The Small Enterprise Guide to People and Resource Management

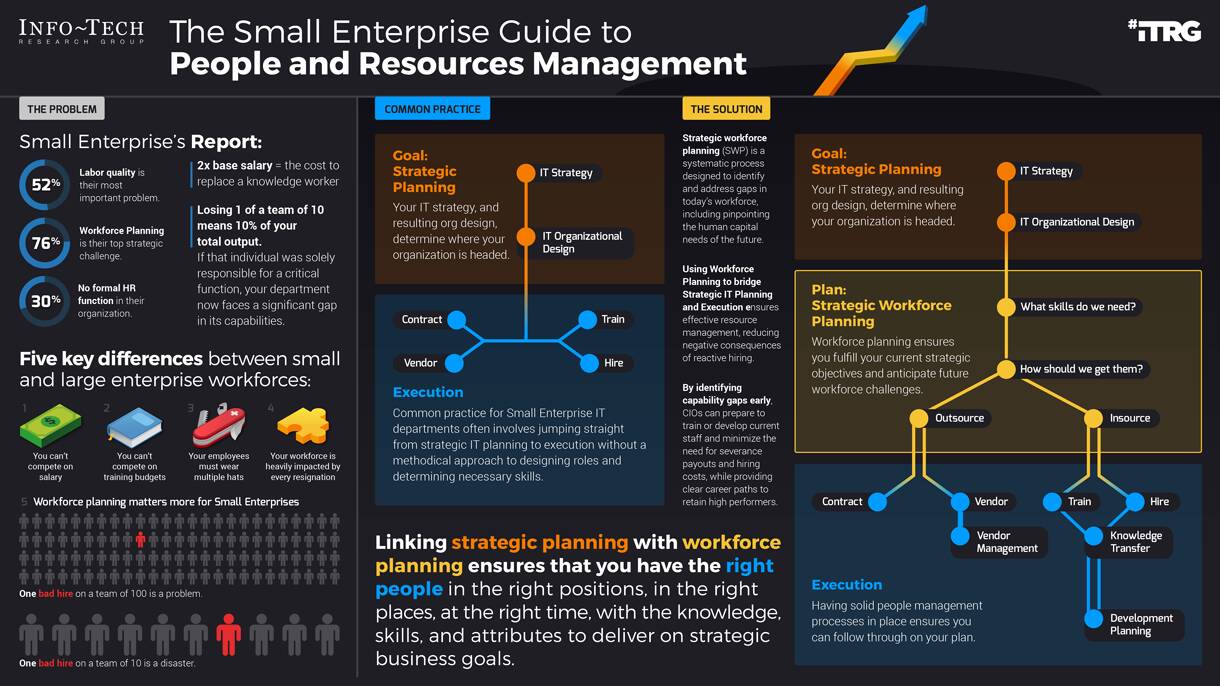
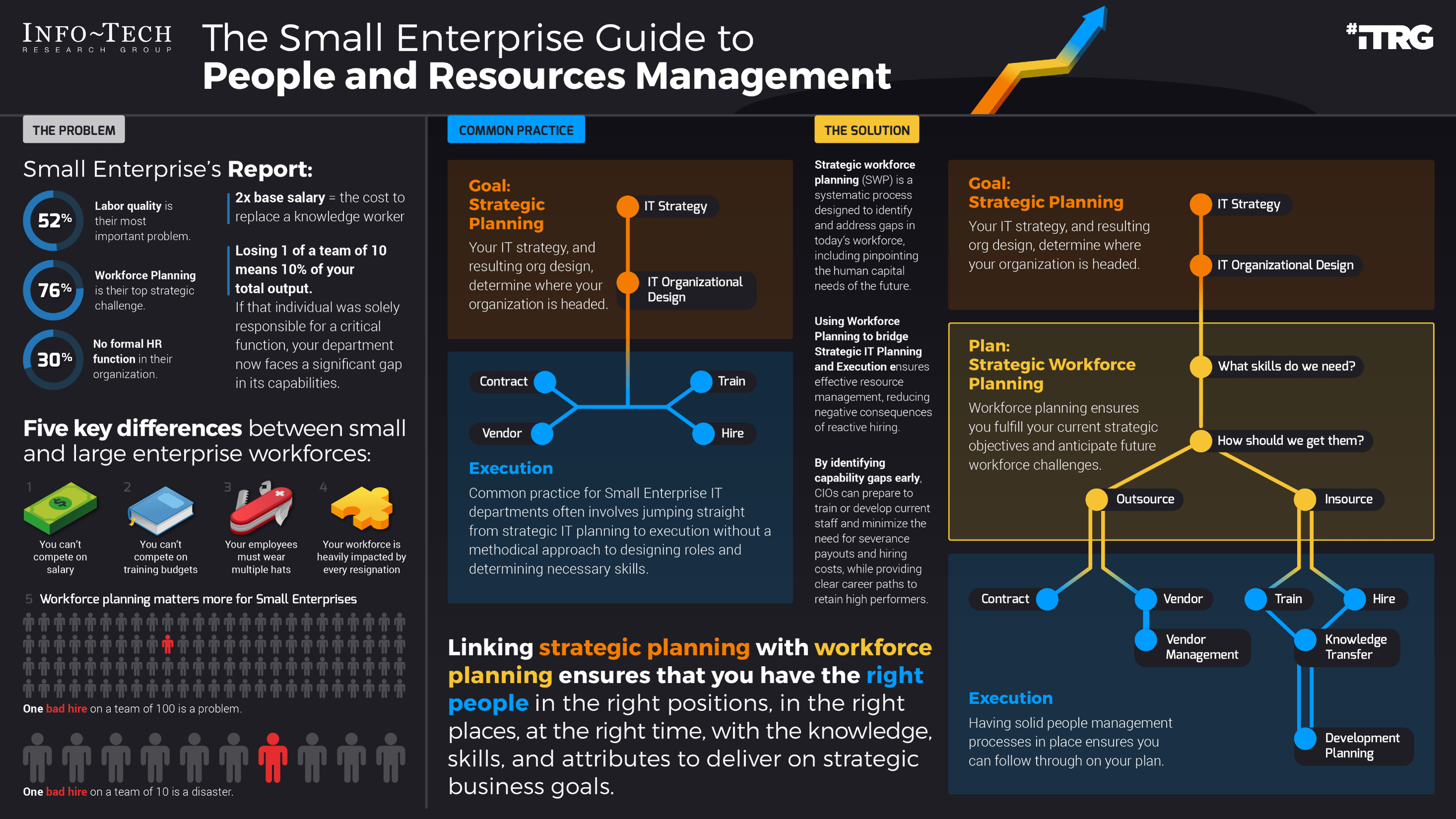
- 52% of small business owners agree that labor quality is their most important problem, and 76% of executives expect the talent market to get even more challenging.
- The problem? You can't compete on salary, training budgets are slim, you need people skilled in all areas, and even one resignation represents a large part of your workforce.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- The usual, reactive approach to workforce management is risky:
- Optimizing tactics helps you hire faster, train more, and negotiate better contracts.
- But fulfilling needs as they arise costs more, has greater risk of failure, and leaves you unprepared for future needs.
- In a small enterprise where every resource counts, in which one hire represents 10% of your workforce, it is essential to get it right.
Impact and Result
- Workforce planning helps you anticipate future needs.
- More lead time means better decisions at lower cost.
- Small Enterprises benefit most, since every resource counts.
The Small Enterprise Guide to People and Resource Management Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. The Small Enterprise Guide to People and Resource Management Deck – Find out why workforce planning is critical for small enterprises.
Use this storyboard to lay the foundation of people and resources management practices in your small enterprise IT department.
- The Small Enterprise Guide to People and Resource Management – Phases 1-3
2. Workforce Planning Workbook – Use the tool to successfully complete all of the activities required to define and estimate your workforce needs for the future.
Use these concise exercises to analyze your department’s talent current and future needs and create a skill sourcing strategy to fill the gaps.
- Workforce Planning Workbook for Small Enterprises
3. Knowledge Transfer Tools – Use these templates to identify knowledge to be transferred.
Work through an activity to discover key knowledge held by an employee and create a plan to transfer that knowledge to a successor.
- IT Knowledge Identification Interview Guide Template
- IT Knowledge Transfer Plan Template
4. Development Planning Tools – Use these tools to determine priority development competencies.
Assess employees’ development needs and draft a development plan that fits with key organizational priorities.
- IT Competency Library
- Leadership Competencies Workbook
- IT Employee Career Development Workbook
- Individual Competency Development Plan
- Learning Methods Catalog for IT Employees
Infographic
Workshop: The Small Enterprise Guide to People and Resource Management
Workshops offer an easy way to accelerate your project. If you are unable to do the project yourself, and a Guided Implementation isn't enough, we offer low-cost delivery of our project workshops. We take you through every phase of your project and ensure that you have a roadmap in place to complete your project successfully.
1 Lay Your Foundations
The Purpose
Set project direction and analyze workforce needs.
Key Benefits Achieved
Planful needs analysis ensures future workforce supports organizational goals.
Activities
1.1 Set workforce planning goals and success metrics.
1.2 Identify key roles and competency gaps.
1.3 Conduct a risk analysis to identify future needs.
1.4 Determine readiness of internal successors.
Outputs
Work with the leadership team to:
Extract key business priorities.
Set your goals.
Assess workforce needs.
2 Create Your Workforce Plan
The Purpose
Conduct a skill sourcing analysis, and determine competencies to develop internally.
Key Benefits Achieved
A careful analysis ensures skills are being sourced in the most efficient way, and internal development is highly aligned with organizational objectives.
Activities
2.1 Determine your skill sourcing route.
2.2 Determine priority competencies for development.
Outputs
Create a workforce plan.
2.Determine guidelines for employee development.
3 Plan Knowledge Transfer
The Purpose
Discover knowledge to be transferred, and build a transfer plan.
Key Benefits Achieved
Ensure key knowledge is not lost in the event of a departure.
Activities
3.1 Discover knowledge to be transferred.
3.2 Identify the optimal knowledge transfer methods.
3.3 Create a knowledge transfer plan.
Outputs
Discover tacit and explicit knowledge.
Create a knowledge transfer roadmap.
4 Plan Employee Development
The Purpose
Create a development plan for all staff.
Key Benefits Achieved
A well-structured development plan helps engage and retain employees while driving organizational objectives.
Activities
4.1 Identify target competencies & draft development goals
4.2 Select development activities and schedule check-ins.
4.3 Build manager coaching skills.
Outputs
Assess employees.
Prioritize development objectives.
Plan development activities.
Build management skills.
Further reading
The Small Enterprise Guide to People and Resource Management
Quickly start getting the right people, with the right skills, at the right time
Is this research right for you?
Research Navigation
Managing the people in your department is essential, whether you have three employees or 300. Depending on your available time, resources, and current workforce management maturity, you may choose to focus on the overall essentials, or dive deep into particular areas of talent management. Use the questions below to help guide you to the right Info-Tech resources that best align with your current needs.
| Question | If you answered "no" | If you answered "yes" |
|---|---|---|
|
Does your IT department have fewer than 15 employees, and is your organization's revenue less than $25 million (USD)? |
Review Info-Tech's archive of research for mid-sized and large enterprise clients. |
Follow the guidance in this blueprint. |
|
Does your organization require a more rigorous and customizable approach to workforce management? |
Follow the guidance in this blueprint. |
Review Info-Tech's archive of research for mid-sized and large enterprise clients. |
Analyst Perspective
Workforce planning is even more important for small enterprises than large organizations.
It can be tempting to think of workforce planning as a bureaucratic exercise reserved for the largest and most formal of organizations. But workforce planning is never more important than in small enterprises, where every individual accounts for a significant portion of your overall productivity.
Without workforce planning, organizations find themselves in reactive mode, hiring new staff as the need arises. They often pay a premium for having to fill a position quickly or suffer productivity losses when a critical role goes unexpectedly vacant.
A workforce plan helps you anticipate these challenges, come up with solutions to mitigate them, and allocate resources for the most impact, which means a greater return on your workforce investment in the long run.
This blueprint will help you accomplish this quickly and efficiently. It will also provide you with the essential development and knowledge transfer tools to put your plan into action.

Jane Kouptsova
Senior Research Analyst, CIO Advisory
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
52% of small business owners agree that labor quality is their most important problem.1
Almost half of all small businesses face difficulty due to staff turnover.
76% of executives expect the talent market to get even more challenging.2
Common Obstacles
76% of executives expect workforce planning to become a top strategic priority for their organization.2
But…
30% of small businesses do not have a formal HR function.3
Small business leaders are often left at a disadvantage for hiring and retaining the best talent, and they face even more difficulty due to a lack of support from HR.
Small enterprises must solve the strategic workforce planning problem, but they cannot invest the same time or resources that large enterprises have at their disposal.
Info-Tech's Approach
A modular, lightweight approach to workforce planning and talent management, tailored to small enterprises
Clear activities that guide your team to decisive action
Founded on your IT strategy, ensuring you have not just good people, but the right people
Concise yet comprehensive, covering the entire workforce lifecycle from competency planning to development to succession planning and reskilling
Info-Tech Insight
Every resource counts. When one hire represents 10% of your workforce, it is essential to get it right.
1CNBC & SurveyMonkey. 2ADP. 3Clutch.
Labor quality is small enterprise's biggest challenge
The key to solving it is strategic workforce planning
Strategic workforce planning (SWP) is a systematic process designed to identify and address gaps in today's workforce, including pinpointing the human capital needs of the future.
Linking workforce planning with strategic planning ensures that you have the right people in the right positions, in the right places, at the right time, with the knowledge, skills, and attributes to deliver on strategic business goals.
SWP helps you understand the makeup of your current workforce and how well prepared it is or isn't (as the case may be) to meet future IT requirements. By identifying capability gaps early, CIOs can prepare to train or develop current staff and minimize the need for severance payouts and hiring costs, while providing clear career paths to retain high performers.
|
52% |
of small business owners agree that labor quality is their most important problem.1 |
|---|---|
|
30% |
30% of small businesses have no formal HR function.2 |
|
76% |
of senior leaders expect workforce planning to become the top strategic challenge for their organization.3 |
1CNBC & SurveyMonkey. 2Clutch. 3ADP.
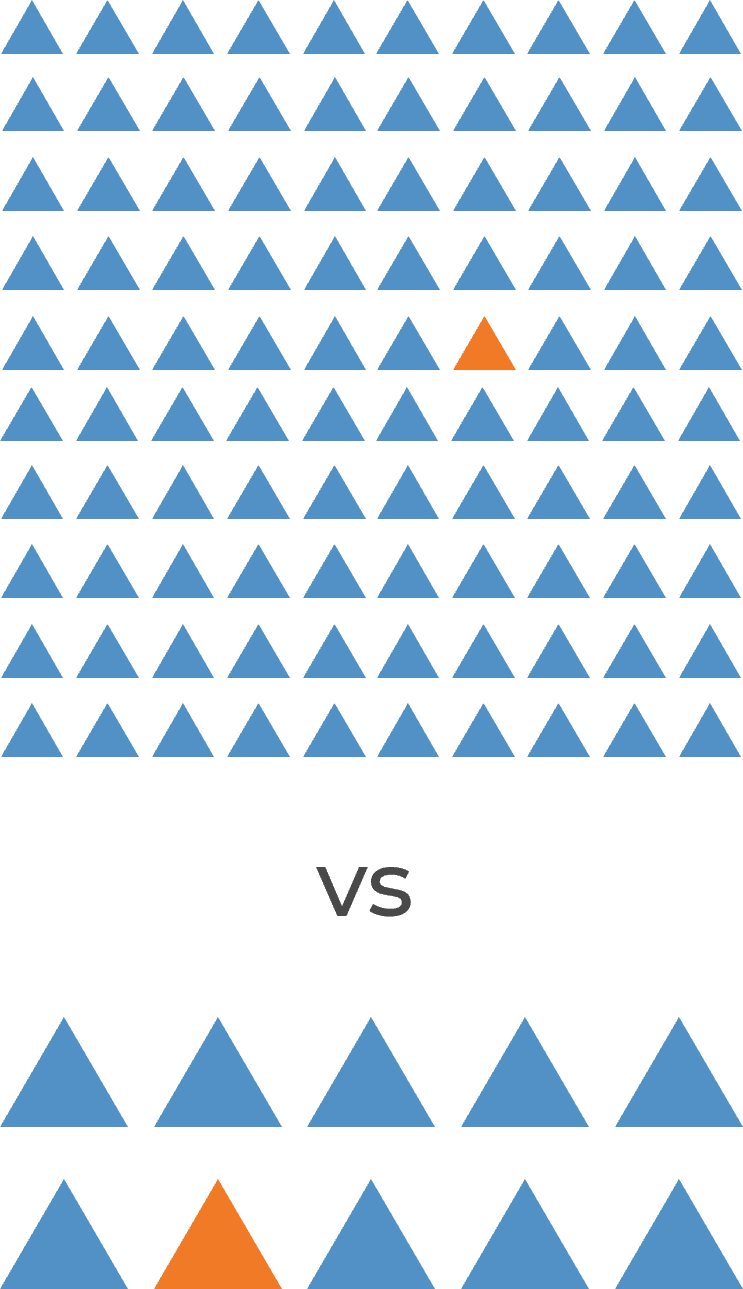
Workforce planning matters more for small enterprises
You know that staffing mistakes can cost your department dearly. But did you know the costs are greater for small enterprises?
The price of losing an individual goes beyond the cost of hiring a replacement, which can range from 0.5 to 2 times that employee's salary (Gallup, 2019). Additional costs include loss of productivity, business knowledge, and team morale.
This is a major challenge for large organizations, but the threat is even greater for small enterprises, where a single individual accounts for a large proportion of IT's productivity. Losing one of a team of 10 means 10% of your total output. If that individual was solely responsible for a critical function, your department now faces a significant gap in its capabilities. And the effect on morale is much greater when everyone is on the same close-knit team.
And the threat continues when the staffing error causes you not to lose a valuable employee, but to hire the wrong one instead. When a single individual makes up a large percentage of your workforce, as happens on small teams, the effects of talent management errors are magnified.
Info-Tech Insight
One bad hire on a team of 100 is a problem. One bad hire on a team of 10 is a disaster.
Blueprint pre-step: Determine your starting point
People and Resource management is essential for any organization. But depending on your needs, you may want to start at different stages of the process. Use this slide as a quick reference for how the activities in this blueprint fit together, how they relate to other workforce management resources, and the best starting point for you.
Your IT strategy is an essential input to your workforce plan. It defines your destination, while your workforce is the vessel that carries you there. Ensure you have at least an informal strategy for your department before making major workforce changes, or review Info-Tech's guidance on IT strategy.
This blueprint covers the parts of workforce management that occur to some extent in every organization:
- Workforce planning
- Knowledge transfer
- Development planning
You may additionally want to seek guidance on contract and vendor management, if you outsource some part of your workload outside your core IT staff.
Track metrics
Consider these example metrics for tracking people and resource management success
| Project Outcome | Metric | Baseline | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reduced training costs | Average cost of training (including facilitation, materials, facilities, equipment, etc.) per IT employee | ||
| Reduced number of overtime hours worked | Average hours billed at overtime rate per IT employee | ||
| Reduced length of hiring period | Average number of days between job ad posting and new hire start date | ||
| Reduced number of project cancellations due to lack of capacity | Total of number of projects cancelled per year | ||
| Increased number of projects completed per year (project throughput) | Total number of project completions per year | ||
| Greater net recruitment rate | Number of new recruits/Number of terminations and departures | ||
| Reduced turnover and replacement costs | Total costs associated with replacing an employee, including position coverage cost, training costs, and productivity loss | ||
| Reduced voluntary turnover rate | Number of voluntary departures/Total number of employees | ||
| Reduced productivity loss following a departure or termination | Team or role performance metrics (varies by role) vs. one year ago |
Info-Tech offers various levels of support to best suit your needs
DIY Toolkit
“Our team has already made this critical project a priority, and we have the time and capability, but some guidance along the way would be helpful.”
Guided Implementation
“Our team knows that we need to fix a process, but we need assistance to determine where to focus. Some check-ins along the way would help keep us on track.”
Workshop
“We need to hit the ground running and get this project kicked off immediately. Our team has the ability to take this over once we get a framework and strategy in place.”
Consulting
“Our team does not have the time or the knowledge to take this project on. We need assistance through the entirety of this project.”
Diagnostics and consistent frameworks used throughout all four options
Guided Implementation
What does a typical GI on this topic look like?
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Call #1: Scope requirements, objectives, and your specific challenges. |
Call #2: Assess current workforce needs. |
Call #4: Determine skill sourcing route. |
Call #6: Identify knowledge to be transferred. |
Call #8: Draft development goals and select activities. |
|
Call #3: Explore internal successor readiness. |
Call #5:Set priority development competencies. |
Call #7: Create a knowledge transfer plan. |
Call #9: Build managers' coaching & feedback skills. |
|
A Guided Implementation (GI) is a series of calls with an Info-Tech analyst to help implement our best practices in your organization.
A typical GI is between 4 to 6 calls over the course of 3 to 4 months.
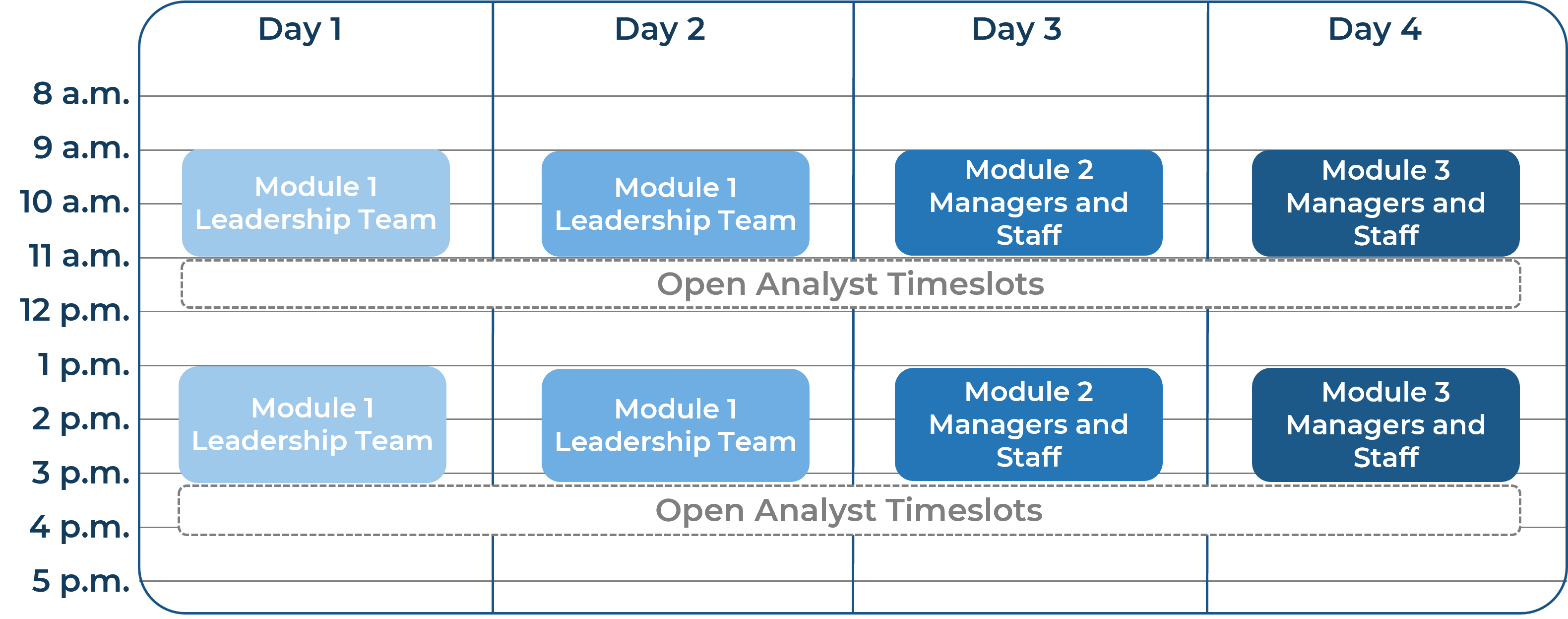
Workshop Overview
Contact your account representative for more information.
workshops@infotech.com 1-888-670-8889
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 |
Day 4 |
Day 5 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.Lay Your Foundations | 2. Create Your Workforce Plan | 3. Plan Knowledge Transfer | 3. Plan Employee Development | Next Steps and Wrap-Up (offsite) | |
| Activities |
1.1 Set workforce planning goals and success metrics 1.2 Identify key roles and competency gaps 1.3 Conduct a risk analysis to identify future needs 1.4 Determine readiness of internal successors |
1.5 Determine your skill sourcing route 1.6 Determine priority competencies for development |
3.1 Discover knowledge to be transferred 3.2 Identify the optimal knowledge transfer methods 3.3 Create a knowledge transfer plan |
4.1 Identify target competencies & draft development goals 4.2 Select development activities and schedule check-ins 4.3 Build manager coaching skills |
|
|
Outcomes |
Work with the leadership team to:
|
Work with the leadership team to:
|
Work with staff and managers to:
|
Work with staff and managers to:
|
Info-Tech analysts complete:
|
Workshop Overview
Contact your account representative for more information.
workshops@infotech.com 1-888-670-8889
Each onsite day is structured with group working sessions from 9-11 a.m. and 1:30-3:30 p.m. and includes Open Analyst Timeslots, where our facilitators are available to expand on scheduled activities, capture and compile workshop results, or review additional components from our comprehensive approach.
Phase 1
Workforce Planning
|
Workforce Planning |
Knowledge Transfer |
Development Planning |
|---|---|---|
|
Identify needs, goals, metrics, and skill gaps. Select a skill sourcing strategy. |
Discover critical knowledge. Select knowledge transfer methods. |
Identify priority competencies. Assess employees. Draft development goals. Provide coaching & feedback. |
The Small Enterprise Guide to People and Resource Management
Phase Participants
- Leadership team
- Managers
- Human resource partner (if applicable)
Additional Resources
Phase pre-step: Gather resources and participants
- Ensure you have an up-to-date IT strategy. If you don't have a formal strategy in place, ensure you are aware of the main organizational objectives for the next 3-5 years. Connect with executive stakeholders if necessary to confirm this information.
If you are not sure of the organizational direction for this time frame, we recommend you consult Info-Tech's material on IT strategy first, to ensure your workforce plan is fully positioned to deliver value to the organization. - Consult with your IT team and gather any documentation pertaining to current roles and skills. Examples include an org chart, job descriptions, a list of current tasks performed/required, a list of company competencies, and a list of outsourced projects.
- Gather the right participants. Most of the decisions in this section will be made by senior leadership, but you will also need input from front-line managers. Ensure they are available on an as-needed basis. If your organization has an HR partner, it can also be helpful to involve them in your workforce planning process.
Formal workforce planning benefits even small teams
Strategic workforce planning (SWP) is a systematic process designed to identify and address gaps in your workforce today and plan for the human capital needs of the future.
Your workforce plan is an extension of your IT strategy, ensuring that you have the right people in the right positions, in the right places, at the right time, with the knowledge, skills, and attributes to deliver on strategic business goals.
SWP helps you understand the makeup of your current workforce and how well prepared it is or isn't (as the case may be) to meet future IT requirements. By identifying capability gaps early, CIOs can prepare to train or develop current staff and minimize the need for severance payouts and hiring costs, while providing clear career paths to retain high performers.
The smaller the business, the more impact each individual's performance has on the overall success of the organization. When a given role is occupied by a single individual, the organization's performance in that function is determined wholly by one employee. Creating a workforce plan for a small team may seem excessive, but it ensures your organization is not unexpectedly hit with a critical competency gap.
Right-size your workforce planning process to the size of your enterprise
Small organizations are 2.2 times more likely to have effective workforce planning processes.1 Be mindful of the opportunities and risks for organizations of your size as you execute the project. How you build your workforce plan will not change drastically based on the size of your organization; however, the scope of your initiative, the size of your team, and the tactics you employ may vary.
|
Small Organization |
Medium Organization |
Large Organization |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Project Opportunities |
|
|
|
|
Project Risks |
|
|
|
1 McLean & Company Trends Report 2014
1.1 Set project outcomes and success metrics
1-3 hours
- As a group, brainstorm key pain points that the IT department experiences due to the lack of a workforce plan. Ask them to consider turnover, retention, training, and talent acquisition.
- Discuss any key themes that arise and brainstorm your desired project outcomes. Keep a record of these for future reference and to aid in stakeholder communication.
- Break into smaller groups (or if too small, continue as a single group):
- For each desired outcome, consider what metrics you could use to track progress. Keep your initial list of pain points in mind as you brainstorm metrics.
- Write each of the metric suggestions on a whiteboard and agree to track 3-5 metrics. Set targets for each metric. Consider the effort required to obtain and track the metric, as well as its reliability.
- Assign one individual for tracking the selected metrics. Following the meeting, that individual will be responsible for identifying the baseline and targets, and reporting on metrics progress.
|
Input |
Output |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Materials |
Participants |
|
|
1.2 Identify key roles and competency gaps
1-3 hours
- As a group, identify all strategic, core, and supporting roles by reviewing the organizational chart:
- Strategic: What are the roles that must be filled by top performers and cannot be left vacant in order to meet strategic objectives?
- Core: What roles are important to drive operational excellence?
- Supporting: What roles are required for day-to-day work, but are low risk if the role is vacant for a period of time?
- Working individually or in small groups, have managers for each identified role define the level of competence required for the job. Consider factors such as:
- The difficulty or criticality of the tasks being performed
- The impact on job outcomes
- The impact on the performance of other employees
- The consequence of errors if the competency is not present
- How frequently the competency is used on the job
- Whether the competency is required when the job starts or can be learned or acquired on the job within the first six months
- Continue working individually and rate the level of proficiency of the current incumbent.
- As a group, review the assessment and make any adjustments.
Record this information in the Workforce Planning Workbook for Small Enterprises.
Download the Workforce Planning Workbook for Small Enterprises
1.2 Identify key roles and competency gaps
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
|
|
| Materials | Participants |
|
|
Conduct a risk-of-departure analysis
A risk-of-departure analysis helps you plan for future talent needs by identifying which employees are most likely to leave the organization (or their current role).
A risk analysis takes into account two factors: an employee's risk for departure and the impact of departure:
Employees are high risk for departure if they:
- Have specialized or in-demand skills (tenured employees are more likely to have this than recent hires)
- Are nearing retirement
- Have expressed career aspirations that extend outside your organization
- Have hit a career development ceiling at your organization
- Are disengaged
- Are actively job searching
- Are facing performance issues or dismissal OR promotion into a new role
Employees are low risk for departure if they:
- Are a new hire or new to their role
- Are highly engaged
- Have high potential
- Are 5-10 years out from retirement
If you are not sure where an employee stands with respect to leaving the organization, consider having a development conversation with them. In the meantime, consider them at medium risk for departure.
To estimate the impact of departure, consider:
- The effect of losing the employee in the near- and medium-term, including:
- Impact on the organization, department, unit/team and projects
- The cost (in time, resources, and productivity loss) to replace the individual
- The readiness of internal successors for the role
1.3 Conduct a risk analysis to identify future needs
1-3 hours
Preparation: Your estimation of whether key employees are at risk of leaving the organization will depend on what you know of them objectively (skills, age), as well as what you learn from development conversations. Ensure you collect all relevant information prior to conducting this activity. You may need to speak with employees' direct managers beforehand or include them in the discussion.
- As a group, list all your current employees, and using the previous slide for guidance, rank them on two parameters: risk of departure and impact of departure, on a scale of low to high. Record your conclusions in a chart like the one on the right. (For a more in-depth risk assessment, use the "Risk Assessment Results" tab of the Key Roles Succession Planning Tool.)
- Employees that fall in the "Mitigate" quadrant represent key at-risk roles with at least moderate risk and moderate impact. These are your succession planning priorities. Add these roles to your list of key roles and competency gaps, and include them in your workforce planning analysis.
- Employees that fall in the "Manage" quadrants represent secondary priorities, which should be looked at if there is capacity after considering the "Mitigate" roles.
Record this information in the Workforce Planning Workbook for Small Enterprises.
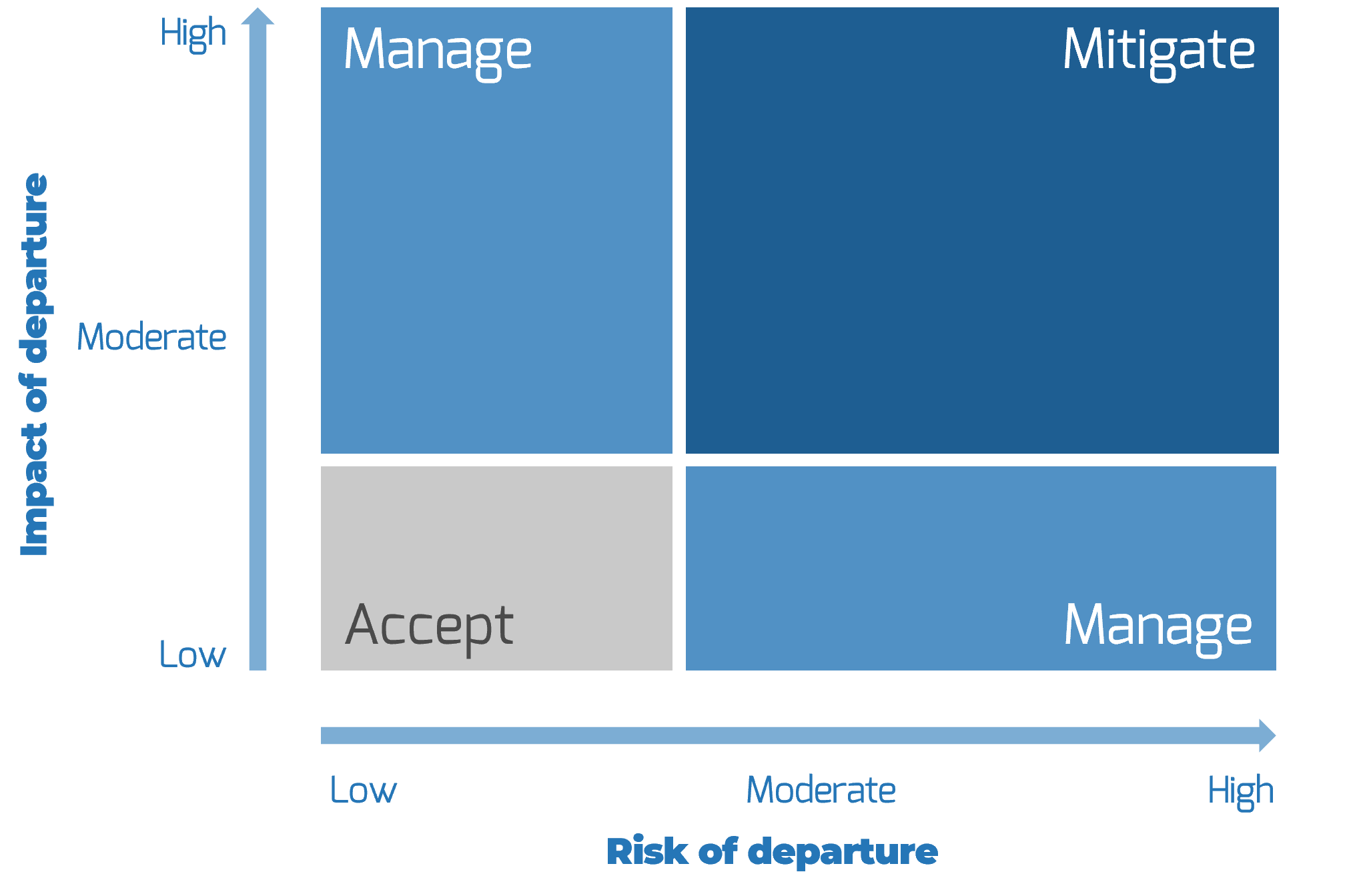
Info-Tech Insight
Don't be afraid to rank most or all your staff as "high impact of departure." In a small enterprise, every player counts, and you must plan accordingly.
1.3 Conduct a risk analysis to identify future needs
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
|
|
| Materials | Participants |
|
|
Determine your skill sourcing route
The characteristics of need steer hiring managers to a preferred choice, while the marketplace analysis will tell you the feasibility of each option.
|
Sourcing Options |
Preferred Options |
Final Choice |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|

|

|
|
| State of the Marketplace |
State of the Marketplace |
|||
|
Urgency: How soon do we need this skill? What is the required time-to-value? Criticality: How critical, i.e. core to business goals, are the services or systems that this skill will support? Novelty: Is this skill brand new to our workforce? Availability: How often, and at what hours, will the skill be needed? Durability: For how long will this skill be needed? Just once, or indefinitely for regular operations? |
Scarcity: How popular or desirable is this skill? Do we have a large enough talent pool to draw from? What competition are we facing for top talent? Cost: How much will it cost to hire vs. contract vs. outsource vs. train this skill? Preparedness: Do we have internal resources available to cultivate this skill in house? |
1.4 Determine your skill sourcing route
1-3 hours
- Identify the preferred sourcing method as a group, starting with the most critical or urgent skill need on your list. Use the characteristics of need to guide your discussion. If more than one option seems adequate, carry several over to the next step.
- Consider the marketplace factors applicable to the skill in question and use these to narrow down to one final sourcing decision.
- If it is not clear whether a suitable internal candidate is available or ready, refer to the next activity for a readiness assessment.
- Be sure to document the rationale supporting your decision. This will ensure the decision can be clearly communicated to any stakeholders, and that you can review on your decision-making process down the line.
Record this information in the Workforce Planning Workbook for Small Enterprises.
Info-Tech Insight
Consider developing a pool of successors instead of pinning your hopes on just one person. A single pool of successors can be developed for either one key role that has specialized requirements or even multiple key roles that have generic requirements.
Input | Output |
|---|---|
|
|
Materials | Participants |
|
|
1.5 Determine readiness of internal successors
1-3 hours
- As a group, and ensuring you include the candidates' direct managers, identify potential successors for the first role on your list.
- Ask how effectively the potential successor would serve in the role today. Review the competencies for the key role in terms of:
- Relationship-building skills
- Business skills
- Technical skills
- Industry-specific skills or knowledge
- Determine what competencies the succession candidate currently has and what must be learned. Be sure you know whether the candidate is open to a career change. Don't assume – if this is not clear, have a development conversation to ensure everyone is on the same page.
- Finally, determine how difficult it will be for the successor to acquire missing skills or knowledge, whether the resources are available to provide the required development, and how long it will take to provide it.
- As a group, decide whether training an internal successor is a viable option for the role in question, considering the successor's readiness and the characteristics of need for the role. If a clear successor is not readily apparent, consider:
- If the development of the successor can be fast-tracked, or if some requirements can be deprioritized and the successor provided with temporary support from other employees.
- If the role in question is being discussed because the current incumbent is preparing to leave, consider negotiating an arrangement that extends the incumbent's employment tenure.
- Record the decision and repeat for the next role on your list.
Info-Tech Insight
A readiness assessment helps to define not just development needs, but also any risks around the organization's ability to fill a key role.
Input | Output |
|---|---|
|
|
Materials | Participants |
|
|
Use alternative work arrangements to gain time to prepare successors
Alternative work arrangements are critical tools that employers can use to achieve a mutually beneficial solution that mitigates the risk of loss associated with key roles.
Alternative work arrangements not only support employees who want to keep working, but more importantly, they allow the business to retain employees that are needed in key roles who are departure risks due to retirement.
Viewing retirement as a gradual process can help you slow down skill loss in your organization and ensure you have sufficient time to train successors. Retiring workers are becoming increasingly open to alternative work arrangements. Among employed workers aged 50-75, more than half planned to continue working part-time after retirement.
Source: Statistics Canada.
Flexible work options are the most used form of alternative work arrangement

Source: McLean & Company, N=44
Choose the alternative work arrangement that works best for you and the employee
| Alternative Work Arrangement | Description | Ideal Use | Caveats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible work options | Employees work the same number of hours but have flexibility in when and where they work (e.g. from home, evenings). | Employees who work fairly independently with no or few direct reports. | Employee may become isolated or disconnected, impeding knowledge transfer methods that require interaction or one-on-one time. |
| Contract-based work | Working for a defined period of time on a specific project on a non-salaried or non-wage basis. | Project-oriented work that requires specialized knowledge or skills. | Available work may be sporadic or specific projects more intensive than the employee wants. Knowledge transfer must be built into the contractual arrangement. |
| Part-time roles | Half days or a certain number of days per week; indefinite with no end date in mind. | Employees whose roles can be readily narrowed and upon whom people and critical processes are not dependent. | It may be difficult to break a traditionally full-time job down into a part-time role given the size and nature of associated tasks. |
| Graduated retirement | Retiring employee has a set retirement date, gradually reducing hours worked per week over time. | Roles where a successor has been identified and is available to work alongside the incumbent in an overlapping capacity while he or she learns. | The role may only require a single FTE, and the organization may not be able to afford the amount of redundancy inherent in this arrangement. |
Choose the alternative work arrangement that works best for you and the employee
| Alternative Work Arrangement | Description | Ideal Use | Caveats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Part-year jobs or job sharing | Working part of the year and having the rest of the year off, unpaid. | Project-oriented work where ongoing external relationships do not need to be maintained. | The employee is unavailable for knowledge transfer activities for a large portion of the year. Another risk is that the employee may opt not to return at the end of the extended time off with little notice. |
| Increased paid time off | Additional vacation days upon reaching a certain age. | Best used as recognition or reward for long-term service. This may be a particularly useful retention incentive in organizations that do not offer pension plans. | The company may not be able to financially afford to pay for such extensive time off. If the role incumbent is the only one in the role, this may mean crucial work is not being done. |
| Altered roles | Concentration of a job description on fewer tasks that allows the employee to focus on his or her specific expertise. | Roles where a successor has been identified and is available to work alongside the incumbent, with the incumbent's new role highly focused on mentoring. | The role may only require a single FTE, and the organization may not be able to afford the amount of redundancy inherent in this arrangement. |
Phase 2
Knowledge Transfer
Workforce Planning | Knowledge Transfer | Development Planning |
|---|---|---|
Identify needs, goals, metrics, and skill gaps. Select a skill sourcing strategy. | Discover critical knowledge. Select knowledge transfer methods. | Identify priority competencies. Assess employees. Draft development goals. Provide coaching & feedback. |
The Small Enterprise Guide to People and Resource Management
Phase Participants
- Leadership/management team
- Incumbent & successor
Additional Resources
Determine your skill sourcing route
Knowledge transfer plans have three key components that you need to complete for each knowledge source:
|
Define what knowledge needs to be transferred |
Each knowledge source has unique information which needs to be transferred. Chances are you don't know what you don't know. The first step is therefore to interview knowledge sources to find out. |
|---|---|
|
Identify the knowledge receiver |
Depending on who the information is going to, the knowledge transfer tactic you employ will differ. Before deciding on the knowledge receiver and tactic, consider three key factors:
|
|
Identify which knowledge transfer tactics you will use for each knowledge asset |
Not all tactics are good in every situation. Always keep the "knowledge type" (information, process, skills, and expertise), knowledge sources' engagement level, and the knowledge receiver in mind as you select tactics. |
Don't miss tacit knowledge
There are two basic types of knowledge: "explicit" and "tacit." Ensure you capture both to get a well-rounded overview of the role.
| Explicit | Tacit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||
|
Types of explicit knowledge |
Types of tacit knowledge |
||
| Information | Process | Skills | Expertise |
|
Specialized technical knowledge. Unique design capabilities/methods/models. Legacy systems, details, passwords. Special formulas/algorithms/ techniques/contacts. |
|
|
|
|
e.g. Knowing the lyrics to a song, building a bike, knowing the alphabet, watching a YouTube video on karate. |
e.g. Playing the piano, riding a bike, reading or speaking a language, earning a black belt in karate. |
||
Embed your knowledge transfer methods into day-to-day practice
Multiple methods should be used to transfer as much of a person's knowledge as possible, and mentoring should always be one of them. Select your method according to the following criteria:
Info-Tech Insight
The more integrated knowledge transfer is in day-to-day activities, the more likely it is to be successful, and the lower the time cost. This is because real learning is happening at the same time real work is being accomplished.
Type of Knowledge
- Tacit knowledge transfer methods are often informal and interactive:
- Mentoring
- Multi-generational work teams
- Networks and communities
- Job shadowing
- Explicit knowledge transfer methods tend to be more formal and one way:
- Formal documentation of processes and best practices
- Self-published knowledge bases
- Formal training sessions
- Formal interviews
Incumbent's Preference/Successor's Preference
Ensure you consult the employees, and their direct manager, on the way they are best prepared to teach and learn. Some examples of preferences include:
- Prefer traditional classroom learning, augmented with participation, critical reflection, and feedback.
- May get bored during formal training sessions and retain more during job shadowing.
- Prefer to be self-directed or self-paced, and highly receptive to e-learning and media.
- Prefer informal, incidental learning, tend to go immediately to technology or direct access to people. May have a short attention span and be motivated by instant results.
- May be uncomfortable with blogs and wikis, but comfortable with SharePoint.
Cost
Consider costs beyond the monetary. Some methods require an investment in time (e.g. mentoring), while others require an investment in technology (e.g. knowledge bases).
The good news is that many supporting technologies may already exist in your organization or can be acquired for free.
Methods that cost time may be difficult to get underway since employees may feel they don't have the time or must change the way they work.
2.1 Create a knowledge transfer plan
1-3 hours
- Working together with the current incumbent, brainstorm the key information pertaining to the role that you want to pass on to the successor. Use the IT Knowledge Identification Interview Guide Template to ensure you don't miss anything.
- Consider key knowledge areas, including:
- Specialized technical knowledge.
- Specialized research and development processes.
- Unique design capabilities/methods/models.
- Special formulas/algorithms/techniques.
- Proprietary production processes.
- Decision-making criteria.
- Innovative sales methods.
- Knowledge about key customers.
- Relationships with key stakeholders.
- Company history and values.
- Ask questions of both sources and receivers of knowledge to help determine the best knowledge transfer methods to use.
- What is the nature of the knowledge? Explicit or tacit?
- Why is it important to transfer?
- How will the knowledge be used?
- What knowledge is critical for success?
- How will the users find and access it?
- How will it be maintained and remain relevant and usable?
- What are the existing knowledge pathways or networks connecting sources to recipients?
- Consider key knowledge areas, including:
- Once the knowledge has been identified, use the information on the following slides to decide on the most appropriate methods. Be sure to consult the incumbent and successor on their preferences.
- Prioritize your list of knowledge transfer activities. It's important not to try to do too much too quickly. Focus on some quick wins and leverage the success of these initiatives to drive the project forward. Follow these steps as a guide:
- Take an inventory of all the tactics and techniques which you plan to employ. Eliminate redundancies where possible.
- Start your implementation with your highest risk role or knowledge item, using explicit knowledge transfer tactics. Interviews, use cases, and process mapping will give you some quick wins and will help gain momentum for the project.
- Then move forward to other tactics, the majority of which will require training and process design. Pick 1-2 other key tactics you would like to employ and build those out. For tactics that require resources or monetary investment, start with those that can be reused for multiple roles.
Record your plan in the IT Knowledge Transfer Plan Template.
Download the IT Knowledge Identification Interview Guide Template
Download the Knowledge Transfer Plan Template
Info-Tech Insight
Wherever possible, ask employees about their personal learning styles. It's likely that a collaborative compromise will have to be struck for knowledge transfer to work well.
2.1 Create a knowledge transfer plan
Input | Output |
|---|---|
|
|
Materials | Participants |
|
|
Not every transfer method is effective for every type of knowledge
| Knowledge Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tactic | Explicit | Tacit | ||
| Information | Process | Skills | Expertise | |
| Interviews | Very Strong | Strong | Strong | Strong |
| Process Mapping | Medium | Very Strong | Very Weak | Very Weak |
| Use Cases | Medium | Very Strong | Very Weak | Very Weak |
| Job Shadow | Very Weak | Medium | Very Strong | Very Strong |
| Peer Assist | Strong | Medium | Very Strong | Very Strong |
| Action Review | Medium | Medium | Strong | Strong |
| Mentoring | Weak | Weak | Strong | Very Strong |
| Transition Workshop | Strong | Strong | Strong | Weak |
| Storytelling | Weak | Weak | Strong | Very Strong |
| Job Share | Weak | Weak | Very Strong | Very Strong |
| Communities of Practice | Strong | Weak | Very Strong | Very Strong |
This table shows the relative strengths and weaknesses of each knowledge transfer tactic compared against four different knowledge types.
Not all techniques are effective for all types of knowledge; it is important to use a healthy mixture of techniques to optimize effectiveness.
Employees' engagement can impact knowledge transfer effectiveness
| Level of Engagement | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tactic | Disengaged/ Indifferent | Almost Engaged - Engaged |
| Interviews | Yes | Yes |
| Process Mapping | Yes | Yes |
| Use Cases | Yes | Yes |
| Job Shadow | No | Yes |
| Peer Assist | Yes | Yes |
| Action Review | Yes | Yes |
| Mentoring | No | Yes |
| Transition Workshop | Yes | Yes |
| Storytelling | No | Yes |
| Job Share | Maybe | Yes |
| Communities of Practice | Maybe | Yes |
When considering which tactics to employ, it's important to consider the knowledge holder's level of engagement. Employees who you would identify as being disengaged may not make good candidates for job shadowing, mentoring, or other tactics where they are required to do additional work or are asked to influence others.
Knowledge transfer can be controversial for all employees as it can cause feelings of job insecurity. It's essential that motivations for knowledge transfer are communicated effectively.
Pay particular attention to your communication style with disengaged and indifferent employees, communicate frequently, and tie communication back to what's in it for them.
Putting disengaged employees in a position where they are mentoring others can be a risk, as their negativity could influence others not to participate, or it could negate the work you're doing to create a positive knowledge sharing culture.
Employees' engagement can impact knowledge transfer effectiveness
|
Effort by Stakeholder |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Tactic |
Business Analyst |
IT Manager |
Knowledge Holder |
Knowledge Receiver |
|
Interviews These tactics require the least amount of effort, especially for organizations that are already using these tactics for a traditional requirements gathering process. |
Medium |
N/A |
Low |
Low |
|
Process Mapping |
Medium |
N/A |
Low |
Low |
|
Use Cases |
Medium |
N/A |
Low |
Low |
|
Job Shadow |
Medium |
Medium |
Medium |
Medium |
|
Peer Assist |
Medium |
Medium |
Medium |
Medium |
|
Action Review These tactics generally require more involvement from IT management and the BA in tandem for preparation. They will also require ongoing effort for all stakeholders. It's important to gain stakeholder buy-in as it is key for success. |
Low |
Medium |
Medium |
Low |
|
Mentoring |
Medium |
High |
High |
Medium |
|
Transition Workshop |
Medium |
Low |
Medium |
Low |
|
Storytelling |
Medium |
Medium |
Low |
Low |
|
Job Share |
Medium |
High |
Medium |
Medium |
|
Communities of Practice |
High |
Medium |
Medium |
Medium |
Phase 3
Development Planning
Workforce Planning | Knowledge Transfer | Development Planning |
|---|---|---|
Identify needs, goals, metrics, and skill gaps. Select a skill sourcing strategy. | Discover critical knowledge. Select knowledge transfer methods. | Identify priority competencies. Assess employees. Draft development goals. Provide coaching & feedback. |
The Small Enterprise Guide to People and Resource Management
Phase Participants
- Leadership team
- Managers
- Employees
Additional Resources
Effective development planning hinges on robust performance management
Your performance management framework is rooted in organizational goals and defines what it means to do any given role well.
Your organization's priority competencies are the knowledge, skills and attributes that enable an employee to do the job well.
Each individual's development goals are then aimed at building these priority competencies.
|
Mission Statement |
To be the world's leading manufacturer and distributor of widgets. |
|---|---|
|
Business Goal |
To increase annual revenue by 10%. |
|
IT Department Objective |
To ensure reliable communications infrastructure and efficient support for our sales and development teams. |
|
Individual Role Objective |
To decrease time to resolution of support requests by 10% while maintaining quality. |
Info-Tech Insight
Without a performance management framework, your employees cannot align their development with the organization's goals. For detailed guidance, see Info-Tech's blueprint Setting Meaningful Employee Performance Measures.
What is a competency?
The term "competency" refers to the collection of knowledge, skills, and attributes an employee requires to do a job well.
Often organizations have competency frameworks that consist of core, leadership, and functional competencies.
Core competencies apply to every role in the organization. Typically, they are tied to organizational values and business mission and/or vision.
Functional competencies are at the department, work group, or job role levels. They are a direct reflection of the function or type of work carried out.
Leadership competencies generally apply only to people managers in the organization. Typically, they are tied to strategic goals in the short to medium term
| Generic | Functional |
|---|---|
|
|
Use the SMART model to make sure goals are reasonable and attainable
S |
Specific: Be specific about what you want to accomplish. Think about who needs to be involved, what you're trying to accomplish, and when the goal should be met. |
|---|---|
M |
Measurable: Set metrics that will help to determine whether the goal has been reached. |
A |
Achievable: Ensure that you have both the organizational resources and employee capability to accomplish the goal. |
R |
Relevant: Goals must align with broader business, department, and development goals in order to be meaningful. |
T |
Time-bound: Provide a target date to ensure the goal is achievable and provide motivation. |
Example goal:
"Learn Excel this summer."
Problems:
Not specific enough, not measurable enough, nor time bound.
Alternate SMART goal:
"Consult with our Excel expert and take the lead on creating an Excel tool in August."
3.2 Identify target competencies & draft development goals
1 hour
Pre-work: Employees should come to the career conversation having done some self-reflection. Use Info-Tech's IT Employee Career Development Workbook to help employees identify their career goals.
- Pre-work: Managers should gather any data they have on the employee's current proficiency at key competencies. Potential sources include task-based assessments, performance ratings, supervisor or peer feedback, and informal conversation.
Prioritize competencies. Using your list of priority organizational competencies, work with your employees to help them identify two to four competencies to focus on developing now and in the future. Use the Individual Competency Development Plan template to document your assessment and prioritize competencies for development. Consider the following questions for guidance:- Which competencies are needed in my current role that I do not have full proficiency in?
- Which competencies are related to both my career interests and the organization's priorities?
- Which competencies are related to each other and could be developed together or simultaneously?
- Draft goals. Ask your employee to create a list of multiple simple goals to develop the competencies they have selected to work on developing over the next year. Identifying multiple goals helps to break development down into manageable chunks. Ensure goals are concrete, for example, if the competency is "communication skills," your development goals could be "presentation skills" and "business writing."
- Review goals:
- Ask why these areas are important to the employee.
- Share your ideas and why it is important that the employee develop in the areas identified.
- Ensure that the goals are realistic. They should be stretch goals, but they must be achievable. Use the SMART framework on the previous slide for guidance.
Info-Tech Insight
Lack of career development is the top reason employees leave organizations. Development activities need to work for both the organization and the employee's own development, and clearly link to advancing employees' careers either at the organization or beyond.
Download the IT Employee Career Development Workbook
Download the Individual Competency Development Plan
3.2 Identify target competencies & draft development goals
Input | Output |
|---|---|
|
|
Materials | Participants |
|
Apply a blend of learning methods
- Info-Tech recommends the 70-20-10 principle for learning and development, which places the greatest emphasis on learning by doing. This experiential learning is then supported by feedback from mentoring, training, and self-reflection.
- Use the 70-20-10 principle as a guideline – the actual breakdown of your learning methods will need to be tailored to best suit your organization and the employee's goals.
Spend development time and effort wisely:
70% |
On providing challenging on-the-job opportunities |
|---|---|
20% |
On establishing opportunities for people to develop learning relationships with others, such as coaching and mentoring |
10% |
On formal learning and training programs |
Internal initiatives are a cost-effective development aid
|
Internal Initiative |
What Is It? |
When to Use It |
|---|---|---|
|
Special Project |
Assignment outside of the scope of the day-to-day job (e.g. work with another team on a short-term initiative). |
As an opportunity to increase exposure and to expand skills beyond those required for the current job. |
|
Stretch Assignment |
The same projects that would normally be assigned, but in a shorter time frame or with a more challenging component. |
Employee is consistently meeting targets and you need to see what they're capable of. |
|
Training Others |
Training new or more junior employees on their position or a specific process. |
Employee wants to expand their role and responsibility and is proficient and positive. |
|
Team Lead On an Assignment |
Team lead for part of a project or new initiative. |
To prepare an employee for future leadership roles by increasing responsibility and developing basic managerial skills. |
|
Job Rotation |
A planned placement of employees across various roles in a department or organization for a set period of time. |
Employee is successfully meeting and/or exceeding job expectations in their current role. |
Incorporating a development objective into daily tasks
What do we mean by incorporating into daily tasks?
The next time you assign a project to an employee, you should also ask the employee to think about a development goal for the project. Try to link it back to their existing goals or have them document a new goal in their development plan.
For example: A team of employees always divides their work in the same way. Their goal for their next project could be to change up the division of responsibility so they can learn each other's roles.
Another example:
"I'd like you to develop your ability to explain technical terms to a non-technical audience. I'd like you to sit down with the new employee who starts tomorrow and explain how to use all our software, getting them up and running."
Info-Tech Insight
Employees often don't realize that they are being developed. They either think they are being recognized for good work or they are resentful of the additional workload.
You need to tell your employees that the activity you are asking them to do is intended to further their development.
However, be careful not to sell mundane tasks as development opportunities – this is offensive and detrimental to engagement.
Establish manager and employee accountability for following up
Ensure that the employee makes progress in developing prioritized competencies by defining accountabilities:
|
Tracking Progress |
Checking In |
Development Meetings |
Coaching & Feedback |
|---|---|---|---|
Employee accountability:
Manager accountability:
|
Employee accountability:
Manager accountability:
|
Employee accountability:
Manager accountability:
|
Employee accountability:
Manager accountability:
|
3.3 Select development activities and schedule check-ins
1-3 hours
Pre-work: Employees should research potential development activities and come prepared with a range of suggestions.
Pre-work: Managers should investigate options for employee development, such as internal training/practice opportunities for the employee's selected competencies and availability of training budget.
- Communicate your findings about internal opportunities and external training allowance to the employee. This can also be done prior to the meeting, to help guide the employee's own research. Address any questions or concerns.
- Review the employee's proposed list of activities, and identify priority ones based on:
- How effectively they support the development of priority competencies.
- How closely they match the employee's original goals.
- The learning methods they employ, and whether the chosen activities support a mix of different methods.
- The degree to which the employee will have a chance to practice new skills hands-on.
- The amount of time the activities require, balanced against the employee's work obligations.
- Guide the employee in selecting activities for the short and medium term. Establish an understanding that this list is tentative and subject to ongoing revision during future check-ins.
- If in doubt about whether the employee is over-committing, err on the side of fewer activities to start.
- Schedule a check-in for one month out to review progress and roadblocks, and to reaffirm priorities.
- Check-ins should be repeated regularly, typically once a month.
Download the Learning Methods Catalog
Info-Tech Insight
Adopt a blended learning approach using a variety of techniques to effectively develop competencies. This will reinforce learning and accommodate different learning styles. See Info-Tech's Learning Methods Catalog for a description of popular experiential, relational, and formal learning methods.
3.3 Select development activities and schedule check-ins
Input | Output |
|---|---|
|
|
Materials | Participants |
|
Tips for tricky conversations about development
What to do if…
Employees aren't interested in development:
- They may have low aspiration for advancement.
- Remind them about the importance of staying current in their role given increasing job requirements.
- Explain that skill development will make their job easier and make them more successful at it; sell development as a quick and effective way to learn the skill.
- Indicate your support and respond to concerns.
Employees have greater aspiration than capability:
- Explain that there are a number of skills and capabilities that they need to improve in order to move to the next level. If the specific skills were not discussed during the performance appraisal, do not hesitate to explain the improvements that you require.
- Inform the employee that you want them to succeed and that by pushing too far and too fast they risk failure, which would not be beneficial to anyone.
- Reinforce that they need to do their current job well before they can be considered for promotion.
Employees are offended by your suggestions:
- Try to understand why they are offended. Before moving forward, clarify whether they disagree with the need for development or the method by which you are recommending they be developed.
- If it is because you told them they had development needs, then reiterate that this is about helping them to become better and that everyone has areas to develop.
- If it is about the development method, discuss the different options, including the pros and cons of each.
Coaching and feedback skills help managers guide employee development
Coaching and providing feedback are often confused. Managers often believe they are coaching when they are just giving feedback. Learn the difference and apply the right approach for the right situation.
What is coaching?
A conversation in which a manager asks questions to guide employees to solve problems themselves.
Coaching is:
- Future-focused
- Collaborative
- Geared toward growth and development
What is feedback?
Information conveyed from the manager to the employee about their performance.
Feedback is:
- Past-focused
- Prescriptive
- Geared toward behavior and performance
Info-Tech Insight
Don't forget to develop your managers! Ensure coaching, feedback, and management skills are part of your management team's development plan.
|
Understand the foundations of coaching to provide effective development coaching: |
||
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge | Mindset | Relationship |
|
|
|
Apply the "4A" behavior-focused coaching model
Using a model allows every manager, even those with little experience, to apply coaching best practices effectively.
|
Actively Listen |
Ask |
Action Plan |
Adapt |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Engage with employees and their message, rather than just hearing their message. Key active listening behaviors:
|
Ask thoughtful, powerful questions to learn more information and guide employees to uncover opportunities and/or solutions. Key asking behaviors:
|
Hold employees and managers accountable for progress and results. During check-ins, review each development goal to ensure employees are meeting their targets. Key action planning behaviors:
|
Adapt to individual employees and situations. Key adapting behaviors:
|
Use the following questions to have meaningful coaching conversations
Opening Questions
- What's on your mind?
- Do you feel you've had a good week/month?
- What is the ideal situation?
- What else?
Problem-Identifying Questions
- What is most important here?
- What is the challenge here for you?
- What is the real challenge here for you?
- What is getting in the way of you achieving your goal?
Problem-Solving Questions
- What are some of the options available?
- What have you already tried to solve this problem? What worked? What didn't work?
- Have you considered all the possibilities?
- How can I help?
Next-Steps Questions
- What do you need to do, and when, to achieve your goal?
- What resources are there to help you achieve your goal? This includes people, tools, or even resources outside our organization.
- How will you know when you have achieved your goal? What does success look like?
The purpose of asking questions is to guide the conversation and learn something you didn't already know. Choose the questions you ask based on the flow of the conversation and on what information you would like to uncover. Approach the answers you get with an open mind.
Info-Tech Insight
Avoid the trap of "hidden agenda" questions, whose real purpose is to offer your own advice.
Use the following approach to give effective feedback
Provide the feedback in a timely manner
- Plan the message you want to convey.
- Provide feedback "just-in-time."
- Ensure recipient is not preoccupied.
- Try to balance the feedback; refer to successful as well as unsuccessful behavior.
Communicate clearly, using specific examples and alternative behaviors
- Feedback must be honest and helpful.
- Be specific and give a recent example.
- Be descriptive, not evaluative.
- Relate feedback to behaviors that can be changed.
- Give an alternative positive behavior.
Confirm their agreement and understanding
- Solicit their thoughts on the feedback.
- Clarify if not understood; try another example.
- Confirm recipient understands and accepts the feedback.
Manager skill is crucial to employee development
Development is a two-way street. This means that while employees are responsible for putting in the work, managers must enable their development with support and guidance. The latter is a skill, which managers must consciously cultivate.
For more in-depth management skills development, see the Info-Tech "Build a Better Manager" training resources:
- Basic Management Skills: Time management, delegation, accountability.
- Manage Your People: Communication, coaching, and performance management.
- Personal Leadership: Manager's role in the organization, decision-making, and conflict management.
Bibliography
Anderson, Kelsie. "Is Your IT Department Prepared for the 4 Biggest Challenges of 2017?" 14 June 2017.
Atkinson, Carol, and Peter Sandiford. "An Exploration of Older Worker Flexible Working Arrangements in Smaller Firms." Human Resource Management Journal, vol. 26, no. 1, 2016, pp. 12–28. Wiley Online Library.
BasuMallick, Chiradeep. "Top 8 Best Practices for Employee Cross-Training." Spiceworks, 15 June 2020.
Birol, Andy. "4 Ways You Can Succeed With a Staff That 'Wears Multiple Hats.'" The Business Journals, 26 Nov. 2013.
Bleich, Corey. "6 Major Benefits To Cross-Training Employees." EdgePoint Learning, 5 Dec. 2018.
Cancialosi, Chris. "Cross-Training: Your Best Defense Against Indispensable Employees." Forbes, 15 Sept. 2014.
Cappelli, Peter, and Anna Tavis. "HR Goes Agile." Harvard Business Review, Mar. 2018.
Chung, Kai Li, and Norma D'Annunzio-Green. "Talent Management Practices of SMEs in the Hospitality Sector: An Entrepreneurial Owner-Manager Perspective." Worldwide Hospitality and Tourism Themes, vol. 10, no. 4, Jan. 2018.
Clarkson, Mary. Developing IT Staff: A Practical Approach. Springer Science & Business Media, 2012.
"CNBC and SurveyMonkey Release Latest Small Business Survey Results." Momentive, 2019. Press Release. Accessed 6 Aug. 2020.
Cselényi, Noémi. "Why Is It Important for Small Business Owners to Focus on Talent Management?" Jumpstart:HR | HR Outsourcing and Consulting for Small Businesses and Startups, 25 Mar. 2013.
dsparks. "Top 10 IT Concerns for Small Businesses." Stratosphere Networks IT Support Blog - Chicago IT Support Technical Support, 16 May 2017.
Duff, Jimi. "Why Small to Mid-Sized Businesses Need a System for Talent Management | Talent Management Blog | Saba Software." Saba, 17 Dec. 2018.
Employment and Social Development Canada. "Age-Friendly Workplaces: Promoting Older Worker Participation." Government of Canada, 3 Oct. 2016.
Exploring Workforce Planning. Accenture, 23 May 2017.
"Five Major IT Challenges Facing Small and Medium-Sized Businesses." Advanced Network Systems. Accessed 25 June 2020.
Harris, Evan. "IT Problems That Small Businesses Face." InhouseIT, 17 Aug. 2016.
Heathfield, Susan. "What Every Manager Needs to Know About Succession Planning." Liveabout, 8 June 2020.
---. "Why Talent Management Is an Important Business Strategy." Liveabout, 29 Dec. 2019.
Herbert, Chris. "The Top 5 Challenges Facing IT Departments in Mid-Sized Companies." ExpertIP, 25 June 2012.
How Smaller Organizations Can Use Talent Management to Accelerate Growth. Avilar. Accessed 25 June 2020.
Krishnan, TN, and Hugh Scullion. "Talent Management and Dynamic View of Talent in Small and Medium Enterprises." Human Resource Management Review, vol. 27, no. 3, Sept. 2017, pp. 431–41.
Mann Jackson, Nancy. "Strategic Workforce Planning for Midsized Businesses." ADP, 6 Feb. 2017.
McCandless, Karen. "A Beginner's Guide to Strategic Talent Management (2020)." The Blueprint, 26 Feb. 2020.
McFeely, Shane, and Ben Wigert. "This Fixable Problem Costs U.S. Businesses $1 Trillion." Gallup.com, 13 Mar. 2019.
Mihelič, Katarina Katja. Global Talent Management Best Practices for SMEs. Jan. 2020.
Mohsin, Maryam. 10 Small Business Statistics You Need to Know in 2020 [May 2020]. 4 May 2020.
Ramadan, Wael H., and B. Eng. The Influence of Talent Management on Sustainable Competitive Advantage of Small and Medium Sized Establishments. 2012, p. 15.
Ready, Douglas A., et al. "Building a Game-Changing Talent Strategy." Harvard Business Review, no. January–February 2014, Jan. 2014.
Reh, John. "Cross-Training Employees Strengthens Engagement and Performance." Liveabout, May 2019.
Rennie, Michael, et al. McKinsey on Organization: Agility and Organization Design. McKinsey, May 2016.
Roddy, Seamus. "The State of Small Business Employee Benefits in 2019." Clutch, 18 Apr. 2019.
SHRM. "Developing Employee Career Paths and Ladders." SHRM, 28 Feb. 2020.
Strandberg, Coro. Sustainability Talent Management: The New Business Imperative. Strandberg Consulting, Apr. 2015.
Talent Management for Small & Medium-Size Businesses. Success Factors. Accessed 25 June 2020.
"Top 10 IT Challenges Facing Small Business in 2019." Your IT Department, 8 Jan. 2019.
"Why You Need Workforce Planning." Workforce.com, 24 Oct. 2022.
Buying Options
The Small Enterprise Guide to People and Resource Management
IT Risk Management · IT Leadership & Strategy implementation · Operational Management · Service Delivery · Organizational Management · Process Improvements · ITIL, CORM, Agile · Cost Control · Business Process Analysis · Technology Development · Project Implementation · International Coordination · In & Outsourcing · Customer Care · Multilingual: Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese · Entrepreneur
Tymans Group is a brand by Gert Taeymans BV
Gert Taeymans bv
Europe: Koning Albertstraat 136, 2070 Burcht, Belgium — VAT No: BE0685.974.694 — phone: +32 (0) 468.142.754
USA: 4023 KENNETT PIKE, SUITE 751, GREENVILLE, DE 19807 — Phone: 1-917-473-8669
Copyright 2017-2022 Gert Taeymans BV