Network Segmentation
- Many legacy networks were built for full connectivity and overlooked potential security ramifications.
- Malware, ransomware, and bad actors are proliferating. It is not a matter of if you will be compromised but how can the damage be minimized.
- Cyber insurance will detective control, not a preventative one. Prerequisite audits will look for appropriate segmentation.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Lateral movement amplifies damage. Contain movement within the network through segmentation.
- Good segmentation is a balance between security and manageability. If solutions are too complex, they won’t be updated or maintained.
- Network services and users change over time, so must your segmentation strategy. Networks are not static; your segmentation must maintain pace.
Impact and Result
- Create a common understanding of what is to be built, for whom, and why.
- Define what services will be offered and how they will be governed.
- Understand which assets that you already have can jump start the project.
Network Segmentation Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Network Segmentation Deck – A deck to help you minimize risk by controlling traffic flows within the network.
Map out appropriate network segmentation to minimize risk in your network.
- Network Segmentation Storyboard
Further reading
Network Segmentation
Protect your network by controlling the conversations within it.
Executive Summary
Info-Tech Insight
Lateral movement amplifies damage |
From a security perspective, bad actors often use the tactic of “land and expand.” Once a network is breached, if east/west or lateral movement is not restricted, an attacker can spread quickly within a network from a small compromise. |
|---|---|
Good segmentation is a balance between security and manageability |
The ease of management in a network is usually inversely proportional to the amount of segmentation in that network. Highly segmented networks have a lot of potential complications and management overhead. In practice, this often leads to administrators being confused or implementing shortcuts that circumvent the very security that was intended with the segmentation in the first place. |
Network services and users change over time, so must your segmentation strategy |
Network segmentation projects should not be viewed as singular or “one and done.” Services and users on a network are constantly evolving; the network segmentation strategy must adapt with these changes. Be sure to monitor and audit segmentation deployments and change or update them as required to maintain a proper risk posture. |
Executive Summary
Your Challenge |
Common Obstacles |
Info-Tech’s Approach |
|---|---|---|
Networks are meant to facilitate communication, and when devices on a network cannot communicate, it is generally seen as an issue. The simplest answer to this is to design flat, permissive networks. With the proliferation of malware, ransomware, and advanced persistent threats (ATPs) a flat or permissive network is an invitation for bad actors to deliver more damage at an increased pace. Cyber insurance may be viewed as a simpler mitigation than network reconfiguration or redesign, but this is not a preventative solution, and the audits done before policies are issued will flag flat networks as a concern. |
Network segmentation is not a “bolt on” fix. To properly implement a minimum viable product for segmentation you must, at a minimum:
Implementing appropriate segmentation often involves elements of (if not a full) network redesign. |
To ensure the best results in a timely fashion, Info-Tech recommends a methodology that consists of:
|
Info-Tech Insight
The aim of networking is communication, but unfettered communication can be a liability. Appropriate segmentation in networks, blocking communications where they are not required or desired, restricts lateral movement within the network, allowing for better risk mitigation and management.
Network segmentation
Compartmentalization of risk: Segmentation is the practice of compartmentalizing network traffic for the purposes of mitigating or reducing risk. Segmentation methodologies can generally be grouped into three broad categories: 1. Physical Segmentation The most common implementation of physical segmentation is to build parallel networks with separate hardware for each network segment. This is sometimes referred to as “air gapping.” 2. Static Virtual Segmentation Static virtual segmentation is the configuration practice of using technologies such as virtual LANs (VLANs) to assign ports or connections statically to a network segment. 3. Dynamic Virtual Segmentation Dynamic virtual segmentation assigns a connection to a network segment based on the device or user of the connection. This can be done through such means as software defined networking (SDN), 802.1x, or traffic inspection and profiling. |
Common triggers for network segmentation projects 1. Remediate Audit Findings Many security audits (potentially required for or affecting premiums of cyber insurance) will highlight the potential issues of non-segmented networks. 2. Protect Vulnerable Technology Assets Whether separating IT and OT or segmenting off IoT/IIoT devices, keeping vulnerable assets separated from potential attack vectors is good practice. 3. Minimize Potential for Lateral Movement Any organization that has experienced a cyber attack will realize the value in segmenting the network to slow a bad actor’s movement through technology assets. |
How do you execute on network segmentation?
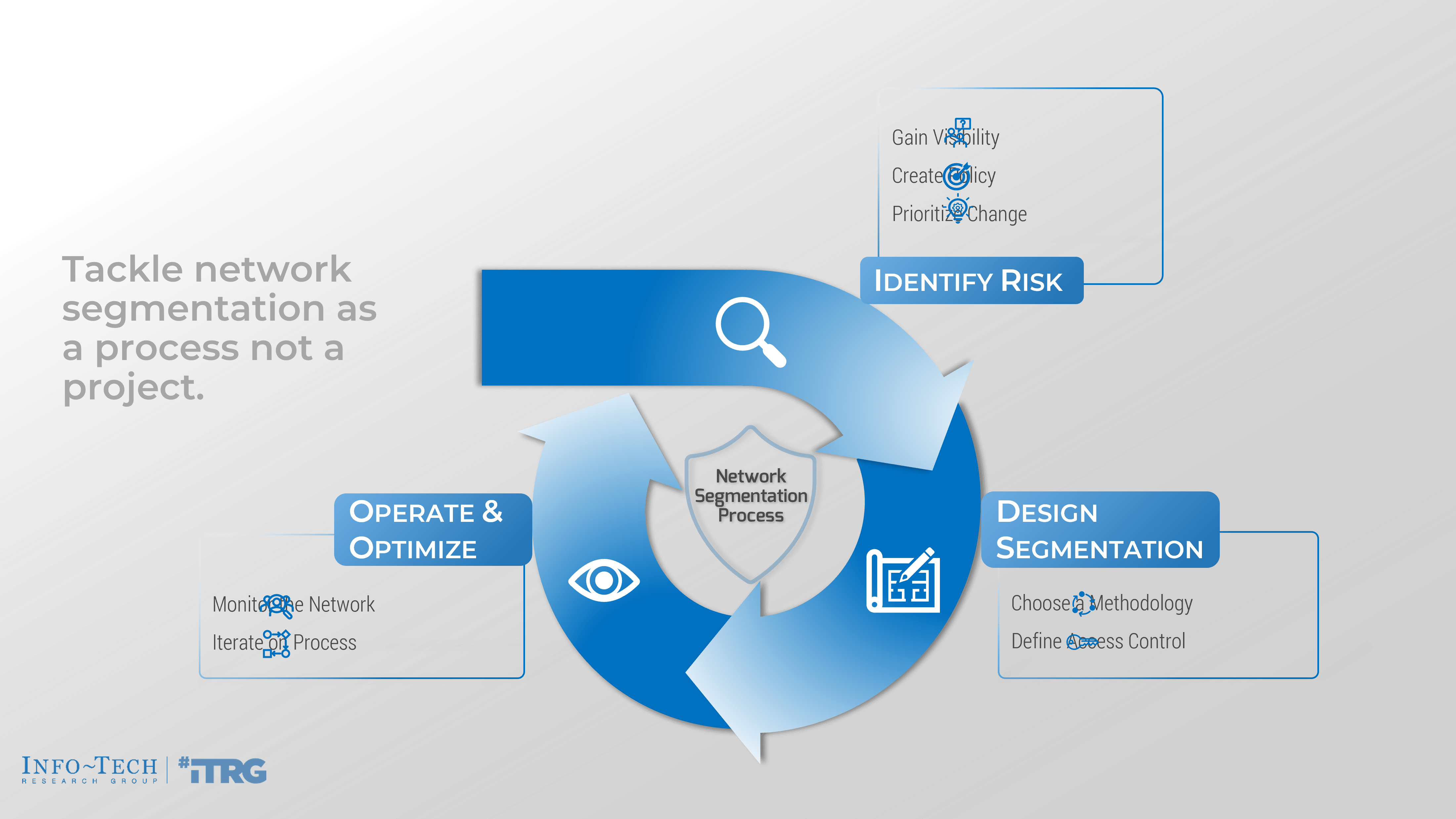
Identify risks by understanding access across the network
Gain visibility |
Create policy |
Prioritize change |
|
|---|---|---|---|
"Security, after all, is a risk business. As companies don't secure everything, everywhere, security resilience allows them to focus their security resources on the pieces of the business that add the most value to an organization, and ensure that value is protected." – Helen Patton, CISO, Cisco Security Business Group, qtd. In PR News, 2022 |
Discover the data flows within the network. This should include all users on the network and the environments they are required to access as well as access across environments. |
Examine the discovered flows and define how they should be treated. |
Change takes time. Use a risk assessment to prioritize changes within the network architecture. |
Understand the network space
A space is made up of both services and users. Before starting to consider segmentation solutions, define whether this exercise is aimed at addressing segmentation globally or at a local level. Not all use cases are global and many can be addressed locally. When examining a network space for potential segmentation we must include:
To keep the space a consumable size, both of these areas should be approached in the abstract. To abstract, users and services should be logically grouped and generalized. Groupings in the users and services categories may be different across organizations, but the common thread will be to contain the amount of groupings to a manageable size. |
Service Groupings
User Groupings
|
Info-Tech Insight
The more granular you are in the definition of the network space, the more granular you can be in your segmentation. The unfortunate corollary to this is that the difficulty of managing your end solution grows with the granularity of your segmentation.
Create appropriate policy
Understand which assets to protect and how. Context is key in your ability to create appropriate policy. Building on the definition of the network space that has been created, context in the form of the appropriateness of communications across the space and the vulnerabilities of items within the space can be layered on. To decide where and how segmentation might be appropriate, we must first examine the needs of communication on the network and their associated risk. Once defined, we can assess how permissive or restrictive we should be with that communication. The minimum viable product for this exercise is to define the communication channel possibilities, then designate each possibility as one of the following:
|
Appropriate Communications
Potential Vulnerabilities
|
Prioritize the potential segmentation
Use risk as a guide to prioritize segmentation. For most organizations, the primary reason for network segmentation is to improve security posture. It follows that the prioritization of initiatives and/or projects to implement segmentation should be based on risk. When examining risk, an organization needs to consider both:
The assets or users that are associated with risk levels higher than the tolerance of the organization should be prioritized to be addressed. |
Service Risks
User Risks
|
Info-Tech Insight
Be sure to keep this exercise relative so that a clear ranking occurs. If it turns out that everything is a priority, then nothing is a priority. When ranking things relative to others in the exercise, we ensure clear “winners” and “losers.”
Assess risk and prioritize action
1-3 hours
- Define a list of users and services that define the network space to be addressed. If the lists are too long, use an exercise like affinity diagramming to appropriately group them into a smaller subset.
- Create a matrix from the lists (put users and services along the rows and columns). In the intersecting points, label how the traffic should be treated (e.g. Permissive, Restricted, Rejected).
- Examine the matrix and assess the intersections for risk using the lens of impact and likelihood of an adverse event. Label the intersections for risk level with one of green (low impact/likelihood), yellow (medium impact/likelihood), or red (high impact/likelihood).
- Find commonalities within the medium/high areas and list the users or services as priorities to be addressed.
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
|
|
| Materials | Participants |
OR
|
|
Design segmentation
Segmentation comes in many flavors; decide which is right for the specific circumstance.
Methodology |
Access control |
|
|---|---|---|
"Learning to choose is hard. Learning to choose well is harder. And learning to choose well in a world of unlimited possibilities is harder still, perhaps too hard." ― Barry Schwartz, The Paradox of Choice: Why More Is Less |
What is the best method to segment the particular user group, service, or environment in question? |
How can data or user access move safely and securely between network segments? |
Decide on which methods work for your circumstances
You always have options…
There are multiple lenses to look through when making the decision of what the correct segmentation method might be for any given user group or service. A potential subset could include:
- Effort to deploy
- Cost of the solution
- Skills required to operate
- Granularity of the segmentation
- Adaptability of the solution
- Level of automation in the solution
Info-Tech Insight
Network segmentation within an organization is rarely a one-size-fits-all proposition. Be sure to look at each situation that has been identified to need segmentation and align it with an appropriate solution. The overall number of solutions deployed has to maintain a balance between that appropriateness and the effort to manage multiple environments.
Framework to examine segmentation methods
To assess we need to understand.
To assess when technologies or methodologies are appropriate for a segmentation use case, we need to understand what those options are. We will be examining potential segmentation methods and concepts within the following framework:
WHAT
A description of the segmentation technology, method, or concept.
WHY
Why would this be used over other choices and/or in what circumstances?
HOW
A high-level overview of how this option could or would be deployed.
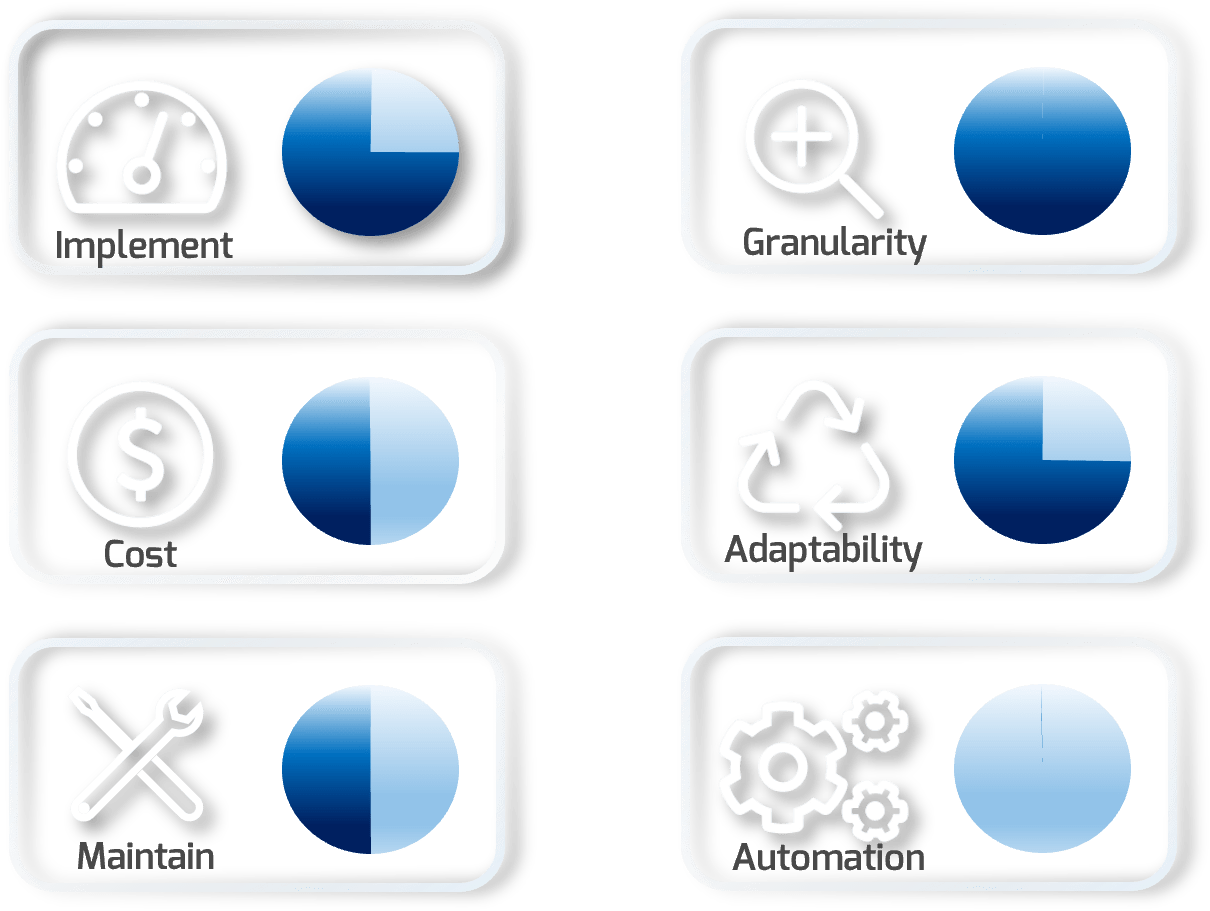
Notional assessments will be displayed in a sidebar to give an idea of Effort, Cost, Skills, Granularity, Adaptability, and Automation.
Implement |
Notional level of effort to implement on a standard network |
|---|---|
| Cost | Relative cost of implementing this segmentation strategy |
| Maintain | Notional level of time and skills needed to maintain |
| Granularity | How granular this type of segmentation is in general |
| Adaptability | The ability of the solution to be easily modified or changed |
| Automation | The level of automation inherent in the solution |
Air gap
… And never the twain shall meet.
– Rudyard Kipling, “The Ballad of East and West.”
WHAT
Air gapping is a strategy to protect portions of a network by segmenting those portions and running them on completely separate hardware from the primary network. In an air gap scenario, the segmented network cannot have connectivity to outside networks. This difference makes air gapping a very specific implementation of parallel networks (which are still segmented and run on separate hardware but can be connected through a control point).
WHY
Air gap is a traditional choice when environments need to be very secure. Examples where air gaps exist(ed) are:
- Operational technology (OT) networks
- Military networks
- Critical infrastructure
HOW
Most networks are not overprovisioned to a level that physical segmentation can be done without purchasing new equipment. The major steps required for constructing an air gap include:
- Design segmentation
- Purchase and install new hardware
- Cable to new hardware
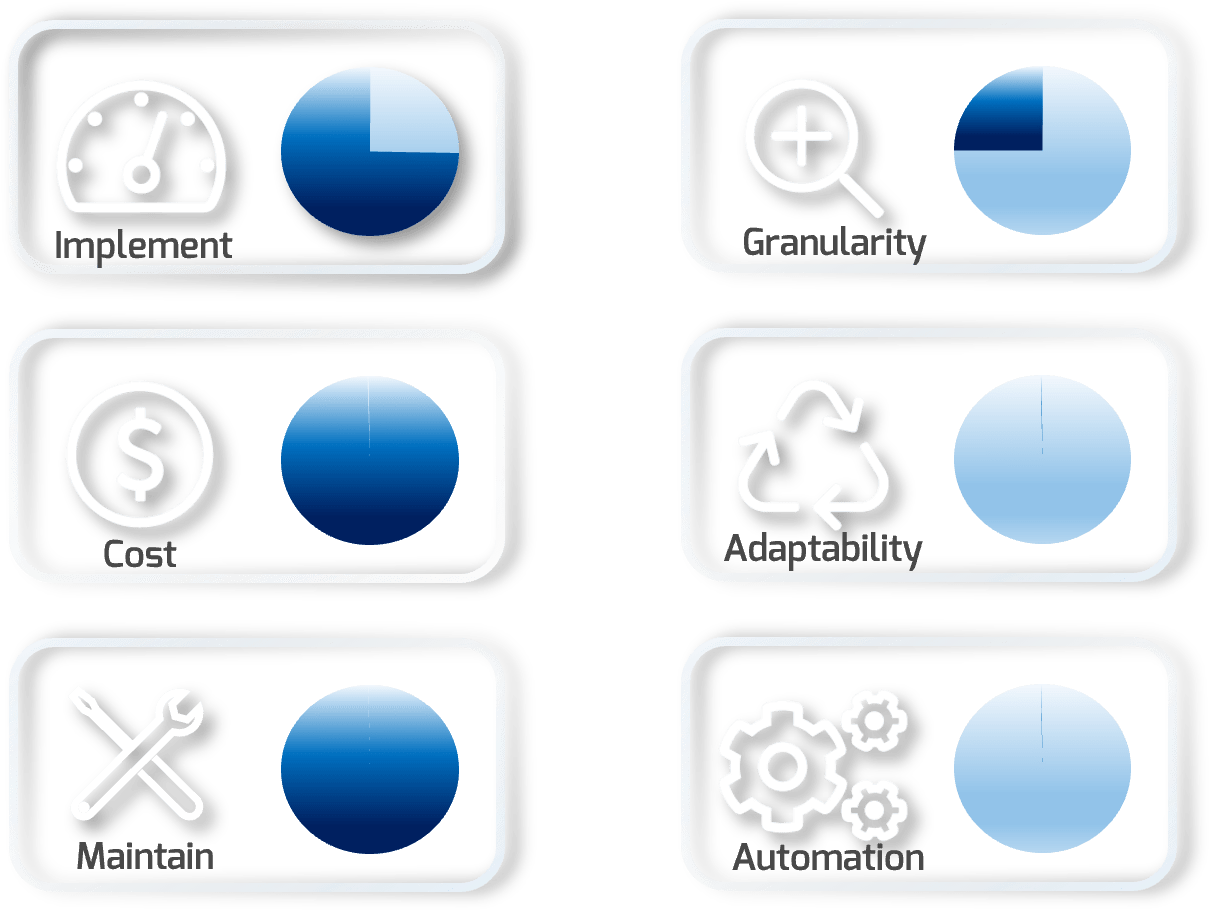
Info-Tech Insight
An air gapped network is the ultimate in segmentation and security … as long as the network does not require connectivity. It is unfortunately rare in today’s world that a network will stand on its own without any need for external connectivity.
VLAN
Do what you can, with what you’ve got…
– Theodore Roosevelt
WHAT
Virtual local area networks (VLANs) are a standard feature on today’s firewalls, routers, and manageable switches. This configuration option allows for network traffic to be segmented into separate virtual networks (broadcast domains) on existing hardware. This segmentation is done at layer 2 of the OSI model. All traffic will share the same hardware but be partitioned based on “tags” that the local device applies to the traffic. Because of these tags, traffic is handled separately at layer 2 of the OSI model, but traffic can pass between segments at layer 3 (e.g. IP layer).
WHY
VLANs are commonly used because most existing deployments already have the technology available without extra licensing. VLANs are also potentially used as foundational components in more complex segmentation strategies such as static or dynamic overlays.
HOW
VLANs allow for segmentation of a device at the port level. VLAN strategies are generally on a location level (e.g. most VLAN deployments are local to a site, though the same structure may be used among sites). To deploy VLANs you must:
- Define VLAN segments
- Assign ports appropriately
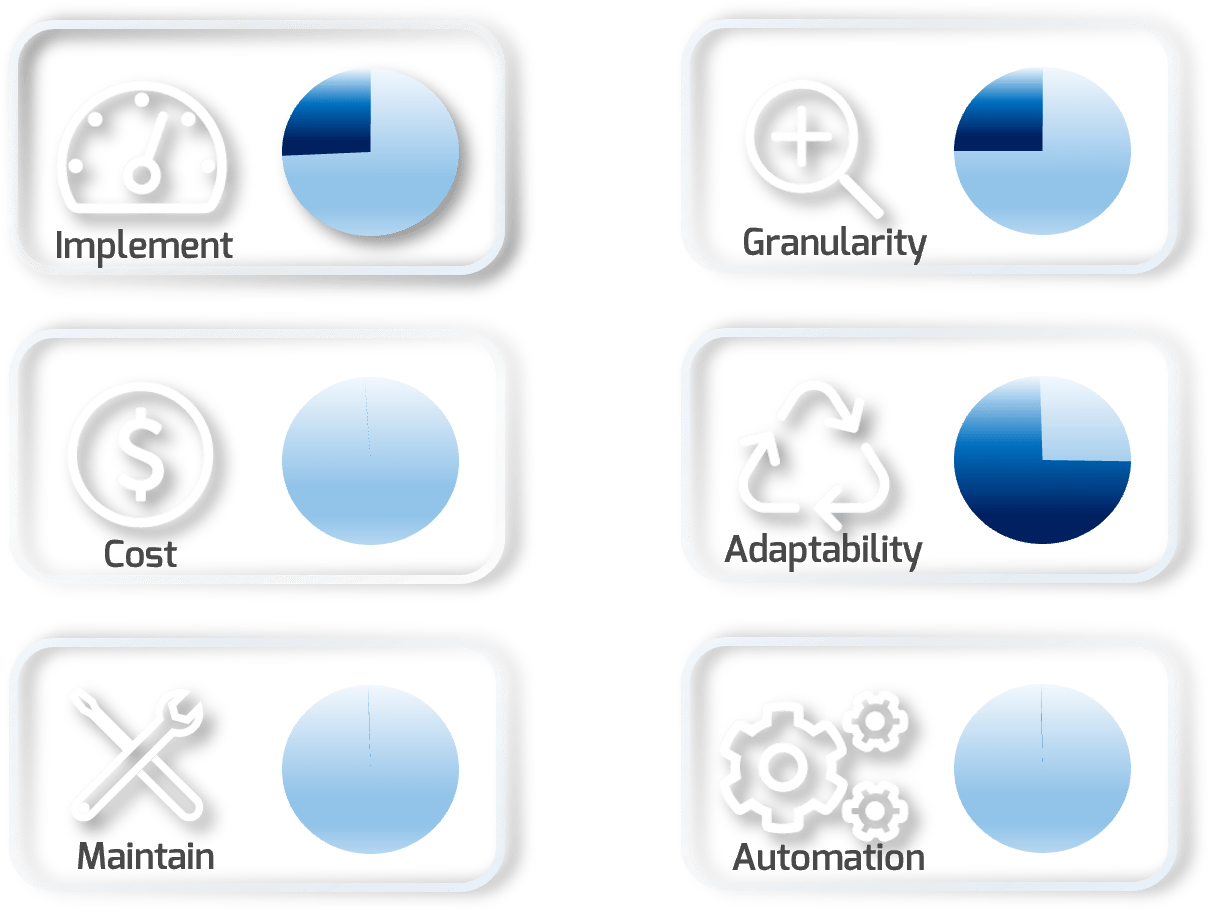
Info-Tech Insight
VLANs are tried and true segmentation workhorses. The fact that they are already included in modern manageable solutions means that there is very little reason to not have some level of segmentation within a network.
Micro-segmentation
Everyone is against micromanaging, but macro managing means you’re working on the big picture but don’t understand the details.
– Henry Mintzberg
WHAT
Micro-segmentation is used to secure and control network traffic between workloads. This is a foundational technology when implementing zero trust or least-privileged access network designs. Segmentation is done at or directly adjacent to the workload (on the system or its direct network connectivity) through firewall or similar policy controls. The controls are set to only allow the network communication required to execute the workload and is limited to appropriate endpoints. This restrictive design restricts all traffic (including east-west) and reduces the attack surface.
WHY
Micro-segmentation is primarily used:
- In server-to-server communication.
- When lateral movement by bad actors is identified as a concern.
HOW
Micro-segmentation can be deployed at different places within the connectivity depending on the technologies used:
- Workload/server (e.g. server firewall)
- VM network overlay (e.g. VMware NSX)
- Network port (e.g. ACL, firewall, ACI)
- Cloud native (e.g. Azure Firewall)
Info-Tech Insight
Micro-segmentation is necessary in the data center to limit lateral movement. Just be sure to be thorough in defining required communication as this technology works on allowlists, not traditional blocklists.
Static overlay
Adaptability is key.
– Marc Andreessen
WHAT
Static overlays are a form of virtual segmentation that allows multiple network segments to exist on the same device. Most of these solutions will also allow for these segments to expand across multiple devices or sites, creating overlay virtual networks on top of the existing physical networks. The static nature of the solution is because the ports that participate in the overlays are statically assigned and configured. Connectivity between devices and sites is done through encapsulation and may have a dynamic component of the control plane handled through routing protocols.
WHY
Static overlays are commonly deployed when the need is to segment different use cases or areas of the organization consistently across sites while allowing easy access within the segments between sites. This could be representative of segmenting a department like Finance or extending a layer 2 segment across data centers.
HOW
Static overlays are can segment and potentially extend a layer 2 or layer 3 network. These solutions could be executed with technologies such as:
- VXLAN (Virtual eXtensible LAN)
- MPLS (Multi Protocol Label Switching)
- VRF (Virtual Routing & Forwarding)
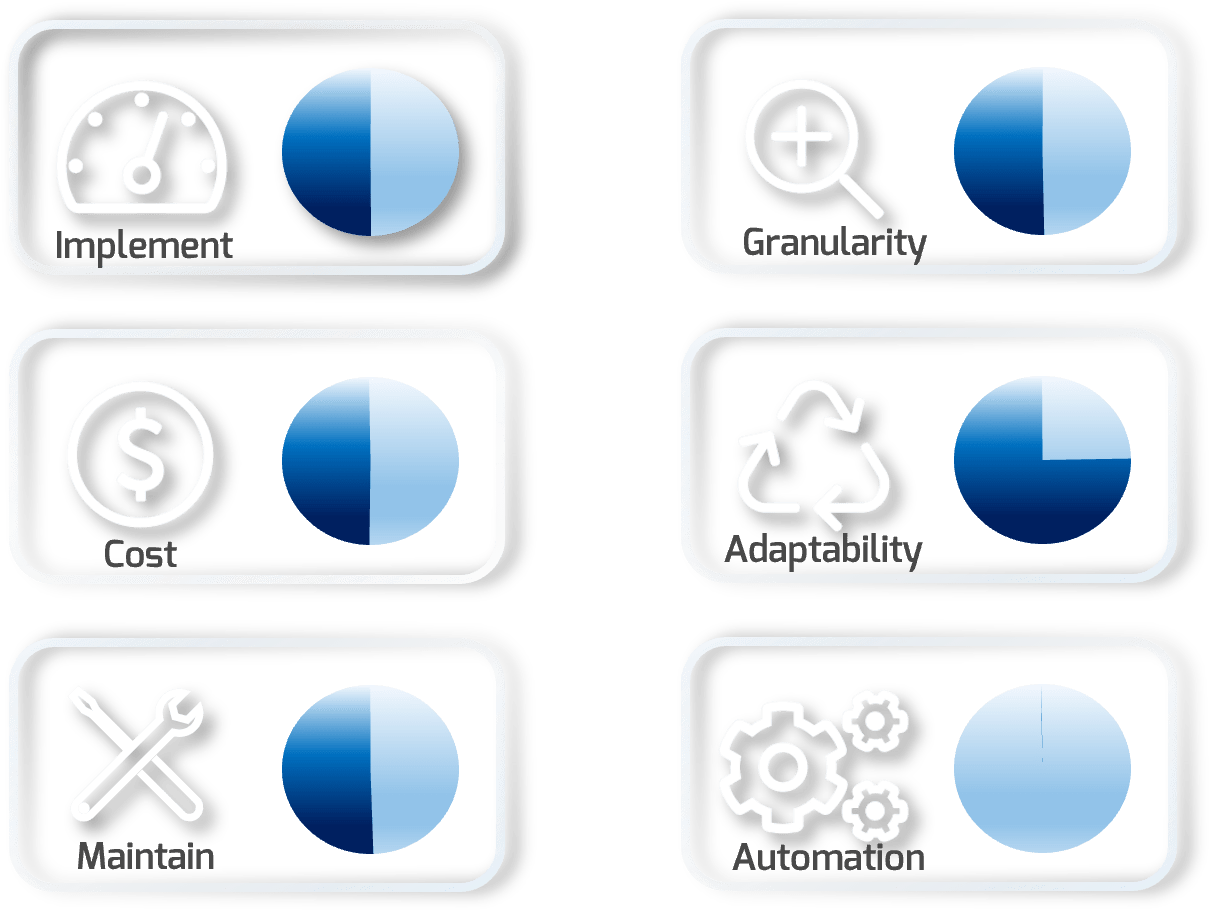
Info-Tech Insight
Static overlays are commonly deployed by telecommunications providers when building out their service offerings due to the multitenancy requirements of the network.
Dynamic overlay
Never tell people how to do things. Tell them what to do and they will surprise you with their ingenuity.
– George S. Patton
WHAT
A dynamic overlay segmentation solution has the ability to make security or traffic decisions based on policy. Rather than designing and hardcoding the network architecture, the policy is architected and the network makes decisions based on that policy. Differing levels of control exist in this space, but the underlying commonality is that the segmentation would be considered “software defined” (SDN).
WHY
Dynamic overlay solutions provide the most flexibility of the presented solutions. Some use cases such as BYOD or IoT devices may not be easily identified or controlled through static means. As a general rule of thumb, the less static the network is, the more dynamic your segmentation solution must be.
HOW
Policy is generally applied at the network ingress. When applying policy, which policy to be applied can be identified through different methodologies such as:
- Authentication (e.g. 802.1x)
- Device agents
- Device profiling
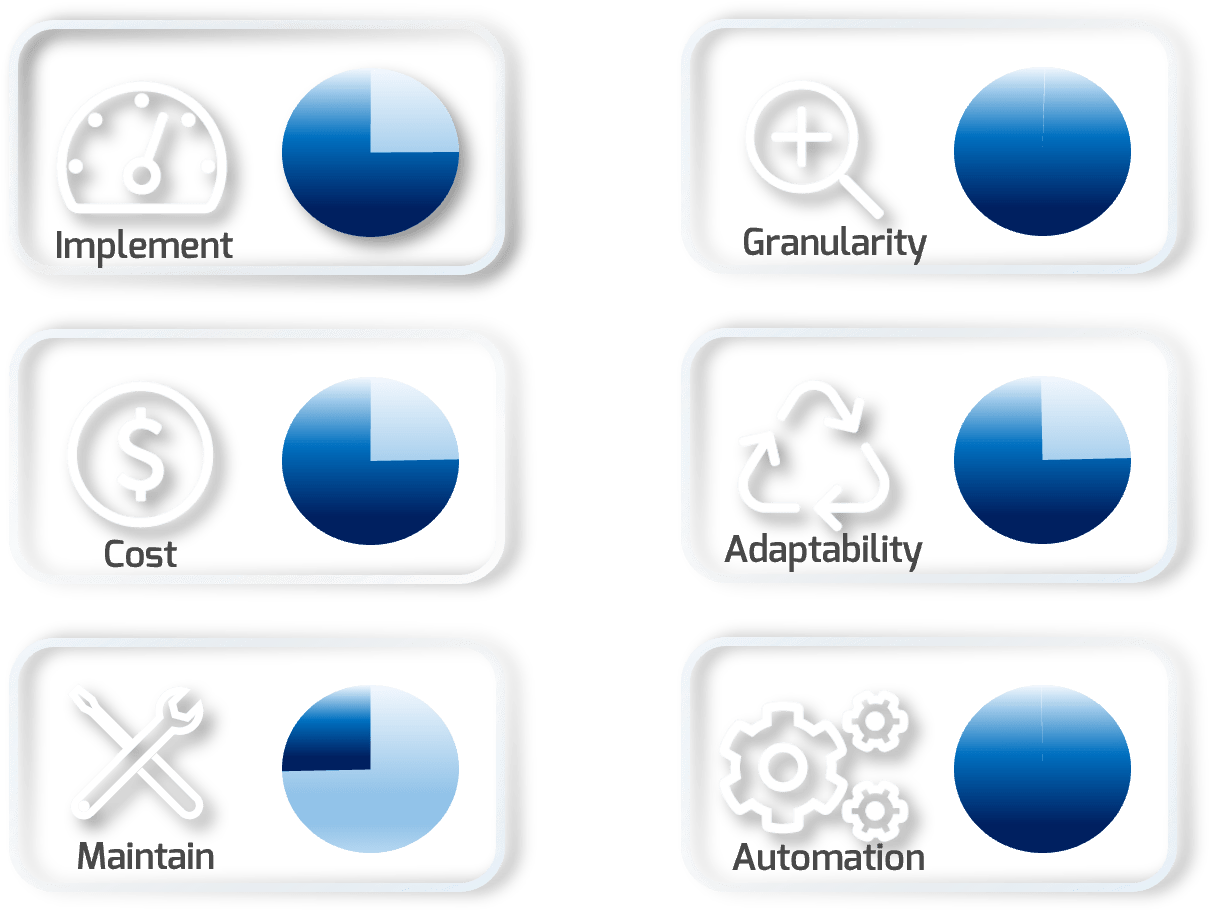
Info-Tech Insight
Dynamic overlays allow for more flexibility through its policy-based configurations. These solutions can provide the highest value when positioned where we have less control of the points within a network (e.g. BYOD scenarios).
Define how your segments will communicate
No segment is an island…
Network segmentation allows for protection of devices, users, or data through the act of separating the physical or virtual networks they are on. Counter to this protective stance, especially in today’s networks, these devices, users, or data tend to need to interact with each other outside of the neat lines we draw for them. Proper network segmentation has to allow for the transfer of assets between networks in a safe and secure manner.
Info-Tech Insight
The solutions used to facilitate the controlled communication between segments has to consider the friction to the users. If too much friction is introduced, people will try to find a way around the controls, potentially negating the security that is intended with the solution.
Potential access methods
A ship in harbor is safe, but that is not what ships are built for.
– John A. Shedd
Firewall Two-way controlled communication |
Firewalls are tried and true control points used to join networks. This solution will allow, at minimum, port-level control with some potential for deeper inspection and control beyond that. |
|
|---|---|---|
Jump Box A place between worlds |
Also sometimes referred to as a “Bastion Host,” a jump box is a special-purpose computer/server that has been hardened and resides on multiple segments of a network. Administrators or users can log into this box and use it to securely use the tools installed to act on other segments of the network. |
|
Protocol Gateway Command-level control |
A protocol gateway is a specific and special subset of a firewall. Whereas a firewall is a security generalist, a protocol gateway is designed to understand and have rule-level control over the commands passing through it within defined protocols. This granularity, for example, allows for control and filtering to only allow defined OT commands to be passed to a secure SCADA network. |
|
Network Pump One-way data extraction |
A network pump is a concept designed to allow data to be transferred from a secure network to a less secure network while still protecting against covert channels such as using the ACK within a transfer to transmit data. A network pump will consist of trusted processes and schedulers that allow for data to pass but control channels to be sufficiently modified so as to not allow security concerns. |
|
Operate and optimize
Security is not static. Monitor and iterate on policies within the environment.
Monitor |
Iterate |
|
|---|---|---|
Two in three businesses (68%) allow more employee data access than necessary. |
Are the segmentation efforts resulting in the expected traffic changes? Are there any anomalies that need investigation? |
Using the output from the monitoring stage, refine and optimize the design by iterating on the process. |
Monitor for efficacy, compliance, and the unknown
Monitor to ensure your intended results and to identify new potential risks.
Monitoring network segments
A combination of passive and active monitoring is required to ensure that:
- The rules that have been deployed are working as expected.
- Appropriate proof of compliance is in place for auditing and insurance purposes.
- Environments are being monitored for unexpected traffic.
Active monitoring goes beyond the traditional gathering of information for alerts and dashboards and moves into the space of synthetic users and anomaly detection. Using these strategies helps to ensure that security is enforced appropriately and responses to issues are timely.
"We discovered in our research that insider threats are not viewed as seriously as external threats, like a cyberattack. But when companies had an insider threat, in general, they were much more costly than external incidents. This was largely because the insider that is smart has the skills to hide the crime, for months, for years, sometimes forever."
– Dr. Larry Ponemon, Chairman Ponemon Institute, at SecureWorld Boston
Info-Tech Insight
Using solutions like network detection and response (NDR) will allow for monitoring to take advantage of advanced analytical techniques like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies can help identify anomalies that a human might miss.
Monitoring options
It’s not what you look at that matters, it’s what you see.
– Henry David Thoreau
Traditional Monitor cumulative change in a variable |
Traditional network monitoring is a minimum viable product. With this solution variables can be monitored to give some level of validation that the segmentation solution is operating as expected. Potential areas to monitor include traffic volumes, access-list (ACL) matches, and firewall packet drops. |
|
|---|---|---|
Rules Based Inspect traffic to find a match against a library of signatures |
Rules-based systems will monitor traffic against a library of signatures and alert on any matches. These solutions are good at identifying the “known” issues on the network. Examples of these systems include security incident and event management (SIEM) and intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS). |
|
Anomaly Detection Use computer intelligence to compare against baseline |
Anomaly detection systems are designed to baseline the network traffic then compare current traffic against that to find anomalies using technologies like Bayesian regression analysis or artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML). This strategy can be useful in analyzing large volumes of traffic and identifying the “unknown unknowns.” |
|
Synthetic Data Mimic potential traffic flows to monitor network reaction |
Rather than wait for a bad actor to find a hole in the defenses, synthetic data can be used to mimic real-world traffic to validate configuration and segmentation. This often takes the form of real user monitoring tools, penetration testing, or red teaming. |
|
Gather feedback, assess the situation, and iterate
Take input from operating the environment and use that to optimize the process and the outcome.
Optimize through iteration
Output from monitoring must be fed back into the process of maintaining and optimizing segmentation. Network segmentation should be viewed as an ongoing process as opposed to a singular structured project.
Monitoring can and will highlight where and when the segmentation design is successful and when new traffic flows arise. If these inputs are not fed back through the process, designs will become stagnant and admins or users will attempt to find ways to circumvent solutions for ease of use.
"I think it's very important to have a feedback loop, where you're constantly thinking about what you've done and how you could be doing it better. I think that's the single best piece of advice: constantly think about how you could be doing things better and questioning yourself."
– Elon Musk, qtd. in Mashable, 2012
Info-Tech Insight
The network environment will not stay static; flows will change as often as required for the business to succeed. Take insights from monitoring the environment and integrate them into an iterative process that will maintain relevance and usability in your segmentation.
Bibliography
Andreessen, Marc. “Adaptability is key.” BrainyQuote, n.d.
Barry Schwartz. The Paradox of Choice: Why More Is Less. Harper Perennial, 18 Jan. 2005.
Capers, Zach. “GetApp’s 2022 Data Security Report—Seven Startling Statistics.” GetApp,
19 Sept. 2022.
Cisco Systems, Inc. “Cybersecurity resilience emerges as top priority as 62 percent of companies say security incidents impacted business operations.” PR Newswire, 6 Dec. 2022.
“Dynamic Network Segmentation: A Must-Have for Digital Businesses in the Age of Zero Trust.” Forescout Whitepaper, 2021. Accessed Nov. 2022.
Eaves, Johnothan. “Segmentation Strategy - An ISE Prescriptive Guide.” Cisco Community,
26 Oct. 2020. Accessed Nov. 2022.
Kambic, Dan, and Jason Fricke. “Network Segmentation: Concepts and Practices.” Carnegie Mellon University SEI Blog, 19 Oct. 2020. Accessed Nov. 2022.
Kang, Myong H., et al. “A Network Pump.” IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, vol. 22 no. 5, May 1996.
Kipling, Rudyard. “The Ballad of East and West.” Ballads and Barrack-Room Ballads, 1892.
Mintzberg, Henry. “Everyone is against micro managing but macro managing means you're working at the big picture but don't know the details.” AZ Quotes, n.d.
Murphy, Greg. “A Reimagined Purdue Model For Industrial Security Is Possible.” Forbes Magazine, 18 Jan. 2022. Accessed Oct. 2022.
Patton, George S. “Never tell people how to do things. Tell them what to do and they will surprise you with their ingenuity.” BrainyQuote, n.d.
Ponemon, Larry. “We discovered in our research […].” SecureWorld Boston, n.d.
Roosevelt, Theodore. “Do what you can, with what you've got, where you are.” Theodore Roosevelt Center, n.d.
Sahoo, Narendra. “How Does Implementing Network Segmentation Benefit Businesses?” Vista Infosec Blog. April 2021. Accessed Nov. 2022.
“Security Outcomes Report Volume 3.” Cisco Secure, Dec 2022.
Shedd, John A. “A ship in harbor is safe, but that is not what ships are built for.” Salt from My Attic, 1928, via Quote Investigator, 9 Dec. 2023.
Singleton, Camille, et al. “X-Force Threat Intelligence Index 2022” IBM, 17 Feb. 2022.
Accessed Nov. 2022.
Stone, Mark. “What is network segmentation? NS best practices, requirements explained.” AT&T Cyber Security, March 2021. Accessed Nov. 2022.
“The State of Breach and Attack Simulation and the Need for Continuous Security Validation: A Study of US and UK Organizations.” Ponemon Institute, Nov. 2020. Accessed Nov. 2022.
Thoreau, Henry David. “It’s not what you look at that matters, it’s what you see.” BrainyQuote, n.d.
Ulanoff, Lance. “Elon Musk: Secrets of a Highly Effective Entrepreneur.” Mashable, 13 April 2012.
“What Is Microsegmenation?” Palo Alto, Accessed Nov. 2022.
“What is Network Segmentation? Introduction to Network Segmentation.” Sunny Valley Networks, n.d.