Embed Business Relationship Management in IT

- While organizations realize they need to improve business relationships, they often don’t know how.
- IT doesn’t know what their business needs and so can’t add as much value as they’d like.
- They find that their partners often reach out to third parties before they connect with internal IT.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Business relationship management (BRM) is not just about communication, it’s about delivering on business value.
- Build your BRM program on establishing trust.
Impact and Result
- Drive business value into the organization via innovative technology solutions.
- Improve ability to meet and exceed business goals and objectives, resulting in more satisfied stakeholders (C-suite, board of directors).
- Enhance ability to execute business activities to meet end customer requirements and expectations, resulting in more satisfied customers.
Embed Business Relationship Management in IT Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Embed Business Relationship Management Deck – A step-by-step document that walks you through how to establish a practice with well-embedded business relationships, driving IT success.
This blueprint helps you to establish a relationship with your stakeholders, both within and outside of IT. You’ll learn how to embed relationship management throughout your organization.
- Embed Business Relationship Management in IT – Phases 1-5
2. BRM Workbook Deck – A workbook for you to capture the results of your thinking on the BRM practice.
Use this tool to capture your findings as you work through the blueprint.
- Embed Business Relationship Management in IT Workbook
3. BRM Buy-In and Communication Template – A template to help you communicate what BRM is to your organization, that leverages feedback from your business stakeholders and IT.
Customize this tool to obtain buy in from leadership and other stakeholders. As you continue through the blueprint, continue to leverage this template to communicate what your BRM program is about.
- BRM Buy-In and Communication Template
4. BRM Role Expectations Worksheet – A tool to help you establish how the BRM role and/or other roles will be managing relationships.
This worksheet template is used to outline what the BRM practice will do and associate the expectations and tasks with the roles throughout your organization. Use this to communicate that while your BRM role has a strategic focus and perspective of the relationship, other roles will continue to be important for relationship management.
- Role Expectations Worksheet
5. BRM Stakeholder Engagement Plan Worksheet – A tool to help you establish your stakeholders and your engagement with them.
This worksheet allows you to list the stakeholders and their priority in order to establish how you want to engage with them.
- BRM Stakeholder Engagement Plan Worksheet
6. Business Relationship Manager Job Descriptions – These templates can be used as a guide for defining the BRM role.
These job descriptions will provide you with list of competencies and qualifications necessary for a BRM operating at different levels of maturity. Use this template as a guide, whether hiring internally or externally, for the BRM role.
- Business Relationship Manager – Level 1
- Business Relationship Manager – Level 2
- Business Relationship Manager – Level 3
Workshop: Embed Business Relationship Management in IT
Workshops offer an easy way to accelerate your project. If you are unable to do the project yourself, and a Guided Implementation isn't enough, we offer low-cost delivery of our project workshops. We take you through every phase of your project and ensure that you have a roadmap in place to complete your project successfully.
1 Foundation: Assess and Situate
The Purpose
Set the foundation for your BRM practice – understand your current state and set the vision.
Key Benefits Achieved
An understanding of current pain points and benefits to be addressed through your BRM practice. Establish alignment on what your BRM practice is – use this to start obtaining buy-in from stakeholders.
Activities
1.1 Define BRM
1.2 Analyze Satisfaction
1.3 Assess SWOT
1.4 Create Vision
1.5 Create the BRM Mission
1.6 Establish Goals
Outputs
BRM definition
Identify areas to be addressed through the BRM practice
Shared vision, mission, and understanding of the goals for the brm practice
2 Plan
The Purpose
Determine where the BRM fits and how they will operate within the organization.
Key Benefits Achieved
Learn how the BRM practice can best act on your goals.
Activities
2.1 Establish Guiding Principles
2.2 Determine Where BRM Fits
2.3 Establish BRM Expectations
2.4 Identify Roles With BRM Responsibilities
2.5 Align Capabilities
Outputs
An understanding of where the BRM sits in the IT organization, how they align to their business partners, and other roles that support business relationships
3 Implement
The Purpose
Determine how to identify and work with key stakeholders.
Key Benefits Achieved
Determine ways to engage with stakeholders in ways that add value.
Activities
3.1 Brainstorm Sources of Business Value
3.2 Identify Key Influencers
3.3 Categorize the Stakeholders
3.4 Create the Prioritization Map
3.5 Create Your Engagement Plan
Outputs
Shared understanding of business value
A plan to engage with stakeholders
4 Reassess and Embed
The Purpose
Determine how to continuously improve the BRM practice.
Key Benefits Achieved
An ongoing plan for the BRM practice.
Activities
4.1 Create Metrics
4.2 Prioritize Your Projects
4.3 Create a Portfolio Investment Map
4.4 Establish Your Annual Plan
4.5 Build Your Transformation Roadmap
4.6 Create Your Communication Plan
Outputs
Measurements of success for the BRM practice
Prioritization of projects
BRM plan
Further reading
Embed Business Relationship Management in IT
Show that IT is worthy of Trusted Partner status.
Executive Brief
Analyst Perspective
Relationships are about trust.
As long as humans are involved in enabling technology, it will always remain important to ensure that business relationships support business needs. At the cornerstone of those relationships is trust and the establishment of business value. Without trust, you won’t be believed, and without value, you won’t be invited to the business table.
Business relationship management can be a role, a capability, or a practice – either way it’s essential to ensure it exists within your organization. Show that IT can be a trusted partner by showing the value that IT offers.

|
Allison Straker
|
Your challenge: Why focus on business relationship management?
| Is IT saying this about business partners?
I don’t know what my business needs and so we can’t add as much value as we’d like. My partners don’t give us the opportunity to provide new ideas to solve business problems My partners listen to third parties before they listen to IT. We’re too busy and don’t have the capacity to help my partners. |
|
Are business partners saying this about IT?
IT does not create and deliver valuable services/solutions that resolve my business pain points. IT does not come to me with innovative solutions to my business problems/challenges/issues. IT blocks my efforts to drive the business forward using innovative technology solutions. IT does not advocate for my needs with the decision makers in the organization. |
Common obstacles
While organizations realize they need to do better, they often don’t know how to improve.
Organizations want to:
- Understand and strategically align to business goals
- Ensure stakeholders are satisfied
- Show project value/success
… these are all things that a mature business relationship can do to improve your organization.
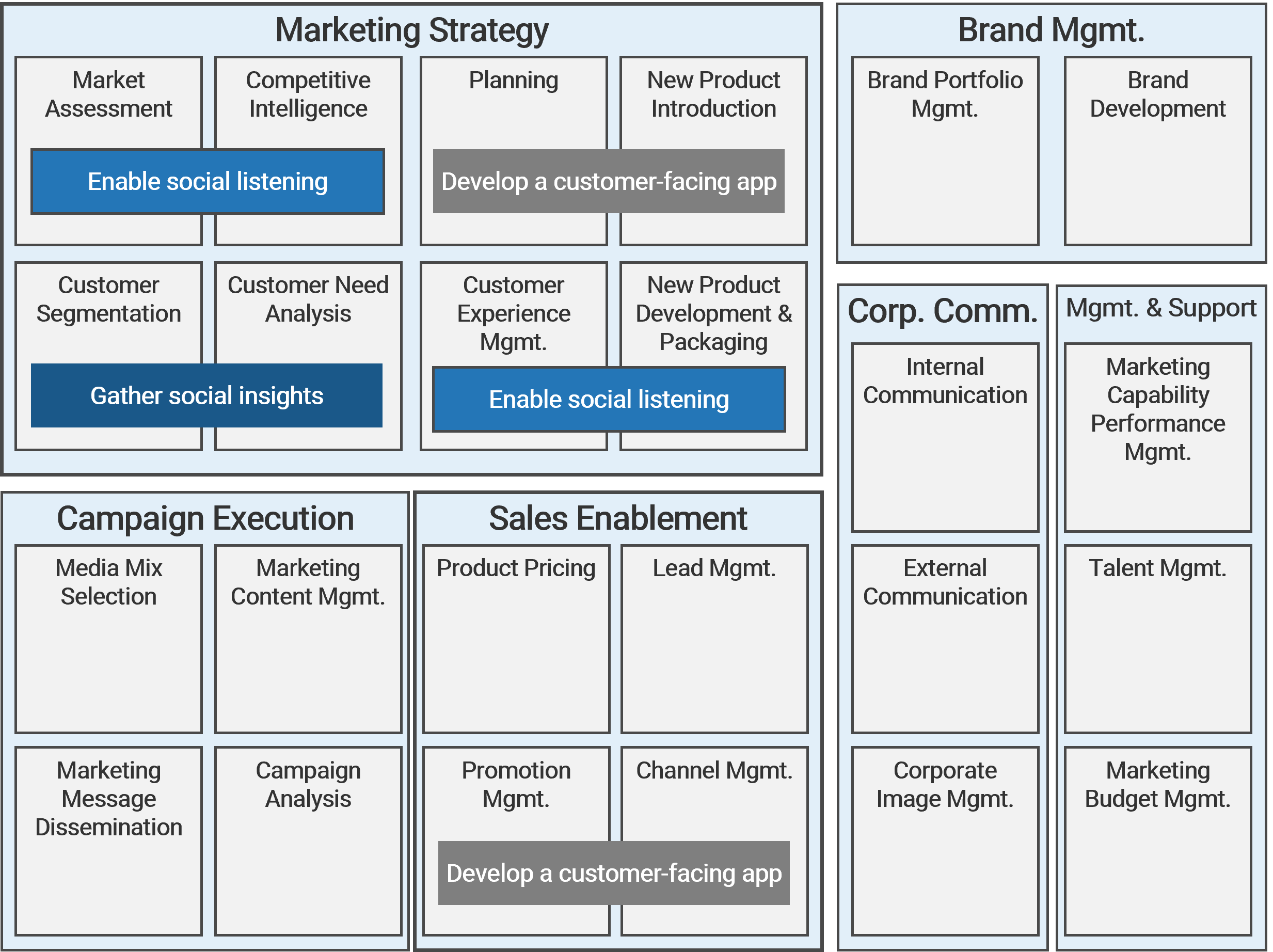
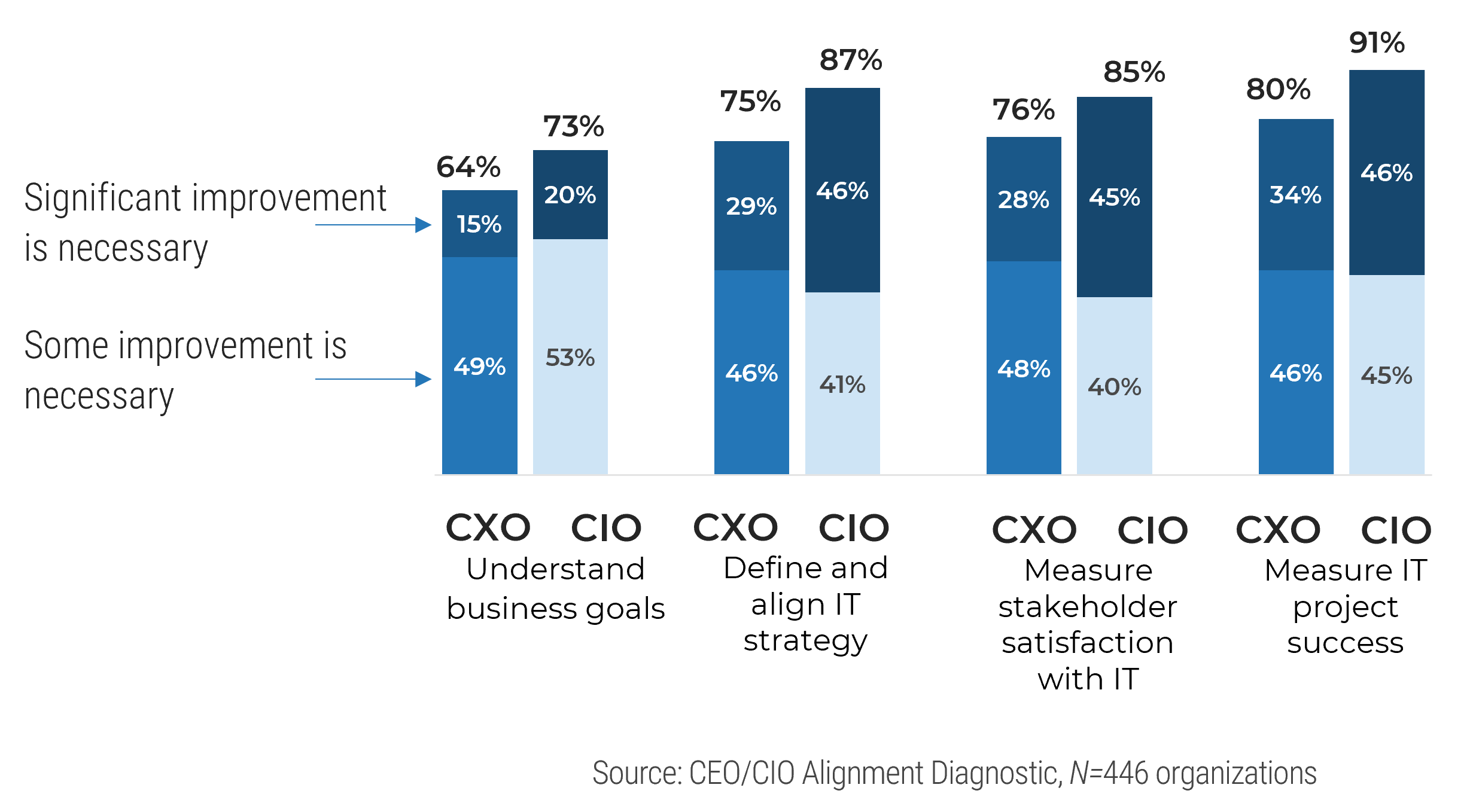
Key improvement areas identified by business leaders and IT leaders
Info-Tech’s approach
BRMs who focus on achieving business value can improve organizational results.
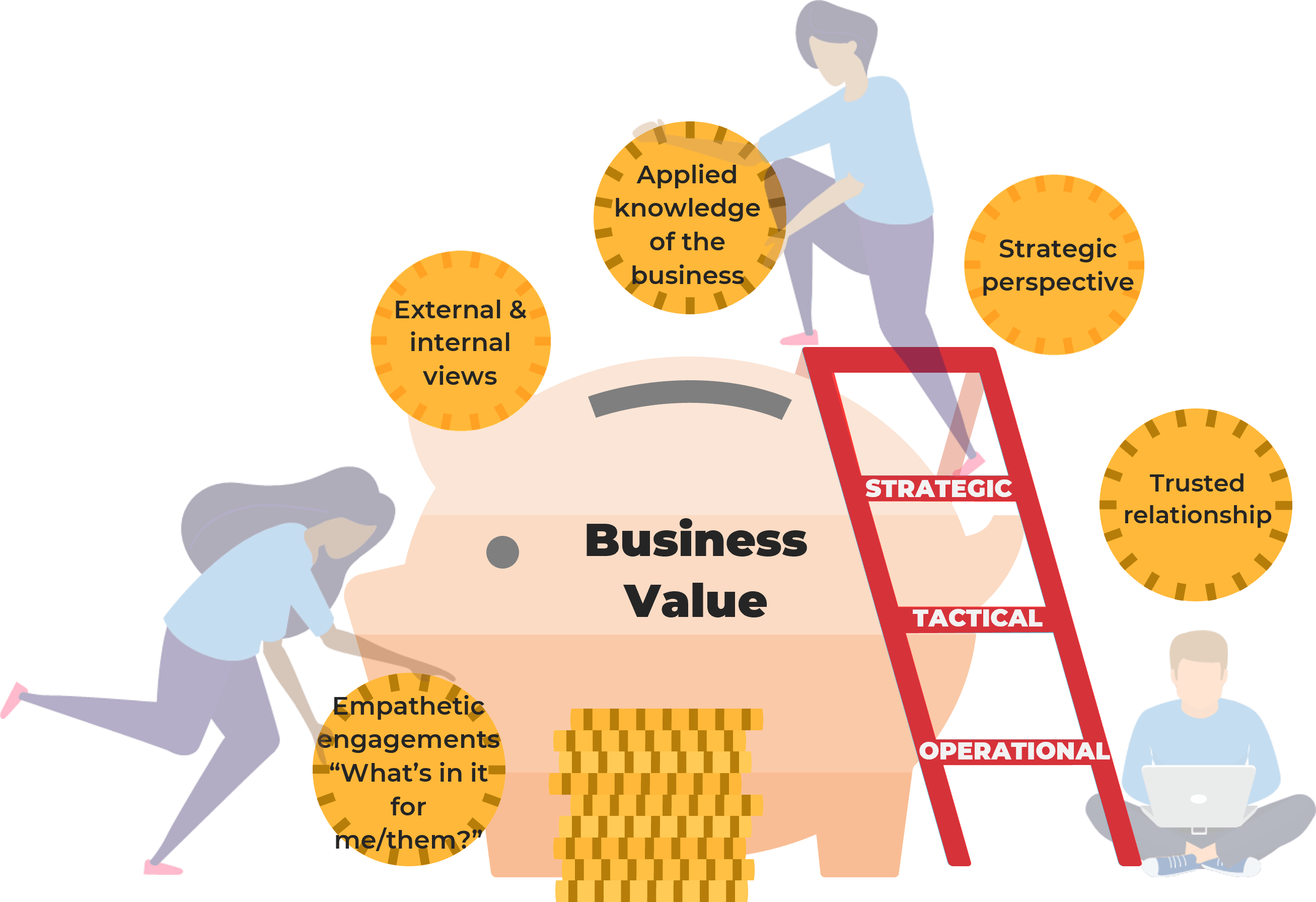
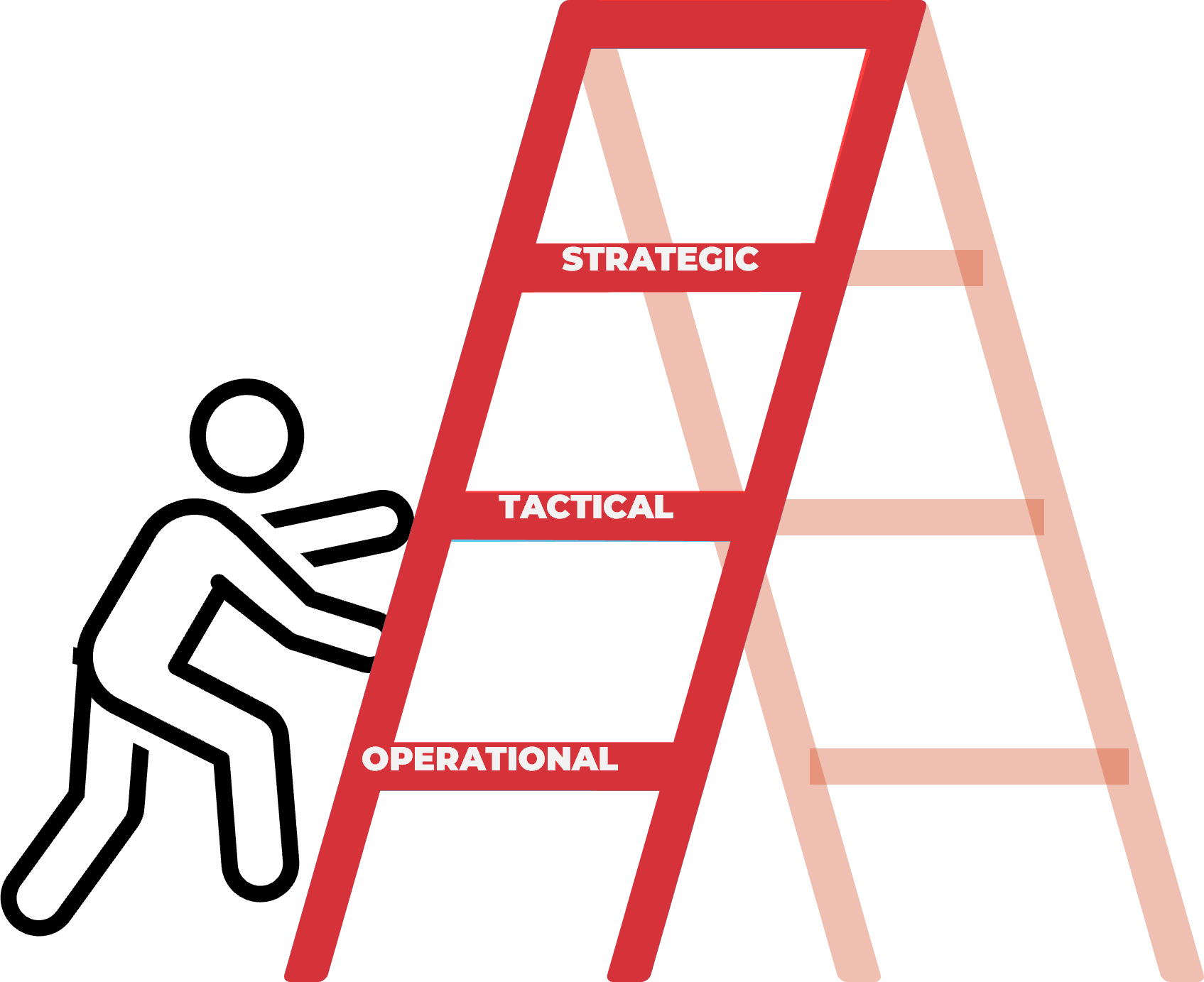
Business relationships can take a strategic, tactical, or operational perspective.
While all levels are needed, focus on a strategic perspective for optimal outcomes.
Create business value through:
- Applying your knowledge of the business so that conversations aren’t about what IT provides. Focus on what the overall business requires.
- Ensuring your knowledge includes what is going on internally at your organization and also what occurs externally within and outside the industry (e.g. vendors, technologies used in similar industries or with similar customer interactions).
- Discussing with the perspective of “what’s in it for [insert business partner here]” – don’t just present IT’s views.
- Building a trusted strategic relationship – don’t just do well at the basics but also focus on the strategy that can move the organization to where it needs to be.
Neither you nor your partners can view IT as separate from your overall business…
…your IT goals need to be aligned with those of the overall business
IT and other lines of business need to partner together – they are all part of the same overall business.
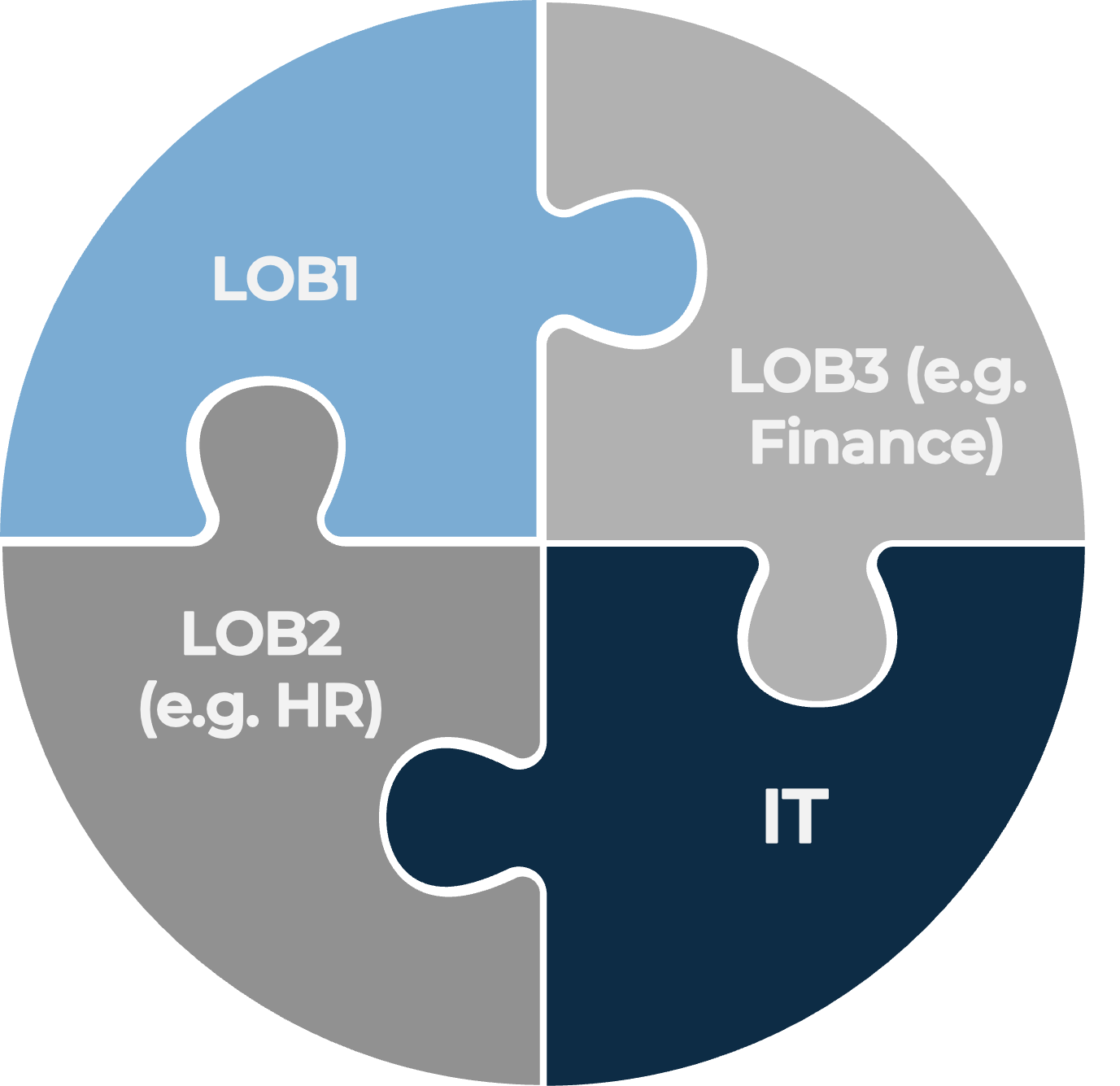
Why it’s important to establish a BRM program
IT Benefits
|
Business Benefits
|
||

|
Increase your business benefits by moving up higher – from operational to tactical to strategic. |
|
|
When IT understands the business, they provide better value
Understanding all parties – including the business needs and context – is critical to effective business relationships.
Establishing a focus on business relationship management is key to improving IT satisfaction.
When business partners are satisfied that IT understands their needs, they have a higher perception of the value of overall IT
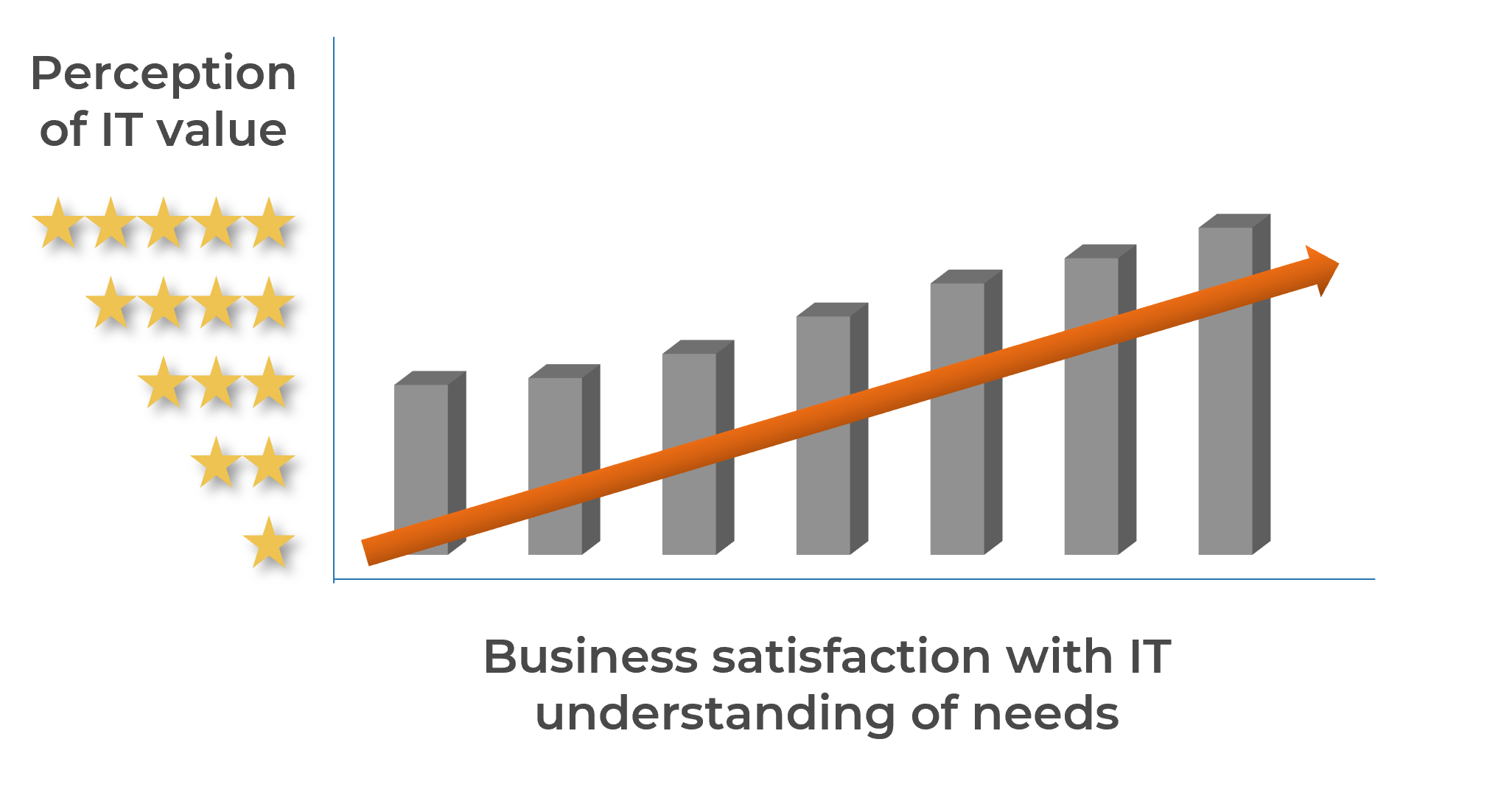
The relationship between the perception of IT value and business satisfaction is strong (r=0.89). Can you afford not to increase your understanding of business needs?
(Source: Info-Tech Research Group diagnostic data/Business-Aligned IT Strategy blueprint (N=652 first-year organizations that completed the CIO Business Vision diagnostic))
A tale of two IT partners
One IT partner approached their business partner without sufficient background knowledge to provide insights. The relationship was not strong and did not provide the business with the value they desired. |
Research your business and be prepared to apply your knowledge to be a better partner.
The other IT partner approached with knowledge of the business and external parties (vendors, competitors, industry). The business partners received this positively. They invited the IT partners to meetings as they knew IT would bring value to their sessions. |
BRM success is measurable 
| 1) Survey your stakeholders to measure improvements in customer satisfaction | 2) Measure BRM success against the goals for the practice | |
Business satisfaction survey
|
|
|
|
||
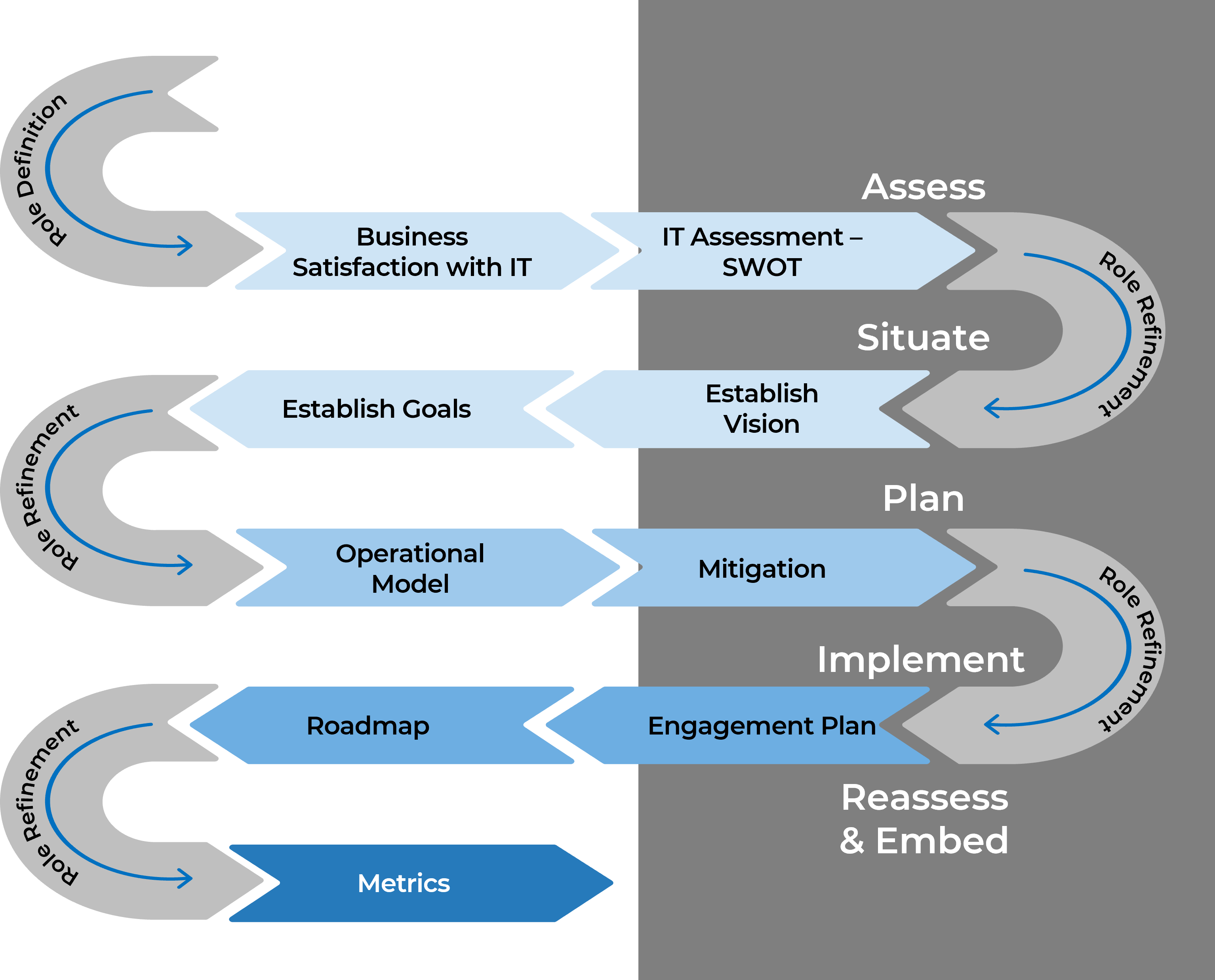
Maturing your BRM practice is a journey
Info-Tech has developed an approach that can be used by any organization to improve or successfully implement BRM.
|
Become a Trusted Partner and Advisor | |
KNOWLEDGE OF INDUSTRY
STRATEGIC |
Value Creator and Innovator
Strategic view of IT and the business with knowledge of the market and trends; a connector driving value-added services. |
|
KNOWLEDGE OF FUNCTIONS
TACTICAL |
Influencer and Advocate
Two-way voice between IT and business, understanding business processes and activities including IT touchpoints and growing tactical and strategic view of services and value. |
|
| TABLE STAKES:
COMMUNICATION SERVICE DELIVERY PROJECT DELIVERY OPERATIONAL |
Deliver
Communication, service, and project delivery and fulfillment, initial engagement with and knowledge of the business. |
|
| Foundation: Define and communicate the meaning and vision of BRM | ||
At each level, keep maturing your BRM practice
| IT | Partner | What to do to move to the next level | ||
Strategic PartnerShared goals for maximizing value and shared risk and reward | 5 | Strategic view of IT and the business with knowledge of the market and trends; a connector driving value-added services. Value Creator and Innovator | See partners as integral to business success and growth | Focus on continuous learning and improvement. |
Trusted AdvisorCooperation based on mutual respect and understanding | 4 | Partners understand, work with, and help improve capabilities. Influencer and Advocate | Sees IT as helpful and reliable | Strategic: IT needs to demonstrate and apply knowledge of business, industry, and external influences. |
Service ProviderRoutine – innovation is a challenge | 3 | Two-way voice between IT and business; understanding business processes and activities including IT touchpoints and growing tactical and strategic view of services and value. Priorities set but still always falling behind. | Views IT as helpful but they don’t provide guidance | IT needs to excel in portfolio and transition management. Business needs to engage IT in strategy. |
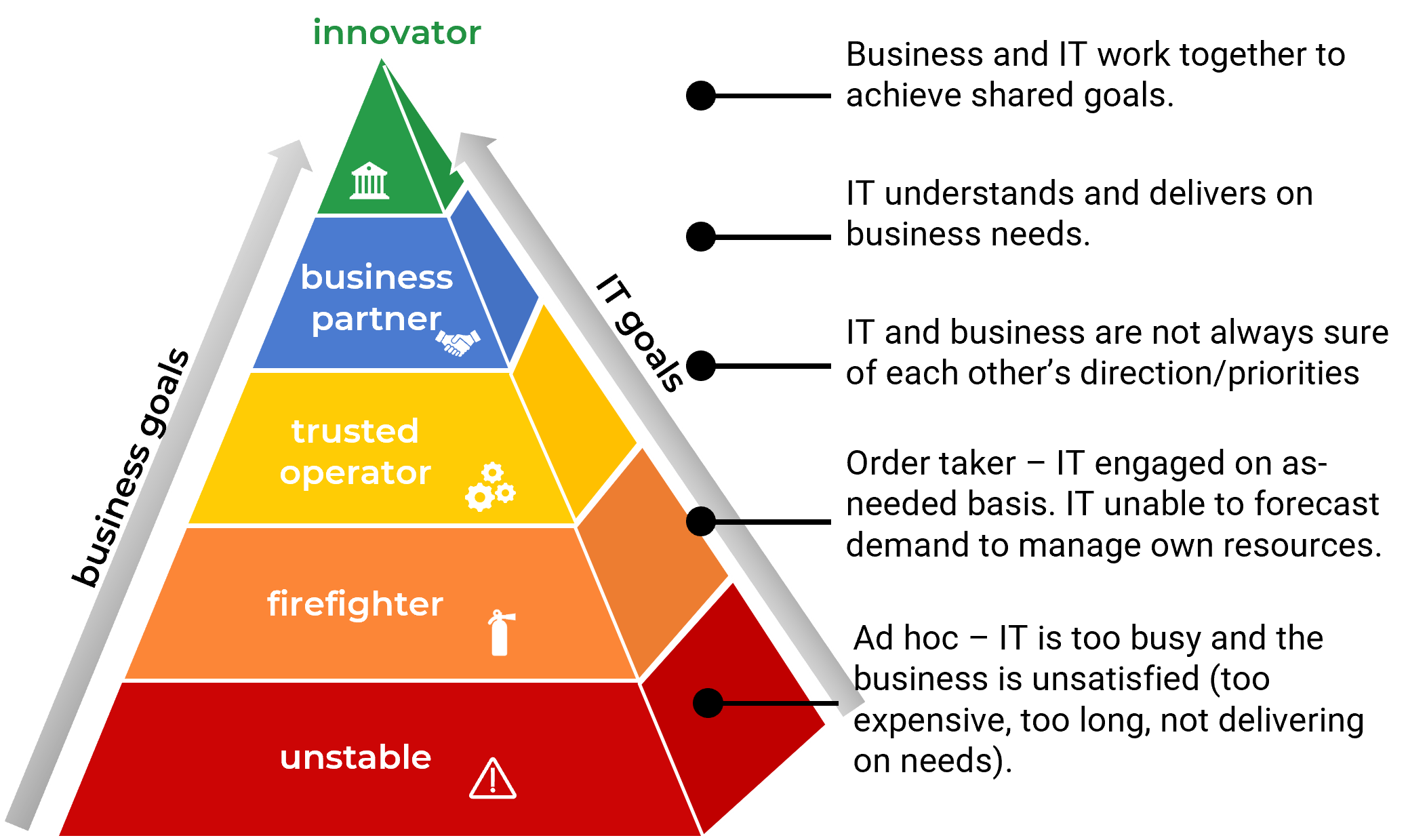
Order TakerDistrust, reactive | 2 | Focuses on communication, service, and project delivery and fulfillment, initial engagement with and knowledge of the business. Delivery Service | Engages with IT on an as-needed basis | Improve Tactical: IT needs to demonstrate knowledge of the business they are in. IT to improve BRM and service management. Business needs to embrace BRM role and service management. |
Ad HocLoudest in, first out | 1 | Too busy doing the basics; in firefighter mode. | Low satisfaction (cost, duration, quality) | Improve Operational Behavior: IT to show value with “table stakes” – communication, service delivery, project delivery. IT needs to establish intake/demand management.
|
(Adapted from BRM Institute Maturity Model and Info-Tech’s own model)
The Info-Tech path to implement BRM
Use Info-Tech’s ASPIRe method to create a continuously improving BRM practice.
Insight summary
BRM is not just about communication, it’s about delivering on business value.
Business relationship management isn’t just about having a pleasant relationship with stakeholders, nor is it about just delivering things they want. It’s about driving business value in everything that IT does and leveraging relationships with the business and IT, both within and outside your organization.
Understand your current state to determine the best direction forward.
Every organization will apply the BRM practice differently. Understand what’s needed within your organization to create the best fit.
BRM is not just a communication conduit between IT and the business.
When implemented properly, a BRM is a value creator, advocate, innovator, and influencer.
The BRM role must be designed to match the maturity level of the IT organization and the business.
Before you can create incremental business value, you must master the fundamentals of service and project delivery.
Info-Tech Insight
Knowledge of your current situation is only half the battle; knowledge of the business/industry is key.
Info-Tech offers various levels of support to best suit your needs
DIY Toolkit |
Guided Implementation |
Workshop |
Consulting |
| "Our team has already made this critical project a priority, and we have the time and capability, but some guidance along the way would be helpful." | "Our team knows that we need to fix a process, but we need assistance to determine where to focus. Some check-ins along the way would help keep us on track." | "We need to hit the ground running and get this project kicked off immediately. Our team has the ability to take this over once we get a framework and strategy in place." | "Our team does not have the time or the knowledge to take this project on. We need assistance through the entirety of this project." |
Diagnostics and consistent frameworks used throughout all four options
Blueprint deliverables
Each step of this blueprint is accompanied by supporting deliverables to help you accomplish your goals:
Key deliverable:
Executive Buy-In and Communication Presentation TemplateExplain the need for the BRM practice and obtain buy-in from leadership and staff across the organization.
|
BRM WorkbookCapture the thinking behind your organization’s BRM program. |
|
BRM Stakeholder Engagement Plan WorksheetWorksheet to capture how the BRM practice will engage with stakeholders across the organization. |
|
BRM Role Expectations WorksheetHow business relationship management will be supported throughout the organization at a strategic, tactical, and operational level. |

|
Guided Implementation
A Guided Implementation (GI) is a series of calls with an Info-Tech analyst to help implement our best practices in your organization.
A typical GI is between 8 to 12 calls over the course of 4 to 6 months.
What does a typical GI on this topic look like?
Phase 1 |
Phase 2 |
Phase 3 |
Phase 4 |
Phase 5 |
| Call #1: Discuss goals, current state, and an overview of BRM.
Call #2: Examine business satisfaction and discuss results of SWOT. |
Call #3: Establish BRM mission, vision, and goals. | Call #4: Develop guiding principles.
Call #5: Establish the BRM operating model and role expectations. |
Call #6: Establish business value. Discuss stakeholders and engagement planning. | Call #7: Develop metrics. Discuss portfolio management.
Call #8: Develop a communication or rollout plan. |
Workshop OverviewComplete the CIO-Business Vision diagnostic prior to the workshop. |
Contact your account representative for more information.
|
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Post-Workshop | |
| Activities |
Set the FoundationAssess & Situate |
Define the Operating ModelPlan |
Define EngagementImplement |
Implement BRMReassess |
Next steps and Wrap-Up (offsite) |
|
1.1 Discuss rationale and importance of business relationship management 1.2 Review CIO BV results 1.3 Conduct SWOT analysis (analyze strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) 1.4 Establish BRM vision and mission 1.5 Define objectives and goals for maturing the practice |
2.1 Create your list of guiding principles (optional) 2.2 Define business value 2.3. Establish the operating model for the BRM practice 2.4 Define capabilities |
3.1. Identify key stakeholders 3.2 Map, prioritize, and categorize the stakeholders 3.4 Create an engagement plan |
4,1 Define metrics 4.2 Identify remaining enablers/blockers for practice implementation 4.3 Create roadmap 4.4 Create communication plan |
5.1 Complete in-progress deliverables from previous four days 5.2 Set up review time for workshop deliverables and to discuss next steps |
|
| Deliverables |
|
|
|
|
|
ASSESS
| Assess
1.1 Define BRM 1.2 Analyze Satisfaction 1.3 Assess SWOT |
Situate
2.1 Create Vision 2.2 Create the BRM Mission 2.3 Establish Goals |
Plan
3.1 Establish Guiding Principles 3.2 Determine Where BRM Fits 3.3 Establish BRM Expectations 3.4 Identify Roles With BRM Responsibilities 3.5 Align Capabilities |
||
| Implement
4.1 Brainstorm Sources of Business Value 4.2 Identify Key Influencers 4.3 Categorize the Stakeholders 4.4 Create the Prioritization Map 4.5 Create Your Engagement Plan |
Reassess & Embed
5.1 Create Metrics 5.2 Prioritize Your Projects 5.3 Create a Portfolio Investment Map 5.4 Establish Your Annual Plan 5.5 Build Your Transformation Roadmap 5.6 Create Your Communication Plan |
To assess BRM, clarify what it means to you
| Who are BRM relationships with? | 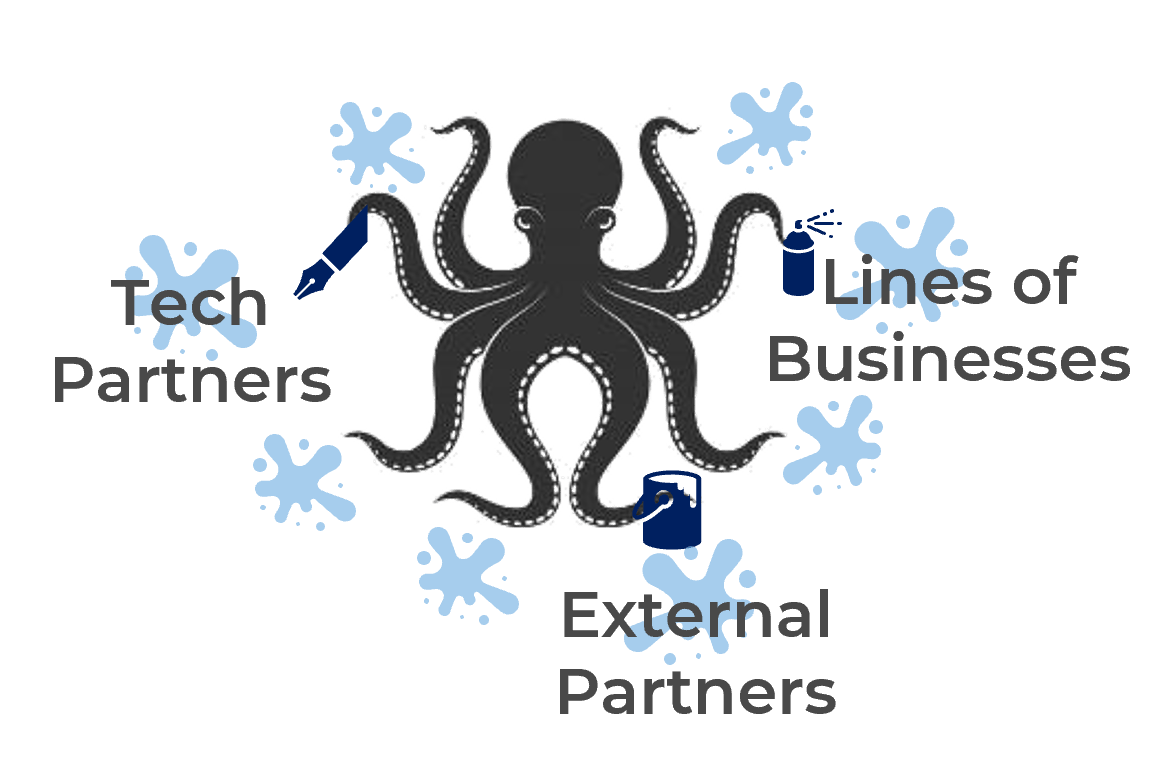
|
The BRM has multiple arms/legs to ensure they’re aligned with multiple parties – the partners within the lines of business, external partners, and technology partners. | |
| What does a BRM do? | Engage the right stakeholders – orchestrate key roles, resources, and capabilities to help stimulate, shape, and harvest business value.
Connect partners (IT and other business) with the resources needed. Help stakeholders navigate the organization and find the best path to business value. |
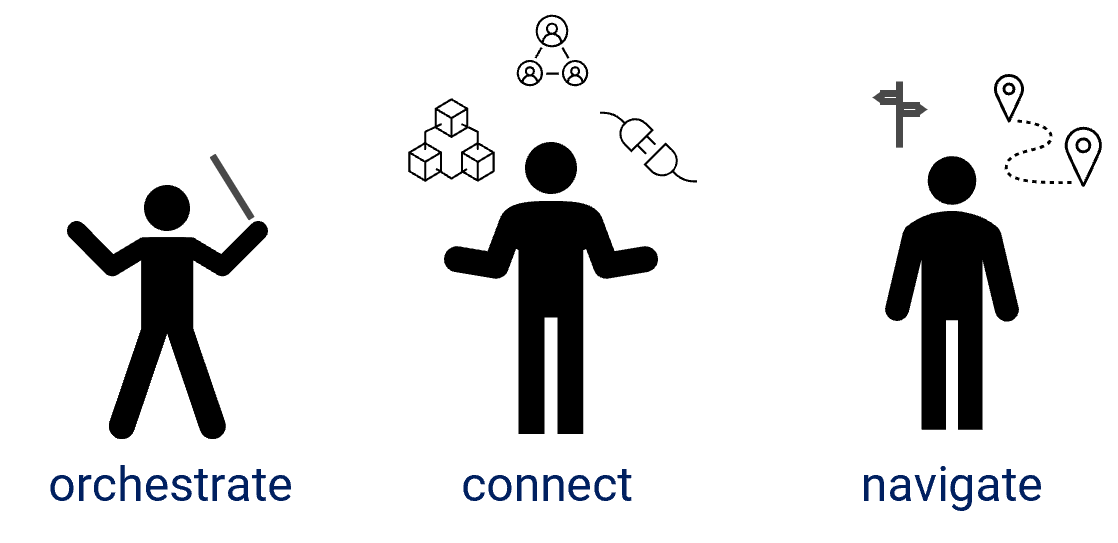
|
|
| What does a BRM focus on? | 
|
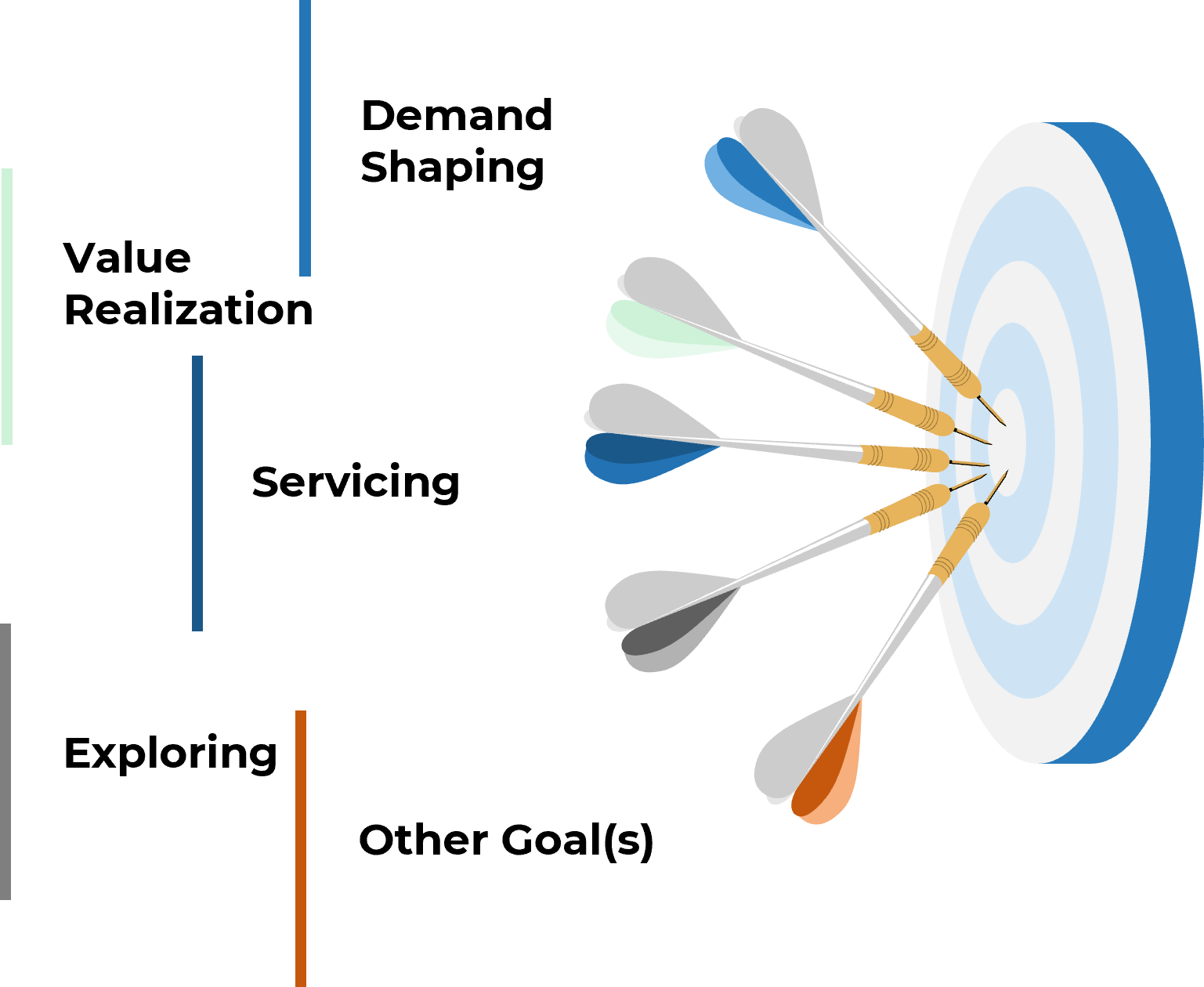
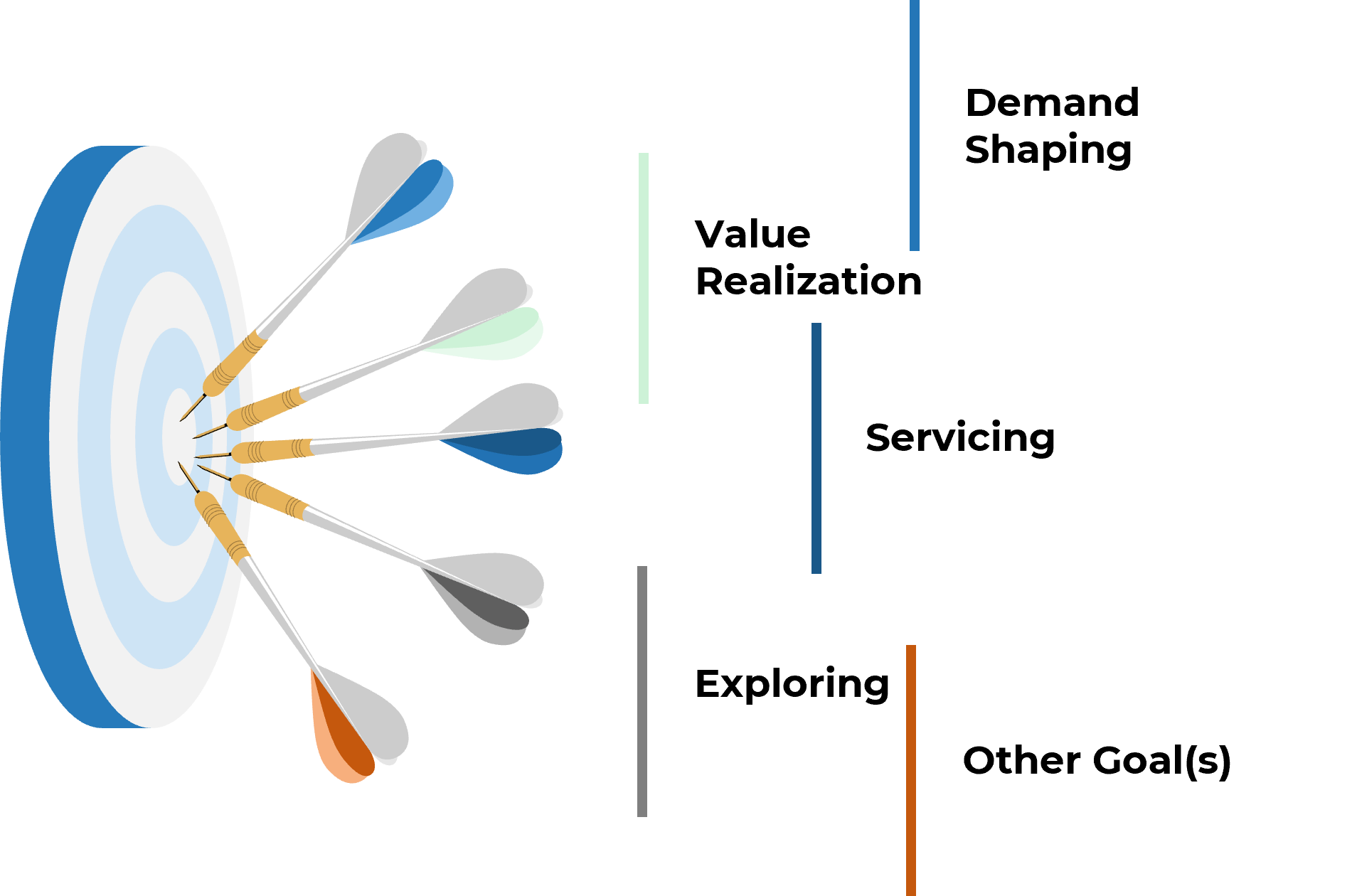
Demand Shaping – Surfacing and shaping business demand
Value Harvesting – Identifying ways to increase business value and providing insights Exploring – Rationalizing demand and reviewing new business, technology, and industry insights Servicing – Managing expectations and facilitating business strategy; business capability road mapping |
|
Determine what business relationship management is
Many organizations face business dissatisfaction because they do not understand what the role of a BRM should be.
A BRM Is NOT:
|
A BRM Is:
|
1.1 What is BRM?
1 hourInput: Your preliminary thoughts and ideas on BRM
Output: Themes summarizing what BRM will be at your organization
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Each team member will take a colored sticky note to capture what BRM is and what it isn’t.
- As a group, review and discuss the sticky notes.
- Group them into themes summarizing what BRM will be at your organization.
- Leverage the workbook to brainstorm the definition of BRM at your organization.
- Create a refined summary statement and capture it in the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template.
Download the BRM Workbook
Download the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template
It’s important to understand what the business thinks; ask them the right questions
Leverage the CIO Business Vision Diagnostic to provide clarity on:
|
|
1.2 Use their responses to help guide your BRM program
1 hour
Input: CIO-Business Vision Diagnostic, Other business feedback
Output: Summary of your partners’ view of the IT relationship
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: CIO, IT management team
- Complete the CIO Business Vision diagnostic.
- Analyze the findings from the Business Vision diagnostic or other business relationship and satisfaction surveys. Key areas to look at include:
- Overall IT Satisfaction
- IT Value
- Relationship (Understands Needs, Communicates Effectively, Executes Requests, Trains Effectively)
- Shadow IT
- Capacity Needs
- Business Objectives
- Capture the following on your analysis:
- Success stories – what your business partners are satisfied with
- Challenges – are the responses consistent across departments?
- Leverage the workbook to capture your findings the goals. Key highlights should be documented in the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template.
Use the BRM Workbook to capture ideas
Polish the goals in the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template
Perform a SWOT analysis to explore internal and external business factors
A SWOT analysis is a structured planning method organizations use to evaluate the effects of internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats on a project or business venture.
Why It Is Important
- Business SWOT reveals internal and external trends that affect the business. You may uncover relevant information about the business that the other analysis methods did not reveal.
- The organizational strengths or weaknesses will shed some light on implications that you might not have considered otherwise, such as brand perception or internal staff capability to change.
Key Tips/Information
- Although this activity is simple in theory, there is much value to be gained when performed effectively.
- Focus on weaknesses that can cause a competitive disadvantage and strengths that can cause a competitive advantage.
- Rank your opportunities and threats based on impact and probability.
- Info-Tech members who have derived the most insights from a business SWOT analysis usually involved business stakeholders in the analysis.
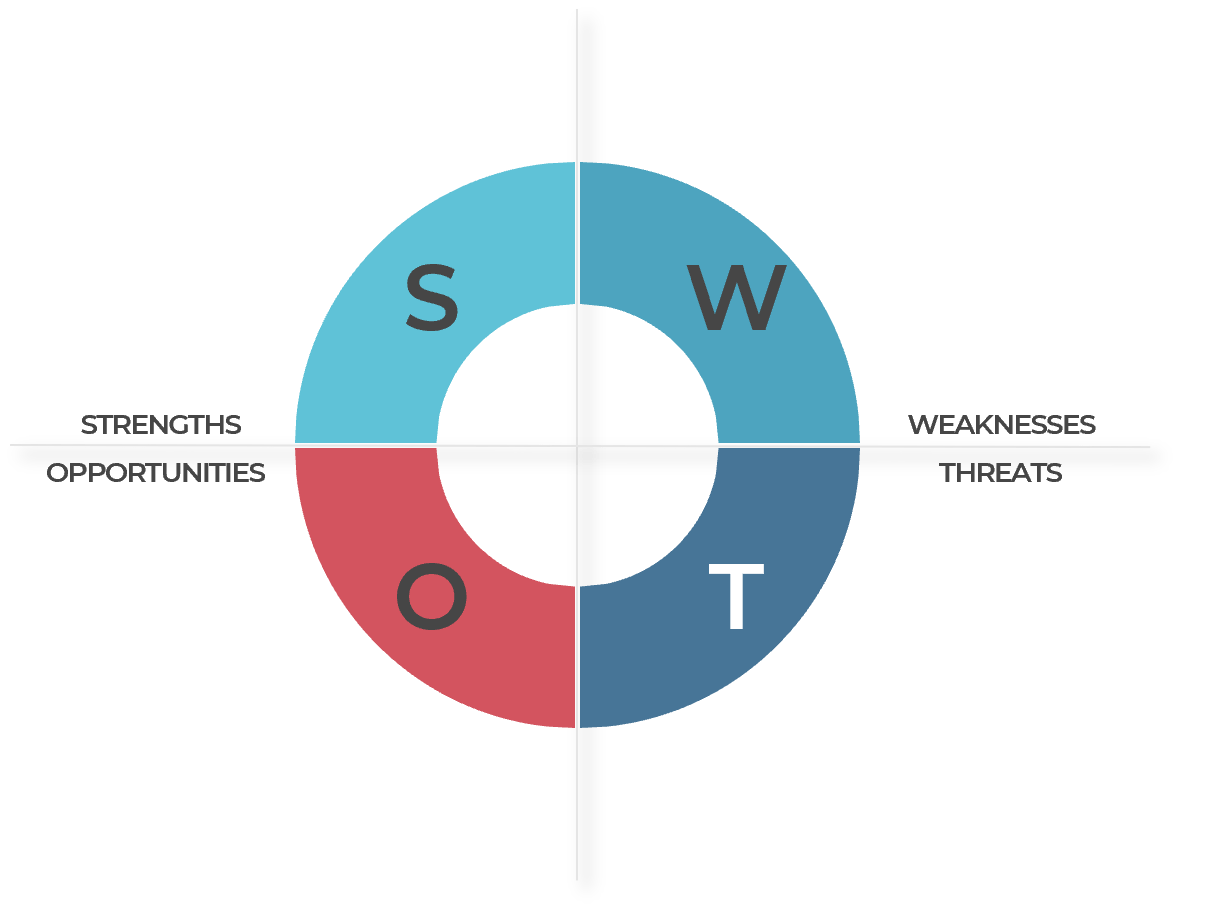
Review these questions to help you conduct your SWOT analysis on the business
Strengths (Internal)
|
Weaknesses (Internal)
|
Opportunities (External)
|
Threats (External)
|
1.3 Analyze internal and external business factors using a SWOT analysis
1 hour
Input: IT and business stakeholder expertise
Output: Analysis of internal and external factors impacting the IT organization
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: CIO, IT management team
- Break the group into two teams:
- Assign team A internal strengths and weaknesses.
- Assign team B external opportunities and threats.
- Think about strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats as they pertain to the IT-business relationship. Consider people, process, and technology elements.
- Have the teams brainstorm items that fit in their assigned grids. Use the prompt questions on the previous slide as guidance.
- Pick someone from each group to fill in the SWOT grid.
- Conduct a group discussion about the items on the list; identify implications for the BRM/IT.
Capture in the BRM Workbook
SITUATE
| Assess 1.1 Define BRM 1.2 Analyze Satisfaction 1.3 Assess SWOT | Situate 2.1 Create Vision 2.2 Create the BRM Mission 2.3 Establish Goals | Plan 3.1 Establish Guiding Principles 3.2 Determine Where BRM Fits 3.3 Establish BRM Expectations 3.4 Identify Roles With BRM Responsibilities 3.5 Align Capabilities | ||
| Implement 4.1 Brainstorm Sources of Business Value 4.2 Identify Key Influencers 4.3 Categorize the Stakeholders 4.4 Create the Prioritization Map 4.5 Create Your Engagement Plan | Reassess & Embed 5.1 Create Metrics 5.2 Prioritize Your Projects 5.3 Create a Portfolio Investment Map 5.4 Establish Your Annual Plan 5.5 Build Your Transformation Roadmap 5.6 Create Your Communication Plan |
Your strategy informs your BRM program
| Your strategy is a critical input into your program. Extract critical components of your strategy and convert them into a set of actionable principles that will guide the selection of your operating model.
|
|
Outline your mission and vision for your BRM practice
If you don’t know where you’re trying to go, how do you know if you’ve arrived?
Establish the vision of what your BRM practice will achieve.
Your vision will paint a picture for your stakeholders, letting them know where you want to go with your BRM practice.

The vision will also help motivate and inspire your team members so they understand how they contribute to the organization. Your strategy must align with and support your organization’s strategy. |
Good Visions
|
When Visions Fail
|
Derive the BRM vision statement

|
Begin the process of deriving the business relationship management vision statement by examining your business and user concerns. These are the problems your organization is trying to solve.
Paint the picture for your team and stakeholders so that they align on what BRM will achieve. |
Vision statements demonstrate what your practice “aspires to be”
Your vision statement communicates a desired future state of the BRM organization. The statement is expressed in the present tense. It seeks to articulate the desired role of business relationship management and how it will be perceived.
Sample vision statements:
- To be a trusted advisor and partner in enabling business innovation and growth through an engaged design practice.
- The group will strive to become a world-class value center that is a catalyst for innovation.
- Apple: “We believe that we are on the face of the earth to make great products and that’s not changing.” (Mission Statement Academy, May 2019.)
- Coca-Cola: “To refresh the world in mind, body, and spirit, to inspire moments of optimism and happiness through our brands and actions, and to create value and make a difference.” (Mission Statement Academy, August 2019.)
2.1 Vision generation
1 hour
Input: IT and business strategies
Output: Vision statement
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Review the goals and the sample vision statements provided on the previous slide.
- Brainstorm possible vision statements that can apply to your practice. Refer to the guidance provided on the previous page – ensure that it paints a picture for the reader to show the desired target state.
- Leverage the workbook to brainstorm the vision. Capture the refined statement in the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template.
| Strong vision statements have the following characteristics |
|
|
Use the BRM Workbook to capture ideas
Polish the goals in the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template
Create the mission statement from the problems and the vision statement
Your mission demonstrates your current intent and the purpose driving you to achieve your vision.
It reflects what the organization does for users/customers.
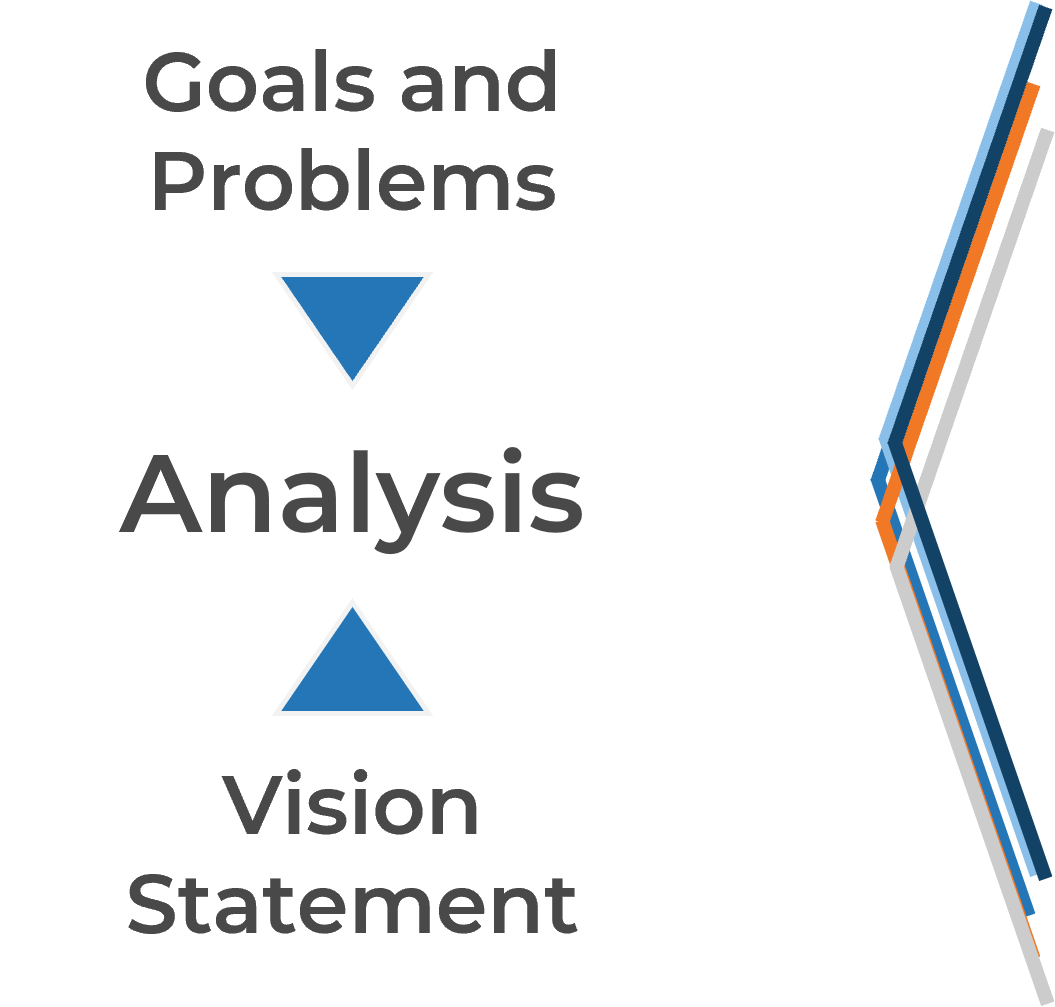
|
Make sure the practice’s mission statement reflects answers to the questions below:
The questions:
|
“A mission statement illustrates the purpose of the organization, what it does, and what it intends on achieving. Its main function is to provide direction to the organization and highlight what it needs to do to achieve its vision.” (Joel Klein, BizTank (in Hull, “Answer 4 questions to get a great mission statement.”))
Sample mission statements
|
To enhance the lives of our end users through our products so that our brand becomes synonymous with user-centricity. To enable innovative services that are seamless and enjoyable to our customers so that together we can inspire change. Apple’s mission statement: “To bring the best user experience to its customers through its innovative hardware, software, and services.” (Mission Statement Academy, May 2019.) Coca Cola’s mission statement: “To refresh the world in mind, body, and spirit, to inspire moments of optimism and happiness through our brands and actions, and to create value and make a difference.” (Mission Statement Academy, August 2019.) Tip: Using the “To … so that” format helps to keep your mission focused on the “why.” |
2.2 Develop your own mission statement
1 hour
Input: IT and business strategies, Vision
Output: Mission statement
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Review the goals and the vision statement generated in the previous activities.
- Brainstorm possible mission statements that can apply to your BRM practice. Capture this in your BRM workbook.
- Refine your mission statement. Refer to the guidance provided on the previous page – ensure that the mission provides “the why”. Document the refined mission statement in the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template.
“People don't buy what you do; they buy why you do it and what you do simply proves what you believe.” (Sinek, Transcript of “How Great Leaders Inspire Action.”)
Download the BRM Workbook
Download the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template
Areas that BRMs focus on include:
Establish how much of these your practice will focus on.
VALUE HARVESTING
|
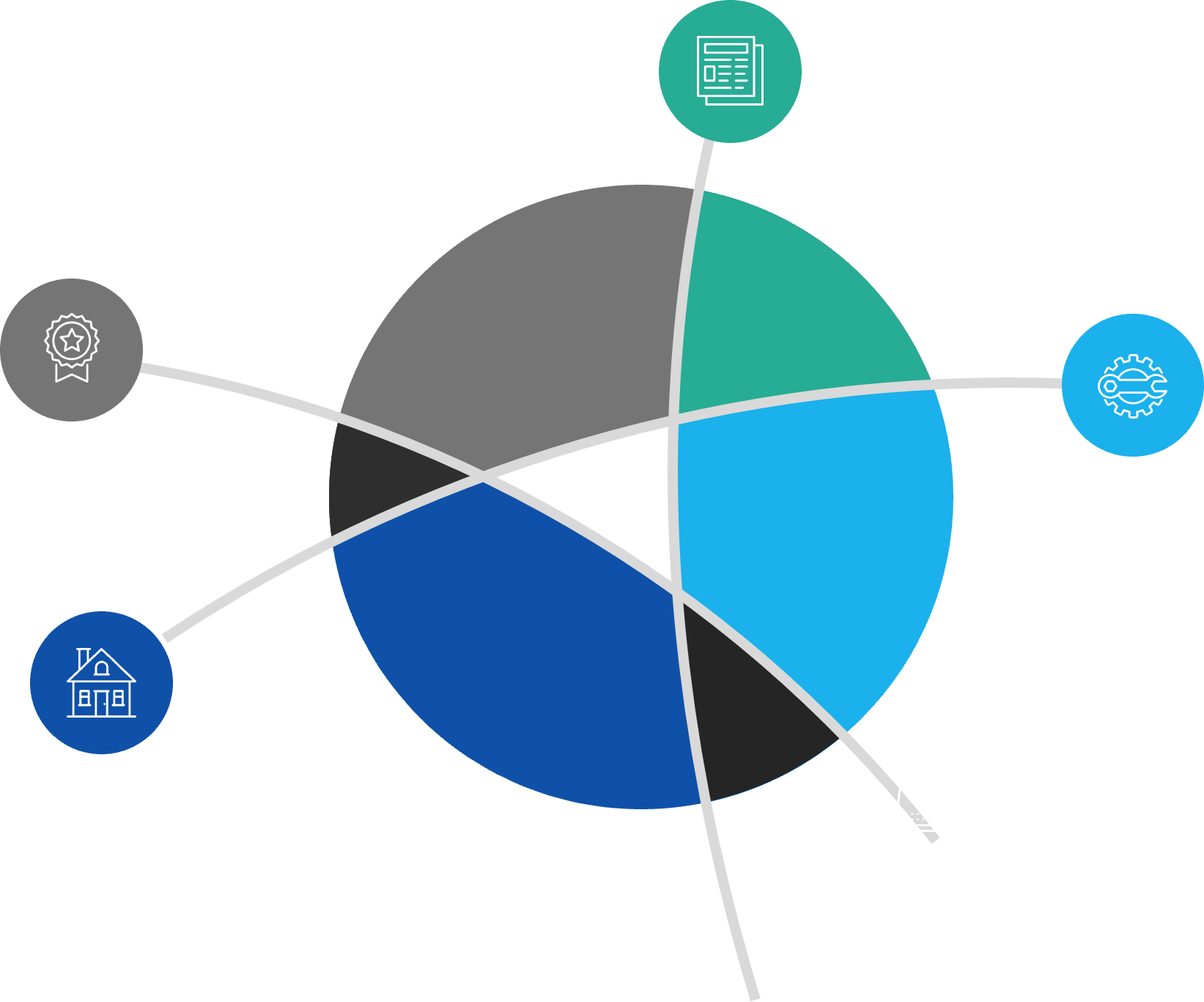
|
DEMAND SHAPING
|
SERVICING
|
EXPLORING
|
Establish what success means for your focus areas
Brainstorm objectives and success areas for your BRM practice.

|
VALUE HARVESTING
Success may mean that you:
|
DEMAND SHAPING
Success may mean that you:
|
| SERVICING
Success may mean that you:
|
EXPLORING
Success may mean that you:
|
2.3 Establish BRM goals
1 hour
Input: Mission and vision statements
Output: List of goals
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: CIO, IT management team, BRM team
- Use the previous slides as a starting point – review the focus areas and sample associated objectives.
- Determine if all apply to your role.
- Brainstorm the objectives for your BRM practice.
- Discuss and refine the objectives and goals until the team agrees on your starting set.
- Leverage the workbook to establish the goals. Capture refined goals in the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template.
Download the BRM Workbook
Download the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template
PLAN
| Assess 1.1 Define BRM 1.2 Analyze Satisfaction 1.3 Assess SWOT | Situate 2.1 Create Vision 2.2 Create the BRM Mission 2.3 Establish Goals | Plan 3.1 Establish Guiding Principles 3.2 Determine Where BRM Fits 3.3 Establish BRM Expectations 3.4 Identify Roles With BRM Responsibilities 3.5 Align Capabilities | ||
| Implement 4.1 Brainstorm Sources of Business Value 4.2 Identify Key Influencers 4.3 Categorize the Stakeholders 4.4 Create the Prioritization Map 4.5 Create Your Engagement Plan | Reassess & Embed 5.1 Create Metrics 5.2 Prioritize Your Projects 5.3 Create a Portfolio Investment Map 5.4 Establish Your Annual Plan 5.5 Build Your Transformation Roadmap 5.6 Create Your Communication Plan |
Guiding principles help you focus the development of your practice
|
Your guiding principles should define a set of loose rules that can be used to design your BRM practice to the specific needs of the organization and work that needs to be done. These rules will guide you through the establishment of your BRM practice and help you explain to your stakeholders the rationale behind organizing in a specific way. |
Sample Guiding Principles
|
3.1 Establish guiding principles (optional activity)
Input: Mission and vision statements
Output: BRM guiding principles
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Think about strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats as well as the overarching goals, mission, and vision.
- Identify a set of principles that the BRM practice should have. Guiding principles are shared, long-lasting beliefs that guide the use of business relationship management in your organization.
Download the BRM Workbook
Download the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template
Establish the BRM partner model and alignment
Having the right model and support is just as important as having the right people.
Don’t boil the ocean: Start small
| It may be useful to pilot the BRM practice with a small group within the organization – this gives you the opportunity to learn from the pilot and share best practices as you expand your BRM practice.
You can leverage the pilot business unit’s feedback to help obtain buy-in from additional groups. Evaluate the approaches for your pilot: |
Work With an Engaged Business Unit
This approach can allow you to find a champion group and establish quick wins. |
Target Underperforming Area(s)
This approach can allow you to establish significant wins, providing new opportunities for value. |
| Target the Area(s) Driving the Most Business Value
Provide the largest positive impact on your portfolio’s ability to drive business value; for large strategic or transformative goals. |
Work Across a Single Business Process
This approach addresses a single business process or operation that exists across business units, departments, or locations. This, again, will allow you to limit the number of stakeholders. |
Leverage BRM goals to determine where the role fits within the organization
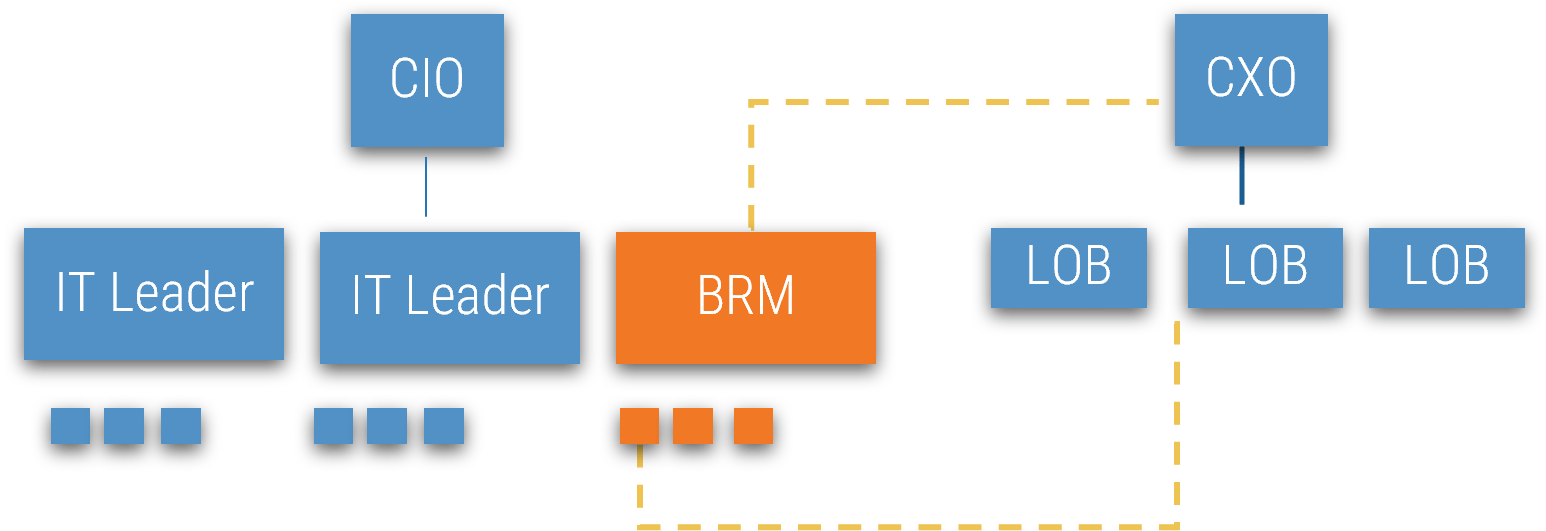
Strategic BRMs are considered IT leaders, often reporting to the CIO.
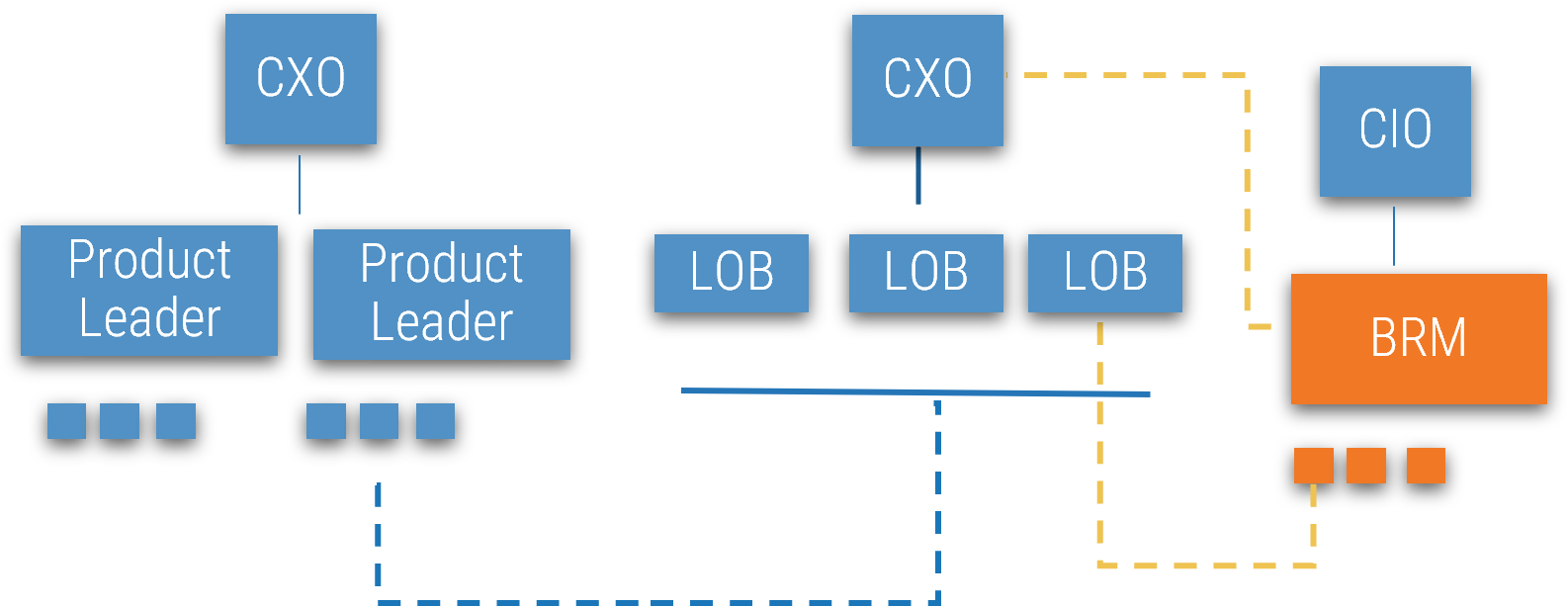
In product-aligned organizations, the product owners will own the strategic business relationship from a product perspective (often across LOB), while BRMs will own the strategic role for the line(s) of businesses (often across products) that they hold a relationship with. The BRM role may be played by a product family leader.
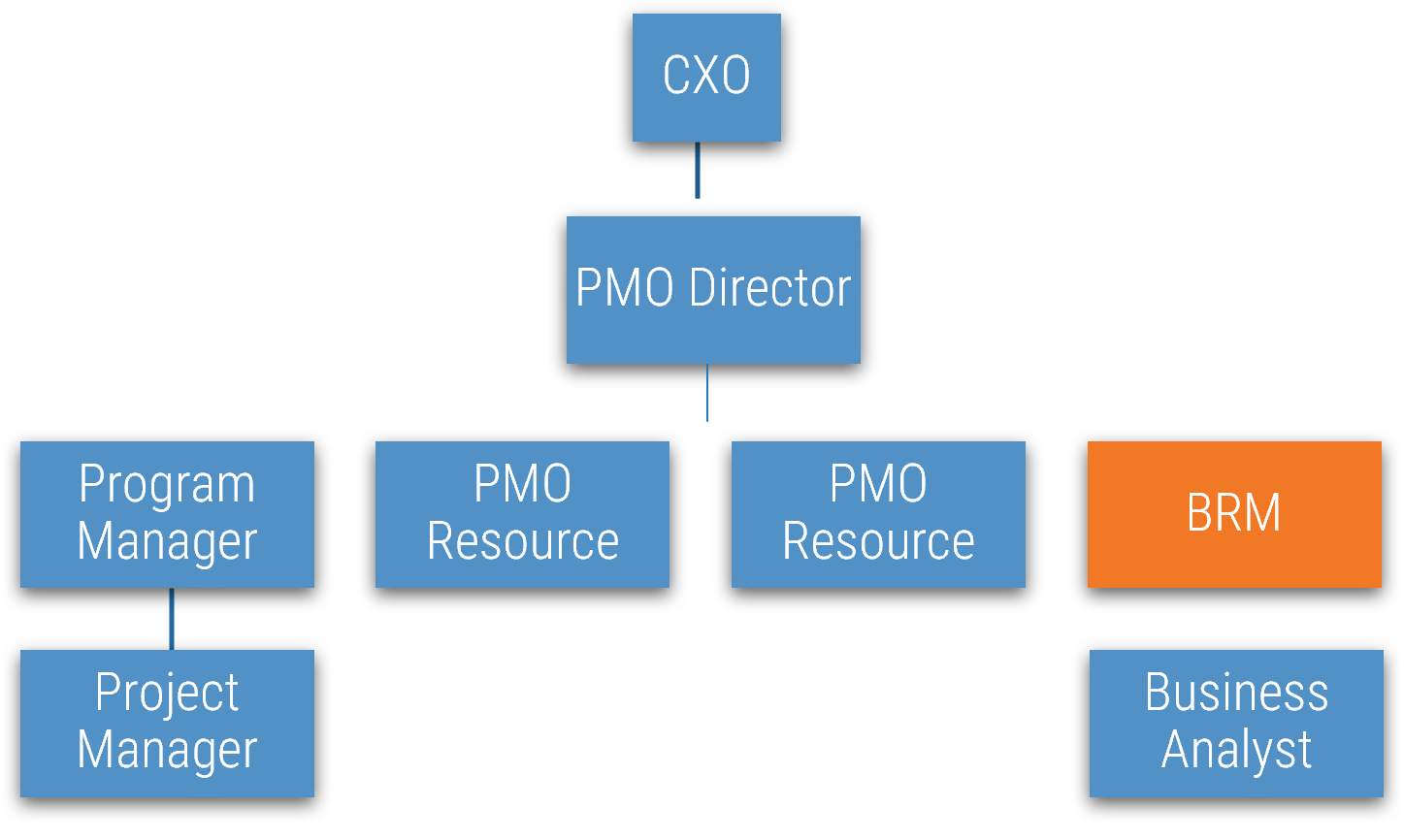
BRMs may take on a more operational function when they are embedded within another group, such as the PMO. This manifests in:
- Accountability for projects and programs
- BRM conversations around projects and programs rather than overall needs
- Often, there is less focus on stimulating need, more about managing demand
- This structure may be useful for smaller organizations or where organizations are piloting the relationship capability
Use the IT structure and the business structure to determine how to align BRM and business partners. Many organizations ensure that each LOB has a designated BRM, but each BRM may work with multiple LOBs. Ensure your alignment provides an even and manageable distribution of work.
Don’t be intimidated by those who play a significant role in relationship management

|
Business Relationship Manager: Portfolio View
|
The BRM will look holistically across a portfolio, rather than on specific projects or products. Their focus is ensuring value is delivered that impacts the overall organization. Multiple BRMs may be responsible for lines of businesses and ensure that products and project enable LOBs effectively. |
Business Analyst: Product or Project View
|
The BA tends to be involved in project work – to that end, they are often brought in a bit before a project begins to better understand the context. They also often remain after the project is complete to ensure project value is delivered. However, their main focus is on delivering the objectives within the project. | |
Product Owner: Product View
|
The Product Owner bridges the gap between the business and delivery to ensure their product continuously delivers value. Their focus is on the product. |
3.2 Establish the BRM’s place in the organizational structure
Input: BRM goals, IT organizational structure, Business organizational structure
Output: BRM operating model
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Review the current organizational structure – both IT and overall business.
- Think about the maturity of the IT organization and what you and your partners will be able to support at this stage in the relationship or journey. Establish whether it is necessary to start with a pilot.
- Consider the reporting relationship that is required to support the desired maturity of your practice – who will your BRM function report into?
- Consider the distribution of work from your business partners. Establish which BRM is responsible for which partners.
- Document where the BRM fits in the organization in the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template.
Download the BRM Workbook
Download the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template
Align your titles to your business partners and ensure it demonstrates your strategic goals
Some titles that may reflect alignment with your partners:
Support BRM team members might have “analyst” or “coordinator” as part of their titles. |
Caution when using these titles:
|
Determine the expectations for your BRM role(s)
Below are standard expectations from BRM job descriptions. Establish whether there are changes required for your organization.
Act as a Relationship Manager
|
Service Delivery
Service delivery breaks out into three activities: service status, changes, and service desk tickets
|
Determine role expectations (slide 2 of 3)
| Knowledge of the Business
Understand the main business activities for each department:
|
Influence Business and IT Stakeholders
|
Determine role expectations (slide 3 of 3)
Value Creator
|
3.3 Establish BRM expectations
Input: BRM goals
Output: BRM expectations
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Review the BRM expectations on the previous slides.
- Customize them – are they the appropriate set of expectations needed for your organization? What needs to be edited in or out?
- Add relevant expectations – what are the things that need to be done in the BRM practice at your organization?
- Leverage the workbook to brainstorm BRM expectations. Make sure you update them in the BRM Role Expectation Spreadsheet.
Download the BRM Workbook
Download the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template
Various roles and levels within your organization may have a part of the BRM pieWhere the BRM sits will impact what they are able to get done.The BRM role is a strategic one, but other roles in the organization have a part to play in impacting IT-partner relationship.Some roles may have a more strategic focus, while others may have a more tactical or operational focus. |
|
3.4 Identify roles with BRM responsibilities
Input: BRM goals
Output: BRM-aligned roles
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Various roles can play a part in the BRM practice, managing business relationships. Which ones make sense in your organization, given the BRM goals?
- Identify the roles and capture in the BRM Role Expectation Spreadsheet. Use the Role Expectation Alignment tab, row 1.
Download the Role Expectations Worksheet
Determine the focus for each role that may manage business relationships
| STRATEGIC | Sets Direction: Focus of the activities is at the holistic, enterprise business level | “relating to the identification of long-term or overall aims and interests and the means of achieving them” | e.g. builds overarching relationships to enable and support the organization’s strategy; has strategic conversations | |
| TACTICAL | Figures Out the How: Focuses on the tactics required to achieve the strategic focus | “skillful in devising means to ends” | e.g. builds relationships specific to tactics (projects, products, etc.) | |
| OPERATIONAL | Executes on the Direction: Day-to-day operations; how things get done | “relating to the routine functioning and activities of a business or organization” | e.g. builds and leverages relationships to accomplish specific goals (within a project or product) |
3.5 Align BRM capabilities to roles
Input: Current-state model, Business value matrix, Objectives and goals
Output: BRM-aligned roles
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Review each group of role expectations – Act as a Relationship Manager, Communicate with Business Stakeholders, etc. For each group, determine the focus each role can apply to it – strategic, tactical, or operational. Refer to the previous slide for examples.
- Capture on the spreadsheet:
- S – This role is required to have a strategic view of the capabilities. They are accountable and set direction for this aspect of relationship management.
- T – Indicate if the role is required to have a tactical view of the capabilities. This would include whether the role is required to figure out how the capabilities will be done; for example, is the role responsible for carrying out service management or are they just involved to ensure that that set of expectations are being performed?
- O – Indicate if the role will have an operational view – are they the ones responsible for doing the work?
- Note: In some organizations, a role may have more than one of these.
- The spreadsheet will highlight the cells in green if the role plays more of the strategic role, yellow for tactical, and brown for operational. This provides an overall visual of each role’s part in relationship management.
- (Optional) Review each detailed expectation within the group. Evaluate whether specific roles will have a different focus on the unique role expectations.
Leverage the Role Expectations Worksheet
Sample role expectation alignment
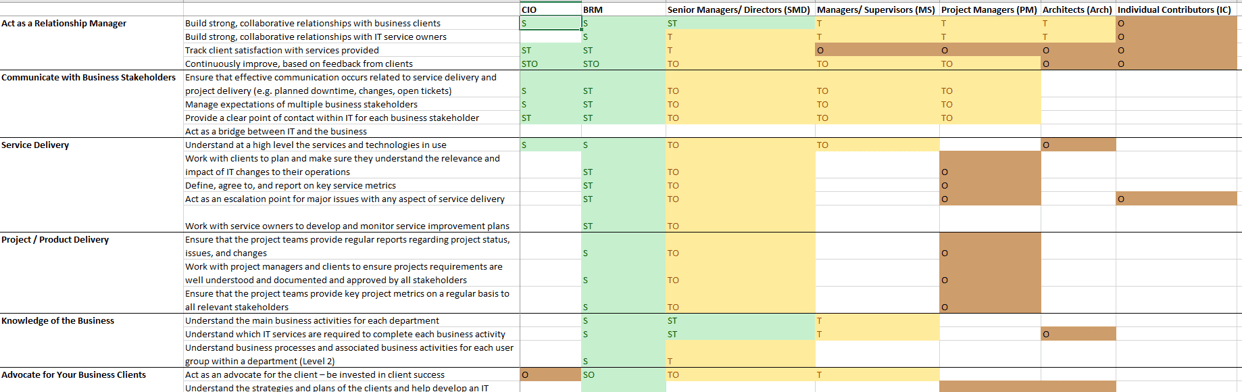
IMPLEMENT
| Assess 1.1 Define BRM 1.2 Analyze Satisfaction 1.3 Assess SWOT | Situate 2.1 Create Vision 2.2 Create the BRM Mission 2.3 Establish Goals | Plan 3.1 Establish Guiding Principles 3.2 Determine Where BRM Fits 3.3 Establish BRM Expectations 3.4 Identify Roles With BRM Responsibilities 3.5 Align Capabilities | ||
| Implement 4.1 Brainstorm Sources of Business Value 4.2 Identify Key Influencers 4.3 Categorize the Stakeholders 4.4 Create the Prioritization Map 4.5 Create Your Engagement Plan | Reassess & Embed 5.1 Create Metrics 5.2 Prioritize Your Projects 5.3 Create a Portfolio Investment Map 5.4 Establish Your Annual Plan 5.5 Build Your Transformation Roadmap 5.6 Create Your Communication Plan |
Speak the same language as your partners: Business Value
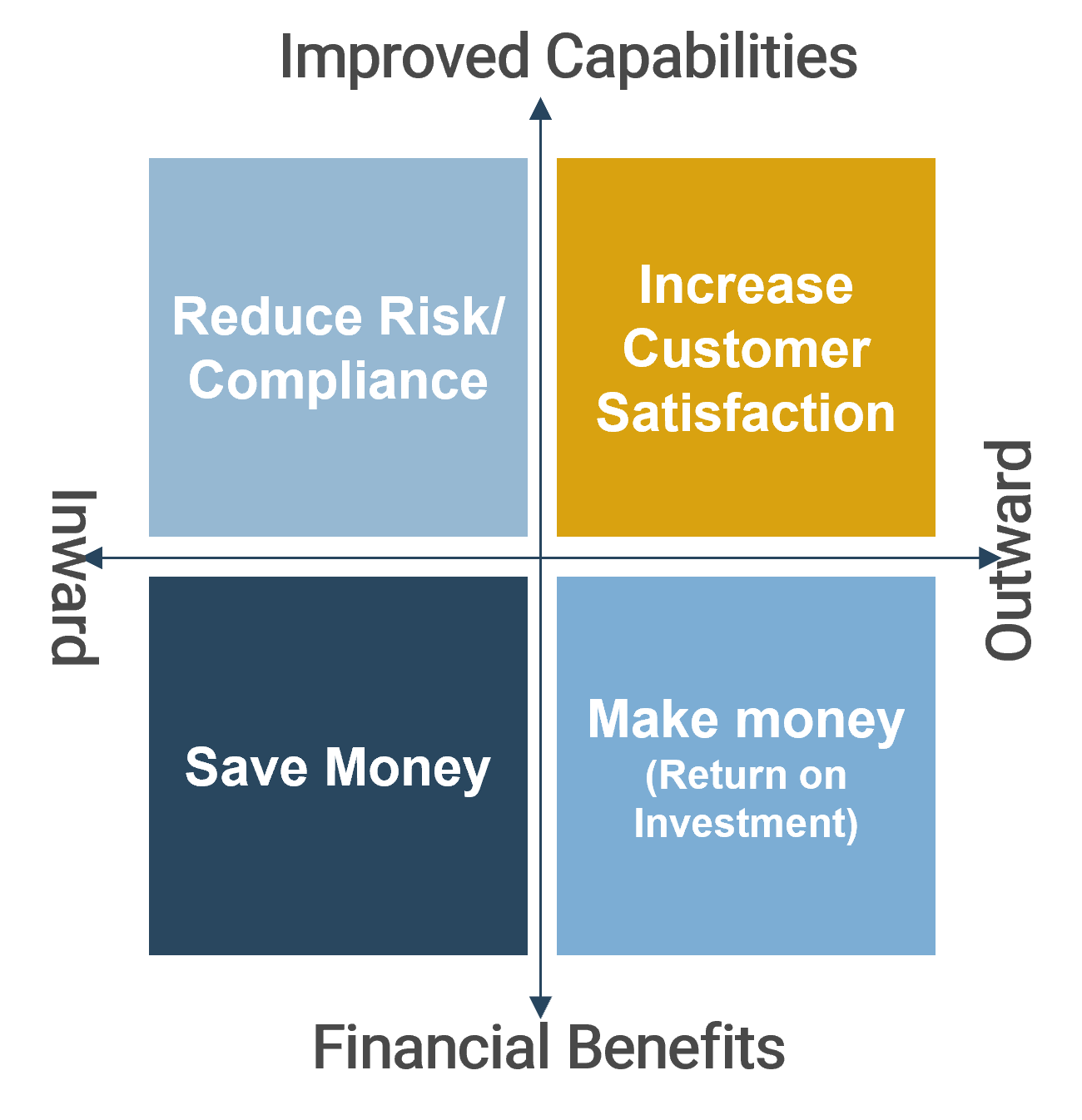
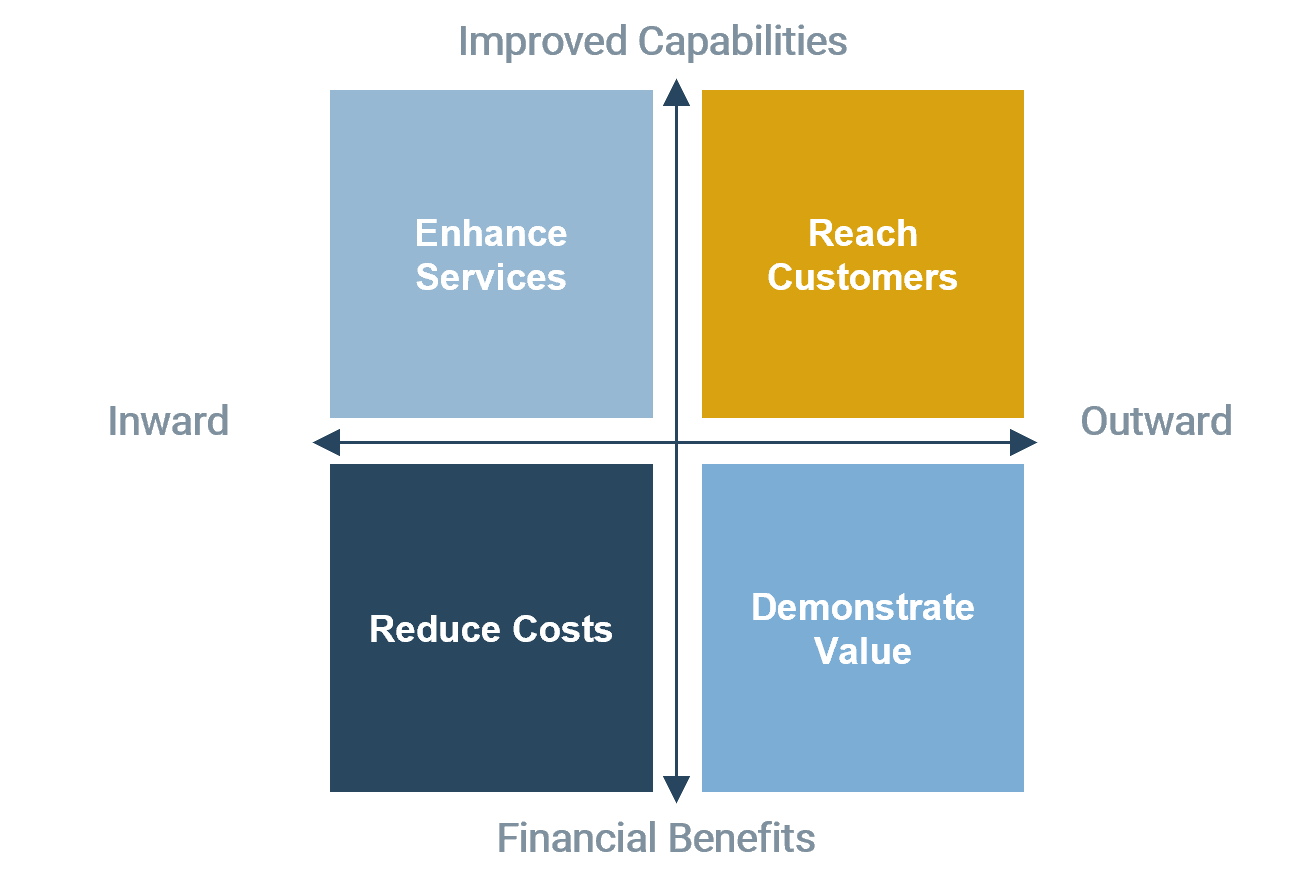
Business value represents the desired outcome from achieving business priorities.
Value is not only about revenue or reduced expenses. Use this internal-external and capability-financial business value matrix to more holistically consider what is valuable to stakeholders.
|
Business Value Matrix Axes:Financial Benefits vs. Improved Capabilities
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
4.1 Activity: Brainstorm sources of business value
Input: Product and service knowledge, Business process knowledge
Output: Understanding of different sources of business value
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Identify your key stakeholders. These individuals are the critical business strategic partners in the organization’s governing bodies.
- Brainstorm the different types of business value that the BRM practice can produce.
- Is the item more focused on improving capabilities or generating financial benefits?
- Is the item focused on the customers you serve or the IT team?
- Enter your value item into a cell on the Business Value Matrix based on where it falls on these axes.
- Start to think about metrics you can use to measure how effective the product or service is at generating the value source.
|
Use the BRM Workbook to capture sources of business value |
Brainstorm the different sources of business value (continued)
See appendix for more information on value drivers:
|
Example:
|
||||||||
Implications of ineffective stakeholder management
|
A stakeholder is any group or individual who is impacted by (or impacts) your objectives. Challenges with stakeholder management can result from a self-focused point of view. Avoid these challenges by taking on the other’s perspectives – what’s in it for them. The key objectives of stakeholder management are to improve outcomes, increase confidence, and enhance trust in IT.
|
Challenges
|
Implications
|
Cheat Sheet: Identify stakeholders
Ask stakeholders “who else should I be talking to?” to discover additional stakeholders and ensure you don’t miss anyone.
| List the people who are identified through the following questions: | Take a 360-degree view of potential internal and external stakeholders who might be impacted by the initiative. | |||
|
|
Executives Peers Direct reports Partners Customers |

|
Subcontractors Suppliers Contractors Lobby groups Regulatory agencies |
Establish your stakeholder network “map”
Follow the trail of breadcrumbs from your direct stakeholders to their influencers to uncover hidden stakeholders.
Your stakeholder map defines the influence landscape your BRM team operates in. It is every bit as important as the teams who enhance, support, and operate your products directly.
Notes on the network map
- Pay special attention to influencers who have many arrows; they are called “connectors,” and due to their diverse reach of influence, should themselves be treated as significant stakeholders.
- Don’t forget to consider the through-lines from one influencer through intermediate stakeholders or influencers to the final stakeholder – a single influencer may have additional influence via multiple, possibly indirect paths to a single stakeholder.
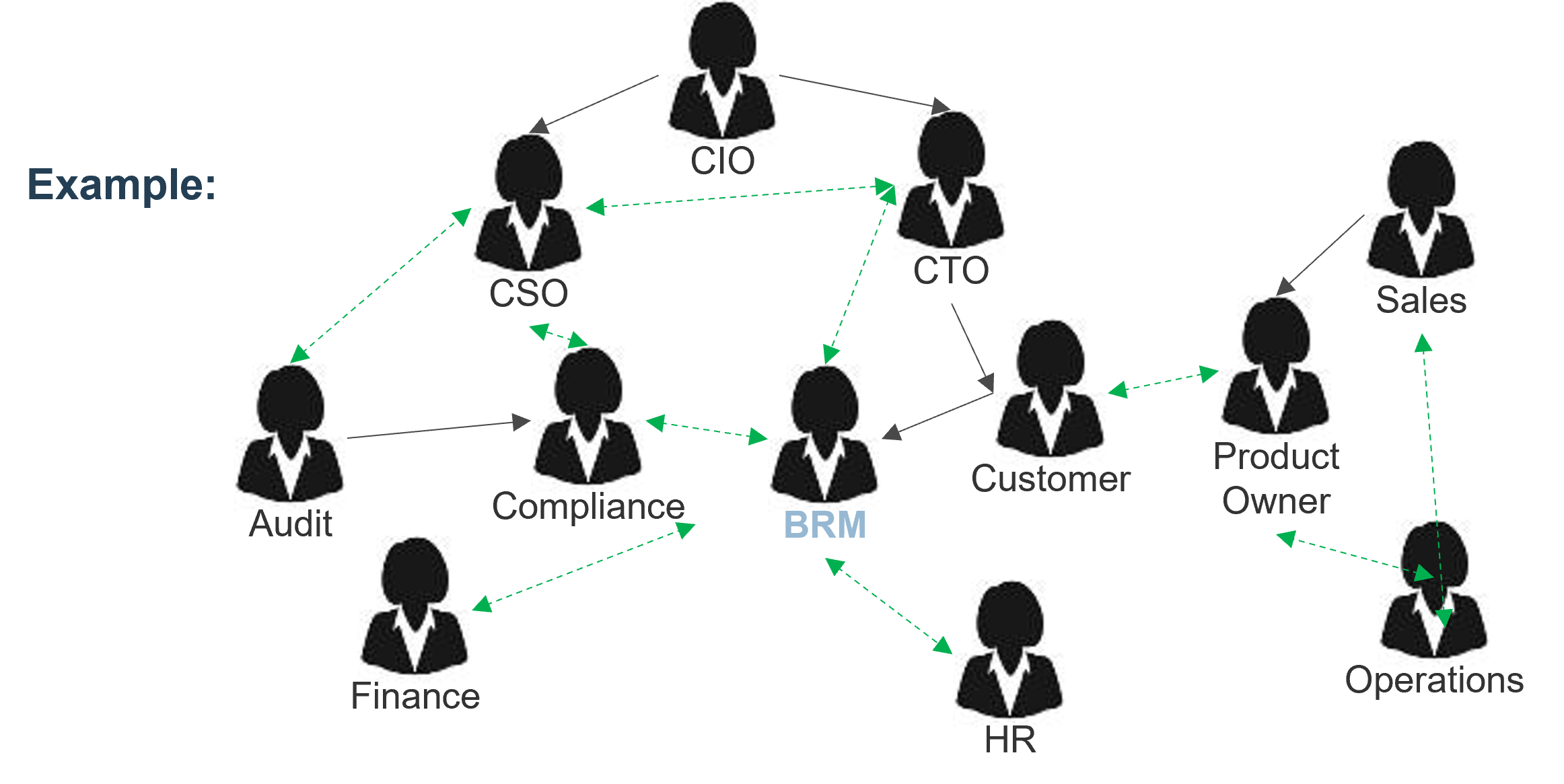
4.2 Visualize interrelationships among stakeholders to identify key influencers
Input: List of stakeholders
Output: Relationships among stakeholders and influencers
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- List direct stakeholders for your area. Ensure it includes stakeholders across the organization (both IT and business units).
- Determine the stakeholders of your stakeholders. Consider adding each of them to the stakeholder list: assess who has either formal or informal influence over your stakeholders; add these influencers to your stakeholder list.
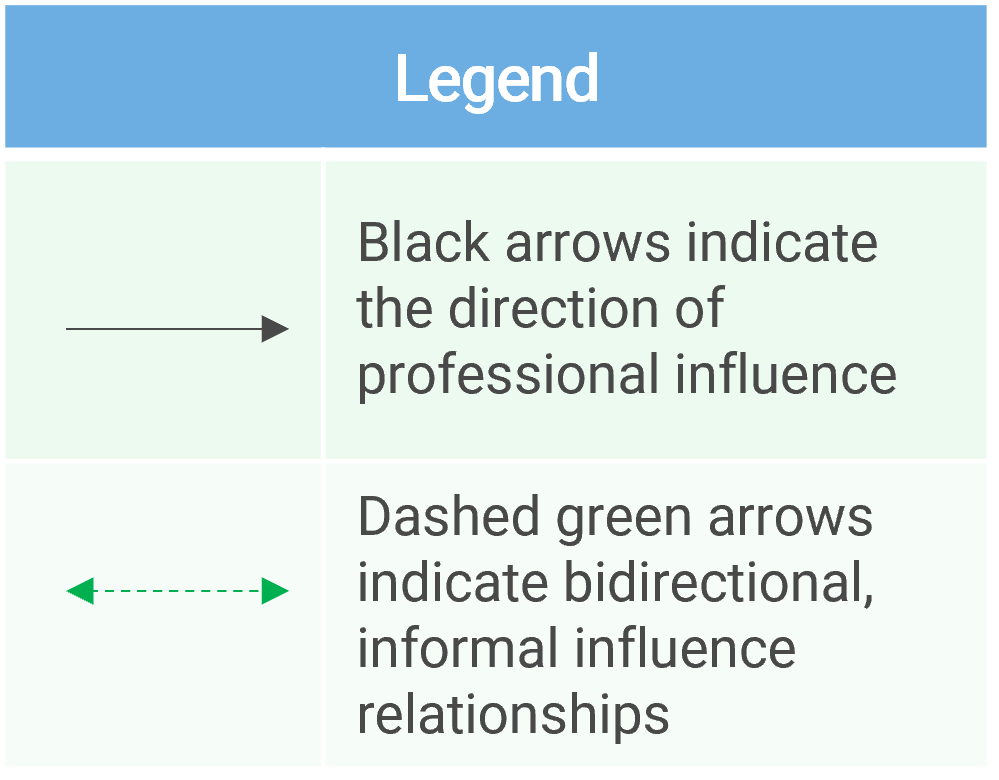
- Create a stakeholder network map to visualize relationships.
- (Optional) Use black arrows to indicate the direction of professional influence.
- (Optional) Use dashed green arrows to indicate bidirectional, informal influence relationships.
- Capture the list or diagram of your stakeholders in your workbook.
|
Use the BRM Workbook to capture stakeholders |
Categorize your stakeholders with a stakeholder prioritization map
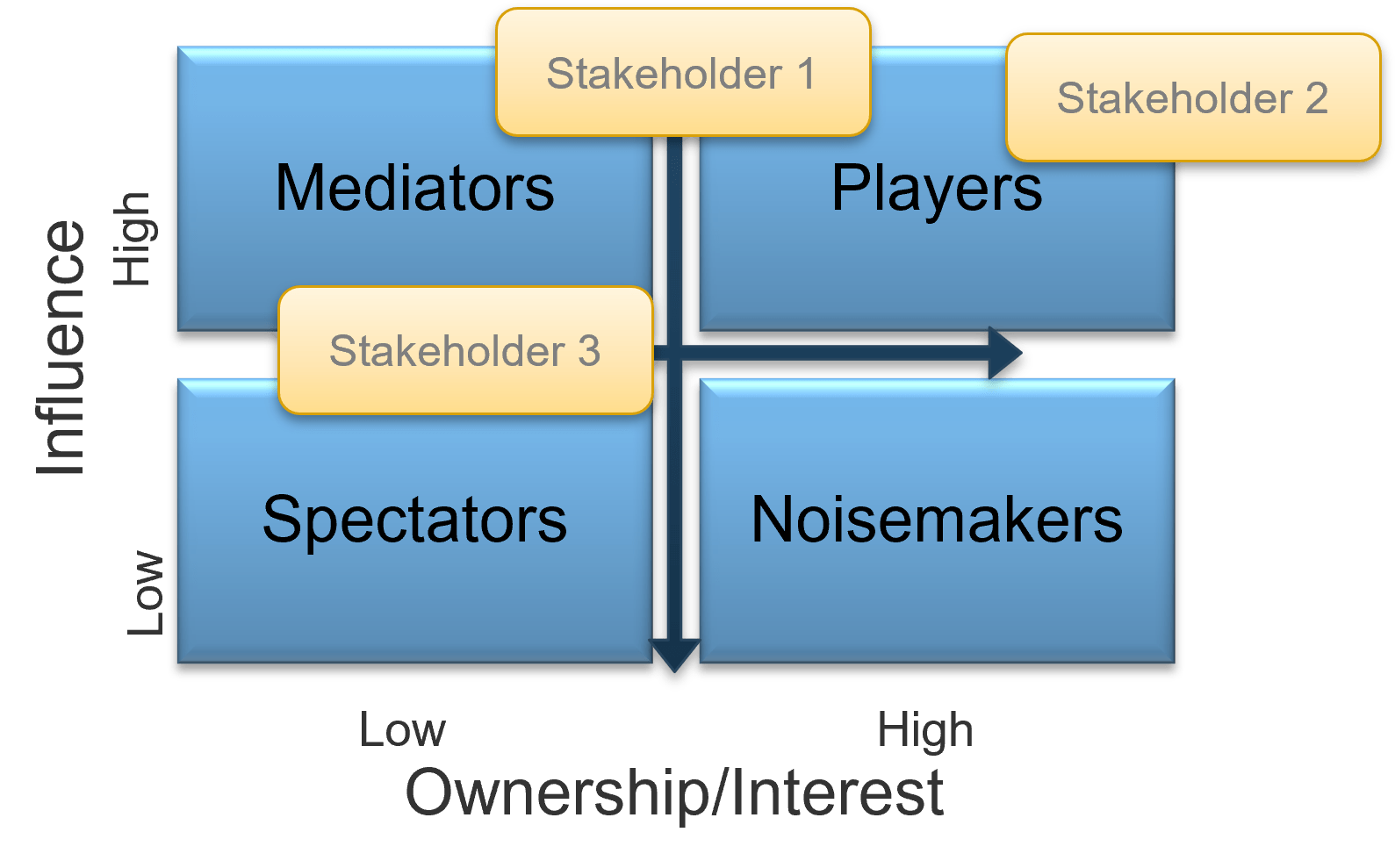
A stakeholder prioritization map help teams categorize their stakeholders by their level or influence and ownership.
There are four areas in the map and the stakeholders within each area should be treated differently.
- Players – players have a high interest in the initiative and the influence to effect change over the initiative. Their support is critical and a lack of support can cause significant impediment to the objectives.
- Mediators – mediators have a low interest but significant influence over the initiative. They can help to provide balance and objective opinions to issues that arise.
- Noisemakers – noisemakers have low influence but high interest. They tend to be very vocal and engaged, either positively or negatively, but have little ability to enact their wishes.
- Spectators – generally, spectators are apathetic and have little influence over or interest in the initiative.
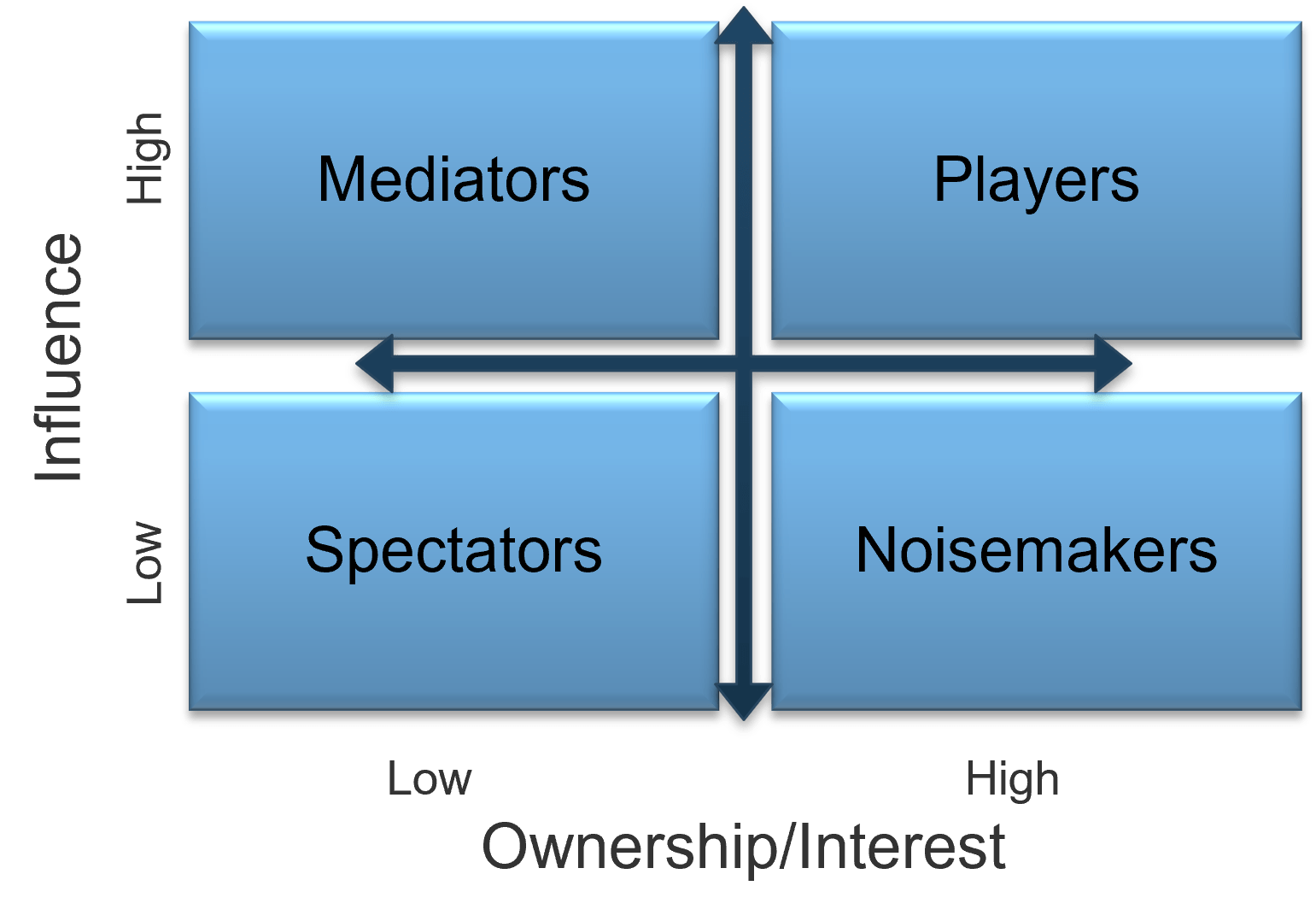
4.3 Group your stakeholders into categories
Input: Stakeholder Map
Output: Categorization of stakeholders and influencers
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
|
Level of Influence
Level of InterestHow much are the stakeholder’s individual performance and goals directly tied to the success or failure of the product? |
Use the BRM Workbook to map your stakeholders
Define strategies for engaging stakeholders by type
Each group of stakeholders draws attention and resources away from critical tasks.
By properly identifying your stakeholder groups, you can develop corresponding actions to manage stakeholders in each group. This can dramatically reduce wasted effort trying to satisfy Spectators and Noisemakers while ensuring the needs of the Mediators and Players are met.
| Type | Quadrant | Actions |
| Players | High influence; high interest | Actively Engage
Keep them engaged through continuous involvement. Maintain their interest by demonstrating their value to its success. |
| Mediators | High influence; low interest | Keep Satisfied
They can be the game changers in groups of stakeholders. Turn them into supporters by gaining their confidence and trust, and include them in important decision-making steps. In turn, they can help you influence other stakeholders. |
| Noisemakers | Low influence; high interest | Keep Informed
Try to increase their influence (or decrease it if they are detractors) by providing them with key information, supporting them in meetings, and using Mediators to help them. |
| Spectators | Low influence; low interest | Monitor
They are followers. Keep them in the loop by providing clarity on objectives and status updates. |
Prioritize your stakeholders
There may be too many stakeholders to be able to manage them all. Focus your attention on the stakeholders that matter most.
Apply a third dimension for stakeholder prioritization: support.
Support, in addition to interest and influence, is used to prioritize which stakeholders are should receive the focus of your attention. This table indicates how stakeholders are ranked:
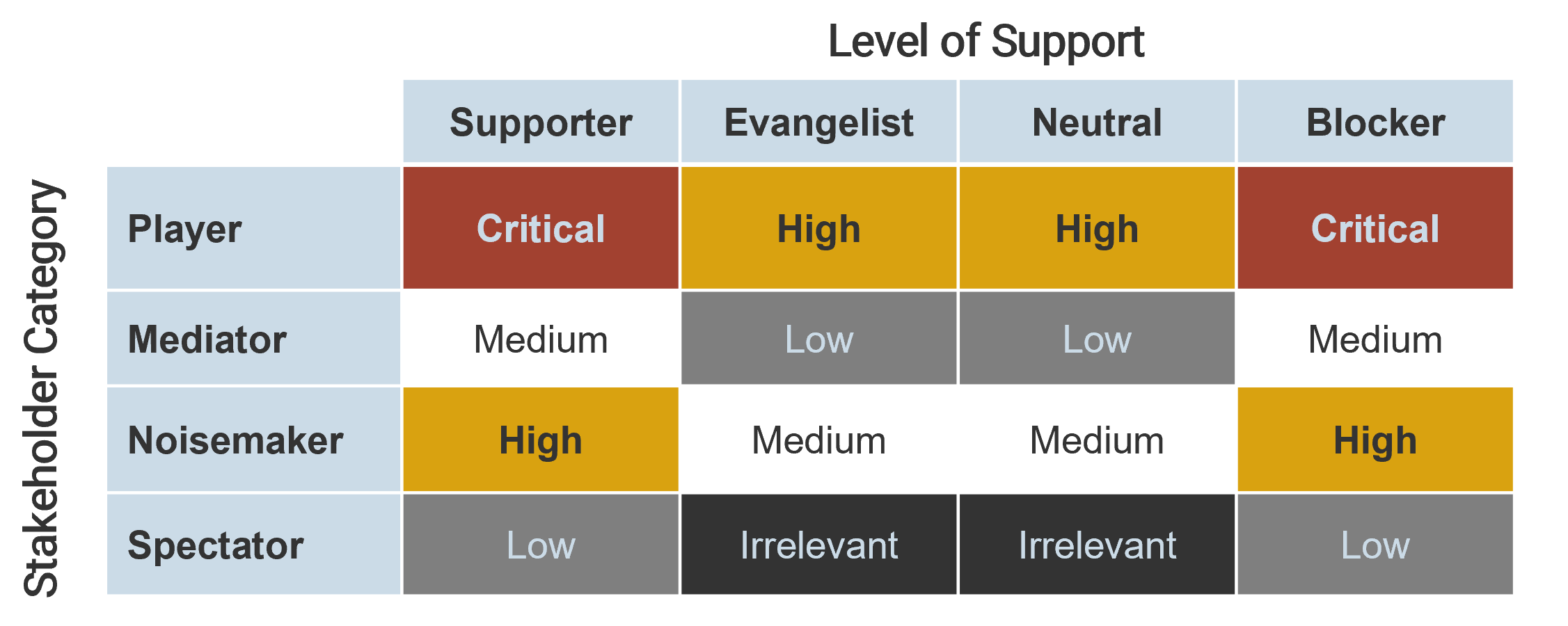
Support can be determined by rating the following question: how likely is it that your stakeholder would recommend IT at your organization/your group? Our four categories of support:
- Blocker – beware of the blocker. These stakeholders do not support your cause and have the necessary drive to impede the achievement of your objectives.
- Semi-Supporter – while these stakeholders are committed to your objectives, they are somewhat apathetic to advocate on your behalf. They will support you so long as it does not require much effort from them to do so.
- Neutral – neutrals do not have much commitment to your objectives and are not willing to expend much energy to either support or detract from them.
- Supporter – these stakeholders are committed to your initiative and are willing to whole-heartedly provide you with support.
4.4 Update your stakeholder quadrant to include the three dimensions
Input: Stakeholder Map
Output: Categorization of stakeholders and influencers
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Identify the level of support of each stakeholder by answering the following question: how likely is it that your stakeholder would support your initiative/endeavor?
- Map your results to the model in your workbook to determine each stakeholder’s category.
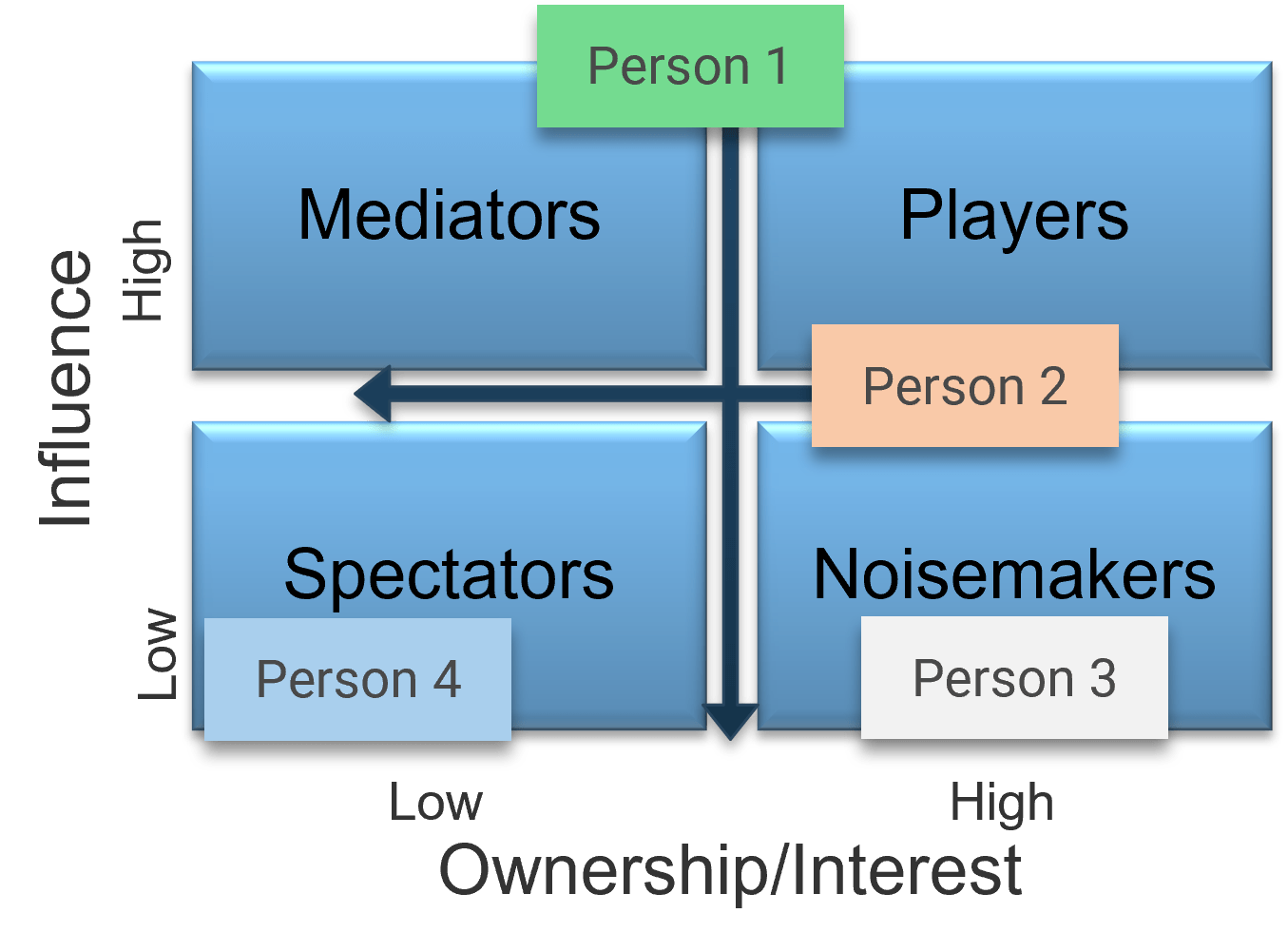
|
Use the BRM Workbook to map your stakeholders |
Leverage your map to think about how to engage with your stakeholders
Not all stakeholders are equal, nor can they all be treated the same. Your stakeholder quadrant highlights areas where you may need to engage differently.
BlockersPay attention to your “blockers,” especially those that appear in the high influence and high interest part of the quadrant. Consider how your engagement with them varies from supporters in this quadrant. Consider what is valuable to these stakeholders and focus your conversations on “what’s in this for them.” |
Neutral & EvangelistsStakeholders that are neutral or evangelists do not require as much attention as blockers and supporters, but they still can’t be ignored – especially those who are players (high influence and engagement). Focus on what’s in it for them to move them to become supporters. |
SupportersDo not neglect supporters – continue to engage with them to ensure that they remain supporters. Focus on the supporters that are influential and impacted, rather than the “spectators.” |
4.5 Create your engagement plan
Input: Stakeholder Map/list of stakeholders
Output: Categorization of stakeholders and influencers
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Leverage the BRM Stakeholder Engagement Plan spreadsheet. List your key stakeholders.
- Consider: how do you show value at your current maturity level so that you can gain trust and your relationship can mature? Establish where your relationship lacks maturity, and consider whether you need to engage with them on a more strategic, tactical, or even operational manner.
- At lower levels of maturity (Table Stakes), focus on service delivery, project delivery, and communication.
- At mid-level maturity (Influencer/Advocate), focus on business pain points and a deeper knowledge of the business.
- At higher maturity levels (Value Creator/Innovator), focus on creating value by leading innovative initiatives that drive the business forward.
- Review the stakeholder quadrant. Update the frequency of your communication accordingly.
- Capture the agenda for your engagements with them.
|
Download and use the BRM Stakeholder Engagement Plan |
Your agenda should vary with the maturity of your relationship
| Agenda | |||||
| Stakeholder | Information Type | Meeting Frequency | Lower Maturity | Mid-Level Maturity | Higher Maturity |
| VP | Strategic | Quarterly |
|
|
|
| Director | Strategic, Tactical | Monthly |
|
|
|
| Manager | Tactical | Monthly |
|
|
|
Lower Maturity – Focus on service delivery, project delivery, and communication
Mid-Level Maturity – Focus on business pain points and a deeper knowledge of the business
Higher Maturity – Focus on creating value by leading innovative initiatives that drive the business forward
Stakeholder – Include both IT and business stakeholders at appropriate levels
Agenda – Manage stakeholders expectations, and clarify how your agenda will progress as the partnership matures
REASSESS & EMBED
| Assess 1.1 Define BRM 1.2 Analyze Satisfaction 1.3 Assess SWOT | Situate 2.1 Create Vision 2.2 Create the BRM Mission 2.3 Establish Goals | Plan 3.1 Establish Guiding Principles 3.2 Determine Where BRM Fits 3.3 Establish BRM Expectations 3.4 Identify Roles With BRM Responsibilities 3.5 Align Capabilities | ||
| Implement 4.1 Brainstorm Sources of Business Value 4.2 Identify Key Influencers 4.3 Categorize the Stakeholders 4.4 Create the Prioritization Map 4.5 Create Your Engagement Plan | Reassess & Embed 5.1 Create Metrics 5.2 Prioritize Your Projects 5.3 Create a Portfolio Investment Map 5.4 Establish Your Annual Plan 5.5 Build Your Transformation Roadmap 5.6 Create Your Communication Plan |
Measure your BRM practice success
|
|
| Questions to ask | Are your metrics achievable? | |
|
S pecific M easurable A chievable R ealistic T ime-bound |
Embedding the BRM practice within your organization must be grounded in achievable outcomes.
Ensure that the metrics your practice is measured against reflect realistic and tangible business expectations. Overpromising the impact the practice will have can lead to long-term implementation challenges. |
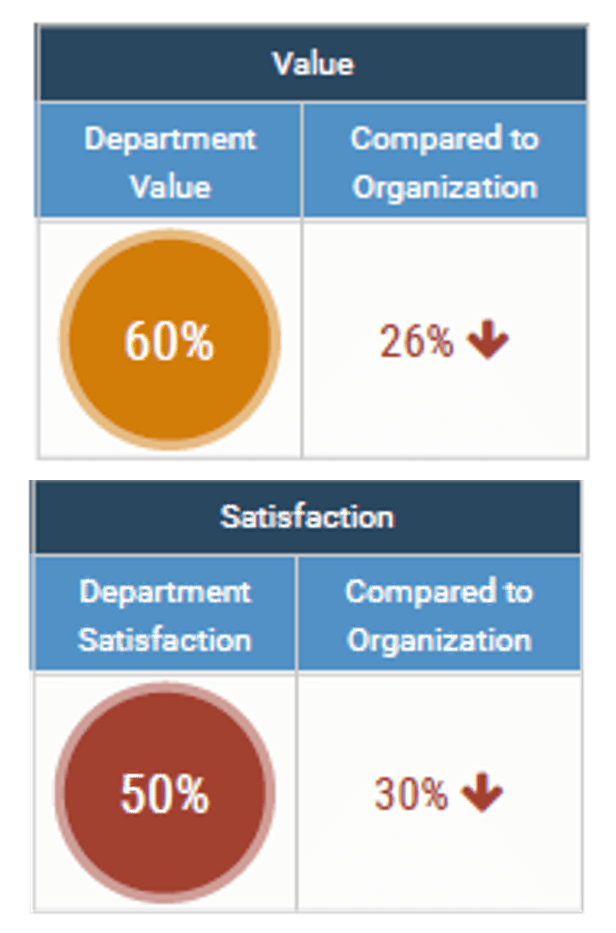
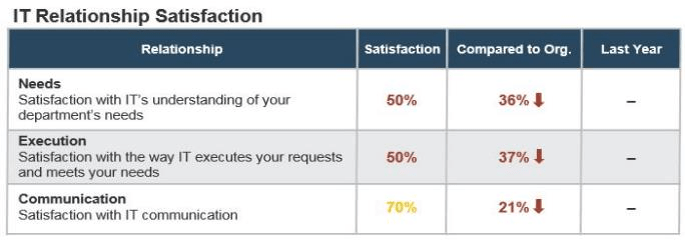
Determine whether your business is satisfied with IT
 | 1 | Survey your stakeholders to measure improvements in customer satisfaction. | Leverage the CIO Business Vision on a regular interval – most find that annual assessments drive success. Evaluate whether the addition or increased maturity of your BRM practice has improved satisfaction with IT. | |
Business satisfaction survey
|  | |||
 | ||||
Check if you’ve met the BRM goals you set out to achieve

|
2 |
Measure BRM success against the goals for the practice. |
Evaluate whether the BRM practice has helped IT to meet the goals that you’ve established. For each of your goals, create metrics to establish how you will know if you’ve been successful. This might be how many or what type of interactions you have with your stakeholders, and/or it could be new connections with internal or external partners. Ensure you have established metrics to measure success at your goals. |
|
|
||||
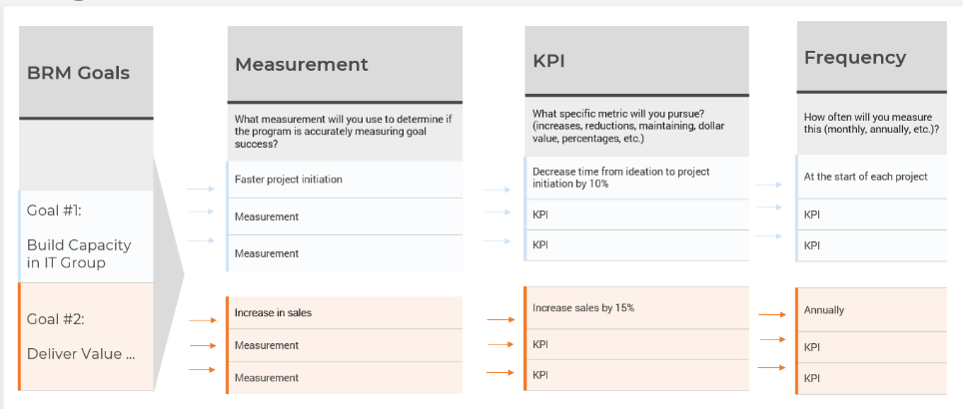
5.1 Create metrics
Input: Goals, The attributes which can align to goal success
Output: Measurements of success
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Start with a consideration of your goals and objectives.
- Identify key aspects that can support confirming if the goal was successful.
- For each aspect, develop a method to measure success with a specific measurement.
- When creating the KPI consider:
- How you know if you are achieving your objective (performance)?
- How frequently will you be measuring this?
- Are you looking for an increase, decrease, or maintenance of the metric?
|
Use the BRM Workbook |
Don’t wait all year to find out if you’re on track
Leverage the below questions to quickly poll your business partners on a more frequent basis.
| Partner instructions:
Please indicate how much you agree with each of the following statements. Use a scale of 1-5, where 1 is low agreement and 5 indicates strong agreement: Demand Shaping: My BRM is at the table and seeks to understand my business. They help me understand IT and helps IT prioritize my needs. Exploring: My BRM surfaces new opportunities based on their understanding of my pain points and growth needs. They engage resources with a focus on the value to be delivered. Servicing: The BRM obtains an understanding of the services and service levels that are required, clarifies them, and communicates costs and risks. Value Harvesting: Focus on value is evident in discussions – the BRM supports IT in ensuring value realization is achieved and tracks value during and beyond deployment. |

|
Embedding the BRM practice also includes acknowledging the BRM’s part in balancing the IT portfolio
| IT needs to juggle “keeping the lights on” initiatives with those required to add value to the organization. Partner with the appropriate resources (Project Management Office, Product Owners, System Owners, and/or others as appropriate within your organization) to ensure that all initiatives focus on value. Info-Tech InsightNot every organization will balance their portfolio in the same way. Some organizations have higher risk tolerance and so their higher priority goals may require that they accept more risk to potentially reap more returns. |  80% of organizations feel their portfolios are dominated by low-value initiatives that do not deliver value to the business. (Source: Stage-Gate International and Product Development Institute, March/April 2009) |
All new requests are not the same; establish a process for intake and manage expectations and IT’s capacity to deliver value.Ensure you communicate your process to support new ideas with your stakeholders. They’ll be clear on the steps to bring new initiatives into IT and will understand and be engaged in the process to demonstrate value. |
|
|
| For support creating your intake process, go to Optimize Project Intake, Approval and Prioritization | 
|
|
Use value as your criteria to evaluate initiativesWork with project managers to ensure that all projects are executed in a way that meets business expectations.
Download Info-Tech’s Project Value Scorecard Development Tool. |
|
|||||||||||
5.2 Prioritize your investments/ projects (optional activity)
Input: Value criteria
Output: Prioritized project listing
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Review and edit (if necessary) the criteria on tab 2 the Project Value Scorecard Development Tool.
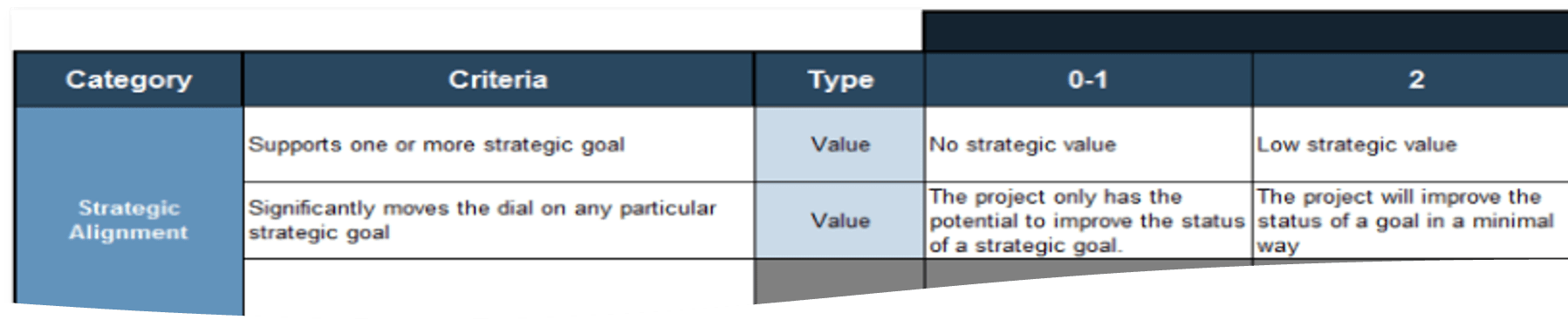
- Score initiatives and investments on tab 3 using your criteria.
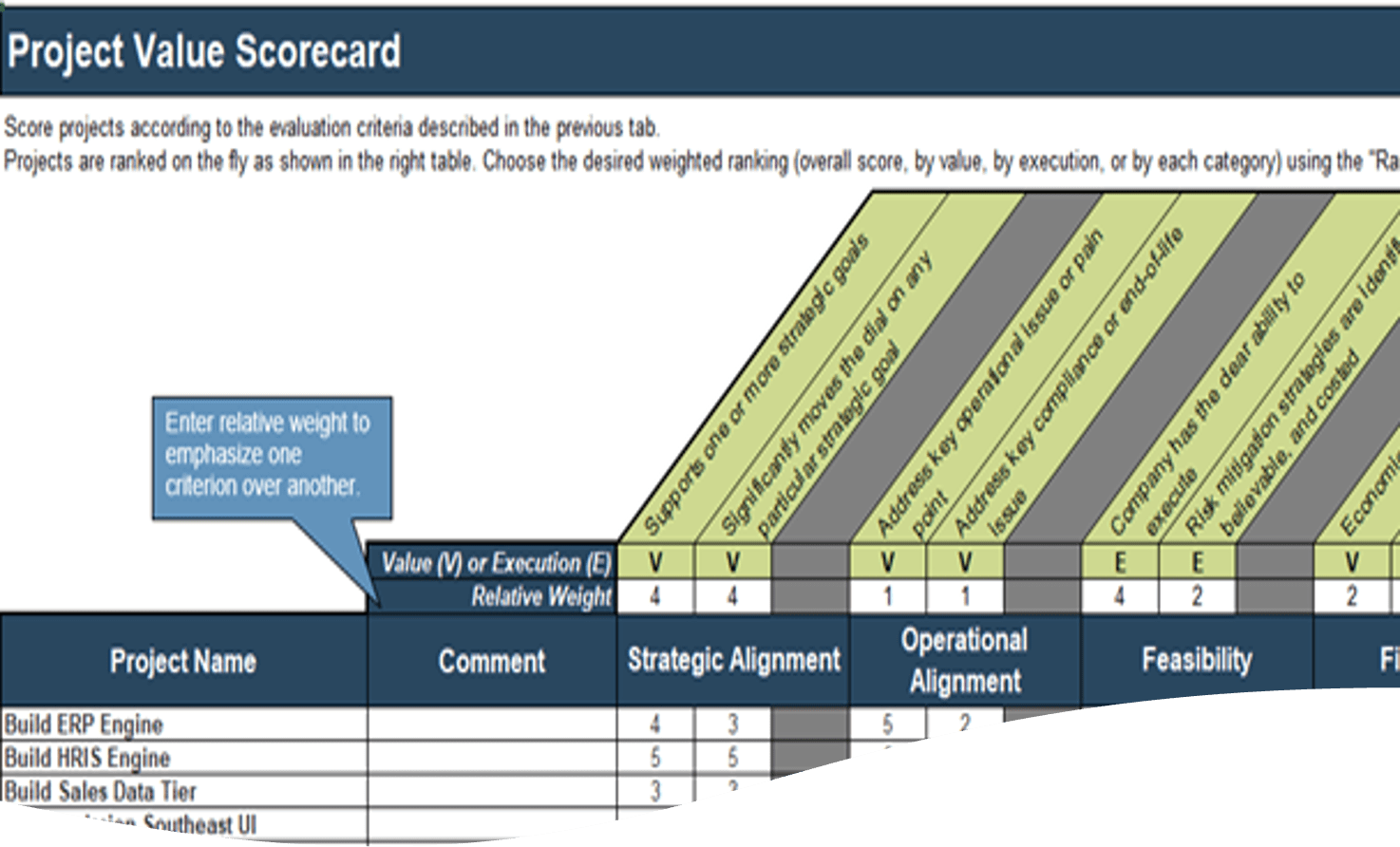
| Download Info-Tech’s Project Value Scorecard Development Tool. |
Visualize where investments add value through an initiative portfolio mapAn initiative portfolio map is a graphic visualization of strategic initiatives overlaid on a business capability map. Leverage the initiative portfolio map to communicate the value of what IT is working on to your stakeholders. Info-Tech InsightProjects will often impact one or more capabilities. As such, your portfolio map will help you identify cross-dependencies when scaling up or scaling down initiatives. | Example initiative portfolio map
|
5.3 Create a portfolio investment map (optional activity)
Input: Business capability map
Output: Portfolio investment map
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Build a capability map, outlining the value streams that support your organization’s goals and the high-level capabilities (level 1) that support the value stream (and goals).
For more support in establishing the capability map, see Document Your Business Architecture.
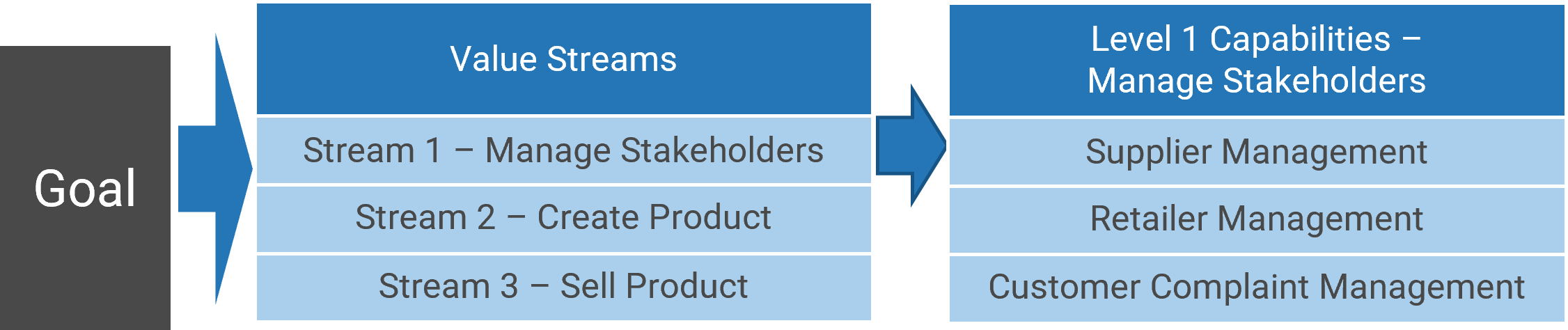
- Identify high-value capabilities for the organization.
- What are the projects and initiatives that will address the critical capabilities? Add these under the high-value capabilities.
- This process will help you demonstrate how projects align to business goals. Enter your capabilities and projects in Info-Tech’s Initiative Portfolio Map Template.
| Download Info-Tech’s Initiative Portfolio Map Template. |
Establish your annual BRM plan
To support the BRM capability at your organization, you’ll want to communicate your plan. This will include:
|

|
5.4 Establish your year-in-the-life plan
Input: Engagement plan, BRM goals
Output: Annual BRM plan
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Start with your business planning activities – what will you as a BRM be doing as your business establishes their plans and strategies? These could include:
- Listening and feedback sessions
- Third-party explorations
- Then look at your activities required to integrate within IT – what activities are required to align business directives within your IT groups? Examples can include:
- Business strategy review
- Capability map creation
- Input into the Business-aligned IT strategy
- IT budget input
- What activities are required to continuously improve the BRM role? This may consist of:
- Feedback discussions with business partners
- Roadshow with colleagues to communicate and refine the practice
- Map these on your annual calendar that can be shared with your colleagues.
| Capture in the BRM Workbook
Communicate using the Executive Buy-In and Communication Template |
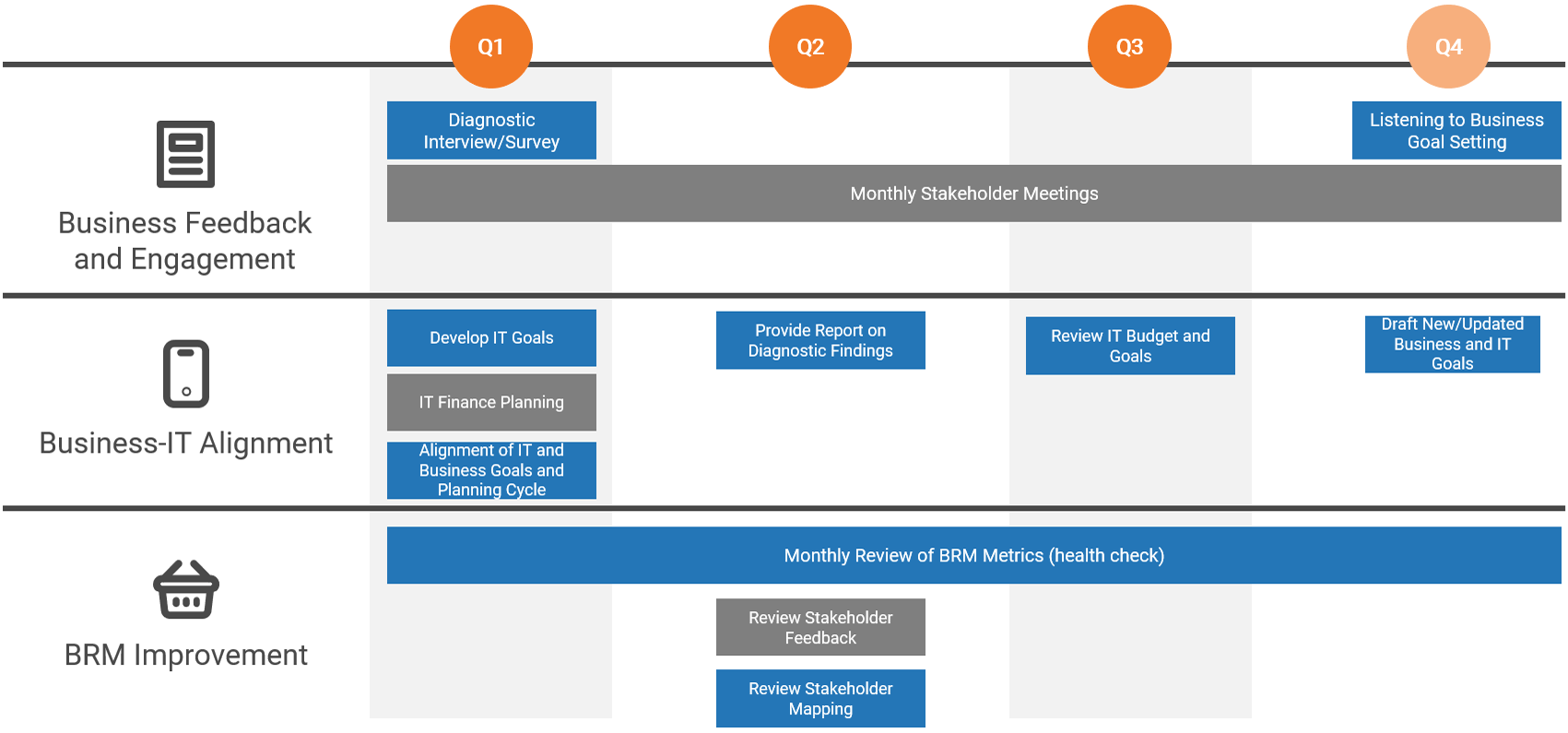
|
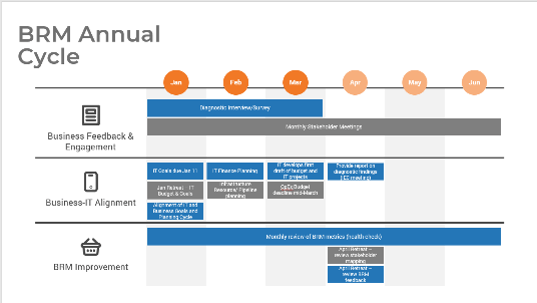
Sample BRM annual cycle
5.5 Build your transformation roadmap
Input: SWOT analysis
Output: Transformation roadmap
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- Brainstorm and discuss the key enablers that are needed to help promote and ease your BRM program.
- Brainstorm and discuss the key blockers (or risks) that may interrupt or derail your BRM program.
- Brainstorm mitigation activities for each blocker.
- Enablers and mitigation activities can be listed on your transformation roadmap.
Example:
Enablers
| Blockers
| Mitigation
|
Capture in the BRM Workbook
5.5 Build your transformation roadmap (cont’d)
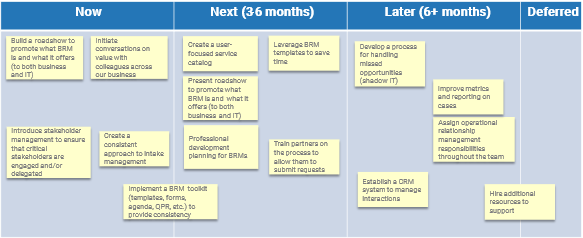
- Roadmap Elements:
- List the artifacts, changes, or actions needed to implement the new BRM program.
- For each item, identify how long it will take to implement or change by moving it into the appropriate swim lane. Use timing that makes sense for your organization: Quick Wins, Short Term, and Long Term; Now, Next, and Later; or Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4.
Communicate the BRM changes to set your practice up for success
| Leaders of successful change spend considerable time developing a powerful change message, i.e. a compelling narrative that articulates the desired end state, and that makes the change concrete and meaningful to staff.
The change message should:
|
Five elements of communicating change
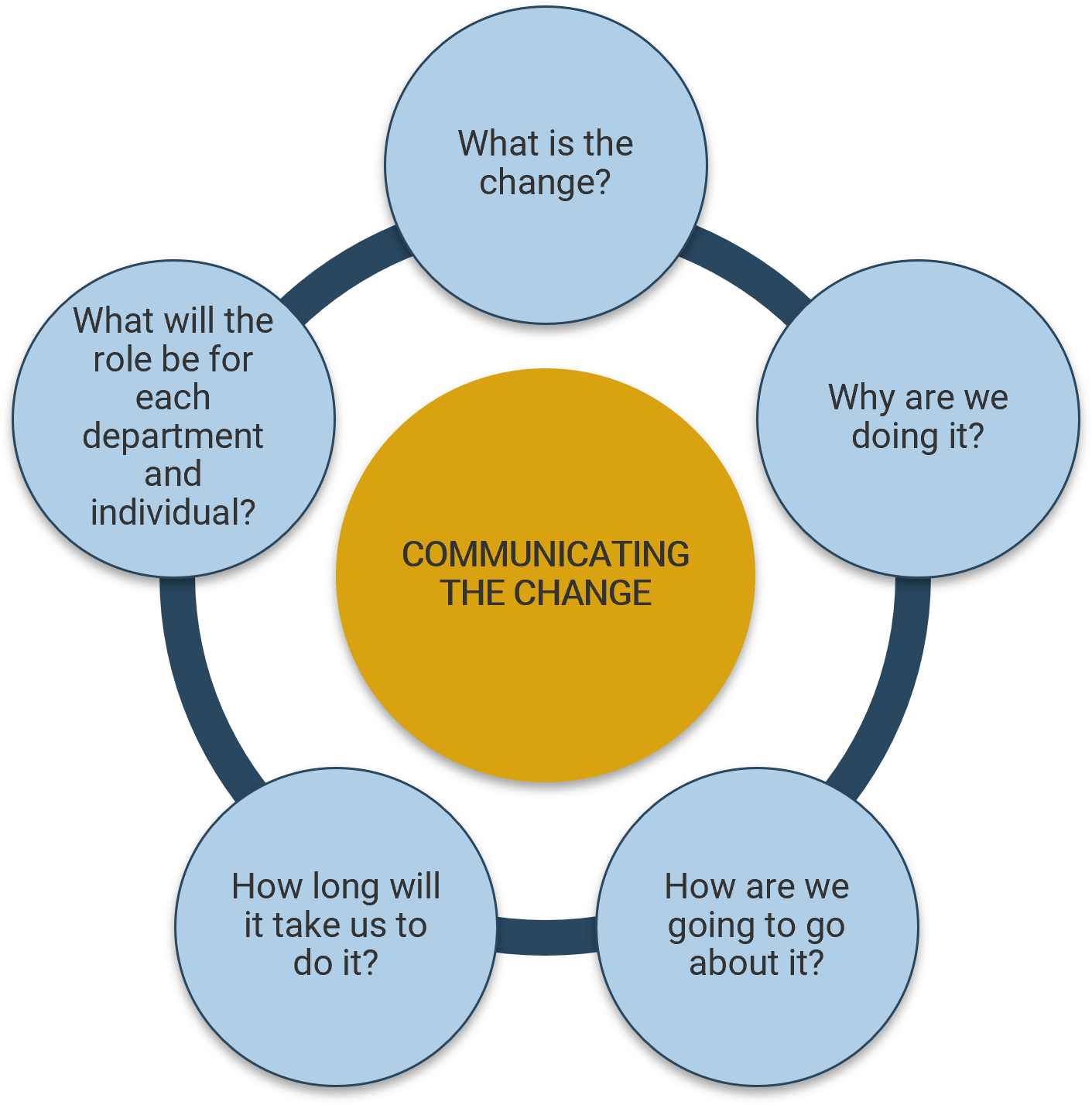
(Source: The Qualities of Leadership: Leading Change) |
Apply the following communication principles to make your BRM changes relevant to stakeholders
“We tend to use a lot of jargon in our discussions, and that is a sure fire way to turn people away. We realized the message wasn’t getting out because the audience wasn’t speaking the same language. You have to take it down to the next level and help them understand where the needs are.” (Jeremy Clement, Director of Finance, College of Charleston, Info-Tech Interview, 2018)
Be Relevant
|
Be Clear
|
Be Concise
|
Be Consistent
|
5.6 Create a communications plan tailored to each of your stakeholders
Input: Prioritized list of stakeholders
Output: Communication Plan
Materials: Whiteboard/flip charts (physical or electronic)
Participants: Team
- List stakeholders in order of importance in the first column.
- Identify the frequency with which you will communicate to each group.
- Determine the scope of the communication:
- What key information needs to be included in the message to ensure they are informed and on board?
- Which medium(s) will you use to communicate to that specific group?
- Develop a concrete timeline that will be followed to ensure that support is maintained from the key stakeholders.
AudienceAll BRM Staff |
Purpose
|
Communication Type
|
CommunicatorCIO |
Timing
|
Related Blueprints
Business Value
Service Catalog
Intake Management
|


|


|
Selected Bibliography
“Apple Mission and Vision Analysis.” Mission Statement Academy, 23 May 2019. Accessed 5 November 2020.
Barnes, Aaron. “Business Relationship Manager and Plan Build Run.” BRM Institute, 8 April 2014.
Barnes, Aaron. “Starting a BRM Team - Business Relationship Management Institute.” BRM Institute, 5 June 2013. Web.
BRM Institute. “Business Partner Maturity Model.” Member Templates and Examples, Online Campus, n.d. Accessed 3 December 2021.
BRM Institute. “BRM Assessment Templates and Examples.” Member Templates and Examples, Online Campus, n.d. Accessed 24 November 2021.
Brusnahan, Jim, et al. “A Perfect Union: BRM and Agile Development and Delivery.” BRM Institute, 8 December 2020. Web.
Business Relationship Management: The BRMP Guide to the BRM Body of Knowledge. Second printing ed., BRM Institute, 2014.
Chapman, Chuck. “Building a Culture of Trust - Remote Leadership Institute.” Remote Leadership Institute, 10 August 2021. Accessed 27 January 2022.
“Coca Cola Mission and Vision Analysis.” Mission Statement Academy, 4 August 2019. Accessed 5 November 2020.
Colville, Alan. “Shared Vision.” UX Magazine, 31 October 2011. Web.
Cooper, Robert, G. “Effective Gating: Make product innovation more productive by using gates with teeth.” Stage-Gate International and Product Development Institute, March/April 2009. Web.
Heller, Martha. “How CIOs Can Make Business Relationship Management (BRM) Work.” CIO, 1 November 2016. Accessed 27 January 2022.
“How Many Business Relationship Managers Should You Have.” BRM Institute, 20 March 2013. Web.
Hull, Patrick. “Answer 4 Questions to Get a Great Mission Statement.” Forbes, 10 January 2013. Web.
Kasperkevic, Jana. “Bill Gates: Good Feedback Is the Key to Improvement.” Inc.com, 17 May 2013. Web.
Merlyn, Vaughan. “Relationships That Matter to the BRM.” BRM Institute, 19 October 2016. Web.
“Modernizing IT’s Business Relationship Manager Role.” The Hackett Group, 22 November 2019. Web.
Monroe, Aaron. “BRMs in a SAFe World...That Is, a Scaled Agile Framework Model.” BRM Institute, 5 January 2021. Web.
Selected Bibliography
“Operational, adj." OED Online, Oxford University Press, December 2021. Accessed 29 January 2022.
Sinek, Simon. “Transcript of ‘How Great Leaders Inspire Action.’” TEDxPuget Sound, September 2009. Accessed 7 November 2020.
“Strategic, Adj. and n.” OED Online, Oxford University Press, December 2016. Accessed 27 January 2022.
“Tactical, Adj.” OED Online, Oxford University Press, September 2018. Accessed 27 January 2022.
“The Qualities of Leadership: Leading Change.” Cornelius & Associates, 23 September 2013. Web.
“Twice the Business Value in Half the Time: When Agile Methods Meet the Business Relationship Management Role.” BRM Institute, 10 April 2015. Web.
“Value Streams.” Scaled Agile Framework, 30 June 2020. Web.
Ward, John. “Delivering Value from Information Systems and Technology Investments: Learning from Success.” Information Systems Research Centre, August 2006. Web.
Appendix
- Business Value Drivers
- Service Blueprint
- Stakeholder Communications
- Job Descriptions
Understand business value drivers for ROI and cost
Make MoneyThis value driver is specifically related to the impact a product or service has on your organization’s ability to show value for the investments. This is usually linked to the value for money for an organization. Return on Investment can be derived from:
Be aware of the difference among your products and services that enable a revenue source and those which facilitate the flow of funding. |
Save MoneyThis value driver relates to the impact of a product or service on cost and budgetary constraints. Reduce costs value can be derived from:
Budgetary pressures tied to critical strategic priorities may defer or delay implementation of initiatives and revision of existing products and services. |
Understand Business Value Drivers that Enhance Your Services
OperationsSome products and services are in place to facilitate and support the structure of the organization. These vary depending on what is important to your organization, but should be assessed in relation to the organizational culture and structure you have identified.
|
Risk and ComplianceA product or service may be required in order to meet a regulatory requirement. In these cases, you need to be aware of the organizational risk of NOT implementing or maintaining a service in relation to those risks. In this case, the product or service is required in order to:
|
Internal InformationUnderstanding internal operations is also critical for many organizations. Data captured through your operations provides critical insights that support efficiency, productivity, and many other strategic goals. Internal information value can be derived by:
|
Collaboration and Knowledge TransferCommunication is integral and products and services can be the link that ties your organization together. In this case, the value generated from products and services can be to:
|
Understand Business Value Drivers that Connect the Business to Your Customers
PolicyProducts and services can also be assessed in relation to whether they enable and support the required policies of the organization. Policies identify and reinforce required processes, organizational culture, and core values. Policy value can be derived from:
|
Customer RelationsProducts and services are often designed to facilitate goals of customer relations; specifically, improve satisfaction, retention, loyalty, etc. This value type is most closely linked to brand management and how a product or service can help execute brand strategy. Customers, in this sense, can also include any stakeholders who consume core offerings. Customer satisfaction value can be derived from:
|
Market InformationUnderstanding demand and market trends is a core driver for all organizations. Data provided through understanding the ways, times, and reasons that consumers use your services is a key driver for growth and stability. Market information value can be achieved when an app:
|
Market ShareMarket share represents the percentage of a market or market segment that your business controls. In essence, market share can be viewed as the potential for more or new revenue sources. Assess the impact on market share. Does the product or service:
|
Service Blueprint
Service design involves an examination of the people, process and technology involved in delivering a service to your customers.
Service blueprinting provides a visual of how these are connected together. It enables you to identify and collaborate on improvements to an existing service.
The main components of a service blueprint are:
Customer actions – this anchors the service in the experiences of the customer
Front-stage – this shows the parts of the service that are visible to the customer
Back-stage – this is the behind-the-scenes actions necessary to deliver the experience to the customer
Support processes – this is what’s necessary to deliver the back-stage (and front-stage/customer experience), but is not aligned from a timing perspective (e.g. it doesn’t matter if the fridge is stocked when the order is put in, as long as the supplies are available for the chef to use)
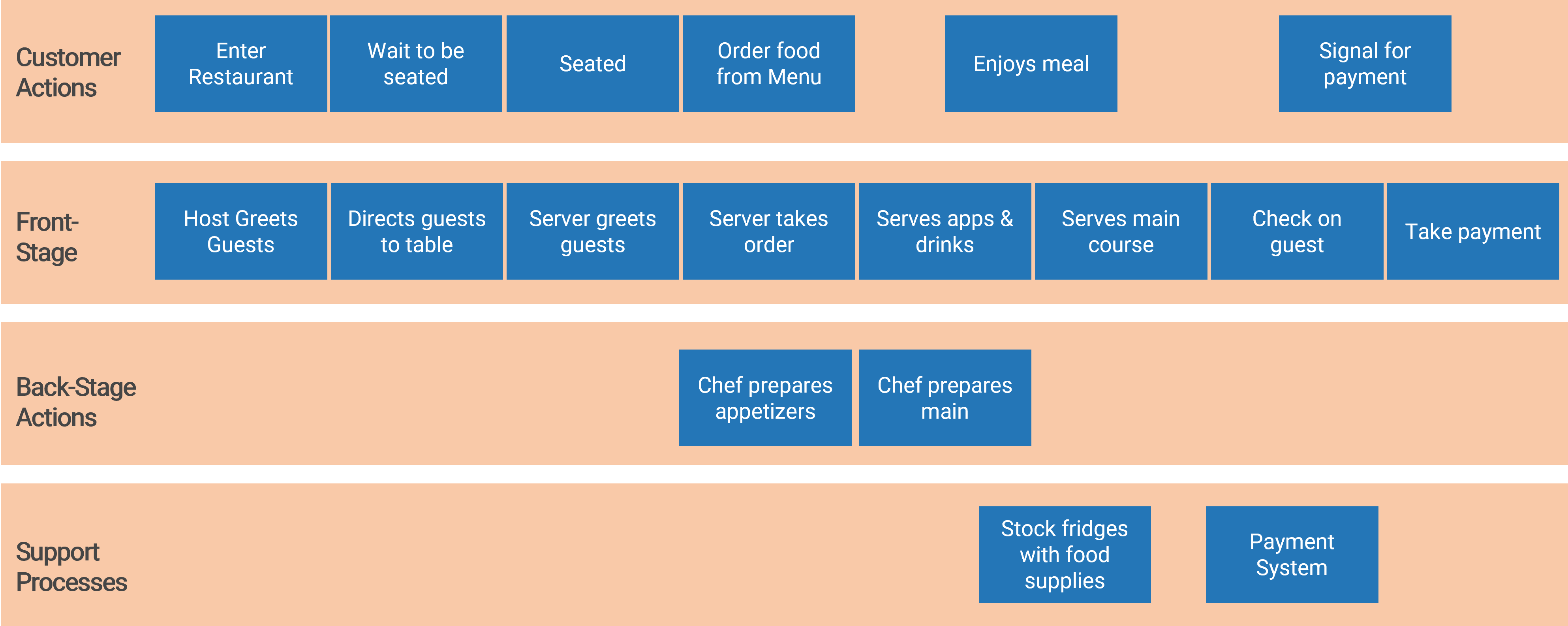
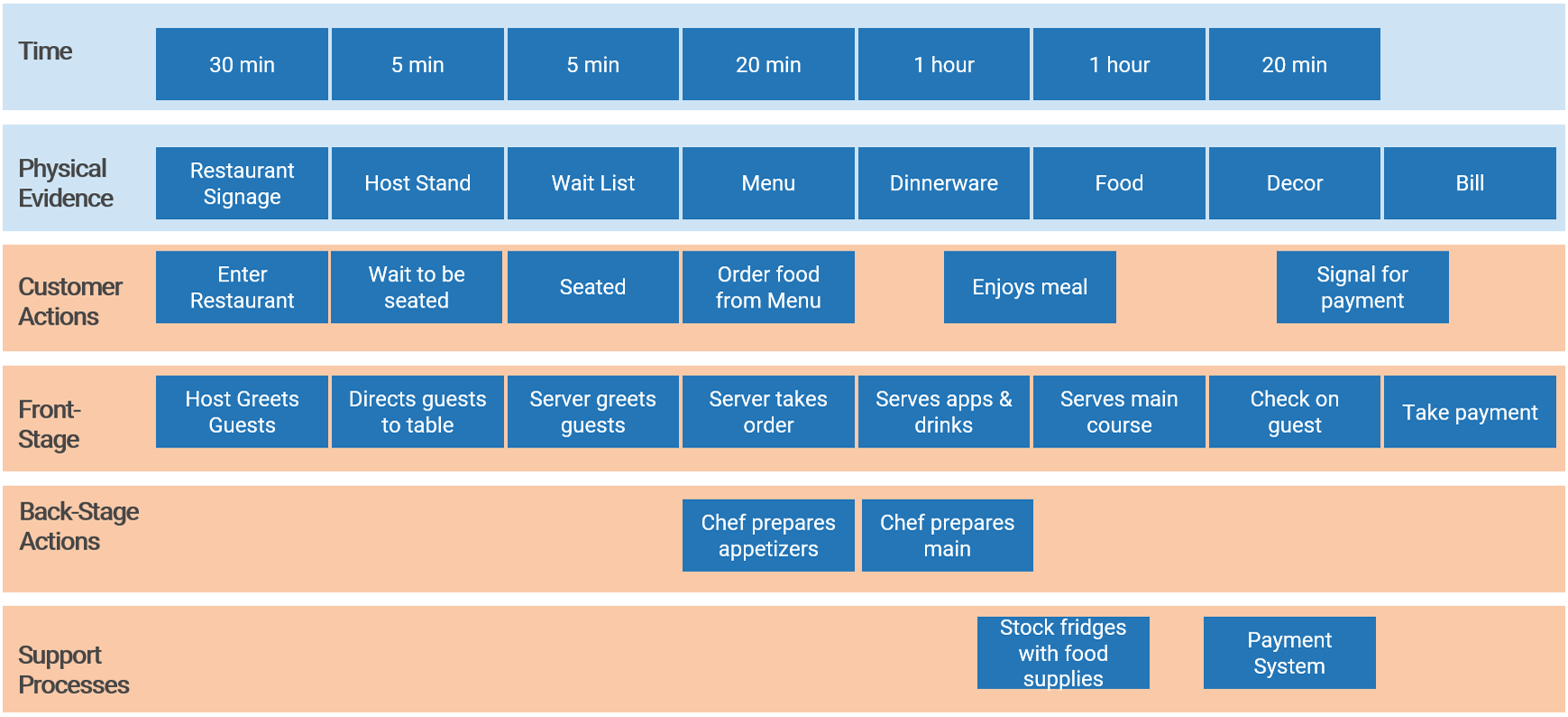
Physical Evidence and Time are blueprint components can be added in to provide additional context & support
Stakeholder Communications
Personalize
|
Show Proof
|
Reference
|
Test & Learn
|
BRM Job Descriptions
Download the Job Descriptions:
Buying Options
Embed Business Relationship Management in IT
Client rating
Cost Savings
Days Saved
IT Risk Management · IT Leadership & Strategy implementation · Operational Management · Service Delivery · Organizational Management · Process Improvements · ITIL, CORM, Agile · Cost Control · Business Process Analysis · Technology Development · Project Implementation · International Coordination · In & Outsourcing · Customer Care · Multilingual: Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese · Entrepreneur
Tymans Group is a brand by Gert Taeymans BV
Gert Taeymans bv
Europe: Koning Albertstraat 136, 2070 Burcht, Belgium — VAT No: BE0685.974.694 — phone: +32 (0) 468.142.754
USA: 4023 KENNETT PIKE, SUITE 751, GREENVILLE, DE 19807 — Phone: 1-917-473-8669
Copyright 2017-2022 Gert Taeymans BV