Create a Service Management Roadmap

- Inconsistent adoption of holistic practices has led to a chaotic service delivery model that results in poor customer satisfaction.
- There is little structure, formalization, or standardization in the way IT services are designed and managed, leading to diminishing service quality and low business satisfaction.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Having effective service management practices in place will allow you to pursue activities, such as innovation, and drive the business forward.
- Addressing foundational elements like business alignment and management practices will enable you to build effective core practices that deliver business value.
- Providing consistent leadership support and engagement is essential to allow practitioners to focus on delivering expected outcomes.
Impact and Result
- Understand the foundational and core elements that allow you to build a successful service management practice focused on outcomes.
- Use Info-Tech’s advice and tools to perform an assessment of your organization’s current state, identify the gaps, and create a roadmap for success.
- Increase business and customer satisfaction by delivering services focused on creating business value.
Create a Service Management Roadmap Research & Tools
Start here – read the Executive Brief
Read our concise Executive Brief to find out why many service management maturity projects fail to address foundational and core elements, review Info-Tech’s methodology, and understand the four ways we can support you in completing this project.Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
- Create a Service Management Roadmap – Phases 1-4
1. Launch the project
Kick-off the project and complete the project charter.
- Create a Service Management Roadmap – Phase 1: Launch Project
- Service Management Roadmap Project Charter
2. Assess the current state
Determine the current state for service management practices.
- Create a Service Management Roadmap – Phase 2: Assess the Current State
- Service Management Maturity Assessment Tool
- Organizational Change Management Capability Assessment Tool
- Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template
3. Build the roadmap
Build your roadmap with identified initiatives.
- Create a Service Management Roadmap – Phase 3: Identify the Target State
4. Build the communication slide
Create the communication slide that demonstrates how things will change, both short and long term.
- Create a Service Management Roadmap – Phase 4: Build the Roadmap
Workshop: Create a Service Management Roadmap
Workshops offer an easy way to accelerate your project. If you are unable to do the project yourself, and a Guided Implementation isn't enough, we offer low-cost delivery of our project workshops. We take you through every phase of your project and ensure that you have a roadmap in place to complete your project successfully.
1 Understand Service Management
The Purpose
Understand service management.
Key Benefits Achieved
Gain a common understanding of service management, the forces that impact your roadmap, and the Info-Tech Service Management Maturity Model.
Activities
1.1 Understand service management.
1.2 Build a compelling vision and mission.
Outputs
Constraints and enablers chart
Service management vision, mission, and values
2 Assess the Current State of Service Management
The Purpose
Assess the organization’s current service management capabilities.
Key Benefits Achieved
Understand attitudes, behaviors, and culture.
Understand governance and process ownership needs.
Understand strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Defined desired state.
Activities
2.1 Assess cultural ABCs.
2.2 Assess governance needs.
2.3 Perform SWOT analysis.
2.4 Define desired state.
Outputs
Cultural improvements action items
Governance action items
SWOT analysis action items
Defined desired state
3 Continue Current-State Assessment
The Purpose
Assess the organization’s current service management capabilities.
Key Benefits Achieved
Understand the current maturity of service management processes.
Understand organizational change management capabilities.
Activities
3.1 Perform service management process maturity assessment.
3.2 Complete OCM capability assessment.
3.3 Identify roadmap themes.
Outputs
Service management process maturity activities
OCM action items
Roadmap themes
4 Build Roadmap and Communication Tool
The Purpose
Use outputs from previous steps to build your roadmap and communication one-pagers.
Key Benefits Achieved
Easy-to-understand roadmap one-pager
Communication one-pager
Activities
4.1 Build roadmap one-pager.
4.2 Build communication one-pager.
Outputs
Service management roadmap
Service management roadmap – Brought to Life communication slide
Further reading
Create a Service Management Roadmap
Implement service management in an order that makes sense.
ANALYST PERSPECTIVE
"More than 80% of the larger enterprises we’ve worked with start out wanting to develop advanced service management practices without having the cultural and organizational basics or foundational practices fully in place. Although you wouldn’t think this would be the case in large enterprises, again and again IT leaders are underestimating the importance of cultural and foundational aspects such as governance, management practices, and understanding business value. You must have these fundamentals right before moving on."
Tony Denford,
Research Director – CIO
Info-Tech Research Group
Our understanding of the problem
This Research Is Designed For:
- CIO
- Senior IT Management
This Research Will Help You:
- Create or maintain service management (SM) practices to ensure user-facing services are delivered seamlessly to business users with minimum interruption.
- Increase the level of reliability and availability of the services provided to the business and improve the relationship and communication between IT and the business.
This Research Will Also Assist
- Service Management Process Owners
This Research Will Help Them:
- Formalize, standardize, and improve the maturity of service management practices.
- Identify new service management initiatives to move IT to the next level of service management maturity.
Executive summary
Situation
- Inconsistent adoption of holistic practices has led to a chaotic service delivery model that results in poor customer satisfaction.
- There is little structure, formalization, or standardization in the way IT services are designed and managed, leading to diminishing service quality and low business satisfaction.
Complication
- IT organizations want to be seen as strategic partners, but they fail to address the cultural and organizational constraints.
- Without alignment with the business goals, services often fail to provide the expected value.
- Traditional service management approaches are not adaptable for new ways of working.
Resolution
- Follow Info-Tech’s methodology to create a service management roadmap that will help guide the optimization of your IT services and improve IT’s value to the business.
- The blueprint will help you right-size your roadmap to best suit your specific needs and goals and will provide structure, ownership, and direction for service management.
- This blueprint allows you to accurately identify the current state of service management at your organization. Customize the roadmap and create a plan to achieve your target service management state.
Info-Tech Insight
Having effective service management practices in place will allow you to pursue activities such as innovation and drive the business forward. Addressing foundational elements like business alignment and management practices will enable you to build effective core practices that deliver business value. Consistent leadership support and engagement is essential to allow practitioners to focus on delivering expected outcomes.
Poor service management manifests in many different pains across the organization
Immaturity in service management will not result in one pain – rather, it will create a chaotic environment for the entire organization, crippling IT’s ability to deliver and perform.
Low Service Management Maturity
These are some of the pains that can be attributed to poor service management practices.
- Frequent service-impacting incidents
- Low satisfaction with the service desk
- High % of failed deployments
- Frequent change-related incidents
- Frequent recurring incidents
- Inability to find root cause
- No communication with the business
- Frequent capacity-related incidents
And there are many more…
Mature service management practices are a necessity, not a nice-to-have
Immature service management practices are one of the biggest hurdles preventing IT from reaching its true potential.
In 2004, PwC published a report titled “IT Moves from Cost Center to Business Contributor.” However, the 2014-2015 CSC Global CIO Survey showed that a high percentage of IT is still considered a cost center.
And low maturity of service management practices is inhibiting activities such as agility, DevOps, digitalization, and innovation.
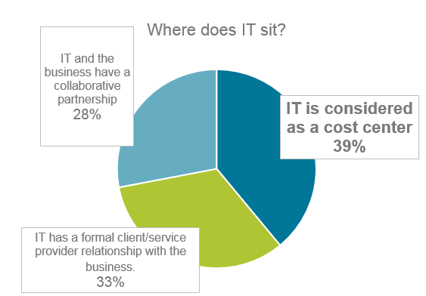
Source: CSC Global CIO Survey: 2014-2015 “CIOs Emerge as Disruptive Innovators”
39%: Resources are primarily focused on managing existing IT workloads and keeping the lights on.
31%: Too much time and too many resources are used to handle urgent incidents and problems.
There are many misconceptions about what service management is
Misconception #1: “Service management is a process”
Effective service management is a journey that encompasses a series of initiatives that improves the value of services delivered.
Misconception #2: “Service Management = Service Desk”
Service desk is the foundation, since it is the main end-user touch point, but service management is a set of people and processes required to deliver business-facing services.
Misconception #3: “Service management is about the ITSM tool”
The tool is part of the overall service management program, but the people and processes must be in place before implementing.
Misconception #4: “Service management development is one big initiative”
Service management development is a series of initiatives that takes into account an organization’s current state, maturity, capacities, and objectives.
Misconception #5: “Service management processes can be deployed in any order, assuming good planning and design”
A successful service management program takes into account the dependencies of processes.
Misconception #6: “Service management is resolving incidents and deploying changes”
Service management is about delivering high-value and high-quality services.
Misconception #7: “Service management is not the key determinant of success”
As an organization progresses on the service management journey, its ability to deliver high-value and high-quality services increases.
Misconception #8: “Resolving Incidents = Success”
Preventing incidents is the name of the game.
Misconception #9: “Service Management = Good Firefighter”
Service management is about understanding what’s going on with user-facing services and proactively improving service quality.
Misconception #10: “Service management is about IT and technical services (e.g. servers, network, database)”
Service management is about business/user-facing services and the value the services provide to the business.
Service management projects often don’t succeed because they are focused on process rather than outcomes
Service management projects tend to focus on implementing process without ensuring foundational elements of culture and management practices are strong enough to support the change.
- Aligning your service management goals with your organizational objectives leads to better understanding of the expected outcomes.
- IT does not know what order is best when implementing new practices or process improvements.
- IT does not follow best practices when implementing a practice.
Understand your customers and what they value, and design your practices to deliver this value.
Don't run before you can walk. Fundamental practices must reach the maturity threshold before developing advanced practices. Implement continuous improvement on your existing processes so they continue to support new practices.
Our best-practice research is based on extensive experience working with clients through advisory calls and workshops.
Info-Tech can help you create a customized, low-effort, and high-value service management roadmap that will shore up any gaps, prove IT’s value, and achieve business satisfaction.
Info-Tech’s methodology will help you customize your roadmap so the journey is right for you
With Info-Tech, you will find out where you are, where you want to go, and how you will get there.
With our methodology, you can expect the following:
- Eliminate or reduce rework due to poor execution.
- Identify dependencies/prerequisites and ensure practices are deployed in the correct order, at the correct time, and by the right people.
- Engage all necessary resources to design and implement required processes.
- Assess current maturity and capabilities and design the roadmap with these factors in mind.
Doing it right the first time around
You will see these benefits at the end
✓ Increase the quality of services IT provides to the business.
✓ Increase business satisfaction through higher alignment of IT services.
✓ Lower cost to design, implement, and manage services.
✓ Better resource utilization, including staff, tools, and budget.
Focus on a strong foundation to build higher value service management practices
Info-Tech Insight
Focus on behaviors and expected outcomes before processes.
Foundational elements
- Operating model facilitates service management goals
- Culture of service delivery
- Governance discipline to evaluate, direct, and monitor
- Management discipline to deliver
Stabilize
- Deliver stable, reliable IT services to the business
- Respond to user requests quickly and efficiently
- Resolve user issues in a timely manner
- Deploy changes smoothly and successfully
Proactive
- Avoid/prevent service disruptions
- Improve quality of service (performance, availability, reliability)
Service Provider
- Understand business needs
- Ensure services are available
- Measure service performance, based on business-oriented metrics
Strategic Partner
- Fully aligned with business
- Drive innovation
- Drive measurable value
Info-Tech Insight
Continued leadership support of the foundational elements will allow delivery teams to provide value to the business. Set the expectation of the desired maturity level and allow teams to innovate.
Follow our model and get to your target state
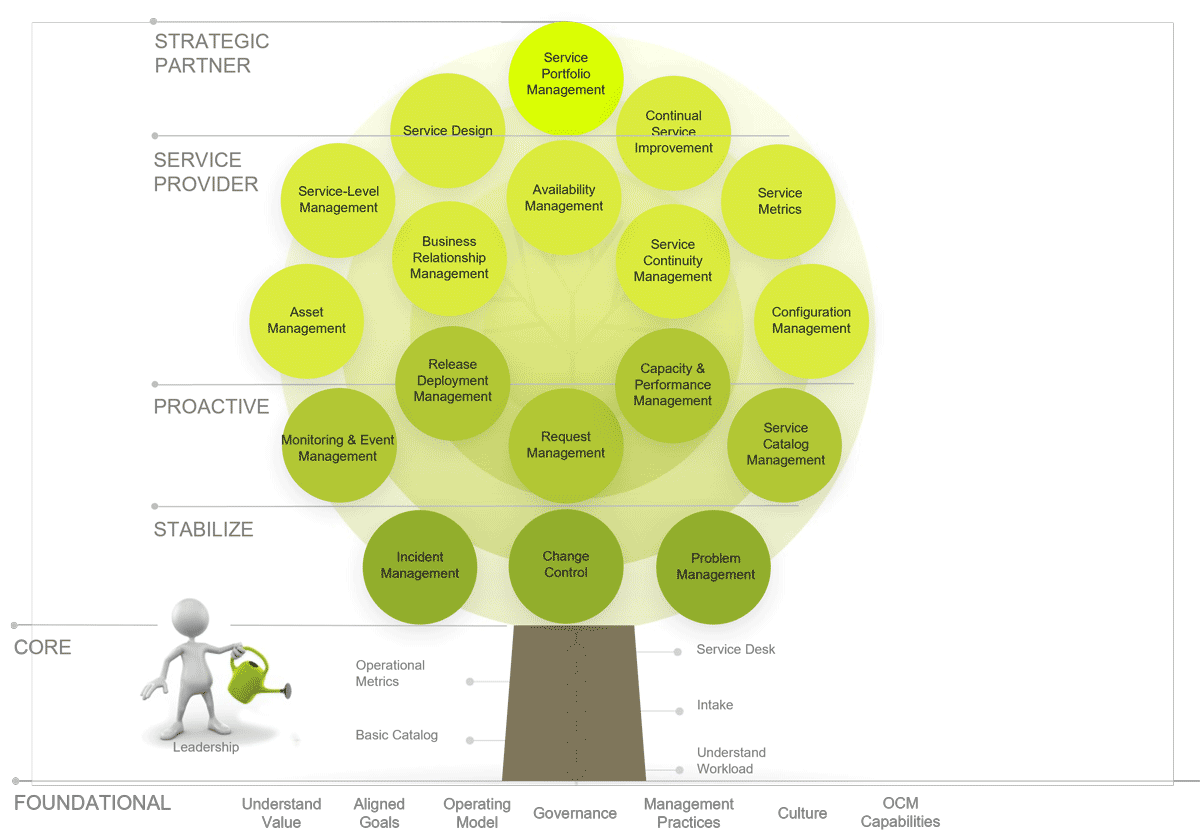
Before moving to advanced service management practices, you must ensure that the foundational and core elements are robust enough to support them. Leadership must nurture these practices to ensure they are sustainable and can support higher value, more mature practices.
Each step along the way, Info-Tech has the tools to help you
Phase 1: Launch the Project
Assemble a team with the right talent and vision to increase the chances of project success.
Phase 2: Assess Current State
Understand where you are currently on the service management journey using the maturity assessment tool.
Phase 3: Build Roadmap
Based on the assessments, build a roadmap to address areas for improvement.
Phase 4: Build Communication slide
Based on the roadmap, define the current state, short- and long-term visions for each major improvement area.
Info-Tech Deliverables:
- Project Charter
- Assessment Tools
- Roadmap Template
- Communication Template
CIO call to action
Improving the maturity of the organization’s service management practice is a big commitment, and the project can only succeed with active support from senior leadership.
Ideally, the CIO should be the project sponsor, even the project leader. At a minimum, the CIO needs to perform the following activities:
- Walk the talk – demonstrate personal commitment to the project and communicate the benefits of the service management journey to IT and the steering committee.
- Select a senior, capable, and results-driven project leader.
- Help to define the target future state of IT’s service management.
- Conduct periodic follow-up meetings to keep track of progress.
Improving or adopting any new practice is difficult, especially for a project of this size. Thus, the CIO needs to show visible support for this project through internal communication and dedicated resources to help complete this project.
Most likely, the implementation of this project will be lengthy and technical in some nature. Therefore, the project leader must have a good understanding of the current IT structure, senior standing within the organization, and the relationship and power in place to propel people into action.
Determine a realistic target state for the organization based on current capability and resource/budget restraints.
Reinforce or re-emphasize the importance of this project to the organization through various communication channels if needed.
Stabilizing your environment is a must before establishing any more-mature processes
CASE STUDY
Industry: Manufacturing
Source: Engagement
Challenge
- The business landscape was rapidly changing for this manufacturer and they wanted to leverage potential cost savings from cloud-first initiatives and consolidate multiple, self-run service delivery teams that were geographically dispersed.
Solution
Original Plan
- Consolidate multiple service delivery teams worldwide and implement service portfolio management.
Revised Plan with Service Management Roadmap:
- Markets around the world had very different needs and there was little understanding of what customers value.
- There was also no understanding of what services were currently being offered within each geography.
Results
- Plan was adjusted to understand customer value and services offered.
- Services were then stabilized and standardized before consolidation.
- Team also focused on problem maturity and drove a continuous improvement culture and increasing transparency.
MORAL OF THE STORY:
Understanding the value of each service allowed the organization to focus effort on high-return activities rather than continuous fire fighting.
Understand the processes involved in the proactive phase
CASE STUDY
Industry: Manufacturing
Source: Engagement
Challenge
- Services were fairly stable, but there were significant recurring issues for certain services.
- The business was not satisfied with the service quality for certain services, due to periodic availability and reliability issues.
- Customer feedback for the service desk was generally good.
Solution
Original Plan
- Review all service desk and incident management processes to ensure that service issues were handled in an effective manner.
Revised Plan with Service Management Roadmap:
- Design and deploy a rigorous problem management process to determine the root cause of recurring issues.
- Monitor key services for events that may lead to a service outage.
Results
- Root cause of recurring issues was determined and fixes were deployed to resolve the underlying cause of the issues.
- Service quality improved dramatically, resulting in high customer satisfaction.
MORAL OF THE STORY:
Make sure that you understand which processes need to be reviewed in order to determine the cause for service instability. Focusing on the proactive processes was the right answer for this company.
Have the right culture and structure in place before you become a service provider
CASE STUDY
Industry: Healthcare
Source:Journal of American Medical Informatics Association
Challenge
- The IT organization wanted to build a service catalog to demonstrate the value of IT to the business.
- IT was organized in technology silos and focused on applications, not business services.
- IT services were not aligned with business activities.
- Relationships with the business were not well established.
Solution
Original Plan
- Create and publish a service catalog.
Revised Plan: with Service Management Roadmap:
- Establish relationships with key stakeholders in the business units.
- Understand how business activities interface with IT services.
- Lay the groundwork for the service catalog by defining services from the business perspective.
Results
- Strong relationships with the business units.
- Deep understanding of how business activities map to IT services.
- Service definitions that reflect how the business uses IT services.
MORAL OF THE STORY:
Before you build and publish a service catalog, make sure that you understand how the business is using the IT services that you provide.
Calculate the benefits of using Info-Tech’s methodology
To measure the value of developing your roadmap using the Info-Tech tools and methodology, you must calculate the effort saved by not having to develop the methods.
A. How much time will it take to develop an industry-best roadmap using Info-Tech methodology and tools?
Using Info-Tech’s tools and methodology you can accurately estimate the effort to develop a roadmap using industry-leading research into best practice.
B. What would be the effort to develop the insight, assess your team, and develop the roadmap?
This metric represents the time your team would take to be able to effectively assess themselves and develop a roadmap that will lead to service management excellence.
C. Cost & time saving through Info-Tech’s methodology
Measured Value |
|
|---|---|
Step 1: Assess current state |
Cost to assess current state:
|
Step 2: Build the roadmap |
Cost to create service management roadmap:
|
Step 3: Develop the communication slide |
Cost to create roadmaps for phases:
|
Potential financial savings from using Info-Tech resources: |
Estimated cost to do “B” – (Step 1 ($A) + Step 2 ($B) + Step 3 ($C)) = $Total Saving |
Info-Tech offers various levels of support to best suit your needs
DIY Toolkit
"Our team has already made this critical project a priority, and we have the time and capability, but some guidance along the way would be helpful."
Guided Implementation
"Our team knows that we need to fix a process, but we need assistance to determine where to focus. Some check-ins along the way would help keeps us on track."
Workshop
"We need to hit the ground running and get this project kicked off immediately. Our team has the ability to take this over once we get a framework and strategy in place."
Consulting
"Our team does not have the time or the knowledge to take this project on. We need assistance through the entirety of this project."
Diagnostics and consistent frameworks are used throughout all four options.
Create a Service Management Roadmap – project overview
Launch the project |
Assess the current state |
Build the roadmap |
Build communication slide |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Best-Practice Toolkit |
1.1 Create a powerful, succinct mission statement 1.2 Assemble a project team with representatives from all major IT teams 1.3 Determine project stakeholders and create a communication plan 1.4 Establish metrics to track the success of the project |
2.1 Assess impacting forces 2.2 Build service management vision, mission, and values 2.3 Assess attitudes, behaviors, and culture 2.4 Assess governance 2.5 Perform SWOT analysis 2.6 Identify desired state 2.7 Assess SM maturity 2.8 Assess OCM capabilities |
3.1 Document overall themes 3.2 List individual initiatives |
4.1 Document current state 4.2 List future vision |
Guided Implementations |
|
|
|
|
Onsite Workshop |
Module 1: Launch the project |
Module 2: Assess current service management maturity |
Module 3: Complete the roadmap |
Module 4: Complete the communication slide |
Workshop overview
Contact your account representative or email Workshops@InfoTech.com for more information
Workshop Day 1 |
Workshop Day 2 |
Workshop Day 3 |
Workshop Day 4 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Activities |
Understand Service Management 1.1 Understand the concepts and benefits of service management. 1.2 Understand the changing impacting forces that affect your ability to deliver services. 1.3 Build a compelling vision and mission for your service management program. |
Assess the Current State of Your Service Management Practice 2.1 Understand attitudes, behaviors, and culture. 2.2 Assess governance and process ownership needs. 2.3 Perform SWOT analysis. 2.4 Define the desired state. |
Complete Current-State Assessment 3.1 Conduct service management process maturity assessment. 3.2 Identify organizational change management capabilities. 3.3 Identify themes for roadmap. |
Build Roadmap and Communication Tool 4.1 Build roadmap one-pager. 4.2 Build roadmap communication one-pager. |
Deliverables |
|
|
|
|
PHASE 1
Launch the Project
Launch the project
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Create a powerful, succinct mission statement based on your organization’s goals and objectives.
- Assemble a project team with representatives from all major IT teams.
- Determine project stakeholders and create a plan to convey the benefits of this project.
- Establish metrics to track the success of the project.
Step Insights
- The project leader should have a strong relationship with IT and business leaders to maximize the benefit of each initiative in the service management journey.
- The service management roadmap initiative will touch almost every part of the organization; therefore, it is important to have representation from all impacted stakeholders.
- The communication slide needs to include the organizational change impact of the roadmap initiatives.
Phase 1 outline
Call 1-888-670-8889 or email GuidedImplementations@InfoTech.com for more information.
Complete these steps on your own, or call us to complete a guided implementation. A guided implementation is a series of 2-3 advisory calls that help you execute each phase of a project. They are included in most advisory memberships.
Guided Implementation 1: Launch the Project |
|
|---|---|
Step 1.1 – Kick-off the Project Start with an analyst kick-off call:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates:
|
Step 1.2 – Complete the Charter Review findings with analyst:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates:
|
Use Info-Tech’s project charter to begin your initiative
1.1 Service Management Roadmap Project Charter
The Service Management Roadmap Project Charter is used to govern the initiative throughout the project. It provides the foundation for project communication and monitoring.
The template has been pre-populated with sample information appropriate for this project. Please review this sample text and change, add, or delete information as required.
The charter includes the following sections:
- Mission Statement
- Goals & Objectives
- Project Team
- Project Stakeholders
- Current State (from phases 2 & 3)
- Target State (from phases 2 & 3)
- Target State
- Metrics
- Sponsorship Signature

Use Info-Tech’s ready-to-use deliverable to customize your mission statement
Adapt and personalize Info-Tech’s Service Management Roadmap Mission Statement and Goals & Objectives below to suit your organization’s needs.
Goals & Objectives
- Create a plan for implementing service management initiatives that align with the overall goals/objectives for service management.
- Identify service management initiatives that must be implemented/improved in the short term before deploying more advanced initiatives.
- Determine the target state for each initiative based on current maturity and level of investment available.
- Identify service management initiatives and understand dependencies, prerequisites, and level of effort required to implement.
- Determine the sequence in which initiatives should be deployed.
- Create a detailed rollout plan that specifies initiatives, time frames, and owners.
- Engage the right teams and obtain their commitment throughout both the planning and assessment of roadmap initiatives.
- both the planning and assessment of roadmap initiatives. Obtain support for the completed roadmap from executive stakeholders.
Example Mission Statement
To help [Organization Name] develop a set of service management practices that will better address the overarching goals of the IT department.
To create a roadmap that sequences initiatives in a way that incorporates best practices and takes into consideration dependencies and prerequisites between service management practices.
To garner support from the right people and obtain executive buy-in for the roadmap.
Create a well-balanced project team
The project leader should be a member of your IT department’s senior executive team with goals and objectives that will be impacted by service management implementation. The project leader should possess the following characteristics:
Leader
- Influence and impact
- Comprehensive knowledge of IT and the organization
- Relationship with senior IT management
- Ability to get things done
Team Members
Identify
The project team members are the IT managers and directors whose day-to-day lives will be impacted by the service management roadmap and its implementation. The service management initiative will touch almost every IT staff member in the organization; therefore, it is important to have representatives from every single group, including those that are not mentioned. Some examples of individuals you should consider for your team:
- Service Delivery Managers
- Director/Manager of Applications
- Director/Manager of Infrastructure
- Director/Manager of Service Desk
- Business Relationship Managers
- Project Management Office
Engage & Communicate
You want to engage your project participants in the planning process as much as possible. They should be involved in the current-state assessment, the establishment of goals and objectives, and the development of your target state.
To sell this project, identify and articulate how this project and/or process will improve the quality of their job. For example, a formal incident management process will benefit people working at the service desk or on the applications or infrastructure teams. Helping them understand the gains will help to secure their support throughout the long implementation process by giving them a sense of ownership.
The project stakeholders should also be project team members
When managing stakeholders, it is important to help them understand their stake in the project as well as their own personal gain that will come out of this project.
For many of the stakeholders, they also play a critical role in the development of this project.
Role & Benefits
- CIO
- Service Delivery Managers/Process Owners
- IT Steering Committee
- Manager/Director – Service Desk
- Manager/Director –Applications & Infrastructure
- Business Relationship Manager
The CIO should be actively involved in the planning stage to help determine current and target stage.
The CIO also needs to promote and sell the project to the IT team so they can understand that higher maturity of service management practices will allow IT to be seen as a partner to the business, giving IT a seat at the table during decision making.
Service Delivery Managers are directly responsible for the quality and value of services provided to the business owners. Thus, the Service Delivery Managers have a very high stake in the project and should be considered for the role of project leader.
Service Delivery Managers need to work closely with the process owners of each service management process to ensure clear objectives are established and there is a common understanding of what needs to be achieved.
The Committee should be informed and periodically updated about the progress of the project.
The Manager of the Service Desk should participate closely in the development of fundamental service management processes, such as service desk, incident management, and problem management.
Having a more established process in place will create structure, governance, and reduce service desk staff headaches so they can handle requests or incidents more efficiently.
The Manager of Applications and Infrastructure should be heavily relied on for their knowledge of how technology ties into the organization. They should be consulted regularly for each of the processes.
This project will also benefit them directly, such as improving the process to deploy a fix into the environment or manage the capacity of the infrastructure.
As the IT organization moves up the maturity ladder, the Business Relationship Manager will play a fundamental role in the more advanced processes, such as business relationship management, demand management, and portfolio management.
This project will be an great opportunity for the Business Relationship Manager to demonstrate their value and their knowledge of how to align IT objectives with business vision.
Ensure you get the entire IT organization on board for the project with a well-practiced change message
Getting the IT team on board will greatly maximize the project’s chance of success.
One of the top challenges for organizations embarking on a service management journey is to manage the magnitude of the project. To ensure the message is not lost, communicate this roadmap in two steps.
1. Communicate the roadmap initiative
The most important message to send to the IT organization is that this project will benefit them directly. Articulate the pains that IT is currently experiencing and explain that through more mature service management, these pains can be greatly reduced and IT can start to earn a place at the table with the business.
2. Communicate the implementation of each process separately
The communication of process implementation should be done separately and at the beginning of each implementation. This is to ensure that IT staff do not feel overwhelmed or overloaded. It also helps to keep the project more manageable for the project team.
Continuously monitor feedback and address concerns throughout the entire process
- Host lunch and learns to provide updates on the service management initiative to the entire IT team.
- Understand if there are any major roadblocks and facilitate discussions on how to overcome them.
Articulate the service management initiative to the IT organization
Spread the word and bring attention to your change message through effective mediums and organizational changes.
Key aspects of a communication plan
The methods of communication (e.g. newsletters, email broadcast, news of the day, automated messages) notify users of implementation.
In addition, it is important to know who will deliver the message (delivery strategy). You need IT executives to deliver the message – work hard on obtaining their support as they are the ones communicating to their staff and should be your project champions.
Anticipate organizational changes
The implementation of the service management roadmap will most likely lead to organizational changes in terms of structure, roles, and responsibilities. Therefore, the team should be prepared to communicate the value that these changes will bring.
Communicating Change
- What is the change?
- Why are we doing it?
- How are we going to go about it?
- What are we trying to achieve?
- How often will we be updated?
Create a project communication plan for your stakeholders
This project cannot be successfully completed without the support of senior IT management.
- After the CIO has introduced this project through management meetings or informal conversation, find out how each IT leader feels about this project. You need to make sure the directors and managers of each IT team, especially the directors of application and infrastructure, are on board.
- After the meeting, the project leader should seek out the major stakeholders (particularly the heads of applications and infrastructure) and validate their level of support through formal or informal meetings. Create a list documenting the major stakeholders, their level of support, and how the project team will work to gain their approval.
- For each identified stakeholder, create a custom communication plan based on their role. For example, if the director of infrastructure is not a supporter, demonstrate how this project will enable them to better understand how to improve service quality. Provide periodic reporting or meetings to update the director on project progress.
INPUT
- A collaborative discussion between team members
OUTPUT
- Thorough briefing for project launch
- A committed team
Materials
- Communication message and plan
- Metric tracking
Participants
- Project leader
- Core project team
If you want additional support, have our analysts guide you through this phase as part of an Info-Tech workshop
Book a workshop with our Info-Tech analysts:

- To accelerate this project, engage your IT team in an Info-Tech workshop with an Info-Tech analyst team.
- Info-Tech analysts will join you and your team onsite at your location or welcome you to Info-Tech’s historic Toronto office to participate in an innovative onsite workshop.
- Contact your account manager (www.infotech.com/account), or email Workshops@InfoTech.com for more information.
The following are sample activities that will be conducted by Info-Tech analysts with your team:
1.1

Create a powerful, succinct mission statement
Using Info-Tech’s sample mission statement as a guide, build your mission statement based on the objectives of this project and the benefits that this project will achieve. Keep the mission statement short and clear.
1.2

Assemble the project team
Create a project team with representatives from all major IT teams. Engage and communicate to the project team early and proactively.
1.3

Identify project stakeholders and create a communication plan
Info-Tech will help you identify key stakeholders who have a vested interest in the success of the project. Determine the communication message that will best gain their support.
1.4

Use metrics to track the success of the project
The onsite analyst will help the project team determine the appropriate metrics to measure the success of this project.
PHASE 2
Assess Your Current Service Management State
Assess your current state
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Use Info-Tech’s Service Management Maturity Assessment Tool to determine your overall practice maturity level.
- Understand your level of completeness for each individual practice.
- Understand the three major phases involved in the service management journey; know the symptoms of each phase and how they affect your target state selection.
Step Insights
- To determine the real maturity of your service management practices, you should focus on the results and output of the practice, rather than the activities performed for each process.
- Focus on phase-level maturity as opposed to the level of completeness for each individual process.
Phase 2 outline
Call 1-888-670-8889 or email GuidedImplementations@InfoTech.com for more information.
Complete these steps on your own, or call us to complete a guided implementation. A guided implementation is a series of 2-3 advisory calls that help you execute each phase of a project. They are included in most advisory memberships.
Guided Implementation 2: Determine Your Service Management Current State | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 2.1 – Assess Impacting Forces Start with an analyst kick-off call:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template | Step 2.2 – Build Vision, Mission, and Values Review findings with analyst:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template | Step 2.3 – Assess Attitudes, Behaviors, and Culture Review findings with analyst:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template | Step 2.4 – Assess Governance Needs Review findings with analyst:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template | Step 2.5 – Perform SWOT Analysis Review findings with analyst:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template | Step 2.6 – Identify Desired State Review findings with analyst:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template | Step 2.7 – Perform SM Maturity Assessment Review findings with analyst:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template Service Management Maturity Assessment | Step 2.8 – Review OCM Capabilities Review findings with analyst:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template Organizational Change Management Assessment |
Understand and assess impacting forces – constraints and enablers
Constraints and enablers are organizational and behavioral triggers that directly impact your ability and approach to establishing Service Management practices.
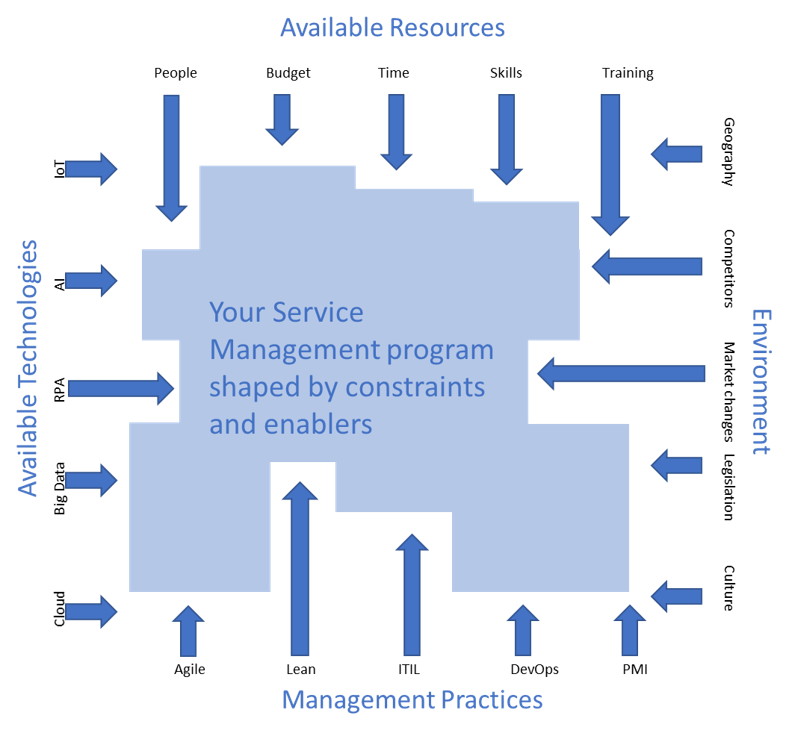
Effective service management requires a mix of different approaches and practices that best fit your organization. There’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. Consider the resources, environment, emerging technologies, and management practices facing your organization. What items can you leverage or use to mitigate to move your service management program forward?
Use Info-Tech’s “Organizational Context” template to list the constraints and enablers affecting your service management
The Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template will help you understand the business environment you need to consider as you build out your roadmap.
Discuss and document constraints and enablers related to the business environment, available resources, management practices, and emerging technologies. Any constraints will need to be addressed within your roadmap and enablers should be leveraged to maximize your results.

Document constraints and enablers
- Discuss and document the constrains and enablers for each aspect of the management mesh: environment, resources, management practices, or technology.
- Use this as a thought provoker in later exercises.
INPUT
- A collaborative discussion
OUTPUT
- Organizational context constraints and enablers
Materials
- Whiteboards or flip charts
Participants
- All stakeholders
Build compelling vision and mission statements to set the direction of your service management program
While you are articulating the vision and mission, think about the values you want the team to display. Being explicit can be a powerful tool to create alignment.
A vision statement describes the intended state of your service management organization, expressed in the present tense.
A mission statement describes why your service management organization exists.
Your organizational values state how you will deliver services.
Use Info-Tech’s “Vision, Mission, and Values” template to set the aspiration & purpose of your service management practice
The Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template will help you document your vision for service management, the purpose of the program, and the values you want to see demonstrated.
If the team cannot gain agreement on their reason for being, it will be difficult to make traction on the roadmap items. A concise and compelling statement can set the direction for desired behavior and help team members align with the vision when trying to make ground-level decisions. It can also be used to hold each other accountable when undesirable behavior emerges. It should be revised from time to time, when the environment changes, but a well-written statement should stand the test of time.

Document your organization’s vision, mission , and values
- Vision: Identify your desired target state, consider the details of that target state, and create a vision statement.
- Mission: Consider the fundamental purpose of your SM program and craft a statement of purpose.
- Values: As you work through the vision and mission, identify values that your organization prides itself in or has the aspiration for.
- Discuss common themes and then develop a concise vision statement and mission statement that incorporates the group’s ideas.
INPUT
- A collaborative discussion
OUTPUT
- Vision statement
- Mission statement
- Organizational values
Materials
- Whiteboards or flip charts
- Sample vision and mission statements
Participants
- All stakeholders
- Senior leadership
Understanding attitude, behavior, and culture
Attitude
- What people think and feel. It can be seen in their demeanor and how they react to change initiatives, colleagues, and users.
Any form of organizational change involves adjusting people’s attitudes, creating buy-in and commitment. You need to identify and address attitudes that can lead to negative behaviors and actions or that are counter-productive. It must be made visible and related to your desired behavior.
Behaviour
- What people do. This is influenced by attitude and the culture of the organization.
To implement change within IT, especially at a tactical level, both IT and organizational behavior needs to change. This is relevant because people don’t like to change and will resist in an active or passive way unless you can sell the need, value, and benefit of changing their behavior.
Culture
- The accepted and understood ways of working in an organization. The values and standards that people find normal and what would be tacitly identified to new resources.
The organizational or corporate “attitude,” the impact on employee behavior and attitude is often not fully understood. Culture is an invisible element, which makes it difficult to identify, but it has a strong impact and must be addressed to successfully embed any organizational change or strategy.
Culture is a critical and under-addressed success factor
43% of CIOs cited resistance to change as the top impediment to a successful digital strategy.
CIO.com
75% of organizations cannot identify or articulate their culture or its impact.
Info-Tech
“Shortcomings in organizational culture are one of the main barriers to company success in the digital age.”
McKinsey – “Culture for a digital age”
Examples of how they apply
Attitude
- “I’ll believe that when I see it”
- Positive outlook on new ideas and changes
Behaviour
- Saying you’ll follow a new process but not doing so
- Choosing not to document a resolution approach or updating a knowledge article, despite being asked
Culture
- Hero culture (knowledge is power)
- Blame culture (finger pointing)
- Collaborative culture (people rally and work together)
Why have we failed to address attitude, behavior, and culture?
✓ While there is attention and better understanding of these areas, very little effort is made to actually solve these challenges.
✓ The impact is not well understood.
✓ The lack of tangible and visible factors makes it difficult to identify.
✓ There is a lack of proper guidance, leadership skills, and governance to address these in the right places.
✓ Addressing these issues has to be done proactively, with intent, rigor, and discipline, in order to be successful.
✓ We ignore it (head in the sand and hoping it will fix itself).
Avoidance has been a common strategy for addressing behavior and culture in organizations.
Use Info-Tech’s “Culture and Environment” template to identify cultural constraints that should be addressed in roadmap
The Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template will help you document attitude, behavior, and culture constraints.
Discuss as a team attitudes, behaviors, and cultural aspects that can either hinder or be leveraged to support your vision for the service management program. Capture all items that need to be addressed in the roadmap.
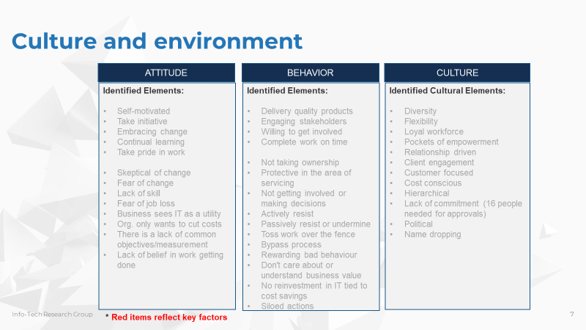
Document your organization’s attitudes, behaviors, and culture
- Discuss and document positive and negative aspects of attitude, behavior, or culture within your organization.
- Identify the items that need to be addressed as part of your roadmap.
INPUT
- A collaborative discussion
OUTPUT
- Culture and environment worksheet
Materials
- Whiteboards or flip charts
Participants
- All stakeholders
The relationship to governance
Attitude, behavior, and culture are still underestimated as core success factors in governance and management.
Behavior is a key enabler of good governance. Leading by example and modeling behavior has a cascading impact on shifting culture, reinforcing the importance of change through adherence.
Executive leadership and governing bodies must lead and support cultural change.
Key Points
- Less than 25% of organizations have formal IT governance in place (ITSM Tools).
- Governance tends to focus on risk and compliance (controls), but forgets the impact of value and performance.
Lack of oversight often limits the value of service management implementations
Organizations often fail to move beyond risk mitigation, losing focus of the goals of their service management practices and the capabilities required to produce value.
Risk Mitigation
- Stabilize IT
- Service Desk
- Incident Management
- Change Management
Gap
- Organizational alignment through governance
- Disciplined focus on goals of SM
Value Production
- Value that meets business and consumer needs
This creates a situation where service management activities and roadmaps focus on adjusting and tweaking process areas that no longer support how the organization needs to work.
How does establishing governance for service management provide value?
Governance of service management is a gap in most organizations, which leads to much of the failure and lack of value from service management processes and activities.
Once in place, effective governance enables success for organizations by:
- Ensuring service management processes improve business value
- Measuring and confirming the value of the service management investment
- Driving a focus on outcome and impact instead of simply process adherence
- Looking at the integrated impact of service management in order to ensure focused prioritization of work
- Driving customer-experience focus within organizations
- Ensuring quality is achieved and addressing quality impacts and dependencies between processes
Four common service management process ownership models
Your ownership structure largely defines how processes will need to be implemented, maintained, and improved. It has a strong impact on their ability to integrate and how other teams perceive their involvement.
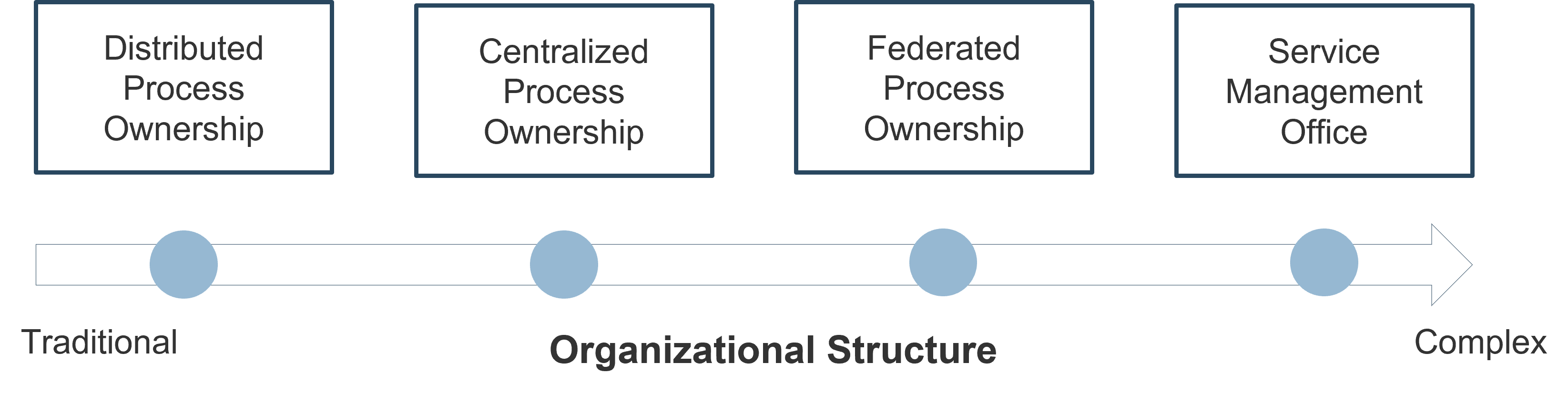
Most organizations are somewhere within this spectrum of four core ownership models, usually having some combination of shared traits between the two models that are closest to them on the scale.
Info-Tech Insight
The organizational structure that is best for you depends on your needs, and one is not necessarily better than another. The next four slides describe when each ownership level is most appropriate.
Distributed process ownership
Distributed process ownership is usually evident when organizations initially establish their service management practices. The processes are assigned to a specific group, who assumes some level of ownership over its execution.
Info-Tech Insight
This model is often a suitable approach for initial implementations or where it may be difficult to move out of siloes within the organization’s structure or culture.
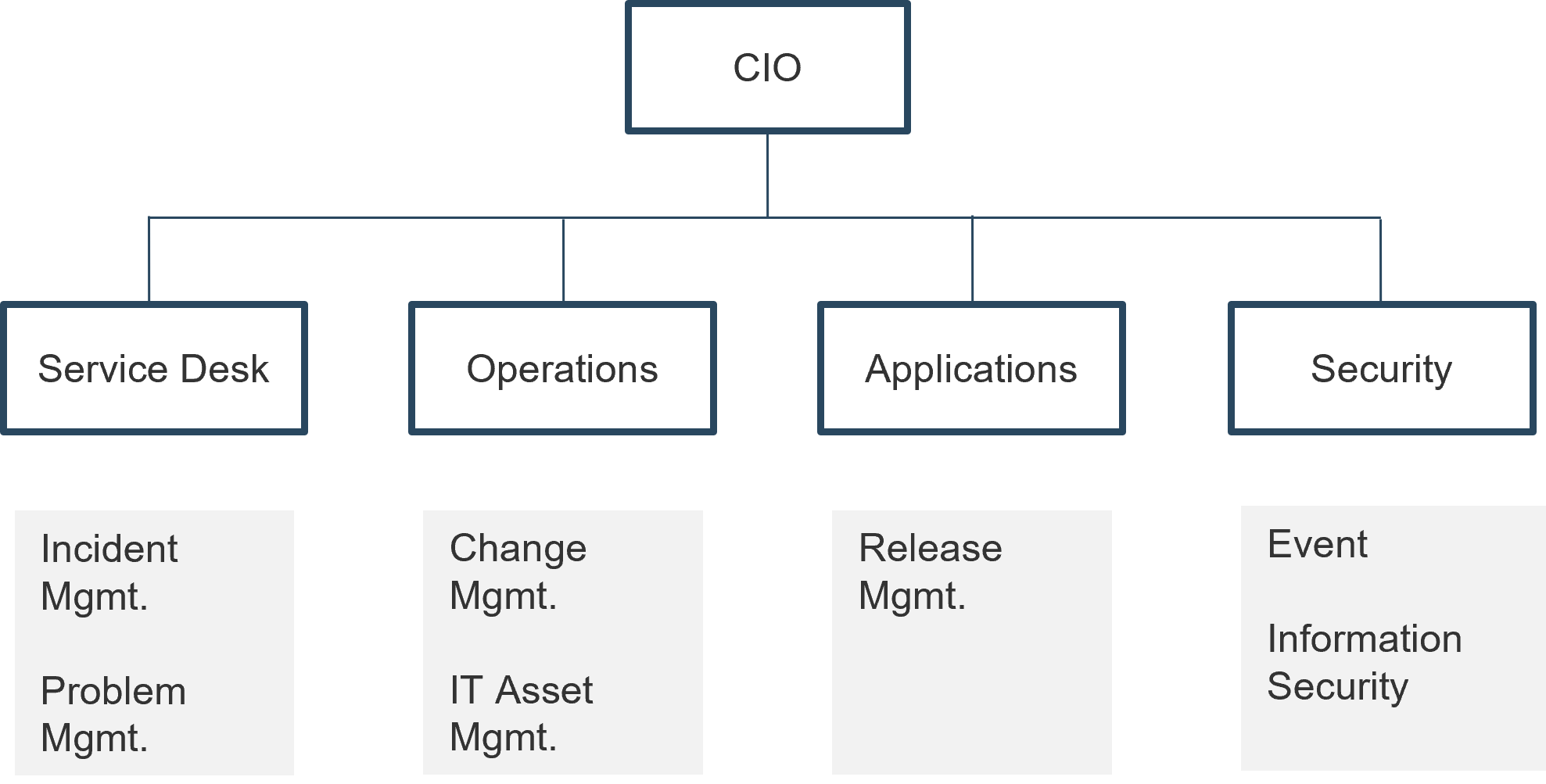
Centralized process ownership
Centralized process ownership usually becomes necessary for organizations as they move into a more functional structure. It starts to drive management of processes horizontally across the organization while still retaining functional management control.
Info-Tech Insight
This model is often suitable for maturing organizations that are starting to look at process integration and shared service outcomes and accountability.
Federated process ownership
Federated process ownership allows for global control and regional variation, and it supports product orientation and Agile/DevOps principles
Info-Tech Insight
Federated process ownership is usually evident in organizations that have an international or multi-regional presence.
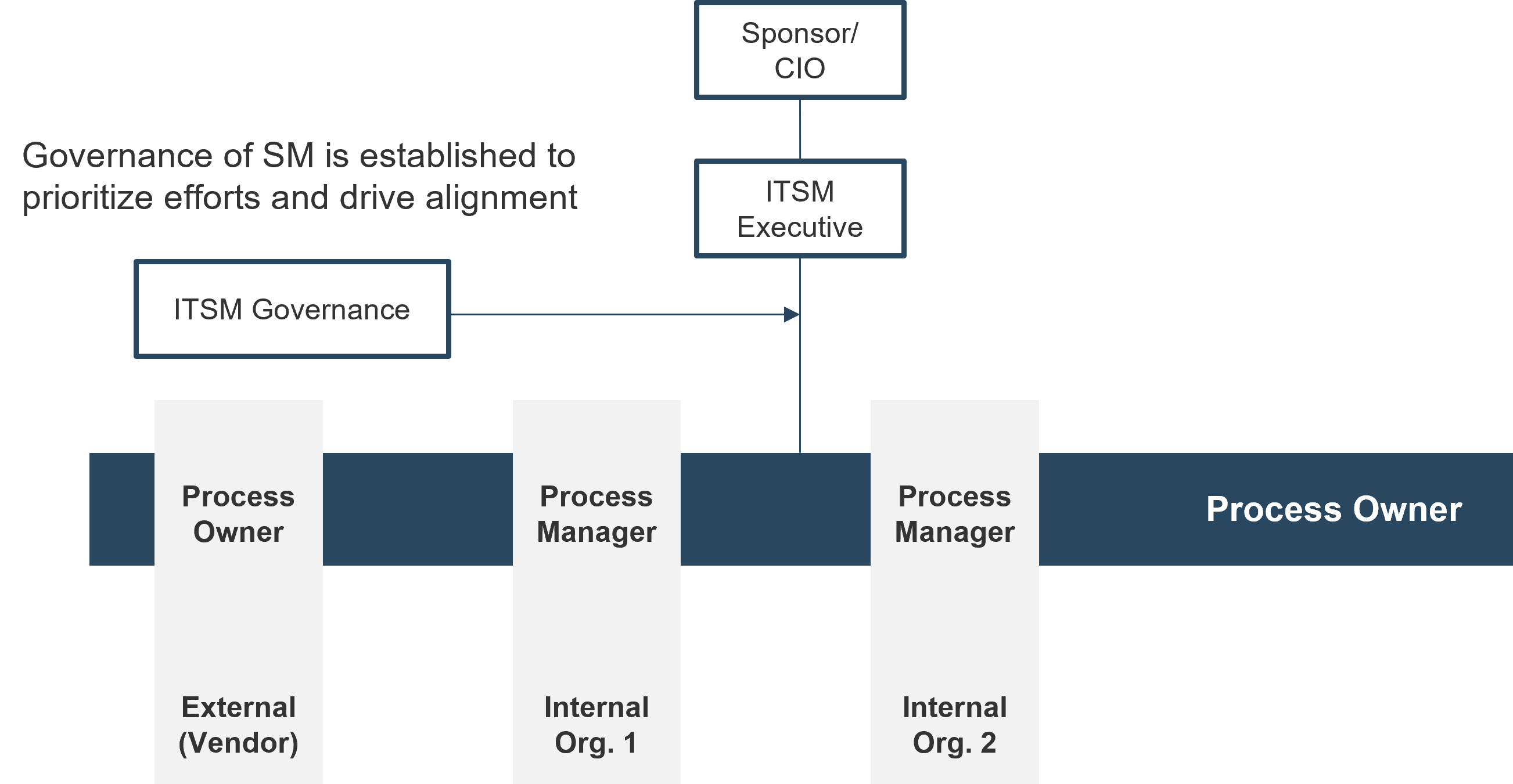
Service management office (SMO)
SMO structures tend to occur in highly mature organizations, where service management responsibility is seen as an enterprise accountability.
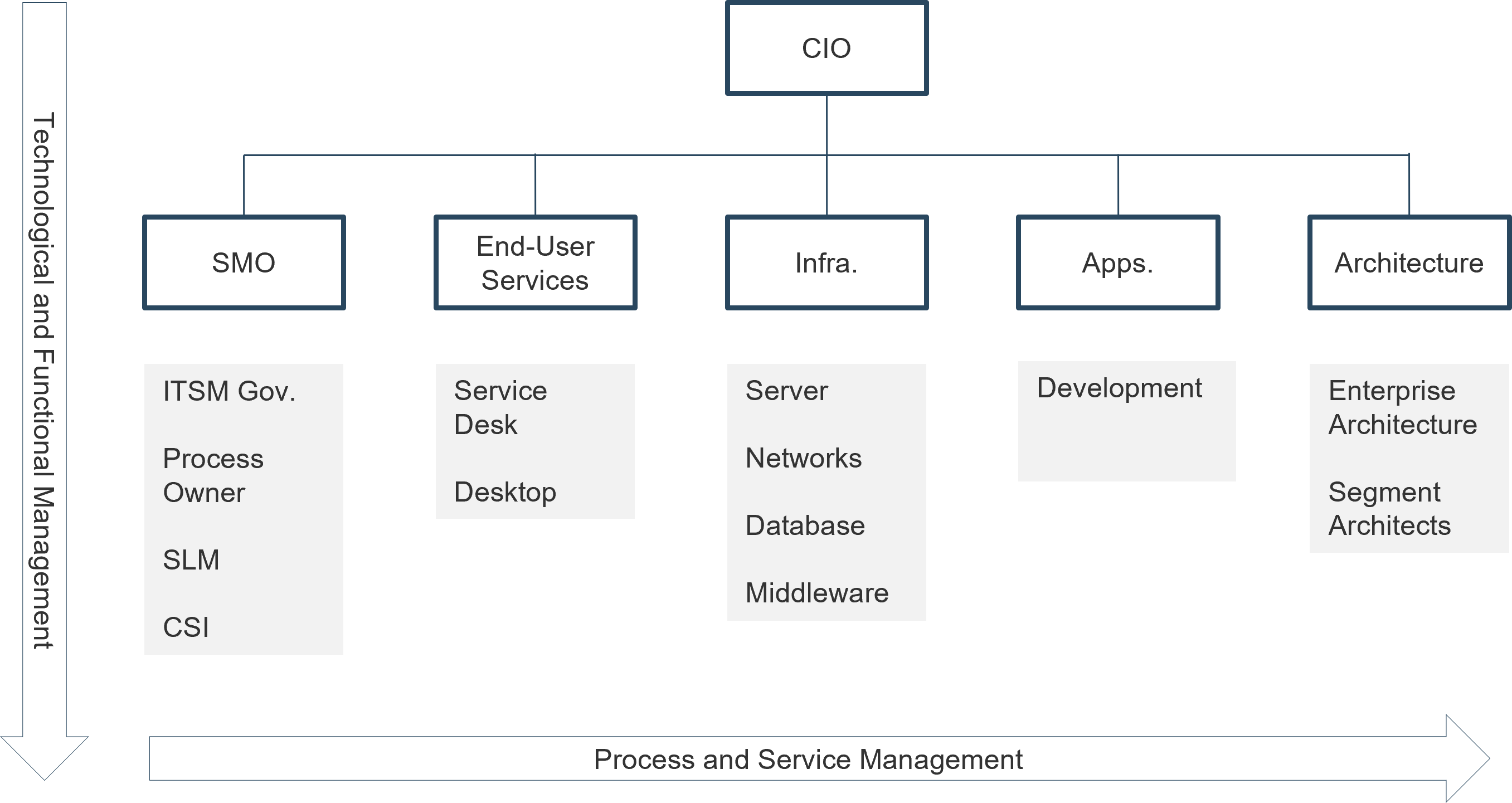
Info-Tech Insight
SMOs are suitable for organizations with a defined IT and organizational strategy. A SMO supports integration with other enterprise practices like enterprise architecture and the PMO.
Determine which process ownership and governance model works best for your organization
The Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template will help you document process ownership and governance model
Example:
Key Goals:
☐ Own accountability for changes to core processes
☐ Understand systemic nature and dependencies related to processes and services
☐ Approve and prioritize improvement and CSI initiatives related to processes and services
☐ Evaluate success of initiative outcomes based on defined benefits and expectations
☐ Own Service Management and Governance processes and policies
☐ Report into ITSM executive or equivalent body
Membership:
☐ Process Owners, SM Owner, Tool Owner/Liaison, Audit
Discuss as a team which process ownership model works for your organization. Determine who will govern the service management practice. Determine items that should be identified in your roadmap to address governance and process ownership gaps.
Use Info-Tech’s “SWOT” template to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities & threats that should be addressed
The Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template will help you document items from your SWOT analysis.

Brainstorm the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to resources, environment, technology, and management practices. Add items that need to be addressed to your roadmap.
Perform a SWOT analysis
- Brainstorm each aspect of the SWOT with an emphasis on:
- Resources
- Environment
- Technologies
- Management Practices
INPUT
- A collaborative discussion
OUTPUT
- SWOT analysis
- Priority items identified
Materials
- Whiteboards or flip charts
Participants
- All stakeholders
Indicate desired maturity level for your service management program to be successful
Discuss the various maturity levels and choose a desired level that would meet business needs.
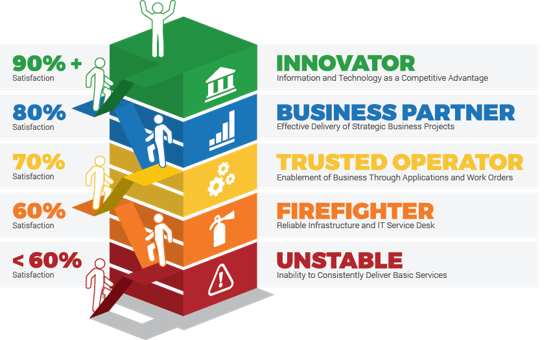
INPUT
- A collaborative discussion
OUTPUT
- Desired state of service management maturity
Materials
- None
Participants
- All stakeholders
Use Info-Tech’s Service Management Process Maturity Assessment Tool to understand your current state
The Service Management Process Maturity Assessment Tool will help you understand the true state of your service management.

Part 1, Part 2, and Part 3 tabs
These three worksheets contain questions that will determine the overall maturity of your service management processes. There are multiple sections of questions focused on different processes. It is very important that you start from Part 1 and continue the questions sequentially.
Results tab
The Results tab will display the current state of your service management processes as well as the percentage of completion for each individual process.
Complete the service management process maturity assessment
The current-state assessment will be the foundation of building your roadmap, so pay close attention to the questions and answer them truthfully.
- Start with tab 1 in the Service Management Process Maturity Assessment Tool. Remember to read the questions carefully and always use the feedback obtained through the end-user survey to help you determine the answer.
- In the “Degree of Process Completeness” column, use the drop-down menu to input the results solicited from the goals and objectives meeting you held with your project participants.
- Host a meeting with all participants following completion of the survey and have them bring their results. Discuss in a round-table setting, keeping a master sheet of agreed upon results.
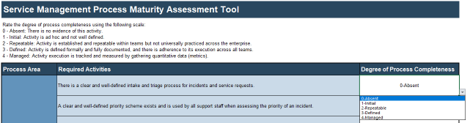
INPUT
- Service Management Process Maturity Assessment Tool questions
OUTPUT
- Determination of current state
Materials
- Service Management Process Maturity Assessment Tool
Participants
- Project team members
Review the results of your current-state assessment
At the end of the assessment, the Results tab will have action items you could perform to close the gaps identified by the process assessment tool.

INPUT
- Maturity assessment results
OUTPUT
- Determination of overall and individual practice maturity
Materials
- Service Management Maturity Assessment Tool
Participants
- Project team members
Use Info-Tech’s OCM Capability Assessment tool to understand your current state
The Organizational Change Management Capabilities Assessment tool will help you understand the true state of your organizational change management capabilities.
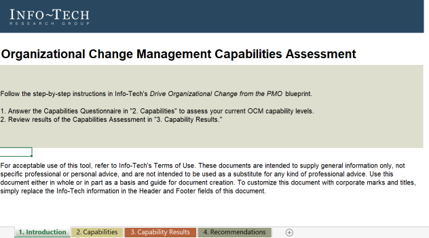
Complete the Capabilities tab to capture the current state for organizational change management. Review the Results tab for interpretation of the capabilities. Review the Recommendations tab for actions to address low areas of maturity.
Complete the OCM capability assessment
- Open Organizational Change Management Capabilities Assessment tool.
- Come to consensus on the most appropriate answer for each question. Use the 80/20 rule.
- Review result charts and discuss findings.
- Identify roadmap items based on maturity assessment.
INPUT
- A collaborative discussion
OUTPUT
- OCM Assessment tool
- OCM assessment results
Materials
- OCM Capabilities Assessment tool
Participants
- All stakeholders
If you want additional support, have our analysts guide you through this phase as part of an Info-Tech workshop
Book a workshop with our Info-Tech analysts:

- To accelerate this project, engage your IT team in an Info-Tech workshop with an Info-Tech analyst team.
- Info-Tech analysts will join you and your team onsite at your location or welcome you to Info-Tech’s historic Toronto office to participate in an innovative onsite workshop.
- Contact your account manager (www.infotech.com/account), or email Workshops@InfoTech.com for more information.
The following are sample activities that will be conducted by Info-Tech analysts with your team:
2.1

Create a powerful, succinct mission statement
Using Info-Tech’s sample mission statement as a guide, build your mission statement based on the objectives of this project and the benefits that this project will achieve. Keep the mission statement short and clear.
2.2

Complete the assessment
With the project team in the room, go through all three parts of the assessment with consideration of the feedback received from the business.
2.3

Interpret the results of the assessment
The Info-Tech onsite analyst will facilitate a discussion on the overall maturity of your service management practices and individual process maturity. Are there any surprises? Are the results reflective of current service delivery maturity?
PHASE 3
Build Your Service Management Roadmap
Build Roadmap
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Document your vision and mission on the roadmap one-pager.
- Using the inputs from the current-state assessments, identify the key themes required by your organization.
- Identify individual initiatives needed to address key themes.
Step Insights
- Using the Info-Tech thought model, address foundational gaps early in your roadmap and establish the management methods to continuously make them more robust.
- If any of the core practices are not meeting the vision for your service management program, be sure to address these items before moving on to more advanced service management practices or processes.
- Make sure the story you are telling with your roadmap is aligned to the overall organizational goals.
Phase 3 outline
Call 1-888-670-8889 or email GuidedImplementations@InfoTech.com for more information.
Complete these steps on your own, or call us to complete a guided implementation. A guided implementation is a series of 2-3 advisory calls that help you execute each phase of a project. They are included in most advisory memberships.
Guided Implementation 3: Determine Your Service Management Target State | |
|---|---|
Step 3.1 – Document the Overall Themes Start with an analyst kick-off call:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template | Step 3.2 – Determine Individual Initiatives Review findings with analyst:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template |
Focus on a strong foundation to build higher value service management practices
Info-Tech Insight
Focus on behaviors and expected outcomes before processes.
Foundational elements
- Operating model facilitates service management goals
- Culture of service delivery
- Governance discipline to evaluate, direct, and monitor
- Management discipline to deliver
Stabilize
- Deliver stable, reliable IT services to the business
- Respond to user requests quickly and efficiently
- Resolve user issues in a timely manner
- Deploy changes smoothly and successfully
Proactive
- Avoid/prevent service disruptions
- Improve quality of service (performance, availability, reliability)
Service Provider
- Understand business needs
- Ensure services are available
- Measure service performance, based on business-oriented metrics
Strategic Partner
- Fully aligned with business
- Drive innovation
- Drive measurable value
Info-Tech Insight
Continued leadership support of the foundational elements will allow delivery teams to provide value to the business. Set the expectation of the desired maturity level and allow teams to innovate.
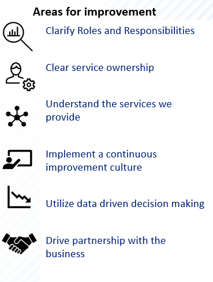
Identify themes that can help you build a strong foundation before moving to higher level practices

Before moving to advanced service management practices, you must ensure that the foundational and core elements are robust enough to support them. Leadership must nurture these practices to ensure they are sustainable and can support higher value, more mature practices.
Use Info-Tech’s “Service Management Roadmap” template to document your vision, themes and initiatives
The Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template contains a roadmap template to help communicate your vision, themes to be addressed, and initiatives
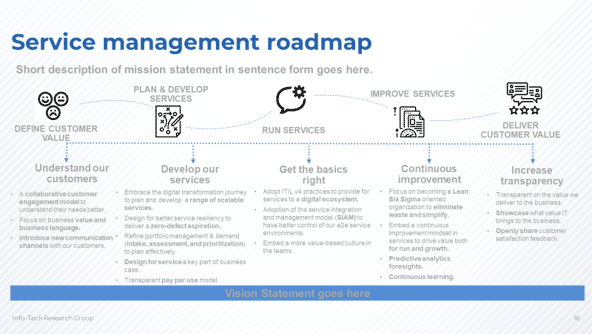
Working from the lower maturity items to the higher value practices, identify logical groupings of initiatives into themes. This will aid in communicating the reasons for the needed changes. List the individual initiatives below the themes. Adding the service management vision and mission statements can help readers understand the roadmap.
Document your service management roadmap
- Document the service management vision and mission on the roadmap template.
- Identify, from the assessments, areas that need to be improved or implemented.
- Group the individual initiatives into logical themes that can ease communication of what needs to happen.
- Document the individual initiatives.
- Document in terms that business partners and executive sponsors can understand.
INPUT
- Current-state assessment outputs
- Maturity model
OUTPUT
- Service management roadmap
Materials
- Whiteboard
- Roadmap template
Participants
- All stakeholders
If you want additional support, have our analysts guide you through this phase as part of an Info-Tech workshop
Book a workshop with our Info-Tech analysts:

- To accelerate this project, engage your IT team in an Info-Tech workshop with an Info-Tech analyst team.
- Info-Tech analysts will join you and your team onsite at your location or welcome you to Info-Tech’s historic Toronto office to participate in an innovative onsite workshop.
- Contact your account manager (www.infotech.com/account), or email Workshops@InfoTech.com for more information.
The following are sample activities that will be conducted by Info-Tech analysts with your team:
3.1

Identify themes to address items from the foundational level up to higher value service management practices
Identify easily understood themes that will help others understand the expected outcomes within your organization.
Document individual initiatives that contribute to the themes
Identify specific activities that will close gaps identified in the assessments.
PHASE 2
Build Communication Slide
Complete your service management roadmap
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Use the current-state assessment exercises to document the state of your service management practices. Document examples of the behaviors that are currently seen.
- Document the expected short-term gains. Describe how you want the behaviors to change.
- Document the long-term vision for each item and describe the benefits you expect to see from addressing each theme.
Step Insights
- Use the communication template to acknowledge the areas that need to be improved and paint the short- and long-term vision for the improvements to be made through executing the roadmap.
- Write it in business terms so that it can be used widely to gain acceptance of the upcoming changes that need to occur.
- Include specific areas that need to be fixed to make it more tangible.
- Adding the values from the vision, mission, and values exercise can also help you set expectations about how the team will behave as they move towards the longer-term vision.
Phase 4 Outline
Call 1-888-670-8889 or email GuidedImplementations@InfoTech.com for more information.
Complete these steps on your own, or call us to complete a guided implementation. A guided implementation is a series of 2-3 advisory calls that help you execute each phase of a project. They are included in most advisory memberships.
Guided Implementation 4: Build the Service Management Roadmap | |
|---|---|
Step 4.1: Document the Current State Start with an analyst kick-off call:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template | Step 4.2: List the Future Vision Review findings with analyst:
Then complete these activities…
With these tools & templates: Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template |
Use Info-Tech’s “Service Management Roadmap – Brought to Life” template to paint a picture of the future state
The Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template contains a communication template to help communicate your vision of the future state
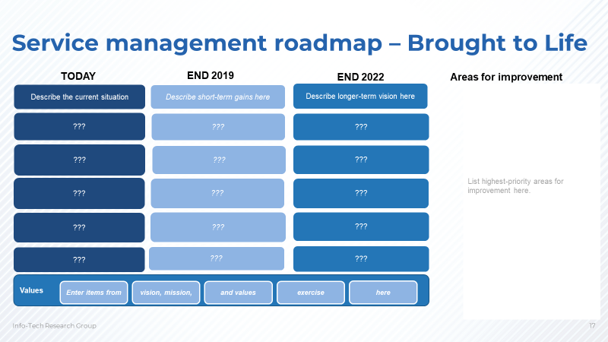
Use this template to demonstrate how existing pain points to delivering services will improve over time by painting a near- and long-term picture of how things will change. Also list specific initiatives that will be launched to affect the changes. Listing the values identified in the vision, mission, and values exercise will also demonstrate the team’s commitment to changing behavior to create better outcomes.
Document your current state and list initiatives to address them
- Use the previous assessments and feedback from business or customers to identify current behaviors that need addressing.
- Focus on high-impact items for this document, not an extensive list.
- List the initiatives or actions that will be used to address the specific pain points.

INPUT
- Current-state assessment outputs
- Feedback from business
OUTPUT
- Service Management Roadmap Communication Tool, in the Service Management Roadmap Presentation
Materials
- Whiteboard
- Roadmap template
Participants
- All stakeholders
Document your future state
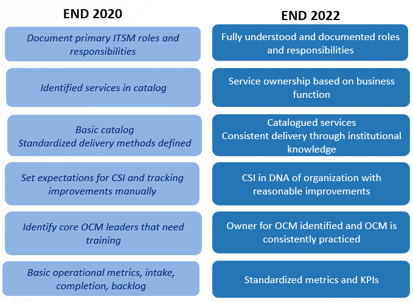
- For each pain point document the expected behaviors, both short term and longer term.
- Write in terms that allow readers to understand what to expect from your service management practice.
INPUT
- Current-state assessment outputs
- Feedback from business
OUTPUT
- Service Management Roadmap Communication Tool, in the Service Management Roadmap Presentation Template
Materials
- Whiteboard
- Roadmap template
Participants
- All stakeholders
If you want additional support, have our analysts guide you through this phase as part of an Info-Tech workshop
Book a workshop with our Info-Tech analysts:

- To accelerate this project, engage your IT team in an Info-Tech workshop with an Info-Tech analyst team.
- Info-Tech analysts will join you and your team onsite at your location or welcome you to Info-Tech’s historic Toronto office to participate in an innovative onsite workshop.
- Contact your account manager (www.infotech.com/account), or email Workshops@InfoTech.com for more information.
The following are sample activities that will be conducted by Info-Tech analysts with your team:
4.1

Identify the pain points and initiatives to address them
Identify items that the business can relate to and initiatives or actions to address them.
4.2

Identify short- and long-term expectations for service management
Communicate the benefits of executing the roadmap both short- and long-term gains.
Research contributors and experts

Valence Howden, Principal Research Director, CIO Practice
Info-Tech Research Group
Valence helps organizations be successful through optimizing how they govern, design, and execute strategies, and how they drive service excellence in all work. With 30 years of IT experience in the public and private sectors, he has developed experience in many information management and technology domains, with focus in service management, enterprise and IT governance, development and execution of strategy, risk management, metrics design and process design, and implementation and improvement.

Graham Price, Research Director, CIO Practice
Info-Tech Research Group
Graham has an extensive background in IT service management across various industries with over 25 years of experience. He was a principal consultant for 17 years, partnering with Fortune 500 clients throughout North America, leveraging and integrating industry best practices in IT service management, service catalog, business relationship management, IT strategy, governance, and Lean IT and Agile.

Sharon Foltz, Senior Workshop Director
Info-Tech Research Group
Sharon is a Senior Workshop Director at Info-Tech Research Group. She focuses on bringing high value to members via leveraging Info-Tech’s blueprints and other resources enhanced with her breadth and depth of skills and expertise. Sharon has spent over 15 years in various IT roles in leading companies within the United States. She has strong experience in organizational change management, program and project management, service management, product management, team leadership, strategic planning, and CRM across various global organizations.
Related Info-Tech Research
Bibliography
- “CIOs Emerge as Disruptive Innovators.” CSC Global CIO Survey: 2014-2015. Web.
- “Digital Transformation: How Is Your Organization Adapting?” CIO.com, 2018. Web.
- Goran, Julie, Laura LaBerge, and Ramesh Srinivasan. “Culture for a digital age.” McKinsey, July 2017. Web.
- The Qualities of Leadership: Leading Change. Cornelius & Associates, 14 April 2012.
- Wilkinson, Paul. “Culture, Ethics, and Behavior – Why Are We Still Struggling?” ITSM Tools, 5 July 2018. Web.
Buying Options
Create a Service Management Roadmap
Client rating
Cost Savings
Days Saved
IT Risk Management · IT Leadership & Strategy implementation · Operational Management · Service Delivery · Organizational Management · Process Improvements · ITIL, CORM, Agile · Cost Control · Business Process Analysis · Technology Development · Project Implementation · International Coordination · In & Outsourcing · Customer Care · Multilingual: Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese · Entrepreneur
Tymans Group is a brand by Gert Taeymans BV
Gert Taeymans bv
Europe: Koning Albertstraat 136, 2070 Burcht, Belgium — VAT No: BE0685.974.694 — phone: +32 (0) 468.142.754
USA: 4023 KENNETT PIKE, SUITE 751, GREENVILLE, DE 19807 — Phone: 1-917-473-8669
Copyright 2017-2022 Gert Taeymans BV