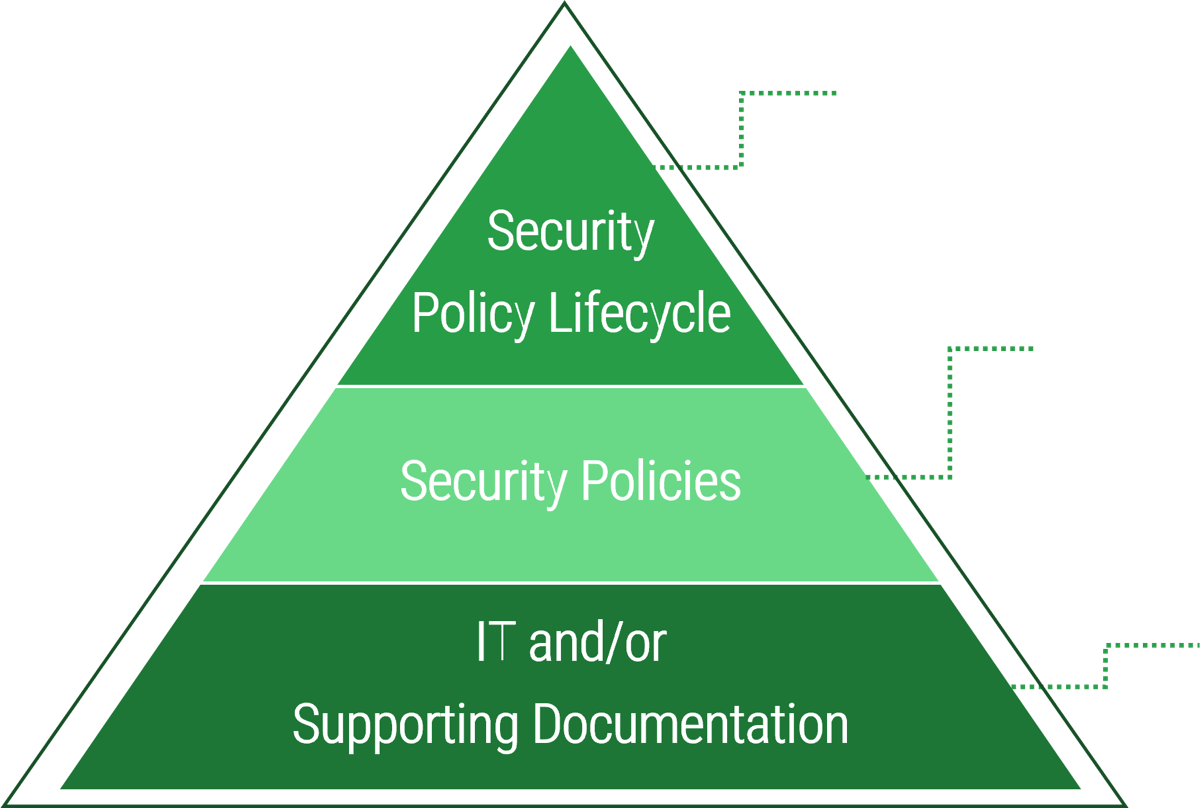 |
Defines the cycle for the security policy program and what must be done but not how to do it. Aligns the business, security program, and policies.
Defines high-level overarching concepts of security within the organization, including the scope, purpose, and objectives of policies.
Defines enterprise/technology – specific, detailed guidelines on how to adhere to policies.
|
Info-Tech Insight
Design separate policies for different areas of focus. Policies that are written as single, monolithic documents are resistant to change. A hierarchical top-level document supported by subordinate policies and/or procedures can be more rapidly revised as circumstances change.
1.3.1 Understand the relationship between policies and other documents
Policy:
 |
||||
Standard:
|
 |
Procedure:
|
 |
Guideline:Recommended actions to consider in absence of an applicable standard, to support a policy. |
This model is adapted from a framework developed by CISA (Certified Information Systems Auditor).
Supporting Documentation |
||||
Considerations for standards
| Standards. These support policies by being much more specific and outlining key steps or processes that are necessary to meet certain requirements within a policy document. Ideally standards should be based on policy statements with a target of detailing the requirements that show how the organization will implement developed policies.
If policies describe what needs to happen, then standards explain how it will happen. A good example is an email policy that states that emails must be encrypted; this policy can be supported by a standard such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption that specifically ensures that all email communication is encrypted for messages “in transit” from one secure email server that has TLS enabled to another. There are numerous security standards available that support security policies/programs based on the kind of systems and controls that an organization would like to put in place. A good selection of supporting standards can go a long way to further protect users, data, and other organizational assets |
|
1.4 Prioritize development of security policies
The Info-Tech Security Policy Prioritization Tool will help you determine which security policies to work on first.
Align policies to recent security concerns. If your organization has recently experienced a breach, it may be crucial to highlight corresponding policies as immediately necessary. Info-Tech InsightIf you have an existing policy that aligns with one of the Info-Tech recommended templates weight Ease to Implement and Ease to Enforce as HIGH (4-5). This will decrease the priority of these policies. | 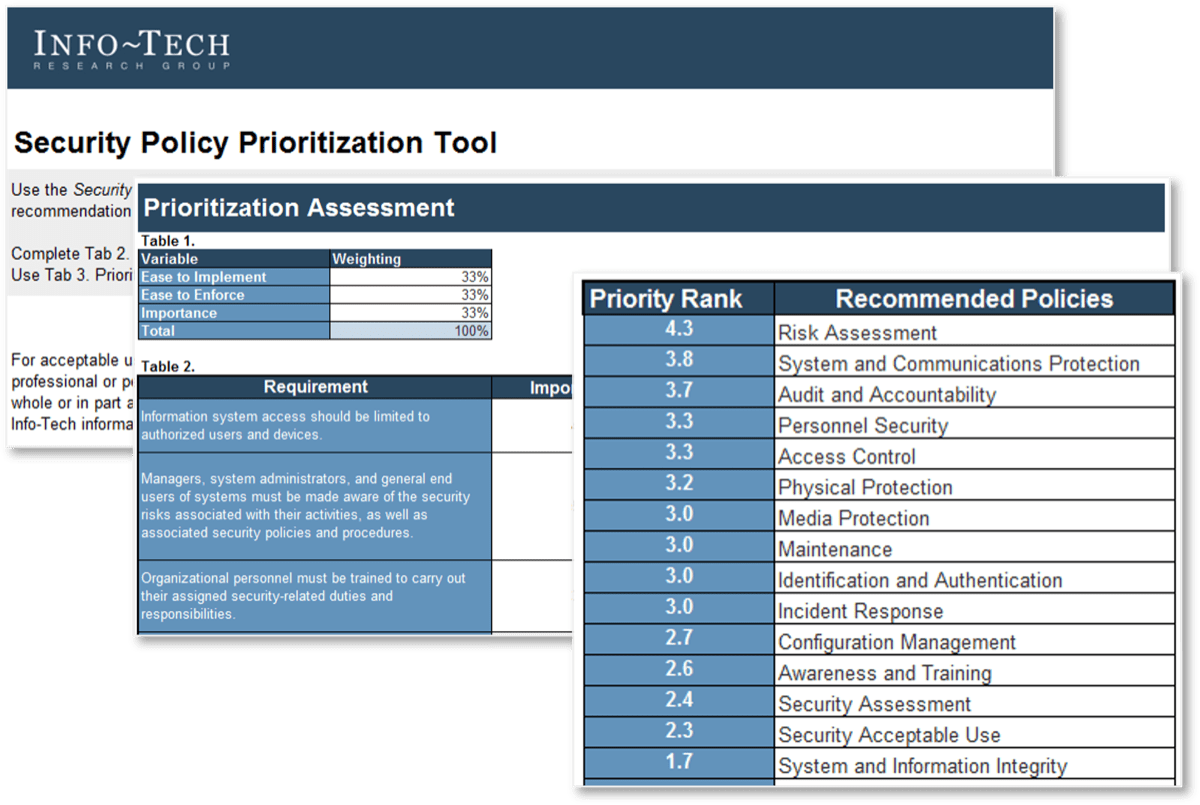 Download the Security Policy Prioritization Tool |
1.5 Leverage stakeholders to champion policies
Info-Tech Insight
While management support is essential to initiating a strong security posture, allow employees to provide input on the development of security policies. This cooperation will lead to easier incorporation of the policies into the daily routines of workers, with less resistance. The security team will be less of a police force and more of a partner.
| Executive champion
Identify an executive champion who will ensure that the security program and the security policies are supported. |
Focus on risk and protection
Security can be viewed as an interference, but the business is likely more responsive to the concepts of risk and protection because it can apply to overall business operations and a revenue-generating mandate. |
| Communicate policy initiatives
Inform stakeholders of the policy initiative as security policies are only effective if they support the business requirements and user input is crucial for developing a strong security culture. |
Current security landscape
Leveraging the current security landscape can be a useful mechanism to drive policy buy-in from stakeholders. |
| Management buy-in
This is key to policy acceptance; it indicates that policies are accurate, align with the business, and are to be upheld, that funds will be made available, and that all employees will be equally accountable. |
Buying Options
Develop and Deploy Security Policies
Client rating
Cost Savings
Days Saved
IT Risk Management · IT Leadership & Strategy implementation · Operational Management · Service Delivery · Organizational Management · Process Improvements · ITIL, CORM, Agile · Cost Control · Business Process Analysis · Technology Development · Project Implementation · International Coordination · In & Outsourcing · Customer Care · Multilingual: Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese · Entrepreneur
Tymans Group is a brand by Gert Taeymans BV
Gert Taeymans bv
Europe: Koning Albertstraat 136, 2070 Burcht, Belgium — VAT No: BE0685.974.694 — phone: +32 (0) 468.142.754
USA: 4023 KENNETT PIKE, SUITE 751, GREENVILLE, DE 19807 — Phone: 1-917-473-8669
Copyright 2017-2022 Gert Taeymans BV