Drive Technology Adoption

The project isn’t over if the new product or system isn’t being used. How do you ensure that what you’ve put in place isn’t going to be ignored or only partially adopted? People are more complicated than any new system and managing them through the change needs careful planning.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
Cultivating a herd mentality, where people adopt new technology merely because everyone else is, is an important goal in getting the bulk of users using the new product or system. The herd needs to gather momentum though and this can be done by using the more tech-able and enthused to lead the rest on the journey. Identifying and engaging these key resources early in the process will greatly assist in starting the flow.
Impact and Result
While communication is key throughout, involving staff in proof-of-concept activities and contests and using the train-the-trainer techniques and technology champions will all start the momentum toward technology adoption. Group activities will address the bulk of users, but laggards may need special attention.
Drive Technology Adoption Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Drive Technology Adoption – A brief deck describing how to encourage users to adopt newly implemented technology.
This document will help you to ensure that newly implemented systems and technologies are correctly adopted by the intended recipients.
- Drive Technology Adoption Storyboard
Further reading
Drive Technology Adoption
The project is over. The new technology is implemented. Now how do we make sure it's used?
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
Technology endlessly changes and evolves. Similarly, business directions and requirements change, and these changes need to be supported by technology. Improved functionality and evolvement of systems, along with systems becoming redundant or unsupported, means that maintaining a static environment is virtually impossible.
Enormous amounts of IT budget are allocated to these changes each year. But once the project is over, how do you manage that change and ensure the systems are being used? Planning your technology adoption is vital.
Common Obstacles
The obstacles to technology adoption can be many and various, covering a broad spectrum of areas including:
- Reluctance of staff to let go of familiar processes and procedures.
- Perception that any change will add complications but not add value, thereby hampering enthusiasm to adopt.
- Lack of awareness of the change.
- General fear of change.
- Lack of personal confidence.
Info-Tech’s Approach
Start by identifying, understanding, categorizing, and defining barriers and put in place a system to:
- Gain an early understanding of the different types of users and their attitudes to technology and change.
- Review different adoption techniques and analyze which are most appropriate for your user types.
- Use a “Follow the Leader” approach, by having technical enthusiasts and champions to show the way.
- Prevent access to old systems and methods.
Info-Tech Insight
For every IT initiative that will be directly used by users, consider the question, “Will the final product be readily accepted by those who are going to use it?” There is no point in implementing a product that no one is prepared to use. Gaining user acceptance is much more than just ticking a box in a project plan once UAT is complete.
The way change should happen is clear
Prosci specializes in change. Its ADKAR model outlines what’s required to bring individuals along on the change journey.
AWARENESS
- Awareness means more than just knowing there’s a change occurring,
- it means understanding the need for change.
DESIRE
- To achieve desire, there needs to be motivation, whether it be from an
- organizational perspective or personal.
KNOWLEDGE
- Both knowledge on how to train during the transition and knowledge
- on being effective after the change are required. This can only be done
- once awareness and desire are achieved.
ABILITY
- Ability is not knowledge. Knowing how to do something doesn’t necessarily translate to having the skills to do it.
REINFORCEMENT
- Without reinforcement there can be a tendency to revert.
When things go wrong
New technology is not being used
The project is seen as complete. Significant investments have been made, but the technology either isn’t being used or is only partially in use.
Duplicate systems are now in place
Even worse. The failure to adopt the new technology by some means that the older systems are still being used. There are now two systems that fail to interact; business processes are being affected and there is widespread confusion.
Benefits not being realized
Benefits promised to the business are not being realized. Projected revenue increases, savings, or efficiencies that were forecast are now starting to be seen as under threat.
There is project blowout
The project should be over, but the fact that the technology is not being used has created a perception that the implementation is not complete and the project needs to continue.
Info-Tech Insight
People are far more complicated than any technology being implemented.
Consider carefully your approach.
Why does it happen?
POOR COMMUNICATION
There isn’t always adequate communications about what’s changing in the workplace.
FEAR
Fear of change is natural and often not rational. Whether the fear is about job loss or not being able to adapt to change; it needs to be managed.
TRAINING
Training can be insufficient or ineffective and when this happens people are left feeling like they don’t have the skills to make the change.
LACK OF EXECUTIVE SUPPORT
A lack of executive support for change means the change is seen as less important.
CONFLICTING VIEWS OF CHANGE
The excitement the project team and business feels about the change is not necessarily shared throughout the business. Some may just see the change as more work, changing something that already works, or a reason to reduce staff levels.
LACK OF CONFIDENCE
Whether it’s a lack of confidence generally with technology or concern about a new or changing tool, a lack of confidence is a huge barrier.
BUDGETARY CONSTRAINTS
There is a cost with managing people during a change, and budget must be allocated to allow for it.
Communications
Info-Tech Insight
Since Sigmund Freud there has been endless work to understand people’s minds.
Don’t underestimate the effect that people’s reactions to change can have on your project.
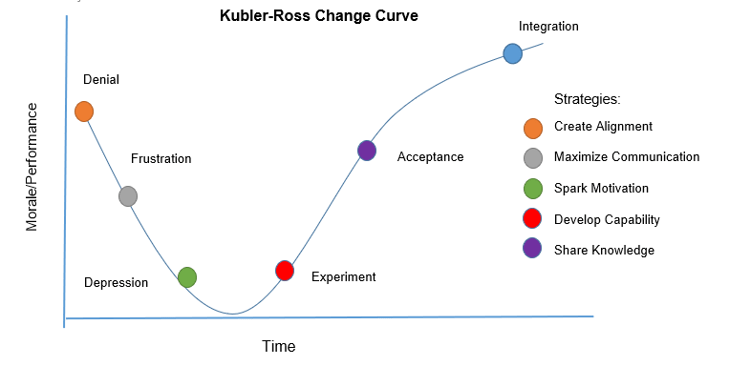
Communication plans are designed to properly manage change. Managing change can be easier when we have the right tools and information to adapt to new circumstances. The Kubler-Ross change curve illustrates the expected steps on the path to acceptance of change. With the proper communications strategy, each can be managed appropriately
Analyst perspective
Paul Binns – Principal Research Advisor, Info-Tech
The rapidly changing technology landscape in our world has always meant that an enthusiasm or willingness to embrace change has been advantageous. Many of us have seen how the older generation has struggled with that change and been left behind.
In the work environment, the events of the past two years have increased pressure on those slow to adopt as in many cases they couldn't perform their tasks without new tools. Previously, for example, those who may have been reluctant to use digital tools and would instead opt for face-to-face meetings, suddenly found themselves without an option as physical meetings were no longer possible. Similarly, digital collaboration tools that had been present in the market for some time were suddenly more heavily used so everyone could continue to work together in the “online world.”
At this stage no one is sure what the "new normal" will be in the post-pandemic world, but what has been clearly revealed is that people are prepared to change given the right motivation.
“Technology adoption is about the psychology of change.”
Bryan Tutor – Executive Counsellor, Info-Tech
The Fix
- Categorize Users
- Gain a clear understanding of your user types.
- Identify Adoption Techniques
- Understand the range of different tools and techniques available.
- Match Techniques To Categories
- Determine the most appropriate techniques for your user base.
- Follow-the-Leader
- Be aware of the different skills in your environment and use them to your advantage.
- Refresh, Retrain, Restrain
- Prevent reversion to old methods or systems.
Categories
Client-Driven Insight
Consider your staff and industry when looking at the Everett Rogers curve. A technology organization may have less laggards than a traditional manufacturing one.
In Everett Rogers’ book Diffusion of Innovations 5th Edition (Free Press, 2005), Rogers places adopters of innovations into five different categories.
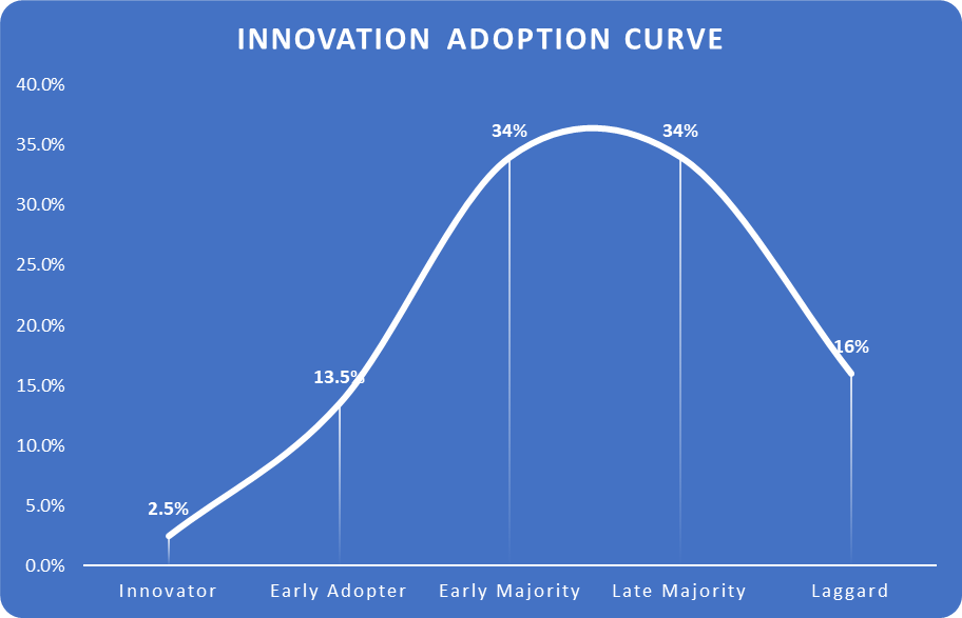
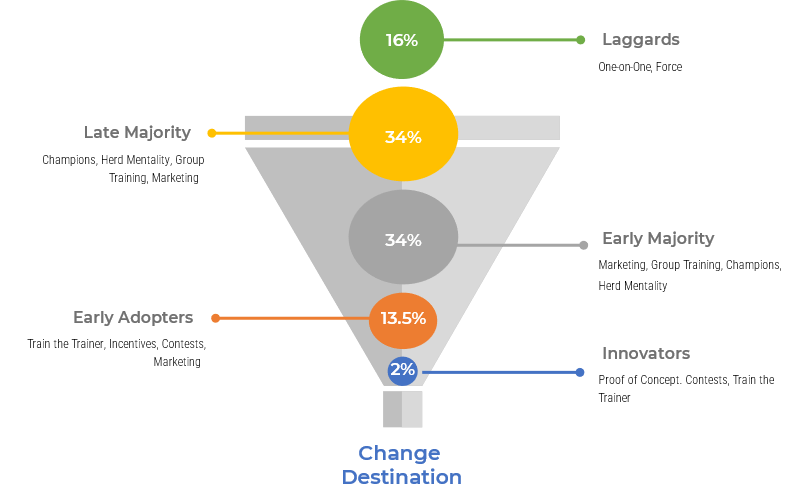
Category 1: The Innovator – 2.5%
Innovators are technology enthusiasts. Technology is a central interest of theirs, either at work, at home, or both. They tend to aggressively pursue new products and technologies and are likely to want to be involved in any new technology being implemented as soon as possible, even before the product is ready to be released.
For people like this the completeness of the new technology or the performance can often be secondary because of their drive to get new technology as soon as possible. They are trailblazers and are not only happy to step out of their comfort zone but also actively seek to do so.
Although they only make up about 2.5% of the total, their enthusiasm, and hopefully endorsement of new technology, offers reassurance to others.
Info-Tech Insight
Innovators can be very useful for testing before implementation but are generally more interested in the technology itself rather than the value the technology will add to the business.
Category 2: The Early Adopter – 13.5%
Whereas Innovators tend to be technologists, Early Adopters are visionaries that like to be on board with new technologies very early in the lifecycle. Because they are visionaries, they tend to be looking for more than just improvement – a revolutionary breakthrough. They are prepared to take high risks to try something new and although they are very demanding as far as product features and performance are concerned, they are less price-sensitive than other groups.
Early Adopters are often motivated by personal success. They are willing to serve as references to other adopter groups. They are influential, seen as trendsetters, and are of utmost importance to win over.
Info-Tech Insight
Early adopters are key. Their enthusiasm for technology, personal drive, and influence make them a powerful tool in driving adoption.
Category 3: The Early Majority – 34%
This group is comprised of pragmatists. The first two adopter groups belong to early adoption, but for a product to be fully adopted the mainstream needs to be won over, starting with the Early Majority.
The Early Majority share some of the Early Adopters’ ability to relate to technology. However, they are driven by a strong sense of practicality. They know that new products aren’t always successful. Consequently, they are content to wait and see how others fare with the technology before investing in it themselves. They want to see well-established references before adopting the technology and to be shown there is no risk.
Because there are so many people in this segment (roughly 34%), winning these people over is essential for the technology to be adopted.
Category 4: The Late Majority – 34%
The Late Majority are the conservatives. This group is generally about the same size as the Early Majority. They share all the concerns of the Early Majority; however, they are more resistant to change and are more content with the status quo than eager to progress to new technology. People in the Early Majority group are comfortable with their ability to handle new technology. People in the Late Majority are not.
As a result, these conservatives prefer to wait until something has become an established standard and take part only at the end of the adoption period. Even then, they want to see lots of support and ensure that there is proof there is no risk in them adopting it.
Category 5: The Laggard – 16%
This group is made up of the skeptics and constitutes 16% of the total. These people want nothing to do with new technology and are generally only content with technological change when it is invisible to them. These skeptics have a strong belief that disruptive new technologies rarely deliver the value promised and are almost always worried about unintended consequences.
Laggards need to be dealt with carefully as their criticism can be damaging and without them it is difficult for a product to become fully adopted. Unfortunately, the effort required for this to happen is often disproportional to the size of the group.
Info-Tech Insight
People aren’t born laggards. Technology projects that have failed in the past can alter people’s attitudes, especially if there was a negative impact on their working lives. Use empathy when dealing with people and respect their hesitancy.
Adoption Techniques
Different strokes for different folks
Technology adoption is all about people; and therefore, the techniques required to drive that adoption need to be people oriented.
The following techniques are carefully selected with the intention of being impactful on all the different categories described previously.
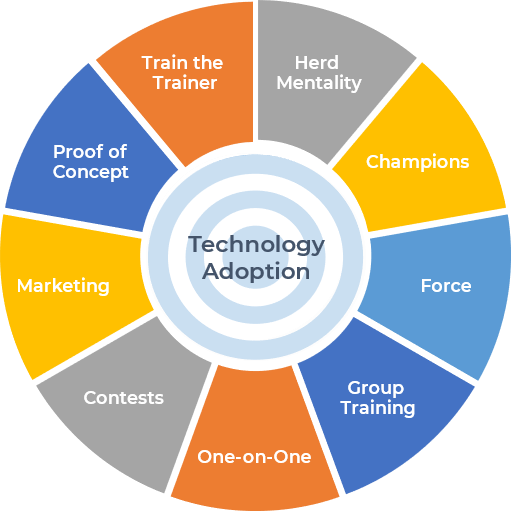
There are multitudes of different methods to get people to adopt new technology, but which is the most appropriate for your situation? Generally, it’s a combination.

Train the Trainer
Use your staff to get your message across.
Abstract
This technique involves training key members of staff so they can train others. It is important that those selected are strong communicators, are well respected by others, and have some expertise in technology.
Advantages
- Cost effective
- Efficient dissemination of information
- Trusted internal staff
Disadvantages
- Chance of inconsistent delivery
- May feel threatened by co-worker
Best to worst candidates
- Early Adopter: Influential trendsetters. Others receptive of their lead.
- Innovator: Comfortable and enthusiastic about new technology, but not necessarily a trainer.
- Early Majority: Tendency to take others’ lead.
- Late Majority: Risk averse and tend to follow others, only after success is proven.
- Laggard: Last to adopt usually. Unsuitable as Trainer.
Marketing
Marketing should be continuous throughout the change to encourage familiarity.
Abstract
Communication is key as people are comfortable with what is familiar to them. Marketing is an important tool for convincing adopters that the new product is mainstream, widely adopted and successful.
Advantages
- Wide communication
- Makes technology appear commonplace
- Promotes effectiveness of new technology
Disadvantages
- Reliant on staff interest
- Can be expensive
Best to worst candidates
- Early Majority: Pragmatic about change. Marketing is effective encouragement.
- Early Adopter: Receptive and interested in change. Marketing is supplemental.
- Innovator: Actively seeks new technology. Does not need extensive encouragement.
- Late Majority: Requires more personal approach.
- Laggard: Resistant to most enticements.
One-on-One
Tailored for individuals.
Abstract
One-on-one training sometimes is the only way to train if you have staff with special needs or who are performing unique tasks.
It is generally highly effective but inefficient as it only addresses individuals.
Advantages
- Tailored to specific need(s)
- Only relevant information addressed
- Low stress environment
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- Possibility of inconsistent delivery
- Personal conflict may render it ineffective
Best to worst candidates
- Laggard: Encouragement and cajoling can be used during training.
- Late Majority: Proof can be given of effectiveness of new product.
- Early Majority: Effective, but not cost efficient.
- Early Adopter: Effective, but not cost-efficient.
- Innovator: Effective, but not cost-efficient.
Group Training
Similar roles, attitudes, and abilities.
Abstract
Group training is one of the most common methods to start people on their journey toward new technology. Its effectiveness with the two largest groups, Early Majority and Late Majority, make it a primary tool in technology adoption.
Advantages
- Cost effective
- Time effective
- Good for team building
Disadvantages
- Single method may not work for all
- Difficult to create single learning pace for all
Best to worst candidates
- Early Majority: Receptive. The formality of group training will give confidence.
- Late Majority: Conservative attitude will be receptive to traditional training.
- Early Adopter: Receptive and attentive. Excited about the change.
- Innovator: Will tend to want to be ahead or want to move ahead of group.
- Laggard: Laggards in group training may have a negative impact.
Force
The last resort.
Abstract
The transition can’t go on forever.
At some point the new technology needs to be fully adopted and if necessary, force may have to be used.
Advantages
- Immediate full transition
- Fixed delivery timeline
Disadvantages
- Alienation of some staff
- Loss of faith in product if there are issues
Best to worst candidates
- Laggard: No choice but to adopt. Forces the issue.
- Late Majority: Removes issue of reluctance to change.
- Early Majority: Content, but worried about possible problems.
- Early Adopter: Feel less personal involvement in change process.
- Innovator: Feel less personal involvement in change process.
Contests
Abstract
Contests can generate excitement and create an explorative approach to new technology. People should not feel pressured. It should be enjoyable and not compulsory.
Advantages
- Rapid improvement of skills
- Bring excitement to the new technology
- Good for team building
Disadvantages
- Those less competitive or with lower skills may feel alienated
- May discourage collaboration
Best to worst candidates
- Early Adopter: Seeks personal success. Risk taker. Effective.
- Innovator: Enthusiastic to explore limits of technology.
- Early Majority: Less enthusiastic. Pragmatic. Less competitive.
- Late Majority: Conservative. Not enthusiastic about new technology.
- Laggard: Reluctant to get involved.
Incentives
Incentives don’t have to be large.
Abstract
For some staff, merely taking management’s lead is not enough. Using “Nudge” techniques to give that extra incentive is quite effective. Incentivizing staff either financially or through rewards, recognition, or promotion is a successful adoption technique for some.
Advantages
Encouragement to adopt from receiving tangible benefit
Draws more attention to the new technology
Disadvantages
Additional expense to business or project
Possible poor precedent for subsequent changes
Best to worst candidates
Early Adopter: Desire for personal success makes incentives enticing.
Early Majority: Prepared to change, but extra incentive will assist.
Late Majority: Conservative attitude means incentive may need to be larger.
Innovator: Enthusiasm for new technology means incentive not necessary.
Laggard: Sceptical about change. Only a large incentive likely to make a difference.
Champions
Strong internal advocates for your new technology are very powerful.
Abstract
Champions take on new technology and then use their influence to promote it in the organization. Using managers as champions to actively and vigorously promote the change is particularly effective.
Advantages
- Infectious enthusiasm encourages those who tend to be reluctant
- Use of trusted internal staff
Disadvantages
- Removes internal staff from regular duties
- Ineffective if champion not respected
Best to worst candidates
- Early Majority: Champions as references of success provide encouragement.
- Late Majority: Management champions in particular are effective.
- Laggard: Close contact with champions may be effective.
- Early Adopter: Receptive of technology, less effective.
- Innovator: No encouragement or promotion required.
Herd Mentality
Follow the crowd.
Abstract
Herd behavior is when people discount their own information and follow others. Ideally all adopters would understand the reason and advantages in adopting new technology, but practically, the result is most important.
Advantages
- New technology is adopted without question
- Increase in velocity of adoption
Disadvantages
- Staff may not have clear understanding of the reason for change and resent it later
- Some may adopt the change before they are ready to do so
Best to worst candidates
- Early Majority: Follow others’ success.
- Late Majority: Likely follow an established proven standard.
- Early Adopter: Less effective as they prefer to set trends rather than follow.
- Innovator: Seeks new technology rather than following others.
- Laggard: Suspicious and reluctant to change.
Proof of Concepts
Gain early input and encourage buy-in.
Abstract
Proof of concept projects give early indications of the viability of a new initiative. Involving the end users in these projects can be beneficial in gaining their support
Advantages
Involve adopters early on
Valuable feedback and indications of future issues
Disadvantages
If POC isn’t fully successful, it may leave lingering negativity
Usually, involvement from small selection of staff
Best to worst candidates
- Innovator: Strong interest in getting involved in new products.
- Early Adopter: Comfortable with new technology and are influencers.
- Early Majority: Less interest. Prefer others to try first.
- Late Majority: Conservative attitude makes this an unlikely option.
- Laggard: Highly unlikely to get involved.
Match techniques to categories
What works for who?
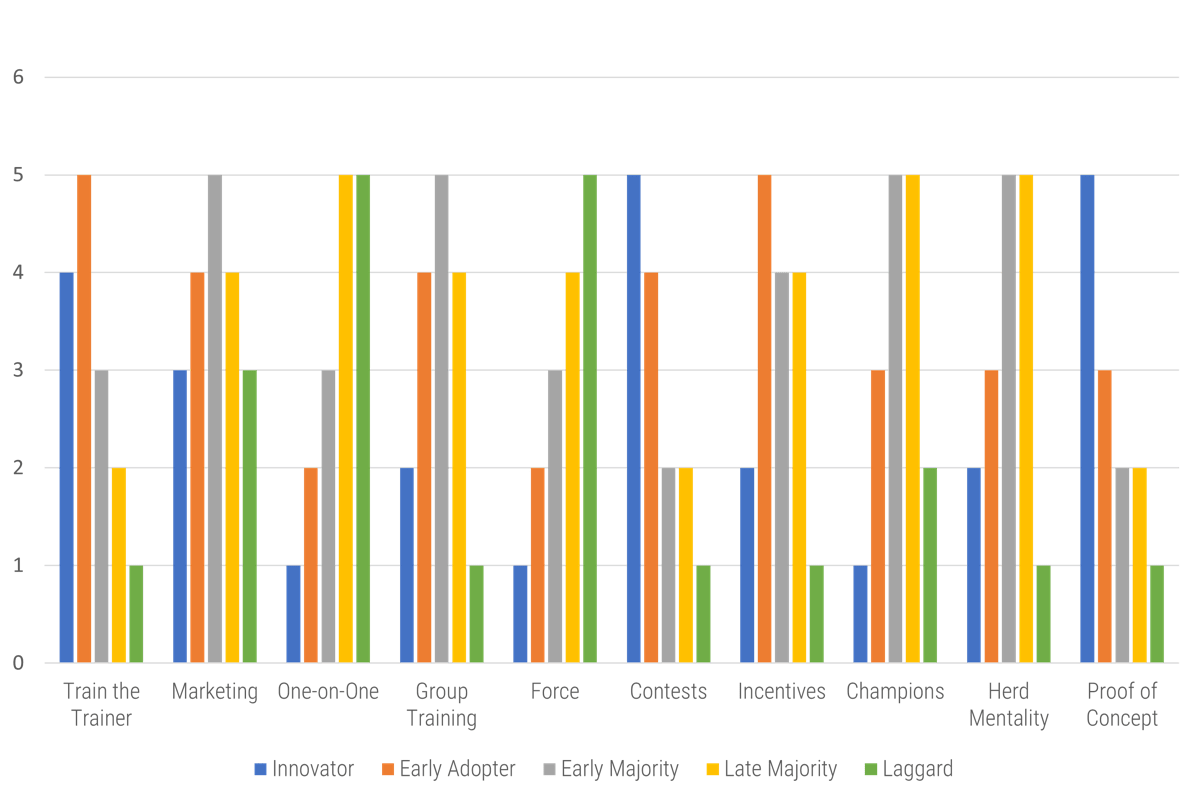
Follow the leader
Engage your technology enthusiasts early to help refine your product, train other staff, and act as champions. A combination of marketing and group training will develop a herd mentality. Finally, don’t neglect the laggards as they can prevent project completion.
Info-Tech Insight
Although there are different size categories, none can be ignored. Consider your budget when dealing with smaller groups, but also consider their impact.
Refresh, retrain, restrain
We don’t want people to revert.
Don’t assume that because your staff have been trained and have access to the new technology that they will keep using it in the way they were trained. Or that they won’t revert back to their old methods or system.
Put in place methods to remove completely or remove access to old systems. Schedule refresh training or skill enhancement sessions and stay vigilant.
Research Authors
Paul Binns
Principal Research Advisor, Info-Tech Research Group
With over 30 years in the IT industry, Paul brings to his work his experience as a Strategic Planner, Consultant, Enterprise Architect, IT Business Owner, Technologist, and Manager. Paul has worked with both small and large companies, local and international, and has had senior roles in government and the finance industry.

Scott Young
Principal Research Advisor, Info-Tech Research Group
Scott Young is a Director of Infrastructure Research at Info-Tech Research Group. Scott has worked in the technology field for over 17 years, with a strong focus on telecommunications and enterprise infrastructure architecture. He brings extensive practical experience in these areas of specialization, including IP networks, server hardware and OS, storage, and virtualization.
Related Info-Tech Research
Use Info-Tech’s workbook to gather information about user groups, business processes, and day-to-day tasks to gain familiarity with your adopters.
Governance and Management of Enterprise Software Implementation
Use our research to engage users and receive timely feedback through demonstrations. Our iterative methodology with a task list focused on the business’ must-have functionality allows staff to return to their daily work sooner.
Quality Management User Satisfaction Survey
This IT satisfaction survey will assist you with early information to use for categorizing your users.
Master Organizational Change Management Practices
Using a soft, empathetic approach to change management is something that all PMOs should understand. Use our research to ensure you have an effective OCM plan that will ensure project success.
Bibliography
Beylis, Guillermo. “COVID-19 accelerates technology adoption and deepens inequality among workers in Latin America and the Caribbean.” World Bank Blogs, 4 March 2021. Web.
Cleland, Kelley. “Successful User Adoption Strategies.” Insight Voices, 25 Apr. 2017. Web.
Hiatt, Jeff. “The Prosci ADKAR ® Model.” PROSCI, 1994. Web.
Malik, Priyanka. “The Kübler Ross Change Curve in the Workplace.” whatfix, 24 Feb. 2022. Web.
Medhaugir, Tore. “6 Ways to Encourage Software Adoption.” XAIT, 9 March 2021. Web.
Narayanan, Vishy. “What PwC Australia learned about fast tracking tech adoption during COVID-19” PWC, 13 Oct. 2020. Web.
Sridharan, Mithun. “Crossing the Chasm: Technology Adoption Lifecycle.” Think Insights, 28 Jun 2022. Web.
Buying Options
Drive Technology Adoption
IT Risk Management · IT Leadership & Strategy implementation · Operational Management · Service Delivery · Organizational Management · Process Improvements · ITIL, CORM, Agile · Cost Control · Business Process Analysis · Technology Development · Project Implementation · International Coordination · In & Outsourcing · Customer Care · Multilingual: Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese · Entrepreneur
Tymans Group is a brand by Gert Taeymans BV
Gert Taeymans bv
Europe: Koning Albertstraat 136, 2070 Burcht, Belgium — VAT No: BE0685.974.694 — phone: +32 (0) 468.142.754
USA: 4023 KENNETT PIKE, SUITE 751, GREENVILLE, DE 19807 — Phone: 1-917-473-8669
Copyright 2017-2022 Gert Taeymans BV
