Build a Continual Improvement Program

- IT managers must work hard to maintain and improve service quality or risk performance deterioration over time.
- Leadership may feel lost about what to do next and which initiatives have higher priority for improvement.
- The backlog of improvement initiatives makes the work even harder. Managers should involve the right people in the process and build a team that is responsible to monitor, measure, prioritize, implement, and test improvements.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Without continual improvement, sustained service quality will be temporary. Organizations need to put in place an ongoing process to detect potential services, enhance their procedures, and sustain their performance, whatever the process maturity is.
Impact and Result
- Set strategic vision for the continual improvement program.
- Build a team to set regulations, processes, and audits for the program.
- Set measurable targets for the program.
- Identify and prioritize improvement initiatives.
- Measure and monitor progress to ensure initiatives achieve the desired outcome.
- Apply lessons learned to the next initiatives.
Build a Continual Improvement Program Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Build a Continual Improvement Program – A step-by-step document to walk you through building a plan for efficient IT continual improvement.
This storyboard will help you craft a continual improvement register and a workflow to ensure sustained service improvements that fulfill ongoing increases in stakeholder expectations.
- Build a Continual Improvement Program Storyboard
2. Continual Improvement Register and Workflow – Structured documents to help you outline improvement initiatives, prioritize them, and build a dashboard to streamline tracking.
Use the Continual Improvement Register and Continual Improvement Workflow to help you brainstorm improvement items, get a better visibility into the items, and plan to execute improvements.
- Continual Improvement Register
- Continual Improvement Workflow (Visio)
- Continual Improvement Workflow (PDF)
Further reading
Build a Continual Improvement Program
Don’t stop with process standardization; plan to continually improve and help those improvements stick.
Analyst Perspective
Go beyond standardizing basics
IT managers often learn how to standardize IT services. Where they usually fail is in keeping these improvements sustainable. It’s one thing to build a quality process, but it’s another challenge entirely to keep momentum and know what to do next.
To fill the gap, build a continual improvement plan to continuously increase value for stakeholders. This plan will help connect services, products, and practices with changing business needs.
Without a continual improvement plan, managers may find themselves lost and wonder what’s next. This will lead to misalignment between ongoing and increasingly high stakeholder expectations and your ability to fulfill these requirements.
Build a continual improvement program to engage executives, leaders, and subject matter experts (SMEs) to go beyond break fixes, enable proactive enhancements, and sustain process changes.

|
Mahmoud Ramin, Ph.D.
Senior Research Analyst Infrastructure and Operations Info-Tech Research Group |
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
|
Common Obstacles
|
Info-Tech’s Approach
|
Info-Tech Insight
Without continual improvement, any process maturity achieved around service quality will not be sustained. Organizations need to put in place an ongoing program to maintain their current maturity and continue to grow and improve by identifying new services and enhancing existing processes.
Purpose of continual improvementThere should be alignment between ongoing improvements of business products and services and management of these products and services. Continual improvement helps service providers adapt to changing environments. No matter how critical the service is to the business, failure to continually improve reduces the service value.
Continual improvement is one of the five elements of ITIL’s Service Value System (SVS). | Continual improvement should be documented in an improvement register to record and manage improvement initiatives.Continual improvement is a proactive approach to service management. It involves measuring the effectiveness and efficiency of people, processes, and technology to:
A continual improvement process helps service management move away from a reactive approach that focuses only on fixing problems as they occur. Info-Tech InsightMake sure the basics are in place before you embark on a continual improvement initiative. |
Benefits of embedding a cross-organizational continual improvement approach
Provide an opportunity to stakeholders to define requirements and raise their concerns. |
Embed continual improvement in all service delivery procedures. |
Turn failures into improvement opportunities rather than contributing to a blame culture. |
Improve practice effectiveness that enhances IT efficiency. |
Improve end-user satisfaction that positively impacts brand reputation. |
Improve operational costs while maintaining a high level of satisfaction. |
Help the business become more proactive by identifying and improving services. |
Info-Tech Insight
It’s the responsibility of the organization’s leaders to develop and promote a continual improvement culture. Work with the business unit leads and communicate the benefits of continual improvement to get their buy-in for the practice and achieve the long-term impact.
Build a feedback program to get input into where improvement initiatives are needed
A well-maintained continual improvement process creates a proper feedback mechanism for the following stakeholder groups:
|
An efficient feedback mechanism should be constructed around the following initiatives:
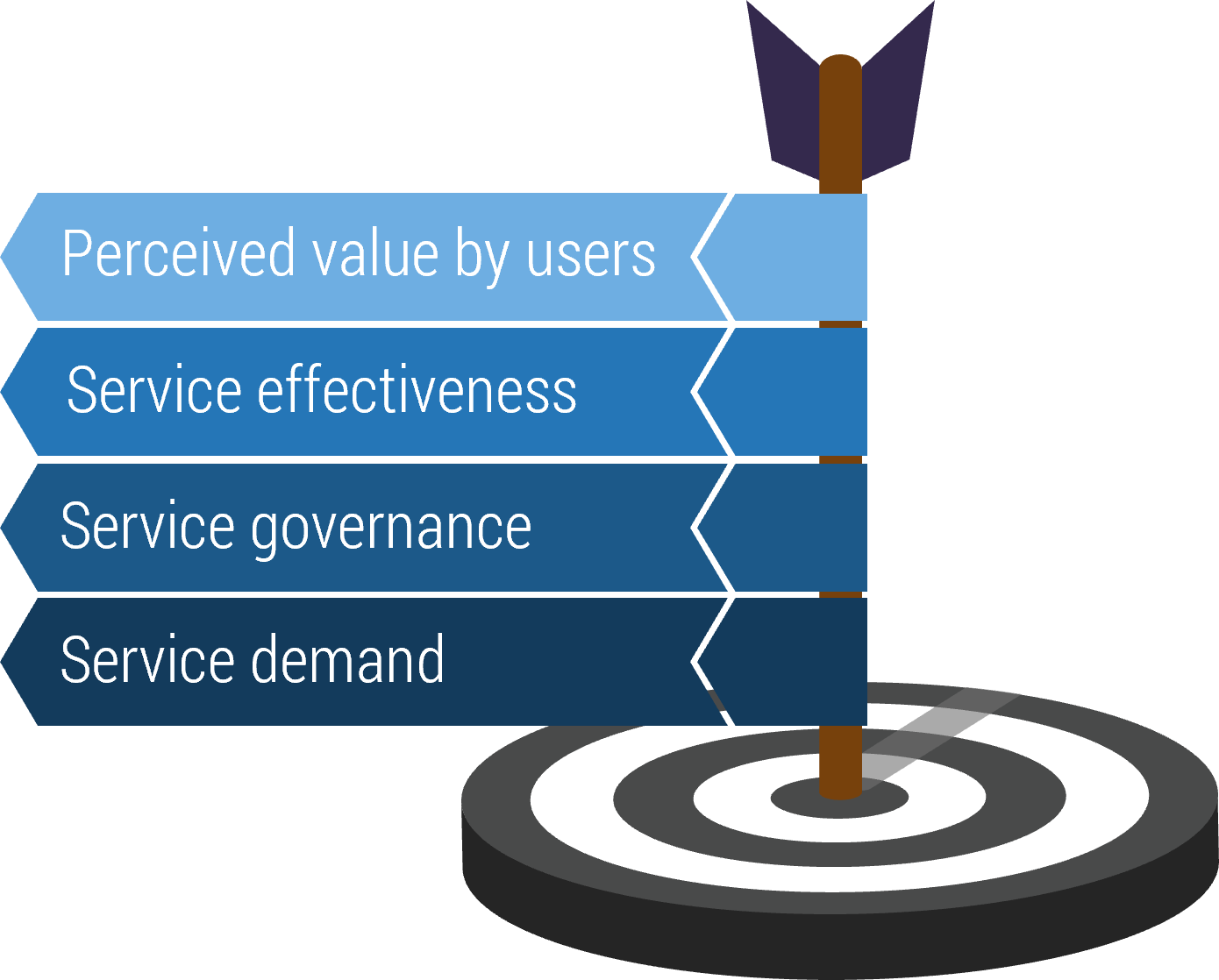
|
Stakeholders who participate in feedback activities should feel comfortable providing suggestions for improvement.
Work closely with the service desk team to build communication channels to conduct surveys. Avoid formal bureaucratic communications and enforce openness in communicating the value of feedback the stakeholders can provide. |
Info-Tech Insight
When conducting feedback activities with users, keep surveys anonymous and ensure users’ information is kept confidential. Make sure everyone else is comfortable providing feedback in a constructive way so that you can seek clarification and create a feedback loop.
Implement an iterative continual improvement model and ensure that your services align with your organizational vision
| Build a six-step process for your continual improvement plan. Make it a loop, in which each step becomes an input for the next step. | 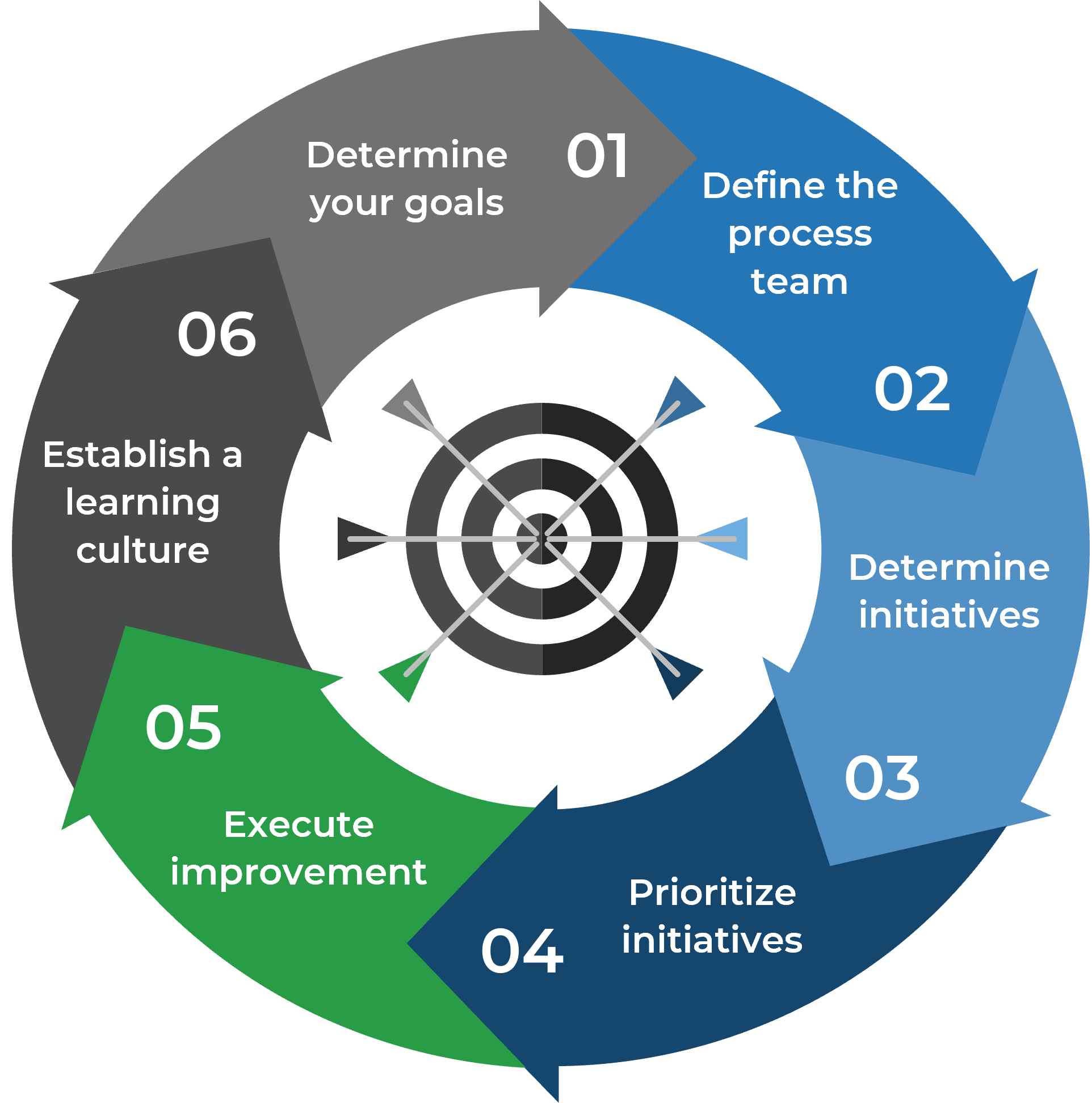
|
1. Determine your goals
A vision statement communicates your desired future state of the IT organization.
Your IT goals should always support your organizational goals. IT goals are high-level objectives that the IT organization needs to achieve to reach a target state.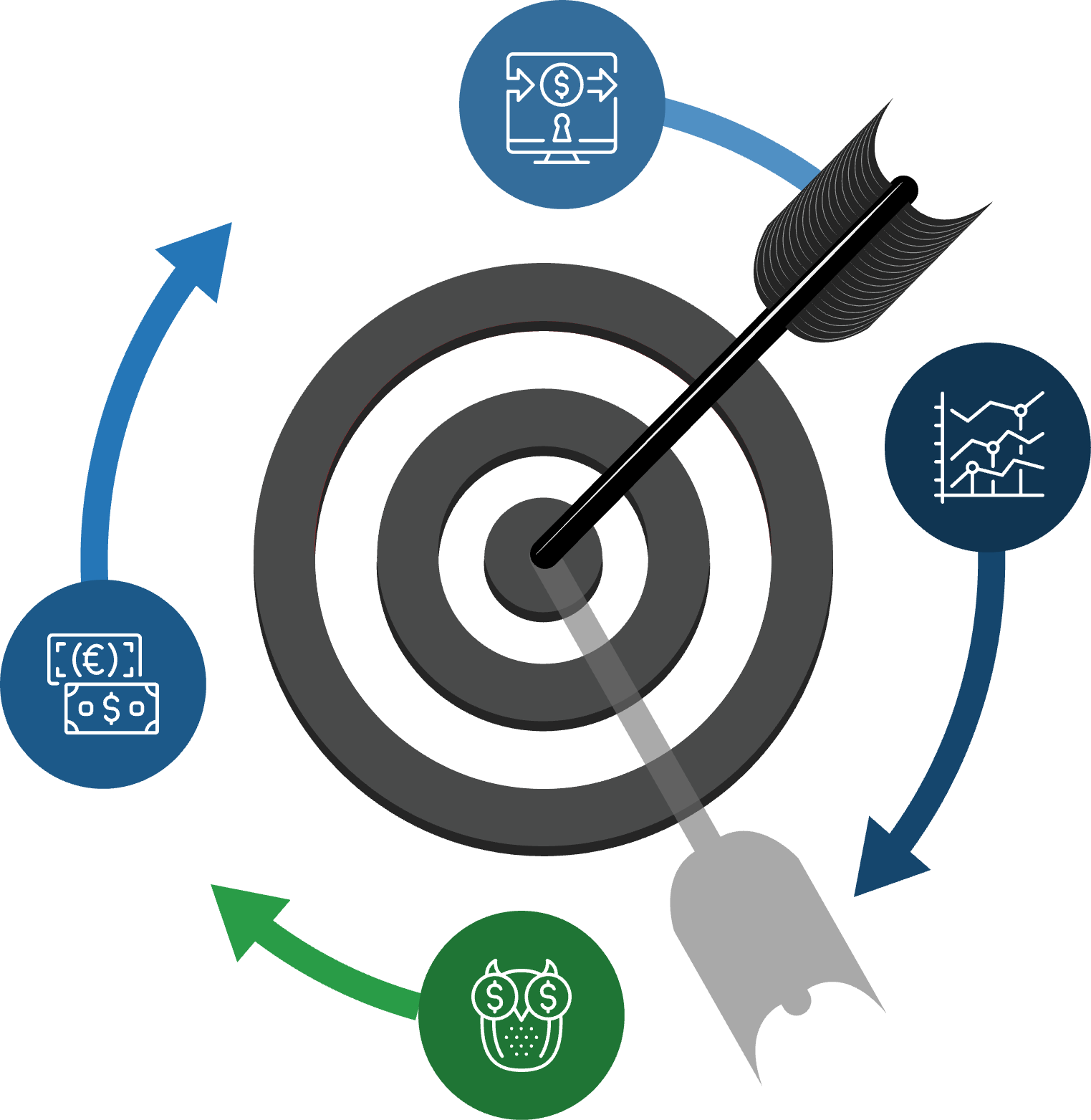
|
Understand the high-level business objectives to set the vision for continual improvement in a way that will align IT strategies with business strategies. Obtaining a clear picture of your organization’s goals and overall corporate strategy is one of the crucial first steps to continual improvement and will set the stage for the metrics you select. Document your continual improvement program goals and objectives. Knowing what your business is doing and understanding the impact of IT on the business will help you ensure that any metrics you collect will be business focused. Understanding the long-term vision of the business and its appetite for commitment and sponsorship will also inform your IT strategy and continual improvement goals. |
Assess the future state
At this stage, you need to visualize improvement, considering your critical success factors.
Critical success factors (CSFs) are higher-level goals or requirements for success, such as improving end-user satisfaction. They’re factors that must be met in order to reach your IT and business strategic vision.
Select key performance indicators (KPIs) that will identify useful information for the initiative: Define KPIs for each CSF. These will usually involve a trend, as an increase or decrease in something. If KPIs already exist for your IT processes, re-evaluate them to assess their relevance to current strategy and redefine if necessary. Selected KPIs should provide a full picture of the health of targeted practice.
KPIs should cover these four vectors of practice performance:
|
Examples of key CSFs and KPIs for continual improvement
CSF |
KPI |
| Adopt and maintain an effective approach for continual improvement | Improve stakeholder satisfaction due to implementation of improvement initiatives. |
| Enhance stakeholder awareness about continual improvement plan and initiatives. | |
| Increase continual improvement adoption across the organization. | |
| Commit to effective continual improvement across the business | Improve the return on investment. |
| Increase the impact of the improvement initiatives on process maturity. | |
| Increase the rate of successful improvement initiatives. |
Prepare a vision statement to communicate the improvement strategy
IT Implications + Business Context –› IT Goals
IT goals will help identify the target state, IT capabilities, and the initiatives that will need to be implemented to enable those capabilities. The vision statement is expressed in the present tense. It seeks to articulate the desired role of IT and how IT will be perceived. |
Strong IT vision statements have the following characteristics:
|
2. Define the process team
The structure of each continual improvement team depends on resource availability and competency levels.
| Make sure to allocate continual improvement activities to the available resources and assess the requirement to bring in others to fulfill all tasks.
Brainstorm what steps should be included in a continual improvement program:
|
Match stakeholder skill sets with available resources to ensure continual improvement processes are handled properly. Brainstorm skills specific to the program:
|
Enable the continual improvement program by clarifying responsibilities
Determine roles and responsibilities to ensure accountability
The continual improvement activities will only be successful if specific roles and responsibilities are clearly identified.
Depending on available staff and resources, you may be able to have full-time continual improvement roles, or you may include continual improvement activities in individuals’ job descriptions. Each improvement action that you identify should have clear ownership and accountability to ensure that it is completed within the specified timeframe. Roles and responsibilities can be reassigned throughout the continual improvement process. Info-Tech InsightCreate cross-functional teams to improve perspective and not focus on only one small group when trying to problem solve. Having other teams hear and reframe the issue or talk about how they can help to solve issues as a team can create bigger solutions that will help the entire IT team, not just one group. | Consider assigning dedicated continual improvement roles
|
3. Determine improvement initiatives
Businesses usually make the mistake of focusing too much on making existing processes better while missing gaps in their practices.
You need to understand the current state of service operations to understand how you can provide value through continual improvement. Give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on IT services. Use Info-Tech’s End User Satisfaction Survey to define the state of your core IT services. Info-Tech InsightBecome proactive to improve satisfaction. Continual improvement is not only about identifying pain points and improving them. It enables you to proactively identify initiatives for further service improvement using both practice functionality and technology enablement. | Understand the current state of your IT practices Determine the maturity level of your IT areas to help you understand which processes need improvement. Involve the practice team in maturity assessment activities to get ideas and input from them. This will also help you get their buy-in and engagement for improvement. Leverage performance metrics to analyze performance level. Metrics play a key role in understanding what needs improvement. After you implement metrics, have an impact report regularly generated to monitor them. Use problem management to identify root causes for the identified gaps. Potential sources of problems can be:
|
Establish an improvement roadmap and execute initiatives
Build a continual improvement register (CIR) for your target initiatives|
A CIR is a document used for recording your action plan from the beginning to the end of the improvement project. If you just sit and plan for improvements without acting on them, nothing will improve. CIR helps you create an action plan and allows you to manage, track, and prioritize improvement suggestions. Consider tracking the following information in your CIR, adjusted to meet the needs of your organization:
|
Populate your register with ideas that come from your first round of assessments and use this document to continually add and track new ideas as they emerge. You can also consider using the register to track the outcomes and benefits of improvement initiatives after they have been completed. |
Activity: Use the Continual Improvement Register template to brainstorm responsibilities, generate improvement initiatives, and action plan
1-3 hours
|
|
Download the Continual Improvement Register template
Activity: Use the Continual Improvement Register template to brainstorm responsibilities, generate improvement initiatives, and action plan
Input
|
Output
|
Materials
|
Participant
|
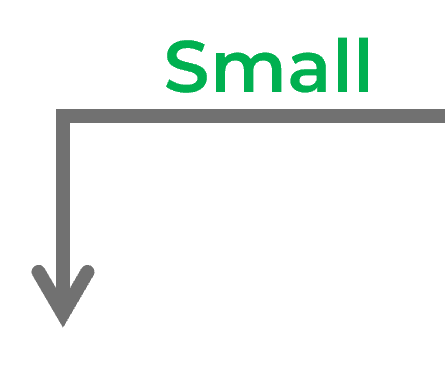
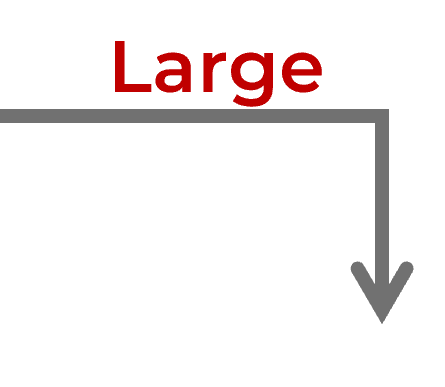
4. Prioritize initiativesPrioritization should be transparent and available to stakeholders.Some initiatives are more critical than others to achieve and should be prioritized accordingly. Some improvements require large investments and need an equally large effort, while some are relatively low-cost, low-effort improvements. Focus on low-hanging fruit and prioritize low-cost, low-effort improvements to help the organization with rapid growth. This will also help you get stakeholder buy-in for the rest of your continual improvement program. Prioritize improvement initiatives in your CIR to increase visibility and ensure larger improvement initiatives are done the next cycle. As one improvement cycle ends, the next cycle begins, which allows the continual improvement team to keep pace with changing business requirements. |

|
Identify “quick wins” that can provide immediate improvement
Prioritize these quick wins to immediately demonstrate the success of the continual service improvement effort to the business.
01 |
Keep the scope of the continual improvement process manageable at the beginning by focusing on a few key areas that you want to improve. |
|
02 |
From your list of proposed improvements, focus on a few of the top pain points and plan to address those. | |
03 |
Choose the right services to improve at the first stage of continual improvement to ensure that the continual improvement process delivers value to the business. |
Activity: Prioritize improvement initiatives
2-3 hours
Input: List of initiatives for continual improvement
Output: Prioritized list of initiatives
Materials: Continual improvement register, Whiteboard/flip charts, Markers, Laptops
Participants: CIO, IT managers, Project managers, Continual improvement manager
- In the CI Register tab of the Continual Improvement Register template, define the status, priority, effort/cost, and timeline according to the definition of each in the data entry tab.
- Review improvement initiatives from the previous activity.
- Record the CI coordinator, business owner, and IT owner for each initiative.
- Fill out submission date to track when the initiative was added to the register.
- According to the updated items, you will get a dashboard of items based on their categories, effort, priority, status, and timeline. You will also get a visibility into the total number of improvement initiatives.
- Focus on the short-term initiatives that are higher priority and require less effort.
- Refer to the Continual Improvement Workflow template and update the steps.
Download the Continual Improvement Register template
Download the Continual Improvement Workflow template
5. Execute improvement
Develop a plan for improvement
Determine how you want to reach your improvement objectives. Define how to make processes work better.| Make a business case for your action plan | Determine budget for implementing the improvement and move to execution. | Find out how long it takes to build the improvement in the practice. | Confirm the resources and skill sets you require for the improvement. | Communicate the improvement plan across the business for better visibility and for seamless organizational change management, if needed. | Lean into incremental improvements to ensure practice quality is sustained, not temporary. | Put in place an ongoing process to audit, enhance, and sustain the performance of the target practice. |
Create a specific action plan to guide your improvement activities
As part of the continual improvement plan, identify specific actions to be completed, along with ownership for each action.
The continual improvement process must:
|
For each action, identify:
|
Choose timelines:
|
Info-Tech Insight
Every organization is unique in terms of its services, processes, strengths, weaknesses, and needs, as well as the expectations of its end users. There is no single action plan that will work for everyone. The improvement plan will vary from organization to organization, but the key elements of the plan (i.e. specific priorities, timelines, targets, and responsibilities) should always be in place.
Build a communication plan to ensure the implementation of continual improvement stakeholder buy-in
1. Throughout the improvement process, share information about both the status of the project and the impact of the improvement initiatives.
| 2. The end users should be kept in the loop so they can feel that their contribution is valued.
Info-Tech InsightTo be effective, continual improvement requires open and honest feedback from IT staff. Debriefings work well for capturing information about lessons learned. Break down the debriefings into smaller, individual activities completed within each phase of the project to better capture the large amount of data and lessons learned within that phase. |
Measure the success of your improvement program
Continual improvement is everybody’s job within the organization.
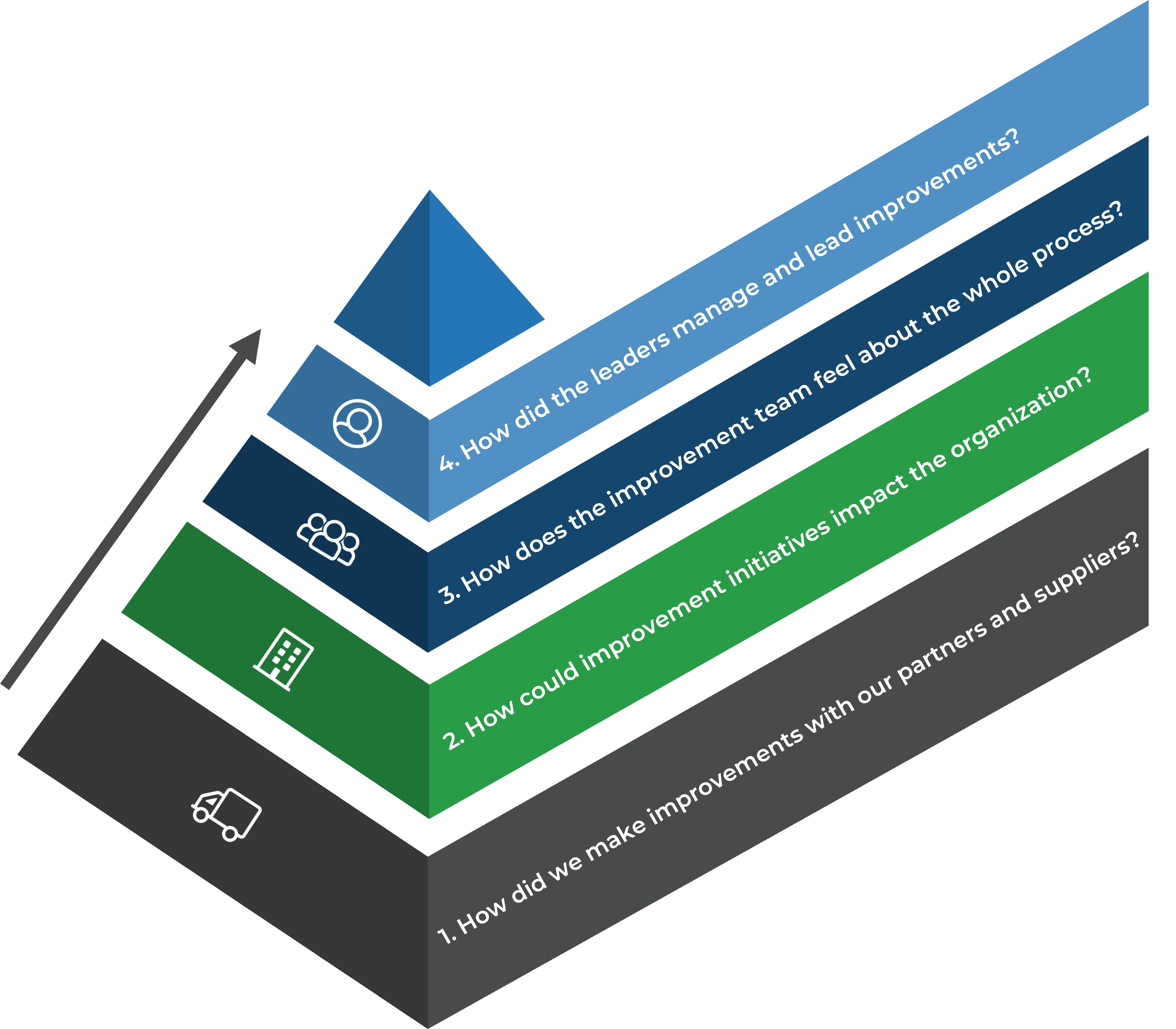
Determine how improvements impacted stakeholders. Build a relationship pyramid to analyze how improvements impacted external users and narrow down to the internal users, implementing team, and leaders.
|
|
Measure changes in selected metrics to evaluate success
Measuring and reporting are key components in the improvement process.
Adjust improvement priority based on updated objectives. Justify the reason. Refer to your CIR to document it.
| Did you get there? Part of the measurement should include a review of CSFs and KPIs determined in step 1 (assess the future state). Some may need to be replaced.
| Outcomes of the continual improvement process should include:
For a guideline to determine a list of metrics, refer to Info-Tech’s blueprints: Info-Tech InsightMake sure you’re measuring the right things and considering all sources of information. Don’t rely on a single or very few metrics. Instead, consider a group of metrics to help you get a better holistic view of improvement initiatives and their impact on IT operations. |
6. Establish a learning culture and apply it to other practices
Reflect on lessons learned to drive change forward
What did you learn?
|
What obstacles prevented you from reaching your target condition?
|
Compare expectations versus reality
| Info-Tech InsightRegardless of the cause, large differences between the EC and the AC provide great learning opportunities about how to approach change in the future. |
|
|
Think long-term to sustain changesThe continual improvement process is ongoing. When one improvement cycle ends, the next should begin in order to continually measure and evaluate processes.The goal of any framework is steady and continual improvement over time that resets the baseline to the current (and hopefully improved) level at the end of each cycle.Have processes in place to ensure that the improvements made will remain in place after the change is implemented. Each completed cycle is just another step toward your target state.
|
Related Info-Tech Research
|
Build a Business-Aligned IT Strategy
Success depends on IT initiatives clearly aligned to business goals, IT excellence, and driving technology innovation. |
|
Develop Meaningful Service Metrics
Reinforce service orientation in your IT organization by ensuring your IT metrics generate value-driven resource behavior. |

|
Improve Incident and Problem Management
Rise above firefighter mode with structured incident management to enable effective problem management. |
Works Cited
“Continual Improvement ITIL4 Practice Guide.” AXELOS, 2020. Accessed August 2022.
“5 Tips for Adopting ITIL 4’s Continual Improvement Management Practice.” SysAid, 2021. Accessed August 2022.
Jacob Gillingham. “ITIL Continual Service Improvement And 7-Step Improvement Process” Invensis Global Learning Services, 2022. Accessed August 2022.
Buying Options
Build a Continual Improvement Program
IT Risk Management · IT Leadership & Strategy implementation · Operational Management · Service Delivery · Organizational Management · Process Improvements · ITIL, CORM, Agile · Cost Control · Business Process Analysis · Technology Development · Project Implementation · International Coordination · In & Outsourcing · Customer Care · Multilingual: Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese · Entrepreneur
Tymans Group is a brand by Gert Taeymans BV
Gert Taeymans bv
Europe: Koning Albertstraat 136, 2070 Burcht, Belgium — VAT No: BE0685.974.694 — phone: +32 (0) 468.142.754
USA: 4023 KENNETT PIKE, SUITE 751, GREENVILLE, DE 19807 — Phone: 1-917-473-8669
Copyright 2017-2022 Gert Taeymans BV