Applications Priorities 2023

- Economic, social, and regulatory conditions have changed livelihoods, businesses, and marketplaces. Modern tools and technologies have acted as lifelines by minimizing operating and delivery costs, and in the process, establishing a strong foundation for growth and maturity.
- These tools and technologies must meet the top business goals of CXOs: ensure service continuity, improve customer experience, and make data-driven decisions.
- While today’s business applications are good and well received, there is still room for improvement. The average business application satisfaction score among IT leadership was 72% (n=1582, CIO Business Vision).
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Applications are critical components in any business strategic plan. They can directly influence an organization’s internal and external brand and reputation, such as their uniqueness, competitiveness and innovativeness in the industry
- Business leaders are continuously looking for innovative ways to better position their application portfolio to satisfy their goals and objectives, i.e., application priorities. Given the scope and costs often involved, these priorities must be carefully crafted to clearly state achievable business outcomes that satisfies the different needs very different customers, stakeholders, and users.
- Unfortunately, expectations on your applications team have increased while the gap between how stakeholders and applications teams perceive effectiveness remains wide. This points to a need to clarify the requirements to deliver valuable and quality applications and address the pressures challenging your teams.
Impact and Result
Learn and explore the technology and practice initiatives in this report to determine which initiatives should be prioritized in your application strategy and align to your business organizational objectives:
- Optimize the effectiveness of the IT organization.
- Boost the productivity of the enterprise.
- Enable business growth through technology.
Applications Priorities 2023 Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Applications Priorities Report 2023 – A report that introduces and describes five opportunities to prioritize in your 2023 application strategy.
In this report, we explore five priorities for emerging and leading-edge technologies and practices that can improve on capabilities needed to meet the ambitions of your organization.
- Applications Priorities 2023 Report
Infographic

Further reading
Applications Priorities 2023
Applications are the engine of the business: keep them relevant and modern
What we are facing today is transforming the ways in which we work, live, and relate to one another. Applications teams and portfolios MUST change to meet this reality.
Economic, social, and regulatory conditions have changed livelihoods, businesses, and marketplaces. Modern tools and technologies have acted as lifelines by minimizing operating and delivery costs, and in the process, establishing a strong foundation for growth and maturity.
As organizations continue to strengthen business continuity, disaster recovery, and system resilience, activities to simply "keep the lights on" are not enough. Be pragmatic in the prioritization and planning of your applications initiatives, and use your technologies as a foundation for your growth.
Your applications must meet the top business goals of your CXOs
- Ensure service continuity
- Improve customer experience
- Make data-driven decisions
- Maximize stakeholder value
- Manage risk
Source: CEO-CIO Alignment Diagnostics, August 2021 to July 2022, n=568.
Select and align your applications priorities to your business goals and objectives
Applications are critical components in any business strategic plan. They can directly influence an organization's internal and external brand and reputation, such as their:
- Uniqueness, competitiveness, and innovativeness in the industry.
- Ability to be dynamic, flexible, and responsive to changing expectations, business conditions, and technologies.
Therefore, business leaders are continuously looking for innovative ways to better position their application portfolios to satisfy their goals and objectives, i.e. applications priorities. Given the scope and costs often involved, these priorities must be carefully crafted to clearly state achievable business outcomes that satisfy
the different needs of very different customers, stakeholders, and users.
Today's business applications are good but leave room for improvement
72%
Average business application satisfaction score among IT leadership in 1582 organizations.
Source: CIO Business Vision, August 2021 to July 2022, N=190.
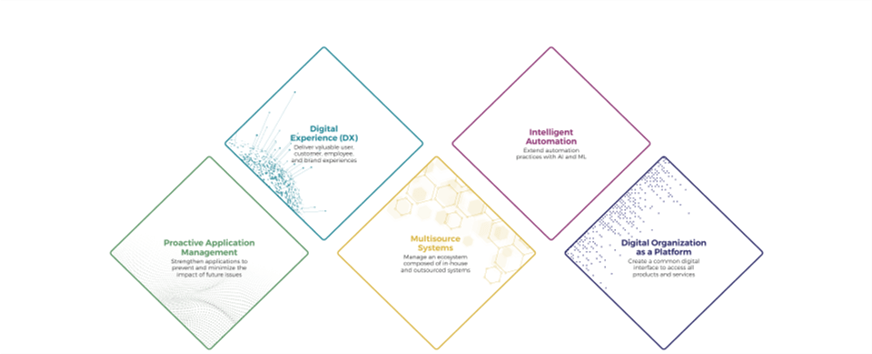
Five Applications Priorities for 2023
In this report, we explore five priorities for emerging and leading-edge technologies and practices that can improve on capabilities needed to meet the Ambitions of your organization.
Strengthen your foundations to better support your applications priorities
These key capabilities are imperative to the success of your applications strategy.
KPI and Metrics
Easily attainable and insightful measurements to gauge the progress of meeting strategic objectives and goals (KPIs), and the performance of individual teams, practices and processes (metrics).
BUSINESS ALIGNMENT
Gain an accurate understanding and interpretation of stakeholder, end-user, and customer expectations and priorities. These define the success of business products and services considering the priorities of individual business units and teams.
EFFICIENT DELIVERY & SUPPORT PRACTICE
Software delivery and support roles, processes, and tools are collaborative, well equipped and resourced, and optimized to meet changing stakeholder expectations.
Data Management & Governance
Ensuring data is continuously reliable and trustworthy. Data structure and integrations are defined, governed, and monitored.
Product & Service Ownership
Complete inventory and rationalization of the product and service portfolio, prioritized backlogs, roadmaps, and clear product and service ownership with good governance. This helps ensure this portfolio is optimized to meet its goals and objectives.
Strengthen your foundations to better support your applications priorities (cont'd)
These key capabilities are imperative to the success of your applications strategy.
Organizational Change Management
Manage the adoption of new and modified processes and technologies considering reputational, human, and operational concerns.
IT Operational Management
Continuous monitoring and upkeep of products and services to assure business continuity, and system reliability, robustness and disaster recovery.
Architectural Framework
A set of principles and standards that guides the consistent, sustainable and scalable growth of enterprise technologies. Changes to the architecture are made in collaboration with affected parties, such as security and infrastructure.
Application Security
The measures, controls, and tactics at the application layer that prevent vulnerabilities against external and internal threats and ensure compliance to industry and regulatory security frameworks and standards.
There are many factors that can stand in your team's way
Expectations on your applications team have increased, while the gap between how stakeholders and applications teams perceive effectiveness remains wide. This points to a need to clarify the requirements to deliver valuable and quality applications and address the pressures challenging your teams.
- Attracting and retaining talent
- Maximizing the return on technology
- Confidently shifting to digital
- Addressing competing priorities
- Fostering a collaborative culture
- Creating high-throughput teams
CIOs agree that at least some improvement is needed across key IT activities
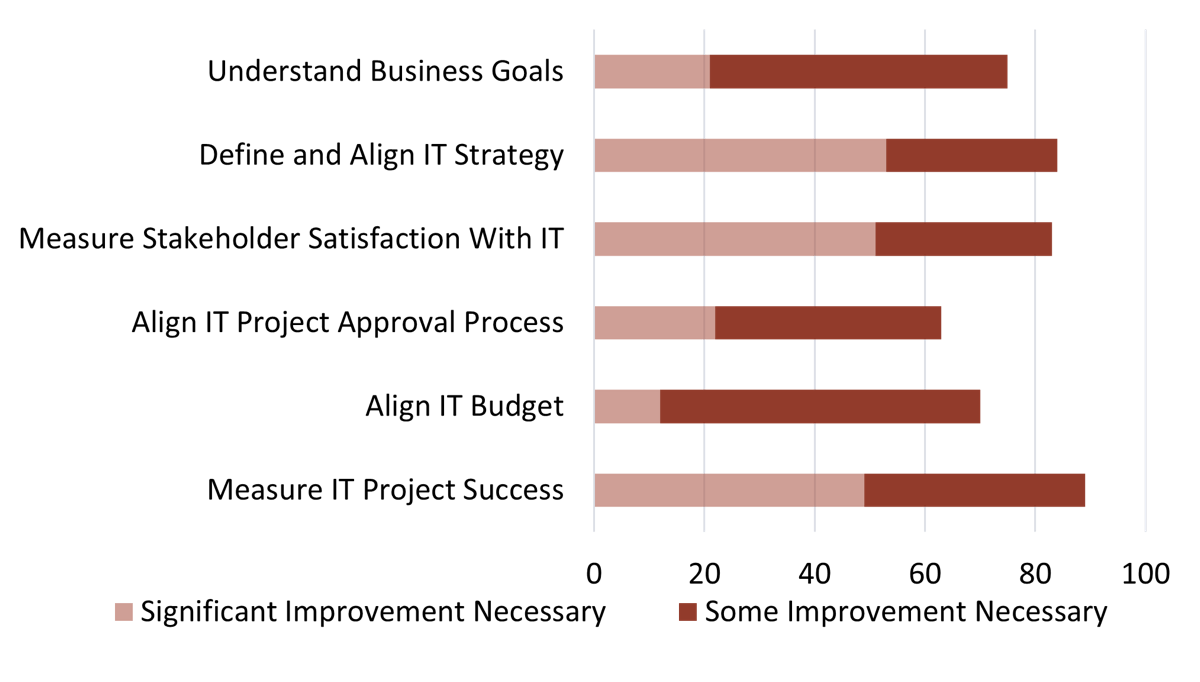
Source: CEO-CIO Alignment Diagnostics, August 2021 to July 2022, n=568.
Pressure Point 1:
Attracting and Retaining Talent
Recent environmental pressures impacted traditional working arrangements and showed more workplace flexibility is often possible. At the same time, many employees' expectations about how, when, and where they choose to work have also evolved. Recruitment and retention are reflections of different sides of the same employee value proposition coin. Organizations that fail to reinvent their approach to attracting and retaining talent by focusing on candidate and employee experience risk turnover, vacancies, and lost opportunities that can negatively impact the bottom line.
Address the underlying challenges
- Lack of employee empowerment and few opportunities for learning and development.
- Poor coworker and manager relationships.
- Compensation and benefits are inadequate to maintain desired quality of life.
- Unproductive work environment and conflicting balance of work and life.
- Unsatisfactory employee experience, including lack of employee recognition
and transparency of organizational change.
While workplace flexibility comes with many benefits, longer work hours jeopardize wellbeing.
62% of organizations reported increased working hours, while 80% reported an increase in flexibility.
Source: McLean & Company, 2022; n=394.
Be strategic in how you fill and train key IT skills and capabilities
- Cybersecurity
- Big Data/Analytics
- Technical Architecture
- DevOps
- Development
- Cloud
Source: Harvey Nash Group, 2021; n=2120.
Pressure Point 2:
Maximizing the Return of Technology
Recent environmental pressures impacted traditional working arrangements and showed more workplace flexibility is often possible. At the same time, many employees' expectations about how, when, and where they choose to work have also evolved. Recruitment and retention are reflections of different sides of the same employee value proposition coin. Organizations that fail to reinvent their approach to attracting and retaining talent by focusing on candidate and employee experience risk turnover, vacancies, and lost opportunities that can negatively impact the bottom line.
Address the underlying challenges
- Inability to analyze, propose, justify, and communicate modernization solutions in language the stakeholders understand and in a way that shows they clearly support business priorities and KPIs and mitigate risks.
- Little interest in documenting and rationalizing products and services through business-IT collaboration.
- Lack of internal knowledge of the system and loss of vendor support.
- Undefined, siloed product and service ownership and governance, preventing solutions from working together to collectively deliver more value.
- Little stakeholder appetite to invest in activities beyond "keeping the lights on."
Only 64% of applications were identified as effective by end users.
Effective applications are identified as at least highly important and have high feature and usability satisfaction.
Source: Application Portfolio Assessment, August 2021 to July 2022; N=315.
"Regardless of the many definitions of modernization floating around, the one characteristic that we should be striving for is to ensure our applications do an outstanding job of supporting the users and the business in the most effective and efficient manner possible."
Source: looksoftware.
Pressure Point 3:
Confidently Shifting to Digital
"Going digital" reshapes how the business operates and drives value by optimizing how digital and traditional technologies and tactics work together. This shift often presents significant business and technical risks to business processes, enterprise data, applications, and systems which stakeholders and teams are not aware of or prepared to accommodate.
Address the underlying challenges
- Differing perspectives on digital can lead to disjointed transformation initiatives, oversold benefits, and a lack of synergy among digital technologies and processes.
- Organizations have difficulty adapting to new technologies or rethinking current business models, processes, and ways of working because of the potential human, ethical, and reputational impacts and restrictions from legacy systems.
- Management lacks a framework to evaluate how their organization manages and governs business value delivery.
- IT is not equipped or resourced to address these rapidly changing business, customer, and technology needs.
- The wrong tools and technologies were chosen to support the shift to digital.
The shift to digital processes is starting, but slowly.
62% of respondents indicated that 1-20% of their processes were digitized during the past year.
Source: Tech Trends and Priorities 2023; N=500
Resistance to change and time/budget constraints are top barriers preventing companies from modernizing their applications.
Source: Konveyor, 2022; n=600.
Pressure Point 4:
Addressing Competing Priorities
Enterprise products and services are not used, operated, or branded in isolation. The various parties involved may have competing priorities, which often leads to disagreements on when certain business and technology changes should be made and how resources, budget, and other assets should be allocated. Without a broader product vision, portfolio vision, and roadmap, the various dependent or related products and services will not deliver the same level of value as if they were managed collectively.
Address the underlying challenges
- Undefined product and service ownership and governance, including escalation procedures when consensus cannot be reached.
- Lack of a unified and grounded set of value and quality definitions, guiding principles, prioritization standards, and broad visibility across portfolios, business capabilities, and business functions.
- Distrust between business units and IT teams, which leads to the scaling of unmanaged applications and fragmented changes and projects.
- Decisions are based on opinions and experiences without supporting data.
55% of CXOs stated some improvement is necessary in activities to understand business goals.
Source: CEO-CIO Alignment Diagnostics, August 2021 to July 2022; n=568.
CXOs are moderately satisfied with IT's performance as a business partner (average score of 69% among all CXOs). This sentiment is similarly felt among CIOs (64%).
Source: CEO-CIO Alignment Diagnostics, August 2021 to July 2022; n=568.
Pressure Point 5:
Fostering a Collaborative Culture
Culture impacts business results, including bottom-line revenue and productivity metrics. Leaders appreciate the impact culture can have on applications initiatives and wish to leverage this. How culture translates from an abstract concept to something that is measurable and actionable is not straightforward. Executives need to clarify how the desired culture will help achieve their applications strategy and need to focus on the items that will have the most impact.
Address the underlying challenges
- Broad changes do not consider the unique subcultures, personalities, and behaviors of the various teams and individuals in the organization.
- Leaders mandate cultural changes without alleviating critical barriers and do not embody the principles of the target state.
- Bureaucracy and politics restrict changes and encourage the status quo.
- Industry standards, technologies, and frameworks do not support or cannot be tailored to fit the desired culture.
- Some teams are deliberately excluded from the scoping, planning, and execution of key product and service delivery and management activities.
Agile does not solve team culture challenges.
43% of organizations cited organizational culture as a significant barrier to adopting and scaling Agile practices.
Source: Digital.ai, 2021.
"Providing a great employee experience" as the second priority (after recruiting) highlights the emphasis organizations are placing on helping employees adjust after having been forced to change the way work gets done.
Source: McLean & Company, 2022; N=826.
Use your applications priorities to help address your pressure points
Success can be dependent on your ability to navigate around or alleviate your pressure points. Design and market your applications priorities to bring attention to your pressure points and position them as key risk factors to their success.
| Applications Priorities | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Experience (DX) | Intelligent Automation | Proactive Application Management | Multisource Systems | Digital Organization as a Platform | |
| Attracting and Retaining Talent | Enhance the employee experience | Be transparent and support role changes | Shift focus from maintenance to innovation | Enable business-managed applications | Promote and showcase achievements and successes |
| Maximizing the Return on Technology | Modernize or extend the use of existing investments | Automate applications across multiple business functions | Improve the reliability of mission-critical applications | Enhance the functionality of existing applications | Increase visibility of underused applications |
| Confidently Shifting to Digital | Prioritize DX in your shift to digital | Select the capabilities that will benefit most from automation | Prepare applications to support digital tools and technologies | Use best-of-breed tools to meet specific digital needs | Bring all applications up to a common digital standard |
| Addressing Competing Priorities | Ground your digital vision, goals, and objectives | Recognize and evaluate the architectural impact | Rationalize the health of the applications | Agree on a common philosophy on system composition | Map to a holistic platform vision, goals, and objectives |
| Fostering a Collaborative Culture | Involve all perspectives in defining and delivering DX | Involve the end user in the delivery and testing of the automated process | Include the technical perspective in the viability of future applications plans | Discuss how applications can work together better in an ecosystem | Ensure the platform is configured to meet the individual needs of the users |
| Creating High-Throughput Teams | Establish delivery principles centered on DX | Remove manual, error-prone, and mundane tasks | Simplify applications to ease delivery and maintenance | Alleviate delivery bottlenecks and issues | Abstract the enterprise system to expedite delivery |
Digital Experience (DX)
PRIORITY 1
- Deliver Valuable User, Customer, Employee, and Brand Experiences
Delivering valuable digital experiences requires the adoption of good management, governance, and operational practices to accommodate stakeholder, employee, customer, and end-user expectations of digital experiences (e.g. product management, automation, and iterative delivery). Technologies are chosen based on what best enables, delivers, and supports these expectations.
Introduction
Digital transformation is not just about new tools and technologies. It is also about delivering a valuable digital experience
What is digital experience (DX)?
Digital experience (DX) refers to the interaction between a user and an organization through digital products and services. Digital products and services are tools, systems, devices, and resources that gather, store, and process data; are continuously modernized; and embody eight key attributes that are described on the following slide. DX is broken down into four distinct perspectives*:
- Customer Experience – The immediate perceptions of transactions and interactions experienced through a customer's journey in the use of the organization's digital
products and services. - End-User Experience – Users' emotions, beliefs, and physical and psychological responses
that occur before, during, or after interacting with a digital product or service. - Brand Experience – The broader perceptions, emotions, thoughts, feelings and actions the public associate with the organization's brand and reputation or its products and services. Brand experience evolves over time as customers continuously engage with the brand.
- Employee Experience – The satisfaction and experience of an employee through their journey with the organization, from recruitment and hiring to their departure. How an employee embodies and promotes the organization brand and culture can affect their performance, trust, respect, and drive to innovate and optimize.
| Digital Products and Services | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Experience | Brand Experience | Employee Experience | End-User Experience |
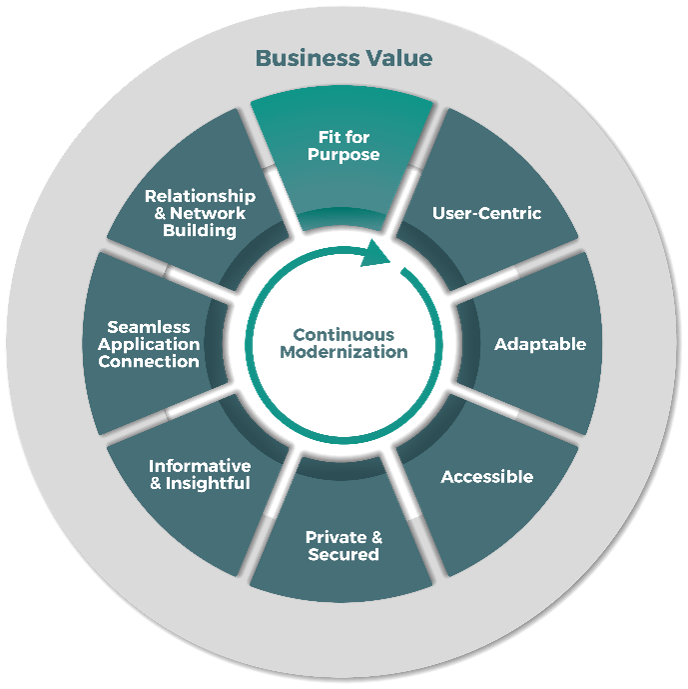
Digital products and services have a common set of attributes
Digital transformation is not just about new tools and technologies. It is also about delivering a valuable digital experience
- Digital products and services must keep pace with changing business and end-user needs as well as tightly supporting your maturing business model with continuous modernization. Focus your continuous modernization on the key characteristics that drive business value.
- Fit for purpose: Functionalities are designed and implemented for the purpose of satisfying the end user's needs and solving their problems.
- User-centric: End users see the product as rewarding, engaging, intuitive, and emotionally satisfying. They want to come back to it.
- Adaptable: The product can be quickly tailored to meet changing end-user and technology needs with reusable and customizable components.
- Accessible: The product is available on demand and on the end user's preferred interface.
End users have a seamless experience across all devices. - Private and secured: The end user's activity and data are protected from unauthorized access.
- Informative and insightful: The product delivers consumable, accurate, and trustworthy real-time data that is important to the end user.
- Seamless application connection: The product facilitates direct interactions with one or more other products through an uninterrupted user experience.
- Relationship and network building: The product enables and promotes the connection and interaction of people.
Signals
DX is critical for business growth and maturity, but the organization may not be ready
A good DX has become a key differentiator that gives organizations an advantage over their competition and peers. Shifts in working environments; employee, customer, and stakeholder expectations; and the advancements in modern technologies have raised the importance of adopting and transitioning to digital processes and tools to stay relevant and responsive to changing business and technology conditions.
Applications teams are critical to ensuring the successful delivery and operation of these digital processes and tools. However, they are often under-resourced and challenged to meet their DX goals.
- 7% of both business and IT respondents think IT has the resources needed to keep up with digital transformation initiatives and meet deadlines (Cyara, 2021).
- 43% of respondents said that the core barrier to digital transformation is a lack of skilled resources (Creatio, 2021).

|
of organizations stated that at least 1% of processes were shifted from being manually completed to digitally completed in the last year. 29% of organizations stated at least 21% were shifted. Source: Tech Trends and Priorities 2023; N=500. |

|
of organizations recognized digital transformation is important for competitive advantage. 94% stated it is important to enhance customer experience, and 91% stated it will have a positive impact on revenue. Source: Cyara, 2021. |
Drivers
Brand and reputation
Customers are swayed by the innovations and advancements in digital technologies and expect your applications team to deliver and support them. Your leaders recognize the importance of these expectations and are integrating them into their business strategy and brand (how the organization presents itself to its customers, employees and the public). They hope that their actions will improve and shape the company's reputation (public perception of the company) as effective, customer-focused, and forward-thinking.
Worker productivity
As you evolve and adopt more complex tools and technology, your stakeholders will expect more from business units and IT teams. Unfortunately, teams employing manual processes and legacy systems will struggle to meet these expectations. Digital products and services promote the simplification of complex operations and applications and help the business and your teams better align operational practices with strategic goals and deliver valuable DX.
Organization modernization
Legacy processes, systems, and ways of working are no longer suitable for meeting the strategic digital objectives and DX needs stakeholders expect. They drive up operational costs without increased benefits, impede business growth and innovation, and consume scarce budgets that could be used for other priorities. Shifting to digital tools and technologies will bring these challenges to light and demonstrate how modernization is an integral part of DX success.
Benefits & Risks
Benefits
- Flexibility & Satisfaction
- Adoption
- Reliability
Employees and customers can choose how they want to access, modify, and consume digital products and services. They can be tailored to meet the specific functional needs, behaviors, and habits of the end user.
The customer, end user, brand, and employee drive selection, design, and delivery of digital products and services. Even the most advanced technologies will fail if key roles do not see the value in their use.
Digital products and services are delivered with technical quality built into them, ensuring they meet the industry, regulatory, and company standards throughout their lifespan and in various conditions.
Risks
- Legacy & Lore
- Bureaucracy & Politics
- Process Inefficiencies
- No Quality Standards
Some stakeholders may not be willing to change due to their familiarity and comfort of business practices.
Competing and conflicting priorities of strategic products and services undermine digital transformation and broader modernization efforts.
Business processes are often burdened by wasteful activities. Digital products and services are only as valuable as the processes they support.
The performance and support of your digital products and services are hampered due to unmanageable technical debt because of a deliberate decision to bypass or omit quality good practices.
Address your pressure points to fully realize the benefits of this priority
Success can be dependent on your ability to address your pressure points.
| Attracting and Retaining Talent |
Enhance the employee experience.Design the digital processes, tools, and technologies to meet the individual needs of the employee. |
|---|---|
| Maximizing the Return on Technology |
Modernize or extend the use of existing investments.Drive higher adoption of applications and higher user value and productivity by implementing digital capabilities to the applications that will gain the most. |
| Confidently Shifting to Digital |
Prioritize DX in your shift to digital. Include DX as part of your definition of success.Your products and services are not valuable if users, customers, and employees do not use them. |
| Addressing Competing Priorities |
Ground your digital vision, goals, and objectivesEstablish clear ownership of DX and digital products and services with a cross-functional prioritization framework. |
| Fostering a Collaborative Culture |
Involve all perspectives in defining and delivering DX.Maintain a committee of owners, stakeholders, and delivery teams to ensure consensus and discuss how to address cross-functional opportunities and risks. |
| Creating High-Throughput Teams |
Establish delivery principles centered on DX.Enforce guiding principles to streamline and simplify DX delivery, such as plug-and-play architecture and quality standards. |
Recommendations
Build a digital business strategy
A digital business strategy clearly articulates the goals and ambitions of the business to adopt digital practices, tools, and technologies. This document:
- Looks for ways to transform the business by identifying what technologies to embrace, what processes to automate, and what new business models to create.
- Unifies digital possibilities with your customer experiences.
- Establishes accountability with the executive leadership.
- States the importance of cross-functional participation from senior management across the organization.
Related Research:
Learn, understand, and empathize with your users, employees, and customers
- To create a better product, solution, or service, understanding those who use it, their needs, and their context is critical.
- A great experience design practice can help you balance those goals so that they are in harmony with those of your users.
- IT leaders must find ways to understand the needs of the business and develop empathy on a much deeper level. This empathy is the foundation for a thriving business partnership.
Related Research:
Recommendations
Center product and service delivery decisions and activities on DX and quality
User, customer, employee, and brand are integral perspectives on the software development lifecycle (SDLC) and the management and governance practices supporting digital products and services. It ensures quality standards and controls are consistently upheld while maintaining alignment with various needs and priorities. The goal is to come to a consensus on a universal definition and approach to embed quality and DX-thinking throughout the delivery process.
Related Research:
Instill collaborative delivery practices
Today's rapidly scaling and increasingly complex digital products and services create mounting pressure on delivery teams to release new features and changes quickly and with sufficient quality. This pressure is further compounded by the competing priorities of individual stakeholders and the nuances among different personas of digital products and services.
A collaborative delivery practice sets the activities, channels, and relationships needed to deliver a valuable and quality product or service with cross-functional awareness, accountability, and agreement.
Related Research:
Recommendations
Continuously monitor and modernize your digital products and services
Today's modern digital products and services are tomorrow's shelfware. They gradually lose their value, and the supporting technologies will become obsolete. Modernization is a continuous need.
Data-driven insights help decision makers decide which products and services to retire, upgrade, retrain on, or maintain to meet the demands of the business.
Enhancements focusing on critical business capabilities strengthen the case for investment and build trust with all stakeholders.
Related Research:
CASE STUDY
Mastercard in Asia
Focus on the customer journey
Chief Marketing Officer M.V. Rajamannar (Raja) wanted to change Mastercard's iconic "Priceless" ad campaign (with the slogan "There are some things money can't buy. For everything else there's Mastercard."). The main reasons were that the campaign relied on one-way communication and targeted end customers, even though Mastercard doesn't issue cards directly to customers; partner banks do. To drive the change in campaign, Raja and his team created a digital engine that leveraged digital and social media. Digital engine is a seven-step process based on insights gleaned from data and real-time optimization.
- Emotional spark: Using data to understand customers' passion points, Mastercard builds videos and creatives to ignite an emotional spark and give customers a reason to engage. For example, weeks before New Year's Eve, Mastercard produced a video with Hugh Jackman to encourage customers to submit a story about someone who deeply mattered to them. The authors of the winning story would be flown to reunite with those both distant and dear.
- Engagement: Mastercard targets the right audience with a spark video through social media to encourage customers to share their stories.
- Offers: To help its partner banks and merchants in driving their business, the company identifies the best offers to match consumers' interests. In the above campaign, Mastercard's Asia-Pacific team found that Singapore was a favorite destination for Indian customers, so they partnered with Singapore's Resorts World Sentosa with an attractive offer.
- Real-time optimization: Mastercard optimizes, in real time, a portfolio of several offers through A/B testing and other analysis.
- Amplification: Real-time testing provides confidence to Mastercard about the potential success of these offers and encourages its bank and merchant partners to co-market and co-fund these campaigns.
- Network effects: A few weeks after consumers submitted their stories about distant loved ones, Mastercard selected winners, produced videos of them surprising their friends and families, and used these videos in social media to encourage sharing.
- Incremental transactions: These programs translate into incremental business for banks who issue cards, for merchants where customers spend money, and for Mastercard, which gets a portion of every transaction.
Source: Harvard Business Review Press
CASE STUDY
Mastercard in Asia (cont'd)
Focus on the customer journey
- Emotional Spark
Drives genuine personal stories - Engagement
Through Facebook
and social media - Offers
From merchants
and Mastercard assets - Optimization
Real-time testing of offers and themes - Amplification
Paid and organic programmatic buying - Network Effects
Sharing and
mass engagement - Incremental Transactions
Win-win for all parties
CASE STUDY
Mastercard in Asia (cont'd)
The Mastercard case highlights important lessons on how to engage customers:
- Have a broad message. Brands need to connect with consumers over how they live and spend their time. Organizations need to go beyond the brand or product message to become more relevant to consumers' lives. Dove soap was very successful in creating a conversation among consumers with its "Real Beauty" campaign, which focused not on the brand or even the product category, but on how women and society view beauty.
- Shift from storytelling to story making. To break through the clutter of advertising, companies need to move from storytelling to story making. A broader message that is emotionally engaging allows for a two-way conversation.
- Be consistent with the brand value. The brand needs to stand for something, and the content should be relevant to and consistent with the image of the brand. Pepsi announced an award of $20 million in grants to individuals, businesses, and nonprofits that promote a new idea to make a positive impact on community. A large number of submissions were about social causes that had nothing to do with Pepsi, and some, like reducing obesity, were in conflict with Pepsi's product.
- Create engagement that drives business. Too much entertainment in ads may engage customers but detract from both communicating the brand message and increasing sales. Simply measuring the number of video views provides only a partial picture of a program's success.
Intelligent Automation
PRIORITY 2
- Extend Automation Practices with AI and ML
AI and ML are rapidly growing. Organizations see the value of machines intelligently executing high-performance and dynamic tasks such as driving cars and detecting fraud. Senior leaders see AI and ML as opportunities to extend their business process automation investments.
Introduction
Intelligent automation is the next step in your business process automation journey
What is intelligent automation (IA)?
Intelligent automation (IA) is the combination of traditional automation technologies, such as business process management (BPM) and robotic process automation (RPA), with AI and ML. The goal is to further streamline and scale decision making across various business processes by:
- Removing human interactions.
- Addressing decisions that involve complex variables.
- Automatically adapting processes to changing conditions.
- Bridging disparate automation technologies into an integrated end-to-end value delivery pipeline.
"For IA to succeed, employees must be involved in the transformation journey so they can experience firsthand the benefits of a new way of working and creating business value," (Cognizant).
What is the difference between IA and hyperautomation?
"Hyperautomation is the act of automating everything in an organization that can be automated. The intent is to streamline processes across an organization using intelligent automation, which includes AI, RPA and other technologies, to run without human intervention. … Hyperautomation is a business-driven, disciplined approach that organizations use to rapidly identify, vet, and automate as many business and IT processes as possible" (IBM, 2021).
Note that hyperautomation often enables IA, but teams solely adopting IA do not need to abide to its automation-first principles.
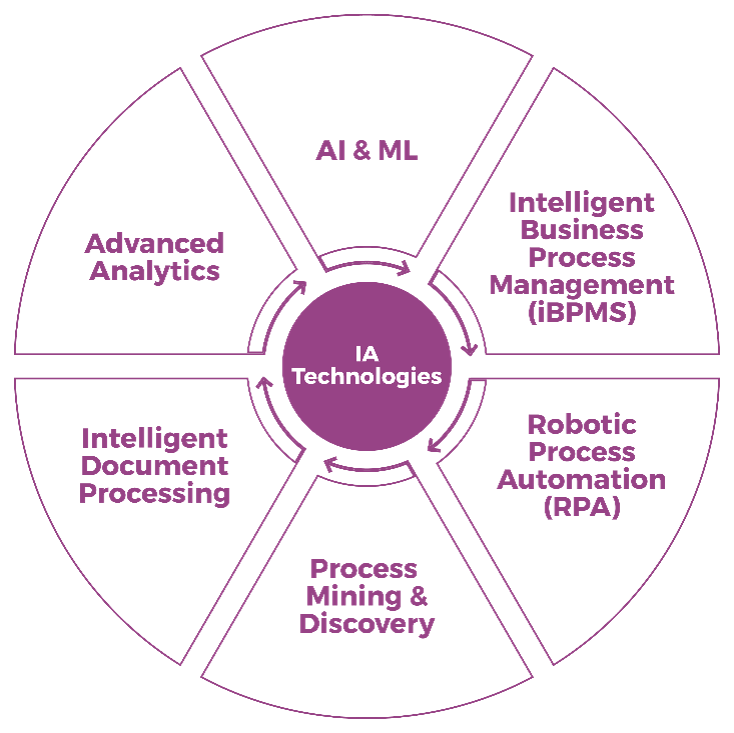
IA is a combination of various tools and technologies
What tools and technologies are involved in IA?
- Artificial intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML) – AI systems perform tasks mimicking human intelligence such as learning from experience and problem solving. AI is making its own decisions without human intervention. Machine learning systems learn from experience and without explicit instructions. They learn patterns from data then analyze and make predictions based on past behavior and the patterns learned. AI is a combination of technologies and can include machine learning.
- Intelligent Business Process Management System (iBPMS) – Combination of BPM tools with AI and other intelligence capabilities.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) – Robots leveraging an application's UI rather than programmatic access. Automate rules-based, repetitive tasks performed by human workers with AI/ML.
- Process Mining & Discovery – Process mining involves reading system event logs and application transactions and applying algorithmic analysis to automatically identify and map inferred business processes. Process discovery involves unintrusive virtual agents that sit on a user's desktop and record and monitor how they interact with applications to perform tasks and processes. Algorithms are then used to map and analyze the processes.
- Intelligent Document Processing – The conversion of physical or unstructured documents into a structured, digital format that can be used in automation solutions. Optical character recognition (OCR) and natural language processing (NPL) are common tools used to enable this capability.
- Advanced Analytics – The gathering, synthesis, transformation, and delivery of insightful and consumable information that supports data-driven decision making. Data is queried from various disparate sources and can take on a variety of structured and unstructured formats.
Signals
Process automation is an executive priority and requires organizational buy-in
Stakeholders recognize the importance of business process automation and AI and are looking for ways to deliver more value using these technologies.
- 90% of executives stated automating business workflows post-COVID-19 will ensure business continuity (Kofax, 2022).
- 88% of executives stated they need to fast-track their end-to-end digital transformation (Kofax, 2022).
However, the advertised benefits to vendors of enabling these desired automations may not be easily achievable because of:
- Manual and undocumented business processes.
- Fragmented and inaccessible systems.
- Poor data quality, insights, and security.
- The lack of process governance and management practice.

|
of CXOs stated staff sufficiency, skill and engagement issues as a minor IT pain point compared to 51% of CIOs stated this issue as a major pain point. Source: CEO-CIO Alignment Diagnostics, August 2021 to July 2022; n=568. |

|
of organizations have already invested in AI or machine learning. Source: Tech Trends and Priorities 2023; N=662 |
Drivers
Quality & throughput
Products and services delivered through an undefined and manual process risk the creation of preventable and catchable defects, security flaws and holes, missing information, and other quality issues. IA solutions consistently reinforce quality standards the same way across all products and services while tailoring outputs to meet an individual's specific needs. Success is dependent on the accurate interpretation and application of quality standards and the user's expectations.
Worker productivity
IA removes the tedious, routine, and mundane tasks that distract and restrict employees from doing more valuable, impactful, and cognitively focused activities. Practical insights can also be generated through IA tools that help employees make data-driven decisions, evaluate problems from different angles, and improve the usability and value of the products and services they produce.
Good process management practices
Automation magnifies existing inefficiencies of a business process management practice, such as unclear and outdated process documentation and incorrect assumptions. IA reinforces the importance of good business process optimization practices, such as removing waste and inefficiencies in a thoughtful way, choosing the most appropriate automation solution, and configuring the process in the right way to maximize the solution's value.
Benefits & Risks
Benefits
- Documentation
- Hands-Off
- Reusability
All business processes must be mapped and documented to be automated, including business rules, data entities, applications, and control points.
IA can be configured and orchestrated to automatically execute when certain business, process, or technology conditions are met in an unattended or attended manner.
IA is applicable in use cases beyond traditional business processes, such as automated testing, quality control, audit, website scraping, integration platform, customer service, and data transfer.
Risks
- Data Quality & Bias
- Ethics
- Recovery & Security
- Management
The accuracy and relevance of the decisions IA makes are dependent on the overall quality of the data
used to train it.
Some decisions can have significant reputational, moral, and ethical impacts if made incorrectly.
The question is whether it is appropriate for a non-human to make that decision.
IA is composed of technologies that can be compromised or fail. Without the proper monitoring, controls,
and recovery protocols, impacted IA will generate significant business and IT costs and can potentially harm customers, employees, and the organization.
Low- and no-code capabilities ease and streamline IA development, which makes it susceptible to becoming unmanageable. Discipline is needed to ensure IA owners are aware of the size and health of the IA portfolio.
Address your pressure points to fully realize the benefits of this priority
Success can be dependent on your ability to address your pressure points.
| Attracting and Retaining Talent |
Be transparent and support role changes.Plan to address the human sentiment with automation (e.g. job security) and the transition of the role to other activities. |
|---|---|
| Maximizing the Return on Technology |
Automate applications across multiple business functions.Recognize the value opportunities of improving and automating the integration of cross-functional processes. |
| Confidently Shifting to Digital |
Maximize the learning of automation fit.Select the right capabilities to demonstrate the value of IA while using lessons learned to establish the appropriate support. |
| Addressing Competing Priorities |
Recognize automation opportunities with capability maps.Use a capability diagram to align strategic IA objectives with tactical and technical IA initiatives. |
| Fostering a Collaborative Culture |
Involve the user in the delivery process.Maximize automation adoption by ensuring the user finds value in its use before deployment. |
| Creating High-Throughput Teams |
Remove manual, error-prone, and mundane tasks.Look for ways to improve team throughput by removing wasteful activities, enforcing quality, and automating away tasks driving down productivity. |
Recommendations
Build your business process automation playbook and practice
Formalize your business process automation practice with a good toolkit and a repeatable set of tactics and techniques.
- Clarify the problem being solved with IA.
- Optimate your processes. Apply good practices to first optimize (opti-) and then automate (-mate) key business processes.
- Deliver minimum viable automations (MVAs). Maximize the learning of automation solutions and business operational changes through small, strategic automation use cases.
Related Research:
Explore the various IA tooling options
Each IA tool will address a different problem. Which tool to choose is dependent on a variety of factors, such as functional suitability, technology suitability, delivery and support capabilities, alignment to strategic business goals, and the value it is designed to deliver.
Related Research:
Recommendations
Introduce AI and ML thoughtfully and with a plan
Despite the many promises of AI, organizations are struggling to fully realize its potential. The reasons boil down to a lack of understanding of when these technologies should and shouldn't be used, as well as a fear of the unknown. The plan to adopt AI should include:
- Understanding of what AI really means in practice.
- Identifying specific applications of AI in the business.
- Understanding the type of AI applicable for the situation.
Related Research:
Mitigate AI and ML bias
Biases can be introduced into an IA system at any stage of the development process, from the data you collect, to the way you collect it, to which algorithms are used and what assumptions were made. In most cases, AI and ML bias is a is a social, political, and business problem.
While bias may not be intentional nor completely prevented or eliminated, early detection, good design, and other proactive preventative steps can be taken to minimize its scope and impact.
Related Research:
CASE STUDY
University Hospitals
Challenge
University Hospitals Cleveland (UH) faces the same challenge that every major hospital confronts regarding how to deliver increasingly complex, high-quality healthcare to a diverse population efficiently and economically. In 2017, UH embarked on a value improvement program aiming to improve quality while saving $400 million over a five-year period.
In emergency department (ED) and inpatient units, leaders found anticipating demand difficult, and consequently units were often over-staffed when demand was low and under-staffed when demand was high. Hospital leaders were uncertain about how to reallocate resources based on capacity needs.
Solution
UH turned to Hospital IQ's Census Solution to proactively manage capacity, staff, and flow in the ED and inpatient areas.
By applying AI, ML, and external data (e.g. weather forecasts) to the hospital's own data (including EMR data and hospital policies), the solution helped UH make two-day census forecasts that managers used to determine whether to open or close in-patient beds and, when necessary, divert low-acuity patients to other hospitals in the system to handle predicted patient volume.
Source: University Hospitals
Results
ED boarding hours have declined by 10% and the hospital has seen a 50% reduction in the number of patients who leave the hospital without
being seen.
UH also predicts in advance patients ready for discharge and identifies roadblocks, reducing the average length of stay by 15%. UH is able to better manage staff, reducing overtime and cutting overall labor costs.
The hospital has also increased staff satisfaction and improved patient safety by closing specific units on weekends and increasing the number of rooms that can be sterilized.
Proactive Application Management
PRIORITY 3
- Strengthen Applications to Prevent and Minimize the Impact of Future Issues
Application management is often viewed as a support function rather than an enabler of business growth. Focus and investments are only placed on application management when it becomes a problem. The lack of governance and practice accountability leaves this practice in a chaotic state: politics take over, resources are not strategically allocated, and customers are frustrated. As a result, application management is often reactive and brushed aside for new development.
Introduction
What is application management?
Application management ensures valuable software is successfully delivered and is maintained for continuous and sustainable business operations. It contains a repeatable set of activities needed to rationalize and roadmap products and services while balancing priorities of new features and maintenance tasks.
Unfortunately, application management is commonly perceived as a practice that solely addresses issues, updates, and incidents. However, application management teams are also tasked with new value delivery that was not part of the original release.
Why is an effective application maintenance (reactive) practice not good enough?
Application maintenance is the "process of modifying a software system or its components after delivery to correct faults, improve performance or other attributes, or adapt to a changed environment or business process," (IEEE, 1998). While it is critical to quickly fix defects and issues when they occur, reactively addressing them is more expensive than discovering them early and employing the practices to prevent them.
Even if an application is working well, its framework, architecture, and technology may not be compatible with the possible upcoming changes stakeholders and vendors may want to undertake. Applications may not be problems now, but they soon can be.
What motivates proactive application changes?
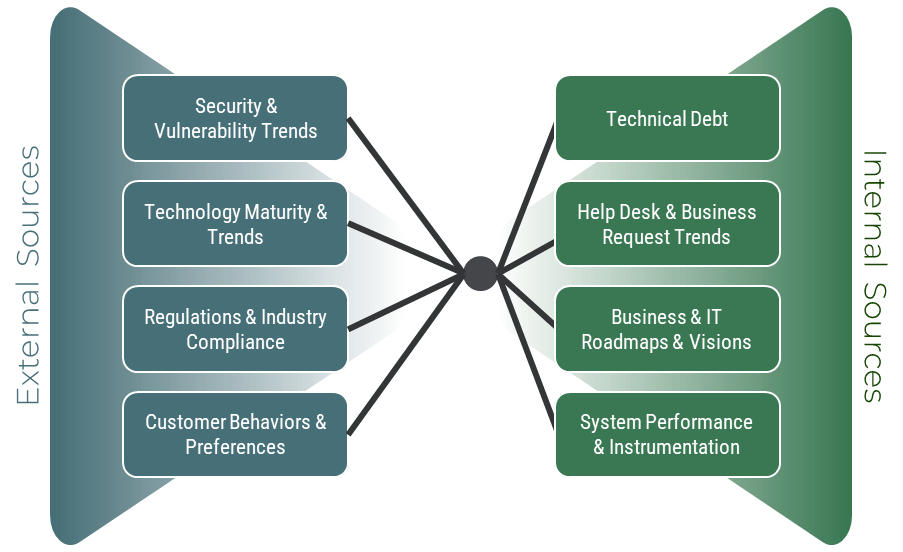
Proactive application management must be disciplined and applied strategically
Proactive application management practices are critical to maintaining business continuity. They require continuous review and modification so that applications are resilient and can address current and future scenarios. Depending on the value of the application, its criticality to business operations, and its susceptibility to technology change, a more proactive management approach may be warranted. Stakeholders can then better manage resources and budget according to the needs of specific products.
Reactive Management
Run-to-Failure
Fix and enhance the product when it breaks. In most cases, a plan is in place ahead of a failure, so that the problem can be addressed without significant disruption and costs.
Preventive
Regularly inspect and optimize the product to reduce the likelihood that it will fail in the future. Schedule inspections based on a specific timeframe or usage threshold.
Predictive
Predict failures before they happen using performance and usage data to alert teams when products are at risk of failure according to specified conditions.
Reliability and Risk Based
Analyze all possible failure scenarios for each component of the product and create tailored delivery plans to improve the stability, reliability, and value of each product.
Proactive Management
Signals
Applications begin to degrade as soon as they are used
Today's applications are tomorrow's shelfware. They gradually lose their value, stability, robustness, and compatibility with other enterprise technologies. The longer these applications are left unattended or simply "keeping the lights on," the more risks they will bring to the application portfolio, such as:
- Discovery and exploitation of security flaws and gaps.
- Increasing the lock-in to specific vendor technologies.
- Inconsistent application performance across various workloads.
These impacts are further compounded by the continuous work done on a system burdened with technical debt. Technical debt describes the result of avoided costs that, over time, cause ongoing business impacts. Left unaddressed, technical debt can become an existential threat that risks your organization's ability to effectively compete and serve its customers. Unfortunately, most organizations have a significant, growing, unmanageable technical debt portfolio.

|
of respondents stated they saw an increase in perceived change in technical debt during the past three years. A quarter of respondents indicated that it stayed the same. Source: McKinsey Digital, 2020. |
|
US |
is the average cost of a data breach in 2022. This figure represents a 2.6% increase from last year. The average cost has climbed 12.7% since 2020. Source: IBM, 2022; N=537. |
|---|
Drivers
Technical debt
Historical decisions to meet business demands by deferring key quality, architectural, or other software delivery activities often lead to inefficient and incomplete code, fragile legacy systems, broken processes, data quality problems, and the other contributors to technical debt. The impacts for this challenge is further heightened if organizations are not actively refactoring and updating their applications behind the scenes. Proactive application management is intended to raise awareness of application fragility and prioritize comprehensive refactoring activities alongside new feature development.
Long-term application value
Applications are designed, developed, and tested against a specific set of parameters which may become less relevant over time as the business matures, technology changes, and user behaviors and interactions shift. Continuous monitoring of the application system, regular stakeholder and user feedback, and active technology trend research and vendor engagement will reveal tasks to prepare an application for future value opportunities or stability and resilience concerns.
Security and resiliency
Innovative approaches to infiltrating and compromising applications are becoming prevailing stakeholder concerns. The loopholes and gaps in existing application security protocols, control points, and end-user training are exploited to gain the trust of unsuspecting users and systems. Proactive application management enforces continuous security reviews to determine whether applications are at risk. The goal is to prevent an incident from happening by hardening or complementing measures already in place.
Benefits & Risks
Benefits
- Consistent Performance
- Robustness
- Operating Costs
Users expect the same level of performance and experience from their applications in all scenarios. A proactive approach ensures the configurations meet the current needs of users and dependent technologies.
Proactively managed applications are resilient to the latest security concerns and upcoming trends.
Continuous improvements to the underlying architecture, codebase, and interfaces can minimize the cost to maintain and operate the application, such as the transition to a loosely coupled architecture and the standardization of REST APIs.
Risks
- Stakeholder Buy-In
- Delayed Feature Releases
- Team Capacity
- Discipline
Stakeholders may not see the association between the application's value and its technical quality.
Updates and enhancements are system changes much like any application function. Depending
on the priority of these changes, new functions may be pushed off to a future release cycle.
Applications teams require dedicated capacity to proactively manage applications, but they are often occupied meeting other stakeholder demands.
Overinvesting in certain application management activities (such as refactoring, re-architecture, and redesign) can create more challenges. Knowing how much to do is important.
Address your pressure points to fully realize the benefits of this priority
Success can be dependent on your ability to address your pressure points.
| Attracting and Retaining Talent |
Shift focus from maintenance to innovation. Work on the most pressing and critical requests first, with a prioritization framework reflecting cross-functional priorities. |
|---|---|
| Maximizing the Return on Technology |
Improve the reliability of mission-critical applications.Regularly verify and validate applications are up to date with the latest patches and fixes and comply with industry good practices and regulations. |
| Confidently Shifting to Digital |
Prepare applications to support digital tools and technologies.Focus enhancements on the key components required to support the integration, performance, and security needs of digital. |
| Addressing Competing Priorities |
Rationalize the health of the applications.Use data-driven, compelling insights to justify the direction and prioritization of applications initiatives. |
| Fostering a Collaborative Culture |
Include the technical perspective in the viability of future applications plans.Demonstrate how poorly maintained applications impede the team's ability to deliver confidently and quickly. |
| Creating High-Throughput Teams |
Simplify applications to ease delivery and maintenance.Refactor away application complexities and align the application portfolio to a common quality standard to reduce the effort to deliver and test changes. |
Recommendations
Reinforce your application maintenance practice
Maintenance is often viewed as a support function rather than an enabler of business growth. Focus and investments are only placed on maintenance when it becomes a problem.
- Justify the necessity of streamlined maintenance.
- Strengthen triaging and prioritization practices.
- Establish and govern a repeatable process.
Ensure product issues, incidents, defects, and change requests are promptly handled to minimize business and IT risks.
Related Research:
Build an application management practice
Apply the appropriate management approaches to maintain business continuity and balance priorities and commitments among maintenance and new development requests.
This practice serves as the foundation for creating exceptional customer experience by emphasizing cross-functional accountability for business value and product and service quality.
Related Research:
Recommendations
Manage your technical debt
Technical debt is a type of technical risk, which in turn is business risk. It's up to the business to decide whether to accept technical debt or mitigate it. Create a compelling argument to stakeholders as to why technical debt should be a business priority rather than just an IT one.
- Define and identify your technical debt.
- Conduct a business impact analysis.
- Identify opportunities to better manage technical debt.
Related Research:
Gauge your application's health
Application portfolio management is nearly impossible to perform without an honest and thorough understanding of your portfolio's alignment to business capabilities, business value, total cost of ownership, end-user reception and satisfaction, and technical health.
Develop data-driven insights to help you decide which applications to retire, upgrade, retrain on, or maintain to meet the demands of the business.
Related Research:
Recommendations
Adopt site reliability engineering (SRE) and DevOps practices
Site reliability engineering (SRE) is an operational model for running online services more reliably by a team of dedicated reliability-focused engineers.
DevOps, an operational philosophy promoting development and operations collaboration, can bring the critical insights to make application management practices through SRE more valuable.
Related Research:
CASE STUDY
Government Agency
Goal
A government agency needed to implement a disciplined, sustainable application delivery, planning, and management process so their product delivery team could deliver features and changes faster with higher quality. The goal was to ensure change requests, fixes, and new features would relieve requester frustrations, reduce regression issues, and allow work to be done on agreeable and achievable priorities organization-wide. The new model needed to increase practice efficiency and visibility in order to better manage technical debt and focus on value-added solutions.
Solution
This organization recognized a number of key challenges that were inhibiting its team's ability to meet its goals:
- The product backlog had become too long and unmanageable.
- Delivery resources were not properly allocated to meet the skills and capabilities needed to successfully meet commitments.
- Quality wasn't defined or enforced, which generated mounting technical debt.
- There was a lack of clear metrics and defined roles and responsibilities.
- The business had unrealistic and unachievable expectations.
Source: Info-Tech Workshop
Key practices implemented
- Schedule quarterly business satisfaction surveys.
- Structure and facilitate regular change advisory board meetings.
- Define and enforce product quality standards.
- Standardize a streamlined process with defined roles.
- Configure management tools to better handle requests.
Multisource Systems
PRIORITY 4
- Manage an Ecosystem Composed of In-House and Outsourced Systems
Various market and company factors are motivating a review on resource and system sourcing strategies. The right sourcing model provides key skills, resources, and capabilities to meet innovation, time to market, financial, and quality goals of the business. However, organizations struggle with how best to support sourcing partners and to allocate the right number of resources to maximize success.
Introduction
A multisource system is an ecosystem of integrated internally and externally developed applications, data, and infrastructure. These technologies can be custom developed, heavily configured vendor solutions, or they may be commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) solutions. These systems can also be developed, supported, and managed by internal staff, in partnership with outsourced contractors, or be completely outsourced. Multisource systems should be configured and orchestrated in a way that maximizes the delivery of specific value drivers for the targeted audience.
Successfully selecting a sourcing approach is not a simple RFP exercise to choose the lowest cost
Defining and executing a sourcing approach can be a significant investment and risk because of the close interactions third-party services and partners will have with internal staff, enterprise applications and business capabilities. A careful selection and design is necessary.
The selection of a sourcing partner is not simple. It involves the detailed inspection and examination of different candidates and matching their fit to the broader vision of the multisource system. In cases where control is critical, technology stack and resource sourcing consolidation to a few vendors and partners is preferred. In other cases, where worker productivity and system flexibility are highly prioritized, a plug-and-play best-of-breed approach is preferred.
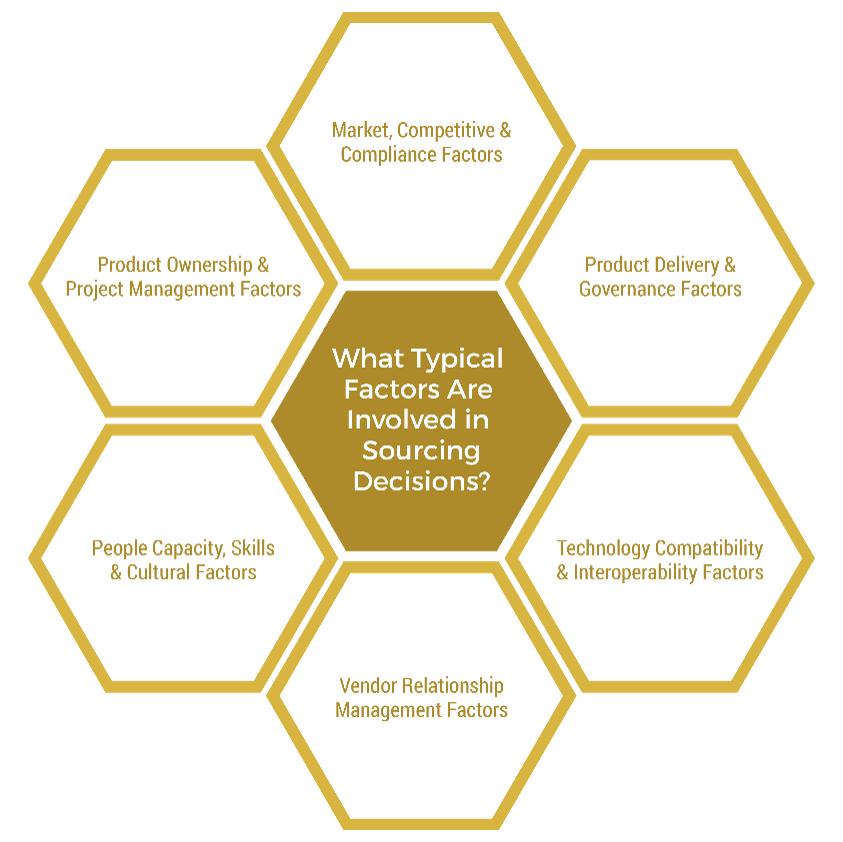
Sourcing needs to be driven by your department and system strategies
How does the department want to be perceived?
The image that your applications department and teams want to reflect is frequently dependent on the applications they deliver and support, the resources they are composed of, and the capabilities they provide.
Therefore, choosing the right sourcing approach should be driven by understanding who the teams are and want to be (e.g. internal builder, an integrator, a plug-in player), what they can or want to do (e.g. custom-develop or implement), and what they can deliver or support (e.g. cloud or on-premises) must be established.
What value is the system delivering?
Well-integrated systems are the lifeblood of your organization. They provide the capabilities needed to deliver value to customers, employees, and stakeholders. However, underlying system components may not be sourced under a unified strategy, which can lead to duplicate vendor services and high operational costs.
The right sourcing approach ensures your partners address key capabilities in your system's delivery and support, and that they are positioned to maximize the value of critical and high-impact components.
Signals
Business demand may outpace what vendors can support or offer
Outsourcing and shifting to a buy-over-build applications strategy are common quick fixes to dealing with capacity and skills gaps. However, these quick fixes often become long-term implementations that are not accounted for in the sourcing selection process. Current application and resource sourcing strategies must be reviewed to ensure that vendor arrangements meet the current and upcoming demands and challenges of the business, customers, and enterprise technologies, such as:
- Pressure from stakeholders to lower operating costs while maintaining or increasing quality and throughput.
- Technology lock-in that addresses short-term needs but inhibits long-term growth and maturity.
- Team capacity and talent acquisition not meeting the needs of the business.

|
of respondents stated they outsourced software development fully or partly in the last 12 months (2021). Source: Coding Sans, 2021. |

|
of respondents stated they were at least somewhat satisfied with the result of outsourcing software development. Source: Coding Sans, 2021. |
Drivers
Business-managed applications
Employees are implementing and building applications without consulting, notifying, or heeding the advice of IT. IT is often ill-equipped and under-resourced to fight against shadow IT. Instead, organizations are shifting the mindset of "fight shadow IT" to "embrace business-managed applications," using good practices in managing multisource systems. A multisource approach strikes the right balance between user empowerment and centralized control with the solutions and architecture that can best enable it.
Unique problems to solve
Point solutions offer features to address unique use cases in uncommon technology environments. However, point solutions are often deployed in siloes with limited integration or overlap with other solutions. The right sourcing strategy accommodates the fragmented nature of point solutions into a broader enterprise system strategy, whether that be:
- Multisource best of breed – integrate various technologies that provide subsets of the features needed for supporting business functions.
- Multisource custom – integrate systems built in-house with technologies developed by external organizations.
- Vendor add-ons and integrations – enhance an existing vendor's offering by using their system add-ons as upgrades, new add-ons, or integrations.
Vendor services
Some vendor services in a multisource environment may be redundant, conflicting, or incompatible. Given that multisource systems are regularly changing, it is difficult to identify what services are affected, what would be needed to fill the gap of the removed solution, or which redundant services should be removed.
A multisource approach motivates the continuous rationalization of your vendor services and partners to determine the right mixture of in-house and outsourced resources, capabilities, and technologies.
Benefits & Risks
Benefits
- Business-Focused Solution
- Flexibility
- Cost Optimization
Multisource systems can be designed to support an employee's ability to select the tools they want and need.
The environment is architected in a loosely coupled approach to allow applications to be easily added, removed, and modified with minimized impact to other integrated applications.
Rather than investing in large solutions upfront, applications are adopted when they are needed and are removed when little value is gained. Disciplined application portfolio management is necessary to see the full value of this benefit.
Risks
- Manageable Sprawl
- Policy Adherence
- Integration & Compatibility
The increased number and diversity of applications in multisource system environments can overwhelm system managers who do not have an effective application portfolio management practice.
Fragmented application implementations risk inconsistent adherence to security and other quality policies, especially in situations where IT is not involved.
Application integration can quickly become tangled, untraceable, and unmanageable because of varying team and vendor preferences for specific integration technologies and techniques.
Address your pressure points to fully realize the benefits of this priority
Success can be dependent on your ability to address your pressure points.
| Attracting and Retaining Talent |
Enable business-managed applications.Create the integrations to enable the easy connection of desired tools to enterprise systems with the appropriate guardrails. |
|---|---|
| Maximizing the Return on Technology |
Enhance the functionality of existing applications.Complement current application capability gaps with data, features, and services from third-party applications. |
| Confidently Shifting to Digital |
Use best-of-breed tools to meet specific digital needs.Select the best tools to meet the unique and special functional needs of the digital vision. |
| Addressing Competing Priorities |
Agree on a common philosophy on system composition.Establish an owner of the multisource system to guide how the system should mature as the organization grows. |
| Fostering a Collaborative Culture |
Discuss how applications can work together better in an ecosystem.Build committees to discuss how applications can better support each other and drive more value. |
| Creating High-Throughput Teams |
Alleviate delivery bottlenecks and issues.Leverage third-party sources to fill skills and capacity gaps until a long-term solution can be implemented. |
Recommendations
Define the goals of your applications department and product vision
Understanding the applications team's purpose and image is critical in determining how the system they are managing and the skills and capacities they need should be sourced.
Changing and conflicting definitions of value and goals make it challenging to convey an agreeable strategy of the multisource system. An achievable vision and practical tactics ensure all parties in the multisource system are moving in the same direction.
Related Research:
Develop a sourcing partner strategy
Almost half of all sourcing initiatives do not realize projected savings, and the biggest reason is the choice of partner (Zhang et al., 2018). Making the wrong choice means inferior products, higher costs and the loss of both clients and reputation.
Choosing the right sourcing partner involves understanding current skills and capacities, finding the right matching partner based on a desired profile, and managing a good working relationship that sees short-term gains and supports long-term goals.
Related Research:
Recommendations
Strengthen enterprise integration practices
Integration strategies that are focused solely on technology are likely to complicate rather than simplify because little consideration is given on how other systems and processes will be impacted. Enterprise integration needs to bring together business process, applications, and data – in that order.
Kick-start the process of identifying opportunities for improvement by mapping how applications and data are coordinated to support business activities.
Related Research:
- Build Effective Enterprise Integration on the Back of Business Process
- Build an Application Integration Strategy
- Build a Data Integration Strategy
Manage your solution architecture and application portfolio
Haphazardly implementing and integrating applications can generate significant security, performance, and data risks. A well-thought-through solution architecture is essential in laying the architecture quality principles and roadmap on how the multisource system can grow and evolve in a sustainable and maintainable way.
Good application portfolio management complements the solution architecture as it indicates when low-value and unused applications should be removed to reduce system complexity.
Related Research:
Recommendations
Embrace business-managed applications
Multisource systems bring a unique opportunity to support the business and end users' desire to implement and develop their own applications. However, traditional models of managing applications may not accommodate the specific IT governance and management practices required to operate business-managed applications:
- A collaborative and trusting business-IT relationship is key.
- The role of IT must be reimagined.
- Business must be accountable for its decisions.
Related Research:
CASE STUDY
Cognizant
Situation
- Strives to be primarily an industry-aligned organization that delivers multiple service lines in multiple geographies.
- Cognizant seeks to carefully consider client culture to create a one-team environment.
- Value proposition is a consultative approach bringing thought leadership and mutually adding value to the relationship vs. the more traditional order-taker development partner.
- Wants to share in solution development to facilitate shared successes. Geographic alignment drives knowledge of the client and their challenges, not just about time zone and supportability.
- Offers one of the largest offshore capabilities in the world, supported by local and nearshore resources to drive local knowledge.
- Today's clients don't typically want a black box, they are sophisticated and want transparency around the process and solution, to have a partner.
- Clients do want to know where the work is being delivered from, how it's being done.
Source: interview with Jay MacIsaac, Cognizant.
Approach
- Best relationship comes where teams operate as one.
- Clients are seeking value, not a development black box.
- Clients want to have a partner they can engage with, not just an order taker.
- Want to build a one-team culture with shared goals and deliver business value.
- Seek a partner that will add to their thinking not echo it.
Results
- Cognizant is continuing to deliver double-digit growth and continues to strive for top quartile performance.
- Growth in the client base has seen the company grow to over 340,000 associates worldwide.
Digital Organization as a Platform
PRIORITY 5
-
Create a Common Digital Interface to Access All Products and Services
A digital platform enables organizations to leverage a flexible, reliable, and scalable foundation to create a valuable DX, ease delivery and management efforts, maximize existing investments, and motivate the broader shift to digital. This approach provides a standard to architect, integrate, configure, and modernize the applications that compose the platform.
Introduction
What is digital organization as a platform (DOaaP)?
Digital organization as a platform (DOaaP) is a collection of integrated digital services, products, applications, and infrastructure that is used as a vehicle to meet and exceed an organization's digital strategies. It often serves as an accessible "place for exchanges of information, goods, or services to occur between producers and consumers as well as the community that interacts
with said platform" (Watts, 2020).
DOaaP involves a strategy that paves the way for organizations to be digital. It helps organizations use their assets (e.g. data, processes, products, services) in the most effective ways and become more open to cooperative delivery, usage, and management. This opens opportunities for innovation and cross-department collaborations.
How is DOaaP described?
- Open and Collaborative
- Open organization: open data, open APIs, transparency, and user participation.
- Collaboration, co-creation, crowdsourcing, and innovation
- Accessible and Connected
- Digital inclusion
- Channel ubiquity
- Integrity and interoperability
- Digital marketplace
- Digital and Programmable
- Digital identity
- Policies and processes as code
- Digital products and services
- Enabling digital platforms
Digital organizations follow a common set of principles and practices
Customer-centricity
Digital organizations are driven by customer focus, meeting and exceeding customer expectations. It must design its services with a "digital first" principle, providing access through every expected channel and including seamless integration and interoperability with various departments, partners, and third-party services. It also means creating trust in its ability to provide secure services and to keep privacy and ethics as core pillars.
Leadership, management, and strategies
Digital leadership brings customer focus to the enterprise and its structures and organizes efficient networks and ecosystems. Accomplishing this means getting rid of silos and a siloed mentality and aligning on a digital vision to design policies and services that are efficient, cost-effective, and provide maximum benefit to the user. Asset sharing, co-creation, and being open and transparent become cornerstones of a digital organization.
Infrastructure
Providing digital services across demographics and geographies requires infrastructure, and that in turn requires long-term vision, smart investments, and partnerships with various source partners to create the necessary foundational infrastructure upon which to build digital services.
Digitization and automation
Automation and digitization of processes and services, as well as creating digital-first products, lead to increased efficiency and reach of the organization across demographics and geographies. Moreover, by taking a digital-first approach, digital organizations future-proof their services and demonstrate their commitment to stakeholders.
Enabling platforms
DOaaP embraces open standards, designing and developing organizational platforms and ecosystems with a cloud-first mindset and sound API strategies. Developer experience must also take center stage, providing the necessary tools and embracing Agile and DevOps practices and culture become prerequisites. Cybersecurity and privacy are central to the digital platform; hence they must be part of the design and development principles and practices.
Signals
The business expects support for digital products and services
Digital transformation continues to be a high-priority initiative for many organizations, and they see DOaaP as an effective way to enable and exploit digital capabilities. However, DOaaP unleashes new strategies, opportunities, and challenges that are elusive or unfamiliar to business leaders. Barriers in current business operating models may limit DOaaP success, such as:
- Department and functional silos
- Dispersed, fragmented and poor-quality data
- Ill-equipped and under-skilled resources to support DOaaP adoption
- System fragmentation and redundancies
- Inconsistent integration tactics employed across systems
- Disjointed user experience leading to low engagement and adoption
DOaaP is not just about technology, and it is not the sole responsibility of either IT or business. It is the collective responsibility of the organization.

|
of organizations plan to unlock new value through digital. 50% of organizations are planning major transformation over the next three years. Source: Nash Squared, 2022. |

|
of organizations are undertaking digital expansion projects focused on scaling their business with technology. This result is up from 57% in 2021. Source: F5 Inc, 2022. |
Drivers
Unified brand and experience
Users should have the same experience and perception of a brand no matter what product or service they use. However, fragmented implementation of digital technologies and inconsistent application of design standards makes it difficult to meet this expectation. DOaaP embraces a single design and DX standard for all digital products and services, which creates a consistent perception of your organization's brand and reputation irrespective of what products and services are being used and how they are accessed.
Accessibility
Rapid advancement of end-user devices and changes to end-user behaviors and expectations often outpace an organization's ability to meet these requirements. This can make certain organization products and services difficult to find, access and leverage. DOaaP creates an intuitive and searchable interface to all products and services and enables the strategic combination of technologies to collectively deliver more value.
Justification for modernization
Many opportunities are left off the table when legacy systems are abstracted away rather than modernized. However, legacy systems may not justify the investment in modernization because their individual value is outweighed by the cost. A DOaaP initiative motivates decision makers to look at the entire system (i.e. modern and legacy) to determine which components need to be brought up to a minimum digital state. The conversation has now changed. Legacy systems should be modernized to increase the collective benefit of the entire DOaaP.
Benefits & Risks
Benefits
- Look & Feel
- User Adoption
- Shift to Digital
A single, modern, customizable interface enables a common look and feel no matter what and how the platform is being accessed.
Organizations can motivate and encourage the adoption and use of all products and services through the platform and increase the adoption of underused technologies.
DOaaP motivates and supports the modernization of data, processes, and systems to meet the goals and objectives outlined in the broader digital transformation strategy.
Risks
- Data Quality
- System Stability
- Ability to Modernize
- Business Model Change
Each system may have a different definition of commonly used entities (e.g. customer), which can cause data quality issues when information is shared among these systems.
DOaaP can stress the performance of underlying systems due to the limitations of some systems to handle increased traffic.
Some systems cannot be modernized due to cost constraints, business continuity risks, vendor lock-in, legacy and lore, or other blocking factors.
Limited appetite to make the necessary changes to business operations in order to maximize the value of DOaaP technologies.
Address your pressure points to fully realize the benefits of this priority
Success can be dependent on your ability to address your pressure points.
| Attracting and Retaining Talent | Promote and showcase achievements and successes. Share the valuable and innovative work of your teams across the organization and with the public. |
|---|---|
| Maximizing the Return on Technology | Increase visibility of underused applications. Promote the adoption and use of all products and services through the platform and use the lessons learned to justify removal, updates or modernizations. |
| Confidently Shifting to Digital | Bring all applications up to a common digital standard. Define the baseline digital state all applications, data, and processes must be in to maximize the value of the platform. |
| Addressing Competing Priorities | Map to a holistic platform vision, goals and objectives. Work with relevant stakeholders, teams and end users to agree on a common directive considering all impacted perspectives. |
| Fostering a Collaborative Culture | Ensure the platform is configured to meet the individual needs of the users. Tailor the interface and capabilities of the platform to address users' functional and personal concerns. |
| Creating High-Throughput Teams | Abstract the enterprise system to expedite delivery. Use the platform to standardize application system access to simplify platform changes and quicken development and testing. |
Recommendations
Define your platform vision
Organizations realize that a digital model is the way to provide more effective services to their customers and end users in a cost-effective, innovative, and engaging fashion. DOaaP is a way to help support this transition.
However, various platform stakeholders will have different interpretations of and preferences for what this platform is intended to solve, what benefits it is supposed to deliver, and what capabilities it will deliver. A grounded vision is imperative to steer the roadmap and initiatives.
Related Research:
- Drive Digital Transformation with Platform Strategies
- Gov 2.0: Government as a Platform
- Deliver Digital Products at Scale
Assess and modernize your applications
Certain applications may not sufficiently support the compatibility, flexibility, and efficiency requirements of DOaaP. While workaround technologies and tactics can be employed to overcome these application challenges, the full value of the DOaaP may not be realized.
Reviewing the current state of the application portfolio will indicate the functional and value limitations of what DOaaP can provide and an indication of the scope of investment needed to bring applications up to a minimum state.
Related Research:
Recommendations
Understand and evaluate end-user needs
Technology has reached a point where it's no longer difficult for teams to build functional and valuable digital platforms. Rather, the difficulty lies in creating an interface and platform that people want to use and use frequently.
While it is important to increase the access and promotion of all products and services, orchestrating and configuring them in a way to deliver a satisfying experience is even more important. Applications teams must first learn about and empathize with the needs of end users.
Related Research:
- Use Experience Design to Drive Empathy With the Business
- Implement and Mature Your User Experience Design Practice
Architect your platform
Formalizing and constructing DOaaP just for the sake of doing so often results in an initiative that is lengthy and costly and ends up being considered a failure.
The build and optimization of the platform must be predicated on a thorough understanding of the DOaaP's goals, objectives, and priorities and the business capabilities and process they are meant to support and enable. The appropriate architecture and delivery practices can then be defined and employed.
Related Research:
CASE STUDY
e-Estonia
Situation
The digital strategy of Estonia resulted in e-Estonia, with the vision of "creating a society with more transparency, trust, and efficiency." Estonia has addressed the challenge by creating structures, organizations, and a culture of innovation, and then using the speed and efficiency of digital infrastructure, apps, and services. This strategy can reduce or eliminate bureaucracy through transparency and automation.
Estonia embarked on its journey to making digital a priority in 1994-1996, focusing on a committed investment in infrastructure and digital literacy. With that infrastructure in place, they started providing digital services like an e-banking service (1996), e-tax and mobile parking (2002), and then went full steam ahead with a digital information interoperability platform in 2001, digital identity in 2002, e-health in 2008, and e-prescription in 2010. The government is now strategizing for AI.
Results
Source: e-Estonia
Practices employed
The e-Estonia digital government model serves as a reference for governments across the world; this is acknowledged by the various awards it has received, like #2 in "internet freedom," awarded by Freedom House in 2019; #1 on the "digital health index," awarded by the Bertelsmann Foundation in 2019; and #1 on "start-up friendliness," awarded by Index Venture in 2018.
References
"15th State of Agile Report." Digital.ai, 2021. Web.
"2022 HR Trends Report." McLean & Company, 2022.
"2022: State of Application Strategy Report." F5 Inc, 2022.
"Are Executives Wearing Rose-Colored Glasses Around Digital Transformation?" Cyara, 2021. Web.
"Cost of a Data Breach Report 2022." IBM, 2022. Web.
Dalal, Vishal, et al. "Tech Debt: Reclaiming Tech Equity." McKinsey Digital, Oct. 2020. Web.
"Differentiating Between Intelligent Automation and Hyperautomation." IBM, 15 October 2021. Web.
"Digital Leadership Report 2021." Harvey Nash Group, 2021.
"Digital Leadership Report 2022: The State of Digital." Nash Squared, 2022. Web.
Gupta, Sunil. "Driving Digital Strategy: A Guide to Reimagining Your Business." Harvard Business Review Press, 2018. Web.
Haff, Gordon. "State of Application Modernization Report 2022." Konveyor, 2022. Web.
"IEEE Standard for Software Maintenance: IEEE Std 1219-1998." IEEE Standard for Software Maintenance, 1998. Accessed Dec. 2015.
"Intelligent Automation." Cognizant, n.d. Web.
"Kofax 2022: Intelligent Automation Benchmark Study". Kofax, 2021. Web.
McCann, Leah. "Barco's Virtual Classroom at UCL: A Case Study for the Future of All University Classrooms?" rAVe, 2 July 2020, Web.
"Proactive Staffing and Patient Prioritization to Decompress ED and Reduce Length of Stay." University Hospitals, 2018. Web.
"Secrets of Successful Modernization." looksoftware, 2013. Web.
"State of Software Development." Coding Sans, 2021. Web.
"The State of Low-Code/No-Code." Creatio, 2021. Web.
"We Have Built a Digital Society and We Can Show You How." e-Estonia. n.d. Web.
Zanna. "The 5 Types of Experience Series (1): Brand Experience Is Your Compass." Accelerate in Experience, 9 February 2020. Web.
Zhang, Y. et al. "Effects of Risks on the Performance of Business Process Outsourcing Projects: The Moderating Roles of Knowledge Management Capabilities." International Journal of Project Management, 2018, vol. 36 no. 4, 627-639.
Research Contributors and Experts

Chris Harrington
Chief Technology Officer
Carolinas Telco Federal Credit Union
Chris Harrington is Chief Technology Officer (CTO) of Carolinas Telco Federal Credit Union. Harrington is a proven leader with over 20 years of experience developing and leading information technology and cybersecurity strategies and teams in the financial industry space.

Benjamin Palacio
Senior Information Technology Analyst County of Placer
Benjamin Palacio has been working in the application development space since 2007 with a strong focus on system integrations. He has seamlessly integrated applications data across multiple states into a single reporting solution for management teams to evaluate, and he has codeveloped applications to manage billions in federal funding. He is also a CSAC-credentialed IT Executive (CA, USA).

Scott Rutherford
Executive Vice President, Technology
LGM Financial Services Inc.
Scott heads the Technology division of LGM Financial Services Inc., a leading provider of warranty and financing products to automotive OEMs and dealerships in Canada. His responsibilities include strategy and execution of data and analytics, applications, and technology operations.

Robert Willatts
IT Manager, Enterprise Business Solutions and Project Services
Town of Newmarket
Robert is passionate about technology, innovation, and Smart City Initiatives. He makes customer satisfaction as the top priority in every one of his responsibilities and accountabilities as an IT manager, such as developing business applications, implementing and maintaining enterprise applications, and implementing technical solutions. Robert encourages communication, collaboration, and engagement as he leads and guides IT in the Town of Newmarket.

Randeep Grewal
Vice President, Enterprise Applications
Red Hat
Randeep has over 25 years of experience in enterprise applications, advanced analytics, enterprise data management, and consulting services, having worked at numerous blue-chip companies. In his most recent role, he is the Vice President of Enterprise Applications at Red Hat. Reporting to the CIO, he is responsible for Red Hat's core business applications with a focus on enterprise transformation, application architecture, engineering, and operational excellence. He previously led the evolution of Red Hat into a data-led company by maturing the enterprise data and analytics function to include data lake, streaming data, data governance, and operationalization of analytics for decision support.
Prior to Red Hat, Randeep was the director of global services strategy at Lenovo, where he led the strategy using market data to grow Lenovo's services business by over $400 million in three years. Prior to Lenovo, Randeep was the director of advanced analytics at Alliance One and helped build an enterprise data and analytics function. His earlier work includes seven years at SAS, helping SAS become a leader in business analytics, and at KPMG consulting, where he managed services engagements at Fortune 100 companies.
Buying Options
Applications Priorities 2023
IT Risk Management · IT Leadership & Strategy implementation · Operational Management · Service Delivery · Organizational Management · Process Improvements · ITIL, CORM, Agile · Cost Control · Business Process Analysis · Technology Development · Project Implementation · International Coordination · In & Outsourcing · Customer Care · Multilingual: Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese · Entrepreneur
Tymans Group is a brand by Gert Taeymans BV
Gert Taeymans bv
Europe: Koning Albertstraat 136, 2070 Burcht, Belgium — VAT No: BE0685.974.694 — phone: +32 (0) 468.142.754
USA: 4023 KENNETT PIKE, SUITE 751, GREENVILLE, DE 19807 — Phone: 1-917-473-8669
Copyright 2017-2022 Gert Taeymans BV
