Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams

- Virtual team members must rely upon collaboration technology to communicate and collaborate.
- Management practices and approaches that work face to face do not always translate effectively in virtual contexts.
- Managers cannot rely upon spontaneous social interactions that happen organically when people are colocated to build meaningful and trusting relationships. Space and time need to be created in a virtual environment for this to happen.
- Observing an employee’s performance or development can be more difficult, and relying on others’ feedback becomes more critical for managing performance and development.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Managing virtual teams does not require developing new manager competencies. Instead, managers need to “dial up” competencies they already have and adjust their approaches.
- Setting clear expectations with virtual teams creates the foundation needed to manage them effectively.
- Virtual employees crave more meaningful interactions about performance and development with their managers.
Impact and Result
- Create a solid foundation for managing virtual teams by setting clear expectations and taking a more planful approach to managing performance and employee development.
- Dial up key management competencies that you already have. Managers do not need to develop new competencies; they just need to adjust and refocus their approaches.
Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Equip managers to effectively manage virtual teams
Equip managers to become more effective with managing remote teams.
The workbook serves as a reference guide participants will use to support formal training.
- Training Deck: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
- Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
- Standard Participant Training Session Evaluation Template
2. Additional Resources
Many organizations are developing plans to allow employees more flexible work options, including remote work. Use these resources to help managers and employees make the most of remote work arrangements.
- Work-From-Home Tips for Managers
- Work-From-Home Tips for Employees
- Health & Safety at Home Infographic
- Wellness and Working From Home
- Ergonomic Workspaces Infographic
Further reading
Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Learning objectives
Describe the benefits of virtual teams.
Create a plan for adopting effective management practices and setting clear expectations with virtual teams.
Identify potential solutions to the challenges of managing performance and developing members of virtual teams.
Create an action plan to increase effectiveness in managing virtual teams.
Target audience
People managers who manage or plan to manage virtual teams.
Training length
Two three-hour sessions
Training material
- Use the speaker’s notes in the notes pane section of each slide to plan and practice the training session.
- Activity slides are scattered throughout this training deck and are clearly numbered in the slide title.
- Notes in italics are written to the facilitator and are not meant to be read aloud.
- Download the Workbook for participants to use.
Suggested materials for activities:
- Index cards or sticky notes
- Markers
- Whiteboard/large table space/flip chart
Agenda & activities
|
Section 1 |
Section 2 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 min |
Welcome: Overview & Introductions
|
10 min |
Welcome: Overview & Introductions
|
| 50 min |
1.1 Introduction to virtual teams
|
55 min |
2.1 Managing wellbeing in a virtual team context
|
| 5 min |
Break |
5 min | Break |
| 45 min |
1.2 Laying the foundation for a virtual team
|
60 min |
2.2 Managing performance in a virtual team context
|
| 10 min |
Break |
10 min | Break |
| 55 min |
1.2 Laying the foundation for a virtual team
|
40 min |
Action planning & conclusion
|
| 5 min |
Session 1 Wrap-Up |
||
Recommended Customization
Review all slides and adjust the language or content as needed to suit your organizational context and culture.
The pencil icon to the left denotes slides requiring customization of the slide and/or the speaker’s notes, e.g. adding in an organization-specific process.
Customization instructions are found in the notes pane.
Tips
- Adjust the speaker’s notes on the slides before (or after) any slides you modify or delete to ensure logical transitions between slides.
- Update the agenda to reflect new timings if major modifications are made.
- Even seasoned leaders need to be reminded of the basics now and again. Rather than delete more basic slides, cut back on the amount of time spent covering them and frame the content as a refresher.
- Participant Workbooks
- Relevant organization-specific documents (see side panel)
- Training Session Feedback Form
Required Information
- Communication guidelines for managers (e.g. cadence of manager interactions)
- Performance management process and guidelines
- Employee development guidelines
- List of available resources (e.g. social collaboration tools)
Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Section 1.1
Practical foundations for managing teams in a remote environment
Feasibility of virtual IT teams
Most organizations are planning some combination of remote and onsite work in 2022.
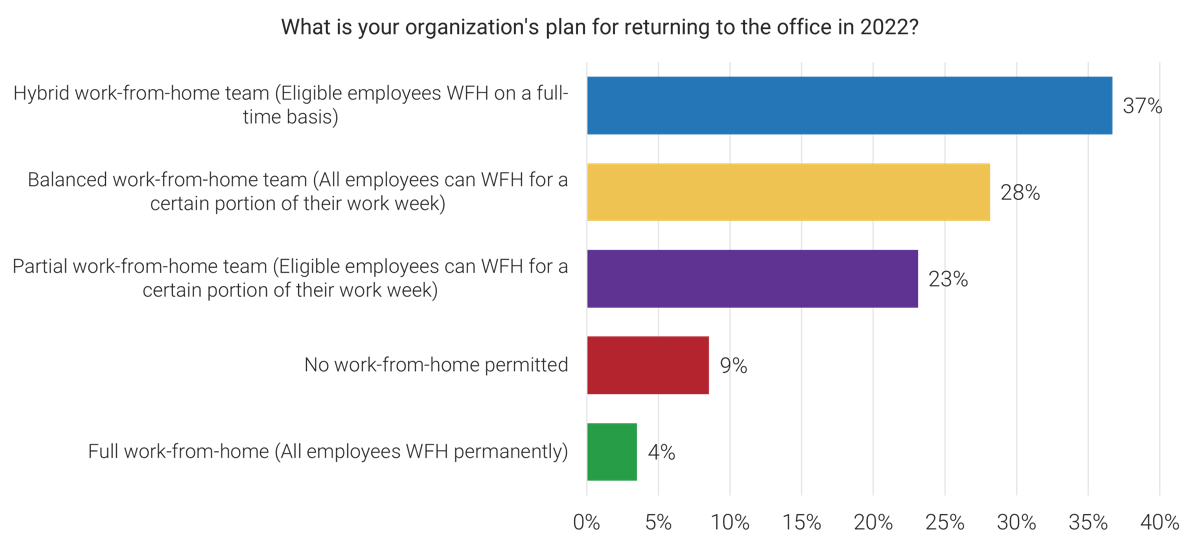
Source: IT Talent Trends, 2022; n=199
Speaker’s Notes:
Most organizations are planning some combination of remote and onsite work in 2022 – the highest reported plans for WFH were hybrid, balanced, and partial work-from-home. This builds on our findings in the IT Talent Trends 2022 report.
Feasibility of virtual IT teams
What percentage of roles in IT are capable of being performed remotely permanently?
Approximately what percentage of roles in IT are capable of being performed remotely permanently?
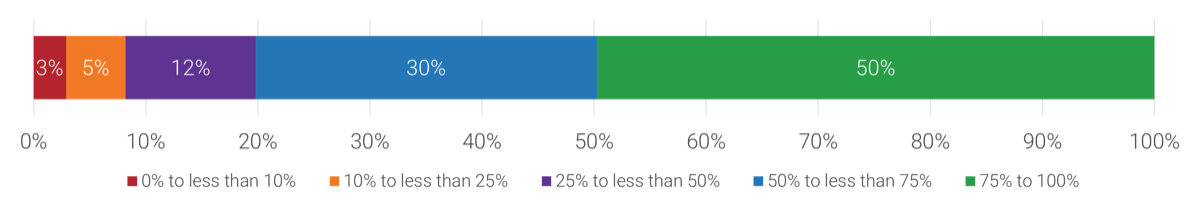
IT Talent Trends, 2022; n=207
Speaker’s Notes:
80% of respondents estimated that 50 to 100% of IT roles can be performed remotely.
Virtual teams take all kinds of forms
A virtual team is any team that has members that are not colocated and relies on technology for communications.
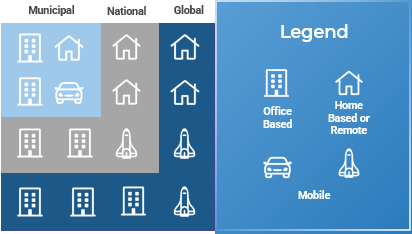
Speaker’s Notes:
Before we start, it will be useful to review what we mean by the term “virtual team.” For our purposes we will be defining a virtual team as any team that has members that are not colocated and relies on technology for communications.
There are a wide variety of virtual work arrangements and a variety of terms used to describe them. For example, some common terms include:
- “Flexible work arrangements”: Employees have the option to work where they see fit (within certain constraints). They may choose to work from the office, home, a shared office space, the road, etc.
- “Remote work,” “work from home,” and “telecommuting”: These are just various ways of describing how or where people are working virtually. They all share the idea that these kinds of employees are not colocated.
- “Multi-office team”: the team members all work in office environments, but they may not always be in the same office as their team members or manager.
Our definition of virtual work covers all of these terms. It is also distance neutral, meaning that it applies equally to teams that are dispersed globally or regionally or even those working in the same cities but dispersed throughout different buildings. Our definition also applies whether virtual employees work full time or part time.
The challenges facing managers arise as soon as some team members are not colocated and have to rely on technology to communicate and coordinate work. Greater distances between employees can complicate challenges (e.g. time zone coordination), but the core challenges of managing virtual teams are the same whether those workers are merely located in different buildings in the same city or in different buildings on different continents.
1.1 What kind of virtual team do you lead?
15 Minutes
Working on your own, take five minutes to figure out what kind of virtual team you lead.
- How many people on your team work virtually (all, most, or a small percentage)?
- How often and how regularly do they tend to work virtually (full time, part time regularly, or part time as needed)?
- What kinds of virtual work arrangements are there on your team (multi-site, work from home, mobile employees)?
- Where do your workers tend to be physically located (different offices but in the same city/region or globally dispersed)?
- Record this information in your workbook.
- Discuss as a group.
Download the Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Input
- Size of virtual team
- Current remote work practices
Output
- Documented list of current state of remote work
Materials
- Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Participants
- All managers with direct reports working virtually
Advantages
|
Benefits to the organization |
Benefits to employees |
|---|---|
|
Operational continuity in disaster situations that prevent employees from coming into the office. |
Cost savings: Employees who WFH half the time can save $2,500 to $4,000 per year (Global Workplace Analytics, 2021). |
|
Cost savings: Organizations save ~$11,000 annually per employee working from home half the time (Global Workplace Analytics, 2021). |
Time savings: Employees who WFH half the time save on average 11 workdays per year (Global Workplace Analytics, 2021). |
|
Increased attraction: 71% of employees would likely choose one employer over another based on WFH offerings (Owl Labs, 2021). |
Improved wellbeing: 83% employees agree that WFH would make them happier. 80% agree that WFH would decrease their stress. 81% agree that WFH would improve their ability to manage their work-life balance. (Owl Labs, 2021) |
|
Increased retention: 74% of employees would be less likely to leave their employer if they could WFH (Owl Labs, 2021). |
Increased flexibility: 32% of employees rated the “ability to have a flexible schedule” as the biggest benefit of WFH (OWL Labs, 2021). |
|
Increased productivity: 50% of employees report they would maintain or increase their productivity while working from home (Glassdoor Team, 2020). |
|
|
Increased engagement: Offsite employees tend to have higher overall engagement than onsite employees (McLean & Company Engagement Survey, 2020). |
Speaker’s Notes:
Remote work arrangements are becoming more and more common, and for good reason: there are a lot of benefits to the organization – and to employees.
#1: Save Money
Perhaps one of the most common reasons for opting for remote-work arrangements is the potential cost savings. One study found that organizations could save about $11,000 per employee working from home half the time (Global Workplace Analytics, 2021).
#2 Increased Attraction
In addition, supporting remote-work arrangements can attract employees. One study found that 71% of employees would likely choose one employer over another based on WFH offerings (Owl Labs, 2019).
#3 Improve productivity.
There are also improvements to productivity. Fifty percent of employees report they would maintain or increase their productivity while working from home (Glassdoor Team, 2020).
Remote work also has benefits to employees.
#1: Save Money
As with organizations, employees also benefit financially from remote work arrangements, saving between $2,500 and $4,000 and on average 11 working days while working from home half of the time.
#2: Improved Wellbeing
Most employees agree that working from home makes them happier, reduces stress, and provides an improved work-life balance through increased flexibility.
Challenges
Organizations
- Concerns that WFH may stifle innovation (Scientific American, 2021), likely due to the potential lack of collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Fewer organic opportunities for informal interaction between employees working from home means active efforts are required to foster organizational culture.
Leaders
- 42% of managers believe that monitoring the productivity of their direct reports is a top challenge of WFH (Ultimate Software, 2019).
- The lack of in-person supervision compounded with a lack of trust in employees leads many leaders to believe that WFH will result in a drop in productivity.
Employees
- 20% of employees report collaboration/communication as their top struggle with WFH (Owl Labs, 2021).
- Employees often experience burnout from working longer hours due to the lack of commute, blurring of work and home life, and the perceived need to prove their productivity.
Many of these barriers can be addressed by changing traditional mindsets and finding alternative ways of working, but the traditional approach to work is so entrenched that it has been hard to make the shift.
Speaker’s Notes:
Many organizations are still grappling with the challenges of remote work. Some are just perceived challenges, while others are quite real.
Limited innovation and a lack of informal interaction are a potential consequence of failing to properly adapt to the remote-work environment.
Leaders also face challenges with remote work. Losing in-person supervision has led to the lack of trust and a perceived drop in productivity.
A study conducted 2021 asked remote workers to identify their biggest struggle with working remotely. The top three struggles remote workers report facing are unplugging after work, loneliness, and collaborating and/or communicating.
Seeing the struggles remote workers identify is a good reminder that these employees have a unique set of challenges. They need their managers to help them set boundaries around their work; create feelings of connectedness to the organization, culture, and team; and be expert communicators.
1.2 Virtual teams: benefits and challenges
20 Minutes
- Discuss and list:
- Any positives you’ve experienced since managing virtual employees.
- Any challenges you’ve had to manage connected to managing virtual employees.
- Record information in the workbook.
Download the Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Input
- Personal experiences managing remote teams
Output
- List of benefits and challenges of remote work
Materials
- Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Participants
- All managers with direct reports working virtually
Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Section 1.2
Laying the foundations for a virtual team
The 3i’s: Inform, interact, and involve your way to effective management:
|
Inform |
Interact | Involve |
|---|---|---|
|
↓ Down |
Connect |
↑ Up |
|
Tell employees the whys |
Get to know employees |
Solicit input from employees |
Speaker’s Notes:
Effectively managing a virtual team really comes down to adopting management approaches that will engage virtual employees.
Managing a virtual team does not actually require a new management style. The basics of effective management are the same in both colocated and virtual teams; however, the emphasis on certain behaviors and actions we take often differs. Managing a virtual team requires much more thoughtfulness and planning in our everyday interactions with our teams as we cannot rely on the relative ease of face-to-face interactions available to colocated teams.
The 3i’s Engaging Management Model is useful when interacting with all employees and provides a handy framework for more planful interactions with virtual employees.
Think of your management responsibilities in these three buckets – they are the most important components of being an effective manager. We’re first going to look at inform and involve before moving on to interact.
Inform: Relay information down from senior management and leaders to employees. Communicate the rationale behind decisions and priorities, and always explain how they will directly affect employees.
Why is this important? According to McLean & Company’s Engagement Survey data, employees who say their managers keep them well informed about decisions that affect them are 3.4 times more likely to be engaged (Source: McLean & Company, 2020; N=77,363). Your first reaction to this might be “I already do this,” which may very well be the case. Keep in mind, though, we sometimes tend to communicate on a “need-to-know basis,” especially when we are stressed or short on time. Engaging employees takes more. Always focus on explaining the “why?” or the rationale behind business decisions.
It might seem like this domain should be the least affected, since important company announcements probably continue in a remote environment. But remember that information like that also flows informally. And even in formal settings, there are question-and-answer opportunities. Or maybe your employee might come to your office to ask for more details. Virtual team members can’t gather around the watercooler. They don’t have the same opportunities to hear information in passing as people who are colocated do, so managers need to make a concerted effort to share information with virtual team members in a clear and timely way.
Swinging over to the other end, we have involve: Involve your employees. Solicit information and feedback from employees and collaborate with them.
However, it’s not enough to just solicit their feedback and input; you also need to act on it.
Make sure you involve your employees in a meaningful way. Such collaboration makes employees feel like a valued part of the team. Not to mention that they often have information and perspectives that can help make your decisions stronger!
Employees who say their department leaders act on feedback from them are 3.9 times more likely to be engaged than those whose leaders don’t. (Source: McLean & Company, 2020; N=59,779). That is a huge difference!
Keeping virtual employees engaged and feeling connected and committed to the organization requires planful and regular application of the 3i’s model.
Finally, Interact: Connect with employees on a personal level; get to know them and understand who they are on a personal and professional level.
Why? Well, over and above the fact that it can be rewarding for you to build stronger relationships with your team, our data shows that human connection makes a significant difference with employees. Employees who believe their managers care about them as a person are 3.8 times more likely to be engaged than those who do not (Source: McLean & Company, 2017; N=70,927).
And you might find that in a remote environment, this is the area that suffers the most, since a lot of these interactions tend to be unscripted, unscheduled, and face to face.
Typically, if we weren’t in the midst of a pandemic, we’d emphasize the importance of allocating some budget to travel and get some face-to-face time with your staff. Meeting and interacting with team members face to face is crucial to building trusting relationships, and ultimately, an effective team, so given the context of our current circumstances, we recommend the use of video when interacting with your employees who are remote.
Relay information down from senior management to employees.
Ensure they’ve seen and understand any organization-wide communication.
Share any updates in a timely manner.
Connect with employees on a personal level.
Ask how they’re doing with the new work arrangement.
Express empathy for challenges (sick family member, COVID-19 diagnosis, etc.).
Ask how you can support them.
Schedule informal virtual coffee breaks a couple of times a week and talk about non-work topics.
Get information from employees and collaborate with them.
Invite their input (e.g. have a “winning remotely” brainstorming session).
Escalate any challenges you can’t address to your VP.
Give them as much autonomy over their work as possible – don’t micromanage.
1.3 Identify behaviors to inform, interact with, and involve team members
20 Minutes
Individually:
- Identify one behavior for each of Inform, Interact, and Involve to improve.
- Record information in the workbook.
As a group:
- Discuss behaviors to improve for each of Inform, Interact, and Involve and record new ideas to incorporate into your leadership practice.
Download the Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Input
- 3i's Model
- Current leadership behaviors to improve
Output
- List of behaviors to better inform, interact, and involve team members
Materials
- Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Participants
- All managers with direct reports working virtually
Laying the foundation: Set clear expectations
Tasks
- What are the daily and weekly team activities? How do they affect one another?
Goals
- Clarify any adjustments to strategy based on the situation; clarify metrics.
Communication
- How often and when will you check in? What should they come to you for? What modalities will you use and when?
Roadblocks
- Involve your team in deciding how to handle roadblocks and challenges.
Speaker’s Notes:
Clear expectations are important in any environment, remote or not. But it is much harder to do in a remote environment. The barrier to seeking clarification is so much higher (For example, email vs. catching someone in hallway, or you can’t notice that a colleague is struggling without them asking).
Communication – This is one area where the importance actually changes in a remote context. We’ve been talking about a lot of practices that are the same in importance whether you’re in an office or remote, and maybe you just enact them differently. But clarity around communication processes is actually tremendously more important in a remote environment.
Adopt a five-step process to set specific and documented expectations
- Check in with how your team member is doing on a daily basis. Don’t forget to ask how they are doing personally.
- Follow up on previously set expectations. Ask how things are going. Discuss if priorities or expectations have changed and update expectations accordingly.
- Ask if they are experiencing any roadblocks and collaborate to find solutions.
- Provide feedback and recognition as appropriate.
- Document newly set expectations – either through a collaboration tool or through email.
Speaker’s Notes:
Suggested best practices: Hold daily team check-ins and hold separate individual check-ins. Increase frequency of these.
During Check-in
- Set up a running Teams chat for your team.
- This is your community. You must be the biggest cheerleader and keep the team feeling like they are contributing. Make sure everyone is involved.
- Ask: What are you planning to work on today? Are there any roadblocks I can help with? Technology working OK?
- Ask: What are you working on today? What will your momentum metrics be? What do you need from me?
- Ask: What went well? What went poorly? How can we improve?
After a Check-in
- Be accessible:
- Ensure your team knows the best way to get in touch with you.
- Email is not ideal for informal, frequent contact – use messaging instead.
- Be available:
- Keep a running conversation going in Teams.
- Respond in a timely manner; address issues quickly so that your team has what they need to succeed.
- Let your team know if you’ll be away/offline for longer than an hour during the workday and ask them to do the same (e.g. for an appointment).
- Help address roadblocks, answer questions, clarify priorities, etc.
Define communication requirements
- Set up an ongoing communication with your team.
- E.g. a running conversation on Slack or Teams
- Schedule daily virtual meetings and check-ins.
- This can help to maintain a sense of normalcy and conduct a pulse check on your team.
- Use video for important conversations.
- Video chat creates better rapport, shows body language, and lessens feelings of isolation, but it can be taxing.
- Set expectations about communication.
- Differentiate between day-to-day communication and updates on the state of events.
- Clearly communicate the collaboration toolkit.
- What do we have available? What is the purpose of each?
Speaker’s Notes:
With organizational expectations set, we need to establish team expectations around how we collaborate and communicate.
Today there is no lack of technology available to support our virtual communication. We can use the phone, conference calls, videoconferencing, Skype, instant messaging, [insert organization-specific technological tools.], etc.
However, it is important to have a common understanding of which tools are most appropriate when and for what.
What are some of the communication channel techniques you’ve found useful in your informal interactions with employees or that you’ve seen work well between employees?
[Have participants share any technological tools they find useful and why.]
Check in with your team on communication requirements
- Should we share our calendars, hours of availability, and/or IM status?
- How often should we meet as a team and one on one? Should we institute a time when we should not communicate virtually?
- Which communication channel should we use in what context? How should we decide which communication method to use?
- Should I share guidelines for email and meeting etiquette (or any other communication methods)?
- Should we establish a new team charter?
- What feedback does the team have regarding how we’ve been communicating?
Speaker’s Notes:
Whenever we interact, we make the following kinds of social exchanges. We exchange:
- Information: Data or opinions
- Emotions: Feelings and evaluations about the data or opinions
- Motivations: What we feel like doing in response to data or opinions
We need to make sure that these exchanges are happening as each team member intends. To do this, we have to be sensitive to what information is being conveyed, what emotions are involved in the interaction, and how we are motivating each other to act through the interaction. Every interaction will have intended and unintended effects on others. No one can pay attention to all of these aspects of communication all the time, but if we develop habits that are conducive to successful exchanges in all three areas, we can become more effective.
In addition to being mindful of the exchange in our communication, as managers it is critical to build trusting relationships and rapport with employees as we saw in the 3i's model. However, in virtual teams we cannot rely on running into someone in the kitchen or hallway to have an informal conversation. We need to be thoughtful and deliberate in our interactions with employees. We need to find alternative ways to build these relationships with and between employees that are both easy and accepted by ourselves and employees. Because of that, it is important to set communication norms and really understand each other’s preferences. For example:
- Timing of responses. Set the expectation that emails should be responded to within X hours/days unless otherwise noted in the actual email.
- When it’s appropriate to send an email vs. using instant messaging.
- A team charter – the team’s objectives, individual roles and responsibilities, and communication and collaboration guidelines.
1.4 Identify and share ways you prefer to communicate for different activities
20 Minutes
- Brainstorm and list the different types of exchanges you have with your virtual employees and they have with each other.
- List the various communication tools in use on your team.
- Assign a preferred communication method for each type of exchange
Download the Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Input
- Current types of exchanges on team
- Communication methods used
Output
- Defined ways to communicate for each communication method
Materials
- Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Participants
- All managers with direct reports working virtually
Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Section 2.1
Balancing wellbeing and performance in a virtual team context
The pandemic has taken a significant toll on employees’ mental wellbeing
44% of employees reported declined mental wellbeing since the start of the pandemic.
- 44% of those who work from home.
- 34% of those who have other work arrangements (i.e. onsite).
(Qualtrics, 2020)
"If one of our colleagues were to fall, break their leg, and get a cast, colleagues would probably rally around that person signing their cast. But, really, we don’t view the health of our brain the same as we do the health of our body."
– Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) Employee
Speaker’s Notes:
Despite being over two years into the pandemic, we are still seeing its effect on the physical and mental health of employees.
The mental health aspect has been often overlooked by organizations, but in order to have a safe, happy, and productive team, you need to give mental health the same level of focus as physical heath. This requires a change in mindset in order for you as a leader to support your team's mental wellbeing during the pandemic and beyond.
Employees are reporting several key mental wellbeing challenges
Stress: 67%
Employees report increasingly high levels of stress from the onset of COVID-19, stating that it has been the most stressful time in their careers.
(Qualtrics, 2020)
Anxiety: 57%
Similarly, employees’ anxiety levels have peaked because of the pandemic and the uncertainty it brings.
(Qualtrics, 2020)
Four main themes surrounding stress & anxiety
- Fear of contracting COVID-19
- Financial pressures
- Job security and uncertainty
- Loneliness caused by social isolation
Speaker’s Notes:
The stress and uncertainty about the future caused by the pandemic and its fallout are posing the biggest challenges to employees.
Organizations shutting down operations, moving to fully remote, or requiring some of their employees to be on site based on the current situation causes a lot of anxiety as employees are not able to plan for what is coming next.
Adding in the loss of social networks and in-person interactions exacerbates the problem employees are facing. As leaders, it is your job to understand and mitigate these challenges wherever possible.
Re-examine your workplace barriers to mental wellbeing
|
New Barriers |
Old Barriers |
|---|---|
|
|
Key considerations:
- Work Environment
- Accessibility of mental wellbeing programs and initiatives
- Organizational Culture
- Modeling of wellbeing
- Paid time off
- Discussions around mental wellbeing
- Total Rewards
- Benefits coverage
- Employee assistance programs (EAPs)
- Manager knowledge
Speaker’s Notes:
Organizational barriers to mental wellbeing are sadly not new. Workloads, stigma around mental health, lack of sick days, and limits to benefits for mental health supports were challenges before the pandemic. Adding in the new barriers can very easily result in a tipping point for many employees who are simply not equipped to deal with or supported in dealing with the added burden of remote work in a post-pandemic world.
To provide the needed support to your employees, it’s important to be mindful of the key considerations.
Holistic employee wellbeing has never been more critical than it is right now
Employee Wellbeing
Physical
The physical body; ensuring a person has the freedom, opportunities, and resources needed to sustainably maintain bodily health.
Mental
The psychological ability to cope with information, emotions, desires, and stressors (e.g. change, threats, etc.) in a healthy and balanced way. Essential for day-to-day living and functioning.
Social
The state of personal and professional relationships, including personal and community engagement. The capability for genuine, authentic, and mutually affirming interactions with others.
Financial
The state of a person’s finances; ensuring that a person feels capable to handle their financial situation and behaviors. The ability to live productively without the weight of financial stress.
Speaker’s Notes:
As a manager, you need to be mindful of all of these. Create an atmosphere where people are able to come to you for help if they are struggling in one of these areas. For example, some people might be more comfortable raising physical safety or comfort concerns (personal protective equipment, ergonomics) than concerns about mental health. Or they might feel like their feelings of loneliness are not appropriate to bring into their professional life.
Wellbeing is a delicate subject, and most of the time, people are reluctant to talk about it. It requires vulnerability. And here’s the thing about it: Your staff will not drive a change in your team around making these topics more acceptable. It has to be the manager. You have to be the one to not just tell but show them that it’s OK to talk about this
Encourage human-centered workplace behaviors
Promote empathy as a focus value
- Listen and show compassion.
- Allow room for emotions.
Encourage social connection
- Leverage networks.
- Infuse fun where possible.
- Encourage community and sense of joint purpose.
Cultivate a growth mindset
- Encourage mindfulness and resilience.
- Express gratitude.
Empower others
- Ask employees what they need and co-create solutions.
- Integrate needs of personal and family life with work life.
- Be clear on accountability.
Speaker’s Notes:
As a leader, your focus should be on encouraging the right behaviors on your team and in yourself.
Show empathy; allowing room for emotion and showing you are willing and able to listen goes a long way to establishing trust.
A growth mindset applies to resilience too. A person with a growth mindset is more likely to believe that even though they’re struggling now, they will get through it.
Infuse fun – schedule social check-ins. This is not wasted time, or time off work – it is an integral part of the workday. We have less of it now organically, so you must bring it back deliberately. Remember that theme? We are deliberately reinfusing important organic elements into the workday.
The last item, empowerment, is interesting – being clear on accountability. Have clear performance expectations. It might sound like telling people what to do would be disempowering, but it’s the opposite. By clarifying the goals of what they need to achieve, you empower them to invent their own “how,” because you and they are both sure they will arrive at the place that you agreed on. We will talk more about this in performance management.
Emphasize the importance of wellbeing by setting the tone for the team
Managers must…
- LEAD BY EXAMPLE
- Employees look to their managers for cues about how to react in a crisis. If the manager reacts with stress and fear, the team will follow.
- ENCOURAGE OPEN COMMUNICATION
- Frequent check-ins and transparent communication are essential during a time of crisis, especially when working remotely.
- ACKNOWLEDGE THE SITUATION
- Recognizing the stress that teams may be facing and expressing confidence in them goes a long way.
- PROMOTE WELLBEING
- Managers who take care of themselves can better support their teams and encourage them to practice good self-care too.
- REDUCE STIGMA
- Reducing stigma around mental health encourages people to come forward with their struggles and get the support they need.
Speaker’s Notes:
Emphasize the importance of wellbeing with what you do. If you do not model self-care behavior, people will follow what you do, not what you say.
Lead by example – Live the behaviors you want to see in your employees. If you show confidence, positivity, and resiliency, it will filter down to your team.
Encourage open communication – Have regular meetings where your team is able to set the agenda, or allow one-on-ones to be guided by the employee. Make sure these are scheduled and keep them a priority.
Acknowledge the situation – Pretending things are normal doesn’t help the situation. Talk about the stress that the team is facing and express confidence that you will get through it together.
Promote wellbeing – Take time off, don’t work when you’re sick, and you will be better able to support your team!
Reduce stigma – Call it out when you see it and be sure to remind people of and provide access to any supports that the organization has.
Conduct dedicated conversations around wellbeing
- Check in with how each team member is doing frequently and ask how they are doing personally.
- Discuss how things are going. Ask: “How is your work situation working out for you so far? Do you feel supported? How are you taking care of yourself in these circumstances?”
- Ask if there are any stressors or roadblocks that they have experienced and collaborate to find solutions.
- Provide reassurance of your support and confidence in them.
- Document the plan for managing stressors and roadblocks – either through a collaboration tool or through email.
Speaker’s Notes:
Going back to the idea of a growth mindset – this may be uncomfortable for you as a manager. So here’s a step-by-step guide that over time you can morph into your own style.
With your team – be prepared to share first and to show it is OK to be vulnerable and address wellbeing seriously.
- Make sure you make time for the personal. Ask about their lives and show compassion.
- Give opportunities for them to bring up things that might stay hidden otherwise. Ask questions that show you care.
- Help identify areas they are struggling with and work with them to move past those areas.
- Make sure they feel supported in what they are going through and reassured of their place on the team.
- Roll wellbeing into your planning process. This signals to team that you see wellbeing as important, not just a checklist to cover during a team meeting, and are ready to follow through on it.
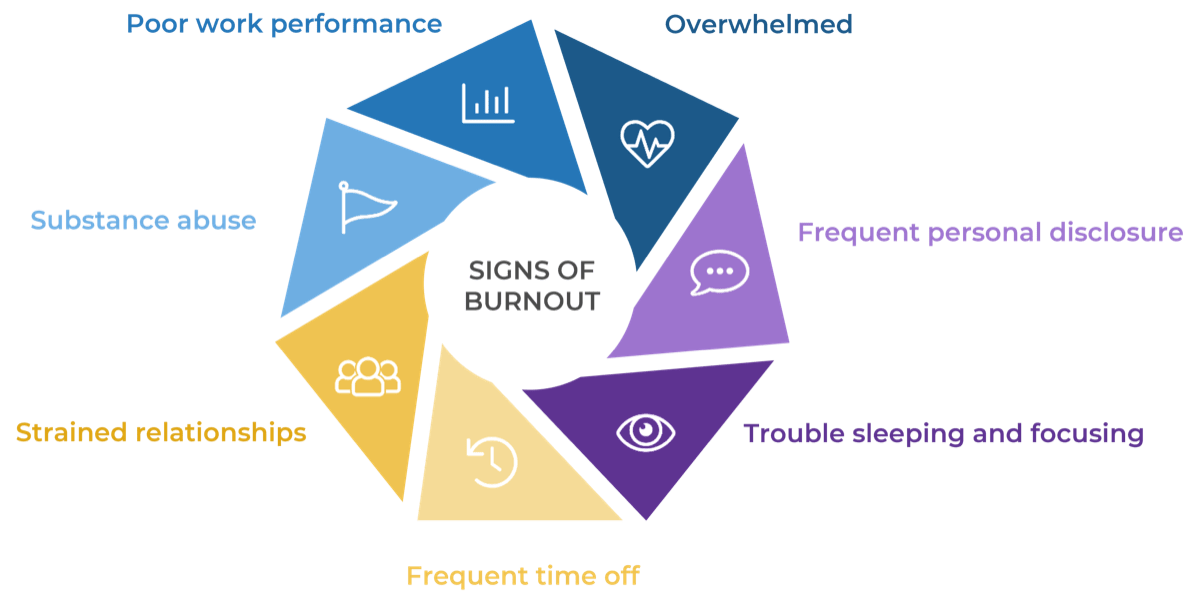
Recognize when professional help is needed
Speaker’s Notes:
As a leader, it is important to be on the lookout for warning signs of burnout and know when to step in and direct individuals to professional help.
Poor work performance – They struggle to maintain work performance, even after you’ve worked with them to create coping strategies.
Overwhelmed – They repeatedly tell you that they feel overwhelmed, very stressed, or physically unwell.
Frequent personal disclosure – They want to discuss their personal struggles at length on a regular basis.
Trouble sleeping and focusing – They tell you that they are not sleeping properly and are unable to focus on work.
Frequent time off – They feel the need to take time off more frequently.
Strained relationships – They have difficulty communicating effectively with coworkers; relationships are strained.
Substance abuse – They show signs of substance abuse (e.g. drunk/high while working, social media posts about drinking during the day).
Keeping an eye out for these signs and being able to step in before they become unmanageable can mean the difference between keeping and losing an employee experiencing burnout.
Remember: Managers also need support
- Added burden
- Lead by example
- Self-care
Speaker’s Notes:
If you’ve got managers under you, be mindful of their unique stressors. Don’t forget to check in with them, too.
If you are a manager, remember to take care of yourself and check in with your own manager about your own wellbeing.
2.1 Balance wellbeing and performance in a virtual team context
30 Minutes
- Brainstorm and list current practices and challenges connected to wellbeing on your teams.
- Choose one or two wellbeing challenges that are most relevant for your team.
- Discuss as a group and identify one solution for each challenge that you can put into action with your own virtual team. Document this under “Action plan to move forward” on the workbook slide “2.1 Balancing wellbeing and performance in a virtual team context.”
Download the Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Input
- Current practices and challenges connected to wellbeing
Output
- Action plan for each challenge listed
Materials
- Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Participants
- All managers with direct reports working virtually
Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Section 2.2
Managing performance in a virtual team context
Virtual employees are craving more meaningful interactions with their managers
A survey indicated that, overall, remote employees showed less satisfaction with manager interactions compared to other non-remote employees.
- 16% less likely to strongly agree their manager involves them in setting goals at work.
- 28% less likely to strongly agree they continually work with their manager to clarify work priorities.
- 29% less likely to strongly agree they have reviewed their greatest successes with their manager in the last six months.
- 30% less likely to strongly agree they have talked with their manager about progress toward goals in the last six months.
Speaker’s Notes:
In many cases, we have put people into virtual roles because they are self-directed and self-motivated workers who can thrive with the kind of autonomy and flexibility that comes with virtual work. As managers, we should expect many of these workers to be proactively interested in how they are performing and in developing their careers.
It would be a mistake to take a hands-off approach when managing virtual workers. A recent survey indicated that, overall, remote employees showed less satisfaction with manager interactions compared to other non-remote employees. It was also one of the aspects of their work experience they were least satisfied with overall (Gallup, State of the American Workplace, 2017). Simply put, virtual employees are craving more meaningful conversations with their managers.
While conversations about performance and development are important for all employees (virtual or non-virtual), managers of remote teams can have a significant positive impact on their virtual employees’ experience and engagement at work by making efforts to improve their involvement and support in these areas.
During this module we will work together to identify ways that each of us can improve how we manage the performance of our virtual employees. At the end of the module everyone will create an action plan that they can put in place with their own teams. In the next module, we go through a similar set of activities to create an action plan for our interactions with employees about their development.
Building blocks of performance management
-
Goal Setting
-
Setting Expectations
-
Measuring Progress
-
Feedback & Coaching
Speaker’s Notes:
[Include a visualization of your existing performance management process in the slide. Walk the participants through the process to remind them of what is expected. While the managers participating in the training should know this, there may be different understandings of it, or it might just be the case that it’s been a while since people looked at the official process. The intention here is merely to ensure everyone is on the same page for the purposes of the activities that follow.]
Now that we’ve reviewed performance management at a high level, let’s dive into what is currently happening with the performance management of virtual teams.
I know that you have some fairly extensive material at your organization around how to manage performance. This is fantastic. And we’re going to focus mainly on how things change in a virtual context.
When measuring progress, how do you as a manager make sure that you are comfortable not seeing your team physically at their desks? This is the biggest challenge for remote managers.
2.2 Share current performance management practices for virtual teams
30 Minutes
- Brainstorm and list current high-level performance management practices connected to each building block. Record in your workbook.
- Discuss current challenges connected to implementing the building blocks with virtual employees.
Download the Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Input
- Current performance management practices
- Challenges surrounding performance management
Output
- Current state of virtual performance management defined
Materials
- Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Participants
- All managers with direct reports working virtually
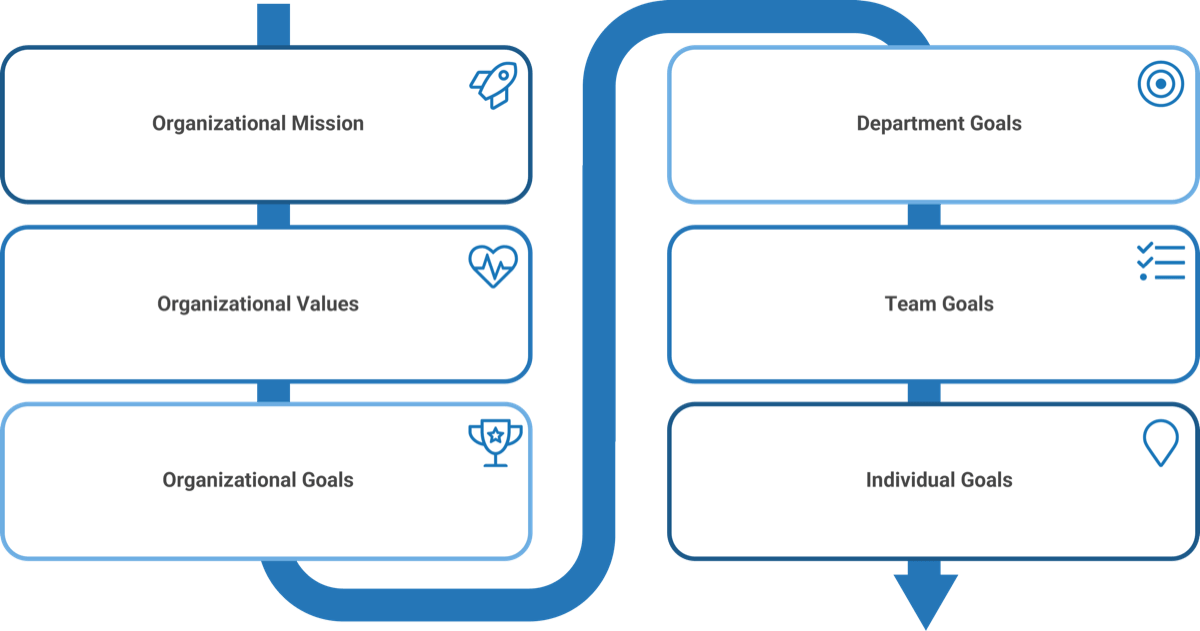
Communicate the “why”: Cascade organizational goals
Speaker’s Notes:
When assisting your employees with their goals, think about the organization’s overall mission and goals to help you determine team and individual goals.
- Organizational goals: Employee goals should align with organizational goals. Goals may cascade down through the organization.
- Department or team goals: Create a clear strategy based on high-level goals for the year so employees can link short-term goals to the larger picture.
- Individual goals: Employees should draw on their individual development plan to help set performance goals.
Sometimes it’s difficult to get employees thinking about goals and they need assistance from managers. It’s also important to be clear on team goals to help guide employees in setting individual ones.
The basic idea is to show people how their individual day-to-day work contributes to the overall success of the organization. It gives them a sense of purpose and a rationale, which translates to motivation. And also helps them problem solve with more autonomy.
You’re giving people a sense of the importance of their own contribution.
How to set clear expectations for job performance
Ensure employees have a clear understanding of what’s expected for their role:
- Review their metrics so they understand how they’re being evaluated.
- Outline daily, weekly, monthly, and quarterly goals.
- If needed, help them plan when and how each part of their job should be done and what to prioritize.
- Ask them to come to you early if they experience a roadblock so that you can help rather than having them flounder on their own.
- Document instances where employees aren’t meeting role or performance expectations.
Speaker’s Notes:
Tailor performance goals to address any root causes of poor performance.
For example:
- If personal factors are getting in the way, work with the employee (and HR if necessary) to create a strategy to address any impediments to performing in the role.
Tips for managing performance remotely
- Reflect on one key question: What needs to happen for my direct reports to continue their work while working remotely?
- Manage for results – not employee visibility at the office.
- Use metrics to measure performance. If you don’t have any, define tasks and deliverables as clearly as possible and conduct regular check-ins.
- Work with the employee to set goals and metrics to measure progress.
Focus on results: Be flexible about how and when work gets done, as long as team members are hitting their targets.
- For example, if they have childcare duties from 3 to 5pm during school closures and want to work later in the evening to make up the time, that’s fine – as long as the work gets done.
- Set clear expectations about which work must be done during normal work hours (e.g. attend team meetings, client calls) and which can be done at other hours.
- Team members must arrange with you any nonstandard working hours before they start using an altered schedule. It is your responsibility to keep track of hours and any alternate arrangements.
- Don’t make team members feel constantly monitored (i.e. “Where were you from 10 to 11am?”); trust them until you have reason not to.
Encourage your team members to unplug: If they’re sending you emails late at night and they haven’t made an alternate work hours agreement with you, encourage them to take time away from work.
- It’s harder to unplug when working at home, and everyone needs a break to stay productive.
Avoid micromanagement with holistic performance measures
Quality
How well tasks are accomplished
Behavior
Related to specific employee actions, skills, or attitudes
Quantity
How much work gets done
Holistic measures demonstrate all the components required for optimal performance. This is the biggest driver in having comfort as a manager of a remote team and avoiding micromanagement. Typically these are set at the organizational level. You may need to adjust for individual roles, etc.
Speaker's Notes:
Metrics come in different types. One way to ensure your metrics capture the full picture is to use a mix of different kinds of metrics.
Some metrics are quantitative: they describe quantifiable or numerical aspects of the goal. This includes timeliness. On the other hand, qualitative metrics have to do with the final outcome or product. And behavioral metrics have to do with employees' actions, skills, or attitudes. Using different kinds of metrics together helps you set holistic measures, which capture all the components of optimal performance toward your goal and prevent gaming the system.
Let's take an example:
A courier might have an objective to do a good job delivering packages. An example of a quantitative measure might be that the courier is required to deliver X number of packages per day on time. The accompanying metrics would be the number of packages delivered per day and the ratio of packages delivered on time vs. late.
Can you see a problem if we use only these quantitative measures to evaluate the courier's performance?
Wait to see if anyone volunteers an answer. Discuss suggestions.
That's right, if the courier's only goal is to deliver more packages, they might start to rush, may ruin the packages, and may offer poor customer service. We can help to guard against this by implementing qualitative and behavioral measures as well. For example, a qualitative measure might be that the courier is required to deliver the packages in mint condition. And the metric would be the number of customer complaints about damaged packages or ratings on a satisfaction survey related to package condition.
For the behavioral aspect, the courier might be required to provide customer-centric service with a positive attitude. The metrics could be ratings on customer satisfaction surveys related to the courier's demeanor or observations by the manager.
Managing poor performance virtually: Look for key signs
It’s crucial to acknowledge that an employee might have an “off week” or need time to balance work and life – things that can be addressed with performance management (PM) techniques. Managers should move into the process for performance improvement when:
- Performance fluctuates frequently or significantly.
- Performance has dropped for an extended period of time.
- Expectations are consistently not being met.
Key signs to look for:
- PM data/performance-related assessments
- Continual absences
- Decreased quality or quantity of output
- Frequent excuses (e.g. repeated internet outages)
- Lack of effort or follow-through
- Missed deadlines
- Poor communication or lack of responsiveness
- Failure to improve
Speaker’s notes:
- Let’s talk more about identifying low performance.
- Everybody has off days or weeks. And what if they are new to the role or new to working remotely? Their performance may be low because they need time to adjust. These sort of situations should be managed, but they don’t require moving into the process for performance improvement.
- When managing employees who are remote or working in a hybrid situation, it is important to be alert to these signs and check in with your employees on a regular basis. Aim to identify and work with employees on addressing performance issues as they arise rather than waiting until it’s too late. Depending on your availability, the needs of the employee, and the complexity of their role, check-ins could occur daily, weekly, and/or monthly. As I mentioned, for remote employees, it’s often better to check-in more frequently but for a shorter period of time.
- You want to be present in their work life and available to help them manage through roadblocks and stay on track, but try to avoid over-monitoring employees. Micromanaging can impact the manager-employee relationship and lead to the employee feeling that there is a lack of trust. Remember, the employee needs to be responsible for their own performance and improvement.
- Check-ins should not just be about the work either. Take some time to check in personally. This is particularly important when managing remotely. It enables you to build a personal relationship with the employee and also keeps you aware if there are other personal issues at play that are impacting their work.
- So, how do you know what does require performance improvement? There are three key things that you should look for that are clear signals that performance improvement is necessary:
- Their performance is fluctuating frequently or significantly.
- Their performance has dropped for an extended period of time.
- Expectations are consistently not being met.
- What do you think are some key signs to look for that indicate a performance issue is occurring?
Managing poor performance virtually: Conducting remote performance conversations
Video calling
Always use video calls instead of phone calls when possible so that you don’t lose physical cues and body language.
Meeting invitations
Adding HR/your leader to a meeting invite about performance may cause undue stress. Think through who needs to participate and whether they need to be included in the invite itself.
Communication
Ensure there are no misunderstandings by setting context for each discussion and having the employee reiterate the takeaways back to you.
Focus on behavior
Don’t assume the intent behind the behavior(s) being discussed. Instead, just focus on the behavior itself.
Policies
Be sure to adhere to any relevant HR policies and support systems. Working with HR throughout the process will ensure none are overlooked.
Speaker’s notes:
There are a few best practices you should follow when having performance conversations:
- First, if you are in a different work environment than your employee, always use video calls instead of phone calls whenever possible so that you don’t miss out on physical cues and body language. If videoconferencing isn’t the norm, encourage them to turn on their video. Be empathic that it can feel awkward but explain the benefits, and you will both have an easier time communicating and understanding each other.
- As I’ve mentioned, be considerate of the environment they are in. If they are in the office and you are working remotely, be sure to book a private meeting room for them to go to for the conversation. If they are working from home, be sure to check that they are prepared and able to focus on the conversation.
- Next, carefully consider who you are adding to the meeting invite and whether it’s necessary for them to be there. Adding HR or your leader to a meeting invite may cause undue stress for the employee.
- Consider the timing of the invite. Don’t send it out weeks in advance. When a performance problem exists, you’ll want to address it as soon as possible. A day or two of notice would be an ideal approach because it gives them a heads up but will not cause them extended stress or worrying.
- Be considerate about the timing of the meeting and what else they may have scheduled. For example, a Friday afternoon before they are heading off on vacation or right before they are leading an important client call would not be appropriate timing.
- As we just mentioned clear communication is critical. Ensure there are no misunderstandings by setting context for each discussion and having the employee reiterate takeaways back to you.
- Focus on the behavior and don’t assume their intent. It can be tempting to say, “I know you didn’t mean to miss the deadline,” but you don’t know what they intended. Often people are not aware of the impact their behavior can have on others.
- Lastly, be sure to adhere to any relevant HR policies and support systems. Working with HR throughout the process will ensure nothing is overlooked.
2.3 Identify challenges of current practices and propose solutions
30 Minutes
- Select one or two challenges from the previous activity.
- Identify one solution for each challenge that you can put into action with your own virtual team. Document in the workbook.
Download the Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Input
- Current performance management practices
- Challenges surrounding performance management
Output
- Action plan to move forward
Materials
- Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Participants
- All managers with direct reports working virtually
Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Optional Section
Employee development in a virtual team setting
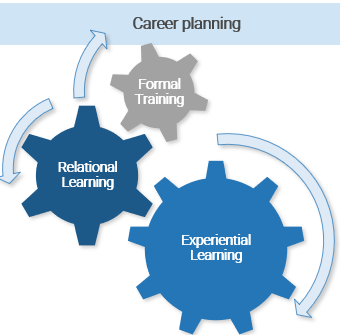
There are three main development approaches for both colocated and virtual employees
Speaker’s Notes:
As we have seen, our virtual employees crave more meaningful interactions with their managers. In addition to performance conversations, managers should also be having regular discussions with their employees about their employee development plans. One key component of these discussions is career planning. Whether you are thinking shorter term – how to become better at their current role – or longer term – how to advance beyond their current role – discussions about employee development are a great way to engage employees. Employees are ultimately responsible for creating and executing their own development plans, but managers are responsible for making sure that employees have thought through these plans and helping employees identify opportunities for executing those plans.
To help us think about our own employee development practices, identify challenges they pose when working with virtual employees, and create solutions to these challenges, it is useful to think about employee development opportunities according to three types:
- The first kind of development opportunity is formal training. Formal training is organized and has a clearly defined curriculum and desired outcome. It usually takes the form of a group training session (like this one) or training videos or materials that employees can watch individually and on their own time. These opportunities usually end with a test or assignment that can be used to evaluate the degree to which the participant achieved the desired learning outcomes.
- The second kind of development opportunity is relational learning. Perhaps the most common form of this type of learning is coaching or mentoring. By establishing a long-term work relationship, checking in with employees about their daily work and development goals, and sharing their own experiences and knowledge, mentors help employees reflect and draw out learning from everyday, on-the-job development activities. Other examples include a peer support group or communities of practice. In these group settings peers share best practices and work together to overcome challenges.
- The third kind of development opportunity is experiential learning. This kind of opportunity provides employees the chance to work on real work problems, and the output of the development work can directly benefit the organization. Most people learn best by doing. On-the-job experiences that are challenging or new can force people to use and develop new skills and knowledge based on what worked effectively and what failed. Examples of experiential learning are on-the-job learning for new hires, stretch assignments, or special projects that take the employee beyond their daily routine and allow them to try new activities and develop competencies that they would not have the chance to develop as part of their regular job.
According to McLean & Company, organizations should use the “70-20-10” rule as a rough guideline when working with employees to create their development plans: 10% of the plan should be dedicated to formal training opportunities, 20% to relational learning, and 70% to experiential learning. Managers should work with employees to identify their performance and career goals, ensure that their development plans are aligned with these goals, and include an appropriate mixture of all three kinds of development opportunities.
To help identify challenges and solutions, think about how virtual work arrangements will impact the employee’s ability to leverage each type of opportunity at our organization.
Here are some examples that can help us start thinking about the kinds of challenges virtual employees on our team face:
Career Planning
- One challenge can be identifying a career path that is consistent with working virtually. If switching from a virtual arrangement to an onsite arrangement is not a viable option for an employee, some career paths may not feasibly be open to them (at least as the company is currently organized). For example, if an employee would eventually like to be promoted to a senior leadership role in their business function but all senior leaders are required to work onsite at corporate headquarters, the employee will need to consider whether such a move is possible for them. In some cases employees may be willing to do this, but in others they may not. The important thing is to have these conversations with virtual employees and avoid the assumption that all career paths can be done virtually, since that might not be the case
Formal Training
- This is probably the least problematic form of employee development for virtual employees. In many cases this kind of training is scheduled well in advance, so virtual employees may be able to join non-virtual employees in person for some group training. When this is not possible (due to distance, budget, or time zone), many forms of group training can be recorded and watched by virtual employees later. Training videos and training materials can also easily be shared with virtual employees using existing collaboration software.
Relational Learning
- One major challenge here is developing a mentoring relationship virtually. As we discussed in the module on performance management, developing relationships virtually can be challenging because people cannot rely upon the kind of informal and spontaneous interactions that occur when people are located in the same office. Mentors and mentees will have to put in more effort and planning to get to know each other and they will have to schedule frequent check-ins so that employees can reflect upon their progress and experience (with the help of their mentors) more often.
- Time zones and technology may pose potential barriers for certain candidates to be mentors. In some cases, employees that are best qualified to be mentors may not be as comfortable with collaborative software as other mentors or their mentees. If there are large time zone differences, some people who would otherwise be interested in acting as a mentor may be dissuaded. Managers need to take this into consideration if they are connecting employees with mentors or if they are thinking of taking on the mentor role themselves.
Experiential Learning
- Virtual employees risk being overlooked for special projects due to the “out of sight, out of mind” bias: When special projects come up, the temptation is to look around the room and see who is the best fit. The problem is, however, that in some cases the highest performers or best fit may not physically be in the room. In these cases it is important for managers to take on an advocate role for their employees and remind other managers that they have good virtual employees on their team that should be included or contacted. It is also important for managers to keep their team informed about these opportunities as often as possible.
- Sometimes certain projects or certain kinds of work just cannot be done virtually in a company for a variety of reasons. The experiential learning opportunities will not be open to virtual employees. If such opportunities are open to the majority of other workers in this role (potentially putting virtual employees’ career development at a disadvantage relative to their peers), managers should work with their virtual employees to identify alternative experiences. Managers may also want to consider advocating for more or for higher quality experiential learning opportunities at the organization.
Now that we have considered some general examples of challenges and solutions, let’s look at our own employee development practices and think about the practical steps we can take as managers to improve employee development for our virtual employees.
Employee development basics
- Career planning & performance improvement
- Formal training
- Relational learning
- Experiential learning
Speaker’s Notes:
[Customize this slide according to your organization’s own policies and processes for employee development. Provide useful images that outline this on the slide, and in these notes describe the processes/policies that are in place. Note: In some cases policies or processes may not be designed with virtual employees or virtual teams in mind. That is okay for the purposes of this training module. In the following activities participants will discuss how they apply these policies and processes with their virtual teams. If your organization is interested in adapting its policies/processes to better support virtual workers, it may be useful to record those conversations to supplement existing policies later.]
Now that we have considered some general examples of challenges and solutions, let’s look at our own employee development practices and think about the practical steps we can take as managers to improve employee development for our virtual employees.
2.4 Share current practices for developing employees on a virtual team
30 Minutes
- Brainstorm and list current high-level employee development practices. Record in your workbook.
- Discuss current challenges connected to developing virtual employees. Record in your workbook.
- Identify one solution for each challenge that you can put into action with your own virtual team.
- Discuss as a group.
Download the Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Input
- Current employee development practices
- Challenges surrounding employee development
Output
- Action plan to move forward
Materials
- Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Participants
- All managers with direct reports working virtually
Refine Action Plans
2.5 Refine your action plan and commit to implementing it
30 Minutes
- Review your action plans for consistency and overlap. Highlight any parts you may struggle to complete.
- Meeting with your group, summarize your plans to each other. Provide feedback and discuss each other’s action plans.
- Discuss how you can hold each other accountable.
Download the Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Input
- Action items from previous activities.
Output
- Action plan to move forward
Materials
- Workbook: Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Participants
- All managers with direct reports working virtually
Summary of Accomplishment
- We do not need to go out and learn a new set of manager responsibilities to better manage our virtual teams; rather, we have to “dial up” certain responsibilities we already have or adjust certain approaches that we already take.
- It is important to set clear expectations. While managers are ultimately responsible for making sure expectations are set and are clearly communicated, they are not the only ones with responsibilities. Employees and managers need to work together to overcome the challenges that virtual work involves.
- Virtual employees crave meaningful interactions with their managers and team. Managers must take charge in fostering an atmosphere of openness around wellbeing and establish effective performance management strategies. By being proactive with our virtual teams’ wellness and mindful of our performance management habits, we can take significant steps toward keeping these employees engaged and productive.
- Effective management in virtual contexts requires being more deliberate than is typical in non-virtual contexts. By working as a group to identify challenges and propose solutions, we have helped each other create action plans that we can use going forward to continually improve our management practices.
If you would like additional support, have our analysts guide you through an info-tech workshop or guided implementation.
Contact your account representative for more information
workshops@infotech.com
1-888-670-8889
Speaker’s Notes:
First, let’s take a moment to summarize the key things we have learned today:
- We do not need to go out and learn a new set of manager competencies to better manage our virtual teams; rather, we have to “dial up” certain competencies we already have or adjust certain approaches that we already take. In many cases we just need to be more aware of the challenges that virtual communication poses and be more planful in our approaches.
- It is important to set clear expectations. While managers are ultimately responsible for making sure expectations are set and clearly communicated, they are not the only ones with responsibilities. Employees and managers need to work together to overcome the challenges that virtual work involves. Making sure that teams have meaningful conversations about expectations, come to a shared understanding of them, and record them will create a firm foundation for all other interactions on the virtual team.
- Virtual employees crave meaningful interactions with their managers related to performance and employee development. By creating action plans for improving these kinds of interactions with our teams, we can take significant steps toward keeping these employees engaged and productive.
- Effective performance management and employee development in virtual contexts require more planfulness than is required in non-virtual contexts. By working as a group to identify challenges and propose solutions, we have helped each other create action plans that we can use going forward to continually improve our management practices.
Is there anything that anyone has learned that is not on this list and that they would like to share with the group?
Finally, were there any challenges identified today that were not addressed?
[Note to facilitator: Take note of any challenges not addressed and commit to getting back to the participants with some suggested solutions.]
Additional resources
Manager Training: Lead Through Change
Train managers to navigate the interpersonal challenges associated with change management and develop their communication and leadership skills. Upload this LMS module into your learning management system to enable online training.
Manager Training: Build a Better Manager: Manage Your People
Management skills training is needed, but organizations are struggling to provide training that makes a long-term difference in the skills managers use in their day to day.
Many training programs are ineffective because they offer the wrong content, deliver it in a way that is not memorable, and are not aligned with the IT department’s business objectives.
Blueprint: Manage Poor Performance While Working From Home
Assess and improve remote work performance with our ready-to-use tools.
Works Cited
April, Richard. “10 KPIs Every Sales Manager Should Measure in 2019.” HubSpot, 24 June 2019. Web.
Banerjea, Peter. “5 Powerful Strategies for Managing a Remote Sales Team.” Badger - Maps for field sales, n.d. Web.
Bibby, Adrianne. “5 Employers’ Awesome Quotes about Work Flexibility.” FlexJobs, 9 January 2017. Web.
Brogie, Frank. “The 14 KPIs every field sales rep should strive to improve.” Repsly, 2018. Web.
Dunn, Julie. “5 smart tips for leading field sales teams.” LevelEleven, March 2015. Web.
Edinger, Scott. “How great sales leaders coach.” Forbes, 2013. Web.
“Employee Outlook: Employee Views on Working Life.” CIPD, April 2016. Web.
Hall, Becki. “The 5 biggest challenges facing remote workers (and how to solve them).” interact, 7 July 2017. Web.
Hofstede, Geert. “National Cultural Dimensions.” Hofstede Insights, 2012. Web.
“Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990-2014 (EPA 430-R-16-002).” Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), 15 April 2016.
“Latest Telecommuting Statistics.” Global Workplace Analytics, June 2021. Web.
Knight, Rebecca. “How to manage remote direct reports.” Harvard Business Review, 2015. Web.
“Rewards and Recognition: 5 ways to show remote worker appreciation.” FurstPerson, 2019. Web.
Palay, Jonathan. "How to build your sales management cadence." CommercialTribe, 22 March 2018. Web.
“Sales Activity Management Matrix.” Asian Sales Guru, 2019. Web.
Smith, Simone. “9 Things to Consider When Recognizing Remote Employees.” hppy, 2018. Web.
“State of Remote Work 2017.” OWL Labs, 2021. Web.
“State of the American Workplace.” Gallup, 2017. Web.
“Telework Savings Potential.” Global Workplace Analytics, June 2021. Web.
“The Future of Jobs Employment Trends.” World Economic Forum, 2016. Web.
“The other COVID-19 crisis: Mental health.” Qualtrics, 14 April 2020. Web.
Thompson, Dan. “The straightforward truth about effective sales leadership.” Sales Hacker, 2017. Web.
Tsipursky, Gleb. “Remote Work Can Be Better for Innovation Than In-Person Meetings.” Scientific American, 14 Oct. 2021. Web.
Walsh, Kim. “New sales manager? Follow this guide to crush your first quarter.” HubSpot, May 2019. Web.
“What Leaders Need to Know about Remote Workers: Surprising Differences in Workplace Happiness and Relationships.” TINYpulse, 2016.
Zenger, Jack, and Joe Folkman. “Feedback: The Leadership Conundrum.” Talent Quarterly: The Feedback Issue, 2015.
Contributors
Anonymous CAMH Employee
Buying Options
Equip Managers to Effectively Manage Virtual Teams
Client rating
Cost Savings
Days Saved
IT Risk Management · IT Leadership & Strategy implementation · Operational Management · Service Delivery · Organizational Management · Process Improvements · ITIL, CORM, Agile · Cost Control · Business Process Analysis · Technology Development · Project Implementation · International Coordination · In & Outsourcing · Customer Care · Multilingual: Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese · Entrepreneur
Tymans Group is a brand by Gert Taeymans BV
Gert Taeymans bv
Europe: Koning Albertstraat 136, 2070 Burcht, Belgium — VAT No: BE0685.974.694 — phone: +32 (0) 468.142.754
USA: 4023 KENNETT PIKE, SUITE 751, GREENVILLE, DE 19807 — Phone: 1-917-473-8669
Copyright 2017-2022 Gert Taeymans BV