
Optimize IT Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization
- Companies are approving more projects than they can deliver. Most organizations say they have too many projects on the go and an unmanageable and ever-growing backlog of things to get to.
- While organizations want to achieve a high throughput of approved projects, many are unable or unwilling to allocate an appropriate level of IT resourcing to adequately match the number of approved initiatives.
- Portfolio management practices must find a way to accommodate stakeholder needs without sacrificing the portfolio to low-value initiatives that do not align with business goals.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Approve only the right projects that you have capacity to deliver. Failure to align projects with strategic goals and resource capacity are the most common causes of portfolio waste across organizations.
- More time spent with stakeholders during the ideation phase to help set realistic expectations for stakeholders and enhance visibility into IT’s capacity and processes is key to both project and organizational success.
- Too much intake red tape will lead to an underground economy of projects that escape portfolio oversight, while too little intake formality will lead to a wild west of approvals that could overwhelm the PMO. Finding the right balance of intake formality for your organization is the key to establishing a PMO that has the ability to focus on the right things.
Impact and Result
- Establish an effective scorecard to create transparency into IT’s capacity and processes. This will help set realistic expectations for stakeholders, eliminate “squeaky wheel” prioritization, and give primacy to the highest value requests.
- Build a centralized process that funnels requests into a single intake channel to eliminate confusion and doubt for stakeholders and staff while also reducing off-the-grid initiatives.
- Clearly define a series of project approval steps, and communicate requirements for passing them.
- Develop practices that incorporate the constraint of resource capacity to cap the amount of project approvals to that which is realistic to help improve the throughput of projects through the portfolio.
Optimize IT Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization Research & Tools
Start here – read the Executive Brief
Read our concise Executive Brief to find out why you should optimize project intake, approval, and prioritization process, review Info-Tech’s methodology, and understand the four ways we can support you in completing this project.Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
- Optimize IT Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization – Phases 1-3
1. Set realistic goals for optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization process
Get value early by piloting a scorecard for objectively determining project value, and then examine your current state of project intake to set realistic goals for optimizing the process.
- Optimize Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization – Phase 1: Set Realistic Goals for Optimizing Process
- Project Value Scorecard Development Tool
- Project Intake Workflow Template - Visio
- Project Intake Workflow Template - PDF
- Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP
2. Build an optimized project intake, approval, and prioritization process
Take a deeper dive into each of the three processes – intake, approval, and prioritization – to ensure that the portfolio of projects is best aligned to stakeholder needs, strategic objectives, and resource capacity.
- Optimize Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization – Phase 2: Build New Optimized Processes
- Light Project Request Form
- Detailed Project Request Form
- Project Intake Classification Matrix
- Benefits Commitment Form Template
- Proposed Project Technology Assessment Tool
- Fast Track Business Case Template
- Comprehensive Business Case Template
- Project Intake and Prioritization Tool
3. Integrate the new optimized processes into practice
Plan a course of action to pilot, refine, and communicate the new optimized process using Info-Tech’s expertise in organizational change management.
- Optimize Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization – Phase 3: Integrate the New Processes into Practice
- Intake Process Pilot Plan Template
- Project Backlog Manager
- Intake and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool
Workshop: Optimize IT Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization
Workshops offer an easy way to accelerate your project. If you are unable to do the project yourself, and a Guided Implementation isn't enough, we offer low-cost delivery of our project workshops. We take you through every phase of your project and ensure that you have a roadmap in place to complete your project successfully.
1 Refocus on Project Value to Set Realistic Goals
The Purpose
Set the course of action for optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization by examining the current state of the process, the team, the stakeholders, and the organization as a whole.
Key Benefits Achieved
The overarching goal of optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization process is to maximize the throughput of the best projects. To achieve this goal, one must have a clear way to determine what are “the best” projects.
Activities
1.1 Define the criteria with which to determine project value.
1.2 Envision your target state for your optimized project intake, approval, and prioritization process.
Outputs
Draft project valuation criteria
Examination of current process, definition of process success criteria
2 Examine, Optimize, and Document the New Process
The Purpose
Drill down into, and optimize, each of the project intake, approval, and prioritization process.
Key Benefits Achieved
Info-Tech’s methodology systemically fits the project portfolio into its triple constraint of stakeholder needs, strategic objectives, and resource capacity, to effectively address the challenges of establishing organizational discipline for project intake.
Activities
2.1 Conduct retrospectives of each process against Info-Tech’s best practice methodology for project intake, approval, and prioritization process.
2.2 Pilot and customize a toolbox of deliverables that effectively captures the right amount of data developed for informing the appropriate decision makers for approval.
Outputs
Documentation of new project intake, approval, and prioritization process
Tools and templates to aid the process
3 Pilot, Plan, and Communicate the New Process
The Purpose
Reduce the risks of prematurely implementing an untested process.
Methodically manage the risks associated with organizational change and maximize the likelihood of adoption for the new process.
Key Benefits Achieved
Engagement paves the way for smoother adoption. An “engagement” approach (rather than simply “communication”) turns stakeholders into advocates who can help boost your message, sustain the change, and realize benefits without constant intervention or process command-and-control.
Activities
3.1 Create a plan to pilot your intake, approval, and prioritization process to refine it before rollout.
3.2 Analyze the impact of organizational change through the eyes of PPM stakeholders to gain their buy-in.
Outputs
Process pilot plan
Organizational change communication plan
Further reading
Optimize IT Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization
Decide which IT projects to approve and when to start them.
ANALYST PERSPECTIVE
Capacity-constrained intake is the only sustainable path forward.
"For years, the goal of project intake was to select the best projects. It makes sense and most people take it on faith without argument. But if you end up with too many projects, it’s a bad strategy. Don’t be afraid to say NO or NOT YET if you don’t have the capacity to deliver. People might give you a hard time in the near term, but you’re not helping by saying YES to things you can’t deliver."
Barry Cousins,
Senior Director, PMO Practice
Info-Tech Research Group
Our understanding of the problem
This Research Is Designed For:
- PMO Directors who have trouble with project throughput
- CIOs who want to improve IT’s responsive-ness to changing needs of the business
- CIOs who want to maximize the overall business value of IT’s project portfolio
This Research Will Help You:
- Align project intake and prioritization with resource capacity and strategic objectives
- Balance proactive and reactive demand
- Reduce portfolio waste on low-value projects
- Manage project delivery expectations and satisfaction of business stakeholders
- Get optimized project intake processes off the ground with low-cost, high-impact tools and templates
This Research Will Also Assist:
- C-suite executives and steering committee members who want to ensure IT’s successful delivery of projects with high business impact
- Project sponsors and product owners who seek visibility and transparency toward proposed projects
This Research Will Help Them:
- Ensure that high-impact projects are approved and delivered in a timely manner
- Gain clarity and visibility in IT’s project approval process
- Improve your understanding of IT’s capacity to set more realistic expectations on what gets done
Executive summary
Situation
- As a portfolio manager, you do not have the authority to decline or defer new projects – but you also lack the capacity to realistically say yes to more project work.
- Stakeholders have unrealistic expectations of what IT can deliver. Too many projects are approved, and it may be unclear why their project is delayed or in a state of suspended animation.
Complication
- The cycle of competition is making it increasingly difficult to follow a longer-term strategy during project intake, making it unproductive to approve projects for any horizon longer than one to two years.
- As project portfolios become more aligned to “transformative” projects, resourcing for smaller, department-level projects becomes increasingly opaque.
Resolution
- Establish an effective scorecard to create transparency into IT’s capacity and processes. This will help set realistic expectations for stakeholders, eliminate “squeaky wheel” prioritization, and give primacy to the highest value requests.
- Build a centralized process that funnels requests into a single intake channel to eliminate confusion and doubt for stakeholders and staff while also reducing off-the-grid initiatives.
- Clearly define a series of project approval steps, and communicate requirements for passing them.
- Developing practices that incorporate the constraint of resource capacity to cap the amount of project approvals to that which is realistic will help improve the throughput of projects through the portfolio.
Info-Tech Insight
- Approve only the right projects… Counterbalance stakeholder needs with strategic objectives of the business and that of IT, in order to maintain the value of your project portfolio at a high level.
- …that you have capacity to deliver. Resource capacity-informed project approval process enables you to avoid biting off more than you can chew and, over time, build a track record of fulfilling promises to deliver on projects.
Most organizations are good at approving projects, but bad at starting them – and even worse at finishing them
Establishing project intake discipline should be a top priority from a long-term strategy and near-term tactical perspective.
Most organizations approve more projects than they can finish. In fact, many approve more than they can even start, leading to an ever-growing backlog where project ideas – often good ones – are never heard from again.
The appetite to approve more runs directly counter to the shortage of resources that plagues most IT departments. This tension of wanting more from less suggests that IT departments need to be more disciplined in choosing what to take on.
Info-Tech’s data shows that most IT organizations struggle with their project backlog (Source: N=397 organizations, Info-Tech Research Group PPM Current State Scorecard, 2017).
“There is a minimal list of pending projects”
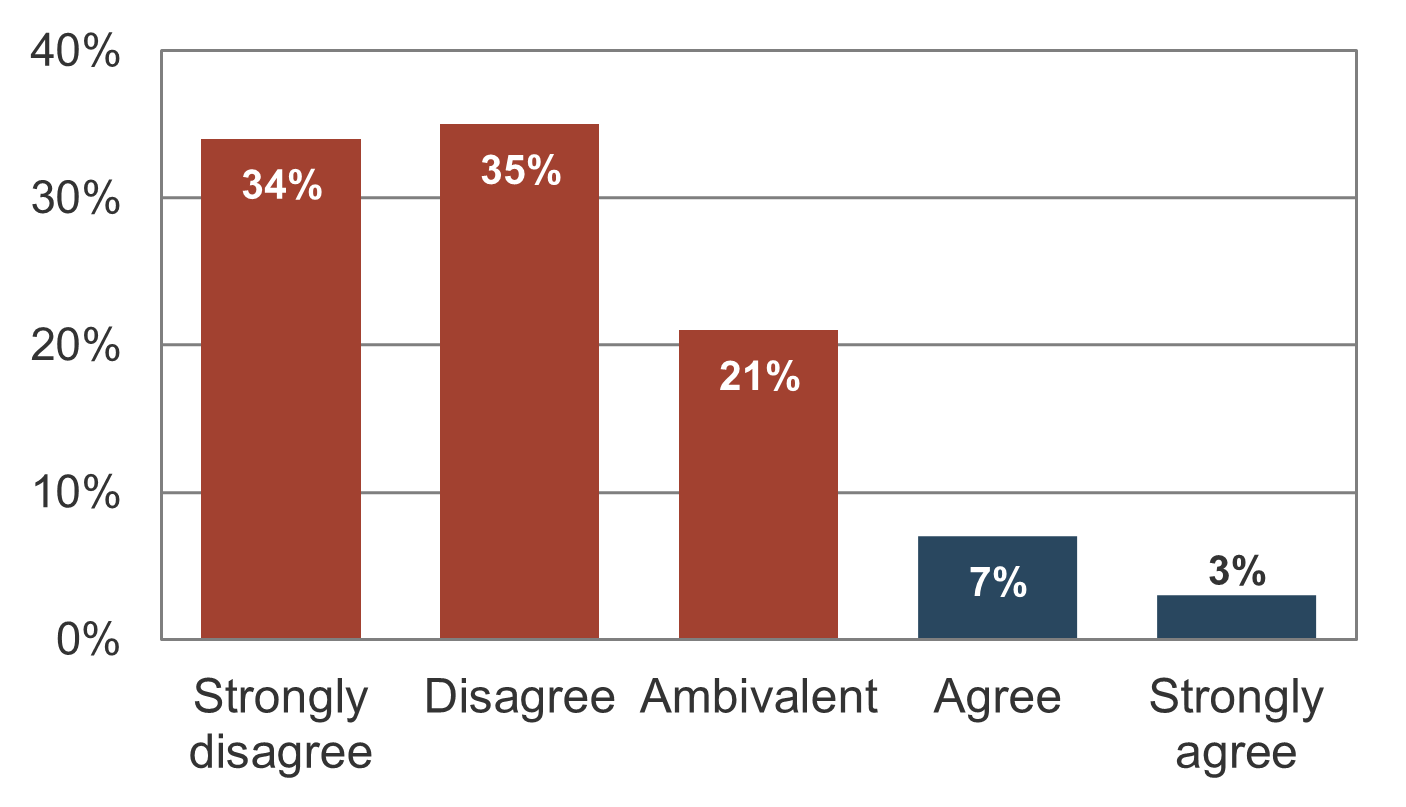
“Last year we delivered the number of projects we anticipated at the start of the year”
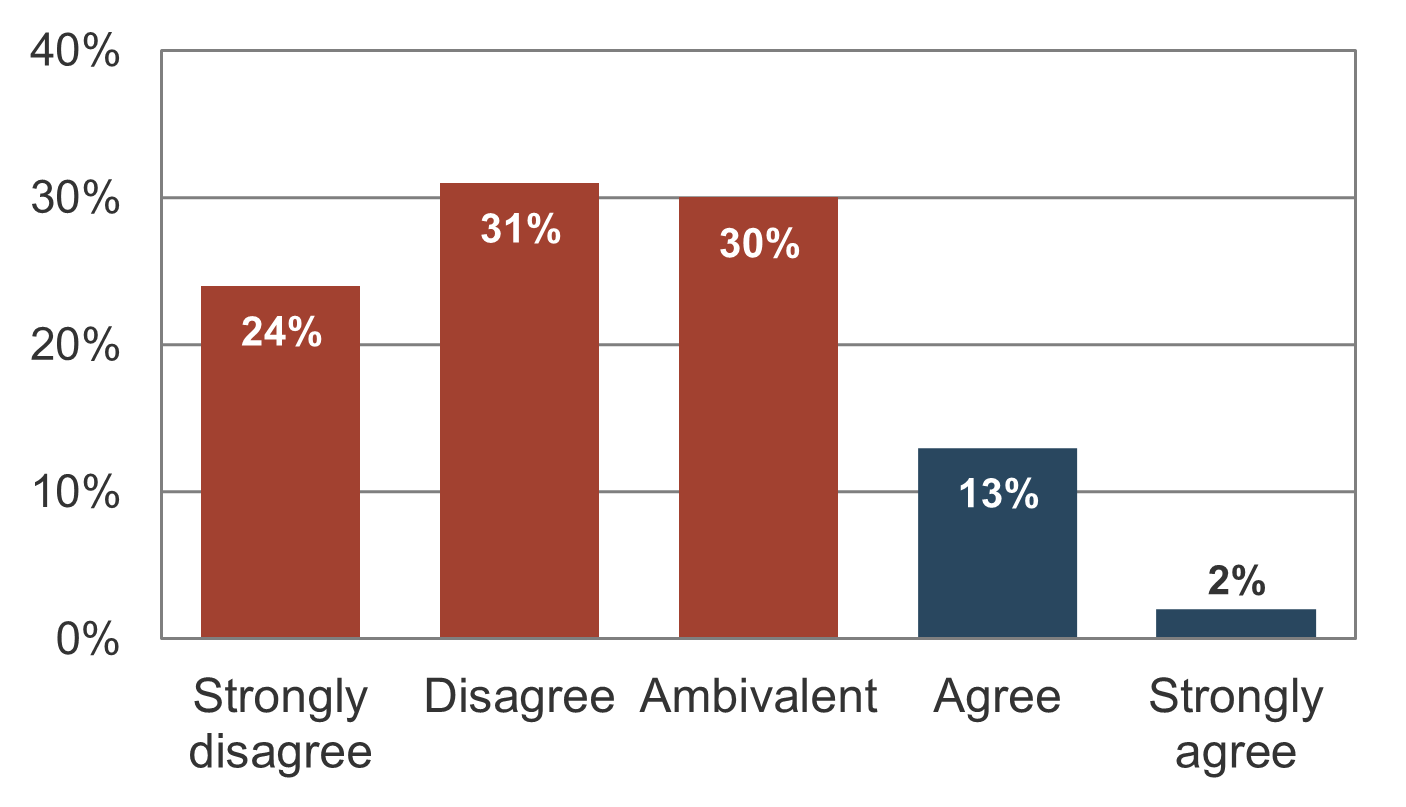
The concept of fiduciary duty demonstrates the need for better discipline in choosing what projects to take on
Unless someone is accountable for making the right investment of resource capacity for the right projects, project intake discipline cannot be established effectively.
What is fiduciary duty?
Officers and directors owe their corporation the duty of acting in the corporation’s best interests over their own. They may delegate the responsibility of implementing the actions, but accountability can't be delegated; that is, they have the authority to make choices and are ultimately answerable for them.
No question is more important to the organization’s bottom line. Projects directly impact the bottom line because they require investment of resource time and money for the purposes of realizing benefits. The scarcity of resources requires that choices be made by those who have the right authority.
Who approves your projects?
Historically, the answer would have been the executive layer of the organization. However, in the 1990s management largely abdicated its obligation to control resources and expenditures via “employee empowerment.”
Controls on approvals became less rigid, and accountability for choosing what to do (and not do) shifted onto the shoulders of the individual worker. This creates a current paradigm where no one is accountable for the malinvestment…
…of resources that comes from approving too many projects. Instead, it’s up to individual workers to sink or swim as they attempt to reconcile, day after day, seemingly infinite organizational demand with their finite supply of working hours.
Ad hoc project selection schemes do not work
Without active management, reconciling the imbalance between demand with available work hours is a struggle that results largely in one of these two scenarios:
“Squeaky wheel”: Projects with the most vocal stakeholders behind them are worked on first.
- IT is seen to favor certain lines of business, leading to disenfranchisement of other stakeholders.
- Everything becomes the highest priority, which reinforces IT’s image as a firefighter, rather than a business value contributor
- High-value projects without vocal support never get resourced; opportunities are missed.
“First in, first out”: Projects are approved and executed in the order they are requested.
- Urgent or important projects for the business languish in the project backlog; opportunities are missed.
- Low-value projects dominate the project portfolio.
- Stakeholders leave IT out of the loop and resort to “underground economy” for getting their needs addressed.
80% of organizations feel that their portfolios are dominated by low-value initiatives that do not deliver value to the business (Source: Cooper).
Approve the right projects that you have capacity to deliver by actively managing the intake of projects
Project intake, approval, and prioritization (collectively “project intake”) reconciles the appetite for new projects with available resource capacity and strategic goals.
Project intake is a key process of project portfolio management (PPM). The Project Management Institute (PMI) describes PPM as:
"Interrelated organizational processes by which an organization evaluates, selects, prioritizes, and allocates its limited internal resources to best accomplish organizational strategies consistent with its vision, mission, and values."
(PMI, Standard for Portfolio Management, 3rd ed.)
Triple Constraint Model of the Project Portfolio
Project Intake:
- Stakeholder Need
- Strategic Objectives
- Resource Capacity
All three components are required for the Project Portfolio
Organizations practicing PPM recognize available resource capacity as a constraint and aim to select projects – and commit the said capacity – to projects that:
- Best satisfy the stakeholder needs that constantly change with the market
- Best align to the strategic objectives and contribute the most to business
- Have sufficient resource capacity available to best ensure consistent project throughput
92% vs. 74%: 92% of high-performing organizations in PPM report that projects are well aligned to strategic initiatives vs. 74% of low performers (PMI, 2015).
82% vs. 55%: 82% of high-performing organizations in PPM report that resources are effectively reallocated across projects vs. 55% of low performers (PMI, 2015)
Info-Tech’s data demonstrates that optimizing project intake can also improve business leaders’ satisfaction of IT
CEOs today perceive IT to be poorly aligned to business’ strategic goals:
43% of CEOs believe that business goals are going unsupported by IT (Source: Info-Tech’s CEO-CIO Alignment Survey (N=124)).
60% of CEOs believe that improvement is required around IT’s understanding of business goals (Source: Info-Tech’s CEO-CIO Alignment Survey (N=124)).
Business leaders today are generally dissatisfied with IT:
30% of business stakeholders are supporters of their IT departments (Source: Info-Tech’s CIO Business Vision Survey (N=21,367)).
The key to improving business satisfaction with IT is to deliver on projects that help the business achieve its strategic goals:
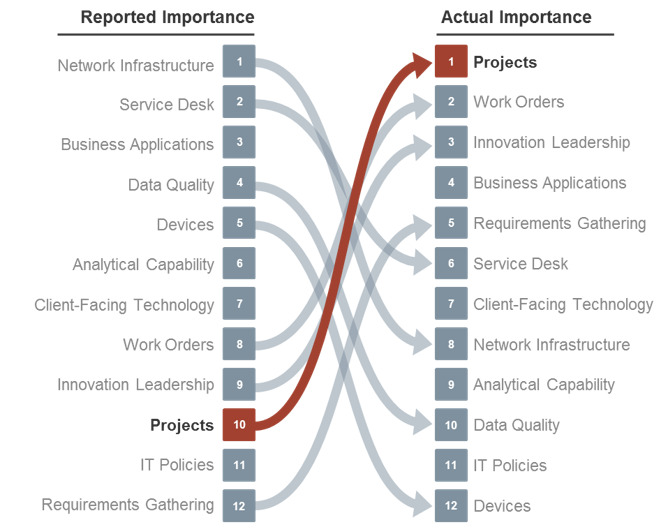
Source: Info-Tech’s CIO Business Vision Survey (N=21,367)
Optimized project intake not only improves the project portfolio’s alignment to business goals, but provides the most effective way to improve relationships with IT’s key stakeholders.
Benchmark your own current state with overall & industry-specific data using Info-Tech’s Diagnostic Program.
However, establishing organizational discipline for project intake, approval, and prioritization is difficult
Capacity awareness
Many IT departments struggle to realistically estimate available project capacity in a credible way. Stakeholders question the validity of your endeavor to install capacity-constrained intake process, and mistake it for unwillingness to cooperate instead.
Many moving parts
Project intake, approval, and prioritization involve the coordination of various departments. Therefore, they require a great deal of buy-in and compliance from multiple stakeholders and senior executives.
Lack of authority
Many PMOs and IT departments simply lack the ability to decline or defer new projects.
Unclear definition of value
Defining the project value is difficult because there are so many different and conflicting ways that are all valid in their own right. However, without it, it's impossible to fairly compare among projects to select what's "best."
Establishing intake discipline requires a great degree of cooperation and conformity among stakeholders that can be cultivated through strong processes.
Info-Tech’s intake, approval, and prioritization methodology systemically fits the project portfolio to its triple constraint
Info-Tech’s Methodology
| Info-Tech’s Methodology | ||
|---|---|---|
| Project Intake | Project Approval | Project Prioritization |
| Project requests are submitted, received, triaged, and scoped in preparation for approval and prioritization. | Business cases are developed, evaluated, and selected (or declined) for investment, based on estimated value and feasibility. | Work is scheduled to begin, based on relative value, urgency, and availability of resources. |
| Stakeholder Needs | Strategic Objectives | Resource Capacity |
| Project Portfolio Triple Constraint | ||
Info-Tech’s methodology for optimizing project intake delivers extraordinary value, fast
In the first step of the blueprint, you will prototype a set of scorecard criteria for determining project value.
Our methodology is designed to tackle your hardest challenge first to deliver the highest-value part of the deliverable. Since the overarching goal of optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization process is to maximize the throughput of the best projects, one must define how “the best projects” are determined.
In nearly all instances…a key challenge for the PPM team is reaching agreement over how projects should rank.
– Merkhofer
A Project Value Scorecard will help you:
- Evolve the discussions on project and portfolio value beyond a theoretical concept
- Enable apples-to-apples comparisons amongst many different kinds of projects
The Project Value Scorecard Development Tool is designed to help you develop the project valuation scheme iteratively. Download the pre-filled tool with content that represents a common case, and then, customize it with your data.

This blueprint provides a clear path to maximizing your chance of success in optimizing project intake
Info-Tech’s practical, tactical research is accompanied by a suite of tools and templates to accelerate your process optimization efforts.
Organizational change and stakeholder management are critical elements of optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization processes because they require a great degree of cooperation and conformity among stakeholders, and the list of key stakeholders are long and far-reaching.
This blueprint will provide a clear path to not only optimize the processes themselves, but also for the optimization effort itself. This research is organized into three phases, each requiring a few weeks of work at your team’s own pace – or all in one week, through a workshop facilitated by Info-Tech analysts.
Set Realistic Goals for Optimizing Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization
Tools and Templates:
- Project Value Scorecard Development Tool (.xlsx)
- PPM Assessment Report (Info-Tech Diagnostics)
- Standard Operating Procedure Template (.docx)
Build Optimized Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization Processes
Tools and Templates:
- Project Request Forms (.docx)
- Project Classification Matrix (.xlsx)
- Benefits Commitment Form (.xlsx)
- Proposed Project Technology Assessment Tool (.xlsx)
- Business Case Templates (.docx)
- Intake and Prioritization Tool (.xlsx)
Integrate the Newly Optimized Processes into Practice
Tools and Templates:
- Process Pilot Plan Template (.docx)
- Impact Assessment and Communication Planning Tool (.xlsx)
Info-Tech’s approach to PPM is informed by industry best practices and rooted in practical insider research
Info-Tech uses PMI and ISACA frameworks for areas of this research.

PMI’s Standard for Portfolio Management, 3rd ed. is the leading industry framework, proving project portfolio management best practices and process guidelines.

COBIT 5 is the leading framework for the governance and management of enterprise IT.
In addition to industry-leading frameworks, our best-practice approach is enhanced by the insights and guidance from our analysts, industry experts, and our clients.

33,000+
Our peer network of over 33,000 happy clients proves the effectiveness of our research.
1,000+
Our team conducts 1,000+ hours of primary and secondary research to ensure that our approach is enhanced by best practices.
Deliver measurable project intake success for your organization with this blueprint
Measure the value of your effort to track your success quantitatively and demonstrate the proposed benefits, as you aim to do so with other projects through improved PPM.
Optimized project intake, approval, and prioritization processes lead to a high PPM maturity, which will improve the successful delivery and throughput of your projects, resource utilization, business alignment, and stakeholder satisfaction ((Source: BCG/PMI).
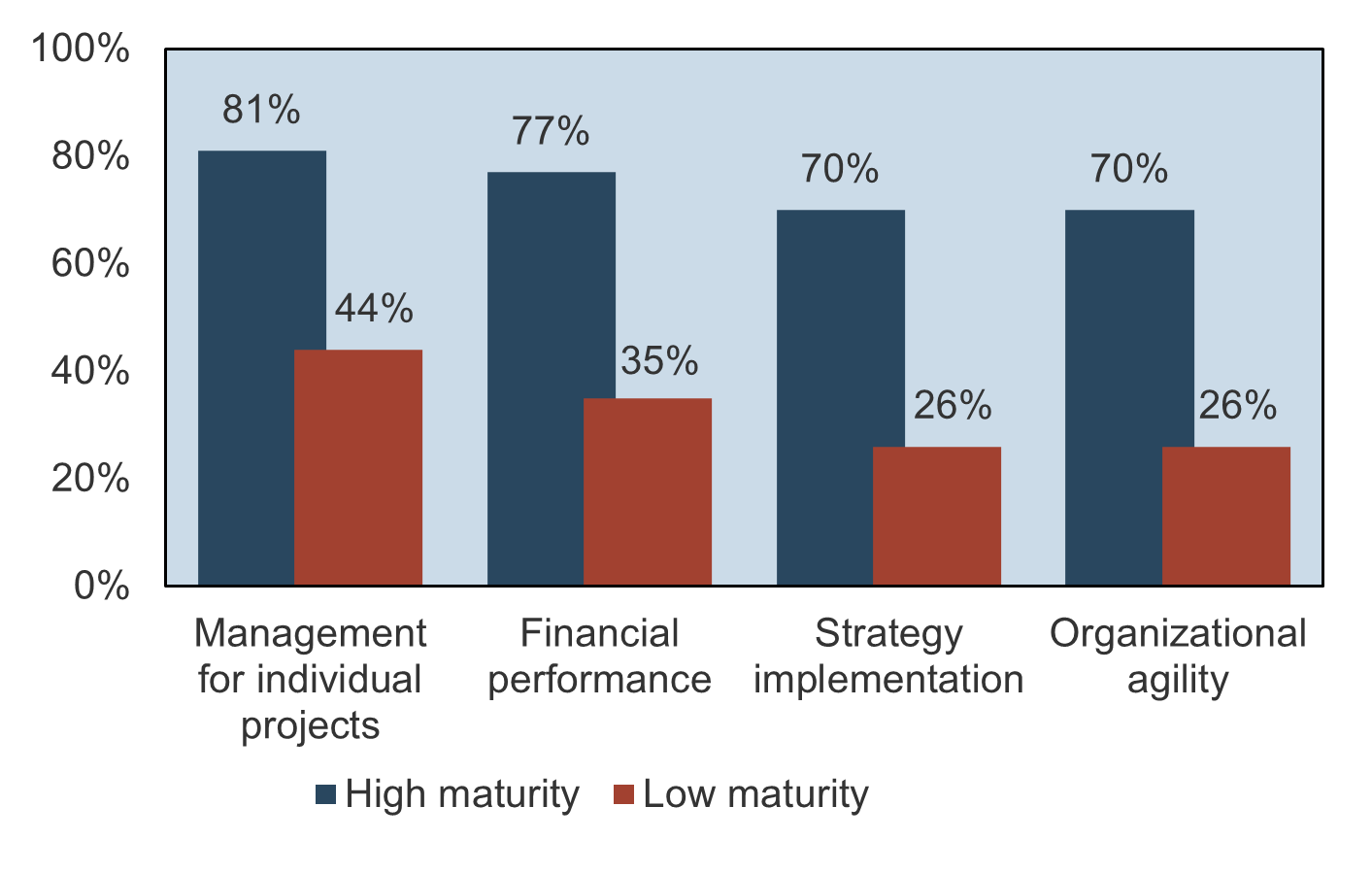
Measure your success through the following metrics:
- Reduced turnaround time between project requests and initial scoping
- Number of project proposals with articulated benefits
- Reduction in “off-the-grid” projects
- Team satisfaction and workplace engagement
- PPM stakeholder satisfaction score from business stakeholders: see Info-Tech’s PPM Customer Satisfaction Diagnostics
$44,700: In the past 12 months, Info-Tech clients have reported an average measured value of $44,700 from undertaking a guided implementation of this research.
Add your own organization-specific goals, success criteria, and metrics by following the steps in the blueprint.
Case Study: Financial Services PMO prepares annual planning process with Project Value Scorecard Development Tool
CASE STUDY
Industry: Financial Services
Source: Info-Tech Client
Challenge
PMO plays a diverse set of roles, including project management for enterprise projects (i.e. PMI’s “Directive” PMO), standards management for department-level projects (i.e. PMI’s “Supportive” PMO), process governance of strategic projects (i.e. PMI’s “Controlling” PMO), and facilitation / planning / reporting for the corporate business strategy efforts (i.e. Enterprise PMO).
To facilitate the annual planning process, the PMO needed to develop a more data-driven and objective project intake process that implicitly aligned with the corporate strategy.
Solution
Info-Tech’s Project Value Scorecard tool was incorporated into the strategic planning process.
Results
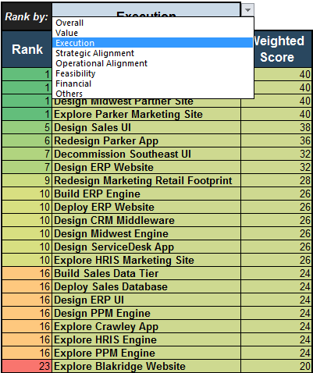
The scorecard provided a simple way to list the competing strategic initiatives, objectively score them, and re-sort the results on demand as the leadership chooses to switch between ranking by overall score, project value, ability to execute, strategic alignment, operational alignment, and feasibility.
The Project Value Scorecard provided early value with multiple options for prioritized rankings.
Info-Tech offers various levels of support to best suit your needs
DIY Toolkit
“Our team has already made this critical project a priority, and we have the time and capability, but some guidance along the way would be helpful.”
Guided Implementation
“Our team knows that we need to fix a process, but we need assistance to determine where to focus. Some check-ins along the way would help keep us on track.”
Workshop
“We need to hit the ground running and get this project kicked off immediately. Our team has the ability to take this over once we get a framework and strategy in place.”
Consulting
“Our team does not have the time or the knowledge to take this project on. We need assistance through the entirety of this project.”
Diagnostics and consistent frameworks used throughout all four options
Optimize Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization – project overview
| 1. Set Realistic Goals for Optimizing Process | 2. Build New Optimized Processes | 3. Integrate the New Processes into Practice | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best-Practice Toolkit |
1.1 Define the criteria with which to determine project value.
|
2.1 Streamline intake to manage stakeholder expectations. 2.2 Set up steps of project approval to maximize strategic alignment while right-sizing the required effort. 2.3 Prioritize projects to maximize the value of the project portfolio within the constraint of resource capacity. |
3.1 Pilot your intake, approval, and prioritization process to refine it before rollout. 3.2 Analyze the impact of organizational change through the eyes of PPM stakeholders to gain their buy-in. |
| Guided Implementations |
|
|
|
| Onsite Workshop |
Module 1: Refocus on Project Value to Set Realistic Goals for Optimizing Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization Process |
Module 2: Examine, Optimize, and Document the New Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization Process |
Module 3: Pilot, Plan, and Communicate the New Process and Its Required Organizational Changes |
Phase 1 Outcome:
|
Phase 2 Outcome:
|
Phase 3 Outcome:
|
Workshop overview
Contact your account representative or email Workshops@InfoTech.com for more information.
| Workshop Day 1 | Workshop Day 2 | Workshop Day 3 | Workshop Day 4 | Workshop Day 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activities |
Benefits of optimizing project intake and project value definition 1.1 Complete and review PPM Current State Scorecard Assessment 1.2 Define project value for the organization 1.3 Engage key PPM stakeholders to iterate on the scorecard prototype |
Set realistic goals for process optimization 2.1 Map current intake, approval, and prioritization workflow 2.2 Enumerate and prioritize process stakeholders 2.3 Determine the current and target capability levels 2.4 Define the process success criteria and KPIs |
Optimize project intake and approval processes 3.1 Conduct focused retrospectives for project intake and approval 3.2 Define project levels 3.3 Optimize project intake processes 3.4 Optimize project approval processes 3.5 Compose SOP for intake and approval 3.6 Document the new intake and approval workflow |
Optimize project prioritization process plan for a process pilot 4.1 Conduct focused retrospective for project prioritization 4.2 Estimate available resource capacity 4.3 Pilot Project Intake and Prioritization Tool with your project backlog 4.4 Compose SOP for prioritization 4.5 Document the new prioritization workflow 4.6 Discuss process pilot |
Analyze stakeholder impact and create communication strategy 5.1 Analyze stakeholder impact and responses to impending organization change 5.2 Create message canvas for at-risk change impacts and stakeholders 5.3 Set course of action for communicating change |
| Deliverables |
|
|
|
|
|
Phase 1
Set Realistic Goals for Optimizing Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization Process
Phase 1 outline
Call 1-888-670-8889 or email GuidedImplementations@InfoTech.com for more information.
Complete these steps on your own, or call us to complete a guided implementation. A guided implementation is a series of 2-3 advisory calls that help you execute each phase of a project. They are included in most advisory memberships.
| Guided Implementation 1: Set Realistic Goals for Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization Process Proposed Time to Completion: 1-2 weeks |
|---|
|
Step 1.1: Define the project valuation criteria Start with an analyst kick-off call:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Project Value Scorecard Development Tool |
Step 1.2: Envision your process target state Start with an analyst kick-off call:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Project Intake Workflow Template Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template |
Phase 1 Results & Insights:
|
|
Get to value early with Step 1.1 of this blueprint
Define how to determine a project’s value and set the stage for maximizing the value of your project portfolio using Info-Tech’s Project Value Scorecard Development Tool.
Where traditional models of consulting can take considerable amounts of time before delivering value to clients, Info-Tech’s methodology for optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization process gets you to value fast.
The overarching goal of optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization process is to maximize the throughput of the best projects. To achieve this goal, one must have a clear way to determine what are “the best” projects.
In the first step of this blueprint, you will pilot a multiple-criteria scorecard for determining project value that will help answer that question. Info-Tech’s Project Value Scorecard Development Tool is pre-populated with a ready-to-use, real-life example that you can leverage as a starting point for tailoring it to your organization – or adopt as is.
Introduce objectivity and clarity to your discussion of maximizing the value of your project portfolio with Info-Tech’s practical IT research that drives measurable results.
Download Info-Tech’s Project Value Scorecard Development Tool.

Step 1.1: Define the criteria with which to determine project value
| PHASE 1 | PHASE 2 | PHASE 3 | ||||
|
1.1 Define project valuation criteria |
1.2 Envision process target state |
2.1 Streamline intake |
2.2 Right-size approval steps |
2.3 Prioritize projects to fit resource capacity |
3.1 Pilot your optimized process |
3.2 Communicate organizational change |
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Learn how to use the Project Value Scorecard Development Tool
- Create a first-draft version of a project value-driven prioritized list of projects
This step involves the following participants:
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- CIO (optional)
Outcomes of this step
- Understand the importance of devising a consensus criteria for project valuation.
- Try a project value scorecard-driven prioritization process with your currently proposed.
- Set the stage for optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization processes.
Intake, Approval, and Prioritization is a core process in Info-Tech’s project portfolio management (PPM) framework
PPM is an infrastructure around projects that aims to ensure that the best projects are worked on at the right time with the right people.
PPM’s goal is to maximize the throughput of projects that provide strategic and operational value to the organization. To do this, a PPM strategy must help to:
| Info-Tech's Project Portfolio Management Process Model |
| 3. Status & Progress Reporting |
| 1. Intake, Approval & Prioritization | 2. Resource Management | 3. Project Management | 4. Project Closure | 5. Benefits Tracking |
| Intake | Execution | Closure |
- Select the best projects
- Pick the right time and people to execute the projects
- Make sure the projects are okay
- Make sure the projects get done
- Make sure they were worth doing
If you don’t yet have a PPM strategy in place, or would like to revisit your existing PPM strategy before optimizing your project intake, approval, and prioritization practices, see Info-Tech’s blueprint, Develop a Project Portfolio Management Strategy.

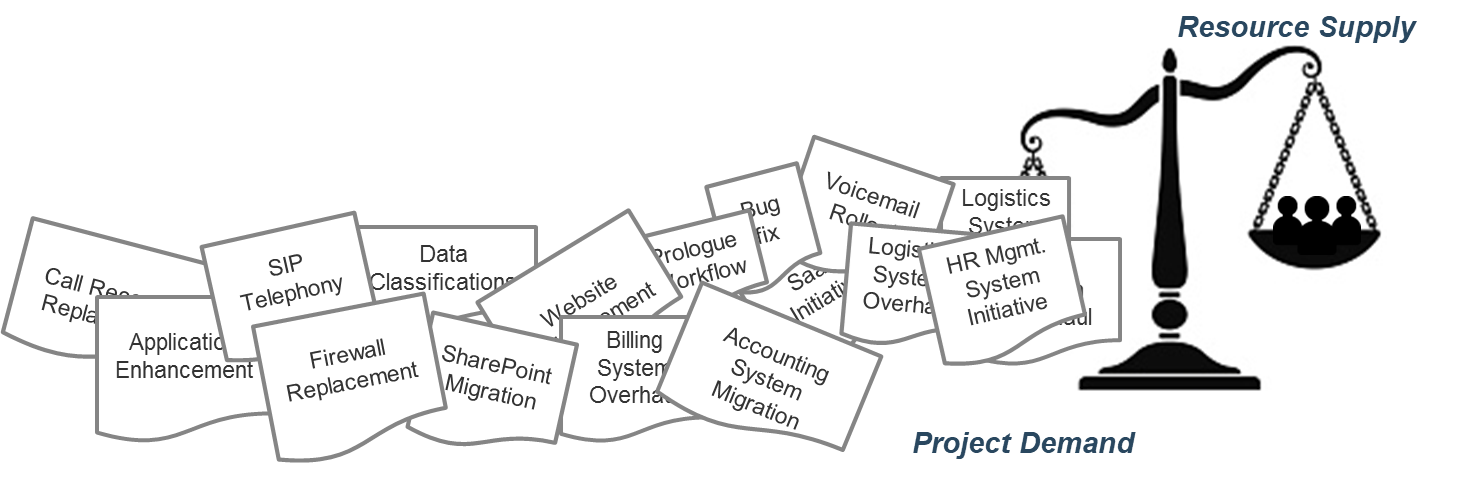
“Too many projects, not enough resources” is the reality of most IT environments
A profound imbalance between demand (i.e. approved project work and service delivery commitments) and supply (i.e. people’s time) is the top challenge IT departments face today.
In today’s organizations, the desires of business units for new products and enhancements, and the appetites of senior leadership to approve more and more projects for those products and services, far outstrip IT’s ability to realistically deliver on everything.
The vast majority of IT departments lack the resourcing to meet project demand – especially given the fact that day-to-day operational demands frequently trump project work.
As a result, project throughput suffers – and with it, IT’s reputation within the organization.
Info-Tech Insight
Where does the time go? The portfolio manager (or equivalent) should function as the accounting department for time, showing what’s available in IT’s human resources budget for projects and providing ongoing visibility into how that budget of time is being spent.
Don’t weigh your portfolio down by starting more than you can finish
Focus on what will deliver value to the organization and what you can realistically deliver.
Most of the problems that arise during the lifecycle of a project can be traced back to issues that could have been mitigated during the initiation phase.
More than simply a means of early problem detection at the project level, optimizing your initiation processes is also the best way to ensure the success of your portfolio. With optimized intake processes you can better guarantee:
- The projects you are working on are of high value
- Your project list aligns with available resource capacity
- Stakeholder needs are addressed, but stakeholders do not determine the direction of the portfolio
80% of organizations feel their portfolios are dominated by low-value initiatives that do not deliver value to the business (Source: Cooper).
"(S)uccessful organizations select projects on the basis of desirability and their capability to deliver them, not just desirability" (Source: John Ward, Delivering Value from Information Systems and Technology Investments).
Establishing project value is the first – and difficult – step for optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization
What is the best way to “deliver value to the organization”?
Every organization needs to explicitly define how to determine project value that will fairly represent all projects and provide a basis of comparison among them during approval and prioritization. Without it, any discussions on reducing “low-value initiatives” from the previous slide cannot yield any actionable plan.
However, defining the project value is difficult, because there are so many different and conflicting ways that are all valid in their own right and worth considering. For example:
- Strategic growth vs. operational stability
- Important work vs. urgent work
- Return on investment vs. cost containment
- Needs of a specific line of business vs. business-wide needs
- Financial vs. intangible benefits
This challenge is further complicated by the difficulty of identifying the right criteria for determining project value:
Managers fail to identify around 50% of the important criteria when making decisions (Source: Transparent Choice).
Info-Tech Insight
Sometimes it can be challenging to show the value of IT-centric, operational-type projects that maintain critical infrastructure since they don’t yield net-new benefits. Remember that benefits are only half the equation; you must also consider the costs of not undertaking the said project.
Find the right mix of criteria for project valuation with Info-Tech’s Project Value Scorecard Development Tool
Scorecard-driven approach is an easy-to-understand, time-tested solution to a multiple-criteria decision-making problem, such as project valuation.
This approach is effective for capturing benefits and costs that are not directly quantifiable in financial terms. Projects are evaluated on multiple specific questions, or criteria, that each yield a score on a point scale. The overall score is calculated as a weighted sum of the scores.
Info-Tech’s Project Value Scorecard is pre-populated with a best-practice example of eight criteria, two for each category (see box at bottom right). This example helps your effort to develop your own project scorecard by providing a solid starting point:
60%: On their own, decision makers could only identify around 6 of their 10 most important criteria for making decisions (Source: Transparent Choice).
Finally, in addition, the overall scores of approved projects can be used as a metric on which success of the process can be measured over time.
Download Info-Tech’s Project Value Scorecard Development Tool.

Categories of project valuation criteria
- Strategic alignment: projects must be aligned with the strategic goals of the business and IT.
- Operational alignment: projects must be aligned with the operational goals of the business and IT.
- Feasibility: practical considerations for projects must be taken into account in selecting projects.
- Financial: projects must realize monetary benefits, in increased revenue or decreased costs, while posing as little risk of cost overrun as possible.
Review the example criteria and score description in the Project Value Scorecard Development Tool
1.1.1 Project Value Scorecard Development Tool, Tab 2: Evaluation Criteria
This tab lists eight criteria that cover strategic alignment, operational alignment, feasibility, and financial benefits/risks. Each criteria is accompanied by a qualitative score description to standardize the analysis across all projects and analysts. While this tool supports up to 15 different criteria, it’s better to minimize the number of criteria and introduce additional ones as the organization grows in PPM maturity.
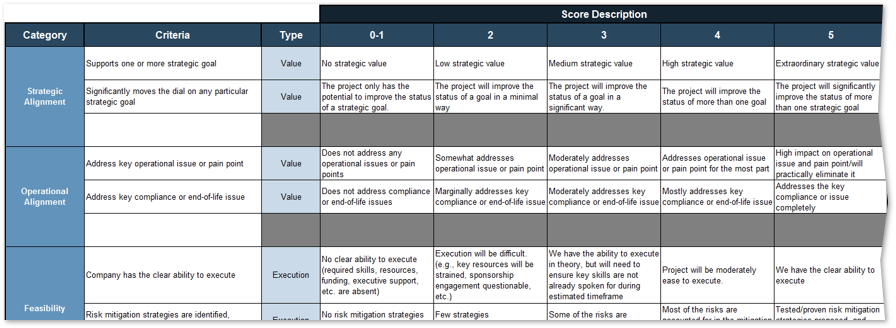
Type: It is useful to break down projects with similar overall scores by their proposed values versus ease of execution.
Scale: Five-point scale is not required for this tool. Use more or less granularity of description as appropriate for each criteria.
Blank Criteria: Rows with blank criteria are greyed out. Enter a new criteria to turn on the row.
Score projects and search for the right mix of criteria weighting using the scorecard tab
1.1.1 Project Value Scorecard Development Tool, Tab 3: Project Scorecard
In this tab, you can see how projects are prioritized when they are scored according to the criteria from the previous tab. You can enter the scores of up to 30 projects in the scorecard table (see screenshot to the right).
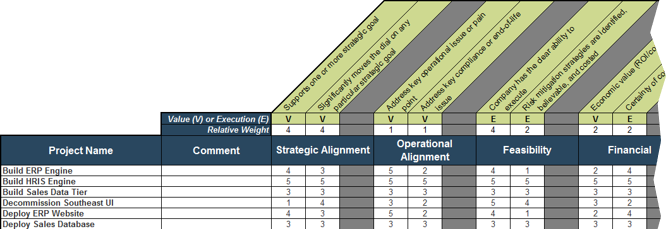
Value (V) or Execution (E) & Relative Weight: Change the relative weights of each criteria and review any changes to the prioritized list of projects change, whose rankings are updated automatically. This helps you iterate on the weights to find the right mix.
Feasibility: Custom criteria category labels will be automatically updated.
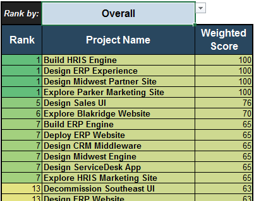
Overall: Choose the groupings of criteria by which you want to see the prioritized list. Available groupings are:
- Overall score
- By value or by execution
- By category
Ranks and weighted scores for each project is shown.
For example, click on the drop-down and choose “Execution.”
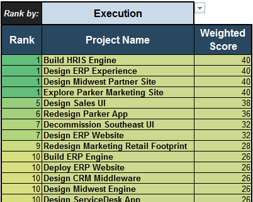
Project ranks are based only on execution criteria.
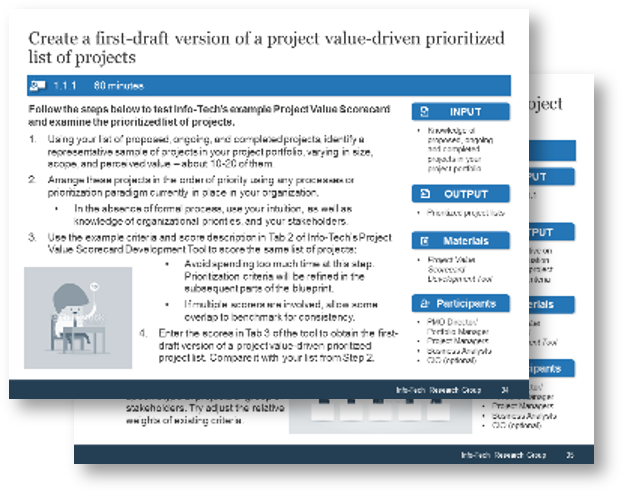
Create a first-draft version of a project value-driven prioritized list of projects
1.1.1 Estimated Time: 60 minutes
Follow the steps below to test Info-Tech’s example Project Value Scorecard and examine the prioritized list of projects.
- Using your list of proposed, ongoing, and completed projects, identify a representative sample of projects in your project portfolio, varying in size, scope, and perceived value – about 10-20 of them.
- Arrange these projects in the order of priority using any processes or prioritization paradigm currently in place in your organization.
- In the absence of formal process, use your intuition, as well as knowledge of organizational priorities, and your stakeholders.
- Avoid spending too much time at this step. Prioritization criteria will be refined in the subsequent parts of the blueprint.
- If multiple scorers are involved, allow some overlap to benchmark for consistency.
INPUT
- Knowledge of proposed, ongoing, and completed projects in your project portfolio
OUTPUT
- Prioritized project lists
Materials
- Project Value Scorecard Development Tool
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- CIO (optional)
Iterate on the scorecard to set the stage for optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization
1.1.2 Estimated Time: 60 minutes
Conduct a retrospective of the previous activity by asking these questions:
- How smooth was the overall scoring experience (Step 3 of Activity 1.1.1)?
- Did you experience challenges in interpreting and applying the example project valuation criteria? Why? (e.g. lack of information, absence of formalized business strategic goals, too much room for interpretation in scoring description)
- Did the prioritized project list agree with your intuition?
Iterate on the project valuation criteria:
- Manipulate the relatives weights of valuation criteria to fine-tune them.
- Revise the scoring descriptions to provide clarity or customize them to better fit your organization’s needs, then update the project scores accordingly.
- For projects that did not score well, will this cause concern from any stakeholders? Are the concerns legitimate? If so, this may indicate the need for inclusion of new criteria.
- For projects that score too well, this may indicate a bias toward a specific type of project or group of stakeholders. Try adjusting the relative weights of existing criteria.
INPUT
- Activity 1.1.1
OUTPUT
- Retrospective on project valuation
- Review of project valuation criteria
Materials
- Project Value Scorecard Development Tool
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- CIO (optional)
Next steps: engage key PPM stakeholders to reach a consensus when establishing how to determine project value
Engage these key players to create the evaluation criteria that all stakeholders will support:
- Business units: Projects are undertaken to provide value to the business. Senior management from business units must help define how project will be valued.
- IT: IT must ensure that technical/practical considerations are taken into account when determining project value.
- Finance: The CFO or designated representative will ensure that estimated project costs and benefits can be used to manage the budget.
- PMO: PMO is the administrator of the project portfolio. PMO must provide coordination and support to ensure the process operates smoothly and its goals are realized.
- Business analysts: BAs carry out the evaluation of project value. Therefore, their understanding of the evaluation criteria and the process as a whole are critical to the success of the process.
- Project sponsors: Project sponsors are accountable for the realization of benefits for which projects are undertaken.
Optimize the process with the new project value definition to focus your discussion with stakeholders
This blueprint will help you not only optimize the process, but also help you work with your stakeholders to realize the benefits of the optimized process.
In this step, you’ve begun improving the definition of project value. Getting it right will require several more iterations and will require a series of discussions with your key stakeholders.
The optimized intake process built around the new definition of project value will help evolve a conceptual discussion about project value into a more practical one. The new process will paint a picture of what the future state will look like for your stakeholders’ requested projects getting approved and prioritized for execution, so that they can provide feedback that’s concrete and actionable. To help you with that process, you will be taken through a series of activities to analyze the impact of change on your stakeholders and create a communication plan in the last phase of the blueprint.
For now, in the next step of this blueprint, you will undergo a series of activities to assess your current state to identify the specific areas for process optimization.
"To find the right intersection of someone’s personal interest with the company’s interest on projects isn’t always easy. I always try to look for the basic premise that you can get everybody to agree on it and build from there… But it’s sometimes hard to make sure that things stick. You may have to go back three or four times to the core agreement."
Step 1.2: Envision your target state for your optimized project intake, approval, and prioritization process
| PHASE 1 | PHASE 2 | PHASE 3 | ||||
1.1 Define project valuation criteria | 1.2 Envision process target state | 2.1 Streamline intake | 2.2 Right-size approval steps | 2.3 Prioritize projects to fit resource capacity | 3.1 Pilot your optimized process | 3.2 Communicate organizational change |
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Map your current project intake, approval, and prioritization workflow, and document it in a flowchart
- Enumerate and prioritize your key process stakeholders
- Determine your process capability level within Info-Tech’s Framework
- Establish your current and target states for project intake, approval, and prioritization process
This step involves the following participants:
- CIO
- PMO Director/Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- Other PPM stakeholders
Outcomes of this step
- Current project intake, approval, and prioritization process is mapped out and documented in a flowchart
- Key process stakeholders are enumerated and prioritized to inform future discussion on optimizing processes
- Current and target organizational process capability levels are determined
- Success criteria and key performance indicators for process optimization are defined
Use Info-Tech’s Diagnostic Program for an initial assessment of your current PPM processes
This step is highly recommended but not required. Call 1-888-670-8889 to inquire about or request the PPM Diagnostics.
Info-Tech's Project Portfolio Management Assessmentprovides you with a data-driven view of the current state of your portfolio, including your intake processes. Our PPM Assessment measures and communicates success in terms of Info-Tech’s best practices for PPM.

Use the diagnostic program to:
- Assess resource utilization across the portfolio.
- Determine project portfolio reporting completeness.
- Solicit feedback from your customers on the clarity of your portfolio’s business goals.
- Rate the overall quality of your project management practices and benchmark your rating over time.
Scope your process optimization efforts with Info-Tech’s high-level intake, approval, and prioritization workflow
Info-Tech recommends the following workflow at a high level for a capacity-constrained intake process that aligns to strategic goals and stakeholder need.
- Intake (Step 2.1)*
- Receive project requests
- Triage project requests and assign a liaison
- High-level scoping & set stakeholder expectations
- Approval (Step 2.2)*
- Concept approval by project sponsor
- High-level technical solution approval by IT
- Business case approval by business
- Resource allocation & greenlight projects
- Prioritization (Step 2.3)*
- Update project priority scores & available project capacity
- Identify high-scoring and “on-the-bubble” projects
- Recommend projects to greenlight or deliberate
* Steps denote the place in the blueprint where the steps are discussed in more detail.
Use this workflow as a baseline to examine your current state of the process in the next slide.
Map your current project intake, approval, and prioritization workflow
1.2.1 Estimated Time: 60-90 minutes
Conduct a table-top planning exercise to map out the processes currently in place for project intake, approval, and prioritization.
- Use white 4”x6” recipe cards / large sticky notes to write out unique steps of a process. Use the high-level process workflow from the previous slides as a guide.
- Arrange the steps into chronological order. Benchmark the arrangement through a group discussion.
- Use green cards to identify artifacts or deliverables that result from a step.
- Use yellow cards to identify who does the work (i.e. responsible parties), and who makes the decisions (i.e. accountable party). Keep in mind that while multiple parties may be responsible, accountability cannot be shared and only a single party can be accountable for a process.
- Use red cards to identify issues, problems, or risks. These are opportunities for optimization.
INPUT
- Documentation describing the current process (e.g. standard operating procedures)
- Info-Tech’s high-level intake workflow
OUTPUT
- Current process, mapped out
Materials
- 4x6” recipe cards
- Whiteboard
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- Other PPM stakeholders
Document the current project intake, approval, and prioritization workflow in a flowchart
1.2.2 Estimated Time: 60 minutes
Document the results of the previous table-top exercise (Activity 1.1.1) into a flow chart. Flowcharts provide a bird’s-eye view of process steps that highlight the decision points and deliverables. In addition, swim lanes can be used to indicate process stages, task ownership, or responsibilities (example below).
Review and customize section 1.2, “Overall Process Workflow” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
"Flowcharts are more effective when you have to explain status and next steps to upper management."
– Assistant Director-IT Operations, Healthcare Industry
Browser-based flowchart tool examples
- draw.io (https://www.draw.io/)
- Gliffy (https://www.gliffy.com/)
- Lucidchart (https://www.lucidchart.com/)
- Smartdraw (https://cloud.smartdraw.com/
INPUT
- Mapped-out project intake process (Activity 1.2.1)
OUTPUT
- Flowchart representation of current project intake workflow
Materials
- Microsoft Visio, flowchart software, or Microsoft PowerPoint
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
Example of a project intake, approval, and prioritization flow chart – without swim lanes
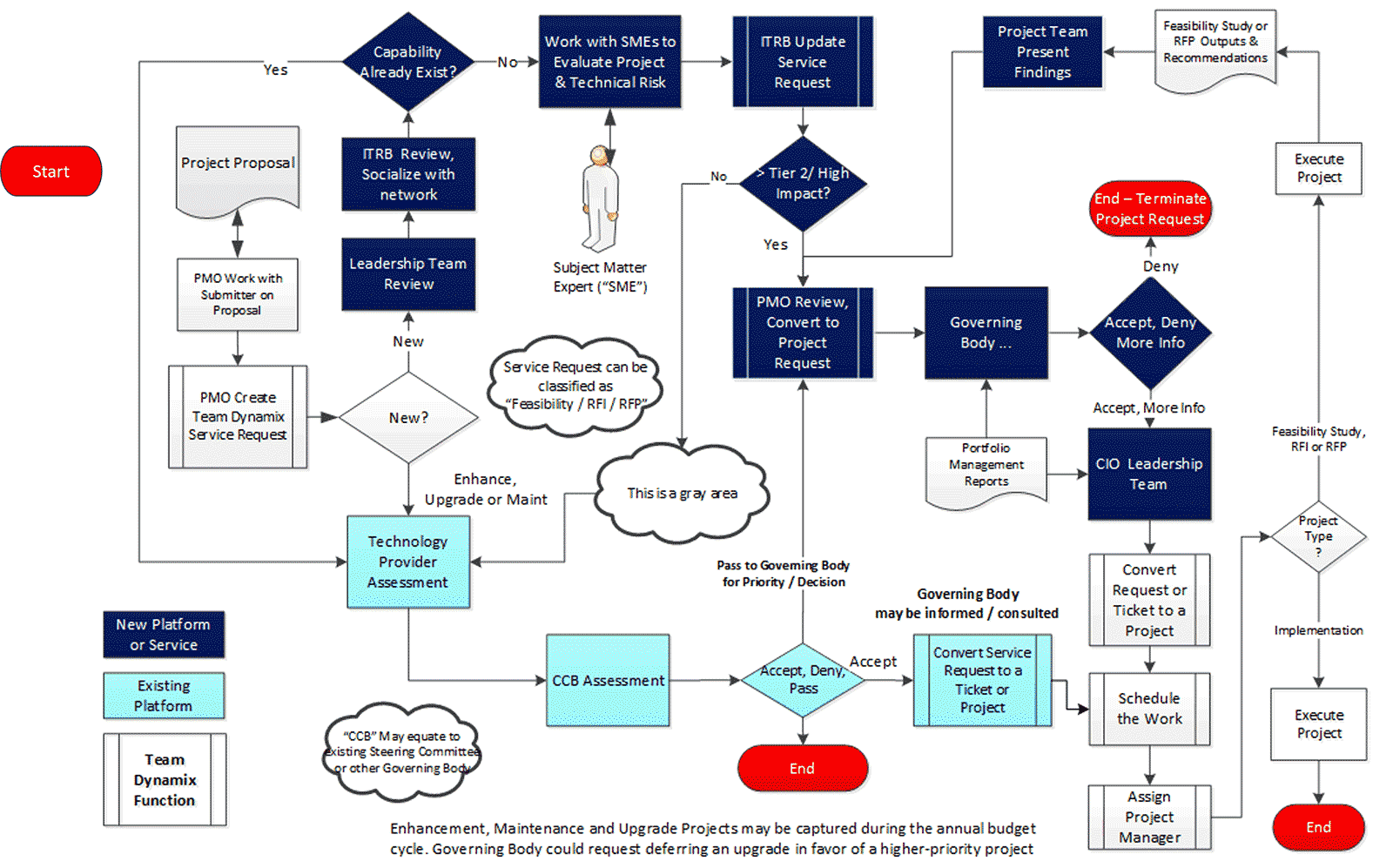
Example of a project intake, approval, and prioritization flow chart – with swim lanes
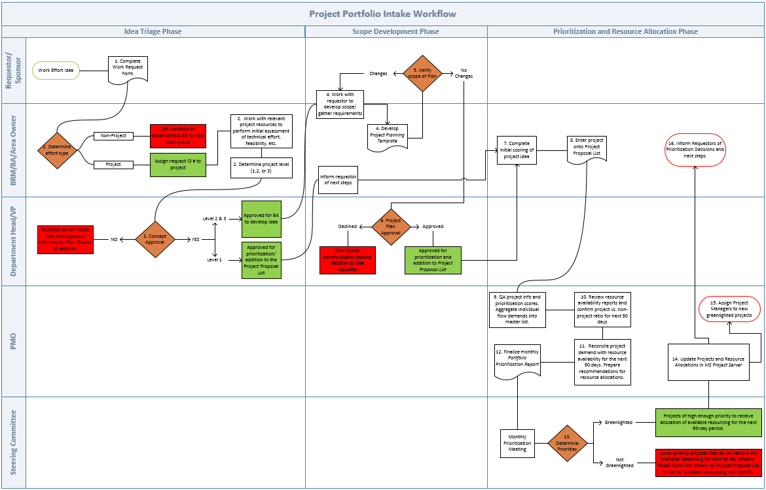
Download Info-Tech’s Project Intake Workflow Template (Visio and PDF)
Enumerate your key stakeholders for optimizing intake, approval, and prioritization process
1.2.3 30-45 minutes
In the previous activity, accountable and responsible stakeholders for each of the steps in the current intake, approval, and prioritization process were identified.
- Based on your knowledge and insight of your organization, ensure that all key stakeholders with accountable and responsible stakeholders are accounted for in the mapped-out process. Note any omissions: it may indicate a missing step, or that the stakeholder ought to be, but are not currently, involved.
- For each step, identify any stakeholders that are currently consulted or informed. Then, examine the whole map and identify any other stakeholders that ought to be consulted or informed.
- Compile a list of stakeholders from steps 1-2, and write each of their names in two sticky notes.
- Put both sets of sticky notes on a wall. Use the wisdom-of-the-crowd approach to arrange one set in a descending order of influence. Record their ranked influence from 1 (least) to 10 (most).
- Rearrange the other set in a descending order of interest in seeing the project intake process optimized. Record their ranked interest from 1 (least) to 10 (most).
INPUT
- Mapped-out project intake process (Activity 1.2.1)
- Insight on organizational culture
OUTPUT
- List of stakeholders in project intake
- Ranked list in their influence and interest
Materials
- Sticky notes
- Walls
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- Other PPM stakeholders
Prioritize your stakeholders for project intake, approval, and prioritization process
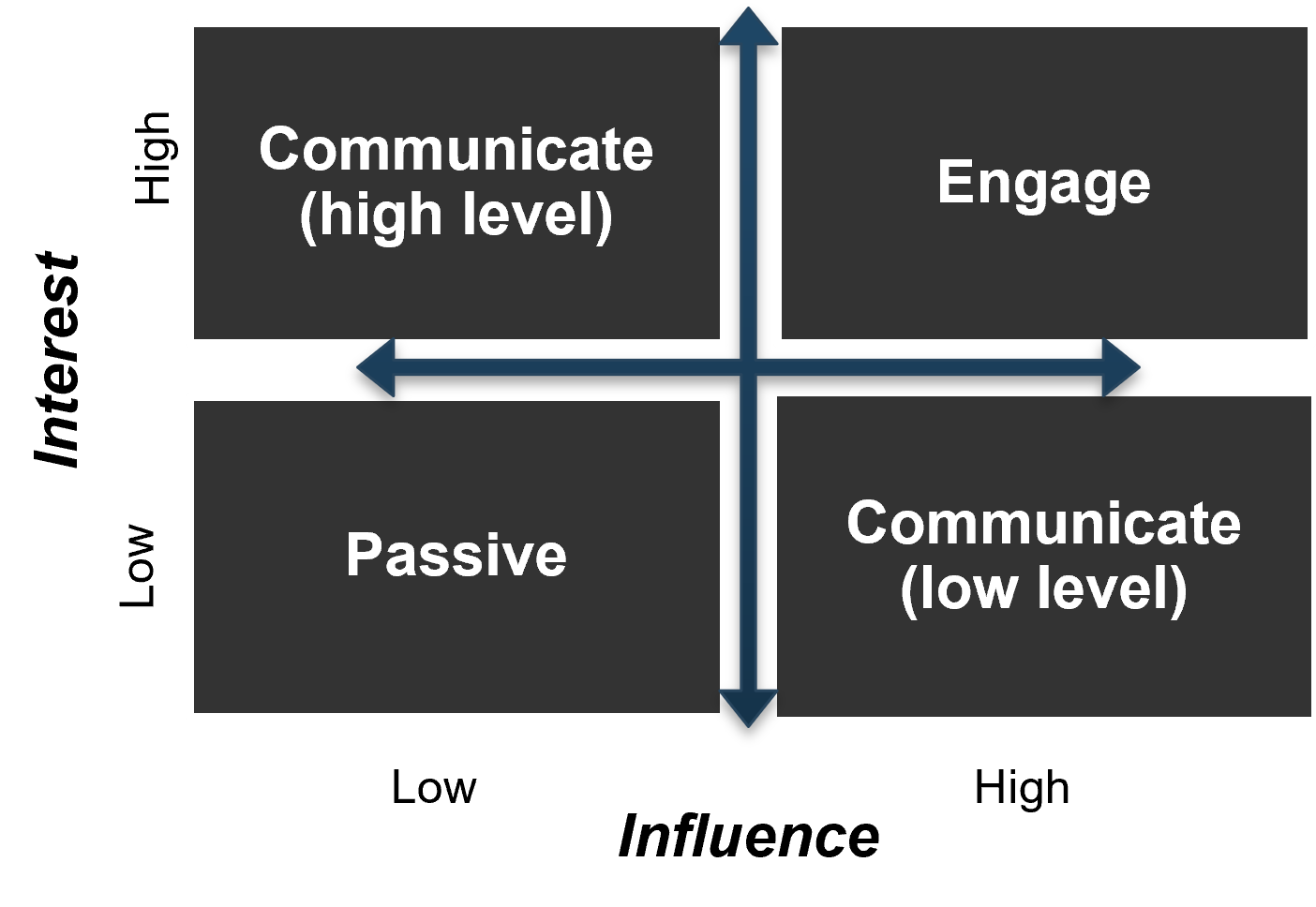
There are three dimensions for stakeholder prioritization: influence, interest, and support.
- Map your stakeholders in a 2D stakeholder power map (top right) according to their relative influence and interest.
- Rate their level of support by asking the following question: how likely is it that your stakeholder would welcome an improved process for project intake?
These parameters will inform how to prioritize your stakeholders according to the stakeholder priority heatmap (bottom right). This priority should inform how to focus your attention during the subsequent optimization efforts.
| Level of Support | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stakeholder Category | Supporter | Evangelist | Neutral | Blocker | |
| Engage | Critical | High | High | Critical | |
| High | Medium | Low | Low | Medium | |
| Low | High | Medium | Medium | High | |
| Passive | Low | Irrelevant | Irrelevant | Low | |
Info-Tech Insight
There may be too many stakeholders to be able to achieve complete satisfaction. Focus your attention on the stakeholders that matter the most.
Most organizations have low to medium capabilities around intake, approval, and prioritization
1.2.4 Estimated Time: 15 minutes
Use Info-Tech’s Intake Capability Framework to help define your current and target states for intake, approval, and prioritization.
| Capability Level | Capability Level Description |
|---|---|
| Capability Level 5: Optimized | Our department has effective intake processes with right-sized administrative overhead. Work is continuously prioritized to keep up with emerging challenges and opportunities. |
| Capability Level 4: Aligned | Our department has very strong intake processes. Project approvals are based on business cases and aligned with future resource capacity. |
| Capability Level 3: Engaged | Our department has processes in place to track project requests and follow up on them. Priorities are periodically re-evaluated, based largely on the best judgment of one or several executives. |
| Capability Level 2: Defined | Our department has some processes in place but no capacity to say no to new projects. There is a formal backlog, but little or no method for grooming it. |
| Capability Level 1: Unmanaged | Our department has no formal intake processes in place. Most work is done reactively, with little ability to prioritize proactive project work. |
Refer to the subsequent slides for more detail on these capability levels.
Level 1: Unmanaged
Use these descriptions to place your organization at the appropriate level of intake capability.
| Intake | Projects are requested through personal conversations and emails, with minimal documentation and oversight. |
|---|---|
| Approval | Projects are approved by default and rarely (if ever) declined. There is no definitive list of projects in the pipeline or backlog. |
| Prioritization | Most work is done reactively, with little ability to prioritize proactive project work. |
Symptoms
- Poorly defined – or a complete absence of – PPM processes.
- No formal approval committee.
- No processes in place to balance proactive and reactive demands.
Long Term
PMOs at this level should work to have all requests funneled through a proper request form within six months. Decision rights for approval should be defined, and a scorecard should be in place within the year.
Quick Win
To get a handle on your backlog, start tracking all project requests using the “Project Data” tab in Info-Tech’s Project Intake and Prioritization Tool.
Level 2: Defined
Use these descriptions to place your organization at the appropriate level of intake capability.
| Intake | Requests are formally documented in a request form before they’re assigned, elaborated, and executed as projects. |
|---|---|
| Approval | Projects are approved by default and rarely (if ever) declined. There is a formal backlog, but little or no method for grooming it. |
| Prioritization | There is a list of priorities but no process for updating it more than annually or quarterly. |
Symptoms
- Organization does not have clear concept of project capacity.
- There is a lack of discipline enforced on stakeholders.
- Immature PPM processes in general.
Long Term
PMOs at this level should strive for greater visibility into the portfolio to help make the case for declining (or at least deferring) requests. Within the year, have a formal PPM strategy up and running.
Quick Win
Something PMOs at this level can accomplish quickly without any formal approval is to spend more time with stakeholders during the ideation phase to better define scope and requirements.
Level 3: Engaged
Use these descriptions to place your organization at the appropriate level of intake capability.
| Intake | Processes and skills are in place to follow up on requests to clarify project scope before going forward with approval and prioritization. |
|---|---|
| Approval | Projects are occasionally declined based on exceptionally low feasibility or value. |
| Prioritization | Priorities are periodically re-evaluated based largely on the best judgment of one or several executives. |
Challenges
- Senior executives’ “best judgement” is frequently fallible or influenced. Pet projects still enter the portfolio and deplete resources.
- While approval processes “occasionally” filter out some low-value projects, many still get approved.
Long Term
PMOs at this level should advocate for a more formal cadence for prioritization and, within the year, establish a formal steering committee that will be responsible for prioritizing and re-prioritizing quarterly or monthly.
Quick Win
At the PMO level, employ Info-Tech’s Project Intake and Prioritization Tool to start re-evaluating projects in the backlog. Make this data available to senior executives when prioritization occurs.
Level 4: Aligned
Use these descriptions to place your organization at the appropriate level of intake capability.
| Intake | Occurs through a centralized process. Processes and skills are in place for follow-up. |
|---|---|
| Approval | Project approvals are based on business cases and aligned with future resource capacity. |
| Prioritization | Project prioritization is visibly aligned with business goals. |
Challenges
- The process of developing business cases can be too cumbersome, distracting resources from actual project work.
- “Future” resource capacity predictions are unreliable. Reactive support work and other factors frequently change actual resource availability.
Long Term
PMOs at this level can strive for more accurate and frequent resource forecasting, establishing a more accurate picture of project vs. non-project work within the year.
Quick Win
PMOs at this level can start using Info-Tech’s Business Case Template (Comprehensive or Fast Track) to help simplify the business case process.
Level 5: Optimizing
Use these descriptions to place your organization at the appropriate level of intake capability.
| Intake | Occurs through a centralized portal. Processes and skills are in place for thorough follow-up. |
|---|---|
| Approval | Project approvals are based on business cases and aligned with future resource capacity. |
| Prioritization | Work is continuously prioritized to keep up with emerging challenges and opportunities. |
Challenges
- Establishing a reliable forecast for resource capacity remains a concern at this level as well.
- Organizations at this level may experience an increasing clash between Agile practices and traditional Waterfall methodologies.

PMOs at this level should look at Info-Tech’s Manage an Agile Portfolio for comprehensive tools and guidance on maintaining greater visibility at the portfolio level into work in progress and committed work.
Establish your current and target states for process intake, approval, and prioritization
1.2.5 Estimated Time: 20 minutes
- Having reviewed the intake capability framework, you should be able to quickly identify where you currently reside in the model. Document this in the “Current State” box below.
- Next, spend some time as a group discussing your target state. Make sure to set a realistic target as well as a realistic timeframe for meeting this target. Level 1s will not be able to become Level 5s overnight and certainly not without passing through the other levels on the way.
- A realistic goal for a Level 1 to become a Level 2 is within six to eight months.
| Current State: | |
|---|---|
| Target State: | |
| Timeline for meeting target |
INPUT
- Intake, approval, and prioritization capability framework (Activity 1.2.4)
OUTPUT
- Current and target state, with stated time goals
Materials
- Whiteboard
Participants
- CIO
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
Align your intake success with the strategic expectations of overall project portfolio management
A successful project intake, approval, and prioritization process puts your leadership in a position to best steer the portfolio, like a conductor of an orchestra.
To frame the discussion on deciding what intake success will look like, review Info-Tech’s PPM strategic expectations:
- Project Throughput: Maximize throughput of the best projects.
- Portfolio Visibility: Ensure visibility of current and pending projects.
- Portfolio Responsiveness: Make the portfolio responsive to executive steering when new projects and changing priorities need rapid action.
- Resource Utilization: Minimize resource waste and optimize the alignment of skills to assignments.
- Benefits Realization: Clarify accountability for post-project benefits attainment for each project, and facilitate the process of tracking/reporting those benefits.

For a more detailed discussion and insight on PPM strategic expectations see Info-Tech’s blueprint, Develop a Project Portfolio Management Strategy.
Decide what successful project intake, approval, prioritization process will look like
1.2.6 Estimated Time: 60 minutes
While assessing your current state, it is important to discuss and determine as a team how success will be defined.
- During this process, it is important to consider tentative timelines for success milestones and to ask the question: what will success look like and when should it occur by?
- Use the below table to help document success factors and timeliness. Follow the lead of our example in row 1.
| Optimization Benefit | Objective | Timeline | Success Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facilitate project intake, prioritization, and communication with stakeholders to maximize time spent on the most valuable or critical projects. | Look at pipeline as part of project intake approach and adjust priorities as required. | July 1st | Consistently updated portfolio data. Dashboards to show back capacity to customers. SharePoint development resources. |
Review and customize section 1.5, “Process Success Criteria” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
Info-Tech Insight
Establish realistic short-term goals. Even with optimized intake procedures, you may not be able to eliminate underground project economies immediately. Make your initial goals realistic, leaving room for those walk-up requests that may still appear via informal channels.
Prepare to optimize project intake and capture the results in the Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is the reference document to get all PPM stakeholders on the same page with the new optimized process.
The current state explored and documented in this step will serve as a starting point for each step of the next phase of the blueprint. The next phase will take a deeper dive into each of the three components of Info-Tech’s project intake methodology, so that they can achieve the success criteria you’ve defined in the previous activity.
Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template is intended to capture the outcome of your process optimization efforts. This blueprint guides you through numerous activities designed for your core project portfolio management team to customize each section.
To maximize the chances of success, it is important that the team makes a concerted effort to participate. Schedule a series of working sessions over the course of several weeks for your team to work through it – or get through it in one week, with onsite Info-Tech analyst-facilitated workshops.
Download Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP.
Contact your account representative or email Workshops@InfoTech.com for more information.
Case study: PMO develops mature intake and prioritization processes by slowly evolving its capability level
CASE STUDY
Industry: Not-for-Profit
Source: Info-Tech Interview
Challenge
- A PMO for a large not-for-profit benefits provider had relatively high project management maturity, but the enterprise had low PPM maturity.
- There were strong intake processes in place for following up on requests. For small projects, project managers would assist as liaisons to help control scope. For corporate initiates, PMs were assigned to work with a sponsor to define scope and write a charter.
Solution
Prioritization was a challenge. Initially, the organization had ad hoc prioritization practices, but they had developed a scoring criteria to give more formality and direction to the portfolio. However, the activity of formally prioritizing proved to be too time consuming.
Off-the-grid projects were a common problem, with initiatives consuming resources with no portfolio oversight.
Results
After trying “heavy” prioritization, the PMO loosened up the process. PMO staff now go through and quickly rank projects, with two senior managers making the final decisions. They re-prioritize quarterly to have discussions around resource availability and to make sure stakeholders are in tune to what IT is doing on a daily basis. IT has a monthly meeting to go over projects consuming resources and to catch anything that has fallen between the cracks.
"Everything isn't a number one, which is what we were dealing with initially. We went through a formal prioritization period, where we painstakingly scored everything. Now we have evolved: a couple of senior managers have stepped up to make decisions, which was a natural evolution from us being able to assign a formal ranking. Now we are able to prioritize more easily and effectively without having to painstakingly score everything."
– PMO Director, Benefits Provider
If you want additional support, have our analysts guide you through this phase as part of an Info-Tech workshop
Book a workshop with our Info-Tech analysts:

- To accelerate this project, engage your IT team in an Info-Tech workshop with an Info-Tech analyst team.
- Info-Tech analysts will join you and your team onsite at your location or welcome you to Info-Tech’s historic Toronto office to participate in an innovative onsite workshop.
- Contact your account manager (www.infotech.com/account), or email Workshops@InfoTech.com for more information.
The following are sample activities that will be conducted by Info-Tech analysts with your team:
1.1.1-2
Pilot Info-Tech’s Project Value Scorecard-driven prioritization method
Use Info-Tech’s example to prioritize your current project backlog to pilot a project value-driven prioritization, which will be used to guide the entire optimization process.
1.2.1-3

Map out and document current project intake, approval, and prioritization process, and the involved key stakeholders
A table-top planning exercise helps you visualize the current process in place and identify opportunities for optimization.
Phase 2
Build an Optimized Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization Process
Phase 2 outline
Call 1-888-670-8889 or email GuidedImplementations@InfoTech.com for more information.
Complete these steps on your own, or call us to complete a guided implementation. A guided implementation is a series of 2-3 advisory calls that help you execute each phase of a project. They are included in most advisory memberships.
| Guided Implementation 2: Build an Optimized Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization Process Proposed Time to Completion: 3-6 weeks | ||
|---|---|---|
Step 2.1: Streamline Intake Start with an analyst kick-off call:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates:
| Step 2.2: Right-Size Approval Start with an analyst call:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates:
| Step 3.3: Prioritize Realistically Start with an analyst call:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates:
|
Phase 2 Results & Insights:
| ||
Step 2.1: Streamline intake to manage stakeholder expectations
| PHASE 1 | PHASE 2 | PHASE 3 | ||||
1.1 Define project valuation criteria | 1.2 Envision process target state | 2.1 Streamline intake | 2.2 Right-size approval steps | 2.3 Prioritize projects to fit resource capacity | 3.1 Pilot your optimized process | 3.2 Communicate organizational change |
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Perform a deeper retrospective on current project intake process
- Optimize your process to receive project requests
- Revisit the definition of a project for triaging requests
- Optimize your process to triage project requests
- Optimize your process to follow up on project requests
This step involves the following participants:
- PMO Director / Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Administrative Staff
Outcomes of this Step
- Retrospective of the current project intake process: to continue doing, to start doing, and to stop doing
- A streamlined, single-funnel intake channel with the right procedural friction to receive project requests
- A refined definition of what constitutes a project, and project levels that will determine the necessary standard of rigor with which project requests should be scoped and developed into a proposal throughout the process
- An optimized process for triaging and following up on project requests to prepare them for the steps of project approval
- Documentation of the optimized process in the SOP document
Understand the risks of poor intake practices
Too much red tape could result in your portfolio falling victim to underground economies. Too little intake formality could lead to the Wild West.
Off-the-grid projects, i.e. projects that circumvent formal intake processes, lead to underground economies that can deplete resource capacity and hijack your portfolio.
These underground economies are typically the result of too much intake red tape. When the request process is made too complex or cumbersome, project sponsors may unsurprisingly seek alternative means to get their projects done.
While the most obvious line of defence against the appearance of underground economies is an easy-to-use and access request form, one must be cautious. Too little intake formality could lead to a Wild West of project intake where everyone gets their initiatives approved regardless of their business merit and feasibility.
| Benefits of optimized intake | Risks of poor intake |
|---|---|
| Alignment of portfolio with business goals | Portfolio overrun by off-the-grid projects |
| Resources assigned to high-value projects | Resources assigned to low-value projects |
| Better throughput of projects in the portfolio | Ever-growing project backlog |
| Strong stakeholder relations | Stakeholders lose faith in value of PMO |
Info-Tech Insight
Intake is intimately bound to stakeholder management. Finding the right balance of friction for your team is the key to successfully walking the line between asking for too much and not asking for enough. If your intake process is strong, stakeholders will no longer have any reason to circumvent formal process.
An excess number of intake channels is the telltale sign of a low capability level for intake
Excess intake channels are also a symptom of a portfolio in turmoil.
If you relate to the graphic below in any way, your first priority needs to be limiting the means by which projects get requested. A single, centralized channel with review and approval done in batches is the goal. Otherwise, with IT’s limited capacity, most requests will simply get added to the backlog.
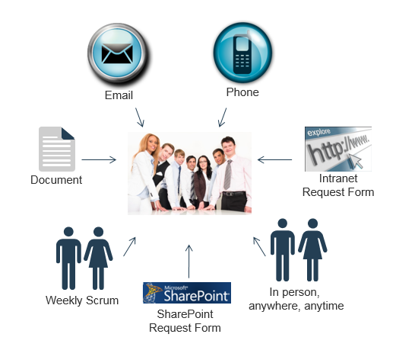
Info-Tech Insight
The PMO needs to have the authority – and needs to exercise the authority – to enforce discipline on stakeholders. Organizations that solicit in verbal requests (by phone, in person, or during scrum) lack the orderliness required for PPM success. In these cases, it needs to be the mission of the PMO to demand proper documentation and accountability from stakeholders before proceeding with requests.
"The golden rule for the project documentation is that if anything during the project life cycle is not documented, it is the same as if it does not exist or never happened…since management or clients will never remember their undocumented requests or their consent to do something."
– Dan Epstein, “Project Initiation Process: Part Two”
Develop an intake workflow
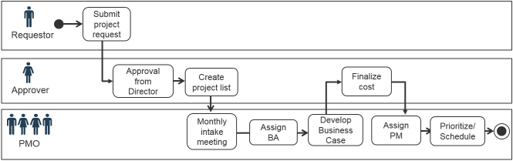
Info-Tech recommends following a four-step process for managing intake.
1. Requestor fills out form and submits the request.
Project Request Form Templates
2. Requests are triaged into the proper queue.
- Divert non-project request
- Quickly assess value and urgency
- Assign specialist to follow up on request
- Inform the requestor
Project Intake Classification Matrix
3. BA or PM prepares to develop requests into a project proposal.
- Follow up with requestor and SMEs to refine project scope, benefits, and risks
- Estimate size of project and determine the required level of detail for proposal
- Prepare for concept approval
Benefits Commitment Form Template
4. Requestor is given realistic expectations for approval process.
Perform a start-stop-continue exercise to help determine what is working and what is not working
2.1.1 Estimated Time: 45 minutes
Optimizing project intake may not require a complete overhaul of your existing processes. You may only need to tweak certain templates or policies. Perhaps you started out with a strong process and simply lost resolve over time – in which case you will need to focus on establishing motivation and discipline, rather than rework your entire process.
Perform a start-stop-continue exercise with your team to help determine what should be salvaged, what should be abandoned, and what should be introduced:
| 1. On a whiteboard or equivalent, write “Start,” “Stop,” and “Continue” in three separate columns. | 3. As a group, discuss the responses and come to an agreement as to which are most valid. |
| 2. Equip your team with sticky notes or markers and have them populate the columns with ideas and suggestions surrounding your current processes. | 4. Document the responses to help structure your game plan for intake optimization. |
| Start | Stop | Continue |
|
|
|
INPUT
- Current project intake workflow (Activity 1.2.2)
- Project intake success criteria (Activity 1.2.6)
OUTPUT
- Retrospective review of current intake process
Materials
- Whiteboard
- Sticky notes/markers
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Admin Staff
Streamline project requests into a single funnel
It is important to identify all of the ways through which projects currently get requested and initiated, especially if you have various streams of intake competing with each other for resources and a place in the portfolio. Directing multiple channels into a single, centralized funnel is step number one in optimizing intake.
To help you identify project sources within your organization, we’ve broken project requests into three archetypes: the good, the bad, and the ugly.
1. The Good – Proper Requests: written formal requests that come in through one appropriate channel.
The Bad – Walk-Ups: requests that do not follow the appropriate intake channel(s), but nevertheless make an effort to get into the proper queue. The most common instance of this is a portfolio manager or CIO filling out the proper project request form on behalf of, and under direction from, a senior executive.
The Ugly – Guerilla Tactics: initiatives that make their way into the portfolio through informal methods or that consume portfolio resources without formal approval, authority, or oversight. This typically involves a key resource getting ambushed to work on a stakeholder’s “side project” without any formal approval from, or knowledge of, the PMO.
Funnel requests through a single portal to streamline intake
Decide how you would funnel project requests on a single portal for submitting project requests. Determining the right portal for your organization will depend on your current infrastructure options, as well as your current and target state capability levels.
Below are examples of a platform for your project request portal.
| Platform | Template document, saved in a repository or shared drive | Email-based form (Outlook forms) | Intranet form (SharePoint, internal CMS) | Dedicated intake solution (PPM tool, idea/innovation tool) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pros | Can be deployed very easily | Consolidates requests into a single receiver | Users have one place to go from any device | All-in-one solution that includes scoring and prioritization |
| Cons | Manual submission and intake process consumes extra effort | Can pose problems in managing requests across multiple people and platforms | Requires existing intranet infrastructure and some development effort | Solution is costly; requires adoption across all lines of business |
Increasing intake capability and infrastructure availability
Introduce the right amount of friction into your intake process
The key to an effective intake process is determining the right amount of friction to include for your organization. In this context, friction comes from the level of granularity within your project request form and the demands or level of accountability your intake processes place on requestors. You will want to have more or less friction on your intake form, depending on your current intake pain points.
If you are inundated with a high volume of requests:
- Make your intake form more detailed to deter “half-baked” requests.
- Have more managerial oversight into the process. Require approval for each request.
If you want to encourage the use of a formal channel:
- Make your intake form more concise and lightweight.
- Have less managerial oversight into the process. Inform managers of each request rather than requiring approval.
Download Info-Tech’s Detailed Project Request Form.
Download Info-Tech’s Light Project Request Form.
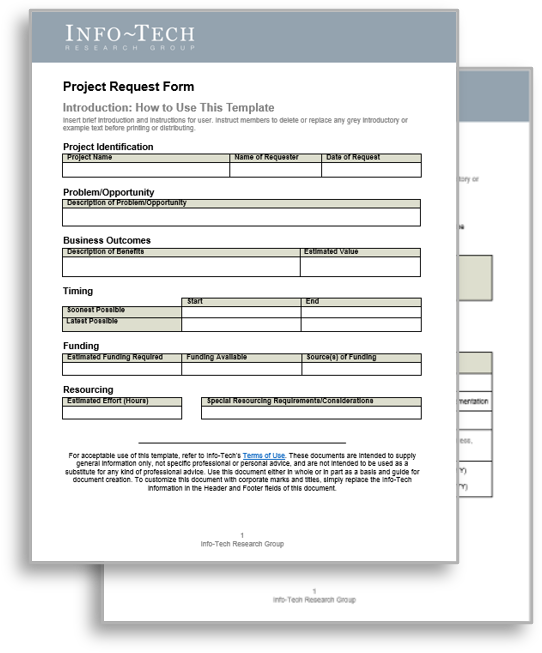
Info-Tech Insight
Optimizing a process should not automatically mean reducing friction. Blindly reducing friction could generate a tidal wave of poorly thought-out requests, which only drives up unrealistic expectations. Mitigate the risk of unrealistic stakeholder expectations by carefully managing the message: optimize friction.
Document your process to receive project requests
2.1.2 Estimated Time: 30-60 minutes
Review and customize section 2.2, “Receive project requests” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
The goal of optimizing this process is to consolidate multiple intake channels into a single funnel with the right amount of friction to improve visibility and manageability of incoming project requests.
The important decisions to document for this step include:
- What data will be collected, and from whom? For example, Info-Tech’s Light Project Request Form Template will be used to collect project requests from everyone.
- How will requests be collected, and from where? For example, the template will be available as a fillable form on a SharePoint site.
- Who will be informed of the requests? For example, the PMO Director and the BA team will be notified with a hyperlink to the completed request form.
- Who will handle exceptions? For example, PMO will maintain this process and will handle any questions or issues that pertain to this part of the process.
INPUT
- Retrospective of current process (Activity 2.1.1)
OUTPUT
- Customized Project Request Form
- Method of implementation
Materials
- Project Request Form Templates
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Business Analysts
Info-Tech Best Practice
Whatever method of request collection you choose, ensure there is no doubt about how requesters can access the intake form.
Establish a triage process to improve portfolio success
Once a request has been submitted, it will need to be triaged. Triage begins as soon as the request is received. The end goal of the triage process is to set appropriate expectations for stakeholders and to ensure that all requests going forward for approval are valid requests.
PPM Triage Process
- Divert non-project requests by validating that what is described on the request form qualifies as a “project.” Make sure requests are in the appropriate queue – for example, service desk request queue, change and release management queue, etc.
- Quickly assess value and urgency to determine whether the request requires fast-tracking or any other special consideration.
- Assign a specialist to follow up on the request. Match the request to the most suitable BA, PM, or equivalent. This person will become the Request Liaison (“RL”) for the request and will work with the requestor to define preliminary requirements.
- Inform the requestor that the request has been received and provide clear direction on what will happen with the request next, such as who will follow up on it and when. See the next slide for some examples of this follow-up.
The PMO Triage Team
- Portfolio Manager, or equivalent
- Request Liaisons (business analysts, project managers, or equivalent)
“Request Liaison” Role
The BAs and PMs who follow up on requests play an especially important role in the triage process. They serve as the main point of contact to the requestor as the request evolves into a business case. In this capacity they perform a valuable stakeholder management function, helping to increase confidence and enhance trust in IT.
To properly triage project requests, define exactly what a project is
Bring color to the grey area that can exist in IT between those initiatives that fall somewhere in between “clearly a service ticket” and “clearly a project.”
What constitutes a project?
Another way of asking this question that gets more to the point for this blueprint – for what types of initiatives is project intake, approval, and prioritization rigor required?
This is especially true in IT where, for some smaller initiatives, there can be uncertainty in many organizations during the intake and initiation phase about what should be included on the formal project list and what should go to help desk’s queue.
As the definitions in the table below show, formal project management frameworks each have similar definitions of “a project.”
| Source | Definition |
|---|---|
| PMI | A temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result.” (553) |
| COBIT | A structured set of activities concerned with delivering a defined capability (that is necessary but not sufficient to achieve a required business outcome) to the enterprise based on an agreed‐on schedule and budget.” (74) |
| PRINCE2 | A temporary organization that is created for the purpose of delivering one or more business products according to an agreed business case. |
For each, a project is a temporary endeavor planned around producing a specific organizational/business outcome. The challenge of those small initiatives in IT is knowing when those endeavors require a business case, formal resource tracking, and project management rigor, and when they don’t.
Separating small projects from non-projects requires a consideration of approval rights
While conventional wisdom says to base your project definition on an estimation of cost, risk, etc., you also need to ask, “does this initiative require formal approval?”
In the next step, we will define a suggested minimum threshold for a small “level 1” project. While these level thresholds are good and necessary for a number of reasons – including triaging your project requests – you may still often need to exercise some critical judgment in separating the tickets from the projects. In addition to the level criteria that we will develop in this step, use the checklist below to help with your differentiating.
| Service Desk Ticket | Small Project |
|---|---|
|
|
Info-Tech Insight
Guard the value of the portfolio. Because tickets carry with them an implicit approval, you need to be wary at the portfolio level of those that might possess a larger scope than their status of ticket implies. Sponsors that, for whatever reason, resist the formal intake process may use the ticketing process to sneak projects in through the backdoor. When assessing tickets and small projects at the portfolio level, you need to ask: is it possible that someone at an executive level might want to get updates on this because of its duration, scope, risk, cost, etc.? Could someone at the management level get upset that the initiative came in as a ticket and is burning up time and driving costs without any visibility?
Sample Project/Non-Project Separation Criteria
| Non-Project | Small Project | |
|---|---|---|
| e.g. Time required | e.g. < 40 hours | e.g. 40 > hours |
| e.g. Complexity | e.g. Very low | e.g. Moderate – Low Difficulty: Does not require highly developed or specialized skill sets |
| e.g. Collaboration | e.g. None required | e.g. Limited coordination and collaboration between resources and departments |
| e.g. Repeatability of work | e.g. Fully repeatable | e.g. Less predictable |
| e.g. Frequency of request type | e.g. Hourly to daily | e.g. Weekly to monthly |
"If you worked for the help desk, over time you would begin to master your job since there is a certain rhythm and pattern to the work…On the other hand, projects are unique. This characteristic makes them hard to estimate and hard to manage. Even if the project is similar to one you have done before, new events and circumstances will occur. Each project typically holds its own challenges and opportunities"
– Jeffrey and Thomas Mochal
Define the minimum-threshold criteria for small projects
2.1.3 Estimated Time: 30 minutes
Follow the steps below to define the specifics of a “level 1” project for your organization.
- Using your project list and/or ticketing system, identify a handful of small projects, large service desk tickets, and especially those items that fall somewhere in the grey area in between (anywhere between 10 to 20 of each). Then, determine the organizationally appropriate considerations for defining your project levels. Options include:
- Duration
- Budget/Cost
- Technology requirements
- Customer involvement
- Integration
- Organizational impact
- Complexity
- Number of cross-functional workgroups and teams involved
INPUT
- Data concerning small projects and service desk tickets, including size, duration, etc.
OUTPUT
- Clarity around how to define your level 1 projects
Materials
- Whiteboard
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
Remove room for stakeholder doubt and confusion by informing requests forward in a timely manner
During triaging, requestors should be notified as quickly as possible (a) that their request has been received and (b) what to expect next for the request. Make this forum as productive and informative as possible, providing clear direction and structure for the future of the request. Be sure to include the following:
- A request ID or ticket number.
- Some direction on who will be following up on the request –provide an individual’s name when possible.
- An estimated timeframe of when they can expect to hear from the individual following up.
The logistic of this follow-up will depend on a number of different factors.
- The number of requests you receive.
- Your ability to automate the responses.
- The amount of detail you would like to, or need to, provide stakeholders with.
Info-Tech Best Practice
Assign an official request number or project ID to all requests during this initial response. An official request number anchors the request to a specific and traceable dataset that will accompany the project throughout its lifecycle.
Sample “request received” emails
If you receive a high volume of requests or need a quick win for improving stakeholder relations:
Sample #1: Less detailed, automatic response
Hello Emma,
Thank you. Your project request has been received. Requests are reviewed and assigned every Monday. A business analyst will follow up with you in the next 5-10 business days. Should you have any questions in the meantime, please reply to this email.
Best regards,
Information Technology Services
If stakeholder management is a priority, and you want to emphasize the customer-facing focus:
Sample #2: More detailed, tailored response
Hi Darren,
Your project request has been received and reviewed. Your project ID number is #556. Business analyst Alpertti Attar has been assigned to follow up on your request. You can expect to hear from him in the next 5-10 business days to set up a meeting for preliminary requirements gathering.
If you have any questions in the meantime, please contact Alpertti at aattar@projectco.com. Please include the Project ID provided in this email in all future correspondences regarding this request.
Thank you for your request. We look forward to helping you bring this initiative to fruition.
Sincerely,
Jim Fraser
PMO Director, Information Technology Services
Info-Tech Insight
A simple request response will go a long way in terms of stakeholder management. It will not only help assure stakeholders that their requests are in progress but the request confirmation will also help to set expectations and take some of the mystery out of IT’s processes.
Document your process to triage project requests
2.1.4 Estimated Time: 30-60 minutes
Review and customize section 2.3, “Triage project requests” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
The goal of optimizing this process is to divert non-project requests and set an appropriate initial set of stakeholder expectations for next steps. The important decisions to document for this step include:
- What defines a project? Record the outcomes of Activities 2.1.3 into the SOP.
- Who triages the requests and assign request liaisons? Who are they? For example, a lead BA can assign a set roster of BAs to project requests.
- What are the steps to follow for sending the initial response? See the previous slides on automated responses vs. detailed, tailored responses.
- How will you account for the consumption of resource capacity? For example, impose a maximum of four hours per week per analyst, and track the hours worked for each request to establish a pattern for capacity consumption.
- Who will handle exceptions? For example, PMO will maintain this process and will handle any questions or issues that pertain to this part of the process.
INPUT
- Results of activity 2.1.3
OUTPUT
- SOP for triaging project requests
Materials
- SOP Template
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Business Analysts
Info-Tech Best Practice
Whatever method of request collection you choose, ensure there is no doubt about how requesters can access the intake form.
Follow up on requests to define project scope and set realistic expectations
The purpose of this follow-up is to foster communication among the requestor, IT, and the sponsor to scope the project at a high level. The follow-up should:
- Clarify the goals and value of the request.
- Begin to manage expectations based on initial assessment of feasibility.
- Ensure the right information is available for evaluating project proposals downstream. Every project should have the below key pieces of scope defined before any further commitments are made.
Focus on Defining Key Pieces of Scope
- Budget (funding, source)
- Business outcome
- Completion criteria
- Timeframes (start date and duration)
- Milestones/deliverables
Structure the Follow-Up Process to Enhance Alignment Between IT and the Business
Once a Request Liaison (RL) has been assigned to a request, it is their responsibility to schedule time (if necessary) with the requestor to perform a scoping exercise that will help define preliminary requirements. Ideally, this follow-up should occur no later than a week of the initial request.
Structure the follow-up for each request based on your preliminary estimates of project size (next slide). Use the “Key Pieces of Scope” to the left as a guide.
It may also be helpful for RLs and stakeholders to work together to produce a rough diagram or mock-up of the final deliverable. This will ensure that the stakeholder’s idea has been properly communicated, and it could also help refine or broaden this idea based on IT’s capabilities.
After the scoping exercise, it is the RL’s responsibility to inform the requestor of next steps.
Info-Tech Insight
More time spent with stakeholders defining high-level requirements during the ideation phase is key to project success. It will not only improve the throughput of projects, but it will enhance the transparency of IT’s capacity and enable IT to more effectively support business processes.
Perform a preliminary estimation of project size
Project estimation is a common pain point felt by many organizations. At this stage, a range-of-magnitude (ROM) estimate is sufficient for the purposes of sizing the effort required for developing project proposals with appropriate detail.
A way to structure ROM estimates is to define a set of standard project levels. It will help you estimate 80% of projects with sufficient accuracy over time with little effort. The remaining 20% of projects that don’t meet their standard target dates can be managed as exceptions.
The increased consistency of most projects will enable you to focus more on managing the exceptions.
Example of standard project sizes:
| Level | Primary unit of estimation | Target completion date* |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Weeks | 3 weeks – 3 months |
| 2 | Months | 3 months – 6 months |
| 3 | Quarters | 2 – 4 quarters |
| 3+ | Years | 1 year or more |
* Target completion date is simply that – a target, not a service level agreement (SLA). Some exceptions will far exceed the target date, e.g. projects that depend heavily on external or uncontrollable factors.
Info-Tech Best Practice
Project levelling is useful for right-sizing many downstream processes; it sets appropriate levels of detail and scrutiny expected for project approval and prioritization steps, as well as the appropriate extent of requirements gathering, project management, and reporting requirements afterwards.
Set your thresholds for level 2 and level 3 projects
2.1.5 Estimated Time: 30 minutes
Now that the minimum threshold for your smallest projects has been identified, it’s time to identify the maximum threshold in order to better apply project intake, approval, and prioritization rigor where it’s needed.
- Looking at your project list (e.g. Activity 1.1.1, or your current project backlog), isolate the medium and large projects. Examine the two categories in turn.
- Start with the medium projects. Using the criteria identified in Activity 2.1.3, identify where your level one category ends.
- What are the commonly recurring thresholds that distinguish medium-sized projects from smaller initiatives?
- Are there any criteria that would need to take on a greater importance when making the distinction? For instance, will cost or duration take on a greater weighting when determining level thresholds?
- Once you have reached consensus, record these in the table on the next slide.
- What are the commonly recurring thresholds that distinguish large and extra-large projects from medium-sized initiatives?
- Once you have reached consensus, records these in the table on the next slide.
INPUT
- Leveling criteria from Activity 2.1.3
- Project backlog, or list of projects from Activity 1.1.1
OUTPUT
- Clarity around how to define your level two and three projects
Materials
- Whiteboard
- The project level table on the next slide
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Admin Staff
Sample Project Levels Table
| Project Level | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work Effort | 40-100 hours | 100-500 hours | 500+ hours |
| Budget | $100,000 and under | $100,000 to $500,000 | $500,000 and over |
| Technology | In-house expertise | Familiar | New or requires system-wide change/training |
| Complexity | Well-defined solution; no problems expected | Solution is known; some problems expected | Solution is unknown or not clearly defined |
| Cross-Functional Workgroups/Teams | 1-2 | 3-5 | > 6 |
Apply a computation decision-making method for project levelling
2.1.5 Project Intake Classification Matrix
Capture the project levels in Info-Tech’s Project Intake Classification Matrix Tool to benchmark your levelling criteria and to determine project levels for proposed projects.
Download Info-Tech’s Project Intake Classification Matrix tool.
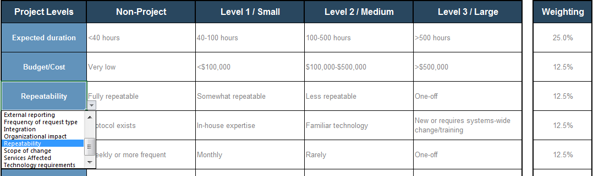
- Pick a category to define project levels.
- Enter the descriptions for each project level.
- Assign a relative weight for each category.
- Enter a project name.
- Choose the description that best fits the project. If unknown, leave it blank.
- Suggested project levels are displayed.
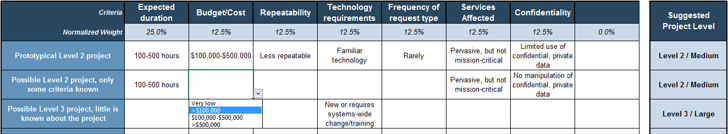
Get tentative buy-in and support from an executive sponsor for project requests
In most organizations a project requires sponsorship from the executive layer, especially for strategic initiatives. The executive sponsor provides several vital factors for projects:
- Funding and resources
- Direct support and oversight of the project leadership
- Accountability, acting as the ultimate decision maker for the project
- Ownership of, and commitment to, project benefits
Sometimes a project request may be made directly by a sponsor; in other times, the Request Liaison may need to connect the project request to a project sponsor.
In either case, project request has a tentative buy-in and support of an executive sponsor before a project request is developed into a proposal and examined for approval – the subject of this blueprint’s next step.
PMs and Sponsors: The Disconnect
A study in project sponsorship revealed a large gap between the perception of the project managers and the perception of sponsors relative to the sponsor capability. The widest gaps appear in the areas of:
- Motivation: 34% of PMs say sponsors frequently motivate the team, compared to 82% of executive sponsors who say they do so.
- Active listening: 42% of PMs say that sponsors frequently listen actively, compared to 88% of executive sponsors who say they do so.
- Effective communication: 47% of PMs say sponsors communicate effectively and frequently, compared to 92% of executive sponsors who say they do so.
- Managing change: 37% of PMs say sponsors manage change, compared to 82% of executive sponsors who say they do so.
Source: Boston Consulting Group/PMI, 2014
Actively engaged executive sponsors continue to be the top driver of whether projects meet their original goals and business intent.
– PMI Pulse of the Profession, 2017
76% of respondents [organizations] agree that the role of the executive sponsor has grown in importance over the past five years.
– Boston Consulting Group/PMI, 2014
Document your process to follow up on project requests
2.1.6 45 minutes
Review and customize section 2.4, “Follow up on project requests” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
The goal of optimizing this process is to initiate communication among the requestor, IT, and the sponsor to scope the project requests at a high level. The important decisions to document for this step include:
- How will you perform a scoping exercise with the requestor? Leverage existing organizational processes (e.g. high-level requirements gathering). Look to the previous slides for suggested outcomes of the exercise.
- How will you determine project levels? Record the outcomes of activities 2.1.5 into the SOP.
- How will the RL follow up on the scoped project request with a project sponsor? For example, project requests scoped at a high level will be presented to senior leadership whose lines of business are affected by the proposed project to gauge their initial interest.
- How will you account for the consumption of resource capacity? For example, impose a maximum of 8 hours per week per analyst, and track the hours worked for each request to establish a pattern for capacity consumption.
- Who will handle exceptions? For example, PMO will maintain this process and will handle any questions or issues that pertain to this part of the process.
INPUT
- Activity 2.1.5
- Existing processes for scoping exercises
OUTPUT
- SOP for following up on project requests
Materials
- SOP Template
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Admin Staff
Examine the new project intake workflow as a whole and document it in a flow chart
2.1.7 Estimated Time: 30-60 minutes
Review and customize section 2.1, “Project Intake Workflow” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
In Step 1.2 of the blueprint, you mapped out the current project intake, approval, and prioritization workflow and documented it in a flow chart. In this step, take the time to examine the new project intake process as a whole, and document the new workflow in the form of a flow chart.
- Requestor fills out form and submits the request.
- Requests are triaged into the proper queue.
- BA or PM prepares to develop requests into a project proposal.
- Requestor is given realistic expectations for approval process.
Consider the following points:
- Are the inputs and outputs of each step clear? Who’s doing the work? How long will each step take, on average?
- Is the ownership of each step clear? How will we ensure a smooth handoff between each step and prevent requests from falling through the cracks?
INPUT
- New process steps for project intake (Activities 2.1.2-6)
OUTPUT
- Flowchart representation of new project intake workflow
Materials
- Microsoft Visio, flowchart software, or Microsoft PowerPoint
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Admin Staff
Case study: Portfolio manager achieves intake and project success through detailed request follow-up
Case Study
Industry: Municipal Government
Source: Info-Tech Client
Challenge
- There is an IT department with a relatively high level of project management maturity.
- They have approximately 30 projects on the go, ranging from small to large.
- To help with intake, IT assembled a project initiation team. It was made up of managers from throughout the county. This group “owned the talent” and met once a month to assess requests. As a group, they were able to assemble project teams quickly.
Solution
- Project initiation processes kept failing. A lot of time was spent within IT getting estimations precise, only to have sponsors reject business cases because they did not align with what those sponsors had in mind.
- Off-the-grid projects were a challenge. Directors did not follow intake process and IT talent was torn in multiple directions. There was nothing in place for protecting the talent and enforcing processes on stakeholders.
Results
- IT dedicated a group of PMs and BAs to follow up on requests.
- Working with stakeholders, this group collects specific pieces of information that allows IT to get to work on requests faster. Through this process, requests reach the charter stage more quickly and with greater success.
- An intake ticketing system was established to protect IT talent. Workers are now better equipped to redirect stakeholders through to the proper channels.
Step 2.2: Set up steps of project approval to maximize strategic alignment while right-sizing the required effort
| PHASE 1 | PHASE 2 | PHASE 3 | ||||
1.1 Define project valuation criteria | 1.2 Envision process target state | 2.1 Streamline intake | 2.2 Right-size approval steps | 2.3 Prioritize projects to fit resource capacity | 3.1 Pilot your optimized process | 3.2 Communicate organizational change |
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Perform a deeper retrospective on current project approval process
- Define the approval steps, their accountabilities, and the corresponding terminologies for approval
- Right-size effort and documentation required for each project level through the approval steps
This step involves the following participants:
- PMO Director / Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Administrative Staff
Outcomes of this step
- Retrospective of the current project intake process: to continue doing, to start doing, and to stop doing
- A series of approval steps are defined, in which their accountabilities, responsibilities, and the nomenclature for what is approved at each steps are clarified and documented
- A toolbox of deliverables for proposed projects that captures key information developed to inform project approval decisions at each step of the approval process, and the organizational standard for what to use for which project level
- Documentation of the optimized process in the SOP document
Set up an incremental series of approval stage-gates to tackle common challenges in project approval
This section will help you address key challenges IT leaders face around project approval.
| Challenges | Info-Tech’s Advice |
|---|---|
| Project sponsors receive funding from their business unit or other source (possibly external, such as a grant), and assume this means their project is “approved” without any regard to IT costs or resource constraints. | Clearly define a series of approval steps, and communicate requirements for passing them. |
| Business case documentation is rarely updated to reflect unforeseen costs, emerging opportunities, and changing priorities. As a result, time and money is spent finishing diminished priority projects while the value of more recent projects erodes in the backlog. | Approve projects in smaller pieces, with early test/pilot phases focused on demonstrating the value of later phases. |
| Project business cases often focus on implementation and overlook ongoing operating costs imposed on IT after the project is finished. These costs further diminish IT’s capacity for new projects, unless investment in more capacity (such as hiring) is included in business cases. | Make ongoing support and maintenance costs a key element in business case templates and evaluations. |
| Organizations approve new projects without regard to the availability of resource capacity (or lack thereof). Project lead times grow and stakeholders become more dissatisfied because IT is unable to show how the business is competing with itself for IT’s time. | Increase visibility into what IT is already working on and committed to, and for whom. |
Develop a project approval workflow
Clearly define a series of approval steps, and communicate requirements for passing them. “Approval” can be a dangerous word in project and portfolio management, so it is important to clarify what is required to pass each step, and how long the process will take.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approval step | Concept Approval | Feasibility Approval | Business Case Approval | Resource Allocation (Prioritization) |
| Alignment Focus | Business need / Project sponsorship | Technology | Organization-wide business need | Resource capacity |
| Possible dispositions at each gate |
|
|
|
|
| Accountability | e.g. Project Sponsor | e.g. CIO | e.g. Steering Committee | e.g. CIO |
| Deliverable | Benefits Commitment Form Template | Proposed Project Technology Assessment Tool | Business Case (Fast Track, Comprehensive) | Intake and Prioritization Tool |
Identify the decision-making paradigm at each step
In general, there are three different, mutually exclusive decision-making paradigms for approving projects:
| Paradigm | Description | Benefits | Challenges | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unilateral authority | One individual makes decisions. | Decisions tend to be made efficiently and unambiguously. Consistency of agenda is easier to preserve. | Decisions are subject to one person’s biases and unseen areas. | Decision maker should solicit and consider input from others and seek objective rigor. |
| Ad hoc deliberation | Stakeholders informally negotiate and communicate decisions between themselves. | Deliberation helps ensure different perspectives are considered to counterbalance individual biases and unseen areas. | Ad hoc decisions tend to lack documentation and objective rationale, which can perpetuate disagreement. | Use where unilateral decisions are unfeasible (due to complexity, speed of change, culture, etc.), and stakeholders are very well aligned or highly skilled negotiators and communicators. |
| Formal steering committee | A select group that represent various parts of the organization is formally empowered to make decisions for the organization. | Formal committees can ensure oversight into decisions, with levers available to help resolve uncertainty or disagreement. | Formal committees introduce administrative overhead and effort that might not be warranted by the risks involved. | Formal steering committees are best where formality is warranted by the risks and costs involved, and the organizational culture has an appetite for administrative oversight. |
Info-Tech Insight
The individual or party who has the authority to make choices, and who is ultimately answerable for those decisions, is said to be accountable. Understanding the needs of the accountable party is critical to the success of the project approval process optimization efforts.
Perform a start-stop-continue exercise to help determine what is working and what is not working
2.2.1 Estimated Time: 45 minutes
Optimizing project approval may not require a complete overhaul of your existing processes. You may only need to tweak certain templates or policies. Perhaps you started out with a strong process and simply lost resolve over time – in which case you will need to focus on establishing motivation and discipline, rather than rework your entire process.
Perform a start-stop-continue exercise with your team to help determine what should be salvaged, what should be abandoned, and what should be introduced:
| 1.On a whiteboard or equivalent, write “Start,” “Stop,” and “Continue” in three separate columns. | 3.As a group, discuss the responses and come to an agreement as to which are most valid. |
| 2.Equip your team with sticky notes or markers and have them populate the columns with ideas and suggestions surrounding your current processes. | 4.;Document the responses to help structure your game plan for intake optimization. |
| Start | Stop | Continue |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
INPUT
- Current project approval workflow (Activity 1.2.2)
- Project approval success criteria (Activity 1.2.6)
OUTPUT
- Retrospective review of current approval process
Materials
- Whiteboard
- Sticky notes/markers
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Admin Staff
Customize the approval steps and describe them at a high level
2.2.2 Estimated Time: 30-60 minutes
Review and customize section 3.2, “Project Approval Steps” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
The goal of this activity is to customize the definition of the approval steps for your organization, so that it makes sense for the existing organizational governance structure, culture, and need. Use the results of the start-stop-continue to inform what to customize. Consider the following factors:
- Order of steps: given the current decision-making paradigm, does it make sense to reorder the steps?
- Dispositions at each step: what are the possible dispositions, and who is accountable for making the dispositions?
- Project levels: do all projects require three-step approval before they’re up for prioritization? For example, IT steering committee may wish to be involved only for Level 3 projects and Level 2 projects with significant business impact, and not for Level 1 projects and IT-centric Level 2 projects.
- Accountability at each step: who makes the decisions?
- Who will handle exceptions? Aim to prevent the new process from being circumvented by vocal stakeholders, but also allow for very urgent requests. A quick win to strike this balance is to clarify who will exercise this discretion.
INPUT
- Retrospective of current process (Activity 2.2.1)
- Project level definition
- Approval steps in the previous slide
OUTPUT
- Customized project approval steps for each project level
Materials
- Whiteboard
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Admin Staff
Specify what “approval” really means to manage expectations for what project work can be done and when
2.2.3 Estimated Time: 15 minutes
Review and customize section 3.2, “Project Approval Steps” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
In the old reality, projects were approved and never heard back from again, which effectively gave your stakeholders a blanket default expectation of “declined.” With the new approval process, manage your stakeholder expectations more explicitly by refining your vocabulary around approval.
Within this, decision makers should view their role in approval as approving that which can and should be done. When a project is approved and slated to backlog, the intention should be to allocate resources to it within the current intake cycle.
Customize the table to the right with organizationally appropriate definitions, and update your SOP.
| “No” | Declined. |
|---|---|
| “Not Now” | “It’s a good idea, but the time isn’t right. Try resubmitting next intake cycle.” |
| “Concept Approval” | Approval to add the item to the backlog with the intention of starting it this intake cycle. |
| “Preliminary Approval” | Approval for consumption of PMO resources to develop a business case. |
| “Full Approval” | Project is greenlighted and project resources are being allocated to it. |
Info-Tech Insight
Refine the nomenclature. Add context to “approved” and “declined.” Speak in terms of “not now” or “you can have it when these conditions are met.” With clear expectations of the resources required to support each request, you can place accountability for keeping the request alive back on the sponsors.
Continuously work out a balance between disciplined decision making and “analysis paralysis"
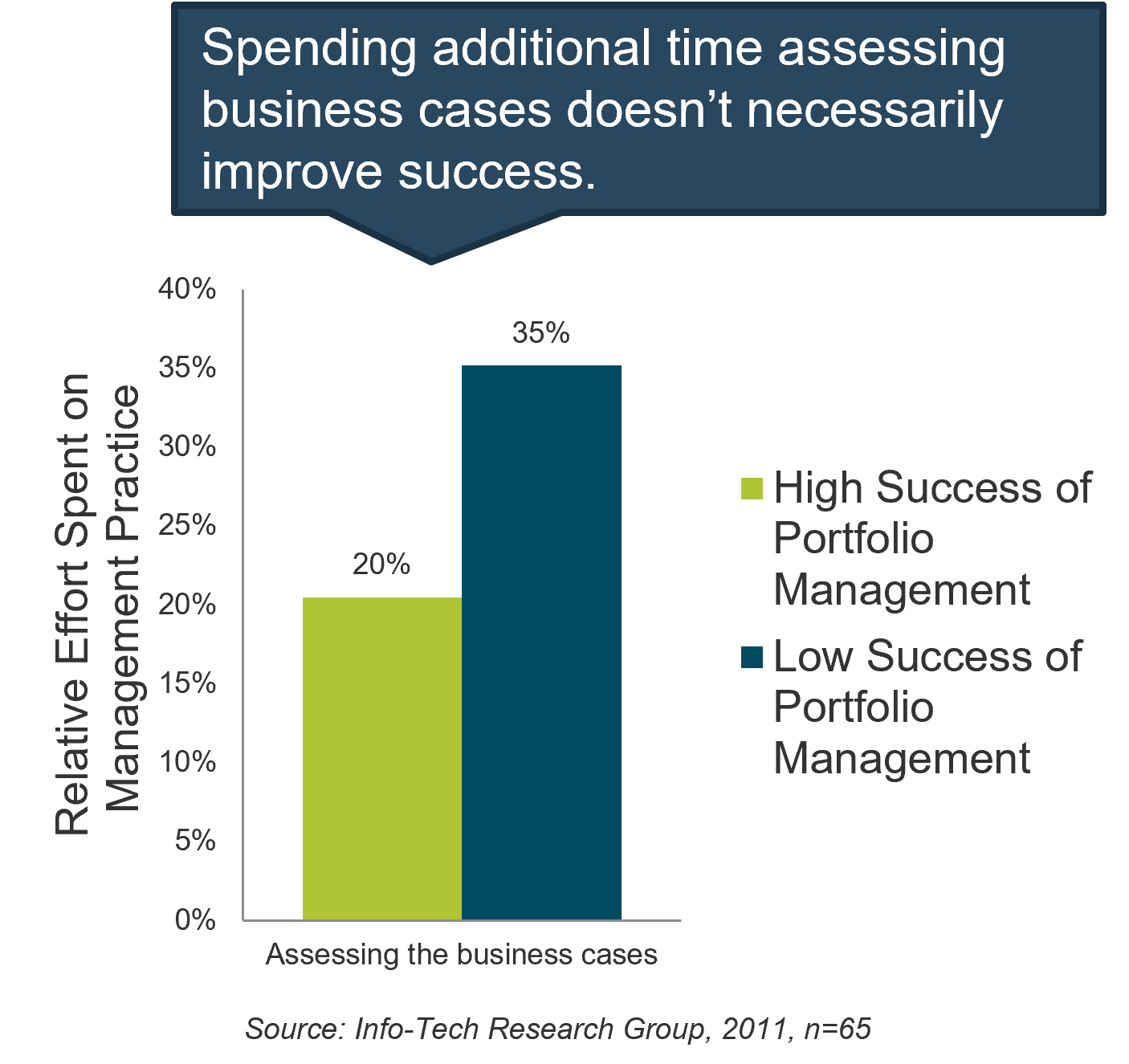
Info-Tech Insight
Estimates that form the basis of business cases are often based on flawed assumptions. Use early project phases or sprints to build working prototypes to test the assumptions on which business cases are built, rather than investing time improving precision of estimates without improving accuracy.
Right-size project approval process with Info-Tech’s toolbox of deliverables
Don’t paint every project with the same brush. Choose the right set of information needed for each project level to maximize the throughput of project approval process.
The next several slides will take you through a series of tools and templates that help guide the production of deliverables. Each deliverable wireframes the required analysis of the proposed project for one step of the approval process, and captures that information in a document. This breaks down the overall work for proposal development into digestible chunks.
As previously discussed, aim to right-size the approval process rigor for project levels. Not all project levels may call for all steps of approval, or the extent of required analysis within an approval step may differ. This section will conclude by customizing the requirement for deliverables for each project level.
Tools and Templates for the Project Approval Toolbox
- Benefits Commitment Form Template (.xlsx) Document the project sponsor’s buy-in and commitment to proposed benefits in a lightweight fashion.
- Proposed Technology Assessment Tool (.xlsx) Determine the proposed project’s readiness for adoption from a technological perspective.
- Business Case Templates (.docx) Guide the analysis process for the overall project proposal development in varying levels of detail.
Use Info-Tech’s lightweight Benefits Commitment Form Template to document the sponsor buy-in and support
2.2.4 Benefits Commitment Form Template
Project sponsors are accountable for the realization of project benefits. Therefore, for a project to be approved by a project sponsor, they must buy-in and commit to the proposed benefits.
Defining project benefits and obtaining project sponsor commitment has been demonstrated to improve the project outcome by providing the focal point of the project up-front. This will help reduce wasted efforts to develop parts of the proposals that are not ultimately needed.
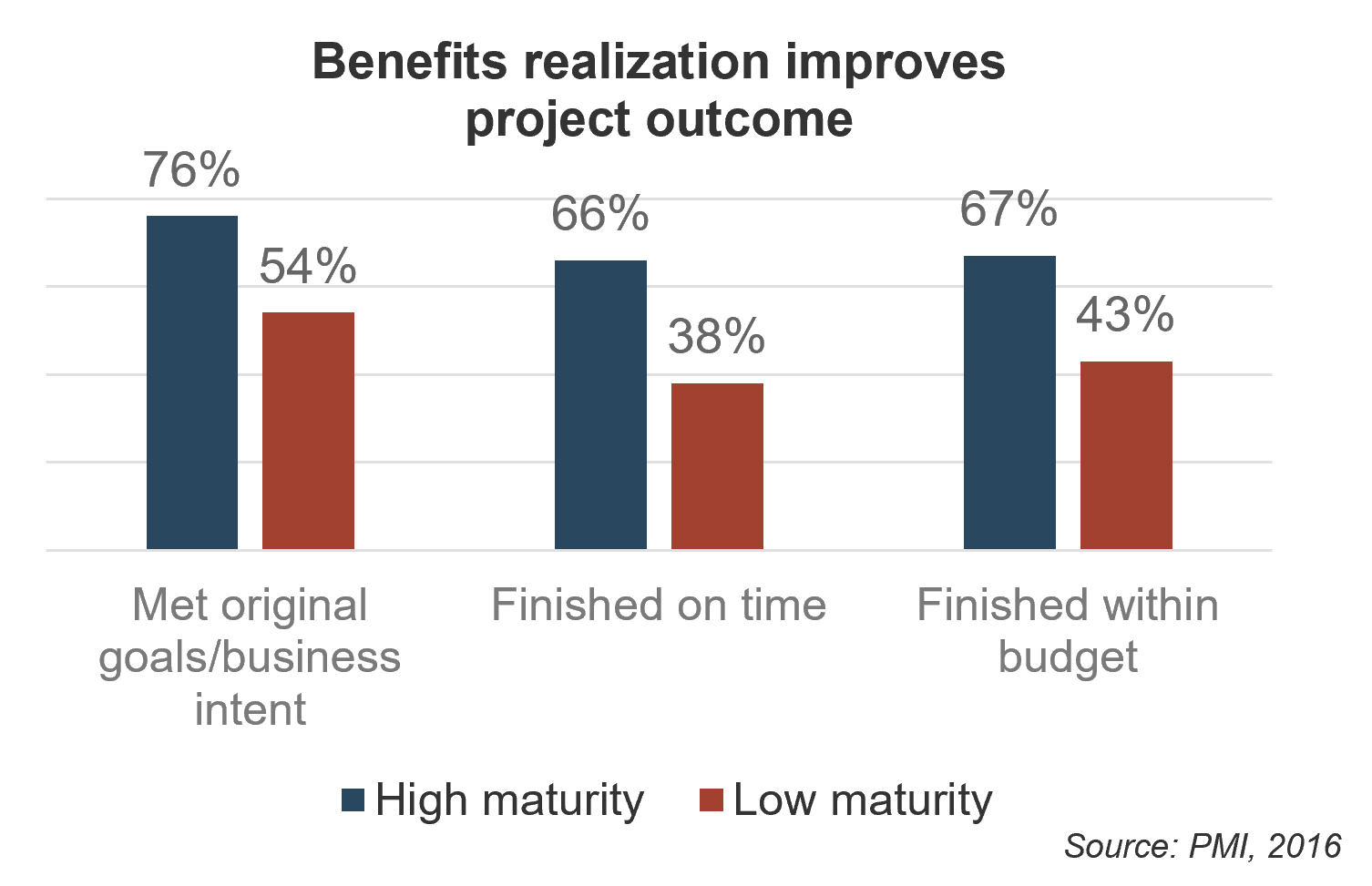
Download Info-Tech’s Benefits Commitment Form Template.
Contents of a Benefits Commitment Form
- One-sentence highlight of benefits and risks
- Primary benefit, hard (quantitative) and soft (qualitative)
- Proposed measurements for metrics
- Responsible and accountable parties for benefits

For further discussion on benefits realization, use Info-Tech’s blueprint, Establish the Benefits Realization Process.
Use Info-Tech’s Proposed Project Technology Assessment Tool to analyze a technology’s readiness for adoption
2.2.4 Proposed Project Technology Assessment Tool
In some projects, there needs to be an initial idea of what the project might look like. Develop a high-level solution for projects that:
- Are very different from previous projects.
- Are fairly complex, or not business as usual.
- Require adoption of new technology or skill set.
IT should advise and provide subject matter expertise on the technology requirements to those that ultimately approve the proposed projects, so that they can take into account additional costs or risks that may be borne from it.
Info-Tech’s Proposed Project Technology Assessment Tool has a series of questions to address eight categories of considerations to determine the project’s technological readiness for adoption. Use this tool to ensure that you cover all the bases, and help you devise alternate solutions if necessary – which will factor into the overall business case development.
Download Info-Tech’s Proposed Project Technology Assessment Tool.
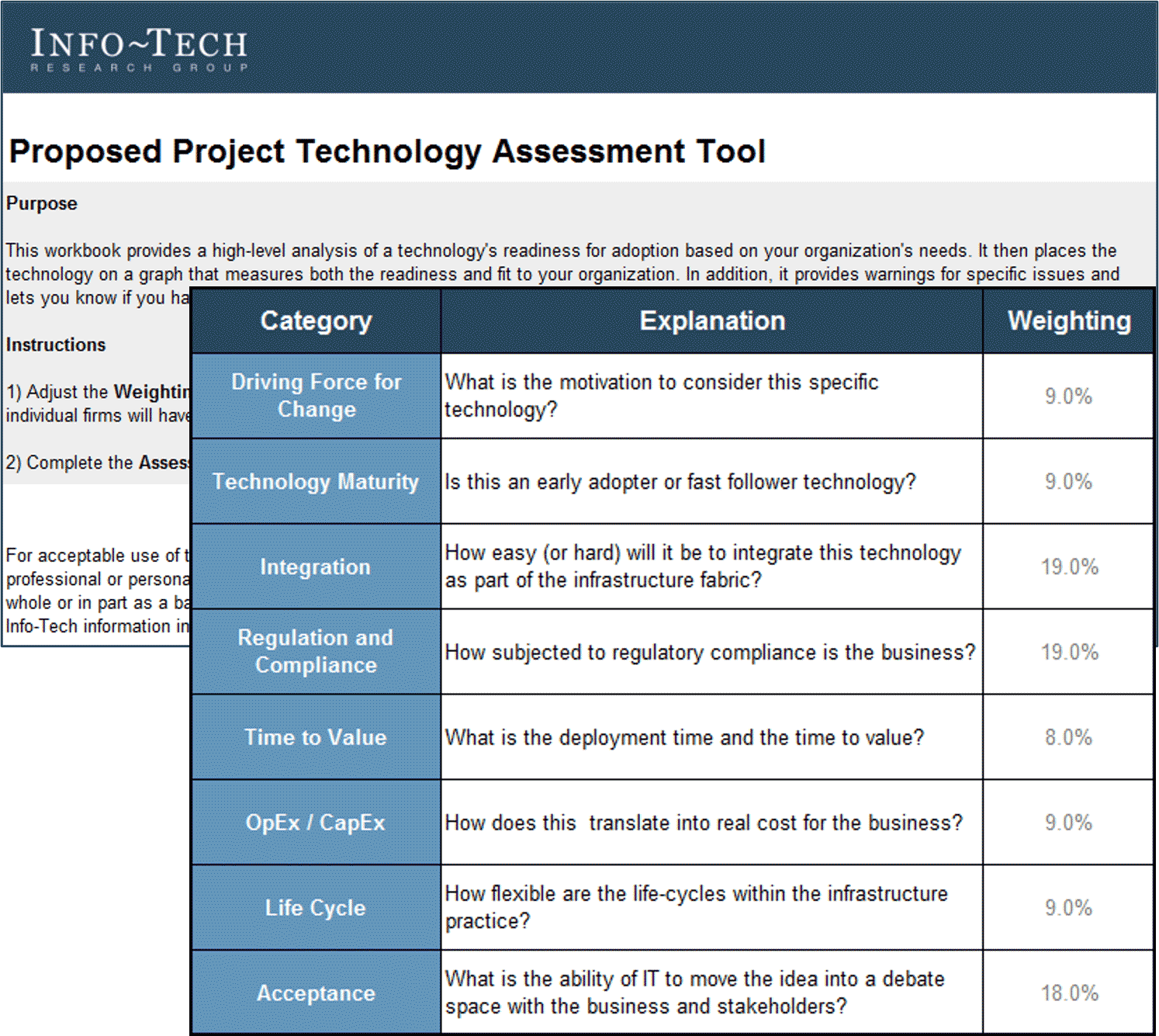
Enable project valuation beyond financial metrics with Info-Tech’s Business Case Templates
2.2.4 Business Case Template (Comprehensive and Fast Track)
Traditionally, a business case is centered around financial metrics. While monetary benefits and costs are matters of bottom line and important, financial metrics are only part of a project’s value. As the project approval decisions must be based on the holistic comparison of project value, the business case document must capture all the necessary – and only those that are necessary – information to enable it.
However, completeness of information does not always require comprehensiveness. Allow for flexibility to speed up the process of developing business plan by making a “fast-track” business case template available. This enables the application of the project valuation criteria with all other projects, with right-sized effort.
Alarming business case statistics
- Only one-third of companies always prepare a business case for new projects.
- Nearly 45% of project managers admit they are unclear on the business objectives of their IT projects.
(Source: Wrike)
Download Info-Tech’s Comprehensive Business Case Template.

Download Info-Tech’s Fast Track Business Case Template.

Info-Tech Insight
Pass on that which is known. Valuable information about projects is lost due to a disconnect between project intake and project initiation, as project managers are typically not brought on board until project is actually approved. This will be discussed more in Phase 3 of this blueprint.
Document the right-sized effort and documentation required for each project level
2.2.4 Estimated Time:60-90 minutes
Review and customize section 3.3, “Project Proposal Deliverables” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
The goal of this activity is to customize the requirements for project proposal deliverables, so that it properly informs each of the approval steps discussed in the previous activity. The deliverables will also shape the work effort required for projects of various levels. Consider the following factors:
- Project levels: what deliverables should be required, recommended, or suggested for each of the project levels? How will exceptions be handled, and who will be accountable?
- Existing project proposal documents: what existing proposal documents, tools and templates can we leverage for the newly optimized approval steps?
- Skills availability: do these tools and templates represent a significant departure from the current state? If so, is there capacity (time and skill) to achieve the desired target state?
- How will you account for the consumption of resource capacity? Do a rough order of estimate for the resource capacity consumed the new deliverable standard.
- Who will handle exceptions? For example, PMO will maintain this process and will handle any questions or issues that pertain to this part of the process.
INPUT
- Process steps (Activity 2.2.2)
- Current approval workflow(Activity 1.2.1)
- Artifacts introduced in the previous slides
OUTPUT
- Requirement for artifacts and effort for each approval step
Materials
- Whiteboard
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Admin Staff
Examine the new project approval workflow as a whole and document it in a flow chart
2.2.5 Estimated Time: 30-60 minutes
Review and customize section 3.1, “Project Approval Workflow” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
In Step 1.2 of the blueprint, you mapped out the current project intake, approval, and prioritization workflow and documented it in a flow chart. In this step, take the time to examine the new project intake process as a whole, and document the new workflow in the form of a flow chart.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approval Step | Concept Approval | Feasibility Approval | Business Case Approval | Resource Allocation (Prioritization) |
| Alignment Focus | Business need/ Project Sponsorship | Technology |
Organization-wide Business need |
Resource capacity |
Consider the following points:
- Are the inputs and outputs of each step clear? Who’s doing the work? How long will each step take, on average?
- Is the ownership of each step clear? How will we ensure a smooth hand-off between each step and prevent requests from falling through the cracks?
INPUT
- New process steps for project approval (Activities 2.2.2-4)
OUTPUT
- Flowchart representation of new project approval workflow
Materials
- Microsoft Visio, flowchart software, or Microsoft PowerPoint
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Admin Staff
Step 2.3: Prioritize projects to maximize the value of the project portfolio within the constraint of resource capacity
| PHASE 1 | PHASE 2 | PHASE 3 | ||||
1.1 Define project valuation criteria | 1.2 Envision process target state | 2.1 Streamline intake | 2.2 Right-size approval steps | 2.3 Prioritize projects to fit resource capacity | 3.1 Pilot your optimized process | 3.2 Communicate organizational change |
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Perform a deeper retrospective on current project prioritization process
- Optimize your process to maintain resource capacity supply and project demand data
- Optimize your process to formally make disposition recommendations to appropriate decision makers
This step involves the following participants:
- PMO Director / Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Administrative Staff
Outcomes of this step
- Retrospective of the current project prioritization process: to continue doing, to start doing, and to stop doing
- Realistic estimate of available resource capacity, in the absence of a resource management practice
- Optimized process for presenting the decision makers with recommendations and facilitating capacity-constrained steering of the project portfolio
- Project Intake and Prioritization Tool for facilitating the prioritization process
- Documentation of the optimized process in the SOP document
The availability of staff time is rarely factored into IT project and service delivery commitments
A lot gets promised and worked on, and staff are always busy, but very little actually gets done – at least not within given timelines or to expected levels of quality.
Organizations tend to bite off more than they can chew when it comes to project and service delivery commitments involving IT resources.
While the need for businesses to make an excess of IT commitments is understandable, the impacts of systemically over-allocating IT are clearly negative:
- Stakeholder relations suffer. Promises are made to the business that can’t be met by IT.
- IT delivery suffers. Project timelines and quality frequently suffer, and service support regularly lags.
- Employee engagement suffers. Anxiety and stress levels are consistently high among IT staff, while morale and engagement levels are low.
76%: 76% of organizations say they have too many projects on the go and an unmanageable and ever-growing backlog of things to get to.
– Cooper, 2014
70%: Almost 70% of workers feel as though they have too much work on their plates and not enough time to do it.
– Reynolds, 2016
Unconstrained, unmanaged demand leads to prioritization of work based on consequences rather than value
Problems caused by the organizational tendency to make unrealistic delivery commitments is further complicated by the reality of the matrix environment.
Today, many IT departments use matrix organization. In this system, demands on a resource’s time come from many directions. While resources are expected to prioritize their work, they lack the authority to formally reject any demand. As a result, unconstrained, unmanaged demand frequently outstrips the supply of work-hours the resource can deliver.
When this happens, the resource has three options:
- Work more hours, typically without compensation.
- Choose tasks not to do in a way that minimizes personal consequences.
- Diminish work quality to meet quantity demands.
The result is an unsustainable system for all those involved:
- Individual workers cannot meet expectations, leading to frustration and disengagement.
- Managers cannot deliver on the projects or services they manage and struggle to retain skilled resources who are looking elsewhere for “greener pastures.”
- Executives cannot execute strategic plans as they lose decision-making power over their resources.
Prioritize project demand by project value to get the most out of constrained project capacity – but practicing it is difficult
The theory may be simple and intuitive, but the practice is extremely challenging. There are three practical challenges to making project prioritization effective.
| Project Prioritization |
Capacity awareness Many IT departments struggle to realistically estimate available project capacity in a credible way. Stakeholders question the validity of your endeavor to install capacity-constrained intake process, and mistake it for unwillingness to cooperate instead. |
Lack of authority Many PMOs and IT departments simply lack the ability to decline or defer new projects. |
Many moving parts Project intake, approval, and prioritization involve the coordination of various departments. Therefore, they require a great deal of buy-in and compliance from multiple stakeholders and senior executives. |
Project Approval |
|
Unclear definition of value Defining the project value is difficult, because there are so many different and conflicting ways that are all valid in their own right. However, without it, it's impossible to fairly compare among projects to select what's "best." |
Unclear definition of value
In Step 1.1 of the blueprint, we took the first step toward resolving this challenge by prototyping a project valuation scorecard.
"Prioritization is a huge issue for us. We face the simultaneous challenges of not having enough resources but also not having a good way to say no. "
– CIO, governmental health agency
Address the challenges of capacity awareness and authority with a project prioritization workflow
Info-Tech recommends following a four-step process for managing project prioritization.
- Collect and update supply and demand data
- Re-evaluate project value for all proposed, on-hold and ongoing projects
- Estimate available resource capacity for projects
- Prioritize project demand by value
- Identify highest-value, “slam-dunk” projects
- Identify medium-value, “on-the-bubble” projects
- Identify lower-value projects that lie beyond the available capacity
- Approve projects for initiation or continuation
- Submit recommendations for review
- Adjust prioritized list with business judgment
- Steering committee approves projects to work on
- Manage a realistically defined project portfolio
- Stakeholder Need
- Strategic Objectives
- Resource Capacity
Intake and Prioritization Tool
Perform a start-stop-continue exercise to help determine what is working and what is not working
2.3.1 Estimated Time: 60 minutes
Optimizing project prioritization may not require a complete overhaul of your existing processes. You may only need to tweak certain templates or policies. Perhaps you started out with a strong process and simply lost resolve over time – in which case you will need to focus on establishing motivation and discipline, rather than rework your entire process.
Perform a start-stop-continue exercise with your team to help determine what should be salvaged, what should be abandoned, and what should be introduced:
| 1. On a whiteboard or equivalent, write “Start,” “Stop,” and “Continue” in three separate columns. | 3. As a group, discuss the responses and come to an agreement as to which are most valid. |
| 2. Equip your team with sticky notes or markers and have them populate the columns with ideas and suggestions surrounding your current processes. | 4. Document the responses to help structure your game plan for intake optimization. |
| Start | Stop | Continue |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
INPUT
- Current project prioritization workflow (Activity 1.2.2)
- Project prioritization success criteria (Activity 1.2.6)
OUTPUT
- Retrospective review of current prioritization process
Materials
- Whiteboard
- Sticky notes/markers
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Admin Staff
Use Info-Tech’s lightweight Intake and Prioritization Tool to get started on capacity-constrained project prioritization
Use Info-Tech’s Project Intake and Prioritization Tool to facilitate the scorecard-driven prioritization and ensure effective flow of data.
This tool builds on the Project Valuation Scorecard Tool to address the challenges in project prioritization:
- Lack of capacity awareness: quickly estimate a realistic supply of available work hours for projects for a given prioritization period, in the absence of a reliable and well-maintained resource utilization and capacity data.
- Lack of authority to say “no” or “not yet” to projects: save time and effort in presenting the results of project prioritization analysis that will enable the decision makers to make well-informed, high-quality portfolio decisions.
Using standard project sizing, quickly estimate the size of the demand for proposed and ongoing projects and produce a report that recommends the list of projects to greenlight – and highlight the projects within that list that are at risk of being short-charged of resources – that will aim to help you tackle:
The next several slides will walk you through the tool and present activities to facilitate its use for your organization.
Download Info-Tech’s Project Intake and Prioritization Tool.
Create a high-level estimate of available project capacity to inform how many projects can be greenlighted
2.3.2 Project Intake and Prioritization Tool, Tab 2: Project Capacity
Estimate how many work-hours are at your disposal for projects using Info-Tech’s resource calculator.
1. Compile a list of each role within your department, the number of staff, and the hours in a typical work week.
2. Enter the foreseeable out-of-office time (vacation, sick time, etc.). Typically, this value is 12-16% depending on the region.
3. Enter how much working time is spent on non-projects for each role: administrative duties and “keep the lights on” work.
4. Select a period of time for breaking down available resource capacity in hours.
Project Work (%): Percentage of your working time that goes toward project work is calculated as what’s left after your non-project working time allocations have been subtracted.
Project (h) Total Percentage: Take a note of this percentage as your project capacity. This number will put the estimated project demand in context for the rest of the tool.
Example for a five-day work week:
- 2 weeks (10 days) of statutory holidays
- 3 weeks of vacation
- 1.4 weeks (7 days) of sick days on average
- 1 week (5 days) for company holidays
Result: 7.4/52 weeks’ absence = 14%
Estimate your available project capacity for the next quarter, half-year, or year
2.3.2 Estimated Time: 30 minutes
Discover how many work-hours are at your disposal for project work.
- Use the wisdom-of-the-crowd approach or resource utilization data to fill out Tab 2 of the tool. This is intended to be somewhat of a rough estimate; avoid the pitfall of being too granular in role or in time split.
- Choose a time period that corresponds to your project prioritization period: monthly, quarterly, 4 months, semi-annually (6 months), or annually.
- Examine the pie graph representation of your overall capacity breakdown, like the one shown below.
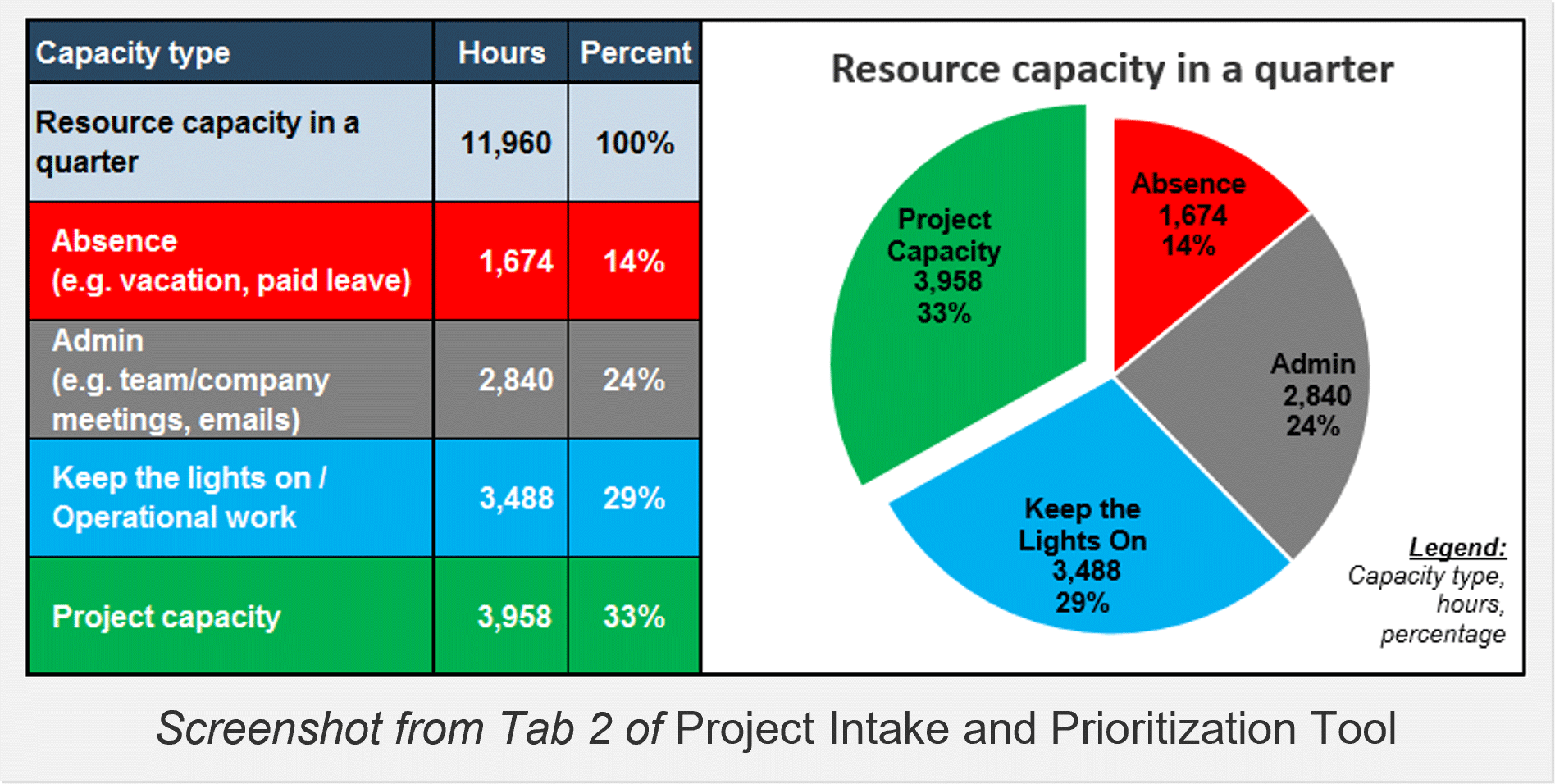
INPUT
- Knowledge of organization’s personnel and their distribution of time
OUTPUT
- Estimate of available project capacity
Materials
- Project Intake and Prioritization Tool
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Admin Staff
On average, only about half of the available project capacity results in productive project work
Place realistic expectations on your resources’ productivity.
Info-Tech’s PPM Current State Scorecard diagnostic provides a comprehensive view of your portfolio management strengths and weaknesses, including project portfolio management, project management, customer management, and resource utilization.
Use the wisdom of the crowd to estimate resource waste in:
- Cancelled projects
- Inefficiency
- Suboptimal assignment of resources
- Unassigned resources
Analyzing, fixing, and redeploying
50% of PPM resource is wasted on average, effectively halving your available project capacity.
Source: Info-Tech PPM Current State Scorecard
Define project capacity and project t-shirt sizes
2.3.3 Project Intake and Prioritization Tool, Tab 3: Settings
The resource capacity calculator in the previous tab yields a likely optimistic estimate for how much project capacity is available. Based on this estimate as a guide, enter your optimistic (maximum) and pessimistic (minimum) estimates of project capacity as a percentage of total capacity:

Info-Tech’s data shows that only about 50% of time spent on project work is wasted: cancelled projects, inefficiency, rework, etc. As a general rule, enter half of your maximum estimate of your project capacity.
Capacity in work hours is shown here from the previous tab, to put the percentages in context. This example shows a quarterly breakdown (Step 4 from the previous slide; cell N5 in Tab 2.).
Next, estimate the percentage of your maximum estimated project capacity that a single project would typically consume in the given period for prioritization.
These project sizes might not line up with the standard project levels from Step 2.1 of the blueprint: for example, an urgent mid-sized project that requires all hands on deck may need to consume almost 100% of maximum available project capacity.
Estimate available project capacity and standard project demand sizes for prioritizing project demand
2.3.3 Estimated Time: 30 minutes
Refine your estimates of project capacity supply and demand as it applies to a prioritization period.
- The estimated project capacity from Activity 2.3.2 represents a theoretical limit. It is most likely an overestimation (see box below). As a group, discuss and decide on a more realistic available project capacity:
- Optimistic estimate, assuming sustained peak productivity from everyone in your organization;
- Pessimistic estimate, taking into account the necessary human downtime and the PPM resource waste (see previous slide).
- Refine the choices of standard project effort sizes, expressed as percentages of maximum project capacity. As a reminder, this sizing is for the chosen prioritization period, and is independent from the project levels set previously in Activity 2.1.4 and 2.1.5.
Dedicated work needs dedicated break time
In a study conducted by the Draugiem Group, the ideal work-to-break ratio for maximizing focus and productivity was 52 minutes of work, followed by 17 minutes of rest (Evans). This translates to 75% of resource capacity yielding productive work, which could inform your optimistic estimate of project capacity.
INPUT
- Project capacity (Activity 2.3.2)
- PPM Current State Scorecard (optional)
OUTPUT
- Capacity and demand estimate data for tool use
Materials
- Project Intake and Prioritization Tool
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Admin Staff
Finish setting up the Project Intake and Prioritization Tool
2.3.4 Project Intake and Prioritization Tool, Tab 3: Settings
Enter the scoring criteria, which was worked out from Step 1.1 of the blueprint. This workbook supports up to ten scoring criteria; use of more than ten may make the prioritization step unwieldy.
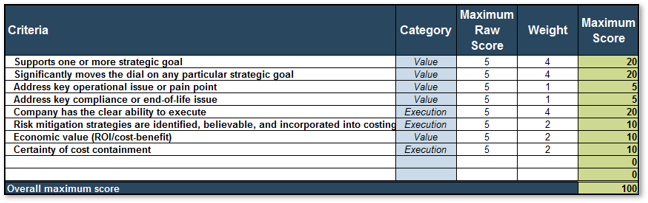
Leave unused criteria rows blank.
Choose “value” or “execution” from a drop-down.
Score does not need to add up to 100.
Finally, set up the rest of the drop-downs used in the next tab, Project Data. These can be customized to fit your unique project portfolio needs.
Enter project data into the Project Intake and Prioritization Tool
2.3.4 Project Intake and Prioritization Tool, Tab 4: Project Data
Ensure that each project has a unique name.
Completed (or cancelled) projects will not be included in prioritization.
Choose the standard project size defined in the previous tab.
Change the heading when you customize the workbook.
Days in Backlog is calculated from the Date Added column.
Overall weighted project prioritization score is calculated as a sum of value and execution scores.
Weighted value and execution scores are calculated according to the scoring criteria table in the 2. Settings tab.
Enter the raw scores. Weights will be taken into calculation behind the scenes.
Spaces for unused intake scores will be greyed out. You can enter data, but they will not affect the calculated scores.
Document your process to maintain resource capacity supply and project demand data
2.3.4 Estimated Time: 30 minutes
Review and customize section 4.2, “Maintain Supply and Demand Data” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
The goal of this activity is to document the process with which the supply and demand information will be updated for projects. Consider the following factors:
- Estimates of resource supply: how often will the resource supply be updated? How are you estimating the range (maximum vs. minimum, optimistic vs. pessimistic)? Leverage your existing organizational process assets for resource management.
- Updating project data for proposed projects: when and how often will the project valuation scores be updated? Do you have sufficient inputs? Examine the overall project approval process from Step 2.2 of the blueprint, and ensure that sufficient information is available for project valuation (Activity 2.2.3).
- Updating project data for ongoing projects: will you prioritize ongoing projects along with proposed projects? When and how often will the project valuation scores be updated? Do you have sufficient inputs?
- How will you account for the consumption of resource capacity? Do a rough order of estimate for the resource capacity consumed in this process.
- Who will handle exceptions? For example, PMO will maintain this process and will handle any questions or issues that pertain to this part of the process.
INPUT
- Organizational process assets for resource management, strategic planning, etc.
- Activity 2.3.3
- Activity 2.2.3
OUTPUT
- Process steps for refreshing supply and demand data
Materials
- SOP Template
- Project Intake and Prioritization Tool
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- PMO Admin Staff
Prioritized list of projects shows what fits under available project capacity for realizing maximum value
2.3.5 Project Intake and Prioritization Tool, Tab 5: Results
The output of the Project Intake and Prioritization Tool is a prioritized list of projects with indicators to show that their demand on project capacity will fit within the estimated available project capacity for the prioritization period.
Status indicates whether the project is proposed or ongoing; completed projects are excluded.
Disposition indicates the course of recommended action based on prioritization.
Proposed projects display how long they have been sitting in the backlog.
Projects highlighted yellow are marked as “deliberate” for their dispositions. These projects pose risks of not getting properly resourced. One must proceed with caution if they are to be initiated or continued.
Provide better support to decision makers with the prioritized list, and be prepared for their steering
It is the portfolio manager’s responsibility to provide the project portfolio owners with reliable data and enable them to make well-informed decisions for the portfolio.
The prioritized list of proposed and ongoing projects, and an approximate indication for how they fill out the estimated available resource capacity, provide a meaningful starting ground for discussion on which projects to continue or initiate, to hold, or to proceed with caution.
However, it is important to recognize the limitation of the prioritization methodology. There may be legitimate reasons why some projects should be prioritized over another that the project valuation method does not successfully capture. At the end of the day, it’s the prerogative of the portfolio owners who carry on the accountabilities to steer the portfolio.
The portfolio manager has a responsibility to be prepared for reconciling the said steering with the unchanged available resource capacity for project work. What comes off the list of projects to continue or initiate? Or, will we outsource capacity if we must meet irreconcilable demand? The next slide will show how Info-Tech’s tool helps you with this process.
Info-Tech Best Practice
Strive to become the best co-pilot. Constantly iterate on the scoring criteria to better adapt to the portfolio owners’ preference in steering the project portfolio.
Manipulate the prioritized list with the Force Disposition list
2.3.5 Project Intake and Prioritization Tool, Tab 5: Results
The Force Disposition list enables you to inject subjective judgment in project prioritization. Force include and outsource override project prioritization scores and include the projects for approval:
- Force include counts the project demand against capacity.
- Outsource, on the other hand, does not count the project demand.
- Force exclude removes a project from prioritized list altogether, without deleting the row and losing its data.
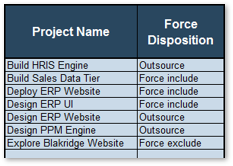
Choose a project name and a disposition using a drop-down.
Use this list to test out various scenarios, useful for what-if analysis.
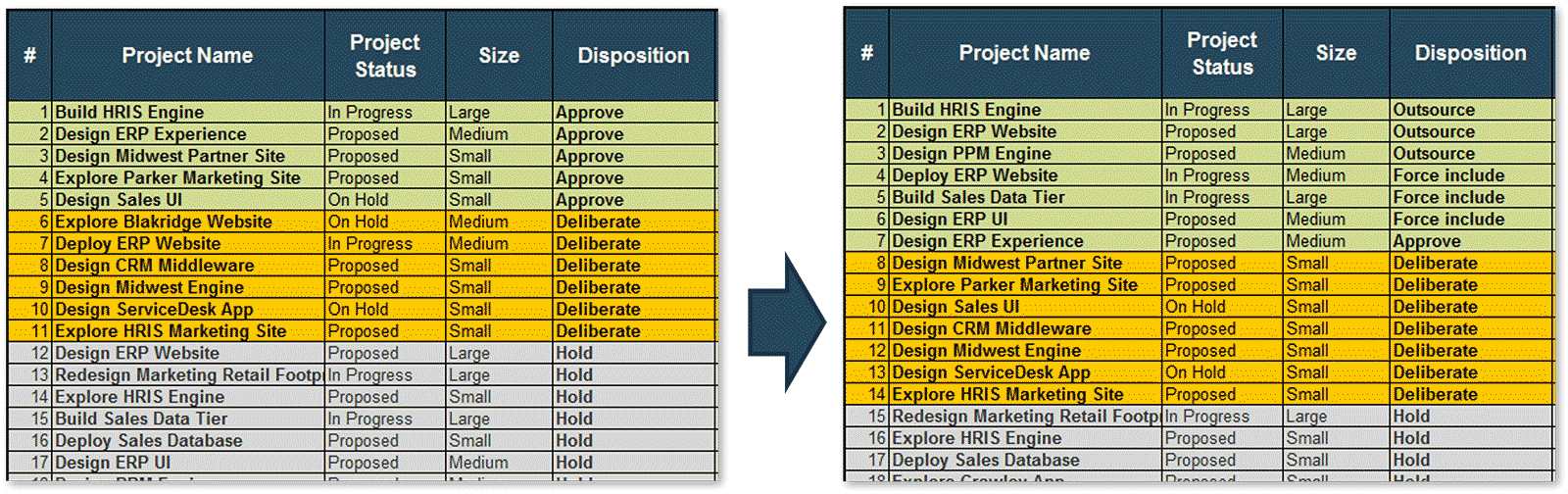
Document your process to formally make disposition recommendations to appropriate decision-making party
2.3.5 Estimated Time: 60 minutes
Review and customize section 4.3, “Approve projects for initiation or continuation” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
The goal of this activity is to formalize the process of presenting the prioritized list of projects for review, modify the list based on steering decisions, and obtain the portfolio owners’ approval for projects to initiate or continue, hold, or terminate. Consider the following factors:
- Existing final approval process: what are the new injections to the current decision-making process for final approval?
- Meeting prep, agenda, and follow-up: what are the activities that must be carried out by PMO / portfolio manager to support the portfolio decision makers and obtain final approval?
- “Deliberate” projects: what additional information should portfolio owners be presented with, in order to deliberate on the projects at risk of being not properly resourced? For example, consider a value-execution plot (right).
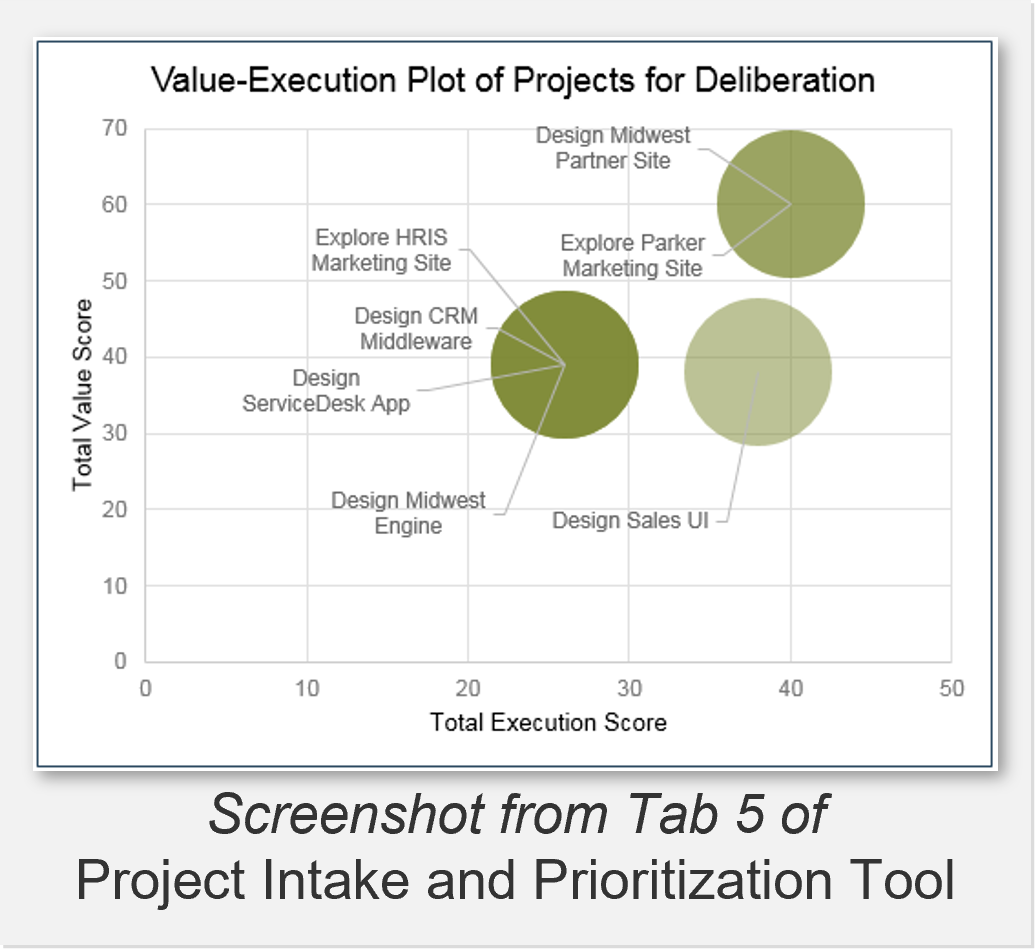
INPUT
- Approval process steps (Activity 2.2.2)
- Steering Committee process documentation
OUTPUT
- Activities for supporting the decision-making body
Materials
- SOP Template
- Project Intake and Prioritization Tool
Participants
- CIO
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
Once a project is approved, pass that which is known on to those responsible for downstream processes
Aim to be responsible stewards of important and costly information developed throughout project intake, approval, and prioritization processes.
Once the proposed project is given a green light, the project enters an initiation phase.
No matter what project management methodology is employed, it is absolutely vital to pass on the knowledge gained and insights developed through the intake, approval, and prioritization processes. This ensures that the project managers and team are informed of the project’s purpose, business benefits, rationale for the project approval, etc. and be able to focus their efforts in realizing the project’s business goals.
Recognize that this does not aim to create any new artifacts. It is simply a procedural safeguard against the loss of important and costly information assets for your organization.
Information from the intake process directly feeds into, for example, developing a project charter.
Source: PMBOK, 6th edition
"If the project manager can connect strategy to the project they are leading (and therefore the value that the organization desires by sanctioning the project), they can ensure that the project is appropriately planned and managed to realize those benefits."
– Randall T. Black, P.Eng., PMP; source: PMI Today
Examine the new project intake workflow as a whole and document it in a flow chart
2.3.6 Estimated Time: 30-60 minutes
Review and customize section 4.1, “Project Prioritization Workflow” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template.
In Step 1.2 of the blueprint, you mapped out the current project intake, approval, and prioritization workflow and documented it in a flow chart. In this step, take the time to examine the new project intake process as a whole, and document the new workflow in the form of a flow chart.
- Collect and update supply and demand data
- Prioritize project demand by value
- Approve projects for initiation or continuation
- Manage a realistically defined project portfolio
Consider the following points:
- Are the inputs and outputs of each step clear? Who’s doing the work? How long will each step take, on average?
- Is the ownership of each step clear? How will we ensure a smooth handoff between each step and prevent requests from falling through the cracks?
INPUT
- New process steps for project prioritization (Activities 2.3.x-y)
OUTPUT
- Flowchart representation of new project prioritization workflow
Materials
- Microsoft Visio, flowchart software, or Microsoft PowerPoint
Participants
- CIO
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
Leverage Info-Tech’s other blueprints to complement your project prioritization processes
|
The project capacity estimates overlook a critical piece of the resourcing puzzle for the sake of simplicity: skills. You need the right skills at the right time for the right project. Use Info-Tech’s Balance Supply and Demand with Realistic Resource Management Practices blueprint to enhance the quality of information on your project supply. 
|
There is more to organizing your project portfolio than a strict prioritization by project value. For example, as with a financial investment portfolio, project portfolio must achieve the right investment mix to balance your risks and leverage opportunities. Use Info-Tech’s Maintain an Organized Portfolio blueprint to refine the makeup of your project portfolio. 
|
|
Continuous prioritization of projects allow organizations to achieve portfolio responsiveness. Use Info-Tech’s Manage an Agile Portfolio blueprint to take prioritization of your project portfolio to the next level. 
|
46% of organizations use a homegrown PPM solution. Info-Tech’s Grow Your Own PPM Solution blueprint debuts a spreadsheet-based Portfolio Manager tool that provides key functionalities that integrates those of the Intake and Prioritization Tool with resource management, allocation and portfolio reporting capabilities. 
|
If you want additional support, have our analysts guide you through this phase as part of an Info-Tech workshop
Book a workshop with our Info-Tech analysts:

- To accelerate this project, engage your IT team in an Info-Tech workshop with an Info-Tech analyst team.
- Info-Tech analysts will join you and your team onsite at your location or welcome you to Info-Tech’s historic Toronto office to participate in an innovative onsite workshop.
- Contact your account manager (www.infotech.com/account), or email Workshops@InfoTech.com for more information.
The following are sample activities that will be conducted by Info-Tech analysts with your team:
2.1.2-6
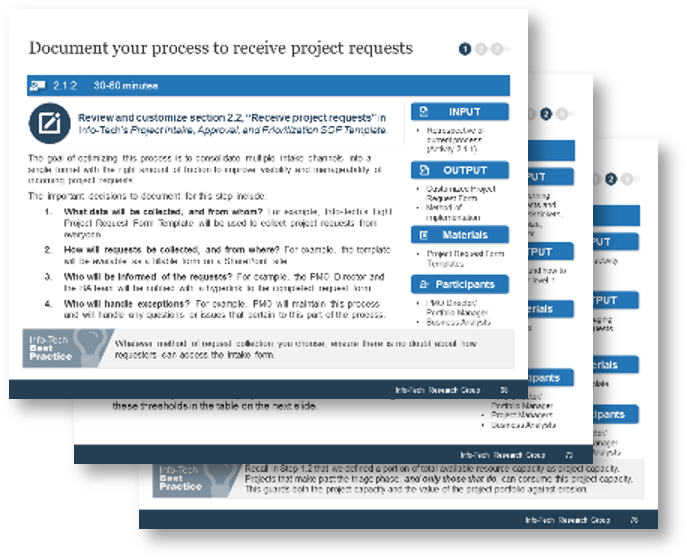
Optimize your process to receive, triage, and follow up on project requests
Discussion on decision points and topics of consideration will be facilitated to leverage the diverse viewpoints amongst the workshop participants.
2.3.2-5

Set up a capacity-informed project prioritization process using Info-Tech’s Project Intake and Prioritization Tool
A table-top planning exercise helps you visualize the current process in place and identify opportunities for optimization.
Phase 3
Integrate the New Optimized Processes into Practice
Phase 3 outline
Call 1-888-670-8889 or email GuidedImplementations@InfoTech.com for more information.
Complete these steps on your own, or call us to complete a guided implementation. A guided implementation is a series of 2-3 advisory calls that help you execute each phase of a project. They are included in most advisory memberships.
Guided Implementation 3: Integrate the New Optimized Processes into Practice Proposed Time to Completion: 6-12 weeks | |
Step 3.1: Pilot your process to refine it prior to rollout Start with an analyst kick-off call:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates:
| Step 3.2: Analyze the impact of organizational change Review findings with analyst:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates:
|
Phase 3 Results & Insights:
| |
Step 3.1: Pilot your intake, approval, and prioritization process to refine it before rollout
| PHASE 1 | PHASE 2 | PHASE 3 | ||||
1.1 Define project valuation criteria | 1.2 Envision process target state | 2.1 Streamline intake | 2.2 Right-size approval steps | 2.3 Prioritize projects to fit resource capacity | 3.1 Pilot your optimized process | 3.2 Communicate organizational change |
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Select receptive managers to work with during your pilot
- Define the scope of your pilot and determine logistics
- Plan to obtain feedback, document lessons learned, and create an action plan for any changes
- Finalize Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP
This step involves the following participants:
- PMO Director / Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
Outcomes of this step
- A pilot team
- A process pilot plan that defines the scope, logistics, and process for retrospection
- Project Backlog Manager job description
- Finalized Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP for rollout
Pilot your new processes to test feasibility and address issues before a full deployment
Adopting the right set of practices requires a significant degree of change that necessitates buy-in from varied stakeholders throughout IT and the business.
Rome wasn’t built in a day. Similarly, benefits of optimized project intake, approval, and prioritization process will not be realized overnight.
Resist the urge to deploy a big-bang roll out of your new intake practices. The approach is ill advised for two main reasons:
- It will put more of a strain on the implementation team in the near term, with a larger pool of end users to train and collect data from.
- Putting untested practices in a department-wide spotlight could lead to mass confusion in the near-term and color the new processes in a negative light, leading to a loss of stakeholder trust and engagement right out-of-the-gate.
Start with a pilot phase. Identify receptive lines of business and IT resources to work with, and leverage their insights to help iron out the kinks in your process before unveiling your practices to IT and all business users at large.
This step will help you to:
- Plan and execute a pilot of the processes we developed in Phase 2.
- Incorporate the lessons learned from that pilot to strengthen your SOP and ease the communication process.
Info-Tech Insight
Engagement paves the way for smoother adoption. An “engagement” approach (rather than simply “communication”) turns stakeholders into advocates who can help boost your message, sustain the change, and realize benefits without constant intervention or process command-and-control.
Plan your pilot like you would any project to ensure it’s well defined and its goals are clearly articulated
Use Info-Tech’s Intake Process Pilot Plan Template to help define the scope of your pilot and set appropriate goals for the test-run of your new processes.
A process pilot is a limited scope of an implementation (constrained by time and resources involved) in order to test the viability and effectiveness of the process as it has been designed.
- Investing time and energy into a pilot phase can help to lower implementation risk, enhance the details and steps within a process, and improve stakeholder relations prior to a full scale rollout.
- More than a dry run, however, a pilot should be approached strategically, and planned out to limit the scope of it and achieve specific outcomes.
- Leverage a planning document to ensure your process pilot is grounded in a common set of definitions, that the pilot is delivering value and insight, and that ultimately the pilot can serve as a starting point for a full-scale process implementation.
Download Info-Tech’s Process Pilot Plan Template

"The advantages to a pilot are several. First, risk is constrained. Pilots are closely monitored so if a problem does occur, it can be fixed immediately. Second, the people working in the pilot can become trainers as you roll the process out to the rest of the organization. Third, the pilot is another opportunity for skeptics to visit the pilot process and learn from those working in it. There’s nothing like seeing a new process working for people to change their minds."
Select receptive stakeholders to work with during your pilot
3.1.1 Estimated Time: 20-60 minutes
Info-Tech recommends selecting PPM stakeholders who are aware of your role and some of the challenges in project intake, approval, and prioritization to assist in the implementation process.
- If receptive PPM stakeholders are known, schedule a 15-minute meeting with them to inquire if they would be willing to be part of the pilot process.
- If receptive project managers are not known, use Info-Tech’s Stakeholder Engagement Workbook to conduct a formal selection process.
- Enter a list of potential participants for pilot in tab 3.
- Rate project managers in terms of influence, pilot interest, and potential deployment contribution within tab 4.
- Review tab 5 in the workbook. Receptive PPM stakeholders will appear in the top quadrants. Ideal PPM stakeholders for the pilot are located in the top right quadrant of the graph.
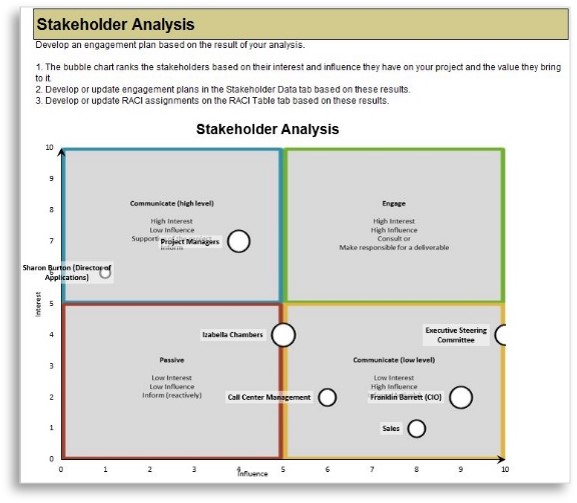
INPUT
- Project portfolio management stakeholders (Activity 1.2.3)
OUTPUT
- Pilot project team
Materials
- Stakeholder Engagement Workbook
- Process Pilot Plan Template
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- CIO (optional)
Document the PPM stakeholders involved in your pilot in Section 3 of Info-Tech’s Process Pilot Plan Template.
Define the scope of your pilot and determine logistics
3.1.2 Estimated Time: 60-90 minutes
Use Info-Tech’s Process Pilot Plan Template to design the details of your pilot.
Investing time into planning your pilot phase strategically will ensure a clear scope, better communications for those piloting the processes, and – overall – better, more actionable results for the pilot phase. The Pilot Plan Template is broken into five sections to assist in these goals:
- Pilot Overview and Scope
- Success and Risk Factors
- Stakeholders Involved and Communications Plan
- Pilot Retrospective and Feedback Protocol
The duration of your pilot should go at least one prioritization period, e.g. one to two quarters.
Estimates of time commitments should be captured for each stakeholder. During the retrospective at the end of the pilot you should capture actuals to help determine the time-cost of the process itself and measure its sustainability.
Once the Plan Template is completed, schedule time to share and communicate it with the pilot team and executive sponsors of the process.
While you should invest time in this planning document, continue to lean on the Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP throughout the pilot phase.
INPUT
- Sections 1 through 4 of the Process Pilot Plan Template
OUTPUT
- A process pilot plan
Materials
- Process Pilot Plan Template
Participants
- PMO Director / Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- CIO (optional)
Execute your pilot and prepare to make process revisions before the full rollout
Hit play! Begin the process pilot and get familiar with the work routine and resource management solution.
Some things to keep in mind during the pilot include:
- Depending on the solution you are using, you will likely need to spend one day or less to populate the tool. During the pilot, measure the time and effort required to manage the data within the tool. Determine whether time and effort required is viable on an ongoing basis (i.e. can you do it every month or quarter) and has value.
- Meet with the pilot team and other stakeholders regularly during the pilot, at least biweekly. Allow the team (and yourself) to speak honestly and openly about what isn’t working. The pilot is your chance to make things better.
- Keep notes about what will need to change in the SOP. For major changes, you may have to tweak the process during the pilot itself. Update the process documents as needed and communicate the changes and why they’re being made. If required, update the scope of the pilot in the Pilot Plan Template.

Obtain feedback from the pilot group to improve your processes before a wider rollout
3.1.3 Estimated Time: 30 minutes
Pilot projects allow you to validate your assumptions and leverage lessons learned. During the planning of the pilot, you should have scheduled a retrospective meeting with the pilot team to formally assess strengths and weaknesses in the process you have drafted.
- Schedule the retrospective shortly after the pilot is completed. Info-Tech recommends performing a Stop/Start/Continue meeting with pilot participants to obtain and capture feedback.
- Have members of the meeting record any processes/activities on sticky notes that should:
- Stop: because they are ineffective or not useful
- Start: because they would be useful for the tool and have not been incorporated into current processes
- Continue: because they are useful and positively contribute to intended process outcomes.
An example of how to structure a Stop/Start/Continue activity on a whiteboard using sticky notes.
INPUT
- What’s working and what isn’t in the process
OUTPUT
- Ideas to improve process
Materials
- Whiteboard
- Sticky notes
- Process Pilot Plan Template
Participants
- Process owner (PMO director or portfolio owner)
- Pilot team
See the following slide for additional instructions.
Document lessons learned and create an action plan for any changes to the processes
3.1.4 Estimated Time: 30 minutes

As a group, discuss everyone’s responses and organize according to top priority (mark with a 1) and lower priority/next steps (mark with a 2). At this point, you can also remove any sticky notes that are repetitive or no longer relevant.
Once you have organized based on priority, be sure to come to a consensus with the group regarding which actions to take. For example, if the group agrees that they should “stop holding meetings weekly,” come to a consensus regarding how often meetings will be held, i.e. monthly.
| Priority | Action Required | Who is Responsible | Implementation Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stop: Holding meetings weekly | Hold meetings monthly | Jane Doe, PMO | Next Meeting: August 1, 2017 |
| Start: Discussing backlog during meetings | Ensure that backlog data is up to date for discussion on date of next meeting. | John Doe, Portfolio Manager | August 1, 2017 |
Create an action plan for the top priority items that require changes (the Stops and Starts). Record in this slide, or your preferred medium. Be sure to include who is responsible for the action and the date that it will be implemented.
Document the outcomes of the start/stop/continue and your action plan in Section 6 of Info-Tech’s Process Pilot Plan Template.
Use Info-Tech’s Backlog Manager Job Description Template to help fill any staffing needs around data maintenance
3.1 Project Backlog Manager Job Description
You will need to determine responsibilities and accountabilities for portfolio management functions within your team.
If you do not have a clearly identifiable portfolio manager at this time, you will need to clarify who will wear which hats in terms of facilitating intake and prioritization, high-level capacity awareness, and portfolio reporting.
- Use Info-Tech’s Project Backlog Manager job description template to help clarify some of the required responsibilities to support your intake, approval, and prioritization strategy.
- If you need to bring in an additional staff member to help support the strategy, you can customize the job description template to help advertise the position. Simply edit the text in grey within the template.
- If you have other PPM tasks that you need to define responsibilities for, you can use the RASCI chart on the final tab of the PPM Strategy Development Tool.
Download Info-Tech’s Project Backlog Manager job description template.

Finalize the Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP and prepare to communicate your processes
Once you’ve completed the pilot process and made the necessary tweaks, you should finalize your Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP and prepare to communicate it.
Update section 1.2, “Overall Process Workflow” in Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP Template with the new process flow.
Revisit your SOP from Phase 2 and ensure it has been updated to reflect the process changes that were identified in activity 3.1.4.
- If during the pilot process the data was too difficult or time consuming to maintain, revisit the dimensions you have chosen and choose dimensions that are easier to accurately maintain. Tweak your process steps in the SOP accordingly.
- In the long term, if you are not observing any progress toward achieving your success criteria, revisit the impact analysis that we’ll prepare in step 3.2 and address some of these inhibitors to organizational change.
Download Info-Tech’s Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization SOP template.

Info-Tech Best Practice
Make your SOP high impact. SOPs are often at risk of being left unmaintained and languishing in disuse. Improve the SOP’s succinctness and usability by making it visual; consult Info-Tech’s blueprint, Create Visual SOP Documents that Drive Process Optimization, Not Just Peace of Mind.
Step 3.2: Analyze the impact of organizational change through the eyes of PPM stakeholders to gain their buy-in
| PHASE 1 | PHASE 2 | PHASE 3 | ||||
1.1 Define project valuation criteria | 1.2 Envision process target state | 2.1 Streamline intake | 2.2 Right-size approval steps | 2.3 Prioritize projects to fit resource capacity | 3.1 Pilot your optimized process | 3.2 Communicate organizational change |
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Analyze the stakeholder impact and responses to impending organizational change
- Create message canvases for at-risk change impacts and stakeholders
- Set the course of action for communicating changes to your stakeholders
This step involves the following participants:
- PMO Director / Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
Outcomes of this step
- A thorough organizational change impact analysis, based on Info-Tech’s expertise in organizational change management
- Message canvases and communication plan for your stakeholders
- Go-live for the new intake, approval, and prioritization process
Manage key PPM stakeholders and communicate changes
- Business units: Projects are undertaken to provide value to the business. Senior management from business units must help define how project will be valued.
- IT: IT must ensure that technical/practical considerations are taken into account when determining project value.
- Finance: The CFO or designated representative will ensure that estimated project costs and benefits can be used to manage the budget.
- PMO: PMO is the administrator of the project portfolio. PMO must provide coordination and support to ensure the process operates smoothly and its goals are realized.
- Business analysts: BAs carry out the evaluation of project value. Therefore, their understanding of the evaluation criteria and the process as a whole are critical to the success of the process.
- Project sponsors: Project sponsors are accountable for the realization of benefits for which projects are undertaken.
Impacts will be felt differently by different stakeholders and stakeholder groups
As you assess change impacts, keep in mind that no impact will be felt the same across the organization. Depth of impact can vary depending on the frequency (will the impact be felt daily, weekly, monthly?), the actions necessitated by it (e.g. will it change the way the job is done or is it simply a minor process tweak?), and the anticipated response of the stakeholder (support, resistance, indifference?).
Use the Organizational Change Depth Scale below to help visualize various depths of impact. The deeper the impact, the tougher the job of managing change will be.
| Procedural | Behavioral | Interpersonal | Vocational | Cultural |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Procedural change involves changes to explicit procedures, rules, policies, processes, etc. | Behavioral change is similar to procedural change, but goes deeper to involve the changing tacit or unconscious habits. | Interpersonal change goes beyond behavioral change to involve changing relationships, teams, locations, reporting structures, and other social interactions. | Vocational change requires acquiring new knowledge and skills, and accepting the loss or decline in the value or relevance of previously acquired knowledge and skills. | Cultural change goes beyond interpersonal and vocational change to involve changing personal values, social norms, and assumptions about the meaning of good vs. bad or right vs. wrong. |
| Example: providing sales reps with mobile access to the CRM application to let them update records from the field. | Example: requiring sales reps to use tablets equipped with a custom mobile application for placing orders from the field. | Example: migrating sales reps to work 100% remotely. | Example: migrating technical support staff to field service and sales support roles. | Example: changing the operating model to a more service-based value proposition or focus. |
Perform a change impact analysis to maximize the chances of adoption for the new intake process
Invest time and effort to analyze the impact of change to create an actionable stakeholder communication plan that yields the desirable result: adoption.
Info-Tech’s Drive Organizational Change from the PMO blueprint offers the OCM Impact Analysis Tool to helps document the change impact across multiple dimensions, enabling the project team to review the analysis with others to ensure that the most important impacts are captured.
This tool has been customized for optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization process to deliver the same result in a more streamlined way. The next several slides will take you through the activities to ultimately create an OCM message canvas and a communication plan for your key stakeholders.
Download Info-Tech’s Intake and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool.
"As a general principle, project teams should always treat every stakeholder initially as a recipient of change. Every stakeholder management plan should have, as an end goal, to change recipients’ habits or behaviors."
-PMI, 2015
Set up the Intake Process and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool
3.2.1 Intake and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool, Tab 2-3
In Tab 2, enter your stakeholders’ names. Represent stakeholders as a group if you expect the impact of change on them to be reasonably uniform, as well as their anticipated responses. Otherwise, consider adding them as individuals or subgroups.
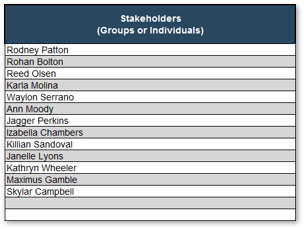
In Tab 3, enter whether you agree or disagree with each statement that represents an element of organizational change that be introduced as the newly optimized intake process is implemented.
As a result of the change initiative in question:

Analyze the impact and the anticipated stakeholder responses of each change
3.2.1 Intake and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool, Tab 4: Impact Analysis Inputs
Each change statement that you agreed with in Tab 3 are listed here in Tab 4 of the Intake and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool. For each stakeholder, estimate and enter the following data:
- Frequency of the Impact: how often will the impact of the change be felt?
- Effort Associated with Impact: what is the demand on a stakeholder’s effort to implement the change?
- Anticipated Response: rate from enthusiastic response to active subversion. Honest and realistic estimates of anticipated responses are critical to the rest of the impact analysis.
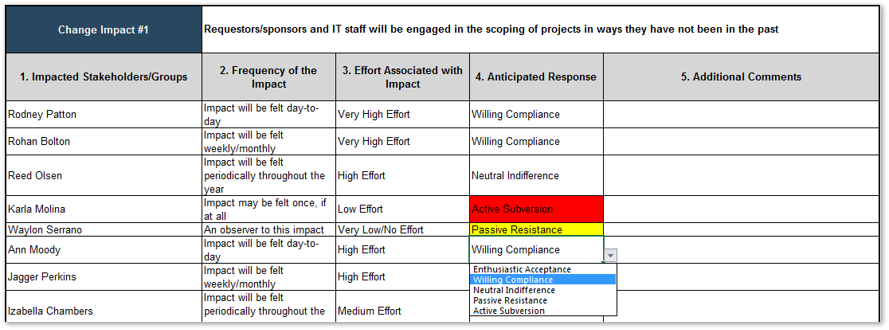
Analyze the stakeholder impact and responses to impending organizational change as a group
3.2.1 Estimated Time: 60-90 minutes
Divide and conquer. Leverage the group to get through the seemingly daunting amount of work involved with impact analysis.
- Divide the activity participants into subgroups and assign a section of the impact analysis. It may be helpful to do one section together as a group to make sure everyone is roughly on the same page for assessing impact.
Suggested ways to divide up the impact analysis include:
- By change impact. This would be suitable when the process owners (or would-be process owners) are available and participating.
- By stakeholders. This would be suitable for large organizations where the activity participants know some stakeholders better than others.
Tip: use a spreadsheet tool that supports multi-user editing (e.g. Google Sheets, Excel Online).
INPUT
- Organizational and stakeholder knowledge
- Optimized intake process
OUTPUT
- Estimates of stakeholder-specific impact and response
Materials
- Intake and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
Info-Tech Insight
Beware of bias. Groups are just as susceptible to producing overly optimistic or pessimistic analysis as individuals, just in different ways. Unrealistic change impact analysis will compromise your chances of arriving at a reasonable, tactful stakeholder communication plan.
Examine your impact analysis report
3.2.2 Intake and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool, Tab 5: Impact Analysis Outputs
These outputs are based on the impacts you analyzed in Tab 4 of the tool (Activity 3.2.1). They are organized in seven sections:
- Top Five Highest Risk Impacts, based on the frequency and effort inputs across all impacts.
- Overall Process Adoption Rating (top right), showing the overall difficulty of this change given likelihood/risk that the stakeholders involved will absorb the anticipated change impacts.
- Top Five Most Impacted Stakeholders, based on the frequency and effort inputs across all impacts.
- Top Five Process Supporters and;
- Top Five Process Resistors, based on the anticipated response inputs across all impacts.
- Impact Register (bottom right): this list breaks down each change’s likelihood of adoption.
- Potential Impacts to Watch Out For: this list compiles all of the "Don't Know" responses from Tab 3.

Tailor messages for at-risk change impacts and stakeholders with Info-Tech’s Message Canvas
3.2.2 Intake and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool, Tab 6: Message Canvas
Use Info-Tech’s Message Canvas on this tab to help rationalize and elaborate the change vision for each group.
Elements of a Message Canvas
- Why is there a need for this process change?
- What will be new for this audience?
- What will go away for this audience?
- What will be meaningfully unchanged for this audience?
- How will this change benefit this audience?
- When and how will the benefits be realized for this audience?
- What does this audience have to do for this change to succeed?
- What does this audience have to stop doing for this change to succeed?
- What should this audience continue doing?
- What support will this audience receive to help manage the transition?
- What should this audience expect to do/happen next?
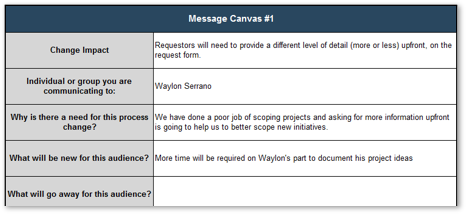
Info-Tech Insight
Change thy language, change thyself.
Jargon, acronyms, and technical terms represent deeply entrenched cultural habits and assumptions.
Continuing to use jargon or acronyms after a transition tends to drag people back to old ways of thinking and working.
You don’t need to invent a new batch of buzzwords for every change (nor should you), but every change is an opportunity to listen for words and phrases that have lost their meaning through overuse and abuse.
Create message canvases for at-risk change impacts and stakeholders as a group
3.2.2 Estimated Time: 90-120 minutes
- Decide on the number of message canvases to complete. This will be based on the number of at-risk change impacts and stakeholders.
- Divide the activity participants into subgroups and assign a section of the message canvas. It may be helpful to do one section together as a group to make sure everyone is roughly on the same page for assessing impact.
- Aggregate the completed work and benchmark the message canvases amongst subgroups.
Remember these guidelines to help your messages resonate:
- People are busy and easily distracted. Tell people what they really need to know first, before you lose their attention.
- Repetition is good. Remember the Aristotelian triptych: “Tell them what you’re going to tell them, then tell them, then tell them what you told them.”
- Don’t use technical terms, jargon, or acronyms. Different groups in organizations tend to develop specialized vocabularies. Everybody grows so accustomed to using acronyms and jargon every day that it becomes difficult to notice how strange it sounds to outsiders. This is especially important when IT communicates with non-technical audiences. Don’t alienate your audience by talking at them in a strange language.
- Test your message. Run focus groups or deliver communications to a test audience (which could be as simple as asking 2–3 people to read a draft) before delivering messages more broadly.
– Info-Tech Blueprint, Drive Organizational Change from the PMO
INPUT
- Impact Analysis Outputs
- Organizational and stakeholder knowledge
OUTPUT
- Estimates of stakeholder-specific impact and response
Materials
- Intake and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
Distill the message canvases into a comprehensive communication plan
3.2.3 Intake and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool, Tab 7: Communication Plan
The communication plan creates an action plan around the message canvases to coordinate the responsibilities of delivering them, so the risks of “dropping the ball” on your stakeholders are minimized.
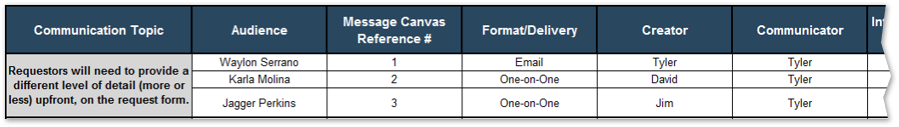
1. Choose a change impact from a drop-down menu.
2. Choose an intended audience...
… and the message canvas to reference.
3. Choose the method of delivery. It will influence how to craft the message for the stakeholder.
4. Indicate who is responsible for creating and communicating the message.
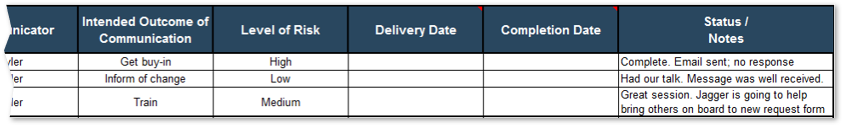
5. Briefly indicate goal of the communication and the likelihood of success.
6. Record the dates to plan and track the communications that take place.
Set the course of action for communicating changes to your stakeholders
3.2.2 Estimated Time: 90-120 minutes
- Divide the activity participants into subgroups and assign communication topics to each group. There should be one communication topic for each change impact. Based on the message canvas, create a communication plan draft.
- Aggregate the completed work and benchmark the communication topic amongst subgroups.
- Share the finished communication plan with the rest of the working group. Do not share this file widely, but keep it private within the group.
Identify critical points in the change curve:
- Honeymoon of “Uninformed Optimism”: There is usually tentative support and even enthusiasm for change before people have really felt or understood what it involves.
- Backlash of “Informed Pessimism” (leading to “Valley of Despair”): As change approaches or begins, people realize they’ve overestimated the benefits (or the speed at which benefits will be achieved) and underestimated the difficulty of change.
- Valley of Despair and beginning of “Hopeful Realism”: Eventually, sentiment bottoms out and people begin to accept the difficulty (or inevitability) of change.
- Bounce of “Informed Optimism”: People become more optimistic and supportive when they begin to see bright spots and early successes.
- Contentment of “Completion”: Change has been successfully adopted and benefits are being realized.
Based on Don Kelley and Daryl Conner’s Emotional Cycle of Change.
INPUT
- Change impact analysis results
- Message canvases
- List of stakeholders
OUTPUT
- Communication Plan
Materials
- Intake and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool
Participants
- PMO Director/ Portfolio Manager
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
Roll out the optimized intake, approval, and prioritization process, and continually monitor adoption and success
As you implement your new project intake process, familiarize yourself with common barriers and challenges.
There will be challenges to watch for in evaluating the effectiveness of your intake processes. These may include circumvention of process by key stakeholders, re-emergence of off-the-grid projects and low-value initiatives.
As a quick and easy way to periodically assess your processes, consider the following questions:
- Are you confident that all work in progress is being tracked via the project list?
- Are your resources all currently working on high-value initiatives?
- Since optimizing, have you been able to deliver (or are you on target to deliver) all that has been approved, with no initiatives in states of suspended animation for long periods of time?
- Thanks to sufficient portfolio visibility and transparency into your capacity, have you been able to successfully decline requests that did not add value or that did not align with resourcing?
If you answer “no” to any of these questions after a sufficient post-implementation period (approximately six to nine months, depending on the scope of your optimizing), you may need to tweak certain aspects of your processes or seek to align your optimization with a lower capability level in the short term.
Small IT department struggles to optimize intake and to communicate new processes to stakeholders
CASE STUDY
Industry: Government
Source: Info-Tech Client
Challenge
There is an IT department for a large municipal government. Possessing a relatively low level of PPM maturity, IT is in the process of establishing more formal intake practices in order to better track, and respond to, project requests. New processes include a minimalist request form (sent via email) coupled with more thorough follow-up from BAs and PMs to determine business value, ROI, and timeframes.
Solution
Even with new user-friendly processes in place, IT struggles to get stakeholders to adopt, especially with smaller initiatives. These smaller requests frequently continue to come in outside of the formal process and, because of this, are often executed outside of portfolio oversight. Without good, reliable data around where staff time is spent, IT lacks the authority to decline new requests.
Results
IT is seeking further optimization through better communication. They are enforcing discipline on stakeholders and reiterating that all initiatives, regardless of size, need to be directed through the process. IT is also training its staff to be more critical. “Don’t just start working on an initiative because a stakeholder asks.” With staff being more critical and directing requests through the proper queues, IT is getting better at tracking and prioritizing requests.
"The biggest challenge when implementing the intake process was change management. We needed to shift our focus from responding to requests to strategically thinking about how requests should be managed. The intake process allows the IT Department to be transparent to customers and enables decision makers."
If you want additional support, have our analysts guide you through this phase as part of an Info-Tech workshop
Book a workshop with our Info-Tech analysts:

- To accelerate this project, engage your IT team in an Info-Tech workshop with an Info-Tech analyst team.
- Info-Tech analysts will join you and your team onsite at your location or welcome you to Info-Tech’s historic Toronto office to participate in an innovative onsite workshop.
- Contact your account manager (www.infotech.com/account), or email Workshops@InfoTech.com for more information.
The following are sample activities that will be conducted by Info-Tech analysts with your team:
3.1.1

Select receptive stakeholders to work with during your pilot
Identify the right team of supportive PPM stakeholders to carry out the process pilot. Strategies to recruit the right people outside the workshop will be discussed if appropriate.
3.2.1

Analyze the stakeholder impact and responses to impending organizational change
Carry out a thorough analysis of change impact in order to maximize the effectiveness of the communication strategy in support of the implementation of the optimized process.
Insight breakdown
Insight 1
- The overarching goal of optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization process is to maximize the throughput of the best projects. To achieve this goal, one must have a clear way to determine what are “the best” projects.
Insight 2
- Info-Tech’s methodology systemically fits the project portfolio into its triple constraint of stakeholder needs, strategic objectives, and resource capacity to effectively address the challenges of establishing organizational discipline for project intake.
Insight 3
- Engagement paves the way for smoother adoption. An “engagement” approach (rather than simply “communication”) turns stakeholders into advocates who can help boost your message, sustain the change, and realize benefits without constant intervention or process command-and-control.
Summary of accomplishment
Knowledge Gained
- Triple constraint model of project portfolio: stakeholder needs, strategic objectives, and resource capacity
- Benefits of optimizing project intake, approval, and prioritization for managing a well-behaved project portfolio
- Challenges of installing well-run project intake
- Importance of piloting the process and communicating impacts to stakeholders
Processes Optimized
- Project valuation process: scorecard, weights
- Project intake process: reception, triaging, follow-up
- Project approval process: steps, accountabilities, deliverables
- Project prioritization process: estimation of resource capacity for projects, project demand
- Communication for organizational change
Deliverables Completed
- Optimized Project Intake, Approval, and Prioritization Process
- Documentation of the optimized process in the form of a Standard Operating Procedure
- Project valuation criteria, developed with Project Value Scorecard Development Tool and implemented through the Project Intake and Prioritization Tool
- Standardized project request form with right-sized procedural friction
- Standard for project level classification, implemented through the Project Intake Classification Matrix
- Toolbox of deliverables for capturing information developed to inform decision makers for approval: Benefits Commitment Form, Technology Assessment Tool, Business Case Templates
- Process pilot plan
- Communication plan for organizational change, driven by a thorough analysis of change impacts on key stakeholders using the Intake and Prioritization Impact Analysis Tool
Research contributors and experts

Kiron D. Bondale, PMP, PMI - RMP
Senior Project Portfolio & Change Management Professional

Scot Ganshert, Portfolio Group Manager
Larimer County, CO

Garrett McDaniel, Business Analyst II – Information Technology
City of Boulder, CO

Joanne Pandya, IT Project Manager
New York Property Insurance Underwriters

Jim Tom, CIO
Public Health Ontario
Related Info-Tech research

Develop a Project Portfolio Management Strategy blueprint"


Balance Supply and Demand with Realistic Resource Management Practices

Maintain an Organized Portfolio


Establish the Benefits Realization Process


Tailor Project Management Processes to Fit Your Projects

Project Portfolio Management Diagnostic Program
The Project Portfolio Management Diagnostic Program is a low-effort, high-impact program designed to help project owners assess and improve their PPM practices. Gather and report on all aspects of your PPM environment to understand where you stand and how you can improve.
Bibliography
Boston Consulting Group. “Executive Sponsor Engagement: Top Driver of Project and Program Success.” PMI, 2014. Web.
Boston Consulting Group. “Winning Through Project Portfolio Management: the Practitioners’ Perspective.” PMI, 2015. Web.
Bradberry, Travis. “Why The 8-Hour workday Doesn’t Work.” Forbes, 7 Jun 2016. Web.
Cook, Scott. Playbook: Best Practices. Business Week
Cooper, Robert, G. “Effective Gating: Make product innovation more productive by using gates with teeth.” Stage-Gate International and Product Development Institute. March/April 2009. Web.
Epstein, Dan. “Project Initiation Process: Part Two.” PM World Journal. Vol. IV, Issue III. March 2015. Web.
Evans, Lisa. “The Exact Amount of Time You Should Work Every Day.” Fast Company, 15 Sep. 2014. Web.
Madison, Daniel. “The Five Implementation Options to Manage the Risk in a New Process.” BPMInstitute.org. n.d. Web.
Merkhofer, Lee. “Improve the Prioritization Process.” Priority Systems, n.d. Web.
Miller, David, and Mike Oliver. “Engaging Stakeholder for Project Success.” PMI, 2015. Web.
Mind Tools. “Kelley and Conner’s Emotional Cycle of Change.” Mind Tools, n.d. Web.
Mochal, Jeffrey and Thomas Mochal. Lessons in Project Management. Appress: September 2011. Page 6.
Newcomer, Eric. “Getting Decisions to Stick.” Standish Group PM2go, 20 Oct 2017. Web.
“PMI Today.” Newtown Square, PA: PMI, Oct 2017. Web.
Project Management Institute. “Standard for Portfolio Management, 3rd ed.” Newtown Square, PA: PMI, 2013.
Project Management Institute. “Pulse of the Profession 2017: Success Rates Rise.” PMI, 2017. Web.
Transparent Choice. “Criteria for Project Prioritization.” n.p., n.d. Web.
University of New Hampshire (UNH) Project Management Office. “University of New Hampshire IT Intake and Selection Process Map.” UNH, n.d. Web.
Ward, John. “Delivering Value from Information Systems and Technology Investments: Learning from Success.” Information Systems Research Centre. August 2006. Web.