Foster Data-Driven Culture With Data Literacy

Organizations are joining the wave and adopting machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to unlock the value in their data and power their competitive advantage. But to succeed with these complex analytics programs, they need to begin by looking at their data – empowering their people to realize and embrace the valuable insights within the organization’s data.
The key to achieve becoming a data-driven organization is to foster a strong data culture and equip employees with data skills through an organization-wide data literacy program.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Start with real business problems in a hands-on format to demonstrate the value of data.
- Use a formalized organization-wide approach to data literacy program to bridge the data skills gap.
- Provide relevant and practical training programs tailored to different learning styles and tenures (e.g. onboarding, development plan).
Impact and Result
Data literacy is critical to the success of digital transformation and AI analytics. Info-Tech’s approach to creating a sustainable and effective data literacy program is recognizing it is:
- More than just technical training. A data literacy program isn’t just about data; it encompasses aspects of business, IT, and data.
- More than a one-off exercise. To keep the literacy skills alive the program must be regular, sustainable, and tailored to different needs across all levels of the organization.
- More than one delivery format. Different delivery methods need to be considered to suit various learning styles to ensure an effective delivery.
Foster Data-Driven Culture With Data Literacy Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Foster Data-Driven Culture With Data Literacy Storyboard – A step-by-step guide to help organizations build an effective and sustainable data literacy program that benefits all employees who work with data.
Data literacy as part of the data governance strategic program should be launched to all levels of employees that will help your organization bridge the data knowledge gap at all levels of the organization. This research recommends approaches to different learning styles to address data skill needs and helps members create a practical and sustainable data literacy program.
- Foster Data-Driven Culture With Data Literacy Storyboard
2. Fundamental Data Literacy Program Template – A document that provides an example of a fundamental data literacy program.
Kick off a data awareness program that explains the fundamental understanding of data and its lifecycle. Explore ways to create or mature the data literacy program with smaller amounts of information on a more frequent basis.
- Fundamental Data Literacy Program Template
Further reading
Foster Data-Driven Culture With Data Literacy
Data literacy is an essential part of a data-driven culture, bridging the data knowledge gaps across all levels of the organization.
Analyst Perspective
Data literacy is the missing link to becoming a data-driven organization.
“Digital transformation” and “data driven” are two terms that are inseparable. With organizations accelerating in their digital transformation roadmap implementation, organizations need to invest in developing data skills with their people. Talent is scarce and the demand for data skills is huge, with 70% of employees expected to work heavily with data by 2025. There is no time like the present to launch an organization-wide data literacy program to bridge the data knowledge gap and foster a data-driven culture.
Data literacy training is as important as your cybersecurity training. It impacts all levels of the organization. Data literacy is critical to success with digital transformation and AI analytics.
Annabel Lui
Principal Advisory Director, Data & Analytics Practice
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive Summary
Your ChallengeOrganizations are joining the wave and adopting machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) to unlock the value in their data and power their competitive advantage. But to succeed with these complex analytics programs, they need to begin by empowering their people to realize and embrace the valuable insights within the organization’s data. The key to becoming a data-driven organization is to foster a strong data culture and equip people with data skills through an organization-wide data literacy program. |
Common ObstaclesChallenges the data leadership is likely to face as digital transformation initiatives drive intensified competition:
|
Info-Tech's ApproachWe interviewed data leaders and instructors to gather insights about investing in data:
|
Info-Tech Insight
By thoughtfully designing a data literacy training program for the audience's own experience, maturity level, and learning style, organizations build the data-driven and engaged culture that helps them to unlock their data's full potential and outperform other organizations.
Your Challenge
Data literacy is the missing link to drive business outcomes from data.
- Having a data-driven culture as an organization’s mission statement without implementing a data literacy program is like making an empty promise and leaving the value unrealized and unattainable.
- A study conducted by the Data Literacy Project clearly indicates that organizations with aggressive data literacy programs will outperform those who do not have such programs. By 2030, data literacy will be one of the most sought-after skill sets. All employees require data literacy skills.
- Everyone has a role in data. From employees who are actively involved in data collection to operational teams who create reports with analytics tools and finally to executives who use data to make business decisions – they all require continuous data literacy training in a data-driven organization. Because of differences in maturity, data literacy strategies cannot be one-size-fits-all.
“Data literacy is the ability to read, work with, analyze, and communicate with data. It's a skill that empowers all levels of workers to ask the right questions of data and machines, build knowledge, make decisions, and communicate meaning to others.” – Qlik, n.d.
75% of organizational employees have access to data tools – only 21% demonstrated confidence in their data skills.
Source: Accenture, 2020.
89% of C-level executives expect team members to explain how data has informed their decisions, but only 11% employees are fully confident in their ability to read, analyze, work with, and communicate with data
Source: Qlik, 2022.
Data debt or data asset?
Manage your data as strategic assets.
“[Data debt is] when you have undocumented, unused, incomplete, and inconsistent data,” according to Secoda (2023). “When … data debt is not solved, data teams could risk wasting time managing reports no one uses and producing data that no one understands.”
Signs of data debt when considering investing in data literacy:
- Lack of definition and understanding of data terms, therefore they don’t speak the same language. Without data literacy, an organization will not succeed in becoming a data-driven organization.
- Putting data literacy as a low priority. Organization sees this as “another” training to put on the list and keeps it on the back burner.
- Data literacy is not seen as the number one skill set needed in the organization. However, anyone who works with data requires data skills.
- End users are not trained on self-serve features and tools.
- Focusing on a minority group of people rather than everyone in the organization or seeing it as a one-off exercise.
- Delays or failure to deliver digital transformation projects due to lack of data skills and data access issues.
66%
of organizations say a backlog of data debt is impacting new data management initiatives.
40%
of organizations say individuals within the business do not trust data insights.
30%
of organizations are unable to become data-driven.
Source: Experian, 2020
Info-Tech’s Approach
Data literacy is critical to success with digital transformation and AI analytics.
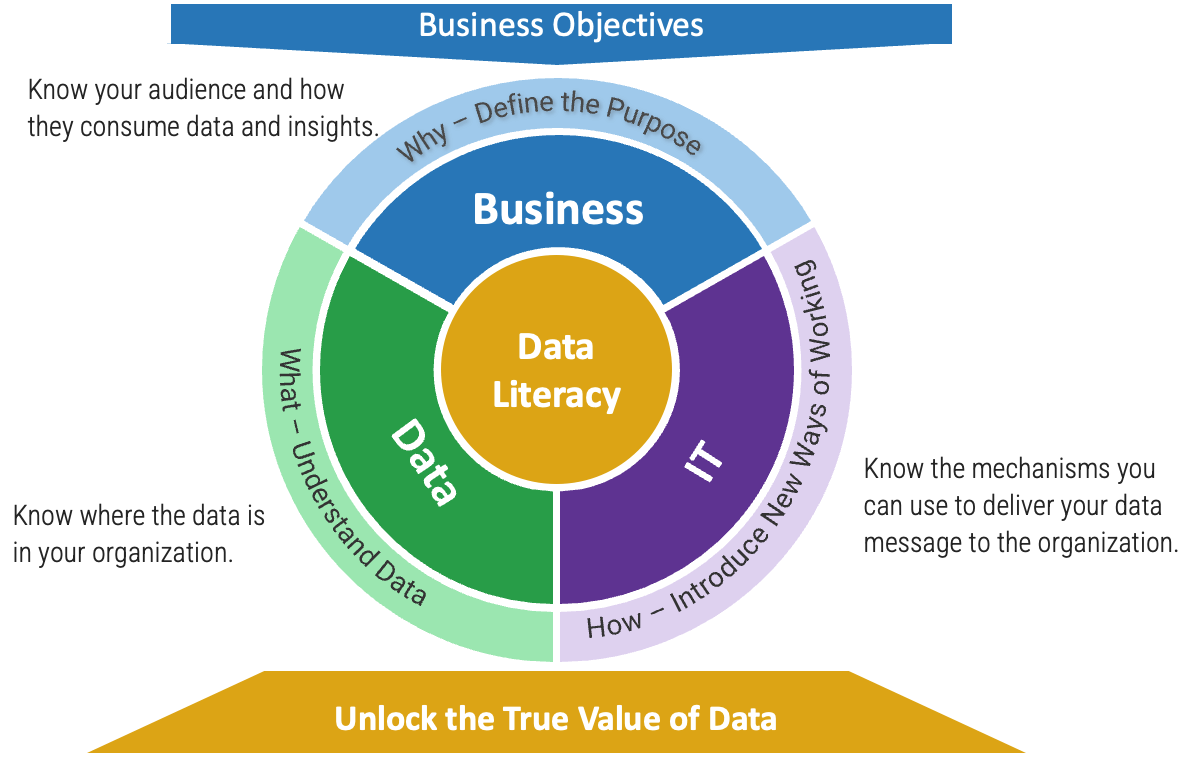
The Info-Tech difference:
- More than just technical training. Data literacy program isn’t just about data but rather encompasses aspects of business, IT, and data.
- More than a one-off exercise. To keep literacy skills alive, the program must be routine and sustainable, tailored to different needs across all levels of the organization.
- More than one delivery format. Different delivery methods need to be considered to suit various learning styles.
Data needs to be processed
Data – facts – are organized, processed, and given meaning to become insights.
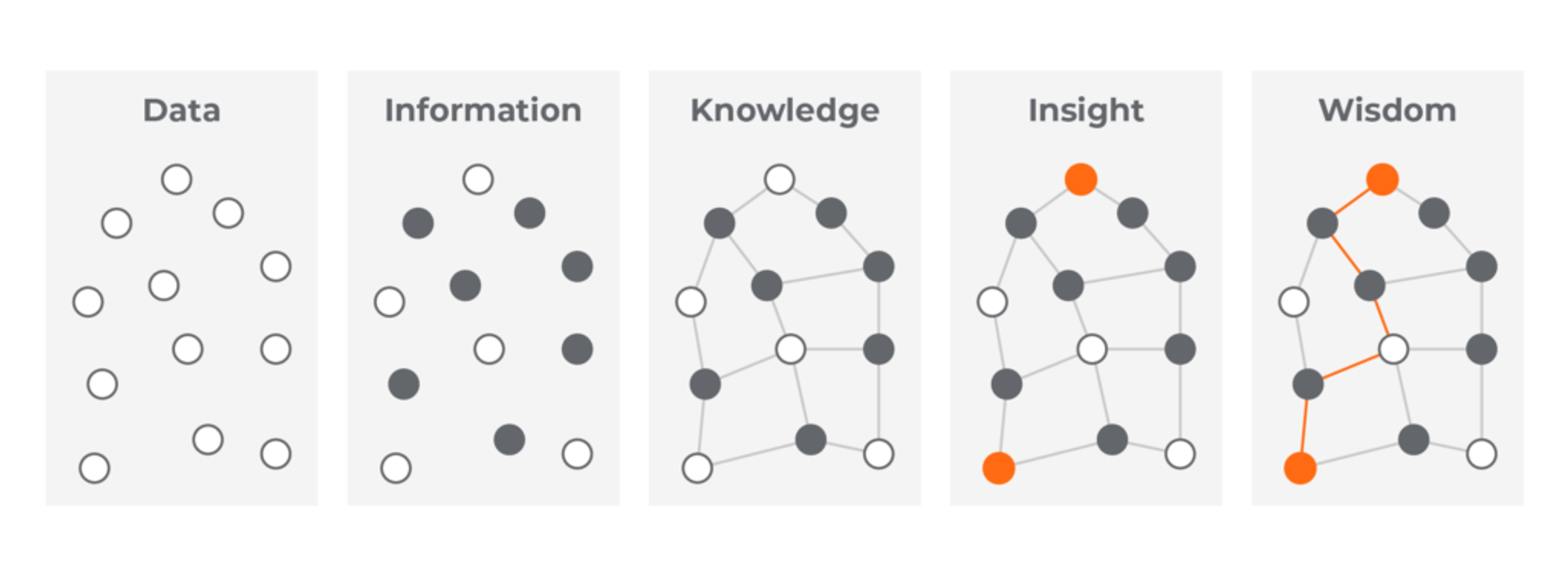
Image source: Welocalize, 2020.
Data represents a discrete fact or event without relation to other things (e.g. it is raining). Data is unorganized and not useful on its own.
Information organizes and structures data so that it is meaningful and valuable for a specific purpose (i.e. it answers questions). Information is a refined form of data.
When information is combined with experience and intuition, it results in knowledge. It is our personal map/model of the world.
Knowledge set with context generates insight. We become knowledgeable as a result of reading, researching, and memorizing (i.e. accumulating information).
Wisdom means the ability to make sound judgments. Wisdom synthesizes knowledge and experiences into insights.
Investment in data literacy is a game changer.
Data literacy is the ability to collect, manage, evaluate, and apply data in a critical manner.
A data-driven culture is “an operating environment that seeks to leverage data whenever and wherever possible to enhance business efficiency and effectiveness” (Forbes).
Info-Tech Insight
Data-driven culture refers to a workplace where decisions are made based on data evidence, not on gut instinct.
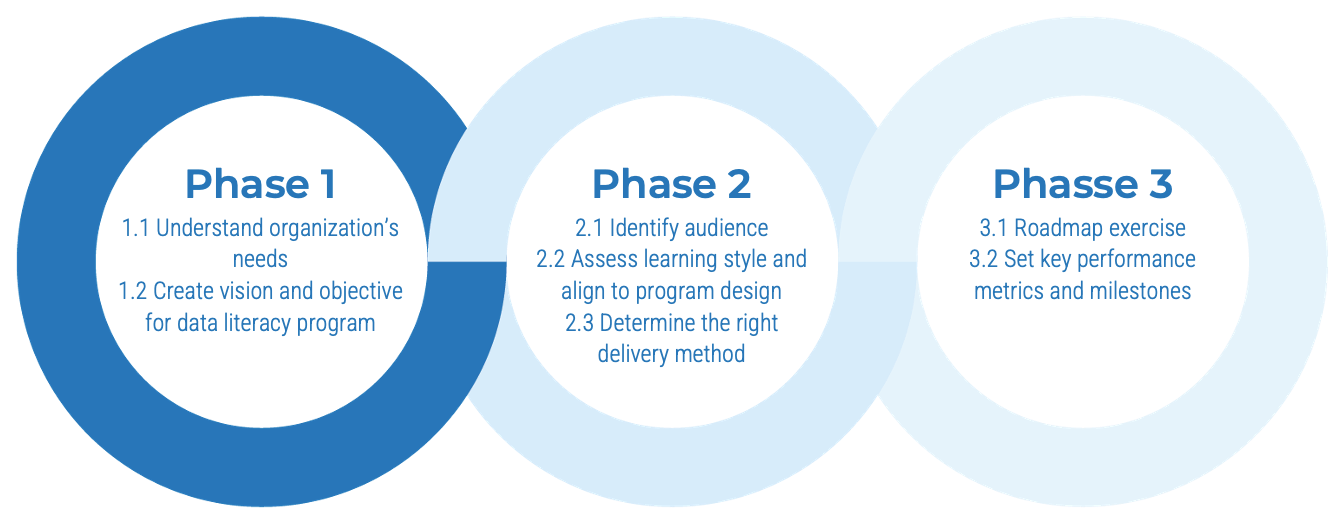
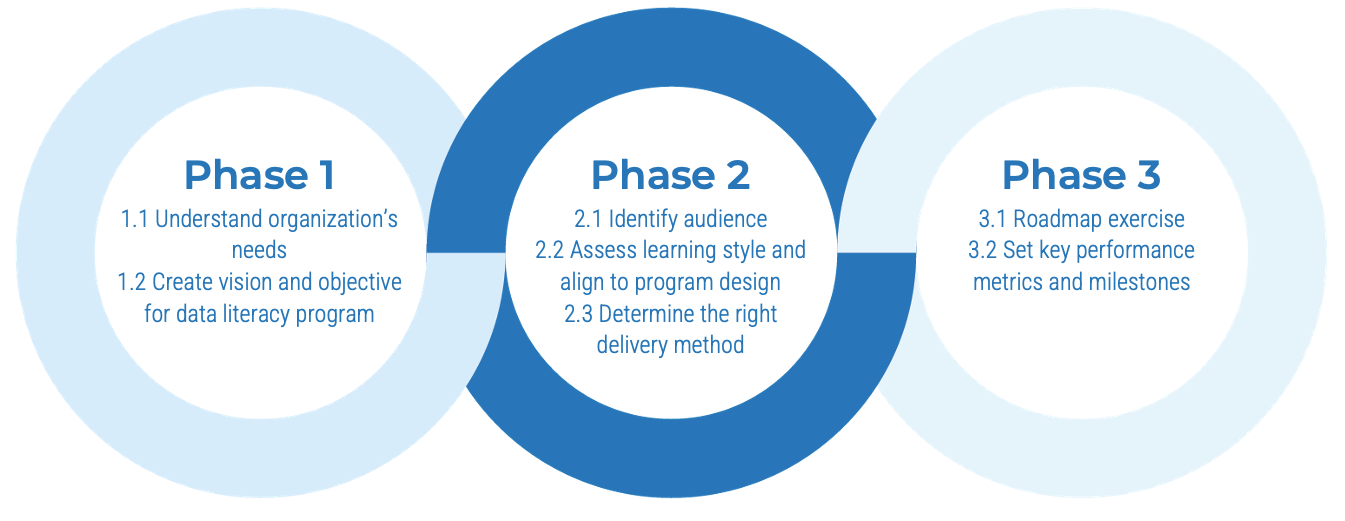
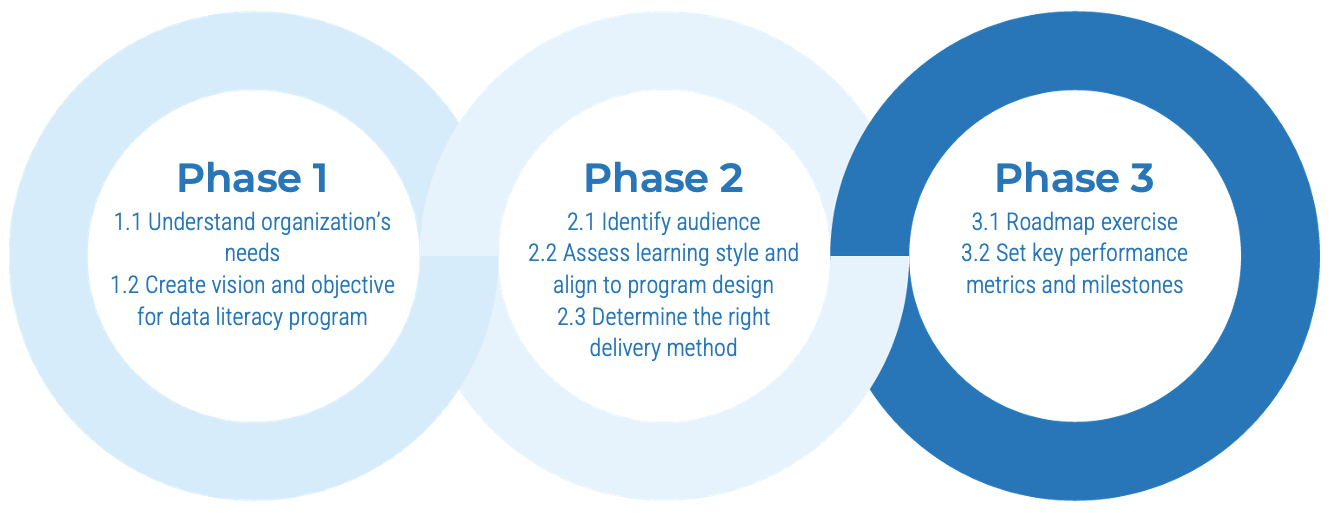
Info-Tech’s methodology for building a data literacy program
Phase Steps |
1. Define Data Literacy Objectives1.1 Understand organization’s needs 1.2 Create vision and objective for data literacy program |
2. Assess Learning Style and Align to Program Design2.1 Create persona and identify audience 2.2 Assess learning style and align to program design 2.3 Determine the right delivery method |
3. Socialize Roadmap and Milestones3.1 Establish a roadmap 3.2 Set key performance metrics and milestones |
Phase Outcomes |
Identify key objectives to establish and grow the data literacy program by articulating the problem and solutions proposed. |
Assess each audience’s learning style and adapt the program to their unique needs. |
Show a roadmap with key performance indicators to track each milestone and tell a data story. |
Insight Summary
“In a world of more data, the companies with more data-literate people are the ones that are going to win.”
– Miro Kazakoff, senior lecturer, MIT Sloan, in MIT Sloan School of Management, 2021
Overarching insight
By thoughtfully designing a data literacy training program personalized to each audience's maturity level, learning style, and experience, organizations can develop and grow a data-driven culture that unlocks the data's full potential for competitive differentiation.
Module 1 insight
We can learn a lot from each other. Literacy works both ways – business data stewards learn to “speak data” while IT data custodians understand the business context and value. Everyone should strive to exchange knowledge.
Module 2 insight
Avoid traditional classroom teaching – create a data literacy program that is learner-centric to allow participants to learn and experiment with data.
Aligning program design to those learning styles will make participants more likely to be receptive to learning a new skill.
Module 3 insight
A data literacy program isn’t just about data but rather encompasses aspects of business, IT, and data. With executive support and partnership with business, running a data literacy program means that it won’t end up being just another technical training. The program needs to address why, what, how questions.
Tactical insight
A lot of programs don’t include the fundamentals. To get data concepts to stick, focus on socializing the data/information/knowledge/wisdom foundation.
Tactical insight
Many programs speak in abstract terms. We present case studies and tangible use cases to personalize training to the audience’s world and showcase opportunities enabled through data.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for your data literacy program
How do you know if your data literacy program is successful? Here are some useful KPIs:
Program Adoption Metrics
- Percentage of employees attending data literacy training
- Percentage of participants who report gains in data management knowledge after training sessions
- Maturity assessment result
- Survey and diagnostic feedback before and after training
- Trend analysis of overall data literacy program
Operational Metrics
- Number of requests for analytics/reporting services
- Number of reports created by users
- Speed and quality of business decisions
- User satisfaction with reports and analytics services
- Improved business performance (customer satisfaction)
- Improved valuation of organization data
A data-driven culture builds tools and skills, builds users’ trust in the quality of data across sources, and raises the skills and understanding among the frontlines by encouraging everyone to leverage data for critical thinking and innovation.
Info-Tech offers various levels of support to best suit your needs
DIY Toolkit
"Our team has already made this critical project a priority, and we have the time and capability, but some guidance along the way would be helpful."
Guided Implementation
"Our team knows that we need to fix a process, but we need assistance to determine where to focus. Some check-ins along the way would help keep us on track."
Workshop
"We need to hit the ground running and get this project kicked off immediately. Our team has the ability to take this over once we get a framework and strategy in place."
Consulting
"Our team does not have the time or the knowledge to take this project on. We need assistance through the entirety of the project."
Diagnostics and consistent frameworks are used throughout all four options.
Workshop Overview
Contact your account representative for more information.
workshops@infotech.com 1-888-670-8889
Session 1 | Session 2 | Session 3 | Session 4 | |
Activities | Define Data Literacy Objectives1.1 Review Data Culture Diagnostic results 1.2 Identify business context: business goals, initiatives 1.3 Create vision and objective for data literacy program | Assess Learning Style and Align to Program Design2.1 Identify audience 2.2 Assess learning style and align to program design 2.3 Determine the right delivery method | Build a Data Literacy Roadmap and Milestones3.1 Identify program initiatives and topics 3.2 Determine delivery methods 3.3 Build the data literacy roadmap | Operational Strategy to implement Data Literacy4.1 Identify key performance metrics 4.2 Identify owners and document RACI matrix 4.3 Discuss next steps and wrap up. |
Deliverables |
|
|
|
|
Phase 1
Define Data Literacy Objectives
Foster Data-Driven Culture With Data Literacy
This phase will walk you through the following activities:
- Understand the organization’s needs.
- Create vision and objective for data literacy program.
This phase involves the following participants:
- Data governance sponsor
- Data owners
- Data stewards
- Data custodians
1.1 Gauge your organization’s current data culture
Conduct data culture survey or diagnostic.
- Identify members of the data user base, data consumers, and other key stakeholders for surveying.
- Conduct an information session to introduce Info-Tech’s Data Culture Diagnostic survey. Explain the objective and importance of the survey and its role in helping to understand the organization’s current data culture and inform the improvement of that culture.
- Roll out the Info-Tech Data Culture Diagnostic survey to the identified users and stakeholders.
- Debrief and document the results and scorecard in the Data Strategy Stakeholder Interview Guide and Findings document.
Input
|
Output
|
Materials
|
Participants
|
Contact your Info-Tech Account Representative for details on launching a Data Culture Diagnostic.
1.2 Define data literacy objectives
- Understand the organization’s needs by identifying opportunities and challenges relating to data. Document the described real-life examples.
- Categorize the list and identify areas where data literacy can address the business problem.
- Create a vision statement for the data literacy program, ensuring that it covers all levels of the organization.
- Articulate the intended targets and goals in planning for a data literacy program.
Input
| Output
|
Materials
| Participants
|
Quick wins for improving data literacy
Data collected through Info-Tech’s Data Culture Diagnostic suggests three ways to improve data literacy:
87%
think more can be done to define and document commonly used terms with methods such as a business data glossary.
68%
think they can have a better understanding of the meaning of all data elements that are being captured or managed.
86%
feel that they can have more training in terms of tools as well as on what data is available at the organization.
Source: Info-Tech Research Group's Data Culture Diagnostic, 2022; N=2,652
Quick Wins
- Create a business data glossary to document and define common terms.
- Provide easy access to the business data glossary and procedures on how data is captured and managed.
- Launch an organization-wide data literacy program.
Delivering value is a means and the goal
Start with real business problems in a hands-on format to demonstrate the value of data.
Identify business problem:
- Business decisions without facts are just guesses.
- Management spends a lot of time finding and fixing data.
- Unknown challenges on data assets and risk.
- Incomplete view of customer/client and industry.
- Not ready for modern data opportunities (e.g. artificial intelligence).
Create an objective
Treat data as a strategic asset to gain insight into our customers for all levels of organization.
The solution: Data-driven culture powered by people who speak data.
- Data dictionary
- Data literacy
- Trusted single source
- Access to analytics tools
- Decision making
"According to Forrester, 91% of organizations find it challenging to improve the use of data insights for decision-making – even though 90% see it as a priority. Why the disconnect? A lack of data literacy."
– Alation, 2020
Fundamental data literacy
Data literacy is more than just a technical training or a one-off exercise.
Info-Tech provides various topics suited for a data literacy program that can accommodate different data skill requirements and encompasses relevant aspects of business, IT, and data.
Info-Tech Research Group’s Data Literacy Program
Use discovery and diagnostics to understand users’ comfort level and maturity with data.
Data lunch 'n' learn
- The power and value of data
- Everyone is a data steward
- Becoming data literate
- Data 101
- The future is data
1 hour
For: General audience, senior leadership, data leads, change managementSpeak data
- What is data
- Meet the data team
- Day in the life of a steward
- How data impacts you
- Tools of the trade
1/2 day
For: New stewards, data owners, pre-data strategy workshopYour data story
- Ask the right questions
- Find the top five data elements
- Understand your data
- Present your data story
- Lessons from COVID-19
1/2 day
For: New stewards, business data owners, pre-BI/analytics workshopPhase 2
Assess Learning Style and Align to Program Design
Foster Data-Driven Culture With Data Literacy
This phase will walk you through the following activities:
- Identify your audience.
- Assess learning styles and align them to the data program design.
- Determine the right delivery method.
This phase involves the following participants:
- Data governance sponsor
- Data owners
- Data stewards
- Data custodians
Avoid common pitfalls
75%
feel that training was too long to remember or to apply in their day-to-day work.
21%
find training had insufficient follow-up to help them apply on the job.
Source: Grovo, 2018.
-
Information Overload
Trying to cover too much useful information results in overwhelm and does not deliver on key training objectives. -
Limited Implementation
Learning is only the beginning. The real results are obtained when learning is followed by practice, which turns new knowledge into reliable habits. -
Lack of Organizational Alignment
Implementing training without a clear link to organizational objectives leaves you unable to clearly communicate its value, undermines your ability to secure buy-in from attendees and executives, and leaves you unable to verify that the training is actually improving effectiveness.
2.1 Understand learning style
- Create persona and identify the audiences and their roles in data across all levels of the organization.
- Identify the data program initiatives and assign the best delivery method to each initiative.
- Assign participants to each program initiative based on their skill gap and learning style.
Input
| Output
|
Materials
| Participants
|
You and data
Is data an integral part of your work?
Do you feel comfortable finding and using data in your organization?
- Many people feel intimidated by data and therefore miss out on what data can do for them.
- Often the obstacle is language. If you don’t understand the semantics around data, you will not feel confident to contribute to discussions around data.
- You use data every day but need additional vocabulary to understand how to handle it properly.
- Data literacy is the ability to “speak data” and to understand what data means (i.e. how to read charts and graphs, draw valid conclusions, and recognize when data is misinterpreted or used inappropriately to be misleading).
- The business often doesn’t understand its role in data governance and how it informs and assists IT in responsible data management.
Info-Tech Insight
IT and data professionals need to understand the business as much as business needs to talk about data. Bidirectional learning and feedback improves the synergy between business and IT.
Create personas
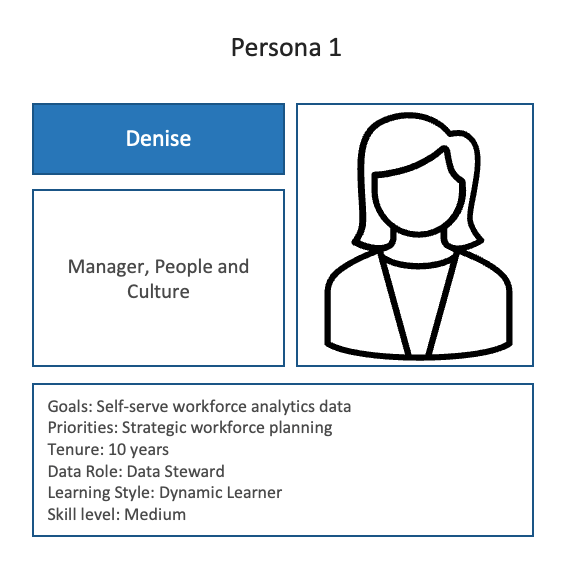
Persona creation is a way to brainstorm ideas for the data literacy program.
Choose a data role (e.g. data steward, data owner, data scientist).
Describe the persona based on goals, priorities, tenures, preferred learning style, type of work with data.
Identify data skill and level of skills required.
Consider these other ways to brainstorm:
- Review current in-flight projects.
- Analyze types of data requests.
- Understand needs by department.
- Share learnings in a community of practice.
Program design
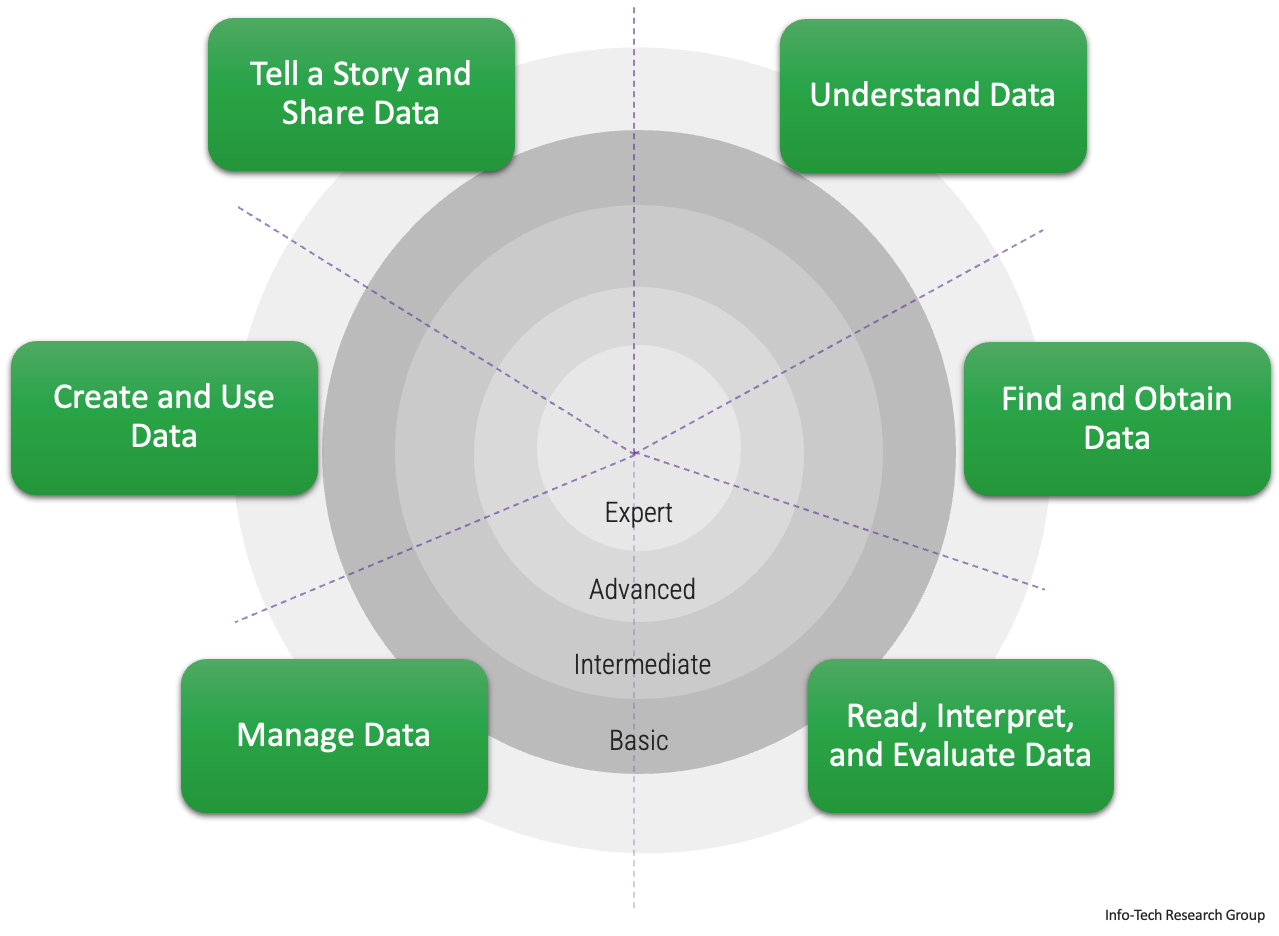
Categorize into six data skill areas
Not everyone needs the same level of skill sets
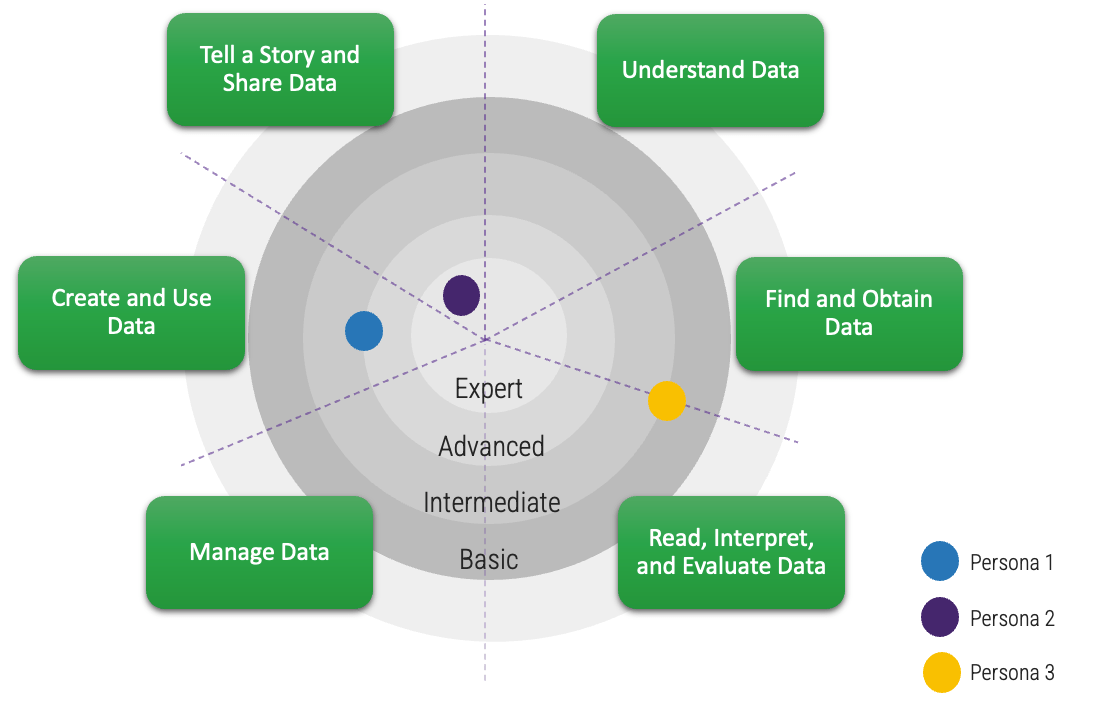
Map the personas to the program
Bridging the data knowledge gap.
- Each component will promote the value of data to all levels of employees when demonstrating the right way for data to be understood, managed, and consumed in the organization.
- Categorizing the data literacy program into six areas and levels of skill sets will provide clarity into which areas to focus on.
- The program is intended to be implemented in stages, allowing the audience to learn and adopt the new skills. Leveraging in-flight projects for rolling out training will have a higher success because the need is already built into the project.
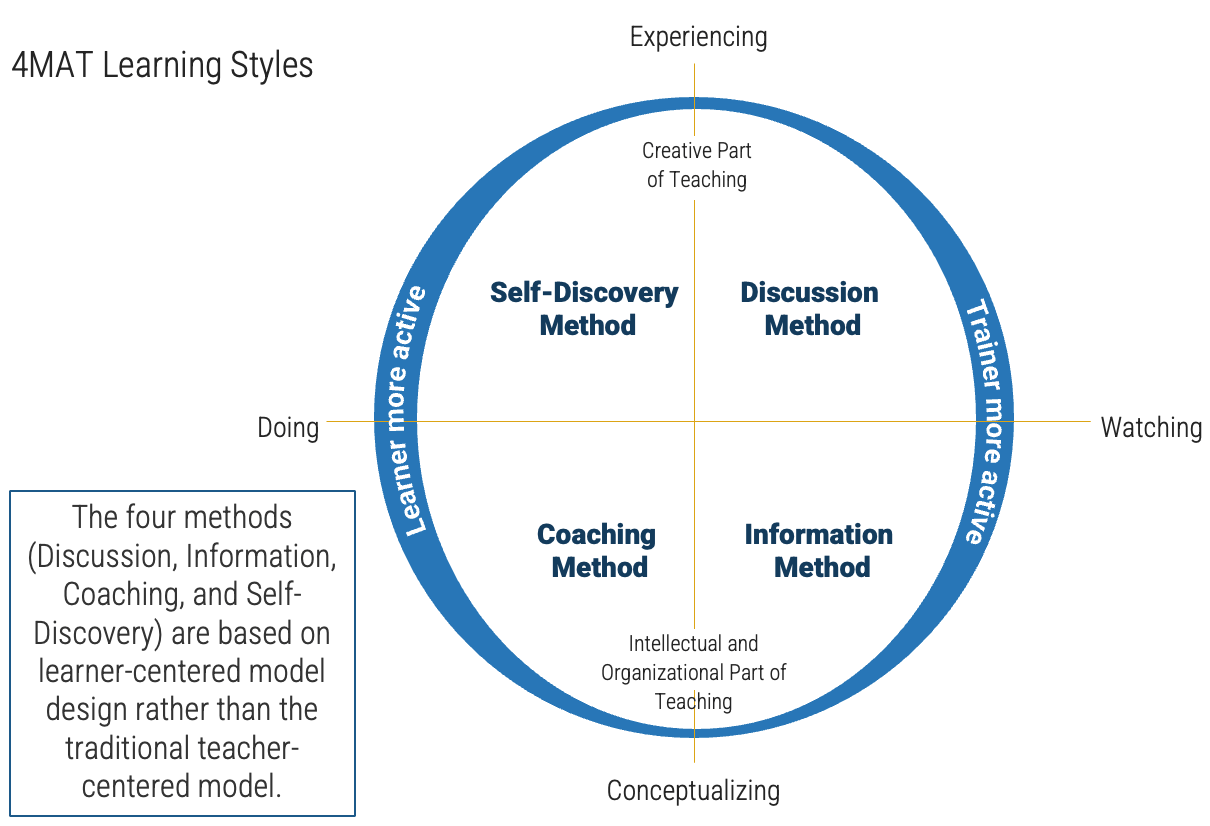
Align program design to learning styles
Info-Tech Insight
Tailor your data literacy program to meet your organization’s needs, filling your range of knowledge gaps and catering to different levels of users.
When it comes to rolling out a data literacy program, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Your data literacy program is intended to spread knowledge throughout your organization. It should target everyone from executive leadership to management to subject matter experts across all functions of the business.
Discussion method
Delivery Method
- Interactive format between instructor and learner
- Instructor empowers and motivates learner through dialogues and exercises
The imaginative learner
The imaginative learner group likes to engage in feelings and spend time on reflection. This type of learner desires personal meaning and involvement. They focus on personal values for themselves and others and make connections quickly.
For this group of learners, their question is: why should I learn this?
Learning characteristics
- Seek meaning
- Need to be personally involved
- Learn by listening and sharing ideas
- Function through social interaction
Information method
Delivery Method
- Instructor does most of the talking in the training
- Instructor is teaching the content, delivering the training content, and demonstrating
Analytical learner
The analytical learner group likes to listen, to think about information, and to come up with ideas. They are interested in acquiring facts and delving into concepts and processes. They can learn effectively and enjoy doing independent research.
For this group of learners, their question is: what should I learn?
Learning characteristics
- Seek and examine the facts
- Need to know what experts think
- Interested in ideas and concepts
- Critique information and collect data
- Function by adapting to experts
Coaching method
Delivery Method
- Learning has on-the-job training or learning through role-play exercises
- Instructor is coaching and facilitating learner
Common sense learner
The common sense learner group likes thinking and doing. They are satisfied when they can carry out experiments, build and design, and create usability. They like tinkering and applying useful ideas.
For this group of learners, their question is: how should I learn?
Learning characteristics
- Seek usability
- Need to know how things work
- Learn by testing theories using practical methods
- Use factual data to build concepts
- Enjoy hands-on experience
Self-discovery method
Delivery Method
- Interactive format between instructor and learner
- Instructor provides evaluation and remedial instruction
Common sense learner
The dynamic learner group learns through doing and experiencing. They are continually looking for hidden possibilities and researching ideas to make original adjustments. They learn through trial and error and self-discovery.
For this group of learners, their question is: what if I learn this?
Learning characteristics
- Seek hidden possibilities
- Need to know what can be done with things
- Learn by trial and error
- Enjoy variety and excel in being flexible
Delivery method considerations
There are four common ways to learn a new skill: by watching, conceptualizing, doing, and experiencing. The following are some suggestions on ways to implement your data literacy program through different delivery methods.
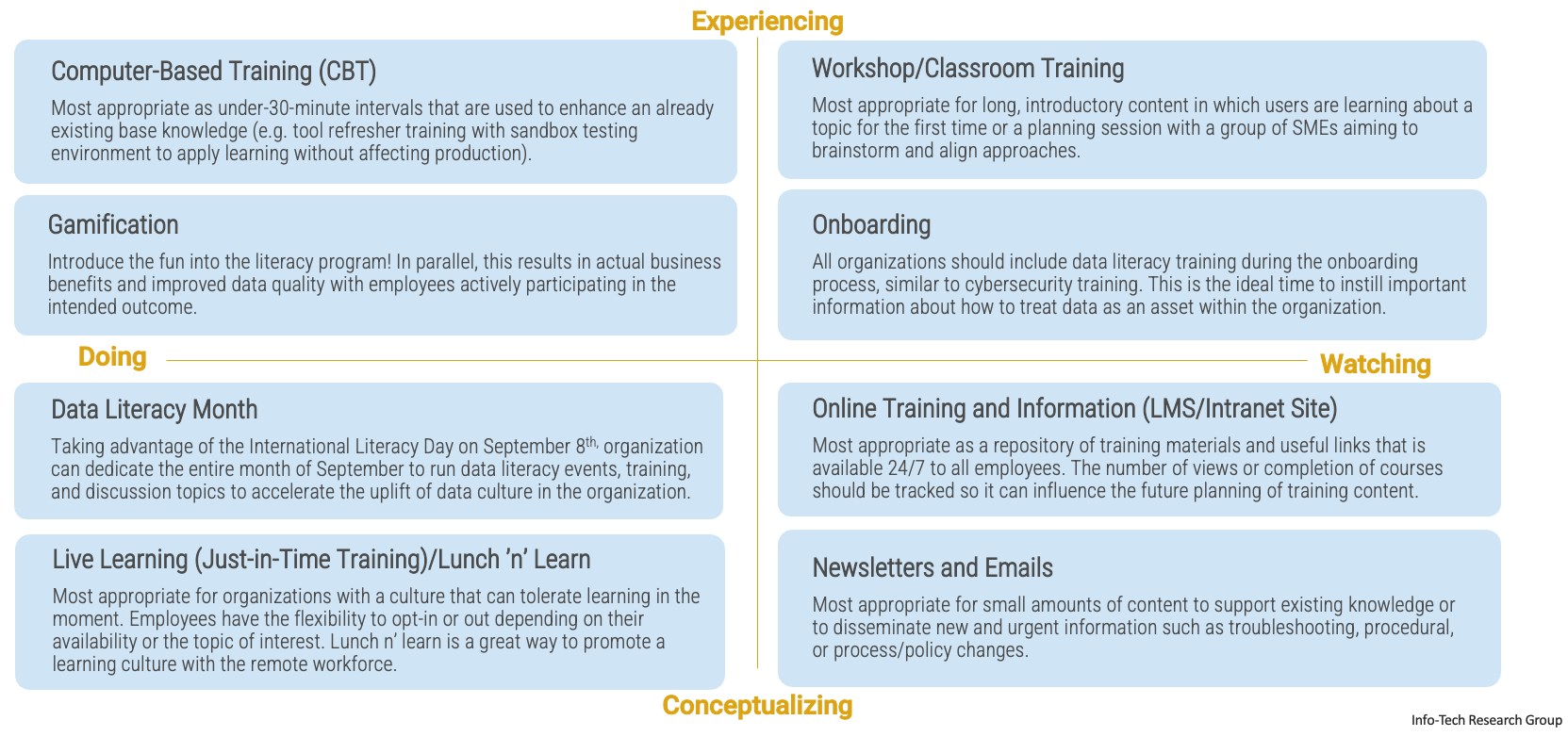
Phase 3
Map Out Data Literacy Roadmap and Milestones
Foster Data-Driven Culture With Data Literacy
This phase will walk you through the following activities:
- Complete a roadmap exercise.
- Set key performance metrics and milestones.
This phase involves the following participants:
- Data governance sponsor
- Data owners
- Data stewards
- Data custodians
3.1 Build the data literacy roadmap and milestones
1-3 hours
- Gather the data literacy objectives and list of program initiatives with their assigned groups.
- Discuss each program initiative with the data literacy creation team, assigning content owners and estimating effort required to build the content.
For the Gantt chart:
- Input the roadmap start year.
- List each data literacy topic and delivery method.
- Populate the planned start and end dates for the prepopulated list of program initiatives.
Input
| Output
|
Materials
| Participants
|
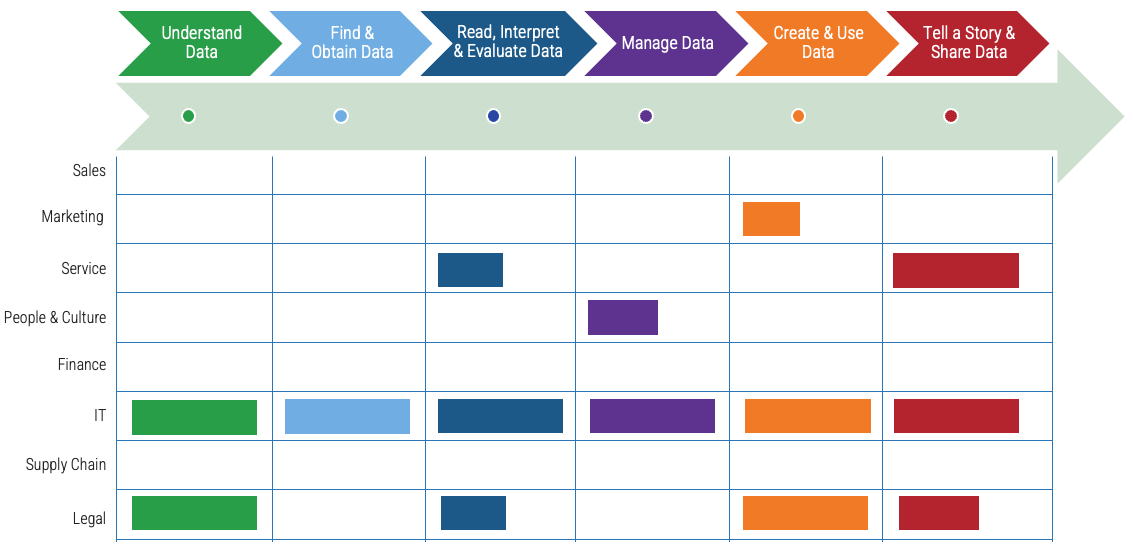
Data literacy journey mapping
Making it sustainable
- Deliver the literacy program in stages to make it easier for the audience to consume the content.
- Allow opportunities to apply the learnings at work.
- Map out the data literacy trainings as they get delivered and identify gaps, if any. Continue to refine and adjust the program and delivery method for better outcome.
- Set clear goals and KPIs measurement up front.
- Conduct Info-Tech Research Group’s Data Culture Diagnostics to set the baseline and repeat the assessment in 12 to 18 months.
- Assign champions to lead change and influence end users to adopt better processes.
Research contributors
Name |
Position |
| Andrea Malick | Advisory Director, Info-Tech Research Group |
| Andy Neill | AVP, Data and Analytics, Chief Enterprise Architect, Info-Tech Research Group |
| Crystal Singh | Research Director, Info-Tech Research Group |
| Imad Jawadi | Senior Manager, Consulting Advisory, Info-Tech Research Group |
| Irina Sedenko | Research Director, Info-Tech Research Group |
| Reddy Doddipalli | Senior Workshop Director, Info-Tech Research Group |
| Sherwick Min | Technical Counselor, Info-Tech Research Group |
| Wayne Cain | Principal Advisory Director, Info-Tech Research Group |
Info-Tech’s Data Literacy Program
Contact your account representative for more information.
workshops@infotech.com 1-888-670-8889
Session 1 |
Session 2 |
Session 3 |
Session 4 |
|
Activities |
Understand the WHY and Value of Data1.1 Business context, business objectives, and goals 1.2 You and data 1.3 Data journey from data to insights 1.4 Speak data – common terminology |
Learn about the WHAT Through Data Flow2.1 Data creation 2.2 Data ingestion 2.3 Data accumulation 2.4 Data augmentation 2.5 Data delivery 2.6 Data consumption |
Explore the HOW Through Data Visualization Training3.1 Ask the right questions 3.2 Find the top five data elements 3.3 Understand your data 3.4 Present your data story 3.5 Sharing of lessons learned |
Put Them All Together Through Data Governance Awareness4.1 Data governance framework 4.2 Data roles and responsibilities 4.3 Data domain and owners |
Deliverables |
|
|
|
|
Related Info-Tech Research
Establish Data Governance
Deliver measurable business value.
Build a Robust and Comprehensive Data Strategy
Key to building and fostering a data-driven culture.
Create a Data Management Roadmap
Streamline your data management program with our simplified framework.
Bibliography
About Learning. “4MAT overview.” About Learning., 16 Aug. 2001. Web.
Accenture. “The Human Impact of Data Literacy,” Accenture, 2020. Web.
Anand, Shivani. “IDC Reveals India Data and Content Technologies Predictions for 2022 and onwards; Focus on Data Literacy for an Elevated data Culture.” IDC, 14 Mar. 2022. Web.
Belissent, Jennifer, and Aaron Kalb. “Data Literacy: The Key to Data-Driven Decision Making.” Alation, April 2020. Web.
Brown, Sara. “How to build data literacy in your company.” MIT Sloan School of Management, 9 Feb 2021. Web.
---. “How to build a data-driven company.” MIT Sloan School of Management, 24 Sept. 2020. Web.
Domo. “Data Never Sleeps 9.0.” Domo, 2021. Web.
Dykes, Brent. “Creating A Data-Driven Culture: Why Leading By Example Is Essential.” Forbes, 26 Oct. 2017. Web.
Experian. “10 signs you are sitting on a pile of data debt.” Experian, 2020. Accessed 25 June 2021. Web.
Experian. “2019 Global Data Management Research.” Experian, 2019. Web.
Knight, Michelle. “Data Literacy Trends in 2023: Formalizing Programs.” Dataversity, 3 Jan. 2023. Web.
Ghosh, Paramita. “Data Literacy Skills Every Organization Should Build.” Dataversity, 2 Nov. 2022. Web.
Johnson, A., et al., “How to Build a Strategy in a Digital World,” Compact, 2018, vol. 2. Web.
LifeTrain. “Learning Style Quiz.” EMTrain, Web.
Lambers, E., et al. “How to become data literate and support a data-drive culture.” Compact, 2018, vol. 4. Web.
Marr, Benard. “Why is data literacy important for any business?” Bernard Marr & Co., 16 Aug. 2022. Web.
Marr, Benard. “8 simple ways to enhance your data literacy skills.” Bernard Marr & Co., 16 Aug. 2022. Web/
Mendoza, N.F. “Data literacy: Time to cure data phobia” Tech Republic, 27 Sept. 2022. Web.
Mizrahi, Etai. “How to stay ahead of data debt and downtime?” Secoda, 17 April 2023. Web.
Needham, Mass., “IDC FutureScape: Top 10 Predictions for the Future of Intelligence.” IDC, 5 Dec. 2022. Web.
Paton, J., and M.A.P. op het Veld. “Trusted Analytics.” Compact, 2017, vol. 2. Web.
Qlik. “Data Literacy to be Most In-Demand Skill by 2030 as AI Transforms Global Workplaces.” Qlik., 16 Mar 2022. Web.
Qlik. “What is data literacy?” Qlik, n.d. Web.
Reed, David. Becoming Data Literate. Harriman House Publishing, 1 Sept. 2021. Print.
Salomonsen, Summer. “Grovo’s First-Time Manager Microlearning® Program Will Help Your New Managers Thrive in 2018.” Grovos Blog, 5 Dec. 2018. Web.
Webb, Ryan. “More Than Just Reporting: Uncovering Actionable Insights From Data.” Welocalize, 1 Sept. 2020. Web.
Buying Options
Foster Data-Driven Culture With Data Literacy
Client rating
Cost Savings
Days Saved
IT Risk Management · IT Leadership & Strategy implementation · Operational Management · Service Delivery · Organizational Management · Process Improvements · ITIL, CORM, Agile · Cost Control · Business Process Analysis · Technology Development · Project Implementation · International Coordination · In & Outsourcing · Customer Care · Multilingual: Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese · Entrepreneur
Tymans Group is a brand by Gert Taeymans BV
Gert Taeymans bv
Europe: Koning Albertstraat 136, 2070 Burcht, Belgium — VAT No: BE0685.974.694 — phone: +32 (0) 468.142.754
USA: 4023 KENNETT PIKE, SUITE 751, GREENVILLE, DE 19807 — Phone: 1-917-473-8669
Copyright 2017-2022 Gert Taeymans BV