
Define the Role of Project Management in Agile and Product-Centric Delivery
- There are many voices with different opinions on the role of project management. This causes confusion and unnecessary churn.
- Project management and product management naturally align to different time horizons. Harmonizing their viewpoints can take significant work.
- Different parts of the organization have diverse views on how to govern and fund pieces of work, which leads to confusion when it comes to the role of project management.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to product delivery. For many organizations product delivery requires detailed project management practices, while for others it requires much less. Taking an outcome-first approach when planning your product transformation is critical to make the right decision on the balance between project and product management.
Impact and Result
- Get alignment on the definition of projects and products.
- Understand the differences between delivering projects and delivering products.
- Line up your project management activities with the needs of Agile and product-centric projects.
- Understand how funding can change when moving away from project-centric delivery.
Define the Role of Project Management in Agile and Product-Centric Delivery Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Define the Role of Project Management in Agile and Product-Centric Delivery – A guide that walks you through how to define the role of project management in product-centric and Agile delivery environments.
The activities in this research will guide you through clarifying how you want to talk about projects and products, aligning project management and agility, specifying the different activities for project management, and identifying key differences with funding of products instead of projects.
- Define the Role of Project Management in Agile and Product-Centric Delivery Storyboard
Further reading
Define the Role of Project Management in Agile and Product-Centric Delivery
Projects and products are not mutually exclusive.
Table of Contents
7 Step 1.1: Clarify How You Want to Talk About Projects and Products
13 Step 1.2: Align Project Management and Agility
16 Step 1.3: Specify the Different Activities for Project Management
20 Step 1.4: Identify Key Differences in Funding of Products Instead of Projects
26 Bibliography
Analyst Perspective
Project management still has an important role to play!
When moving to more product-centric delivery practices, many assume that projects are no longer necessary. That isn’t necessarily the case!
Product delivery can mean different things to different organizations, and in many cases it can involve the need to maintain both projects and project delivery.
Projects are a necessary vehicle in many organizations to drive value delivery, and the activities performed by project managers still need to be done by someone. It is the form and who is involved that will change the most.

|
Ari Glaizel
|
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
|
Common Obstacles
|
Info-Tech’s Approach
|
Info-Tech Insight
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to product delivery. For many organizations product delivery requires detailed project management practices, while for others it requires much less. Taking an outcome-first approach when planning your product transformation is critical to make the right decision on the balance between project and product management.
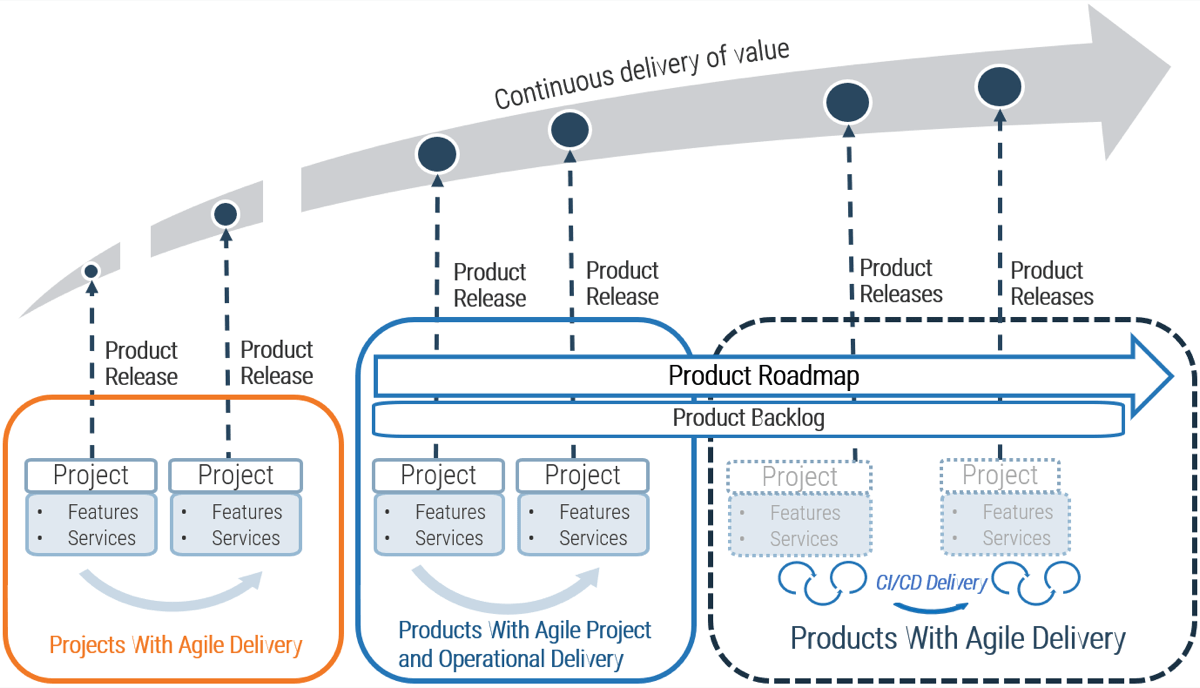
Your evolution of delivery practice is not a binary switch
- PROJECTS WITH WATERFALL The project manager is accountable for delivery of the project, and the project manager owns resources and scope.
- PROJECTS WITH AGILE DELIVERY A transitional state where the product owner is accountable for feature delivery and the project manager accountable for the overall project.
- PRODUCTS WITH AGILE PROJECT AND OPERATIONAL DELIVERY The product owner is accountable for the delivery of the project and products, and the project manager plays a role of facilitator and enabler.
- PRODUCTS WITH AGILE DELIVERY Delivery of products can happen without necessarily having projects. However, projects could be instantiated to cover major initiatives.
Info-Tech Insight
- Organizations do not need to go to full product and Agile delivery to improve delivery practices! Every organization needs to make its own determination on how far it needs to go. You can do it in one step or take each step and evaluate how well you are delivering against your goals and objectives.
- Many organizations will go to Products With Agile Project and Operational Delivery, and some will go to Products With Agile Delivery.
Activities to undertake as you transition to product-centric delivery
- PROJECTS WITH WATERFALL
- Clarify how you want to talk about projects and products. The center of the conversation will start to change.
- PROJECTS WITH AGILE DELIVERY
- Align project management and agility. They are not mutually exclusive (but not necessarily always aligned).
- PRODUCTS WITH AGILE PROJECT AND OPERATIONAL DELIVERY
- Specify the different activities for project management. As you mature your product practices, project management becomes a facilitator and collaborator.
- PRODUCTS WITH AGILE DELIVERY
- Identify key differences in funding. Delivering products instead of projects requires a change in the focus of your funding.
Step 1.1
Clarify How You Want to Talk About Projects and Products
Activities
- 1.1.1 Define “product” and “project” in your context
- 1.1.2 Brainstorm potential changes in the role of projects as you become Agile and product-centric
This step involves the following participants:
- Product owners
- Product managers
- Development team leads
- Portfolio managers
- Business analysts
Outcomes of this step
- An understanding of how the role can change through the evolution from project to more product-centric practices
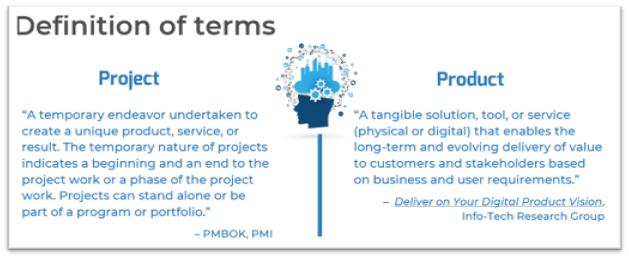
Definition of terms
Project“A temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result. The temporary nature of projects indicates a beginning and an end to the project work or a phase of the project work. Projects can stand alone or be part of a program or portfolio.” (PMBOK, PMI) |

|
Product“A tangible solution, tool, or service (physical or digital) that enables the long-term and evolving delivery of value to customers and stakeholders based on business and user requirements.” (Deliver on Your Digital Product Vision, Info-Tech Research Group) |
Info-Tech InsightLet these definitions be a guide, not necessarily to be taken verbatim. You need to define these terms in your context based on your particular needs and objectives. The only caveat is to be consistent with your usage of these terms in your organization.
1.1.1 Define “product” and “project” in your context
30-60 minutesOutput: Your enterprise/organizational definition of products and projects
Participants: Executives, Product/project managers, Applications teams
- Discuss what “product” and “project” mean in your organization.
- Create common, enterprise-wide definitions for “product” and “project.”
Agile and product management does not mean projects go away
Projects Within Products
Regardless of whether you recognize yourself as a “product-based” or “project-based” shop, the same basic principles should apply.
You go through a period or periods of project-like development to build or implement a version of an application or product.
You also have parallel services along with your project development that encompass the more product-based view. These may range from basic support and maintenance to full-fledged strategy teams or services like sales and marketing.
Info-Tech Note
As your product transformation continues, projects can become optional and needed only as part of your organization’s overall delivery processes
Identify the differences between a project-centric and a product-centric organization
| Project | Product | |
| Fund projects | — Funding –› | Fund teams |
| Line-of-business sponsor | — Prioritization –› | Product owner |
| Project owner | — Accountability –› | Product owner |
| Makes specific changes to a product | —Product management –› | Improves product maturity and support of the product |
| Assignment of people to work | — Work allocation –› | Assignment of work to product teams |
| Project manager manages | — Capacity management –› | Team manages |
Info-Tech Insight
Product delivery requires significant shifts in the way you complete development and implementation work and deliver value to your users. Make the changes that support improving end-user value and enterprise alignment.
1.1.2 Brainstorm potential changes in the role of projects as you become Agile and product-centric
5-10 minutes
Output: Increased appreciation of the relationship between project and product delivery
Participants: Executives, Product/project managers, Applications teams
- Discuss as a group:
- What stands out in the evolution from project to product?
- What concerns do you have with the change?
- What will remain the same?
- Which changes feel the most impactful?

Step 1.2
Align Project Management and Agility
Activities
- 1.2.1 Explore gaps in Agile/product-centric delivery of projects
This step involves the following participants:
- Executives
- Product/Project managers
- Applications teams
Outcomes of this step
- A clearer view of how agility can be introduced into projects.
Challenges with the project management role in Agile and product-centric organizations
Many project managers feel left out in the cold. That should not be the case!
In product-centric, Agile teams, many roles that a project manager previously performed are now taken care of to different degrees by the product owner, delivery team, and process manager.
The overall change alters the role of project management from one that orchestrates all activities to one that supports, monitors, and escalates.
Product Owner
- Defines the “what” and heavily involved in the “when” and the “why”
- Accountable for delivery of value
Delivery team members
- Define the “how”
- Accountable for building and delivering high-quality deliverables
- Can include roles like user experience, interaction design, business analysis, architecture
Process Manager
- Facilitates the other teams to ensure valuable delivery
- Can potentially, in a Scrum environment, play the scrum master role, which involves leading scrums, retrospectives, and sprint reviews and working to resolve team issues and impediments
- Evolves into more of a facilitator and communicator role
1.2.1 Explore gaps in Agile/ product-centric delivery of projects
5-10 minutes
Output: An assessment of what is in the way to effectively deliver on Agile and product-focused projects
Participants: Executives, Product/project managers, Applications teams
- Discuss as a group:
- What project management activities do you see in Agile/product roles?
- What gaps do you see?
- How can project management help Agile/product teams be successful?
Step 1.3
Specify the Different Activities for Project Management
Activities
- 1.3.1 Articulate the changes in a project manager’s role
This step involves the following participants:
- Executives
- Product/Project managers
- Applications teams
Outcomes of this step
- An understanding of the role of project management in an Agile and product context
Kicking off the project
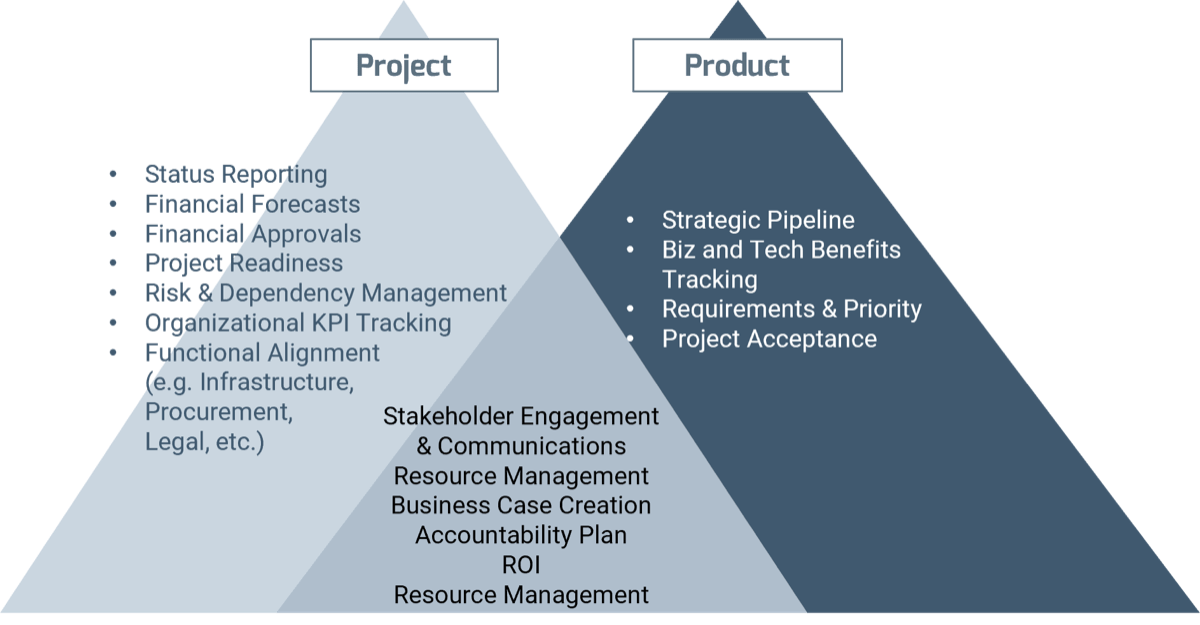
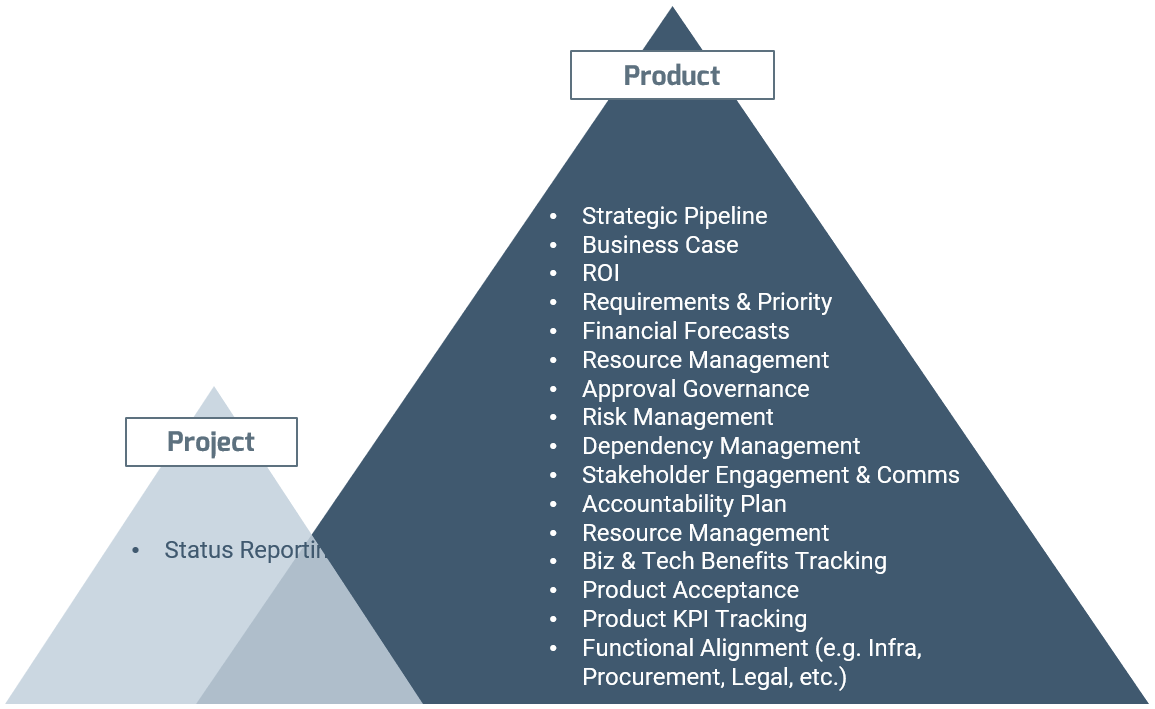
Product-centric delivery still requires key activities to successfully deliver value. Where project managers get their information from does change.
|
|
||||
Info-Tech Insight
- Product management plays a similar role to the one that was traditionally filled by the project sponsor except for a personal accountability to the product beyond the life of the project.
- When fully transitioned to product-centric delivery, these activities could be replaced by a product canvas. See Deliver on Your Digital Product Vision for more information.
During the project: Three key activities
The role of project management evolves from a position of ownership to a position of communication, collaboration, and coordination.
|
|
1.3.1: Articulate the changes in a project manager’s role
5-10 minutes
Output: Current understanding of the role of project management in Agile/product delivery
Participants: Executives, Product/project managers, Applications teams
Why is this important?
Project managers still have a role to play in Agile projects and products. Agreeing to what they should be doing is critical to successfully moving to a product-centric approach to delivery.
- Review how Info-Tech views the role of project management at project initiation and during the project.
- Review the state of your Agile and product transformation, paying special attention to who performs which roles.
- Discuss as a group:
- What are the current activities of project managers in your organization?
- Based on how you see delivery practices evolving, what do you see as the new role of project managers when it comes to Agile-centric and product-centric delivery.
Step 1.4
Identify Key Differences in Funding of Products Instead of Projects
Activities
- 1.4.1 Discuss traditional versus product-centric funding methods
This step involves the following participants:
- Executives
- Product owners
- Product managers
- Project managers
- Delivery managers
Outcomes of this step
- Identified differences in funding of products instead of projects
Planning and budgeting for products and families
Reward for delivering outcomes, not features
| Autonomy
Fund what delivers value Fund long-lived delivery of value through products (not projects). Give autonomy to the team to decide exactly what to build. | Flexibility
Allocate iteratively Allocate to a pool based on higher-level business case. Provide funds in smaller amounts to different product teams and initiatives based on need. |
| Accountability
Measure and adjust Product teams define metrics that contribute to given outcomes. Track progress and allocate more (or less) funds as appropriate. |  Info-Tech InsightChanges to funding require changes to product and Agile practices to ensure product ownership and accountability. |
(Adapted from Bain & Company)
Budgeting approaches must evolve as you mature your product operating environment
| TRADITIONAL PROJECTS WITH WATERFALL DELIVERY | TRADITIONAL PROJECTS WITH AGILE DELIVERY | PRODUCTS WITH AGILE PROJECT DELIVERY | PRODUCTS WITH AGILE DELIVERY | |
WHEN IS THE BUDGET TRACKED? |
Budget tracked by major phases | Budget tracked by sprint and project | Budget tracked by sprint and project | Budget tracked by sprint and release |
HOW ARE CHANGES HANDLED? |
All change is by exception | Scope change is routine; budget change is by exception | Scope change is routine; budget change is by exception | Budget change is expected on roadmap cadence |
WHEN ARE BENEFITS REALIZED? |
Benefits realization post project completion | Benefits realization ongoing throughout the life of the project | Benefits realization ongoing throughout the life of the product | Benefits realization ongoing throughout life of the product |
WHO DRIVES? |
Project Manager
|
Product Owner
|
Product Manager
|
Product Manager
|
| ˆ ˆ
Hybrid Operating Environments |
||||
Info-Tech Insight
As you evolve your approach to product delivery, you will be decoupling the expected benefits, forecast, and budget. Managing them independently will improve your ability adapt to change and drive the right outcomes!
1.4.1 Discuss traditional versus product-centric funding methods
30 minutesOutput: Understanding of funding principles and challenges
Participants: Executives, Product owners, Product managers, Project managers, Delivery managers
- Discuss how projects are currently funded.
- Review how the Agile/product funding models differ from how you currently operate.
- What changes do you need to consider to support a product delivery model?
- For each change, identify the key stakeholders and list at least one action to take.
Case Study
| Global Digital Financial Services Company
This financial services company looked to drive better results by adopting more product-centric practices.
Results
|
|
Where Do I Go Next?
|
Deliver on Your Digital Product Vision
Implement Agile Practices That Work
Implement DevOps Practices That Work
Prepare an Actionable Roadmap for Your PMO
|
Deliver Digital Products at Scale
Extend Agile Practices Beyond IT
Spread Best Practices With an Agile Center of Excellence
Tailor IT Project Management Processes to Fit Your Projects
|
Bibliography
Cobb, Chuck. “Are there Project Managers in Agile?” High Impact Project Management, n.d. Web.
Cohn, Mike. “What Is a Product?” Mountain Goat Software, 6 Sept. 2016. Web.
Cobb, Chuck. “Agile Project Manager Job Description.” High Impact Project Management, n.d. Web.
“How do you define a product?” Scrum.org, 4 April 2017. Web.
Johnson, Darren, et al. “How to Plan and Budget for Agile at Scale.” Bain & Company, 8 Oct. 2019. Web.
“Product Definition.” SlideShare, uploaded by Mark Curphey, 25 Feb. 2007. Web.
Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide). 7th ed., Project Management Institute, 2021.
Schuurman, Robbin. “Scrum Master vs Project Manager – An Overview of the Differences.” Scrum.org, 11 Feb 2020. Web.
Schuurman, Robbin. “Product Owner vs Project Manager.” Scrum.org, 12 March 2020. Web.
Vlaanderen, Kevin. “Towards Agile Product and Portfolio Management.” Academia.edu, 2010. Web.
“What is a Developer in Scrum?” Scrum.org, n.d. Web.
“What is a Scrum Master?” Scrum.org, n.d. Web.
“What is a Product Owner?” Scrum.org, n.d. Web.

