
Improve Email Security
As the sophistication of malicious attacks increases, it has become more difficult to ensure applications such as email software are properly protected and secured. The increase in usage and traffic of email exacerbates the security risks to the organization.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
Email has changed. Your email security needs to evolve as well to ensure you are protecting your organization’s communication.
Impact and Result
- Gain an understanding of the importance of email security and steps to secure your corporate email.
- Develop holistic guidelines on implementing best practices to modernize your organization’s email security.
Improve Email Security Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Improve Email Security Storyboard – A guide to best practices for improving an organization’s email security.
This research provides guidelines to assist organizations in identifying controls to secure their emails along with recommendations on the most common and effective controls to secure and protect corporate emails.
- Improve Email Security Storyboard
2. Email Security Checklist – A checklist tool that enables organizations to monitor their progress in implementing controls to improve their email security.
This checklist of common email security categories and their associated controls helps ensure organizations are following best practices.
- Email Security Checklist
Further reading
Improve Email Security
Follow the latest best practices for email security to mitigate evolving threats.
Analyst Perspective
Protecting your organization’s digital assets begins with securing your email communication.
As organizations increasingly rely on email communication for day-to-day business operations, threat actors are exploiting the increased traction to develop and implement more sophisticated email-based attacks. Furthermore, the lack of investment in measures, tools, and technologies for an organization’s email security exacerbates the vulnerabilities at hand.
Effective use of security procedures and techniques can mitigate and minimize email-based threats have been shown to reduce the ability of these attacks to infiltrate the email inbox. These guidelines and best practices will help your organization conduct due diligence to protect the contents of the email, its transit, and its arrival to the authorized recipient.

Ahmad Jowhar
Research Specialist, Security & Privacy
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive Summary
| Your Challenge | Common Obstacles | Info-Tech’s Approach |
|
|
|
Info-Tech Insight
Email has changed. Your email security must evolve to ensure the safety of your organization’s communication.
Your Challenge
As a security leader, you need to modernize your email security services so you can protect business communications and prevent security incidents.
- Various factors must be considered when deciding how best to safeguard your organization’s communication chain. This includes the frequency of email traffic and the contents of emails.
- The increased number of email-based cyberattacks reveals the sophistication of threat actors in leveraging an organization’s lack of email security to infiltrate their business.
- As organizations continue to rely heavily on email communication, email-based threats will become increasingly prevalent.
75% of organizations have experienced an increase in email-based threats.
97% of security breaches are due to phishing attacks.
82% of companies reported a higher volume of email in 2022.
Source: Mimecast, 2023.
Modern email security controls framework for security leaders
Email has changed. Your email security must evolve to ensure the safety of your organization’s communication.
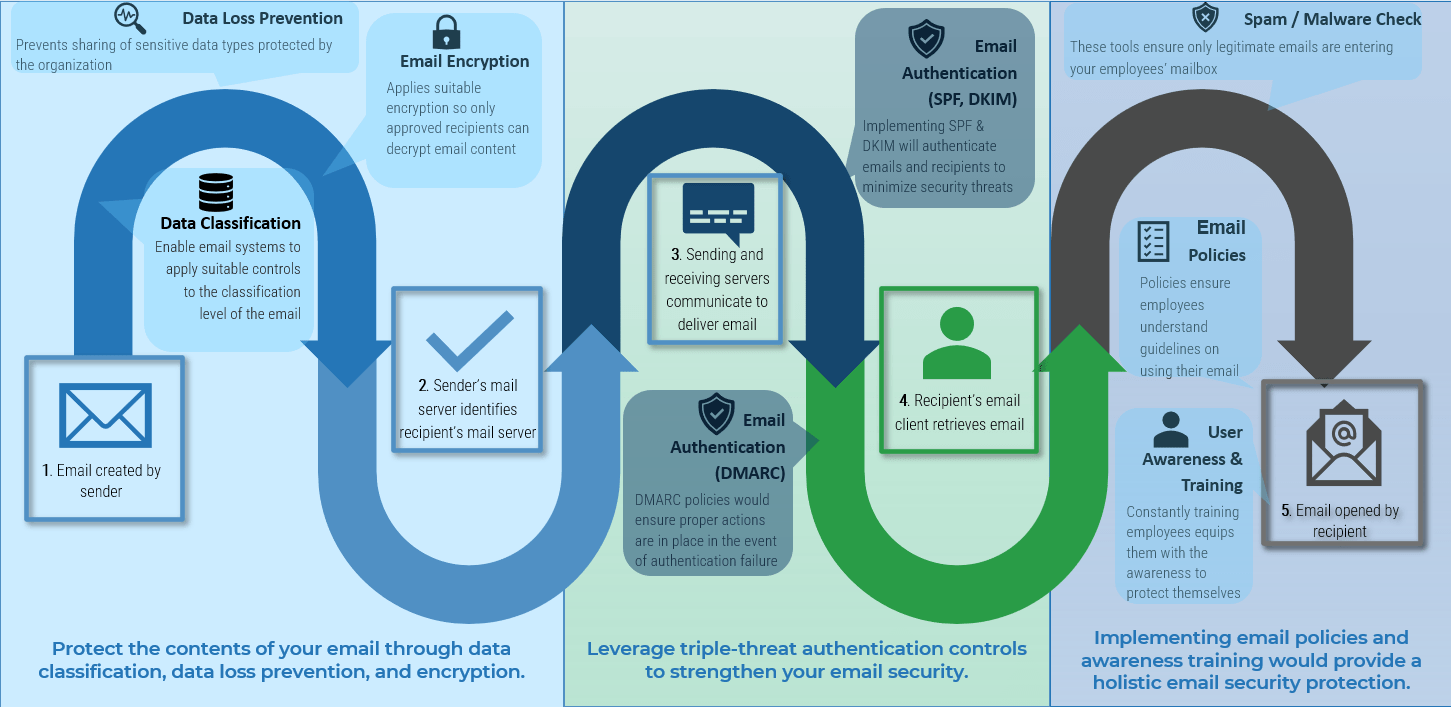
Understand the best practices in securing your organization’s emails
| Enhance your security posture by modernizing your email security Email has changed. Your email security must evolve to ensure the safety of your organization’s communication. |
|||
|
Deploy an added layer of defense by preventing the contents of your email from being intercepted. Encrypting your email communication will provide an additional layer of protection which only allows authorized users to read the email. |
Leverage triple-threat authentication controls to strengthen your email security. Leveraging SPF, DKIM, and DMARC enables you to have the proper authentication controls in place, ensuring that only legitimate users are part of the email communication. |
Protect the contents of your email through data classification and data loss prevention. Having tools and technologies in place to ensure that data is classified and backed up will enable better storage, analysis, and processing of the email. |
Implement email policies for a holistic email security protection. Policies ensure acceptable standards are in place to protect the organization’s assets, including the creation, attachment, sending, and receiving of emails. |
| User awareness and training Training employees on protecting their corporate emails adds an extra layer of defense by ensuring end users are aware of various email-based threats and can confidently safeguard their organizations from attacks. |
|||
Email encryption
Deploy an added layer of defense by preventing the contents of your email from being intercepted.
- Protecting your organization’s emails begins by ensuring only the appropriate recipients can receive and read the email’s contents.
- This process includes encrypting the email’s contents to protect sensitive information from being read by unauthorized recipients.
- This protects the contents even if the email is intercepted by anyone besides the intended recipient.
- Other benefits of email encryption include:
- Reducing any risks associated with regulatory violations.
- Enabling business to confidently communicate sensitive information via email.
- Ensuring protective measures taken to prevent data loss and corporate policy violations.
Along with the increased use of emails, organizations are seeing an increase in the number of attacks orchestrating from emails. This has resulted in 74% of organizations seeing an increase in email-based threats.
Source: Mimecast, 2023.
Info-Tech Insight
Encrypting your email communication will provide an additional layer of protection which only allows authorized users to read the email.
Implementing email encryption
Leverage these protocols and tools to help encrypt your email.
- The most common email encryption protocols and tools include:
- Transport Layer Security (TLS): A cryptographic protocol designed to securely deliver data via the internet, which prevents third parties from intercepting and accessing the data.
- Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension (S/MIME): A protocol for sending digitally signed and encrypted messages by leveraging public key encryption to provide at-rest and in-transit data protection.
- Secure Email Gateway: An email security solution that inspects emails for malicious content prior to it reaching the corporate system. The solution is positioned between the public internet and corporate email servers. An email gateway solution would be provided by a third-party vendor and can be implemented on-premises, through the cloud, or hybrid.
- Email encryption policies can also be implemented to ensure processes are in place when sending sensitive information through emails.
- Email encryption ensures end-to-end privacy for your email and is especially important when the email requires strict content privacy.
Email authentication
Three authentication controls your organization should leverage to stay secure.
- Along with content encryption, it’s important to authenticate both the sender and recipient of an email to ensure that only legitimate users are able to send and receive it.
- Implementing email authentication techniques prevents unsolicited email (e.g. spam) from entering your mailbox.
- This also prevents unauthorized users from sending email on your organization’s behalf.
- Having these standards in place would safeguard your organization from spam, spoofing, and phishing attacks.
- The three authentication controls include:
- Sender Policy Framework (SPF): Email validation control that verifies that the incoming email is from an authorized list of IP addresses provided by the sender’s domain administrator.
- DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM): Enables recipients to verify that an email from a specific domain was authorized by the domain’s owner. This is conducted through cryptographic authentication by adding a digital signature to the message headers of outbound emails.
- Domain Message Authentication Reporting & Conformance (DMARC): Provides domain-level protection of email channel by publishing DMARC records in the organization’s domain name system (DNS) and creates policies which prompts actions to take if an email fails authentication.
Although these authentication controls are available for organizations to leverage, the adoption rate remains low. 73% of survey respondents indicated they didn’t deploy email authentication controls within their organization.
Source: Mimecast, 2023.
Email authentication controls
All three authentication controls should be implemented to effectively secure your organization’s email. They ensure the emails you send and receive are securely authorized and legitimate.
| SPF | DKIM | DMARC |
|---|---|---|
|
Creating an SPF record identifies which IP addresses are allowed to send emails from your domain. Steps to implement SPF include the following:
|
Implementing DKIM helps prevent attackers from sending emails that pretend to come from your domain. Steps to implement DKIM include the following:
|
Setting up DMARC ensures emails are validated and defines actions to take if an email fails authentication. These include:
|
For more information:
Data classification
Ensure sensitive data is securely processed, analyzed, and stored.
- Besides authenticating the legitimacy of an email and its traffic to the recipient, it’s important to have procedures in place to protect the contents of an email.
- Data classification is found not only in databases and spreadsheets, but also in the email messages being communicated. Examples of data most commonly included in emails:
- Personal identifiable information (PII): social security number, financial account number, passcodes/passwords
- Applying data classification to your email can help identify the sensitivity of the information it contains. This ensures any critical data within an email message is securely processed and protected against unauthorized use, theft, and loss.
- Emails can be classified based on various sensitivity levels. such as:
- Top secret, public, confidential, internal
Discover and Classify Your Data
Leverage this Info-Tech blueprint for guidelines on implementing a data classification program for your organization.
Info-Tech Insight
Having tools and technologies in place to ensure that data is classified and backed up will enable better storage, analysis, and processing of the email.
Data loss prevention (DLP)
Protect your data from being lost/stolen.
- Protecting an email’s contents through data classification is only one approach for improving email security. Having a data loss prevention solution would further increase security by minimizing the threat of sensitive information leaving your organization’s email network.
- Examples of tools embedded in DLP solutions that help monitor an organization's email communication:
- Monitoring data sent and received from emails: This ensures the data within an email communication is protected with the necessary encryption based on its sensitivity.
- Detecting suspicious email activity: This includes analyzing users’ email behavior regarding email attachments and identifying irregular behaviors.
- Flagging or blocking email activities which may lead to data loss: This prevents highly sensitive data from being communicated via email and reduces the risk of information being intercepted.
- The types of DLP technologies that can be leveraged include:
- Rule-based: Data that has been tagged by admins as sensitive can be blocklisted, which would flag and/or block data from being sent via email.
- Machine learning: Data on users’ email behavior is collected, processed, and trained to understand the employee’s normal email behavior and detect/flag suspicious activities.
- Implementing DLP solutions would complement your data classification techniques by ensuring proper measures are in place to secure your organization’s assets through policies, technology, and tools.
48% of employees have accidently attached the wrong file to an email.
39% of respondents have accidently sent emails that contained security information such as passwords and passcodes.
Source: Tessian, 2021.
User awareness & training
A strong security awareness & training program is an important element of strengthening your email security.
- Having all these tools and techniques in place to improve your email security will not be effective unless you also improve your employees’ awareness.
- Employees should participate in email security training, especially since the majority utilize this channel of communication for day-to-day operations.
- User awareness and training should go beyond phishing campaigns and should highlight the various types of email-based threats, the characteristics of these threats, and what procedures they can follow to minimize these threats.
- 95% of data breaches are caused by human error. It can take nine months to discover and contain them, and they are expected to cost $8 trillion this year (Mimecast, 2023).
- Investments in employee awareness and training would mitigate these risks by ensuring employees recognize and report suspicious emails, remain mindful of what type of data to share via email, and improve their overall understanding of the importance of email security.
Develop a Security Awareness and Training Program That Empowers End Users
Leverage this Info-Tech blueprint for assistance on creating various user training materials and empower your employees to become a main line of defense for your organization.
64% of organizations conduct formal training sessions (in-person or computer-based).
74% of organizations only focus on providing phishing-based training.
Source: Proofpoint, 2021.
Examples of email-based threats
Phishing
Email sent by threat actors designed to manipulate end user into providing sensitive information by posing as a trustworthy source
Business Email Compromise
Attackers trick a user into sending money or providing confidential information
Spam
Users receive unsolicited email, usually in bulk, some of which contains malware
Spear Phishing
A type of phishing attack where the email is sent to specific and targeted emails within the organization
Whaling
A type of phishing attack similar to spear phishing, but targeting senior executives within the organization
Password/Email Exposure
Employees use organizational email accounts and passwords to sign up for social media, leaving them susceptible to email and/or password exposure in a social media breach
Email policies
Having policies in place will enable these controls to be implemented.
Developing security policies that are reasonable, auditable, enforceable, and measurable ensures proper procedures are followed and necessary measures are implemented to protect the organization. Policies relating to email security can be categorized into two groups:
- User policy: Policies employees must adhere to when using their corporate email. Examples:
- User acceptance of technology: Acknowledgment of legitimate and restrictive actions when using corporate email
- Security awareness and training: Acknowledging completion of email security training
- Administrator-set policy: Policies that are implemented by IT and/or security admins. Examples:
- Email backup: Policy on how long emails should be archived and processes for disposing of them
- Log retention: Policy on how to retain, process, and analyze logs created from email servers
- Throttling: Policies that limit the number of emails sent by a sender and the number of recipients per email and per day depending on the employee’s grouping
Develop and Deploy Security Policies
Leverage this Info-Tech blueprint for assistance on developing and deploying actionable policies and creating an overall policy management lifecycle to keep your policies current, effective, and compliant.
Info-Tech Insight
Policies ensure acceptable standards are in place to protect the organization’s assets, including the creation, attachment, sending, and receiving of emails.
Email security technologies & tools (SoftwareReviews)
SoftwareReviews, a division of Info-Tech Research Group, provides enterprise software reviews to help organizations make more efficient decisions during the software selection process. Reviews are provided by authenticated IT professionals who have leveraged the software and provide unbiased insights on different vendors and their products.
Learn from the collective knowledge of real IT professionals.
- Know the products and features available.
- Explore modules and detailed feature-level data.
- Quickly understand the market.
Evaluate market leaders through vendor rankings and awards.
- Convince stakeholders with professional reports.
- Avoid pitfalls with unfiltered data from real users.
- Choose software with confidence.
Cut through misleading marketing material.
- Negotiate contracts based on data.
- Know what to expect before you sign.
- Effectively manage the vendor.
Email security technologies & tools
Leverage these tools for an enhanced email security solution.
- SoftwareReviews provides vendor and software reviews of various email security solutions. View the details below on the different email security solutions and the top vendors for each solution.
- Cloud Email Security
- Email Backup
- Secure Email Gateway – Enterprise Software
- Secure Email Gateway – Midmarket Software
Email Security Checklist
Follow these guidelines to ensure you are implementing best practices for securing your organization’s emails.
- The Email Security Checklist is a tool to assess the current and future state of your organization’s email security and provides a holistic understanding on monitoring your progress within each category and associated controls.
- The status column allows you to select the feature’s current implementation status, which includes the following options:
- Enabled: The feature is deployed within the organization’s network.
- Implemented: The feature is implemented within the organization’s network, but not yet deployed.
- Not implemented: The feature has not been enabled or implemented.
- Comments can be added for each feature to provide details such as indicating the progress on enabling/implementing a feature and why certain features are not yet implemented.
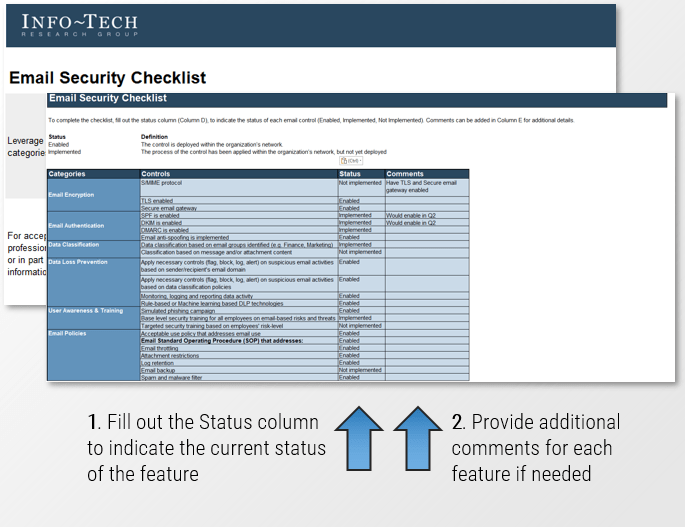
Download the Email Security Checklist tool
Related Info-Tech Research
Discover and Classify Your Data
Leverage this Info-Tech blueprint for guidelines on implementing a data classification program for your organization.
Develop a Security Awareness and Training Program That Empowers End Users
Leverage this Info-Tech blueprint for assistance on creating various user training materials and empower your employees to become a main line of defense for your organization.
Develop and Deploy Security Policies
Leverage this Info-Tech blueprint for assistance on developing and deploying actionable policies and creating an overall policy management lifecycle to keep your policies current, effective, and compliant.
Bibliography
“10 Best Practices for Email Security in 2022.” TitanFile, 22 Sept. 2022. Web.
“2021 State of the Phish.” Proofpoint, 2021. Web.
Ahmad, Summra. “11 Email Security Best Practices You Shouldn't Miss (2023).” Mailmunch, 9 Mar. 2023. Web.
“Blumira's State of Detection and Response.” Blumira, 18 Jan. 2023. Web.
Clay, Jon. “Email Security Best Practices for Phishing Prevention.” Trend Micro, 17 Nov. 2022. Web.
Crane, Casey. “6 Email Security Best Practices to Keep Your Business Safe in 2019.” Hashed Out by The SSL Store™, 7 Aug. 2019. Web.
Hateb, Seif. “Basic Email Security Guide.” Twilio Blog, Twilio, 5 Dec. 2022. Web.
“How DMARC Advances Email Security.” CIS, 9 July 2021. Web.
Pal, Suryanarayan. “10 Email Security Best Practices You Should Know in 2023.” Mailmodo, 9 Feb. 2023. Web.
Pitchkites, Max. “Email Security: A Guide to Keeping Your Inbox Safe in 2023.” Cloudwards, 9 Dec. 2022. Web.
Rudra, Ahona. “Corporate Email Security Checklist.” PowerDMARC, 4 July 2022. Web.
“Sender Policy Framework.” Mimecast, n.d. Web.
Shea, Sharon, and Peter Loshin. “Top 15 Email Security Best Practices for 2023: TechTarget.” TechTarget, 14 Dec. 2022. Web.
“The Email Security Checklist: Upguard.” UpGuard, 16 Feb. 2022. Web.
“The State of Email Security 2023.” Mimecast, 2023. Web.
Wetherald, Harry. “New Product - Stop Employees Emailing the Wrong Attachments.” Tessian, 16 Sept. 2021. Web.
“What Is DMARC? - Record, Verification & More: Proofpoint Us.” Proofpoint, 9 Mar. 2023. Web.
“What Is Email Security? - Defining Security of Email: Proofpoint Us.” Proofpoint, 3 Mar.2023. Web.
Wilton, Laird. “How to Secure Email in Your Business with an Email Security Policy.” Carbide, 31 Jan. 2022. Web.