The State of Black Professionals in Tech
- The experience of Black professionals in IT differs from their colleagues.
- Job satisfaction is also lower for Black IT professionals.
- For organizations to gain from the benefits of diversity, equity, and inclusion, they need to ensure they understand the landscape for many Black professionals.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- As an IT leader, you can make a positive difference in the working lives of your team; this is not just the domain of HR.
- Employee goals can vary depending on the barriers that they encounter. IT leaders must ensure they have an understanding of unique employee needs to better support them, increasing their ability to recruit and retain.
- Improve the experience of Black IT professionals by ensuring your organization has diversity in leadership and supports mentorship and sponsorship.
Impact and Result
- Use the data from Info-Tech’s analysis to inform your DEI strategy.
- Learn about actions that IT leaders can take to improve the satisfaction and career advancement of their Black employees.
The State of Black Professionals in Tech Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. The State of Black Professionals in Tech Report – A report providing you with advice on barriers and solutions for leaders of Black employees.
IT leaders often realize that there are barriers impacting their employees but don’t know how to address them. This report provides insights on the barriers and actions that can help improve the lives of Black professionals in technology.
- The State of Black Professionals in Tech Report
Infographic
Further reading
The State of Black Professionals in Tech
Keep inclusion at the forefront to gain the benefits from diversity.
Analysts' Perspective
The experience of Black professionals in technology is unique.
Diversity in tech is not a new topic, and it's not a secret that technology organizations struggle to attract and retain Black employees. Ever since the early '90s, large tech organizations have been dealing with public critique of their lack of diversity. This topic is close to our hearts, but unfortunately while improvements have been made, progress is quite slow.
In recent years, current events have once again brought diversity to the forefront for many organizations. In addition, the pandemic along with talent trends such as "the great resignation" and "quiet quitting" and preparations for a recession have not only impacted diversity at large but also Black professionals in technology. Our previous research has focused on the wider topic of Recruiting and Retaining People of Color in Tech, but we've found that the experiences of persons of color are not all the same.
This study focuses on the unique experience of Black professionals in technology. Over 600 people were surveyed using an online tool; interviews provided additional insights. We're excited to share our findings with you.

|

|
|
Allison Straker |
Ugbad Farah |
Demographics
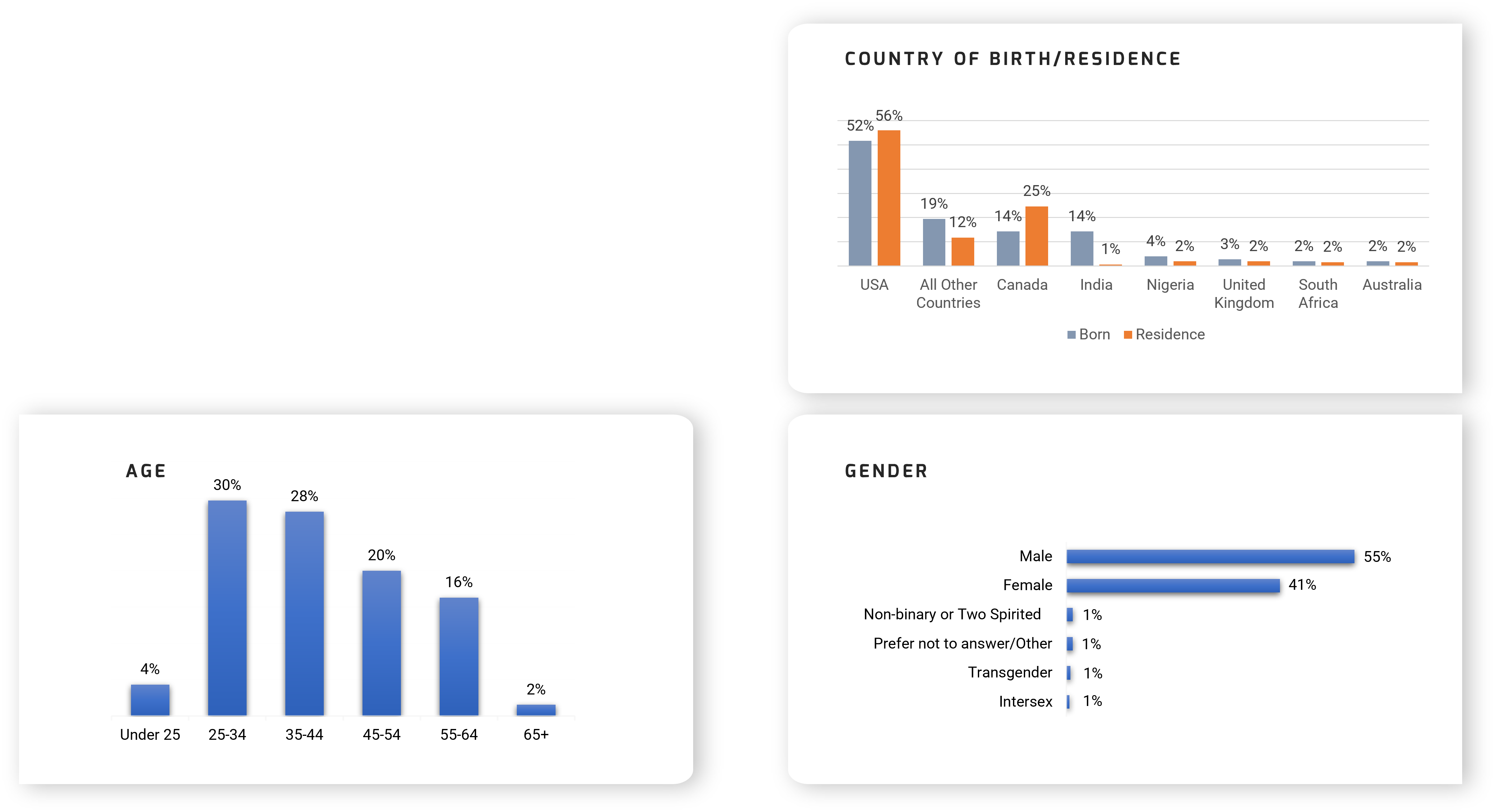
In October 2021, we launched a survey to understand what the Black experience is like for people in technology. We wanted and received a variety of responses which would help us to understand how Black technology professionals experienced their working world. We received responses from 633 professionals, providing us with the data for this report.
For more information on our survey demographics please see the appendix at this end of this report.
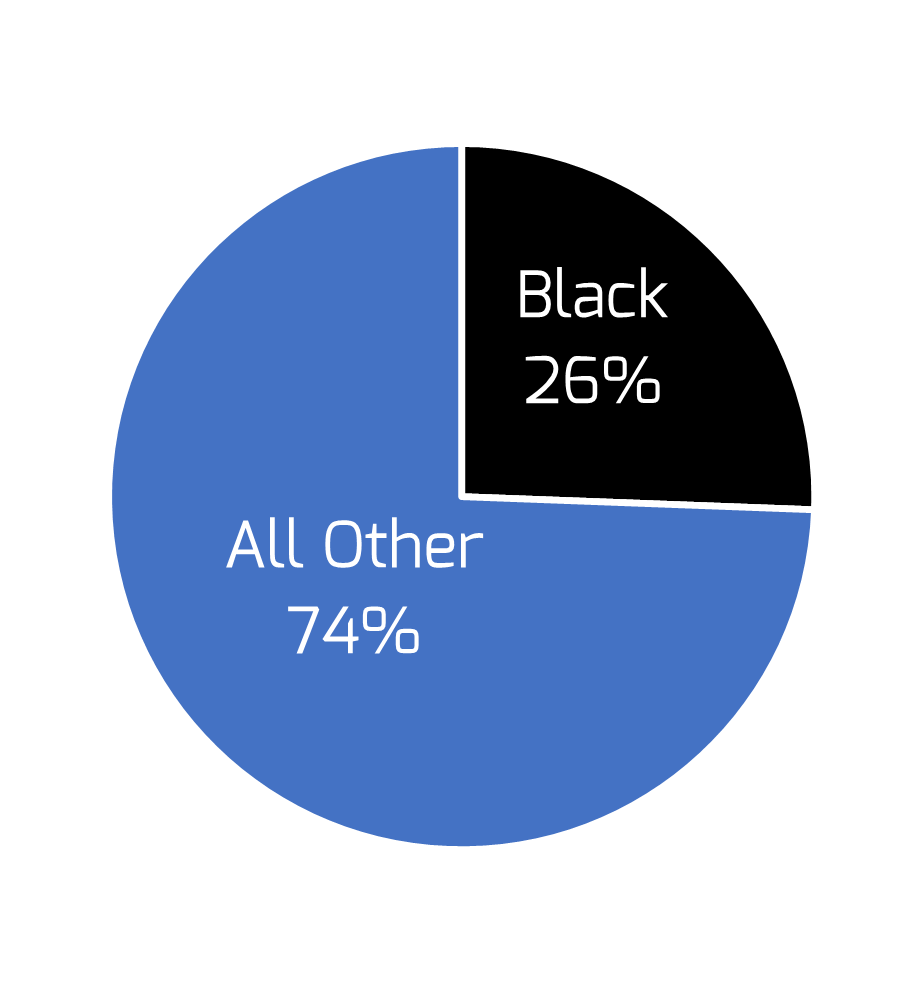
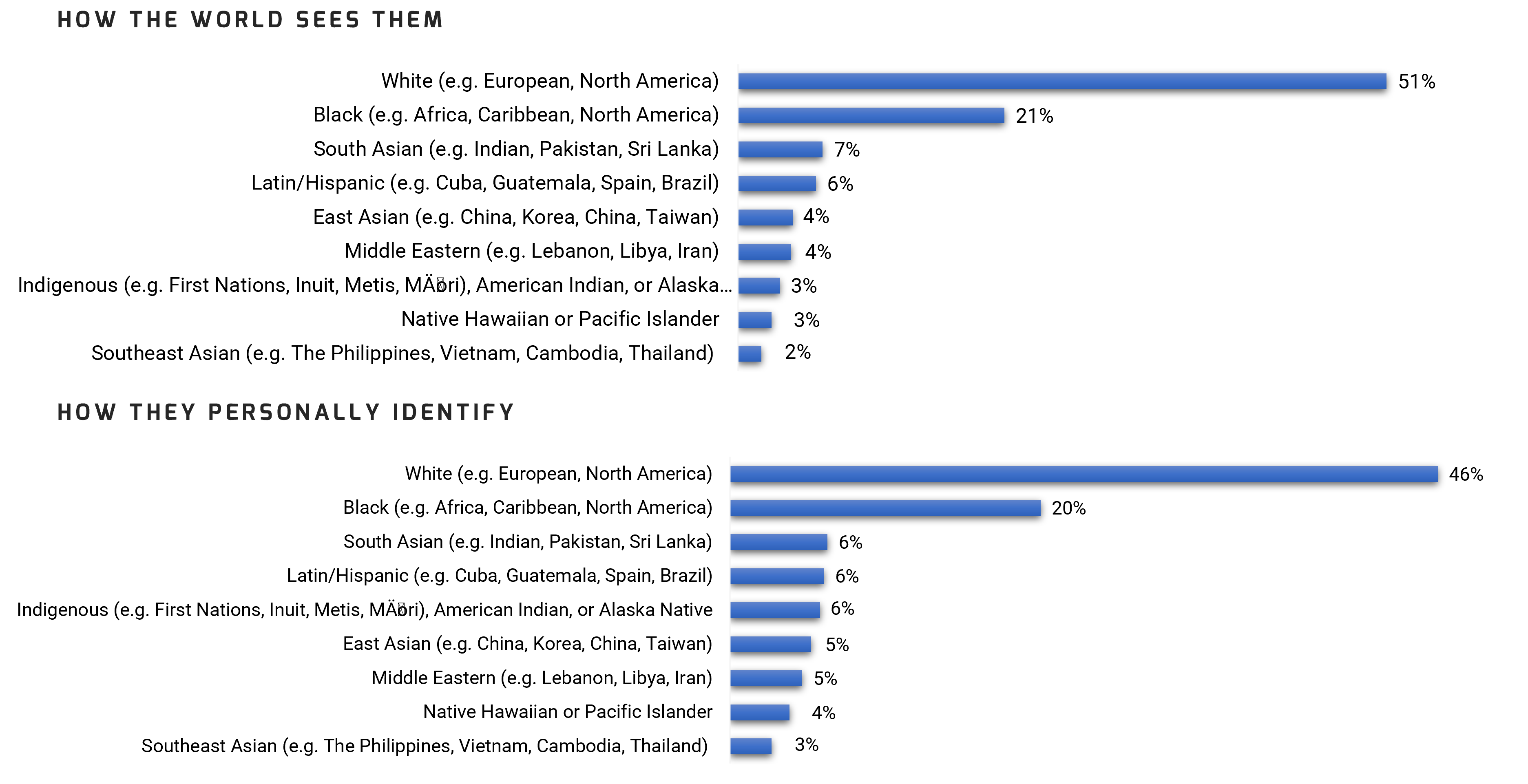
26% of our respondents either identified as Black or felt the world sees them as Black.
Professionals from various countries responded to the survey:
- Most respondents were born in the US (52%), Canada (14%), India (14%), or Nigeria (4%).
- Most respondents live in the US (56%), Canada (25%), Nigeria (2%), or the United Kingdom (2%).
Companies with more diversity achieve more revenue from innovation
Organizations do better and are more innovative when they have more diversity, a key ingredient in an organization's secret sauce.
Organizations also benefit from engaged employees, yet we've seen that organizations struggle with both. Just having a certain number of diverse individuals is not enough. When it comes to reaping the benefits of diversity, organizations can flourish when employees feel safe bringing their whole selves to work.
| 45% | Innovation Revenue by Companies With Above-Average Diversity Scores |
| 26% |
Innovation Revenue by Companies With Below-Average Diversity Scores |
Companies with higher employee engagement experience 19.2% higher earnings.
However, those with lower employee engagement experience 32.7% lower earnings.
(DecisionWise, 2020)
If your workforce doesn't reflect the community it serves, your business may be missing out on the chance to find great employees and break into new and growing markets, both locally and globally.
Diversity makes good business sense.
(Business Development Canada, 2023)
A study about Black professionals
Why is this about Black professionals and not other diverse groups?
While there are a variety of diversity dimensions, it's important to understand what makes up a "multicultural workforce." There is more to diversity than gender, race, and ethnicity. Organizations need to understand that there is diversity within these groups and Black professionals have their own unique experience when it comes to entering and navigating tech that needs to be addressed.

(Brookfield Institute for Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 2019)
The solutions that apply to Black professionals are not only beneficial for Black employees but for all. While all demographics are unique, the solutions in this report can support many.
Unsatisfied and underrepresented
Less Black professionals responded as "satisfied" in their IT careers. The question is: How do we mend the Gap?
Percentage of IT Professionals Who Reported Being Very Satisfied in Their Current Role
- All Other Professionals: 34%
- Black Professionals: 23%
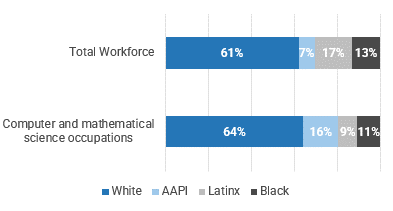
Black workers are underrepresented in most professional roles, especially computer and math Occupations
The gap in satisfaction
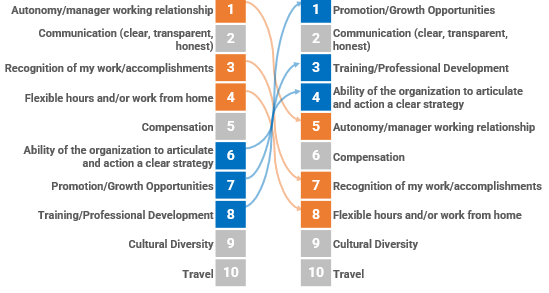
What's Important?
Our research suggests that the differences in satisfaction among ethnic groups are related to differences in value systems. We asked respondents to rank what's important, and we explored why.
Non-Black professionals rated autonomy and their manager working relationships as most important.
For Black professionals, while those were important, #1 was promotion and growth opportunities, ranked #7 by all other professionals. This is a significant discrepancy.
Recognition of my work/accomplishments also was viewed significantly differently, with Black professionals ranking it low on the list at #7 and all other professionals considering it very important at #3.
|
All Other Professionals |
Black Professionals |
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
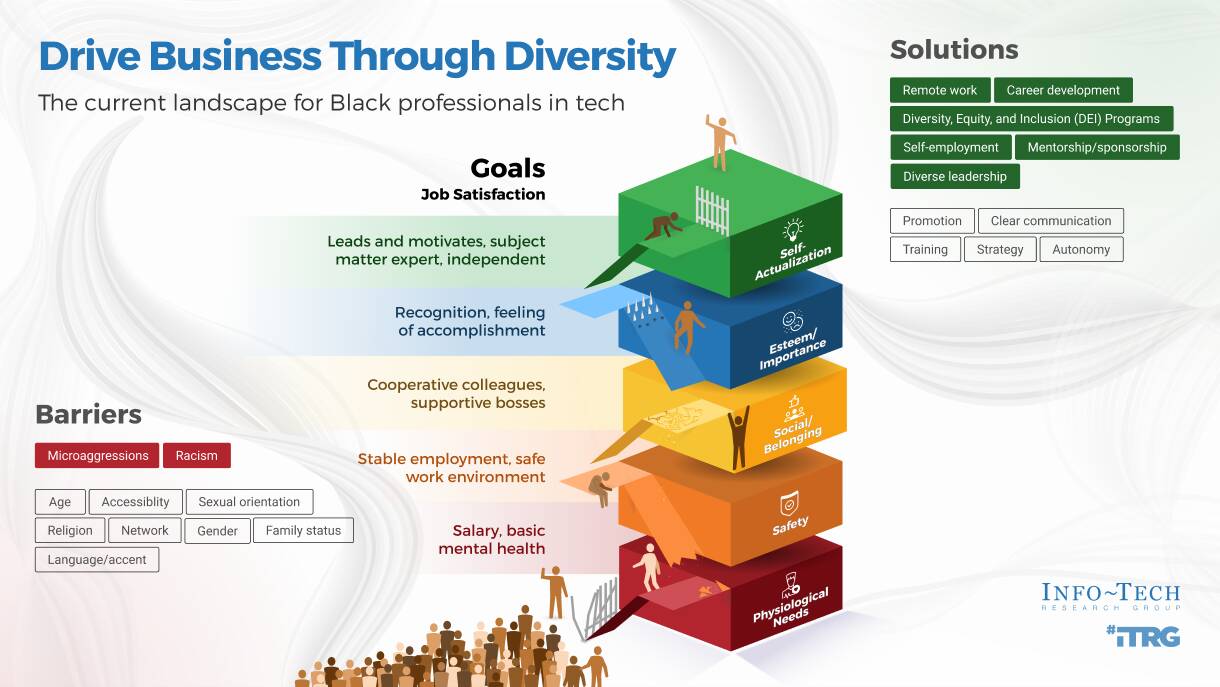
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs applies to job satisfaction
In Maslow's hierarchy, it is necessary for people to achieve items lower on the hierarchy before they can successfully pursue the higher tiers.
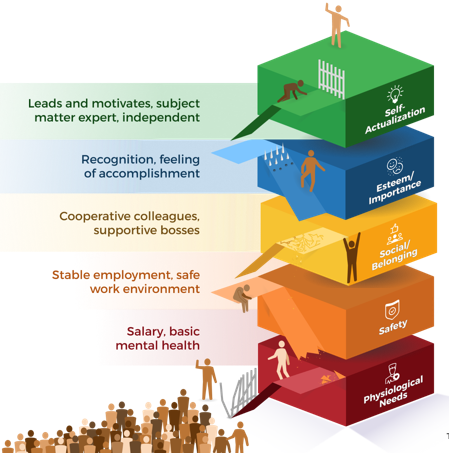
Too many Black professionals in tech are busy trying to achieve some of the lower parts of the hierarchy; it is stopping them from achieving elements higher up that can lead to job satisfaction.
This can stop them from gaining esteem, importance, and ultimately, self-actualization. The barriers that impact safety and social belonging happen on a day-to-day basis, and so the day-to-day lives of Black professionals in tech can look very different from their counterparts.
There are barriers that hinder and solutions that support employees

|

|
| There are various barriers that increase the likelihood for Black professionals to focus on the lower end of the needs hierarchy: |
These are among some of the solutions that, when layered, can support Black professionals in tech in moving up the needs hierarchy. Focusing on these actions can support Black professionals in achieving much needed job satisfaction. |
What does this mean?
The minority experience is not a monolith
The barriers that Black professionals encounter aren't limited to the same barriers as their colleagues, and too often this means that they aren't in a position to grow their careers in a way that leads to job satisfaction.
There is a 11% gap between the satisfaction of Black professionals and their peers.
Early Steps:
Take time to understand the Black experience.
As leaders, it's important to be aware that employee goals vary depending on the barriers they're battling with.
Intermediate:
If Black employees don't have strong relationships, networks, and mentorships it becomes increasingly difficult to navigate the path to upward mobility.
As a leader, you can look for opportunities to bridge the gap on these types of conversations.
Advanced:
Black professionals in tech are not advancing like their counterparts.
Creating clear career paths will not only benefit Black employees but also support your entire organization.
Key metrics:
- Engagement
- Committed Executive Leadership
- Development Opportunities
- Organizational Programs
Black respondents are significantly more likely to report barriers to their career advancement
Common barriers
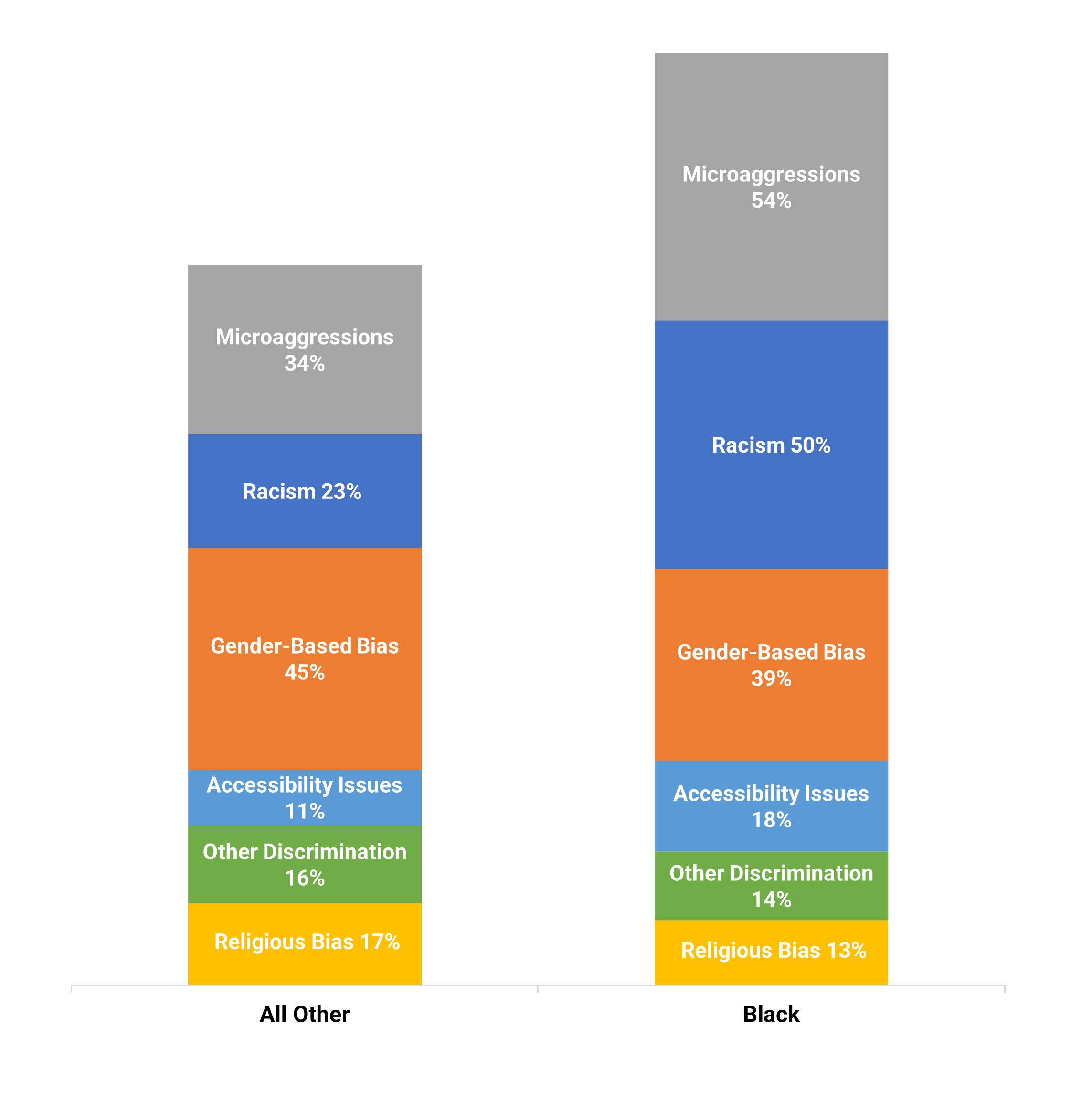
Black professionals, like their colleagues, encounter barriers as they try to advance their careers. The barriers both groups encounter include microaggressions, racism, ageism, accessibility issues, sexual orientation, bias due to religion, lack of a career-supported network, gender bias, family status bias, and discrimination due to language/accents.
What tops the list
Microaggressions and racism are at the top of these barriers, but Black professionals also deal with other barriers that their colleagues may experience, such as gender-based bias, accessibility issues, religion, and more.
One of these barriers alone can be difficult to deal with but when they are compounded it can be very difficult to navigate through the working environment in tech.
What are microaggressions?
Microaggression
A statement, action, or incident regarded as an instance of indirect, subtle, or unintentional discrimination against members of a marginalized group such as a racial or ethnic minority.
(Oxford Languages, 2023)
Why are they significant?
These things may seem innocent enough but the messaging that is received and the lasting impression is often far from it.
Our research shows that racism and discrimination contribute to poor mental health among Black professionals.
Examples
- You're so articulate!
- How do you always have different hair, can I touch it?
- Where are you really from?
- I don't see color.
- I believe the most qualified person should get the job; everyone can succeed in this society if they work hard enough.
"The experience of having to question whether something happened to you because of your race or constantly being on edge because your environment is hostile can often leave people feeling invisible, silenced, angry, and resentful."
Dr. Joy Bradford,
clinical Psychologist, qtd. In Pfizer
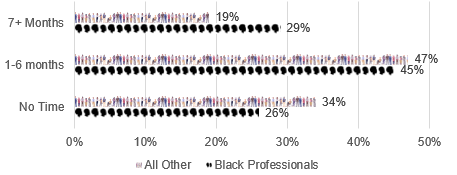
It takes some time to get in the door
For too many Black respondents, It took Longer than their peers to Find Technology Jobs.
Both groups had some success finding jobs in "no time" – however, there was a difference. Thirty-four percent of "all others" found their jobs quickly, while the numbers were less for Black professionals, at 26%. There was also a difference at the opposite end of the spectrum. For 29% of Black professionals, it took seven months or longer to find their IT job, while that number is only 19% for their peers.
.
This points to the need for improvements in recruitment and career advancement.
29% of Black respondents said that it took them 7 months or longer to find their technology job.
Compared to 19% of all other professionals that selected the same response.
And once they're in, it's difficult to advance
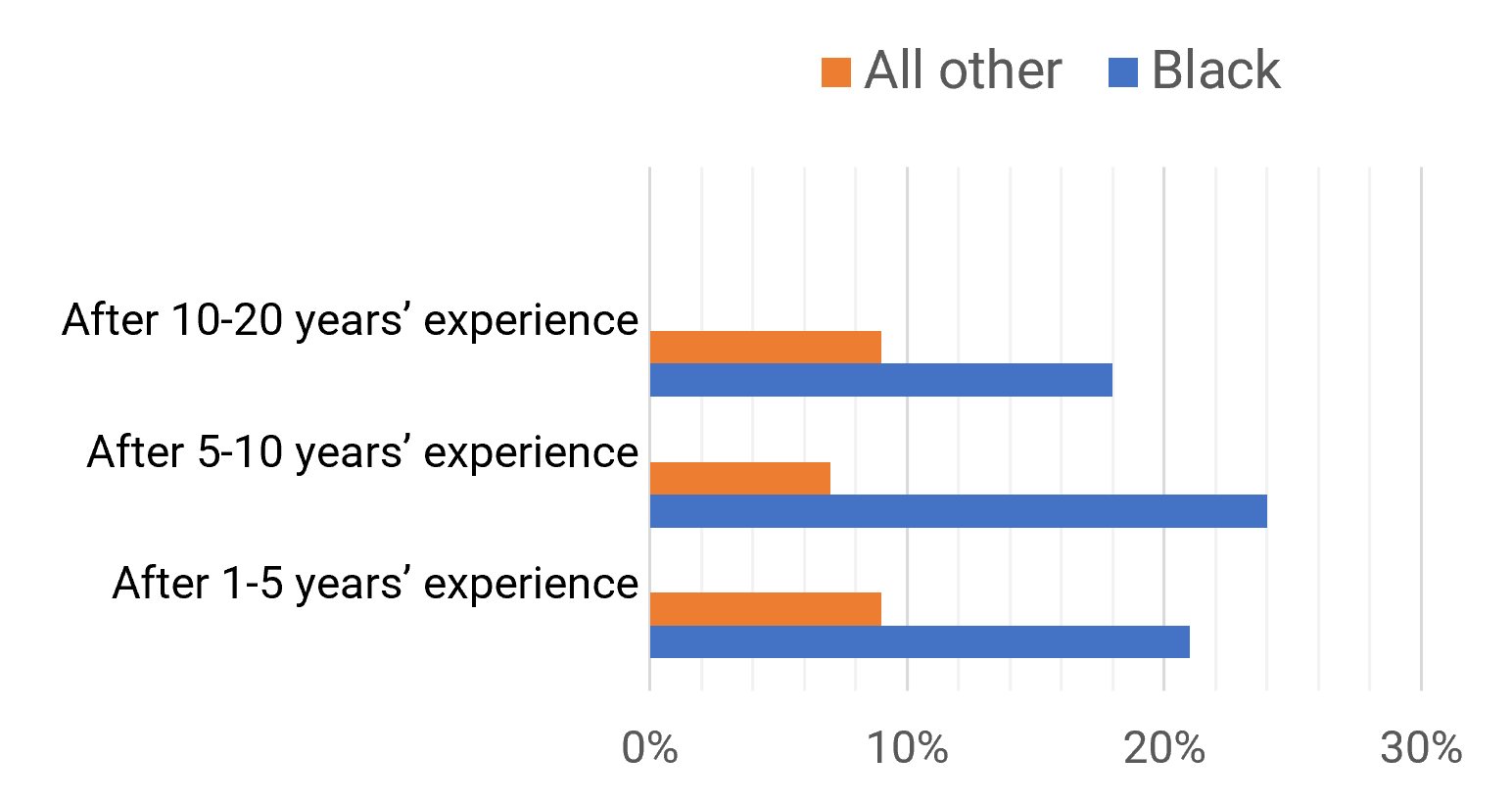
Black Professionals are not Advancing as Quickly as their Colleagues. Especially when you look at their Experience.
Our research shows that compared to all other ethnicities; Black participants were 55% more likely to report that they had no career advancement/promotion in their career. There is a bigger percentage of Black professionals who have never received a promotion; there's also a large number of Black professionals who have been working a significant amount time in the same role without a promotion.
.Career Advancement
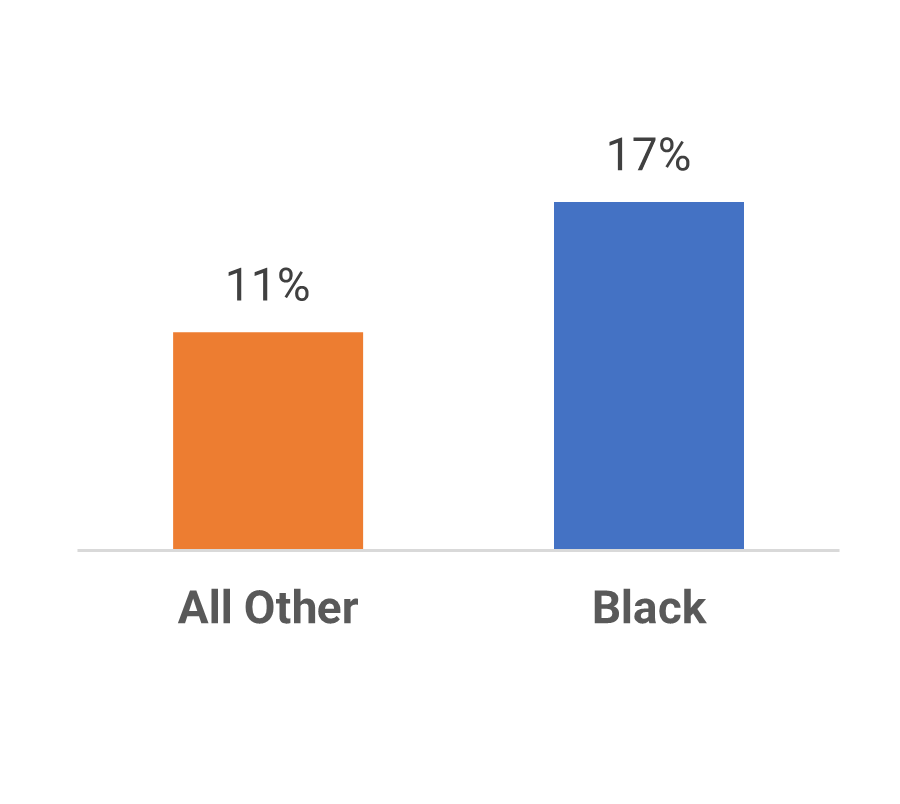
Black participants were 55% more likely to report that they had had no career advancement/promotion in their career.
No advancement
There's a high cost to lack of engagement
When employees feel disillusioned with things like career advancement and microaggressions, they often become disengaged. When you continuously have to steel yourself against microaggressions, racism, and other barriers, it prevents you from bringing your whole self to the office. The barriers can lead to what's been coined as "emotional tax." An emotional tax is the experience of feeling different from colleagues because of your inherent diversity and the associated negative effects on health, wellbeing, and the ability to thrive at work.
|
Earnings of companies with higher employee engagement |
19.2% |
|
Earnings of companies with lower employee engagement |
-32.7% |
(DecisionWise, 2020)
"I've conditioned myself for the corporate world, I don't bring my authentic self to work."
Anonymous Interview Subject
Lack of engagement also costs the organization in terms of turnover, something many organizations today are struggling with how to address. Organizations want to increase the ability of the workforce to remain in the organization. For Black employees, this gets harder when they're not engaged and they're the only one. When the emotional tax gets to be too much, this can lead to turnover. Turnover not only costs companies billions in profits, it also negatively impacts leadership diversity. It's difficult to imagine career growth when you don't see anyone that looks like you at the top. It is a challenge to see your future when there aren't others that you can relate to at top levels in the organization, leading to one of our interview subjects to muse, "How long can I last?"
"Being Black in tech can be hard on your mental health. Your mind is constantly wondering, 'how long can I last?' "
Anonymous Interview Subject
Fewer Black professionals feel like they can be their authentic selves at work
Authentic vs. Successes
For many Black professionals, "code-switching," or altering the way one speaks and acts depending on context, becomes the norm to make others more comfortable. Many feel that being authentic and succeeding in the workplace are mutually exclusive.
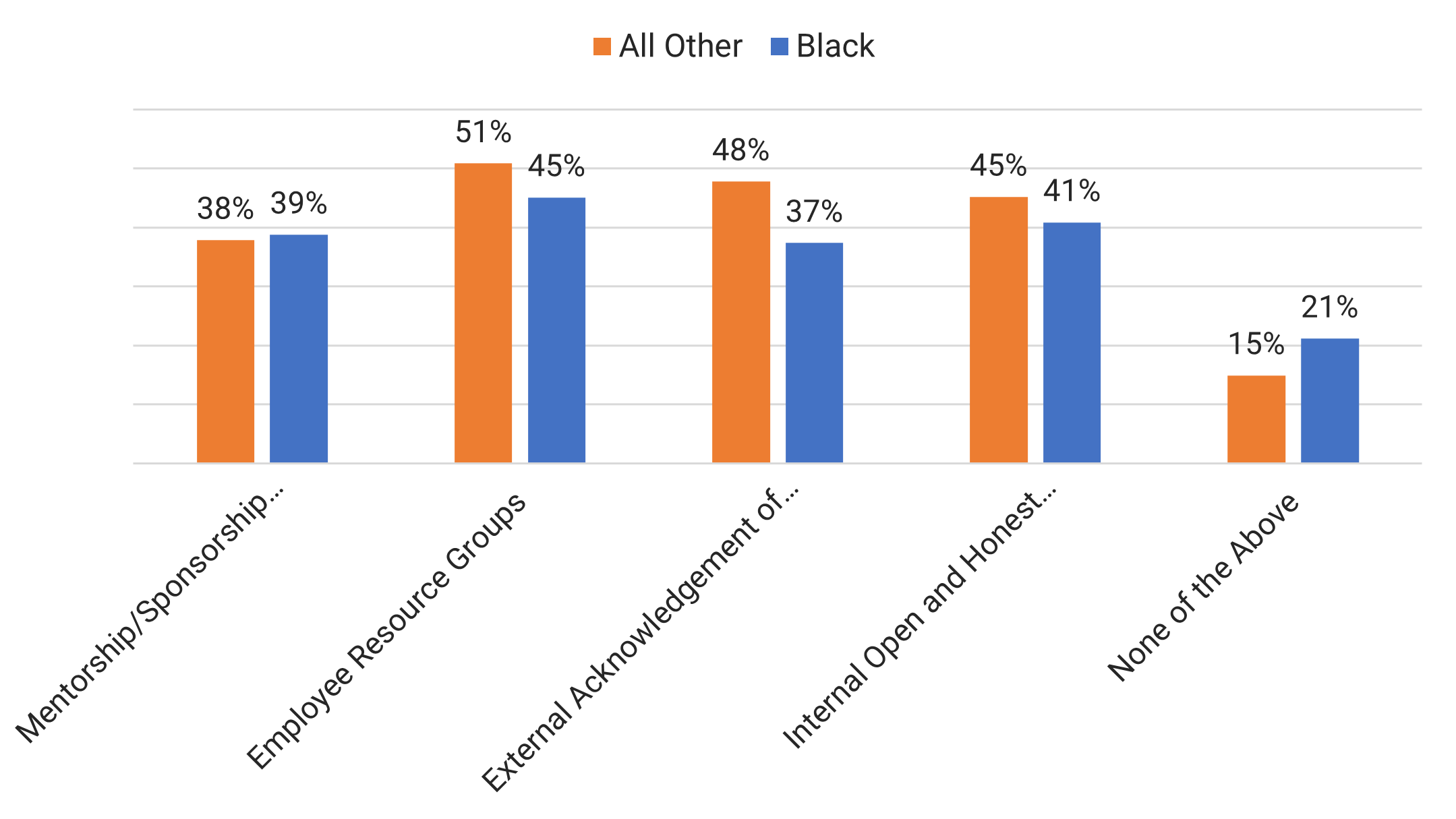
Programs and Resources
We asked respondents "What's in place to build an inclusive culture at your company?" Most respondents (51% and 45%) reported that there were employee resource groups at their organizations.
Do you feel you can be your authentic self at work?

What can be done?
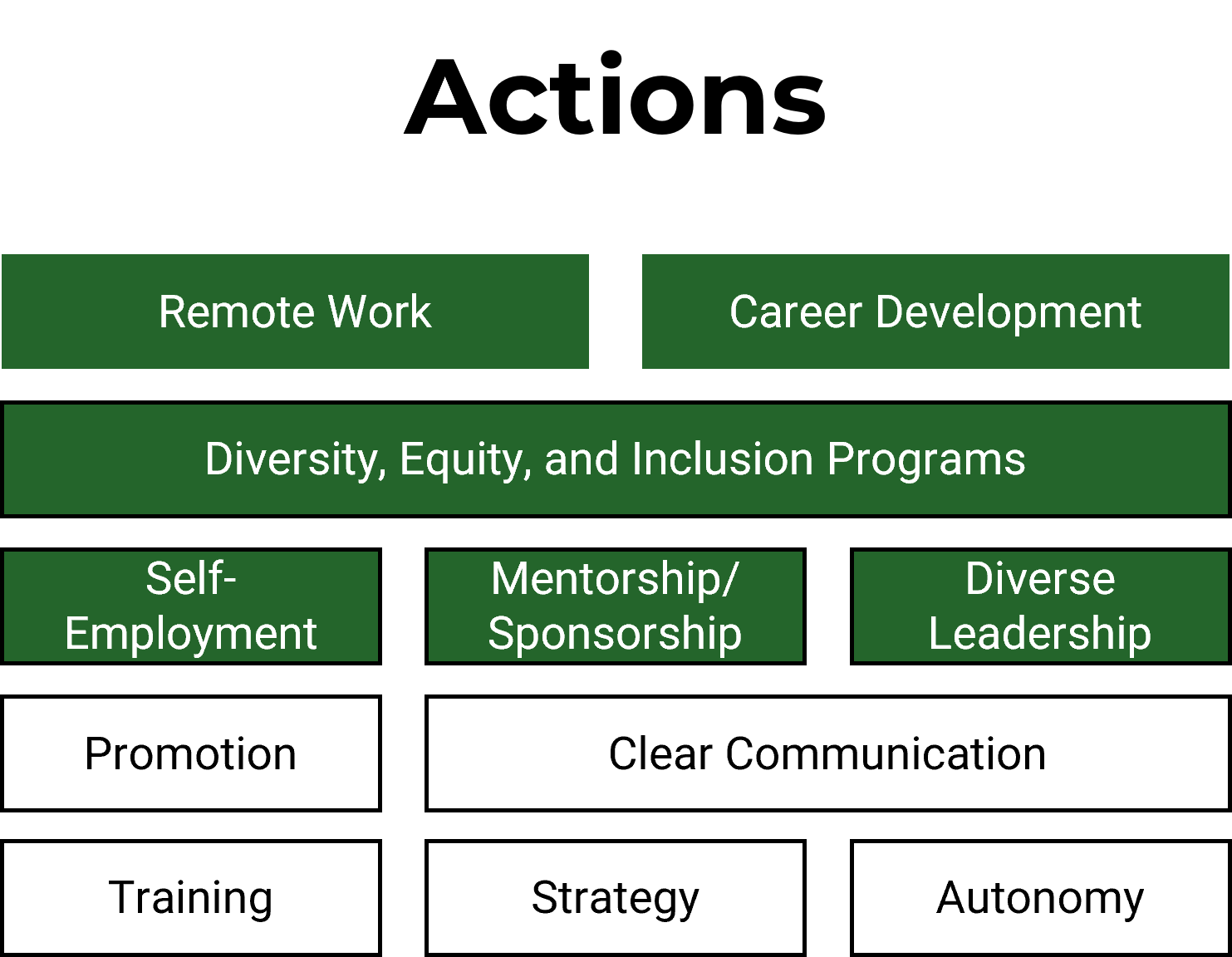
There are various actions that organizations can take to help address barriers.
It's important to ensure these are not put in as band-aid solutions but that they are carefully thought out and layered.
Our findings demonstrate that remote work, career development, and DEI programs along with mentorship and diverse leadership are strong enablers of professional satisfaction. An unfortunate consequence, if professionals are not nurtured, is that we risk losing much needed talent to self-employment or to other organizations.
There are several solutions
Respondents were asked to distribute points across potential solutions that could lead to job satisfaction. The ratings showed that there were common solutions that could be leveraged across all groups.
Respondents were asked what solutions were valuable for their career development.
All groups were mostly aligned on the order of the solutions that would lead to career satisfaction; however, Black professionals rated the importance of employee resource groups as higher than their colleagues did.

Mentorship and sponsorship are seen as key for all employees, as is of course training.
However, employee resource groups (ERGs) were rated significantly higher for Black professionals and discussions around diversity were higher for their colleagues. This may be because other groups feel a need to learn more about diversity, whereas Black professionals live this experience on a day-to day basis, so it's not as critical for them.
Double the number of satisfied Black professionals through mentorship and sponsorship

Mentorship and sponsorship help to close the job satisfaction gap for Black IT professionals. The percentage of satisfied Black employees almost doubles when they have a mentor or sponsorship, moving the satisfaction rate to closer to all other colleagues.
As leaders, you likely benefit from a few different advisors, and your staff should be able to benefit in the same way.
They can have their own personal board of advisors, both inside and outside of your organization, helping them to navigate the working world in IT.
To support your staff, provide guidance and coaching to internal mentors so that they can best support employees, and ensure that your organizational culture supports relationship building and trust.
While all are critical, coaching, mentoring, and sponsorship are not the same
Coaching
Performance-driven guidance geared to support the employee with on-the-job performance. This could be a short-term relationship.
Mentorship
A relationship where the mentor provides guidance, information, and expertise to support the long-term career development of the mentee.
Sponsorship
The act of advocating on the behalf of another for a position, promotion, development opportunity, etc. over a longer period.
For more information on setting up a mentorship program, see Optimize the Mentoring Program to Build a High Performing Learning Organization.
On why mentorship and sponsorship are important:
|
"With some degree of mentorship or sponsorship, it means that your ability to thrive or to have a positive experience in organizations increases substantially. Mentorship and sponsorship are very often the lynchpin of someone being successful and sticking with an organization. Sponsorship is an endorsement to other high-level stakeholders who very often are the gatekeepers of opportunity. Sponsors help to shepherd you through the gate." |

|
|
Carlos Thomas |
What is an employee resource group?
IT Professionals rated ERGs as the third top driver of success at work
Employee resource groups enable employees to connect in their workplace based on shared characteristics or life experiences.
ERGs generally focus on providing support, enhancing career development, and contributing to personal development in the work environment. Some ERGs provide advice to the organization on how they can support their diverse employees.
As leaders, you should support and encourage the formation of ERGs in your organization.
What each ERG does will vary according to the needs of employees in your organization. Your role is to enable the ERGs as they are created and maintained.
On setting up and leveraging employee resource groups:
|
"Employee resource groups, when leveraged in an authentically intentional way, can be the some of the most impactful stakeholders in the development and implementation of the organizational diversity, equity, and inclusion strategy. ERGs are essential to the development of policies, programs, and initiatives that address the needs of equity-seeking groups and are key to driving organizational culture and employee wellbeing, in addition to hiring and recruitment. ERGs must be set up for success by having adequate resources to do the work, which includes adequate budgets, executive sponsorship, training, support, and capacity to do the work. According to a Great Place To Work survey (2021), 50% of ERGs identified the need for adequate resources as a challenge for carrying out the work.:" |

|
|
CINNAMON CLARK |
There is a gap when it comes to diversity in leadership
Representation at leadership levels is especially stagnant.
Black Americans comprise 13.6% of the US population
(2022 data from the US Census Bureau)
And yet only 5.9% of the country's CEOs are Black, with only 6 (1%) at the top of Fortune 500 companies.
(2021 data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics and Fortune.com)
I've never worked for a company that has Black executives. It's difficult to envision long-term growth with an organization when you don't see yourself represented in leadership.
– Anonymous Interview Subject
Having diversity in your leadership team doubles satisfaction
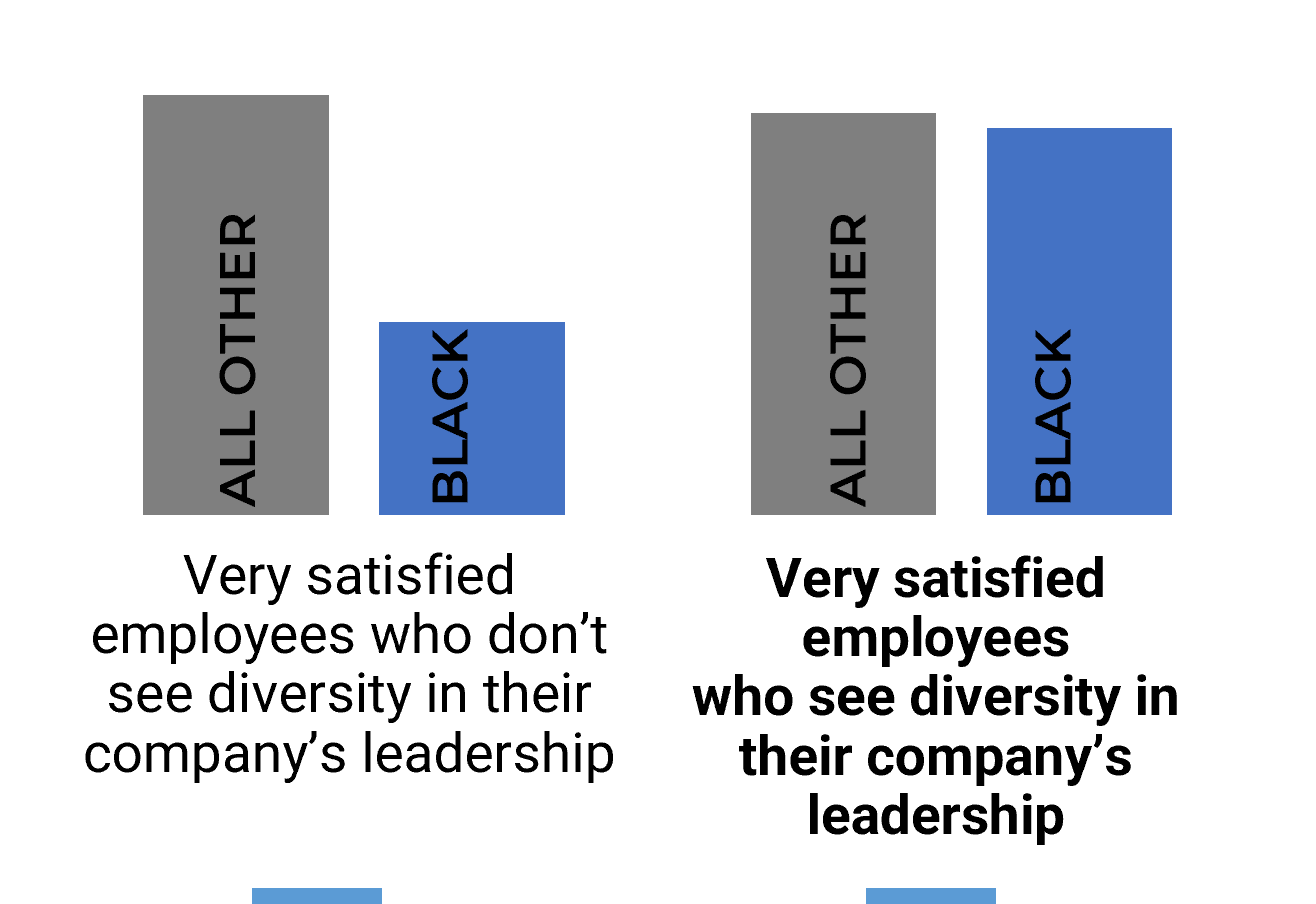
Our research shows that Black professionals are more satisfied in their role when they see leaders that look like them.
Satisfaction of other professionals is not as impacted by diversity in leadership as for Black professionals. Satisfaction doubles in organizations that have a diverse leadership team.
To reap the benefits from diversity, we need to ensure diversity is not just in entry or mid-level positions and provide employees an opportunity to see diversity in their company's leadership.
On the need for diversity in leadership:
|
"As a Black professional leader, it's not lost on me that I have a responsibility. I have to demonstrate authenticity, professionalism, and exemplary behavior that others can mimic. And I must also showcase that there are possibilities for those coming up in their career. I feel very grateful that I can bestow onto others my knowledge, my experience, my journey, and the tips that I've used to help bring me to be where I am. |

|
|
C. Fara Francis |
Work from home
While all groups have embraced the work-from-home movement, many Black professionals find it reduces the impact of racial incidents in the workplace.
Percentage of employees who experienced positive changes in motivation after working remotely.

I have to guard and protect myself from experiencing and witnessing racism every day. I am currently working remotely, and I can say for certain my mood and demeanor have improved. Not having to decide if I should address a racist comment or action has made my day easier.
Source: Slate, 2022
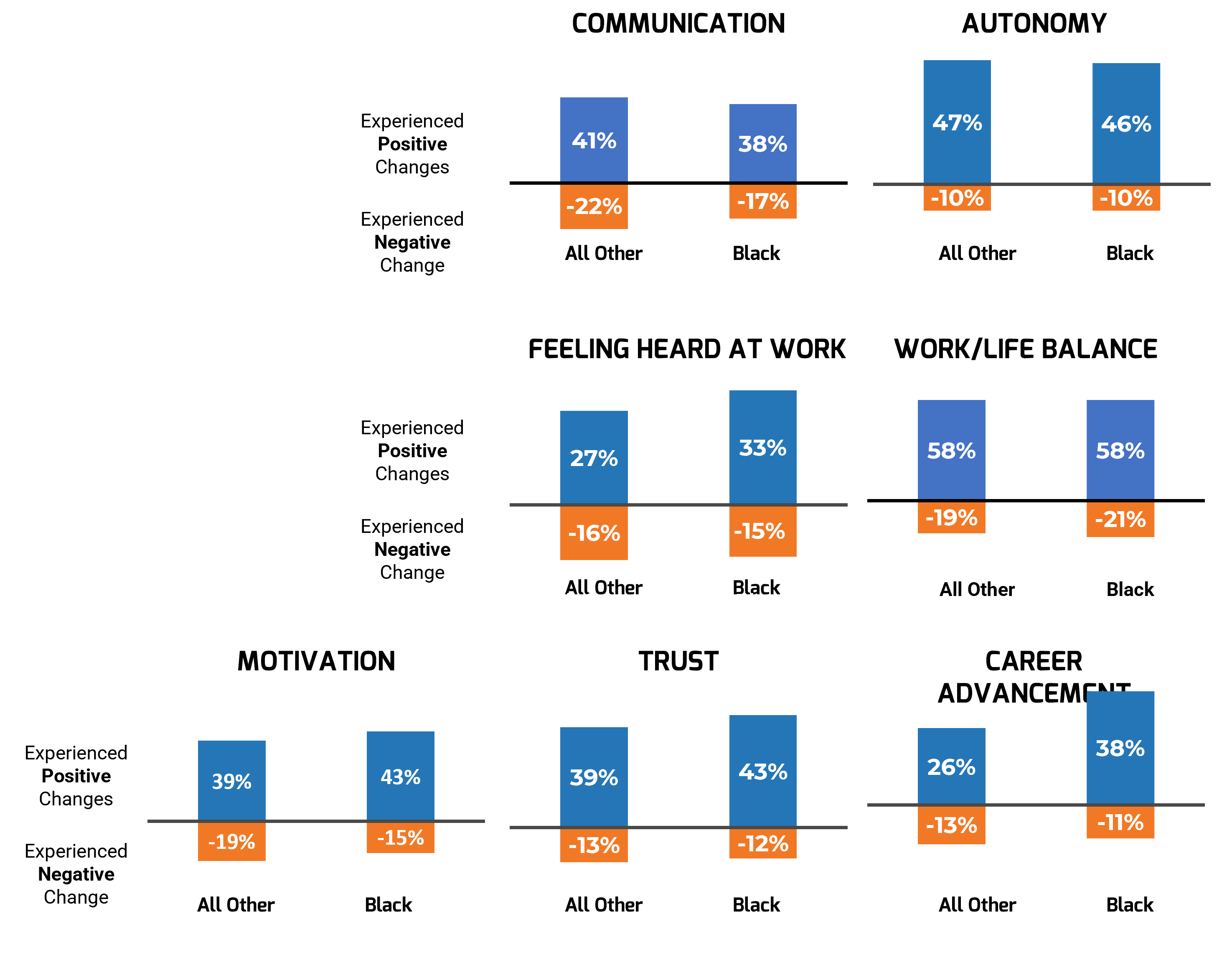
Remote work significantly led to feelings of better chances for career advancement
Survey respondents were asked about the positive and negative changes they saw in their interactions and experiences with remote work. Black employees and their colleagues replied similarly, with mostly positive experiences.
While both groups enjoyed better chances for career advancement, the difference was significantly higher for Black professionals.
Reasons for Self-Employment:
More Black professionals have chosen self-employment than their colleagues.
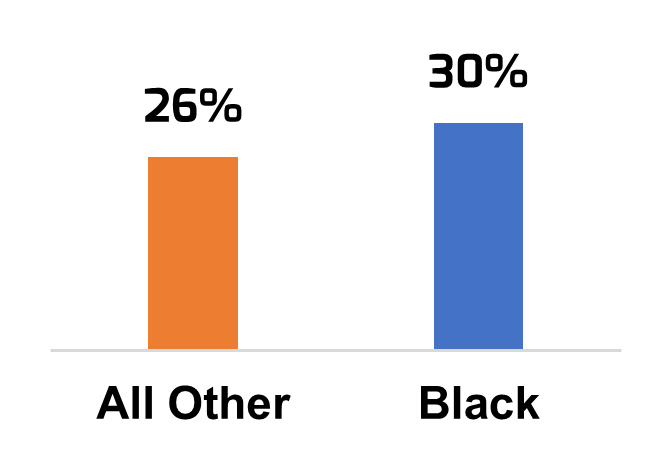
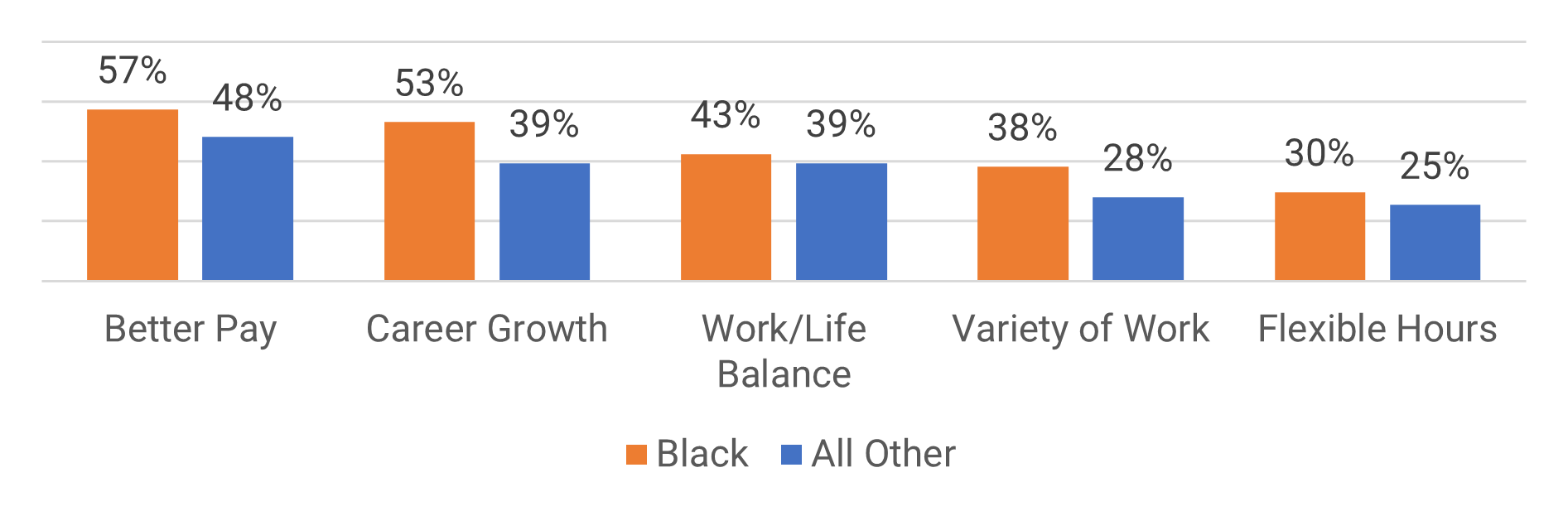
The biggest reasons for both groups in choosing self-employment were for better pay, career growth, and work/life balance.
While the desire for better pay was the highest reason for both groups, for engaged employees salary is a lower priority than other concerns (Adecco Group's Global Workforce of the Future report). Consider salary in conjunction with career growth, work/life balance, and the variety in the work that your employees have.
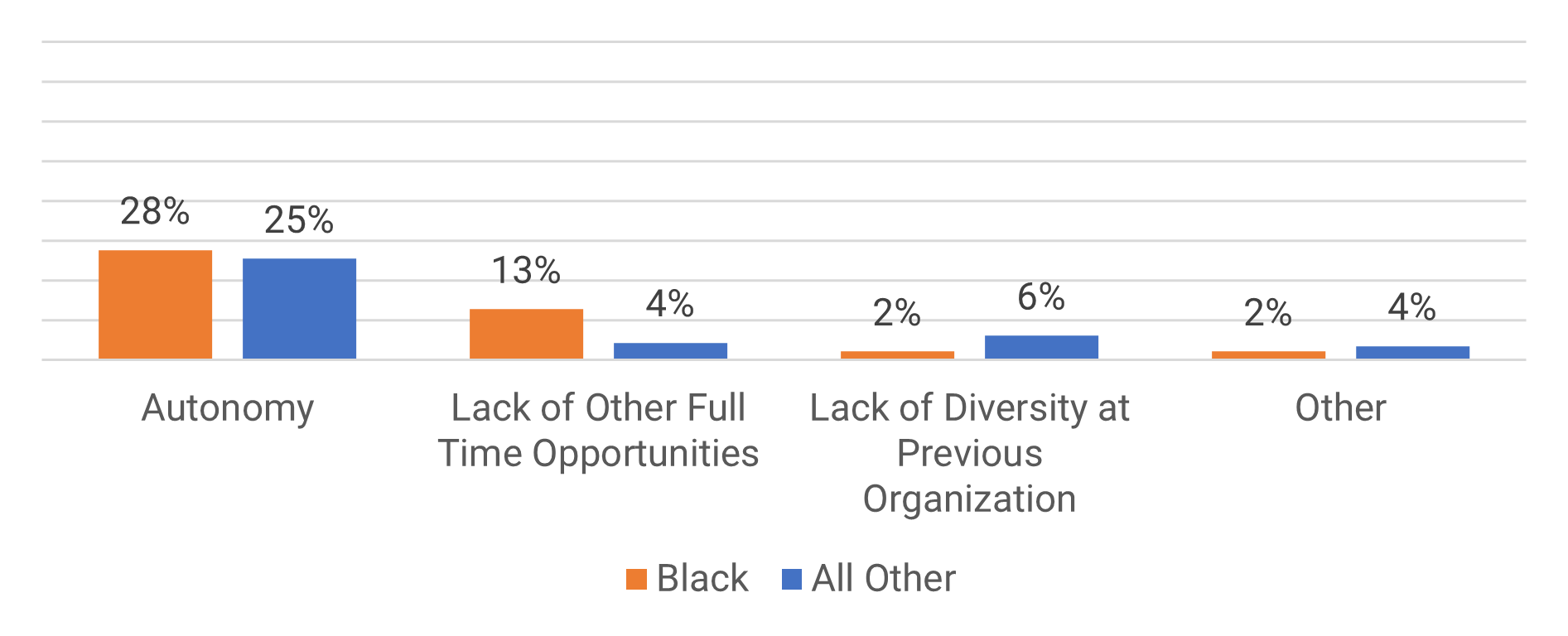
If we don't consider our Black employees, not only do we risk them leaving the organization, but they may decide to just work for themselves.
Most professionals believe their organizations are committed to diversity, equity, and inclusion
38% of all respondents believe their organizations are very committed to DEI
49% believe they are somewhat committed
9% feel they are not committed
4% are unsure
Make sure supports are in place to help your employees grow in their careers:
Leadership
IT Leadership Career Planning Research Center
Diversity and Inclusion Tactics
IT Diversity & Inclusion Tactics
Employee Development Planning
Implement an IT Employee Development Plan
Belief in your organization's diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts isn't consistent across groups: Make sure actions are seen as genuine
While organization's efforts are acknowledged, Black professionals aren't as optimistic about the commitment as their peers. Make sure that your programs are reaching the various groups you want to impact, to increase the likelihood of satisfaction in their roles.
SATISFACTION INCREASES IN BOTH BLACK AND NON-BLACK PROFESSIONALS
When they believe in their company's commitment to diversity, equity. and inclusion.
Of those who believe in their organization's commitment, 61% of Black professionals and 67% of non-Black professionals are very satisfied in their roles.
|
BELIEVE THEIR ORGANIZATION IS NOT COMMITTED TO DEI |
BELIEVE THEIR ORGANIZATION IS VERY COMMITTED TO DEI |
|
|---|---|---|
|
NON-BLACK PROFESSIONALS |
8% |
41% |
|
BLACK PROFESSIONALS |
13% |
30% |
Recommendations
It's important to understand the current landscape:
- The barriers that Black employees often face.
- The potential solutions that can help close the gap in employee satisfaction.
We recognize that resolving this is not easy. Although senior executives are recognizing that a diverse set of experiences, perspectives, and backgrounds is crucial to fostering innovation and competing on the global stage, organizations often don't take the extra step to actively look for racialized talent, and many people still believe that race doesn't play an important part in an individual's ability to access opportunities.
Look at a variety of solutions that you can implement within your organization; layering solutions is the key to driving business diversity. Always keep in mind that diversity is not a monolith, that the experiences of each demographic varies.
Info-Tech resources
Appendix
About the research
Diversity in tech survey
As part of the research process for the State of Black Tech Report, Info-Tech Research Group conducted an open online survey among its membership and wider community of professionals. The survey was fielded from October 2021 to April 2022, collecting 633 responses.
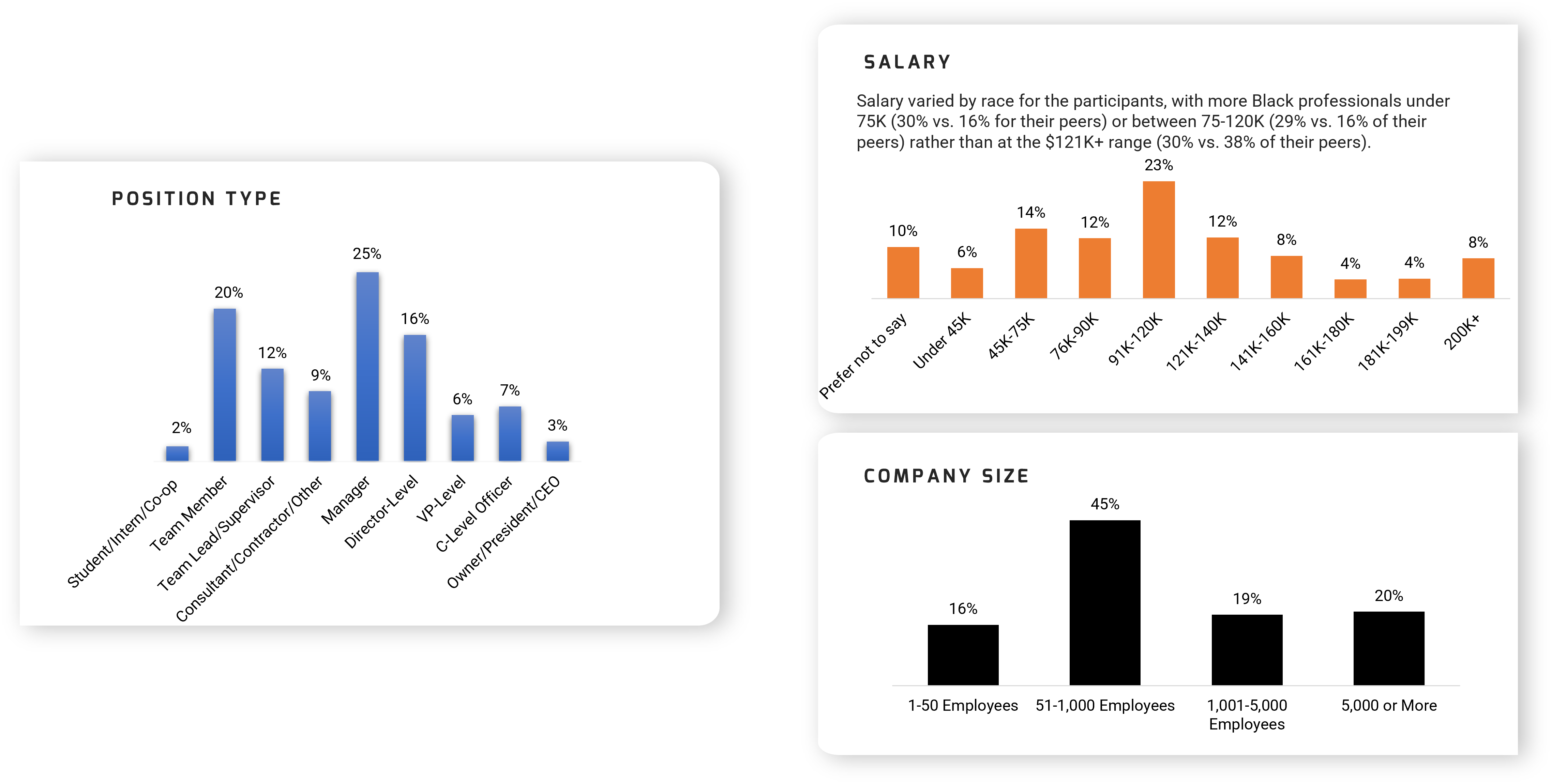
Current Position
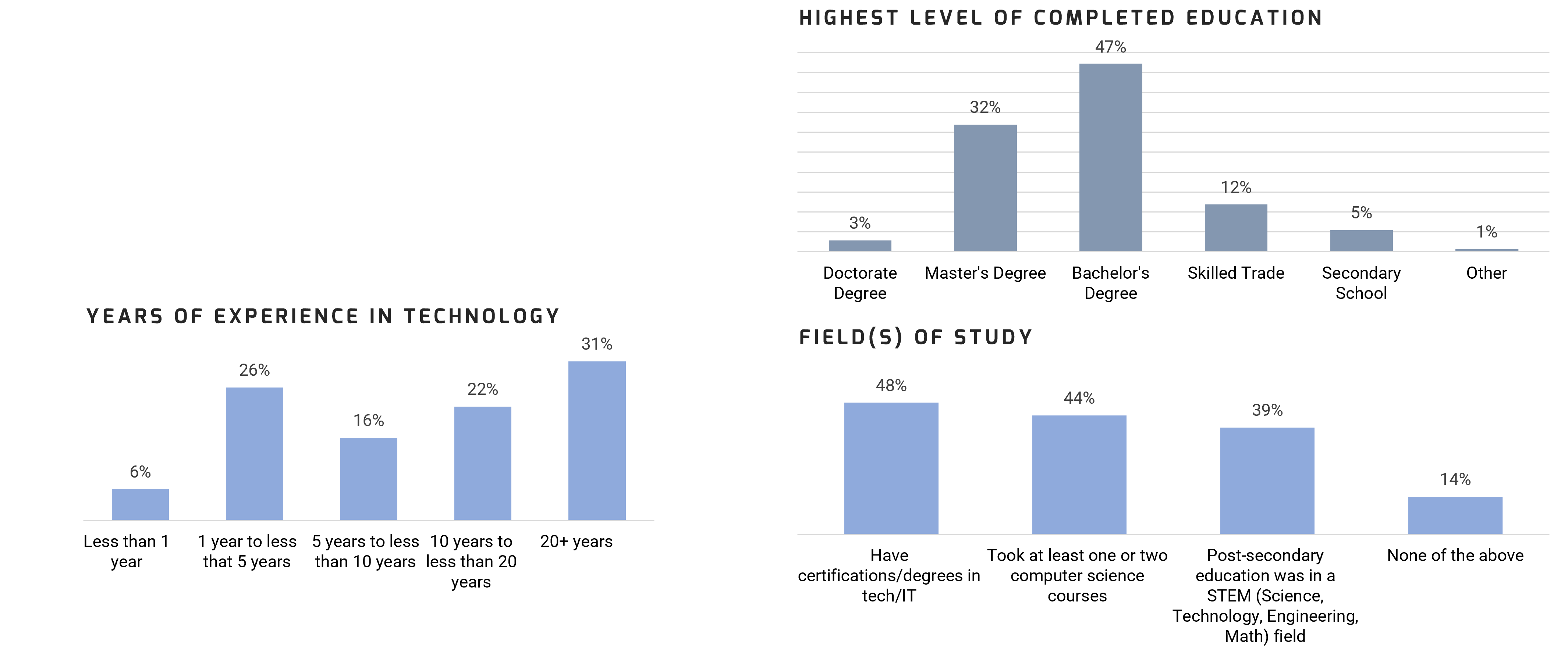
Education and Experience
Education was fairly consistent across both groups, with a few exceptions: more Black professionals had secondary school (9% vs. 4%) and more Black professionals had Doctorate degrees (4% vs. 2%).
We had more non-Black respondents with 20+ years of experience (31% vs. 19%) and more Black respondents with less than 1 year of experience (8% vs. 5%) – the rest of the years of experience were consistent across the two groups.
It is important to recognize that people are often seen by "the world" as belonging to a different race or set of races than what they personally identify as. Both aspects impact a professional's experience in the workplace.
Bibliography
Barton, LeRon. “I’m Black. Remote Work Has Been Great for My Mental Health.” Slate, 15 July 2022.
“Black or African American alone, percent.” U.S. Census Bureau QuickFacts: United States. Accessed 14 February 2023.
Boyle, Matthew. “More Workers Ready to Quit Over ‘Window Dressing’ Racism Efforts.” Bloomberg.com, 9 June 2022.
Boyle, Matthew. “Remote Work Has Vastly Improved the Black Worker Experience.” Bloomberg.com, 5 October 2021.
Cooper, Frank, and Ranjay Gulati. “What Do Black Executives Really Want?” Harvard Business Review, 18 November 2021.
“Emotional Tax.” Catalyst. Accessed 1 April 2022.
“Employed Persons by Detailed Occupation, Sex, Race, and Hispanic or Latino Ethnicity” U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Accessed February 14, 2023.
“Equality in Tech Report - Welcome.” Dice, 9 March 2022. Accessed 23 March 2022.
Erb, Marcus. "Leaders Are Missing the Promise and Problems of Employee Resource Groups." Great Place To Work, 30 June 2021.
Gawlak, Emily, et al. “Key Findings - Being Black In Corporate America.” Coqual, Center for Talent Innovation (CTI), 2019.
“Global Workforce of the Future Research.” Adecco, 2022. Accessed 4 February 2023.
Gruman, Galen. “The State of Ethnic Minorities in U.S. Tech: 2020.” Computerworld, 21 September 2020. Accessed 31 May 2022.
Hancock, Bryan, et al. “Black Workers in the US Private Sector.” McKinsey, 21 February 2021. Accessed 1 April 2022.
“Hierarchy Of Needs Applied To Employee Engagement.” Proactive Insights, 12 February 2020.
Hobbs, Cecyl. “Shaping the Future of Leadership for Black Tech Talent.” Russell Reynolds Associates, 27 January 2022. Accessed 3 August 2022.
Hubbard, Lucas. “Race, Not Job, Predicts Economic Outcomes for Black Households.” Duke Today, 16 September 2021. Accessed 30 May 2022.
Knight, Marcus. “How the Tech Industry Can Be More Inclusive to the Black Community.” Crunchbase, 23 February 2022.
“Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in Employee Engagement (Pre and Post Covid 19).” Vantage Circle HR Blog, 30 May 2022.
McDonald, Autumn. “The Racism of the ‘Hard-to-Find’ Qualified Black Candidate Trope (SSIR).” Stanford Social Innovation Review, 1 June 2021. Accessed 13 December 2021.
McGlauflin, Paige. “The Fortune 500 Features 6 Black CEOs—and the First Black Founder Ever.” Fortune, 23 May 2022. Accessed 14 February 2023.
“Microaggression." Oxford English Dictionary, Oxford Languages, 2023.
Reed, Jordan. "Understanding Racial Microaggression and Its Effect on Mental Health." Pfizer, 26 August 2020.
Shemla, Meir “Why Workplace Diversity Is So Important, And Why It’s So Hard To Achieve.” Forbes, 22 August 2018. Accessed 4 February 2023.
“The State of Black Women in Corporate America.” Lean In and McKinsey & Company, 2020. Accessed 14 January 2022.
Van Bommel, Tara. “The Power of Empathy in Times of Crisis and Beyond (Report).” Catalyst, 2021. Accessed 1 April 2022.
Vu, Viet, Creig Lamb, and Asher Zafar. “Who Are Canada’s Tech Workers?” Brookfield Institute for Innovation and Entrepreneurship, January 2019. Accessed on Canadian Electronic Library, 2021. Web.
Warner, Justin. “The ROI of Employee Engagement: Show Me the Money!” DecisionWise, 1 January 2020. Web.
White, Sarah K. “5 Revealing Statistics about Career Challenges Black IT Pros Face.” CIO (blog), 9 February 2023. Accessed 5 July 2022.
Williams, Joan C. “Stop Asking Women of Color to Do Unpaid Diversity Work.” Bloomberg.com, 14 April 2022.
Williams, Joan C., Rachel Korn, and Asma Ghani. “A New Report Outlines Some of the Barriers Facing Asian Women in Tech.” Fast Company, 13 April 2022.
Wilson, Valerie, Ethan Miller, and Melat Kassa. “Racial representation in professional occupations.” Economic Policy Institute, 8 June 2021.
“Workplace Diversity: Why It’s Good for Business.” Business Development Canada (BDC.ca), 6 Feb. 2023. Accessed 4 February 2023.