Effective IT Communications

IT communications are often considered ineffective. This is demonstrated by:
- A lack of inclusion or time to present in board meetings.
- Confusion around IT priorities and how they align to organizational objectives.
- Segregating IT from the rest of the organization.
- The inability to secure the necessary funding for IT-led initiatives.
- IT employees not feeling supported or engaged.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- No one is born a good communicator. Every IT employee needs to spend the time and effort to grow their communication skills; with constant change and worsening IT crises, IT cannot afford to communicate poorly anymore.
- The skills needed to communicate effectively as a front=line employee or CIO are the same. It is important to begin the development of these skills from the beginning of one's career.
- Time is a non-renewable resource. Any communication needs to be considered valuable and engaging by the audience or they will be unforgiving.
Impact and Result
Communications is a responsibility of all members of IT. This is demonstrated through:
- Engaging in two-way communications that are continuous and evolving.
- Establishing a communications strategy – and following the plan.
- Increasing the skills of all IT employees when it comes to communications.
- Identifying audiences and their preferred means of communication.
Effective IT Communications Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Effective IT Communications Capstone Deck – A resource center to ensure you never start communications from a blank page again.
This capstone blueprint highlights the components, best practices, and importance of good communication for all IT employees.
- Effective IT Communications Storyboard
2. IT Townhall Template – A ready-to-use template to help you engage with IT employees and ensure consistent access to information.
IT town halls must deliver value to employees, or they will withdraw and miss key messages. To engage employees, use well-crafted communications in an event that includes crowd-sourced contents, peer involvement, recognition, significant Q&A time allotment, organizational discussions, and goal alignment.
- IT Townhall Template
3. IT Year in Review Template – A ready-to-use template to help communicate IT successes and future objectives.
This template provides a framework to build your own IT Year In Review presentation. An IT Year In Review presentation typically covers the major accomplishments, challenges, and initiatives of an organization's information technology (IT) department over the past year.
- IT Year in Review Template
Infographic

Further reading
Effective IT Communications
Empower IT employees to communicate well with any stakeholder across the organization.
Analyst perspective
There has never been an expectation for IT to communicate well.

Brittany Lutes
Research Director
Info-Tech Research Group

Diana MacPherson
Senior Research Analyst
Info-Tech Research Group
IT rarely engages in proper communications. We speak at, inform, or tell our audience what we believe to be important. But true communications seldom take place.
Communications only occur when channels are created to ensure the continuous opportunity to obtain two-way feedback. It is a skill that is developed over time, with no individual having an innate ability to be better at communications. Each person in IT needs to work toward developing their personal communications style. The problem is we rarely invest in development or training related to communications. Information and technology fields spend time and money developing hard skills within IT, not soft ones.
The benefits associated with communications are immense: higher business satisfaction, funding for IT initiatives, increased employee engagement, better IT to business alignment, and the general ability to form ongoing partnerships with stakeholders. So, for IT departments looking to obtain these benefits through true communications, develop the necessary skills.
Executive summary
| Your Challenge | Common Obstacles | Info-Tech’s Approach |
IT communications are often considered ineffective. This is demonstrated by:
|
Frequently, these barriers have prevented IT communications from being effective:
|
Communications is a responsibility of all members of IT. This is demonstrated through:
|
Info-Tech Insight
No one is born a good communicator. Every IT employee needs to spend the time and effort to grow their communication skills as constant change and worsening IT crises mean that IT cannot afford to communicate poorly anymore.
Your challenge
Overall satisfaction with IT is correlated to satisfaction with IT communications
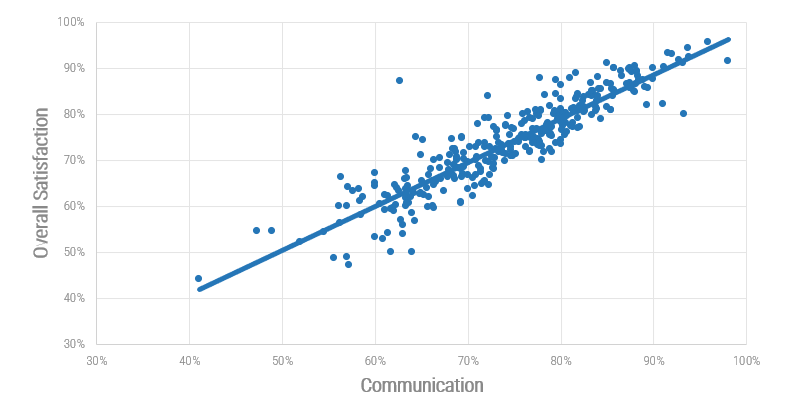
The bottom line? For every 10% increase in communications there 8.6% increase in overall IT satisfaction. Therefore, when IT communicates with the organization, stakeholders are more likely to be satisfied with IT overall.
Info-Tech Diagnostic Programs, N=330 organizations
IT struggles to communicate effectively with the organization:
- CIOs are given minimal time to present to the board or executive leaders about IT’s value and alignment to business goals.
- IT initiatives are considered complicated and confusing.
- The frequency and impact of IT crises are under planned for, making communications more difficult during a major incident.
- IT managers do not have the skills to communicate effectively with their team.
- IT employees do not have the skills to communicate effectively with one another and end users.
Common obstacles
IT is prevented from communicating effectively due to these barriers:
- Difficulty assessing the needs of the audience to inform the language and means of communication that should be used.
- Using technical jargon rather than translating the communication into commonly understood terms.
- Not receiving the training required to develop communication skills across IT employees.
- Frequently speak at organization stakeholders rather than engaging through dialogue.
- Beginning many communications from a blank page, especially crisis communications.
- Difficulty presenting complex concepts in a short time to an audience in a digestible and concise manner without diluting the point.
Effective IT communications are rare:
53% of CXOs believe poor communication between business and IT is a barrier to innovation.
Source: Info-Tech CEO-CIO Alignment Survey, 2022
“69% of those in management positions don’t feel comfortable even communicating with their staff.”
Source: TeamStage, 2022
Info-Tech’s approach
Effective communications is not a broadcast but a dialogue between communicator and audience in a continuous feedback loop.
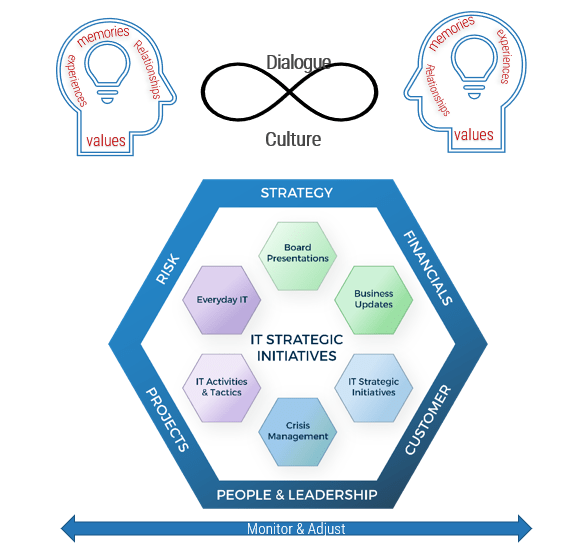
The Info-Tech difference:
- Always treat every communication as a dialogue, enabling the receiver of the message to raise questions, concerns, or ideas.
- Different audiences will require different communications. Be sure to cater the communication to the needs of the receiver(s).
- Never assume the communication was effective. Create measures and adjust the communications to get the desired outcome.
Common IT communications
And the less common but still important communications
Communicating Up to Board or Executives
- Board Presentations
- Executive Leadership Committee Meetings
- Technology Updates
- Budget Updates
- Risk Updates
- Year in Review
Communicating Across the Organization
- Townhalls – external to IT
- Year in Review
- Crisis Email
- Intranet Communication
- Customer/Constituent Requests for Information
- Product Launches
- Watercooler Chat
Communicating Within IT
- Townhalls – internal to IT
- Employee 1:1s
- Team Meetings
- Project Updates
- Project Collaboration Sessions
- Year in Review
- All-Hands Meeting
- Employee Interview
- Onboarding Documentation
- Vendor Negotiation Meetings
- Vendor Product Meetings
- Watercooler Chat
Insight Summary
Overarching insight
IT cannot afford to communicate poorly given the overwhelming impact and frequency of change related to technology. Learn to communicate well or get out of the way of someone who can.
| Insight 1: The skills needed to communicate effectively as a frontline employee or a CIO are the same. It’s important to begin the development of these skills from the beginning of one’s career. |
| Insight 2: Time is a non-renewable resource. Any communication needs to be considered valuable and engaging by the audience or they will be unforgiving. |
| Insight 3: Don’t make data your star. It is a supporting character. People can argue about the collection methods or interpretation of the data, but they cannot argue the story you share. |
| Insight 4: Measure if the communication is being received and resulting in the desired outcome. If not, modify what and how the message is being expressed. |
| Insight 5: Messages are also non-verbal. Practice using your voice and body to set the right tone and impact your audience. |
Communication principles
Follow these principles to support all IT communications.
Two-Way
Incorporate feedback loops into your communication efforts. Providing stakeholders with the opportunity to voice their opinions and ideas will help gain their commitment and buy-in.
Timely
Frequent communications mitigate rumors and the spread of misinformation. Provide warning before the implementation of any changes whenever possible. Communicate as soon as possible after decisions have been made.
Consistent
Make sure the messaging is consistent across departments, mediums, and presenters. Provide managers with key phrases to support the consistency of messages.
Open & Honest
Transparency is a critical component of communication. Always tell employees that you will share information as soon as you can. This may not be as soon as you receive the information but as soon as sharing it is acceptable.
Authentic
Write messages in a way that embodies the personality of the organization. Don’t spin information; position it within the wider organizational context.
Targeted
Use your target audience profiles to determine which audiences need to consume which messages and what mediums should be employed.
Importance of IT being a good communicator
Don’t pay the price for poor communication.
IT needs to communicate well because:
- IT risk mitigation and technology initiative funding are dependent on critical stakeholders comprehending the risk impact and initiative benefit in easy-to-understand terms.
- IT employees need clear and direct information to feel empowered and accountable to do their jobs well.
- End users who have a good experience engaging in communications with IT employees have an overall increase in satisfaction with IT.
- Continuously demonstrating IT’s value to the organization comes when those initiatives are clearly aligned to overall objectives.
- Communication prevents assumptions and further miscommunication from happening among IT employees who are usually impacted and fear change the most.
“Poor communication results in employee misunderstanding and errors that cost approximately $37 billion.”
– Intranet Connections, 2019
Effective communication enables organizational strategy and facilitates a two-way exchange
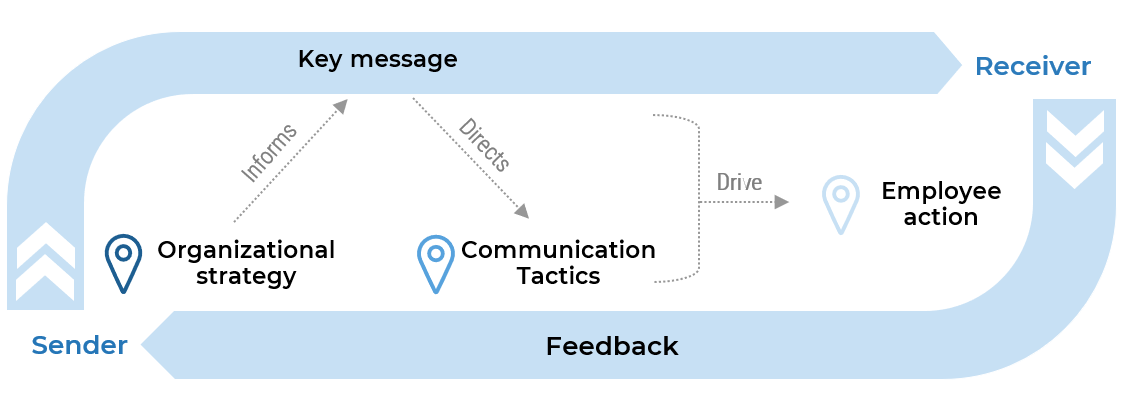
What makes internal communications effective?
To be effective, internal communications must be strategic. They should directly support organizational objectives, reinforce key messages to make sure they drive action, and facilitate two-way dialogue, not just one-way messaging.
Measure the value of the communication
Communication effectiveness can be measured through a variety of metrics:
- Increase in Productivity “When employees are offered better communication technology and skills, productivity can increase by up to 30%” (Expert Market, 2022).
- Increase in Understanding Decision Rationale Employees who report understanding the rationale behind the business decisions made by the executive leadership team (ELT) are 3.6x more likely to be engaged, compared to those who were not (McLean & Company Engagement Survey Database, 2022; N=133,167 responses, 187 organizations).
- Increase in Revenue Collaboration amongst C-suite executives led to a 27% increase in revenue compared to low collaborating C-suites (IBM, 2021).
- Increase in End-User Satisfaction 80.9% of end users are satisfied with IT’s ability to communicate with them regarding the information they need to perform their job (Info-Tech’s End-User Satisfaction Survey Database, N=20,617 end users from 126 organizations).
Methods to determine effectiveness:
- CIO Business Vision Survey
- Engagement surveys
- Focus groups
- Suggestion boxes
- Team meetings
- Random sampling
- Informal feedback
- Direct feedback
- Audience body language
- Repeating the message back
How to navigate the research center
This research center is intended to ensure that IT never starts their communications from a blank page again:
“‘Effectiveness’ can mean different things, and effectiveness for your project is going to look different than it would for any other project.”
– Gale McCreary in WikiHow, 2022
Audience: Organizational leadership
Speaking with Board and executive leaders about strategy, risk, and value
Keep in mind:
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Priorities Differ | Words Matter | The Power of Three |
| What’s important to you as CIO is very different from what is important to a board or executive leadership team or even the individual members of these groups. Share only what is important or relevant to the stakeholder(s). | Simplify the message into common language whenever possible. A good test is to ensure that someone without any technical background could understand the message. | Keep every slide to three points with no more than three words. You are the one to translate this information into a worth-while story to share. |
“Today’s CIOs have a story to tell. They must change the old narrative and describe the art of the (newly) possible. A great leader rises to the occasion and shares a vision that inspires the entire organization.”
– Dan Roberts, CIO, 2019
Communications for board presentations
Secure funding and demonstrate IT as a value add to business objectives.
DEFINING INSIGHT
Stop presenting what is important to you as the CIO and present to the board what is important to them.
Why does IT need to communicate with the board?
- To get their buy-in and funding for critical IT initiatives.
- To ensure that IT risks are understood and receive the funding necessary to mitigate.
- To change the narrative of IT as a service provider to a business enabler.
FRAMEWORK
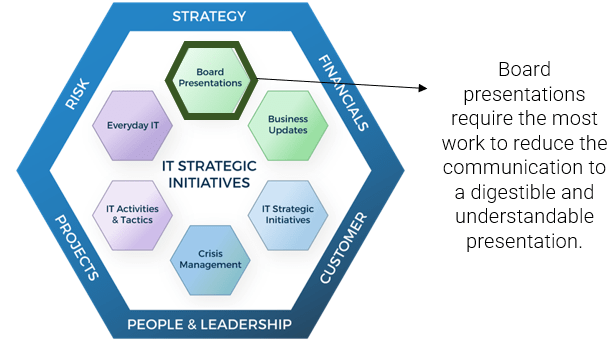
CHECKLIST
Do’s & Don’ts of Communicating Board Presentations:
Do: Ensure you know all the members of the board and their strengths/areas of focus.
Do: Ensure the IT objectives and initiatives align to the business objectives.
Do: Avoid using any technical jargon.
Do: Limit the amount of data you are using to present information. If it can’t stand alone, it isn’t a strong enough data point.
Do: Avoid providing IT service metrics or other operational statistics.
Do: Demonstrate how the organization’s revenue is impacted by IT activities.
Do: Tell a story that is compelling and excited.
OUTCOME
Organization Alignment
- Approved organization objectives and IT objectives are aligned and supporting one another.
Stakeholder Buy-In
- Board members all understand what the future state of IT will look like – and are excited for it!
Awareness on Technology Trends
- It is the responsibility of the CIO to ensure the board is aware of critical technology trends that can impact the future of the organization/industry.
Risks
- Risks are understood, the impact they could have on the organization is clear, and the necessary controls required to mitigate the risk are funded.
Communications for business updates
Continuously build strong relationships with all members of business leadership.
DEFINING INSIGHT
Business leaders care about themselves and their goals – present ideas and initiatives that lean into this self-interest.
Why does IT need to communicate business updates?
- The key element here is to highlight how IT is impacting the organization’s overall ability to meet goals and targets.
- Ensure all executive leaders know about and understand IT’s upcoming initiatives – and how they will be involved.
FRAMEWORK
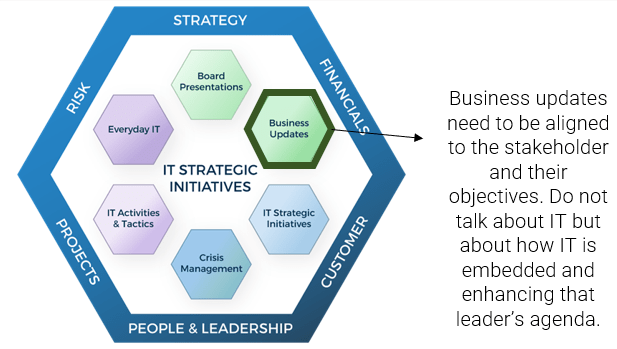
CHECKLIST
Do’s & Don’ts of Communicating Business Updates:
Do: Ensure IT is given sufficient time to present with the rest of the business leaders.
Do: Ensure the goals of IT are clear and can be depicted visually.
Do: Tie every IT goal to the objectives of different business leaders.
Do: Avoid using any technical jargon.
Do: Reinforce the positive benefits business leaders can expect.
Do: Avoid providing IT service metrics or other operational statistics.
Do: Demonstrate how IT is driving the digital transformation of the organization.
OUTCOME
Better Reputation
- Get other business leaders to see IT as a value add to any initiative, making IT an enabler not an order taker.
Executive Buy-In
- Executives are concerned about their own budgets; they want to embrace all the innovation but within reason and minimal impact to their own finances.
Digital Transformation
- Indicate and commit to how IT can help the different leaders deliver on their digital transformation activities.
Relationship Building
- Establish trust with the different leaders so they want to engage with you on a regular basis.
Audience: Organization wide
Speaking with all members of the organization about the future of technology – and unexpected crises.
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Competing to Be Heard | Measure Impact | Enhance the IT Brand |
| IT messages are often competing with a variety of other communications simultaneously taking place in the organization. Avoid the information-overload paradox by communicating necessary, timely, and relevant information. | Don’t underestimate the benefit of qualitative feedback that comes from talking to people within the organization. Ensure they read/heard and absorbed the communication. | IT might be a business enabler, but if it is never communicated as such to the organization, it will only be seen as a support function. Use purposeful communications to change the IT narrative. |
Less than 50% of internal communications lean on a proper framework to support their communication activities.
– Philip Nunn, iabc, 2020
Communications for strategic IT initiatives
Communicate IT’s strategic objectives with all business stakeholders and users.
DEFINING INSIGHT
IT leaders struggle to communicate how the IT strategy is aligned to the overall business objectives using a common language understood by all.
Why does IT need to communicate its strategic objectives?
- To ensure a clear and consistent view of IT strategic objectives can be understood by all stakeholders within the organization.
- To demonstrate that IT strategic objectives are aligned with the overall mission and vision of the organization.
FRAMEWORK
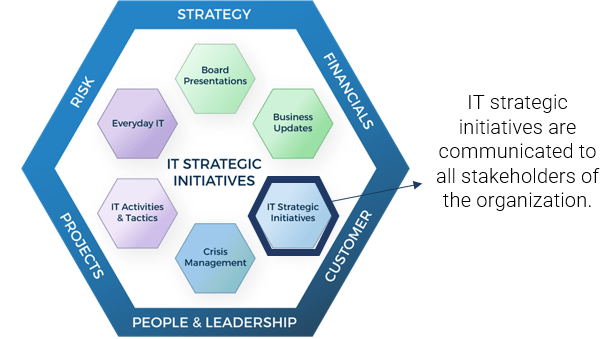
CHECKLIST
Do’s & Don’ts of Communicating IT Strategic Objectives:
Do: Ensure all IT leaders are aware of and understand the objectives in the IT strategy.
Do: Ensure there is a visual representation of IT’s goals.
Do: Ensure the IT objectives and initiatives align to the business objectives.
Do: Avoid using any technical jargon.
Do: Provide metrics if they are relevant, timely, and immediately understandable.
Do: Avoid providing IT service metrics or other operational statistics.
Do: Demonstrate how the future of the organization will benefit from IT initiatives.
OUTCOME
Organization Alignment
- All employees recognize the IT strategy as being aligned, even embedded, into the overall organization strategy.
Stakeholder Buy-In
- Business and IT stakeholders alike understand what the future state of IT will look like – and are excited for it!
Role Clarity
- Employees within IT are clear on how their day-to-day activities impact the overall objectives of the organization.
Demonstrate Growth
- Focus on where IT is going to be maturing in the coming one to two years and how this will benefit all employees.
Communications for crisis management
Minimize the fear and chaos with transparent communications.
DEFINING INSIGHT
A crisis communication should fit onto a sticky note. If it’s not clear, concise, and reassuring, it won’t be effectively understood by the audience.
Why does IT need to communicate when a crisis occurs?
- To ensure all members of the organization have an understanding of what the crisis is, how impactful that crisis is, and when they can expect more information.
- “Half of US companies don’t have a crisis communication plan” (CIO, 2017).
FRAMEWORK
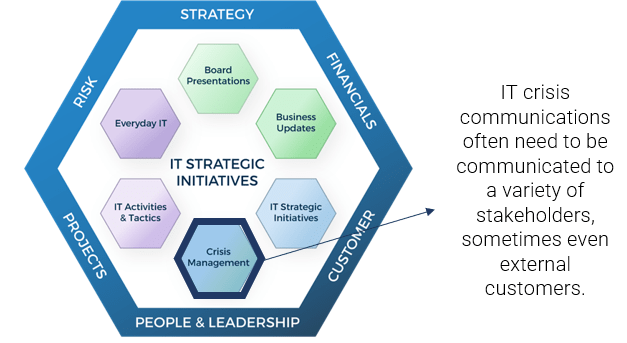
CHECKLIST
Do’s & Don’ts of Communicating During a Crisis:
Do: Provide timely and regular updates about the crisis to all stakeholders.
Do: Involve the Board or ELT immediately for transparency.
Do: Avoid providing too much information in a crisis communication.
Do: Have crisis communication statements ready to be shared at any time for possible or common IT crises.
Do: Highlight that employee safety and wellbeing is top priority.
Do: Work with members of the public relations team to prepare any external communications that might be required.
OUTCOME
Ready to Act
- Holding statements for possible crises will eliminate the time and effort required when the crisis does occur.
Reduce Fears
- Prevent employees from spreading concerns and not feeling included in the crisis.
Maintain Trust
- Ensure Board and ELT members trust IT to respond in an appropriate manner to any crisis or major incident.
Eliminate Negative Reactions
- Any crisis communication should be clear and concise enough when done via email.
Audience: IT employees
IT employees need to receive and obtain regular transparent communications to better deliver on their expectations.
Keep in mind:
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Training for All | Listening Is Critical | Reinforce Collaboration |
| From the service desk technician to CIO, every person within IT needs to have a basic ability to communicate. Invest in the training necessary to develop this skill set. | It seems simple, but as humans we do an innately poor job at listening to others. It’s important you hear employee concerns, feedback, and recommendations, enabling the two-way aspect of communication. | IT employees will reflect the types of communications they see. If IT leaders and managers cannot collaborate together, then teams will also struggle, leading to productivity and quality losses. |
“IT professionals who […] enroll in communications training have a chance to both upgrade their professional capabilities and set themselves apart in a crowded field of technology specialists.”
– Mark Schlesinger, Forbes, 2021
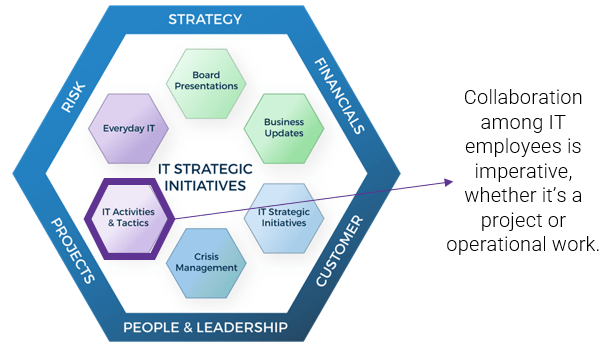
Communications for IT activities and tactics
Get IT employees aligned and clear on their daily objectives.
DEFINING INSIGHT
Depending on IT goals, the structure might need to change to support better communication among IT employees.
Why does IT need to communicate IT activities?
- To ensure all members of the project team are aligned with their tasks and responsibilities related to the project.
- To be able to identify, track, and mitigate any problems that are preventing the successful delivery of the project.
FRAMEWORK
CHECKLIST
Do’s & Don’ts of Communicating IT Activities:
Do: Provide metrics that define how success of the project will be measured.
Do: Demonstrate how each project aligns to the overarching objectives of the organization.
Do: Avoid having large meetings that include stakeholders from two or more projects.
Do: Consistently create a safe space for employees to communicate risks related to the project(s).
Do: Ensure the right tools are being leveraged for in-office, hybrid, and virtual environments to support project collaboration.
Do: Leverage a project management software to reduce unnecessary communications.
OUTCOME
Stakeholder Adoption
- Create a standard communication template so stakeholders can easily find and apply communications.
Resource Allocation
- Understand what the various asks of IT are so employees can be adequately assigned to tasks.
Meet Responsibly
- Project status meetings are rarely valuable or insightful. Use meetings for collaboration, troubleshooting, and knowledge sharing.
Encourage Engagement
- Recognize employees and their work against critical milestones, especially for projects that have a long timeline.
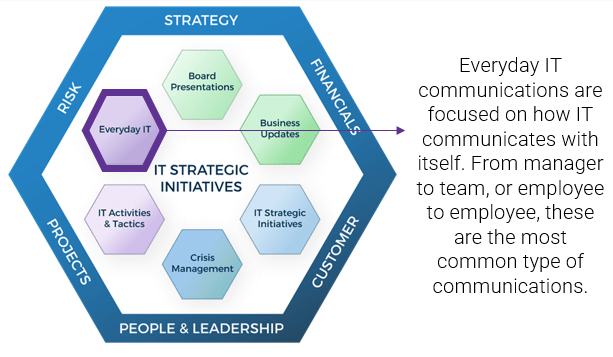
Communications for everyday IT
Engage employees and drive results with clear and consistent communications.
DEFINING INSIGHT
Employees are looking for empathy to be demonstrated by those they are interacting with, from their peers to managers. Yet, we rarely provide it.
Why does IT need to communicate on regularly with itself?
- Regular communication ensures employees are valued, empowered, and clear about their expectations.
- 97% of employees believe that their ability to perform their tasks efficiently is impacted by communication (Expert Market, 2022).
FRAMEWORK
CHECKLIST
Do’s & Don’ts of Communicating within IT:
Do: Have responses for likely questions prepared and ready to go.
Do: Ensure that all leaders are sharing the same messages with their teams.
Do: Avoid providing irrelevant or confusing information.
Do: Speak with your team on a regular basis.
Do: Reinforce the messages of the organization every chance possible.
Do: Ensure employees feel empowered to do their jobs effectively.
Do: Engage employees in dialogue. The worst employee experience is when they are only spoken at, not engaged with.
OUTCOME
Increased Collaboration
- Operating in a vacuum or silo is no longer an option. Enable employees to successfully collaborate and deliver holistic results.
Role Clarity
- Clear expectations and responsibilities eliminate confusion and blame game. Engage employees and create a positive work culture with role clarity.
Prevent Rumors
- Inconsistent communication often leads to information sharing and employees spreading an (in)accurate narrative.
Organizational Insight
- Employees trust the organization’s direction because they are aware of the different activities taking place and provided with a rationale about decisions.
Case Study
Amazon
INDUSTRY
E-Commerce
SOURCE
Harvard Business Review
Jeff Bezos has definitely taken on unorthodox approaches to business and leadership, but one that many might not know about is his approach to communication. Some of the key elements that he focused on in the early 2000s when Amazon was becoming a multi-billion-dollar empire included:
- Banning PowerPoint for all members of the leadership team. They had to learn to communicate without the crutch of the most commonly used presentation tool.
- Leveraging memos that included specific action steps and clear nouns
- Reducing all communication to an eighth-grade reading level, including pitches for new products (e.g. Kindle).
Results
While he was creating the Amazon empire, 85% of Jeff Bezos’ communication was written in a way that an eighth grader could read. Communicating in a way that was easy to understand and encouraging his leadership team to do so as well is one of the many reasons this business has grown to an estimated value of over $800B.
“If you cannot simplify a message and communicate it compellingly, believe me, you cannot get the masses to follow you.”
– Indra Nooyi, in Harvard Business Review, 2022
Communication competency expectations
Communication is a business skill; not a technical skill.
| Demonstrated Communication Behavior | |
| Level 1: Follow | Has sufficient communication skills for effective dialogue with others. |
| Level 2: Assist | Has sufficient communication skills for effective dialogue with customers, suppliers, and partners. |
| Level 3: Apply | Demonstrates effective communication skills. |
| Level 4: Enable | Communicates fluently, orally, and in writing and can present complex information to both technical and non-technical audiences. |
| Level 5: Ensure, Advise | Communicates effectively both formally and informally. |
| Level 6: Initiate, Influence | Communicates effectively at all levels to both technical and non-technical audiences. |
| Level 7: Set Strategy, Inspire, Mobilize | Understands, explains, and presents complex ideas to audiences at all levels in a persuasive and convincing manner. |
Source: Skills Framework for the Information Age, 2021
Key KPIs for communication with any stakeholder
Measuring communication is hard; use these to determine effectiveness.
| Goal | Key Performance Indicator (KPI) | Related Resource |
| Obtain board buy-in for IT strategic initiatives | X% of IT initiatives that were approved to be funded. Number of times technical initiatives were asked to be explained further. | Using our Board Presentation Review service |
| Establish stronger relationships with executive leaders | X% of business leadership satisfied with the statement “IT communicates with your group effectively.” | Using the CIO Business Vision Diagnostic |
| Organizationally, people know what products and services IT provides | X% of end users who are satisfied with communications around changing services or applications. | Using the End-User Satisfaction Survey |
| Organizational reach and understanding of the crisis. | Number of follow-up tickets or requests related to the crisis after the initial crisis communication was sent. | Using templates and tools for crisis communications |
| Project stakeholders receive sufficient communication throughout the initiative. | X% overall satisfaction with the quality of the project communications. | Using the PPM Customer Satisfaction Diagnostic |
| Employee feedback is provided, heard, and acted on | X% of satisfaction employees have with managers or IT leadership to act on employee feedback. | Using the Employee Engagement Diagnostic Program |
Standard workshop communication activities
Introduction
Communications overview.
Plan
Plan your communications using a strategic tool.
Compose
Create your own message.
Deliver
Practice delivering your own message.
Contact your account representative for more information. workshops@infotech.com 1-888-670-8889
Research contributors and experts

Anuja Agrawal
National Communications Director
PwC
Anuja is an accomplished global communications professional, with extensive experience in the insurance, banking, financial, and professional services industries in Asia, the US, and Canada. She is currently the National Communications Director at PwC Canada. Her prior work experience includes communication leadership roles at Deutsche Bank, GE, Aviva, and Veritas. Anuja works closely with senior business leaders and key stakeholders to deliver measurable results and effective change and culture building programs. Anuja has experience in both internal and external communications, including strategic leadership communication, employee engagement, PR and media management, digital and social media, and M&A/change and crisis management. Anuja believes in leveraging digital tools and technology-enabled solutions, combined with in-person engagement, to help improve the quality of dialogue and increase interactive communication within the organization to help build an inclusive culture of belonging.

Nastaran Bisheban
Chief Technology Officer
KFC Canada
A passionate technologist, and seasoned transformational leader. A software engineer and computer scientist by education, a certified Project Manager that holds an MBA in Leadership with Honors and Distinction from University of Liverpool. A public speaker on various disciplines of technology and data strategy with a Harvard Business School executive leadership program training to round it all. Challenges status quo and conventional practices; is an advocate for taking calculated risk and following the principle of continuous improvement. With multiple computer software and project management publications she is a strategic mentor and board member on various non-profit organizations. Nastaran sees the world as a better place only when everyone has a seat at the table and is an active advocate for diversity and inclusion.

Heidi Davidson
Co-Founder & CEO
Galvanize Worldwide and Galvanize On Demand
Dr. Heidi Davidson is the co-founder and CEO of Galvanize Worldwide, the largest distributed network of marketing and communications experts in the world. She also is the co-founder and CEO of Galvanize On Demand, a tech platform that matches marketing and communications freelancers with client projects. Now with 167 active experts, the Galvanize team delivers startup advisory work, outsourced marketing, training, and crisis communications to organizations of all sizes. Before Galvanize, Heidi spent four years as part of the turnaround team at BlackBerry as the Chief Communications Officer and SVP of Corporate Marketing, where she helped the company move from a device manufacturer to a security software provider.

Eli Gladstone
Co-Founder
Speaker Labs
Eli is a co-founder of Speaker Labs. He has spent over six years helping countless individuals overcome their public speaking fears and communicate with clarity and confidence. When he’s not coaching others on how to build and deliver the perfect presentation, you’ll probably find him reading some weird books, teaching his kids how to ski or play tennis, or trying to develop a good-enough jumpshot to avoid being a liability on the basketball court.

Francisco Mahfuz
Keynote Speaker & Storytelling Coach
Francisco Mahfuz has been telling stories in front of audiences for a decade and even became a National Champion of public speaking. Today, Francisco is a keynote speaker and storytelling coach and offers communication training to individuals and international organizations and has worked with organizations like Pepsi, HP, the United Nations, Santander, and Cornell University. He’s the author of Bare: A Guide to Brutally Honest Public Speaking and the host of The Storypowers Podcast, and he’s been part of the IESE MBA communications course since 2020. He’s received a BA in English Literature from Birkbeck University in London.

Sarah Shortreed
EVP & CTO
ATCO Ltd.
Sarah Shortreed is ATCO’s Executive Vice President and Chief Technology Officer. Her responsibilities include leading ATCO’s Information Technology (IT) function as it continues to drive agility and collaboration throughout ATCO’s global businesses and expanding and enhancing its enterprise IT strategy, including establishing ATCO’s technology roadmap for the future. Ms. Shortreed’s skill and expertise are drawn from her more than 30-year career that spans many industries and includes executive roles in business consulting, complex multi-stakeholder programs, operations, sales, customer relationship management, and product management. She was recently the Chief Information Officer at Bruce Power and has previously worked at BlackBerry, IBM, and Union Gas. She sits on the Board of Governors for the University of Western Ontario and is the current Chair of the Chief Information Officer (CIO) Committee at the Conference Board of Canada.

Eric Silverberg
Co-Founder
Speaker Labs
Eric is a co-founder of Speaker Labs and has helped thousands of people build their public speaking confidence and become more dynamic and engaging communicators. When he’s not running workshops to help people grow in their careers, there’s a good chance you’ll find him with his wife and dog, drinking Diet Coke, and rewatching iconic episodes of the reality TV show Survivor! He’s such a die-hard fan, that you’ll probably see him playing the game one day.

Stephanie Stewart
Communications Officer & DR Coordinator
Info Security Services Simon Fraser University

Steve Strout
President
Miovision Technologies
Mr. Strout is a recognized and experienced technology leader with extensive experience in delivering value. He has successfully led business and technology transformations by leveraging many dozens of complex global SFDC, Oracle, and SAP projects. He is especially adept at leading what some call “Project Rescues” – saving people’s careers where projects have gone awry; always driving “on-time and on-budget.” Mr. Strout is the current President of Miovision Technologies and the former CEO and board member of the Americas’ SAP Users” Group (ASUG). His wealth of practical knowledge comes from 30 years of extensive experience in many CxO and executive roles at some prestigious organizations such as Vonage, Sabre, BlackBerry, Shred-it, The Thomson Corporation (now Thomson Reuters), and Morris Communications. He has served on boards including Customer Advisory Boards of Apple, AgriSource Data, Dell, Edgewise, EMC, LogiSense, Socrates.ai, Spiro Carbon Group, and Unifi.
Info-Tech Research Group Contributors:
Sanchia Benedict, Research LeadAntony Chan Executive Counsellor
Janice Clatterbuck, Executive Counsellor
Ahmed Jowar, Research Specialist
Dave Kish, Practice Lead
Nick Kozlo, Senior Research Analyst
Heather Leier Murray, Senior Research Analyst
Amanda Mathieson, Research Director
Carlene McCubbin, Practice Lead
Joe Meier, Executive Counsellor
Andy Neill, AVP Research
Thomas Randall, Research Director
Plus an additional two contributors who wish to remain anonymous.
Related Info-Tech Research
- You will come away with a clear, concise, and compelling board presentation that IT leaders can feel confident presenting in front of their board of directors.
- Add improvements to your current board presentation in terms of visual appeal and logical flow to ensure it resonates with your board of directors.
- Leverage a best-of-breed presentation template.
- Management skills training is needed, but organizations are struggling to provide training that makes a long-term difference in the skills managers actually use in their day to day.
- Many training programs are ineffective because they offer the wrong content, deliver it in a way that is not memorable, and are not aligned with the IT department’s business objectives.
During a crisis it is important to communicate to employees through messages that convey calm and are transparent and tailored to your audience. Use the Crisis Communication Guides to:
- Draft a communication strategy.
- Tailor messages to your audience.
- Draft employee crisis communications.
Bibliography
“Communication in the Workplace Statistics: Importance and Effectiveness in 2022.” TeamStage, 2022.
Gallo, Carmine. “How Great Leaders Communicate.” Harvard Business Review, 23 November 2022
Guthrie, Georgina. “Why Good Internal Communications Matter Now More than Ever.” Nulab, 15 December 2021.
Lambden, Duncan. “The Importance of Effective Workplace Communication – Statistics for 2022.” Expert Market, 13 June 2022.
“Mapping SFIA Levels of Responsibilities to Behavioural Factors.” Skills Framework for the Information Age, 2021.
McCreary, Gale. “How to Measure the Effectiveness of Communication: 14 Steps.” WikiHow, 31 March 2023.
Nowak, Marcin. “Top 7 Communication Problems in the Workplace.” MIT Enterprise Forum CEE, 2021.
Nunn, Philip. “Messaging That Works: A Unique Framework to Maximize Communication Success.” iabc, 26 October 2020.
Picincu, Andra. “How to Measure Effective Communications.” Small Business Chron. 12 January 2021.
Price. David A. “Pixar Story Rules.” Stories From the Frontiers of Knowledge, 2011.
Roberts, Dan. “How CIOs Become Visionary Communicators.” CIO, 2019.
Schlesinger, Mark. “Why building effective communication skill in IT is incredibly important.” Forbes, 2021.
Stanten, Andrew. “Planning for the Worst: Crisis Communications 101.” CIO, 25 May 2017.
State of the American Workplace Report. Gallup, 6 February 2020.
“The CIO Revolution.” IBM, 2021.
“The State of High Performing Teams in Tech 2022.” Hypercontex, 2022.
Walters, Katlin. “Top 5 Ways to Measure Internal Communication.” Intranet Connections, 30 May 2019.
Buying Options
Effective IT Communications
IT Risk Management · IT Leadership & Strategy implementation · Operational Management · Service Delivery · Organizational Management · Process Improvements · ITIL, CORM, Agile · Cost Control · Business Process Analysis · Technology Development · Project Implementation · International Coordination · In & Outsourcing · Customer Care · Multilingual: Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese · Entrepreneur
Tymans Group is a brand by Gert Taeymans BV
Gert Taeymans bv
Europe: Koning Albertstraat 136, 2070 Burcht, Belgium — VAT No: BE0685.974.694 — phone: +32 (0) 468.142.754
USA: 4023 KENNETT PIKE, SUITE 751, GREENVILLE, DE 19807 — Phone: 1-917-473-8669
Copyright 2017-2022 Gert Taeymans BV