Define Requirements for Outsourcing the Service Desk
- Buy Link or Shortcode: {j2store}493|cart{/j2store}
- Parent Category Name: Service Desk
- Parent Category Link: /service-desk
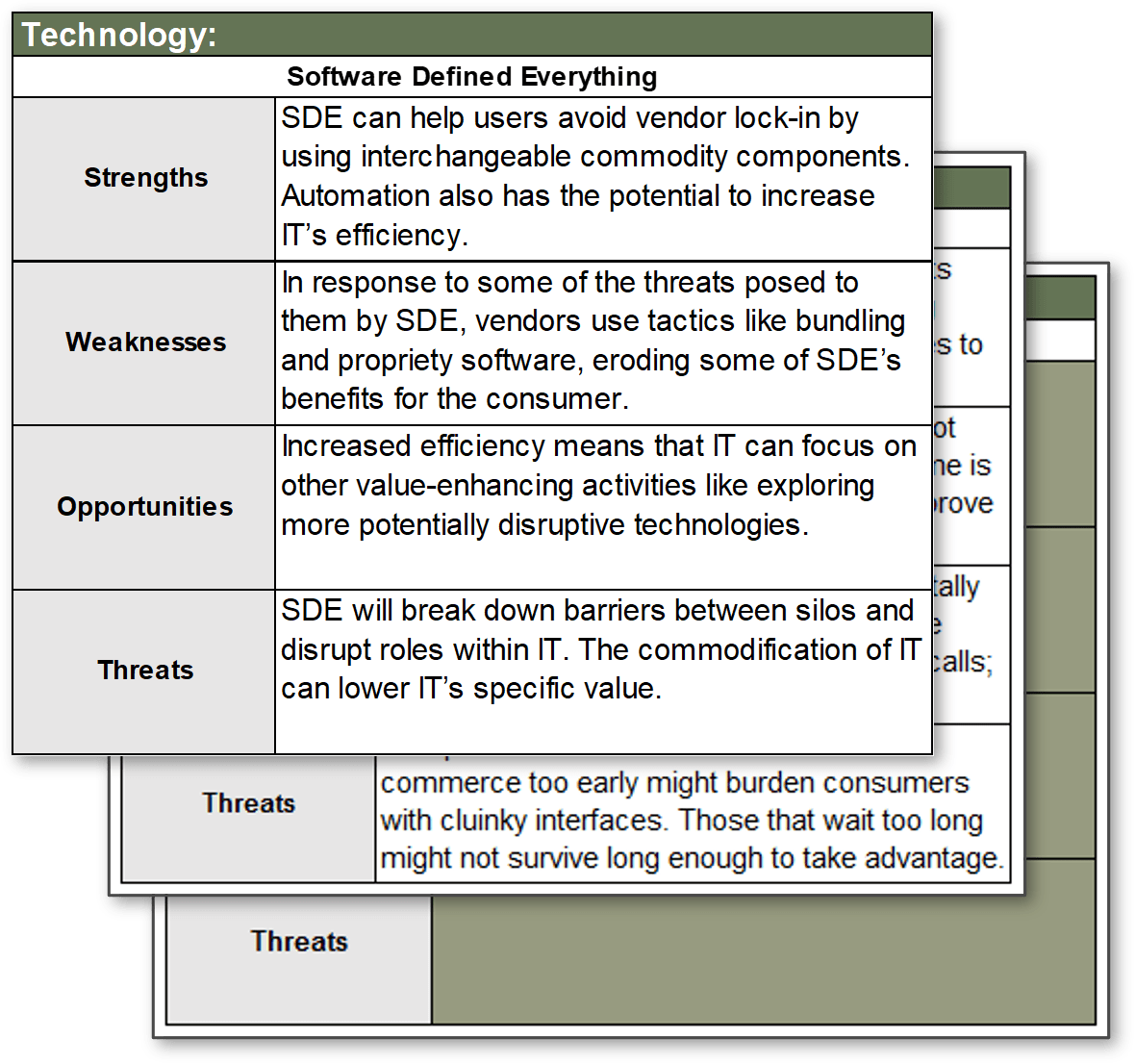
- In organizations where technical support is viewed as non-strategic, many see outsourcing as a cost-effective way to provide this support. However, outsourced projects often fall short of their goals in terms of cost savings and the quality of support.
- Significant administrative work and up-front costs are required to outsource the service desk, and poor planning often results in project failure and a decrease of end-user satisfaction.
- A complete turnover of the service desk can result in lost knowledge and control over processes, and organizations without an exit strategy can struggle to bring their service desk back in house and return the confidence of end users.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Outsourcing is easy. Realizing the expected cost, quality, and focus benefits is hard. Successful outsourcing without being directly involved in service desk management is almost impossible.
- You don’t need to standardize before you outsource, but you still need to conduct your due diligence. If you outsource without thinking about how you want the future to work, you will likely be unsatisfied with the result.
- If cost is your only driver for outsourcing, understand that it comes at a cost. Customer service quality will likely be less, and your outsourcer may not add on frills such as Continual Improvement. Be careful that your specialists don’t end up spending more time working on incidents and service requests.
Impact and Result
- First decide if outsourcing is the correct step; there may be more preliminary work to do beforehand.
- Assess requirements and make necessary adjustments before developing an outsource RFP.
- Clearly define the project and produce an RFP to provide to vendors.
- Plan for long-term success, not short-term gain.
- Prepare to retain some of the higher-level service desk work.
Define Requirements for Outsourcing the Service Desk Research & Tools
Besides the small introduction, subscribers and consulting clients within this management domain have access to:
1. Define Requirements for Outsourcing the Service Desk Deck – A step-by-step document to walk you through building a strategy for efficient service desk outsourcing.
This storyboard will help you craft a project charter, create an RFP, and outline strategies to build a long-term relationship with the vendor.
- Define Requirements for Outsourcing the Service Desk – Storyboard
- Service Desk Outsourcing Requirements Database Library
2. Service Desk Outsourcing Project Charter Template and Requirements Library – Best-of-breed templates to help you determine processes and build a strategy to outsource them.
These templates will help you determine your service desk requirements and document your proposed service desk outsourcing strategy.
- Service Desk Outsourcing Project Charter Template
3. Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template – A structured document to help you outline expectations and communicate requirements to managed service providers.
This template will allow you to create a detailed RFP for your outsourcing agreement, document the statement of work, provide service overview, record exit conditions, and document licensing model and estimated pricing.
- Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template
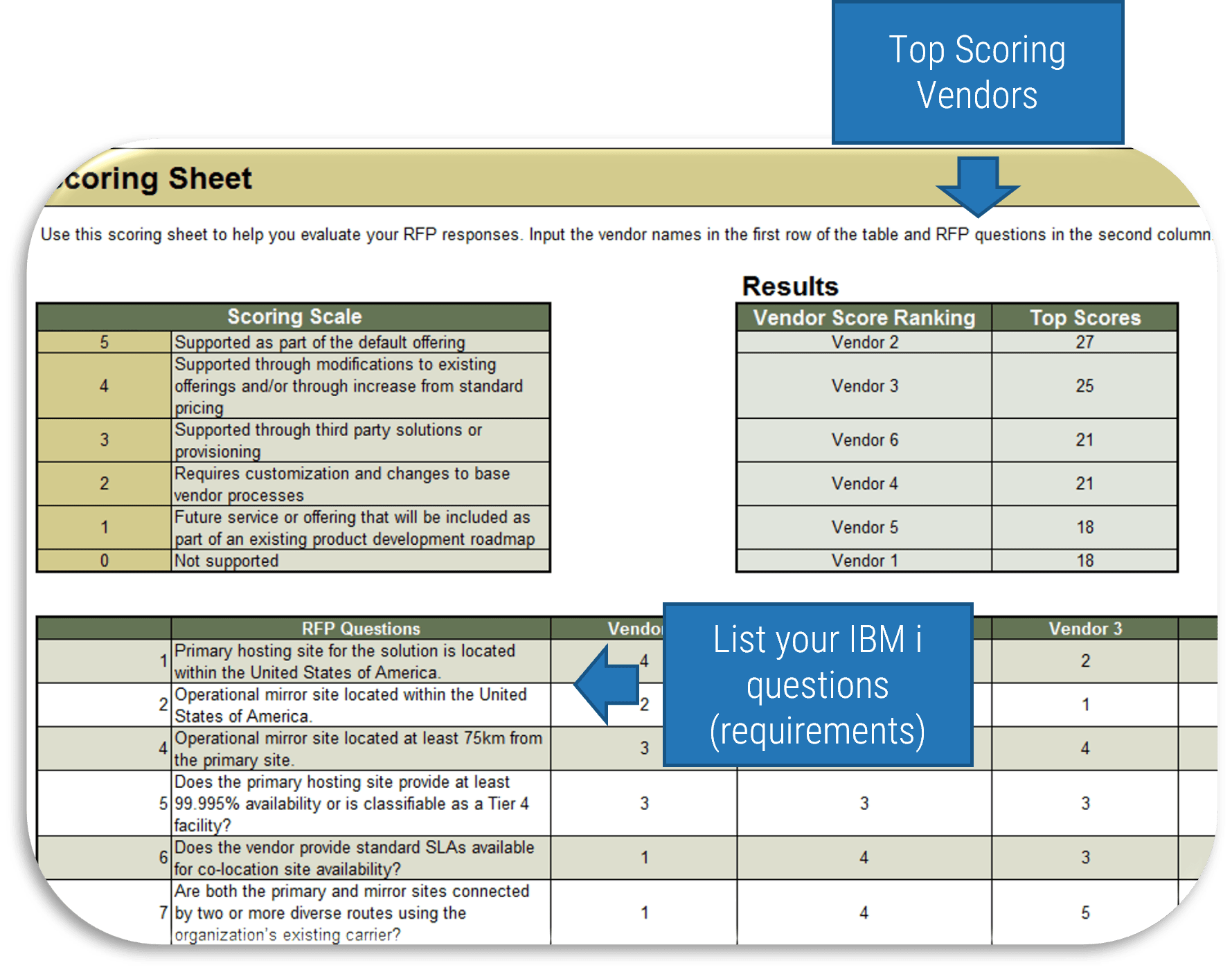
4. Service Desk Outsourcing Reference Interview Template and Scoring Tool – Materials to help you conduct efficient briefings and select the best vendor to fulfill your service desk requirements.
Use the Reference Interview Template to outline a list of questions for interviewing current/previous customers of your candidate vendors. These interviews will help you with unbiased vendor scoring. The RFP Vendor Scoring Tool will help you facilitate vendor briefings with your list of questions and score candidate vendors efficiently through quantifying evaluations.
- Service Desk Outsourcing Reference Interview Template
- Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Scoring Tool
Infographic

Further reading
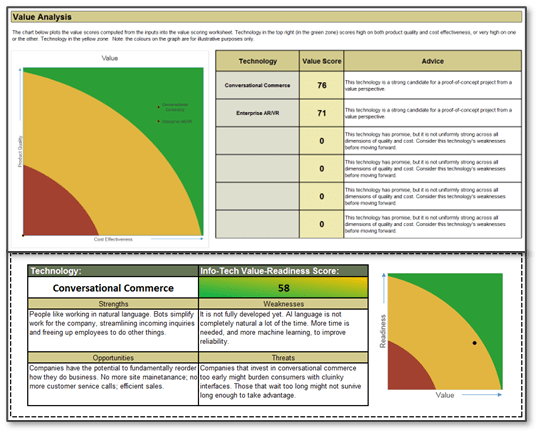
Define Requirements for Outsourcing the Service Desk
Prepare your RFP for long-term success, not short-term gains
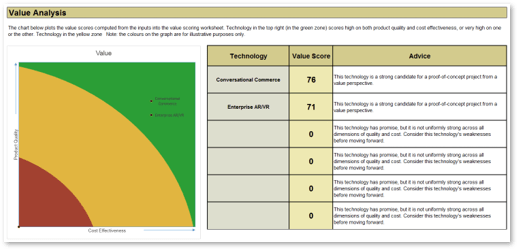
Define Requirements for Outsourcing the Service Desk
Prepare your RFP for long-term success, not short-term gains
EXECUTIVE BRIEF
Analyst Perspective
Outsource services with your eyes wide open.
Cost reduction has traditionally been an incentive for outsourcing the service desk. This is especially the case for organizations that don't have minimal processes in place and those that need resources and skills to fill gaps.
Although cost reduction is usually the main reason to outsource the service desk, in most cases service desk outsourcing increases the cost in a short run. But without a proper model, you will only outsource your problems rather than solving them. A successful outsourcing strategy follows a comprehensive plan that defines objectives, assigns accountabilities, and sets expectations for service delivery prior to vendor outreach.
For outsourcing the service desk, you should plan ahead, work as a group, define requirements, prepare a strong RFP, and contemplate tension metrics to ensure continual improvement. As you build a project charter to outline your strategy for outsourcing your IT services, ensure you focus on better customer service instead of cost optimization. Ensure that the outsourcer can support your demands, considering your long-term achievement.
Think about outsourcing like a marriage deed. Take into account building a good relationship before beginning the contract, ensure to include expectations in the agreement, and make it possible to exit the agreement if expectations are not satisfied or service improvement is not achieved.

Mahmoud Ramin, PhD
Senior Research Analyst
Infrastructure and Operations
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
In organizations where technical support is viewed as non-strategic, many see outsourcing as a cost-effective way to provide this support. However, outsourcing projects often fall short of their goals in terms of cost savings and quality of support.
Common Obstacles
Significant administrative work and up-front costs are required to outsource the service desk, and poor planning often results in project failure and the decrease of end-user satisfaction.
A complete turnover of the service desk can result in lost knowledge and control over processes, and organizations without an exit strategy can struggle to bring their service desk back in house and reestablish the confidence of end users.
Info-Tech's Approach
- First decide if outsourcing is the correct step; there may be more preliminary work to do beforehand.
- Assess requirements and make necessary adjustments before developing an outsource RFP.
- Clearly define the project and produce an RFP to provide to vendors.
- Plan for long-term success, not short-term gains.
- Prepare to retain some of the higher-level service desk work.
Info-Tech Insight
Outsourcing is easy. Realizing all of the expected cost, quality, and focus benefits is hard. Successful outsourcing without being directly involved in service desk management is almost impossible.
Your challenge
This research is designed to help organizations that need to:
- Outsource the service desk or portions of service management to improve service delivery.
- Improve and repatriate existing outsourcing outcomes by becoming more engaged in the management of the function. Regular reviews of performance metrics, staffing, escalation, knowledge base content, and customer satisfaction are critical.
- Understand the impact that outsourcing would have on the service desk.
- Understand the potential benefits that outsourcing can bring to the organization.
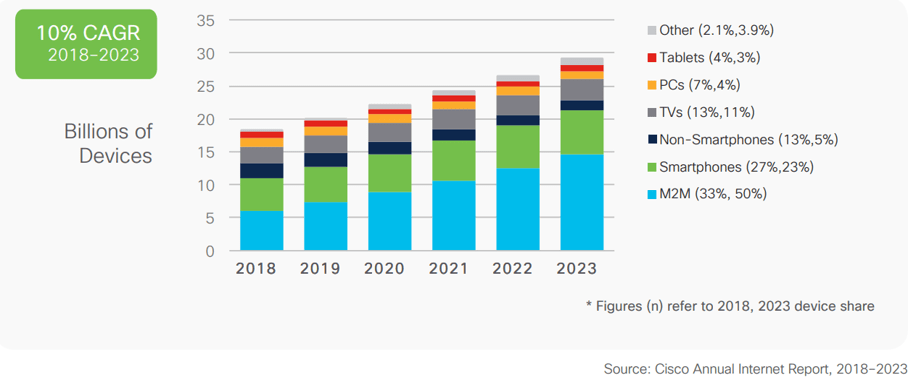
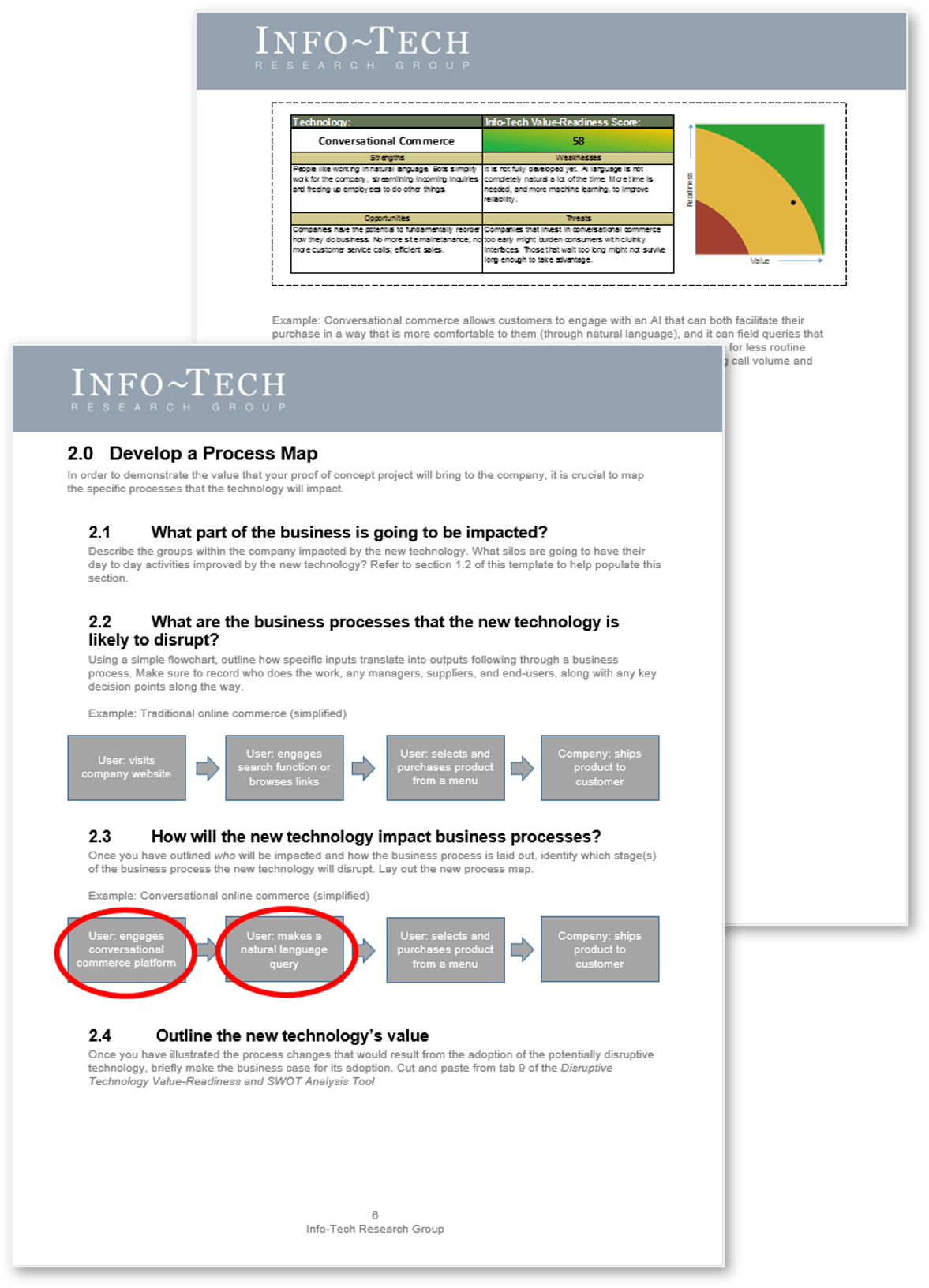
Source: HDI 2017 | About 68.5% of the service desk fund is allocated to agent salaries, while only 9.3% of the service desk fund is spent on technology. The high ratio of salaries and expenses over other expense drives organizations to outsource their service desk without taking other considerations into account. |
Info-Tech Insight
The outsourcing contract must preserve your control, possession, and ownership of the intellectual property involved in the service desk operation. From the beginning of the process, repatriation should be viewed as a possibility and preserved as a capability.
Your challenge
This research helps organizations who would like to achieve these goals:
- Determine objectives and requirements to outsource the service desk.
- Develop a project charter and build an outsourcing strategy to efficiently define processes to reduce risk of failure.
- Build an outsourcing RFP and conduct interviews to identify the best candidate for service delivery.
- Build a long-term relationship with an outsourcing vendor, making sure the vendor is able to satisfy all requirements.
- Include a continual improvement plan in the outsourcing strategy and contain the option upon service delivery dissatisfaction.
New hires require between 10 and 80 hours of training (Forward Bpo Inc., 2019).
A benchmark study by Zendesk from 45,000 companies reveals that timely resolution of issues and 24/7 service are the biggest factors in customer service experience.
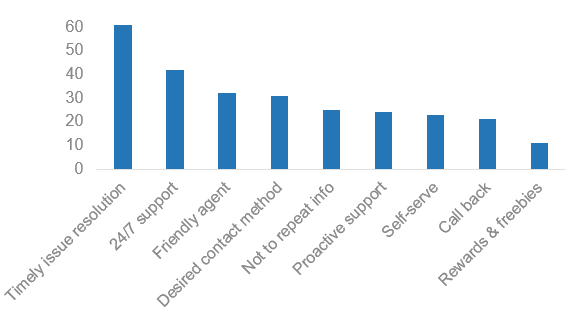
These factors push many businesses to consider service desk outsourcing to vendors that have capabilities to fulfill such requirements.
Common obstacles
These barriers make this challenge difficult to address for many organizations:
- In most cases, organizations must perform significant administrative work before they can make a move. Those that fail to properly prepare impede a smooth transition, the success of the vendor, and the ability to repatriate.
- Successful outsourcing comes from the recognition that an organization is experiencing complete turnover of its service desk staff. These organizations engage the vendor to transition knowledge and process to ensure continuity of quality.
- IT realizes the most profound hidden costs of outsourcing when the rate of ticket escalation increases, diminishing the capacity of senior technical staff for strategic project work.
Many organizations may not get the value they expect from outsourcing in their first year.
Common Reasons:
- Overall lack of due diligence in the outsourcing process
- Unsuitable or unclear service transition plan
- Poor service provider selection and management
Poor transition planning results in delayed benefits and a poor relationship with your outsourcing service provider. A poor relationship with your service provider results in poor communication and knowledge transfer.
Key components of a successful plan:
- Determine goals and identify requirements before developing an RFP.
- Finalize your outsourcing project charter and get ready for vendor evaluation.
- Assess and select the most appropriate provider; manage the transition and vendor relationship.
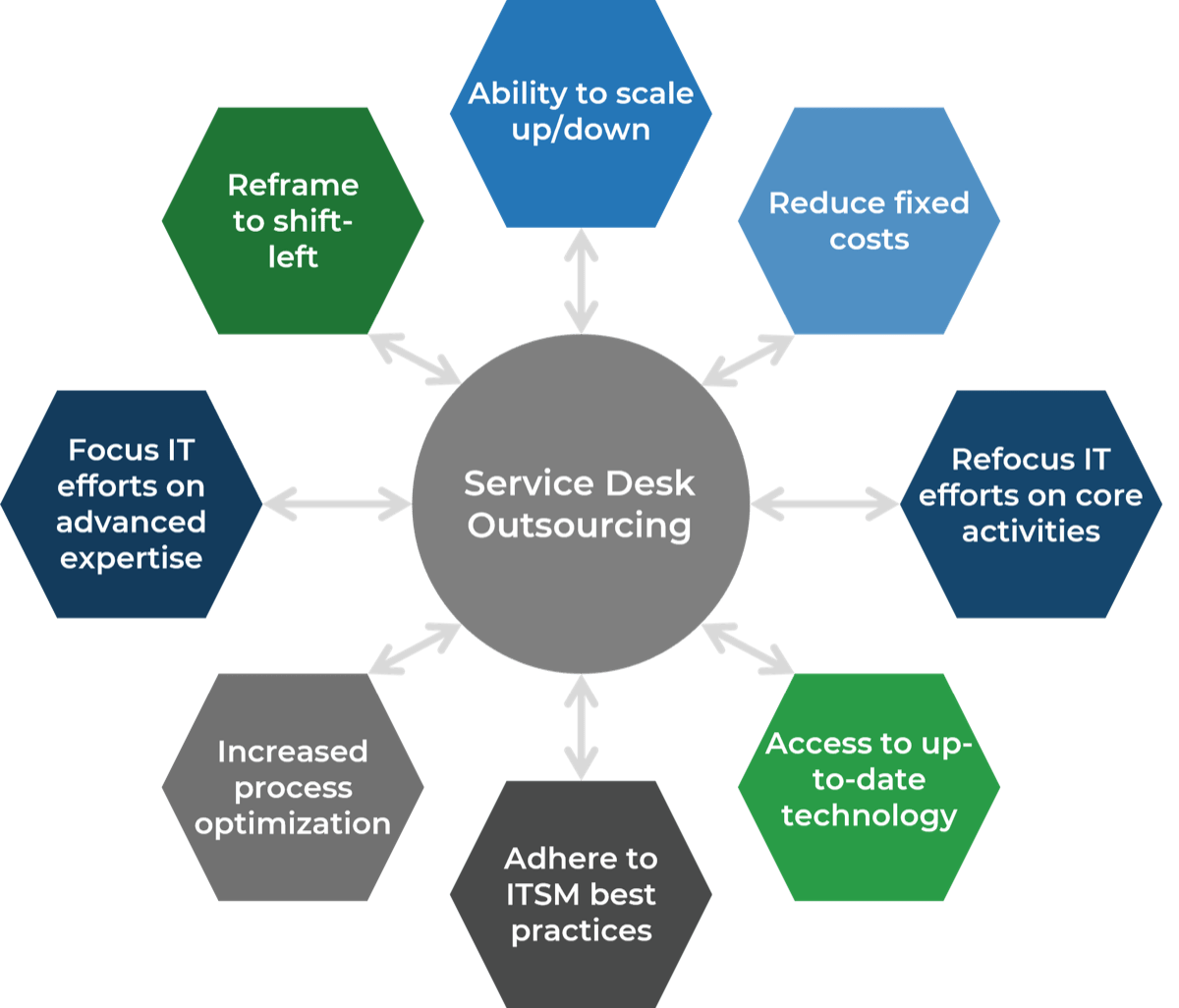
Outsource the service desk properly, and you could see a wide range of benefits
Info-Tech Insight
In your service desk outsourcing strategy, rethink downsizing first-level IT service staff. This can be an opportunity to reassign resources to more valuable roles, such as asset management, development or project backlog. Your current service desk staff are most likely familiar with the current technology, processes, and regulations within IT. Consider the ways to better use your existing resources before reducing headcount.
Info-Tech's Approach
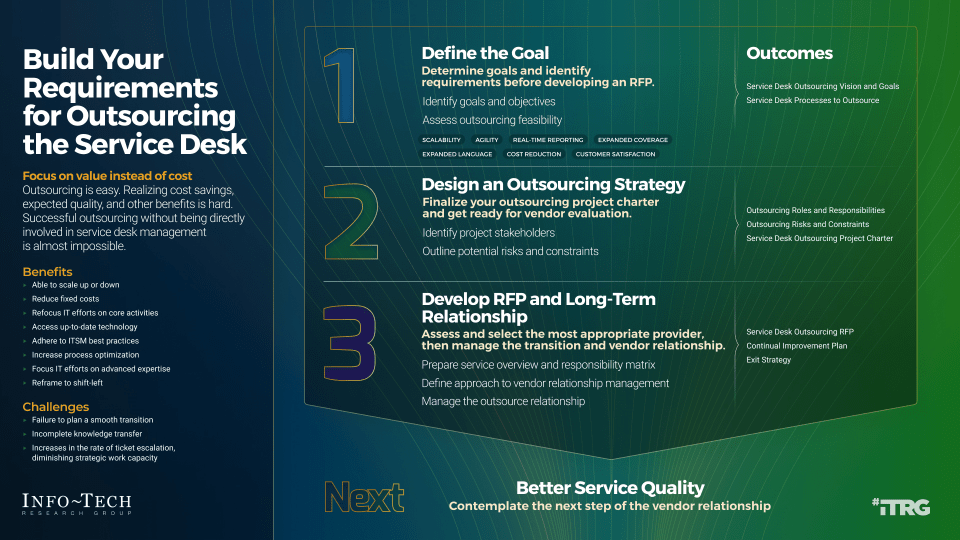
Determine Goals
Conduct activities in the blueprint to pinpoint your current challenges with the service desk and find out objectives to outsource customer service.
Define Requirements
You need to be clear about the processes that will be outsourced. Considering your objectives, we'll help you discover the processes to outsource, to help you achieve your goals.
Develop RFP
Your expectations should be documented in a formal proposal to help vendors provide solid information about how they will satisfy your requirements and what their plan is.
Build Long-Term Relationship
Make sure to plan for continual improvement by setting expectations, tracking the services with proper metrics, and using efficient communication with the provider. Think about the rainy day and include exit conditions for ending the relationship if needed.
Info-Tech's methodology
1. Define the Goal | 2. Design an Outsourcing Strategy | 3. Develop an RFP and Make a Long-Term Relationship | |
|---|---|---|---|
Phase Steps | 1.1 Identify goals and objectives 1.2 Assess outsourcing feasibility | 2.1 Identify project stakeholders 2.2 Outline potential risks and constraints | 3.1 Prepare service overview and responsibility matrix 3.2 Define approach to vendor relationship management 3.3 Manage the outsource relationship |
Phase Outcomes | Service Desk Outsourcing Vision and Goals Service Desk Processes to Outsource | Outsourcing Roles and Responsibilities Outsourcing Risks and Constraints Service Desk Outsourcing Project Charter | Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Continual Improvement Plan Exit Strategy |
Insight summary
Focus on value
Outsourcing is easy. Realizing all of the expected cost, quality, and focus benefits is hard. Successful outsourcing without being directly involved in service desk management is almost impossible.
Define outsourcing requirements
You don't need to standardize before you outsource, but you still need to conduct your due diligence. If you outsource without thinking about how you want the future to work, you will likely be unsatisfied with the result.
Don't focus on cost
If cost is your only driver for outsourcing, understand that there will be other challenges. Customer service quality will likely be less, and your outsourcer may not add on frills such as Continual Improvement. Be careful that your specialists don't end up spending more time working on incidents and service requests.
Emphasize on customer service
A bad outsourcer relationship will result in low business satisfaction with IT overall. The service desk is the face of IT, and if users are dissatisfied with the service desk, then they are much likelier to be dissatisfied with IT overall.
Vendors are not magicians
They have standards in place to help them succeed. Determine ITSM best practices, define your requirements, and adjust process workflows accordingly. Your staff and end users will have a much easier transition once outsourcing proceeds.
Plan ahead to guarantee success
Identify outsourcing goals, plan for service and system integrations, document standard incidents and requests, and track tension metrics to make sure the vendor does the work efficiently. Aim for building a long-term relationship but contemplate potential exit strategy.
Blueprint deliverables
Each step of this blueprint is accompanied by supporting deliverables to help you accomplish your goals:
 | Service Desk Outsourcing Requirements Database LibraryUse this library to guide you through processes to outsource |
 | Service Desk Outsourcing RFP TemplateUse this template to craft a proposal for outsourcing your service desk |
 | Service Desk Outsourcing Reference Interview TemplateUse this template to verify vendor claims on service delivery with pervious or current customers |
 | Service Desk Outsourcing Vendor Proposal Scoring ToolUse this tool to evaluate RFP submissions |
Key deliverable: | |
|---|---|
 | Service Desk Outsourcing Project CharterDocument your project scope and outsourcing strategy in this template to organize the project for efficient resource and requirement allocation |
Blueprint benefits
IT Benefits | Business Benefits |
|---|---|
|
|
Info-Tech offers various levels of support to best suit your needs
DIY Toolkit
"Our team has already made this critical project a priority, and we have the time and capability, but some guidance along the way would be helpful."
Guided Implementation
"Our team knows that we need to fix a process, but we need assistance to determine where to focus. Some check-ins along the way would help keep us on track."
Workshop
"We need to hit the ground running and get this project kicked off immediately. Our team has the ability to take this over once we get a framework and strategy in place."
Consulting
"Our team does not have the time or the knowledge to take this project on. We need assistance through the entirety of this project."
Diagnostics and consistent frameworks used throughout all four options
Guided Implementation
What does a typical GI on this topic look like?
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 |
|---|---|---|
Call #1: Scope your specific challenges and objectives | Call #3: Identify project stakeholders, and potential risks and constraints | Call #5: Create a detailed RFP |
Call #6: Identify strategy risks. | ||
| Call #2: Assess outsourcing feasibility and processes to outsource | Call #4: Create a list of metrics to ensure efficient reporting | Call #7: Prepare for vendor briefing and scoring each vendor |
Call #8: Build a communication plan |
A Guided Implementation (GI) is series of calls with an Info-Tech analyst to help implement our best practices in your organization.
A typical GI is between 8 to 10 calls over the course of 4 to 6 months.
Phase 1
Define the goal
Define the goal | Design an outsourcing strategy | Develop an RFP and make a long-term relationship |
|---|---|---|
1.1 Identify goals and objectives 1.2 Assess outsourcing feasibility | 2.1 Identify project stakeholders 2.2 Outline potential risks and constraints | 3.1 Prepare a service overview and responsibility matrix 3.2 Define your approach to vendor relationship management 3.3 Manage the outsource relationship |
This phase will walk you through the following activities:
- Analysis outsourcing objectives
- Assess outsourcing feasibility
- Identify services and processes to outsource
This phase involves the following participants:
- Service Desk Team
- IT Leadership
Define requirements for outsourcing service desk support
Step 1.1
Identify goals and objectives
Activities
1.1.1 Find out why you want to outsource your service desk
1.1.2 Document the benefits of outsourcing your service desk
1.1.3 Identify your outsourcing vision and goals
1.1.4 Prioritize service desk outsourcing goals to help structure your mission statement
1.1.5 Craft a mission statement that demonstrates your decision to reach your outsourcing objectives
Define the goal
This step requires the following inputs:
- List of strengths and weaknesses of the service desk
- Challenges with the service desk
This step involves the following participants:
- CIO
- IT Leadership
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
Outcomes of this step
- Service desk outsourcing vision and goals
- Benefits of outsourcing the service desk
- Mission statement
What is your rationale to outsource the service desk?
Potential benefits of outsourcing the service desk:
- Bring in the expertise and knowledge to manage tickets according to best-practice guidelines
- Reduce the timeline to response and resolution
- Improve IT productivity
- Enhance IT services and improve performance
- Augment relationship between IT and business through service-level improvement
- Free up the internal team and focus IT on complex projects and higher priority tasks
- Speed up service desk optimization
- Improve end-user satisfaction through efficient IT services
- Reduce impact of incidents through effective incident management
- Increase service consistency via turnover reduction
- Expand coverage hour and access points
- Expand languages to service different geographical areas
1.1.1 Find out why you want to outsource your service desk
1 hour
Service desk is the face of IT. Service desk improvement increases IT efficiency, lowers operation costs, and enhances business satisfaction.
Common challenges that result in deciding to outsource the service desk are:
Participants: IT Director, Service Desk Manager, Service Desk Team
| Challenge | Example |
|---|---|
| Lack of tier 1 support | Startup does not have a dedicated service desk to handle incidents and provide services to end users. |
| Inefficient ticket handling | MTTR is very high and end users are frustrated with their issues not getting solved quickly. Even if they call service desk, they are put on hold for a long time. Due to these inefficiencies, their daily work is greatly impacted. |
| Restricted service hours | Company headquartered in Texas does not have resources to provide 24/7 IT service. When users in the East Asia branch have a laptop issue, they must wait until the next day to get response from IT. This has diminished their satisfaction. |
| Restricted languages | Company X is headquartered in New York. An end user not fluent in English from Madrid calls in for support. It takes five minutes for the agent to understand the issue and log a ticket. |
| Ticket backlog | IT is in firefighting mode, very busy with taking care of critical incidents and requests from upper management. Almost no one is committed to the SLA because of their limited availability. |
Brainstorm your challenges with the service desk. Why have you decided to outsource your service desk? Use the above table as a sample.
1.1.2 Document benefits of outsourcing your service desk
1 hour
- Review the challenges with your current service desk identified in activity 1.1.1.
- Discuss possible ways to tackle these challenges. Be specific and determine ways to resolve these issues if you were to do it internally.
- Determine potential benefits of outsourcing the service desk to IT, business, and end users.
- For each benefit, describe dependencies. For instance, to reduce the number of direct calls (benefit), users should have access to service desk as a single point of contact (dependency).
- Document this activity in the Service Desk Outsourcing Project Charter Template.
Download the Project Charter Template
Input
- List of challenges with the current service desk from activity 1.1.1
Output
- Benefits of outsourcing the service desk
Materials
- Whiteboard/flip charts
- Markers
- Sticky notes
- Laptops
Participants
- IT Director/CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- Service Desk Team
- IT Managers
Why should you not consider cost reduction as a primary incentive to outsourcing the service desk?
Assume that some of the costs will not go away with outsourcing
When you outsource, the vendor's staff tend to gradually become less effective as:
- They are managed by metrics to reduce costs by escalating sooner, reducing talk time, and proposing questionable solutions.
- Turnover results in new employees that get insufficient training.
You must actively manage the vendor to identify and resolve these issues. Many organizations find that service desk management takes more time after they outsource.
You need to keep spending on service desk management, and you may not get away from technology infrastructure spending.
Info-Tech Insight
In their first year, almost 42% of Info-Tech's clients do not get the real value of outsourcing services as expected. This iss primarily because of misalignment of organizational goals with outcomes of the outsourced services.
Consider the hidden costs of outsourcing
Expected Costs | Unexpected Costs | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transition Costs | Severance and staff retention |
|
|
| Fees | Price of the engagement |
|
|
| Management Costs | Time directing account |
|
|
| Rework Costs | Downtime, defect rate, etc. (quality metrics measured in SLAs) |
|
|
Determine strategies to avoid each hidden cost
| Costs related to transitioning into the engagement | Adapting to standards and training costs |
|---|---|
Adapting to standards: Define the process improvements you will need to work with each potential vendor. Training costs for vendor staff: Reduce training costs by keeping the same vendor staff on all of your projects. | |
Fee-related costs | Fees for additional services (that you thought were included) |
Carefully review each proposed statement of work to identify and reduce extra fees. Understand why extra fees occur in the SLA, the contract, and the proposed statement of work, and take steps to protect yourself and the vendor. | |
Management-related costs | Direct management of vendor staff and dispute resolution |
Direct management of vendor staff: Avoid excessive management costs by defining a two-tier management structure on both sides of the engagement. Time spent resolving disputes: Avoid prolonged resolution costs by defining terms of divorce for the engagement up front. | |
Rework costs | Unanticipated requirements and integration with existing systems |
Unanticipated requirements: Use a two-stage process to define requirements, starting with business people and then with review by technical staff. Integration with existing systems: Obtain a commitment from vendors that deliverables will conform to standards at points of integration with your systems. |
Your outsourcing strategy should address the reasons you decided to outsource
A clear vision of strategic objectives prior to entering an outsourcing agreement will allow you to clearly communicate these objectives to the Managed Service Provider (MSP) and use them as a contracted basis for the relationship.
- Define the business' overall approach to outsourcing along with the priorities, rules, and principles that will drive the outsourcing strategy and every subsequent outsourcing decision and activity.
- Define specific business, service, and technical goals for the outsourcing project and relevant measures of success.
"People often don't have a clear direction around what they're trying to accomplish. The strategic goals should be documented. Is this a cost-savings exercise? Is it because you're deficient in one area? Is it because you don't have the tools or expertise to run the service desk yourself? Figure out what problem you're trying to solve by outsourcing, then build your strategy around that.
– Jeremy Gagne, Application Support Delivery Manager, Allegis Group
Most organizations are driven to consider outsourcing their service desk hoping to improve the following:
- Ability to scale (train people and acquire skills)
- Focus on core competencies
- Decrease capital costs
- Access latest technology without large investment
- Resolve labor force constraints
- Gain access to special expertise without paying a full salary
- Save money overall
Info-Tech Insight
Use your goals and objectives as a management tool. Clearly outline your desired project outcomes to both your in-house team and the vendor during implementation and monitoring. It will allow a common ground to unite both parties as the project progresses.
Mitigate pitfalls that lay in the way of desired outcomes of outsourcing
| Desired outcome | Pitfalls to overcome |
|---|---|
| IT can focus on core competencies and strategic initiatives rather than break-fix tasks. | Escalation to second- and third-level support usually increases when the first level has been outsourced. Outsourcers will have less experience with your typical incidents and will give up on trying to solve some issues more quickly than your internal level-one staff. |
| Low outsourcing costs compared to the costs needed to employ internal employees in the same role. | Due to lack of incentive to decrease ticket volume, costs are likely to increase. As a result, organizations often find themselves paying more overall for an outsourced service desk than if they had a few dedicated IT service desk employees in-house. |
| Improved employee morale as a result of being able to focus on more interesting tasks. | Management often expects existing employee morale to increase as a result of shifting their focus to core and strategic tasks, but the fear of diminished job security often spreads to the remaining non-level-one employees. |
1.1.3 Identify outsourcing vision and goals
Identify the goals and objectives of outsourcing to inform your strategy.
Participants: IT Director, Service Desk Manager, Service Desk Team
1-2 hours
- Meet with key business stakeholders and the service desk staff who were involved in the decision to outsource.
- As a group, review the results from activity 1.1.1 (challenges with current service desk operations) and identify the goals and objectives of the outsourcing initiative.
- Determine the key performance indicator (KPI) for each goal.
- Identify the impacted stakeholder/s for each goal.
- Discuss checkpoint schedule for each goal to make sure the list stays updated.
Use the sample table as a starting point:
- Document your table in the Service Desk Outsourcing Project Charter Template.
| ID | Goal Description | KPI | Impacted Stakeholders | Checkpoint Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Provide capacity to take calls outside of current service desk work hours |
|
|
|
| 2 | Take calls in different languages |
|
|
|
| 3 | Provide field support at remote sites with no IT presence without having to fly out an employee |
|
|
|
| 4 | Improve ease of management by vendor helping with managing and optimizing service desk tasks |
|
|
|
Download the Project Charter Template
Evaluate organizational demographics to assess outsourcing rationale
The size, complexity, and maturity of your organization are good indicators of service desk direction with regards to outsourcing.
Organization Size
- As more devices, applications, systems, and users are added to the mix, vendor costs will increase but their ability to meet business needs will decrease.
- Small organizations are often either rejected by vendors for being too small or locked into a contract that is overkill for their actual needs (and budget).
Complexity
- Highly customized environments and organizations with specialized applications or stringent regulatory requirements are very difficult to outsource for a reasonable cost and acceptable quality.
- In these cases, the vendor is required to train skilled support or ends up escalating more tickets back to second- and third-level support.
Requirements
- Organizations looking to outsource must have defined outsourcing requirements before looking at vendors.
- Without a requirement assessment, the vendor won't have guidelines to follow and you won't be able to measure their adherence.
Info-Tech Insight
Although less adherence to service desk best practices can be one of the main incentives to outsourcing the service desk, IT should have minimal processes in place to be able to set expectations with targeting vendors.
1.1.4 Prioritize service desk outsourcing goals to help structure mission statement
0.5-1 hour
The evaluation process for outsourcing the service desk should be done very carefully. Project leaders should make sure they won't panic internal resources and impact their performance through the transition period.
If the outsourcing process is rushed, it will result in poor evaluation, inefficient decision making, and project failure.
- Refer to results in activity 1.1.3. Discuss the service desk outsourcing goals once again.
- Brainstorm the most important objectives. Use sticky notes to prioritize the items from the most important to the least important.
- Edit the order accordingly.
Input
- Project goals from activity 1.1.3
Output
- Prioritized list of outsourcing goals
Materials
- Whiteboard/flip charts
- Markers
- Sticky notes
- Laptops
Participants
- IT Director/CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- Service Desk Team
- IT Managers
Download the Project Charter Template
1.1.5 Craft a mission statement that demonstrates your decision to reach outsourcing objectives
Participants: IT Director, Service Desk Manager
0.5-1 hour
The IT mission statement specifies the function's purpose or reason for being. The mission should guide each day's activities and decisions. The mission statement should use simple and concise terminology and speak loudly and clearly, generating enthusiasm for the organization.
Strong IT mission statements:
- Articulate the IT function's purpose and reason for existence
- Describe what the IT function does to achieve its vision
- Define the customers of the IT function
- Can be described as:
- Compelling
- Easy to grasp
- Sharply focused
- Inspirational
- Memorable
- Concise
Sample mission statements:
- To help fulfill organizational goals, IT has decided to empower business stakeholders with outsourcing the service desk.
- To support efficient IT service provision, better collaboration, and effective communication, [Company Name] has decided to outsource the service desk.
- [Company Name] plans to outsource the service desk so it can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies with current service desk processes and enable [Company Name] to innovate and support business growth.
- Considering the goals and benefits determined in the previous activities, outline a mission statement.
- Document your outsourcing mission statement in the "Project Overview" section of the Project Charter Template.
Download the Project Charter Template
Step 1.2
Assess outsourcing feasibility
Activities
1.2.1 Create a baseline of customer experience
1.2.2 Identify service desk processes to outsource
1.2.3 Design an outsourcing decision matrix for service desk processes and services
1.2.4 Discuss if you need to outsource only service desk or if additional services would benefit from outsourcing too
Define the goal
This step requires the following inputs:
- List of service desk tasks and responsibilities
This step involves the following participants:
- CIO
- IT Leadership
- Service Desk Manager
- Infrastructure Manager
Outcomes of this step
- End-user satisfaction with the service desk
- List of processes and services to outsource
1.2.1 Create a baseline of customer experience
Solicit targeted department feedback on IT's core service capabilities, communications, and business enablement from end users. Use this feedback to assess end-user satisfaction with each service, broken down by department and seniority level.
- Complete an end-user satisfaction survey to define the current state of your IT services, including service desk (timeliness and effectiveness). With Info-Tech's end-user satisfaction program, an analyst will help you set up the diagnostic and will go through the report with you.
- Evaluate survey results.
- Communicate survey results with team leads and discuss the satisfaction rates and comments of the end users.
- Schedule to launch another survey one year after outsourcing the service desk.
- Your results will be compared to the following year's results to analyze the overall success/failure of your outsourcing project.
A decrease of business and end-user satisfaction is a big drive to outsourcing the service desk. Conduct a customer service survey to discover your end-user experience prior to and after outsourcing the service desk.
Don't get caught believing common misconceptions: outsourcing doesn't mean sending away all the work
First-time outsourcers often assume they are transferring most of the operations over to the vendor, but this is often not the case.
- Management of performance, SLAs, and customer satisfaction remain the responsibility of your organization.
- Service desk outsource vendors provide first-line response. This includes answering the phones, troubleshooting simple problems, and redirecting requests that are more complex.
- The vendor is often able to provide specialized support for standard applications (and for customized applications if you'll pay for it). However, the desktop support still needs someone onsite, and that service is very expensive to outsource.
- Tickets that are focused on custom applications and require specialized or advanced support are escalated back to your organization's second- and third-level support teams.
Switching to a vendor won't necessarily improve your service desk maturity
You should have minimal requirements before moving.
Whether managing in-house or outsourcing, it is your job to ensure core issues have been clarified, processes defined, and standards maintained. If your processes are ad-hoc or non-existent right now, outsourcing won't fix them.
You must have the following in place before looking to outsource:
- Defined reporting needs and plans
- Formalized skill-set requirements
- Problem management and escalation guidelines
- Ticket templates and classification rules
- Workflow details
- Knowledge base standards
Info-Tech Insight
If you expect your problems to disappear with outsourcing, they might just get worse.
Define long-term requirements
Anticipate growth throughout the lifecycle of your outsourcing contract and build that into the RFP
- Most outsourcing agreements typically last three to five years. In that time, you risk outgrowing your service provider by neglecting to define your long-term service desk requirements.
- Outgrowing your vendor before your contract ends can be expensive due to high switching costs. Managing multiple vendors can also be problematic.
- It is crucial to define your service desk requirements before developing a request for proposal to make sure the service you select can meet your organization's needs.
- Make sure that the business is involved in this planning stage, as the goals of IT need to scale with the growth strategy of the business. You may select a vendor with no additional capacity despite the fact that your organization has a major expansion planned to begin two years from now. Assessing future requirements also allows you to culture match with the vendor. If your outlooks and practices are similar, the match will likely click.
Info-Tech Insight
Don't select a vendor for what your company is today – select a vendor for what your company will be years from now. Define your future service desk requirements in addition to your current requirements and leave room for growth and development.
You can't outsource everything
Manage the things that stay in-house well or suffer the consequences.
"You can't outsource management; you can only outsource supervision." Barry Cousins, Practice Lead, Info-Tech Research Group | |
|---|---|
What can be the vendor in charge of? | What stays in-house? |
|
|
Info-Tech Insight
The need for a Service Desk Manager does not go away when you outsource. In fact, the need becomes even stronger and never diminishes.
Assess current service desk processes before outsourcing
Process standards with areas such as documentation, workflow, and ticket escalation should be in place before the decision to outsource has been made.
Every effective service desk has a clear definition of the services that they are performing for the end user. You can't provide a service without knowing what the services are.
MSPs typically have their own set of standards and processes in play. If your service desk is not at a similar level of maturity, outsourcing will not be pleasant.
Make sure that your metrics are reported consistently and that they tell a story.
"Establish baseline before outsourcing. Those organizations that don't have enough service desk maturity before outsourcing should work with the outsourcer to establish the baseline."
– Yev Khobrenkov, Enterprise Consultant, Solvera Solutions
Info-Tech Insight
Outsourcing vendors are not service desk builders; they're service desk refiners. Switching to a vendor won't improve your maturity; you must have a certain degree of process maturity and standardization before moving.
Case Study
INDUSTRY: Cleaning Supplies
SOURCE: PicNet
Challenge
- Reckitt Benckiser of Australia determined that its core service desk needed to be outsourced.
- It would retain its higher level service desk staff to work on strategic projects.
- The MSP needed to fulfill key requirements outlined by Reckitt Benckiser.
Solution
- Reckitt Benckiser recognized that its rapidly evolving IT needs required a service desk that could fulfill the following tasks:
- Free up internal IT staff.
- Provide in-depth understanding of business apps.
- Offer efficient, cost-effective support onsite.
- Focus on continual service improvement (CSI).
Results
- An RFP was developed to support the outsourcing strategy.
- With the project structure outlined and the requirements of the vendor for the business identified, Reckitt Benckiser could now focus on selecting a vendor that met its needs.
1.2.1 Identify service desk processes to outsource
2-3 hours
Review your prioritized project goals from activity 1.1.4.
Brainstorm requirements and use cases for each goal and describe each use case. For example: To improve service desk timeliness, IT should improve incident management, to resolve incidents according to the defined SLA and based on ticket priority levels.
Discuss if you're outsourcing just incident management or both incident management and request fulfillment. If both, determine what level of service requests will be outsourced? Will you ask the vendor to provide a service catalog? Will you outsource self-serve and automation?
Document your findings in the service desk outsourcing requirements database library.
Input
- Outsourcing project goals from activity 1.1.4
Output
- List of processes to outsource
Materials
- Sticky notes
- Markers
- Whiteboard/flip charts
- Laptops
Participants
- IT Director/CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- Service Desk Team
Download the Requirements Database Library
1.2.2 Design an outsourcing decision matrix for service desk processes and services
Participants: IT Director, Service Desk Manager, Infrastructure manager
2-3 hours
Most successful service desk outsourcing engagements have a primary goal of freeing up their internal resources to work on complex tasks and projects. The key outsourcing success factor is to find out internal services and processes that are standardized or should be standardized, and then determine if they can be outsourced.
- Review the list of identified service desk processes from activity 1.2.1.
- Discuss the maturity level of each process (low, medium, high) and document under the maturity column of the Outsource the Service Desk Requirements Database Library.
- Use the following decision matrix for each process. Discuss which tasks are important to strategic objectives, which ones provide competitive advantage, and which ones require specialized in-house knowledge.
- Identify processes that receive high vendor's performance advantage. For instance, access to talent, lower cost at scale, and access to technology.
- In your outsourcing assessment, consider a narrow scope of engagement and a broad view of what is important to business outcome.
- Based on your findings, determine the priority of each process to be outsourced. Document results in the service desk outsourcing requirements database library, and section 4.1 of the service desk outsourcing project charter.
|
|
|
Download the Requirements Database Library
Download the Project Charter Template
Maintain staff and training: you need to know who is being hired, how, and why
Define documentation rules to retain knowledge
- Establish a standard knowledge article template and list of required information.
- Train staff on the requirements of knowledge base creation and management. Help them understand the value of the time spent recording their work.
- It is your responsibility to assure the quality of each knowledge article. Outline accountabilities for internal staff and track for performance evaluations.
For information on better knowledge management, refer to Info-Tech's blueprint Optimize the Service Desk With a Shift-Left Strategy.
Expect to manage stringent skills and training standards
- Plan on being more formal about a Service Manager position and spending more time than you allocated previously.
- Complete a thorough assessment of the skills you need to keep the service desk running smoothly.
- Don't forget to account for any customized or proprietary systems. How will you train vendor staff to accommodate your needs? What does their turnaround look like: would it be more likely that you acquire a dependable employee in-house?
- Staffing requirements need to be actively monitored to ensure the outsourcer doesn't have degradation of quality or hiring standards. Don't assume that things run well – complete regular checks and ask for access to audit results.
- Are the systems and data being accessed by the vendor highly sensitive or subject to regulatory requirements? If so, it is your job to ensure that vendor staff are being screened appropriately.
Does your service desk need to integrate to other IT services?
A common challenge when outsourcing multiple services to more than one vendor is a lack of collaboration and communication between vendors.
- Leverage SIAM capabilities to integrate service desk tasks to other IT services, if needed.
- "Service Integration and Management (SIAM) is a management methodology that can be applied in an environment that includes services sourced from a number of service providers" (Scopism Limited, 2020).
- SIAM supports cross-functional integrations. Organizations that look for a single provider will be less likely to get maximum benefits from SIAM.
There are three layers of entities in SIAM:
- Customer Organization: The customer who receives services, who defines the relationship with service providers.
- Service Integrator: End-to-end service governance and integration is done at this layer, making sure all service providers are committed to their services.
- Service Provider: Responsible party for service delivery according to contract. It can be combination of internal provider, managed by internal agreements, and external provider, managed by SLAs between providers and customer organization.
Use SIAM to obtain better results from multiple service providers
In the SIAM model, the customer organization keeps strategic, governance, and business activities, while integrating other services (either internally or externally).
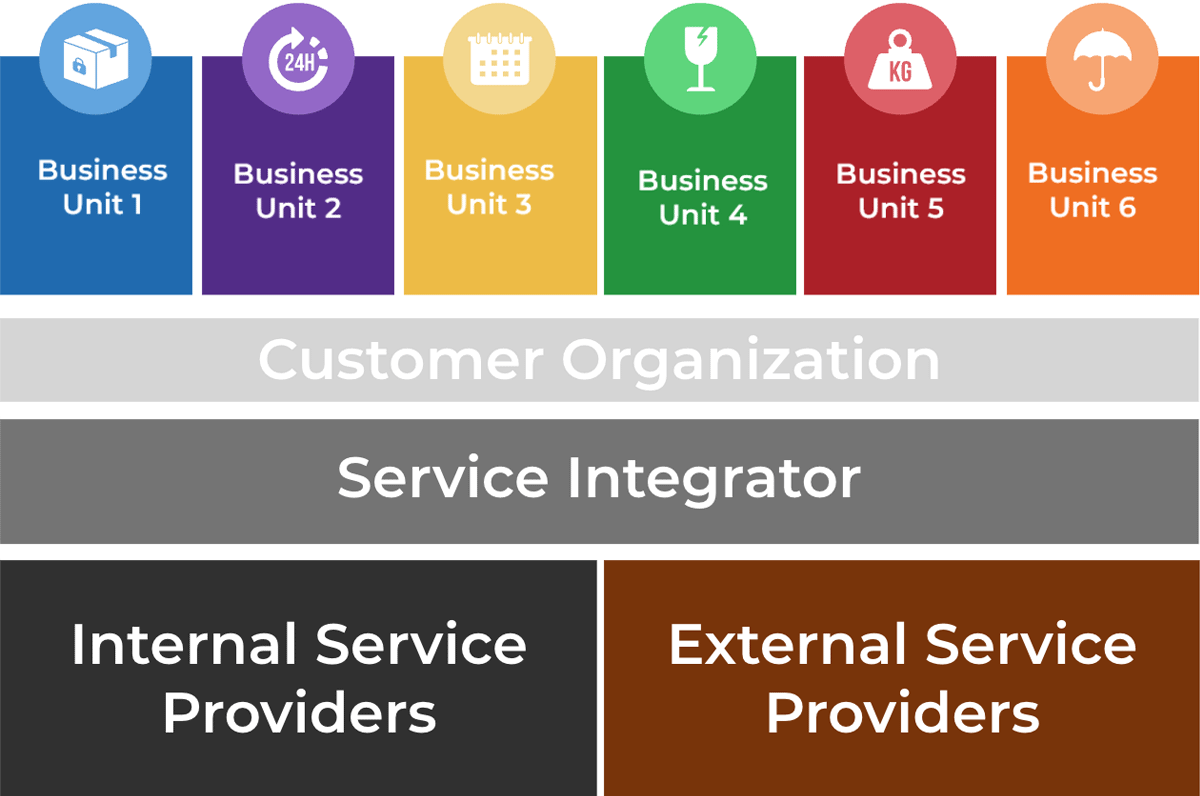
SIAM Layers. Source: SIAM Foundation BoK
Utilize SIAM to obtain better results from multiple service providers
SIAM reduces service duplication and improves service delivery via managing internal and external service providers.
To utilize the SIAM model, determine the following components:
- Service providers
- Service consumers
- Service outcomes
- Service obstacles and boundaries
- Service dependencies
- Technical requirements and interactions for each service
- Service data and information including service levels
To learn more about adopting SIAM, visit Scopism.
1.2.3 Discuss if you need to outsource only service desk or if additional services would benefit from outsourcing too
1-2 hours
- Discuss principles and goals of SIAM and how integrating other services can apply within your processes.
- Review the list of service desk processes and tasks to be outsourced from activities 1.2.1 and 1.2.2.
- Brainstorm a list of other services that are outsourced/need to be outsourced.
- Determine providers of each service (both internal and external). Document the other services to be integrated in the project charter template and requirements database library.
Input
- SIAM objectives
- List of service desk processes to outsource
Output
- List of other services to outsource and integrate in the project
Materials
- Sticky notes
- Markers
- Whiteboard/flip charts
- Laptops
Participants
- IT Director/CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- Service Desk Team
Download the Requirements Database Library
Download the Project Charter Template
Establish requirements for problem management in the outsourcing plan
Your MSP should not just fulfill SLAs – they should be a proactive source of value.
Problem management is a group effort. Make sure your internal team is assisted with sufficient and efficient data by the outsourcer to conduct a better problem management.
Clearly state your organization's expectations for enabling problem management. MSPs may not necessarily need, and cannot do, problem management; however, they should provide metrics to help you discover trends, define recurring issues, and enable root cause analysis.
For more information on problem management, refer to Info-Tech's blueprint Improve Incident and Problem Management.
PROBLEM MANAGEMENT
INCIDENT MANAGEMENT
INTAKE: Ticket data from incident management is needed for incident matching to identify problems. Critical Incidents are also a main input to problem management.
EVENT MANAGEMENT
INTAKE: SMEs and operations teams monitoring system health events can identify indicators of potential future issues before they become incidents.
APPLICATION, INFRASTRUCTURE, and SECURITY TEAMS
ACTION: Problem tickets require investigation from relevant SMEs across different IT teams to identify potential solutions or workarounds.
CHANGE MANAGEMENT
OUTPUT: Problem resolution may need to go through Change Management for proper authorization and risk management.
Outline problem management protocols to gain value from your service provider
- For example, with a deep dive into ticket trend analysis, your MSP should be able to tell you that you've had a large number of tickets on a particular issue in the past month, allowing you to look into means to resolve the issue and prevent it from reoccurring.
- A proactive MSP should be able to help your service levels improve over time. This should be built into the KPIs and metrics you ask for from the outsourcer.
Sample Scenario
Your MSP tracks ticket volume by platform.
There are 100 network tickets/month, 200 systems tickets/month, and 5,000 end-user tickets/month.
Tracking these numbers is a good start, but the real value is in the analysis. Why are there 5,000 end-user tickets? What are the trends?
Your MSP should be providing a monthly root-cause analysis to help improve service quality.
Outcomes:
- Meeting basic SLAs tells a small part of the story. The MSP is performing well in a functional sense, but this doesn't shed any insight on what kind of knowledge or value is being added.
- The MSP should provide routine updates on ticket trends and other insights gained through data analysis.
- A commitment to continual improvement will provide your organization with value throughout the duration of the outsourcing agreement.
Phase 2
Design an Outsourcing Strategy
Define the goal | Design an outsourcing strategy | Develop an RFP and make a long-term relationship |
|---|---|---|
1.1 Identify goals and objectives 1.2 Assess outsourcing feasibility | 2.1 Identify project stakeholders 2.2 Outline potential risks and constraints | 3.1 Prepare a service overview and responsibility matrix 3.2 Define your approach to vendor relationship management 3.3 Manage the outsource relationship |
This phase will walk you through the following activities:
- Identify roles and responsibilities
- Determine potential risks of outsourcing the service desk
- Build a list of metrics
This phase involves the following participants:
- Service Desk Team
- IT Leadership
Define requirements for outsourcing service desk support
Step 2.1
Identify project stakeholders
Activity
2.1.1 Identify internal outsourcing roles and responsibilities
Design an Outsourcing Strategy
This step requires the following inputs:
- List of service desk roles
- Service desk outsourcing goals
This step involves the following participants:
- IT Managers
- Project Team
- Service Desk Manager
Outcome of this step
- Outsourcing roles and responsibilities
Design an outsourcing strategy to capture the vision of your service desk
An outsourcing strategy is crucial to the proper accomplishment of an outsourcing project. By taking the time to think through your strategy beforehand, you will have a clear idea of your desired outcomes. This will make your RFP of higher quality and will result in a much easier negotiation process.
Most MSPs are prepared to offer a standard proposal to clients who do not know what they want. These are agreements that are doomed to fail. A clearly defined set of goals (discussed in Phase 1), risks, and KPIs and metrics (covered in this phase) makes the agreement more beneficial for both parties in the long run.
- Identify goals and objectives
- Determine mission statement
- Define roles and responsibilities
- Identify risks and constraints
- Define KPIs and metrics
- Complete outsourcing strategy
A successful outsourcing initiative depends on rigorous preparation
Outsourcing is a garbage in, garbage out initiative. You need to give your service provider the information they need to provide an effective product.
- Data quality is critical to your outsourcing initiative's success.
- Your vendor will be much better equipped to help you and to better price its services if it has a thorough understanding of your IT environment.
- This means more than just building a catalog of your hardware and software. You will need to make available documented policies and processes so you and your vendor can understand where they fit in.
- Failure to completely document your environment can lead to a much longer time to value as your provider will have to spend much more time (and thus much more money) getting their service up and running.
"You should fill the gap before outsourcing. You should make sure how to measure tickets, how to categorize, and what the cost of outsourcing will be. Then you'll be able to outsource the execution of the service. Start your own processes and then outsource their execution."
– Kris Krishan, Head of IT and business systems, Waymo
Case Study
Digital media company built an outsourcing strategy to improve customer satisfaction
INDUSTRY: Digital Media
SOURCE: Auxis
Challenge
A Canadian multi-business company with over 13,000 employees would like to maintain a growing volume of digital content with their endpoint management.
The client operated a tiered model service desk. Tier 1 was outsourced, and tier 2 tasks were done internally, for more complex tasks and projects.
As a result of poor planning and defining goals, the company had issues with:
- Low-quality ticket handling
- High volume of tickets escalated to tier 2, restraining them from working on complex tickets
- High turn over and a challenge with talent retention
- Insufficient documentation to train external tier 1 team
- Long resolution time and low end-user satisfaction
Solution
The company structured a strategy for outsourcing service desk and defined their expectations and requirements.
They engaged with another outsourcer that would fulfill their requirements as planned.
With the help of the outsourcer's consulting team, the client was able to define the gaps in their existing processes and system to:
- Implement a better ticketing system that could follow best-practices guidelines
- Restructure the team so they would be able to handle processes efficiently
Results
The proactive planning led to:
- Significant improvement in first call resolution (82%).
- MTTR improvement freed tier 2 to focus on business strategic objectives and allowed them to work on higher-value activities.
- With a better strategy around outsourcing planning, the company saved 20% of cost compared to the previous outsourcer.
- As a result of this partnership, the company is providing a 24/7 structure in multiple languages, which is aligned with the company's growth.
- Due to having a clear strategy built for the project, the client now has better visibility into metrics that support long-term continual improvement plans.
Define roles and responsibilities for the outsourcing transition to form the base of your outsourcing strategy
There is no "I" in outsource; make sure the whole team is involved
Outsourcing is a complete top-to-bottom process that involves multiple levels of engagement:
- Management must make high-level decisions about staffing and negotiate contract details with the vendor.
- Service desk employees must execute on the documentation and standardization of processes in an effort to increase maturity.
- Roles and responsibilities need to be clearly defined to ensure that all aspects of the transition are completed on time.
- Implement a full-scale effort that involves all relevant staff. The most common mistake is to have the project design follow the same top-down pattern as the decision-making process.
Info-Tech Insight
The service desk doesn't operate in isolation. The service desk interfaces with many other parts of the organization (such as finance, purchasing, field support, etc.), so it's important to ensure you engage stakeholders from other departments as well. If you only engage the service desk staff in your discussions around outsourcing strategy and RFP development, you may miss requirements that will come up when it's too late.
2.1.1 Identify internal outsourcing roles and responsibilities
2 hours
- The sample RACI chart in section 5 of the Project Charter Template outlines which positions are responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed for each major task within the outsourcing project.
- Responsible, is the group that is responsible for the execution and oversight of activities for the project. Accountable is the owner of the task/process, who is accountable for the results and outcomes. Consulted is the subject matter expert (SME) who is actively involved in the task/process and consulted on decisions. Informed is not actively involved with the task/process and is updated about decisions around the task/process.
- Make sure that you assign only one person as accountable per process. There can be multiple people responsible for each task. Consulted and Informed are optional for each task.
- Complete the RACI chart with recommended participants, and document in your service desk outsourcing project charter, under section 5.
Input
- RACI template
- Org chart
Output
- List of roles and responsibilities for outsource project
Materials
- Whiteboard/flip charts
- Markers
- Laptops
Participants
- IT Director/CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- Service Desk Team
Download the Project Charter Template
Step 2.2
Outline potential risks and constraints
Activities
2.2.1 Identify potential risks and constraints that may impact achievement of objectives
2.2.2 Arrange groups of tension metrics to balance your reporting
Design an Outsourcing Strategy
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Outsourcing objectives
- Potential risks
This step involves the following participants:
- IT Managers
- Project Team
- Service Desk Manager
Outcomes of this step
- Mitigation strategy for each risk
- Service desk metrics
Know your constraints to reduce surprises during project implementation
No service desk is perfect; know your limits and plan accordingly
Define your constraints to outsourcing the service desk.
Consider all types of constraints and opportunities, including:
- Business forces
- Economic cycles
- Disruptive tech
- Regulation and compliance issues
- Internal organizational issues
Within the scope of a scouring decision, define your needs and objectives, measure those as much as possible, and compare them with the "as-is" situation.
Start determining what alternative approaches/scenarios the organization could use to fill the gaps. Start a comparison of scenarios against drivers, goals, and risks.
Constraints | Goals and objectives |
|---|---|
|
|
Plan ahead for potential risks that may impede your strategy
Risk assessment must go hand-in-hand with goal and objective planning
Risk is inherent with any outsourcing project. Common outsourcing risks include:
- Lack of commitment to the customer's goals from the vendor.
- The distraction of managing the relationship with the vendor.
- A perceived loss of control and a feeling of over-dependence on your vendor.
- Managers may feel they have less influence on the development of strategy.
- Retained staff may feel they have become less skilled in their specialist field.
- Unanticipated expenses that were assumed to be offered by the vendor.
- Savings only result from high capital investment in new projects on the part of the customer.
Analyze the risks associated with a specific scenario. This analysis should identify and understand the most common sourcing and vendor risks using a risk-reward analysis for selected scenarios. Use tools and guidelines to assess and manage vendor risk and tailor risk evaluation criteria to the types of vendors and products.
Info-Tech Insight
Plan for the worst to prevent it from happening. Evaluating risk should cover a wide variety of scenarios including the worst possible cases. This type of thinking will be crucial when developing your exit strategy in a later exercise.
2.2.1 Identify potential risks and constraints that may impact achievement of objectives
1-3 hours
- Brainstorm any potential risks that may arise through the outsourcing project. Describe each risk and categorize both its probability of occurring and impact on the organization as high (H), medium (M), or low (L), using the table below:
| Risk Description | Probability(H/M/L) | Impact(H/M/L) | Planned Mitigation |
| Lack of documentation | M | M | Use cloud-based solution to share documents. |
| Knowledge transfer | L | M | Detailed knowledge-sharing agreement in place in the RFP. |
| Processes not followed | L | H | Clear outline and definition of current processes. |
- Identify any constraints for your outsourcing strategy that may restrict, limit, or place certain conditions on the outsourcing project.
- This may include budget restrictions or staffing limitations.
- Identifying constraints will help you be prepared for risks and will lessen their impact.
- Document risks and constraints in section 6 of the Service Desk Outsourcing Project Charter Template.
Input
- RACI template
- Org chart
Output
- List of roles and responsibilities for outsource project
Materials
- Whiteboard/flip charts
- Markers
Participants
- IT Director/CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- Service Desk Team
Download the Project Charter Template
Define service tiers and roles to develop clear vendor SLAs
Management of performance, SLAs, and customer satisfaction remain the responsibility of your organization.
Define the tiers and/or services that will be the responsibility of the MSP, as well as escalations and workflows across tiers. A sample outsourced structure is displayed here:
| External Vendor | Tickets beyond the scope of the service desk staff need to be escalated back to the vendor responsible for the affected system. |
|---|---|
| Tier 3 | Tickets that are focused on custom applications and require specialized or advanced support are escalated back to your organization's second- and third-level support teams. |
| Tier 2 | The vendor is often able to provide specialized support for standard applications. However, the desktop support still needs someone onsite as that service is very expensive to outsource. |
| Tier 1 | Service desk outsource vendors provide first-line response. This includes answering the phones, troubleshooting simple problems, and redirecting requests that are more complex. |
Info-Tech Insight
If you outsource everything, you'll be at the mercy of consultancy or professional services shops later on. You won't have anyone in-house to help you deploy anything; you're at the mercy of a consultant to come in and tell you what to do and how much to spend. Keep your highly skilled people in-house to offset what you'd have to pay for consultancy. If you need to repatriate your service desk later on, you will need skills in-house to do so.
Don't become obsessed with managing by short-term metrics – look at the big picture
"Good" metric results may simply indicate proficient reactive fixing; long-term thinking involves implementing proactive, balanced solutions.
KPIs demonstrate that you are running an effective service desk because:
- You close an average of 300 tickets per week
- Your first call resolution is above 90%
- Your talk time is less than five minutes
- Surveys reveal clients are satisfied
While these results may appear great on the surface, metrics don't tell the whole story.
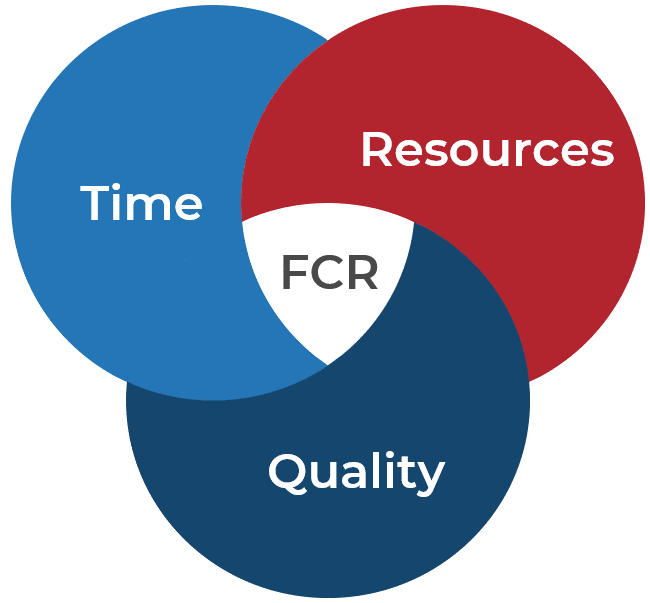
The effort from any support team seeks to balance three elements:
 | First-Contact Resolution (FCR) Rate | Percentage of tickets resolved during first contact with user (e.g. before they hang up or within an hour of submitting ticket). Could be measured as first-contact, first-tier, or first-day resolution. |
|---|---|---|
End-User Satisfaction | Perceived value of the service desk measured by a robust annual satisfaction survey of end users and/or transactional satisfaction surveys sent with a percentage of tickets. | |
| Ticket Volume and Cost Per Ticket | Monthly operating expenses divided by average ticket volume per month. Report ticket volume by department or ticket category, and look at trends for context. | |
Average Time to Resolve (incidents) or Fulfill (service requests) | Time elapsed from when a ticket is "open" to "resolved." Distinguish between ticket resolution vs. closure, and measure time for incidents and service requests separately. |
Focus on tension metrics to achieve long-term success
Tension metrics help create a balance by preventing teams from focusing on a single element.
For example, an MSP built incentives around ticket volume for their staff, but not the quality of tickets. As a result, the MSP staff rushed through tickets and gamed the system while service quality suffered.
Use metrics to establish baselines and benchmarking data:
- If you know when spikes in ticket volumes occur, you can prepare to resource more appropriately for these time periods
- Create KB articles to tackle recurring issues and assist tier 1 technicians and end users.
- Employ a root cause analysis to eliminate recurring tickets.
"We had an average talk time of 15 minutes per call and I wanted to ensure they could handle those calls in 15 minutes. But the behavior was opposite, [the vendor] would wrap up the call, transfer prematurely, or tell the client they'd call them back. Service levels drive behavior so make sure they are aligned with your strategic goals with no unintended consequences."
– IT Services Manager, Banking
Info-Tech Insight
Make sure your metrics work cooperatively. Metrics should be chosen that cause tension on one another. It's not enough to rely on a fast service desk that doesn't have a high end-user satisfaction rate or runs at too high a cost; there needs to be balance.
2.2.2 Arrange groups of tension metrics to balance your reporting
1-3 hours
- Define KPIs and metrics that will be critical to service desk success.
- Distribute sticky notes of different colors to participants around the table.
- Select a space to place the sticky notes – a table, whiteboard, flip chart, etc. – and divide it into three zones.
- Refer to your defined list of goals and KPIs from activity 1.1.3 and discuss metrics to fulfill each KPI. Note that each goal (critical success factor, CSF) may have more than one KPI. For instance:
- Goal 1: Increase end-user satisfaction; KPI 1: Improve average transactional survey score. KPI 2: Improve annual relationship survey score.
- Goal 2: Improve service delivery; KPI 1: Reduce time to resolve incidents. KPI 2: Reduce time to fulfill service requests.
- Recall that tension metrics must form a balance between:
- Time
- Resources
- Quality
- Record the results in section 7 of the Service Desk Outsourcing Project Charter Template.
Input
- Service desk outsourcing goals
- Service desk outsourcing KPIs
Output
- List of service desk metrics
Materials
- Whiteboard/flip charts
- Sticky notes
- Markers
- Laptops
Participants
- Project Team
- Service Desk Manager
Download the Project Charter Template
Phase 3
Develop an RFP and make a long-term relationship
Define the goal | Design an outsourcing strategy | Develop an RFP and make a long-term relationship |
|---|---|---|
1.1 Identify goals and objectives 1.2 Assess outsourcing feasibility | 2.1 Identify project stakeholders 2.2 Outline potential risks and constraints | 3.1 Prepare a service overview and responsibility matrix 3.2 Define your approach to vendor relationship management 3.3 Manage the outsource relationship |
This phase will walk you through the following activities:
- Build your outsourcing RFP
- Set expectations with candidate vendors
- Score and select your vendor
- Manage your relationship with the vendor
This phase involves the following participants:
- CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
- Project Managers
Define requirements for outsourcing service desk support
Step 3.1
Prepare a service overview and responsibility matrix
Activities
3.1.1 Evaluate your technology, people, and process requirements
3.1.2 Outline which party will be responsible for which service desk processes
This step requires the following inputs:
- Service desk processes and requirements
This step involves the following participants:
- CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
- Project Managers
Outcomes of this step
- Knowledge management and technology requirements
- Self-service requirements
Develop an RFP and make a long-term relationship
Create a detailed RFP to ensure your candidate vendor will fulfill all your requirements
At its core, your RFP should detail the outcomes of your outsourcing strategy and communicate your needs to the vendor.
The RFP must cover business needs and the more detailed service desk functions required. Many enterprises only consider the functionality they need, while ignoring operational and selection requirements.
Negotiate a supply agreement with the preferred outsourcer for delivery of the required services. Ensure your RFP covers:
- Service specification
- Service levels
- Roles and responsibilities
- Transition period and acceptance
- Prices, payment, and duration
- Agreement administration
- Outsourcing issues
In addition to defining your standard requirements, don't forget to take into consideration the following factors when developing your RFP:
- Employee onboarding and hardware imaging for new users
- Applications you need current and future support for
- Reporting requirements
- Self-service options
- Remote support needs and locations
Although it may be tempting, don't throw everything over the wall at your vendor in the RFP. Evaluate your service desk functions in terms of quality, cost effectiveness, and the value provided from the vendor. Organizations should only outsource functions that the vendor can operate better, faster, or cheaper.
Info-Tech Insight
Involve the right stakeholders in developing your RFP, not just service desk. If only service desk is involved in RFP discussion, the connection between tier 1 and specialists will be broken, as some processes are not considered from IT's point of view.
Identify ITSM solution requirements
Your vendor probably uses a different tool to manage their processes; make sure its capabilities align with the vision of your service desk.
Your service desk and outsourcing strategy were both designed with your current ITSM solution in mind. Before you hand the reins to an MSP, it is crucial that you outline how your current ITSM solution is being used in terms of functionality.
Find out if it's better to have the MSP use their own ITSM tools or your ITSM solution.
Benefits of operating within your own ITSM while outsourcing the service desk: | Disadvantages of using your own ITSM while outsourcing the service desk: |
|---|---|
|
|
Info-Tech Insight
Defining your tool requirements can be a great opportunity to get the tool functionality you always wanted. Many MSPs offer enterprise-level ITSM tools and highly mature processes that may tempt you to operate within their ITSM environment. However, first define your goals for such a move, as well as pros and cons of operating in their service management tool to weigh if its benefits overweigh its downfalls.
Case Study
Lone Star College learned that it's important to select a vendor whose tool will work with your service desk
INDUSTRY: Education
SOURCE: ServiceNow
Challenge
Lone Star College has an end-user base of over 100,000 staff and students.
The college has six campuses across the state of Texas, and each campus was using its own service desk and ITSM solution.
Initially, the decision was to implement a single ITSM solution, but organizational complexity prevented that initiative from succeeding.
A decision was made to outsource and consolidate the service desks of each of the campuses to provide more uniform service to end users.
Solution
Lone Star College selected a vendor that implemented FrontRange.
Unfortunately, the tool was not the right fit for Lone Star's service and reporting needs.
After some discussion, the outsourcing vendor made the switch to ServiceNow.
Some time later, a hybrid outsourced model was implemented, with Lone Star and the vendor combining to provide 24/7 support.
Results
The consolidated, standardized approach used by Lone Star College and its vendor has created numerous benefits:
- Standardized reporting
- High end-user satisfaction
- All SLAs are being met
- Improved ticket resolution times
- Automated change management.
Lone Star outsourced in order to consolidate its service desks quickly, but the tools didn't quite match.
It's important to choose a tool that works well with your vendor's, otherwise the same standardization issues can persist.
Design your RFP to help you understand what the vendor's standard offerings are and what it is capable of delivering
Your RFP should be worded in a way that helps you understand what your vendor's standard offerings are because that's what they're most capable of delivering. Rather than laying out all your requirements in a high level of detail, carefully craft your questions in a probing way. Then, understand what your current baseline is, what your target requirements are, and assess the gap.
Design the RFP so that responses can easily be compared against one another.
It is common to receive responses that are very different – RFPs don't provide a response framework. Comparing vastly different responses can be like comparing apples to oranges. Not only are they immensely time consuming to score, their scores also don't end up accurately reflecting the provider's capabilities or suitability as a vendor.
If your RFP is causing a ten minute printer backlog, you're doing something wrong.
Your RFP should not be hundreds of pages long. If it is, there is too much detail.
Providing too much detail can box your responses in and be overly limiting on your responses. It can deter potentially suitable provider candidates from sending a proposal.
Request
For
Proposal
"From bitter experience, if you're too descriptive, you box yourself in. If you're not descriptive enough, you'll be inundated with questions or end up with too few bidders. We needed to find the best way to get the message across without putting too much detail around it."
– Procurement Manager, Utilities
Info-Tech's Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template contains nine sections
- Statement of work
- Purpose, coverage, and participation ààInsert the purpose and goals of outsourcing your service desk, using steps 1.1 findings in this blueprint as reference.
- General information
- Information about the document, enterprise, and schedule of events ààInsert the timeline you developed for the RFP issue and award process in this section.
- Proposal preparation instructions
- The vendor's understanding of the RFP, good faith statement, points of contact, proposal submission, method of award, selection and notification.
- Service overview
- Information about organizational perspective, service desk responsibility matrix, vendor requirements, and service level agreements (SLAs).
- Scope of work, specifications and requirements
- Technical and functional requirements à Insert the requirements gathered in Phase 1 in this section of the RFP. Remember to include both current and future requirements.
- Exit conditions
- Overview of exit strategy and transition process.
- Vendor qualifications and references
- Account management and estimated pricing
- Vendor certification
 | The main point of focus in this document is defining your requirements (discussed in Phase 1) and developing proposal preparation instructions. The rest of the RFP consists mostly of standard legal language. Review the rest of the RFP template and adapt the language to suit your organization's standards. Check with your legal departments to make sure the RFP adheres to company policies. |
3.1.1 Evaluate your technology, people, and process requirements
1-2 hours
- Review the outsourcing goals you identified in Phase 1 (activity 1.1.3).
- For each goal, divide the defined requirements from your requirements database library (activity 1.2.1) into three areas:
- People Requirements
- Process Requirements
- Technical Requirements
- Group your requirements based on characteristics (e.g. recovery capabilities, engagement methodology, personnel, etc.).
- Validate these requirements with the relevant stakeholders.
- Document your results in section 4 of the Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template.
Input
- Identified key requirements
Output
- Refined requirements to input into the RFP
Materials
- Whiteboard/flip charts
- Markers
- Laptops
Participants
- IT Director/CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
Download the Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template
Assess knowledge management and technology requirements to enable the outsourcer with higher quality work
Retain ownership of the knowledgebase to foster long-term growth of organizational intelligence
With end users becoming more and more tech savvy, organizational intelligence is becoming an increasingly important aspect of IT support. Modern employees are able and willing to troubleshoot on their own before calling into the service desk. The knowledgebase and FAQs largely facilitate self-serve trouble shooting, both of which are not core concerns for the outsource vendor.
Why would the vendor help you empower end users and decrease ticket volume when it will lead to less revenue in the future? Ticket avoidance is not simply about saving money by removing support. It's about the end-user community developing organizational intelligence so that it doesn't need as much technical support.
Organizational intelligence occurs when shared knowledge and insight is used to make faster, better decisions.
When you outsource, the flow of technical insight to your end-user community slows down or stops altogether unless you proactively drive it. Retain ownership of the knowledgebase and ensure that the content is:
- Validated to ensure it accurately describes the best solution.
- Actionable to ensure it prescribes repeatable, verifiable steps.
- Contextual to ensure the reader knows when NOT to apply the knowledge.
- Maintained to ensure the solution remains current.
- Applied, since knowledge is a cost with no benefit unless you apply it and turn it into organizational intelligence.
Info-Tech Insight
Include knowledge management process in your ticket handling workflows to make sure knowledge is transferred to the MSP and end users. For more information on knowledge management, refer to Info-Tech's Standardize the Service Desk and Optimize the Service Desk With a Shift-Left Strategy blueprints.
Assess self-service requirements in your outsourcing plan
When outsourcing the service desk, determine who will take ownership of the self-service portal.
Nowadays, outsourcers provide innovative services such as self-serve options. However, bear in mind that the quality of such services is a differentiating factor. A well-maintained portal makes it easy to:
- Report incidents efficiently via use-case-based forms
- Place requests via a business-oriented service catalog
- Automate request processes
- Give visibility on ticket status
- Access knowledgebase articles
- Provide status on critical systems
- Look for services by both clicking service lists and searching them
- Provide 24/7 service via interactive communication with live agent and AI-powered machine
- Streamline business process in multiple departments rather than only IT
In the outsourcing process, determine your expectations from your vendor on self-serve options and discuss how they will fulfill these requirements. Similar to other processes, work internally to define a list of services your organization is providing that you can pass over to the outsourcer to convert to a service catalog.
Use Info-Tech's Sample Enterprise Services document to start determining your business's services.
Assess admin rights in your outsourcing plan to give access to the outsourcer while you keep ownership
Provide accessibility to account management to improve self-service, which enables:
- Group owners to be named who can add or remove people from their operating units
- Users to update attributes such as photos, address, phone number
- Synchronization with HRIS (Human Resource Information Systems) to enable two-way communication on attribute updates
- Password reset self-service
Ensure the vendor has access rights to execute regular clean up to help:
- Find stale and inactive user and computer accounts (inactive, expired, stale, never logged in)
- Bulk move and disable capabilities
- Find empty groups and remove
- Find and assess NTFS permissions
- Automated tasks to search and remediate
Give admin rights to outsourcer to enable reporting and auditing capabilities, such as:
- Change tracking and notifications
- Password reset attempts, account unlocks, permission and account changes
- Anomaly detection and remediation
- Privilege abuse, such as password sharing
Info-Tech Insight
Provide your MSP with access rights to enable the service desk to have account management without giving too much authentication. This way you'll enable moving tickets to the outsourcer while you keep ownership and supervision.
3.1.2 Outline which party will be responsible for which service desk processes
1-2 hours
This activity is an expansion to the outcomes of activity 1.2.1, where you determined the outsourcing requirements and the party to deliver each requirement.
- Add your identified tasks from the requirements database library to the service desk responsibility matrix (section 4.2 of the Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template).
- Break each task down into more details. For instance, incident management may include tier 1, tier 2/3, KB creation and update, reporting, and auditing.
- Refer to section 4.1 of your Project Charter to review the responsible party for each use case.
- Considering the use cases, assess whether your organization, the MSP, or both parties will be responsible for the task.
- Document the results in section 4.2 of the RFP.
Input
- Identified key requirements
Output
- Responsible party to deliver each task
Materials
- Whiteboard/flip charts
- Markers
- Laptops
Participants
- IT Director/CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
Download the Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template
Step 3.2
Define your approach to vendor relationship management
Activities
3.2.1 Define your SLA requirements
3.2.2 Score each vendor to mitigate the risk of failure
3.2.3 Score RFP responses
3.2.4 Get referrals, conduct reference interviews and evaluate responses for each vendor
Develop an RFP and make a long-term relationship
This step requires the following inputs:
- Service desk outsourcing RFP
- List of service desk outsourcing requirements
This step involves the following participants:
- CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
- Project Managers
Outcomes of this step
- Service desk SLA
- RFP scores
Don't rush to judgment; apply due diligence when selecting your vendor
The most common mistake in vendor evaluation is moving too quickly. The process leading to an RFP evaluation can be exhausting, and many organizations simply want to be done with the whole process and begin outsourcing.
The most common mistake in vendor evaluation is moving too quickly. The process leading to an RFP evaluation can be exhausting, and many organizations simply want to be done with the whole process and begin outsourcing.
- Call around to get referrals for each vendor
- Create a shortlist
- Review SLAs and contract terms
- Select your vendor
Recognize warning signs in the MSP's proposal to ensure a successful negotiation
Vendors often include certain conditions in their proposals that masquerade as appealing but may spell disaster. Watch for these red flags:
- Discounted Price
- Vendors know the market value of their competitors' services. Price is not what sets them apart; it's the type of services offered as well as the culture present.
- A noticeably low price is often indicative of a desperate organization that is not focused on quality managed services.
- No Pushback
- Vendors should work to customize their proposal to suit both their capabilities and your needs. No pushback means they are not invested in your project as deeply as they should be.
- You should be prepared for and welcome negotiations; they're a sign that both sides are reaching a mutually beneficial agreement.
- Continual SLA Improvement
- Continual improvement is a good quality that your vendor should have, but it needs to have some strategic direction.
- Throwing continual SLA improvement into the deal may seem great, but make sure that you'll benefit from the value-added service. Otherwise, you'll be paying for services that you don't actually need.
Clearly define core vendor qualities before looking at any options
Vendor sales and marketing people know just what to say to sway you: don't talk to them until you know what you're looking for.
Geography
Do you prefer global or local data centers? Do you need multiple locations for redundancy in case of disaster? Will language barriers be a concern?
Contract Length
Ensure you can terminate a poor arrangement by having shorter terms with optional renewals. It's better to renew and renegotiate if one side is losing in the deal in order to keep things fair. Don't assume that proposed long-term cost savings will provide a satisfactory service.
Target Market
Vendors are aiming at different business segments, from startups to large enterprises. Some will accept existing virtual machines, and others enforce compliance to appeal to government and health agencies.
SLA
A robust SLA strengthens a vendor's reliability and accountability. Agencies with special needs should have room in negotiations for customization. Providers should also account for regular SLA reviews and updates. Vendors should be tracking call volume and making projections that should translate directly to SLAs.
Support
Even if you don't need a vendor with 24/7 availability, vendors who cannot support this timing should be eliminated. You may want to upgrade later and will want to avoid the hassle of switching.
Maturity
Vendors must have the willingness and ability to improve processes and efficiencies over time. Maintaining the status-quo isn't acceptable in the constantly evolving IT world.
Cost
Consider which model makes the most sense: will you go with per call or per user pricing? Which model will generate vendor motivation to continually improve and meet your long-term goals? Watch out for variable pricing models.
Define your SLA requirements so your MSP can create a solution that fits
SLAs ensure accountability from the service provider and determine service price
SLAs define the performance of the service desk and clarify what the provider and customer can expect in their outsourcing relationship.
- Service categories
- The acceptable range of end-user satisfaction
- The scope of what functions of the service desk are being measured (availability, time to resolve, time to respond, etc.)
- Credits and penalties for achieving or missing targets
- Frequency of measurement/reporting
- Provisions and penalties for ending the contractual relationship early
- Management and communication structure
- Escalation protocol for incidents relating to tiers 2 or 3
Each MSP's RFP response will help you understand their basic SLA terms and enhanced service offerings. You need to understand the MSP's basic SLA terms to make sure they are adequate enough for your requirements. A well-negotiated SLA will balance the requirements of the customer and limit the liability of the provider in a win/win scenario.
For more information on defining service level requirements, refer to Info-Tech's blueprint Reduce Risk With Rock-Solid Service-Level Agreements.
3.2.1 Define your SLA requirements
2-3 hours
- As a team, review your current service desk SLA for the following items:
- Response time
- Resolution time
- Escalation time
- End-user satisfaction
- Service availability
- Determine your SLA expectations from the outsourcer.
- Document your SLA expectations in section 4.4 of the RFP template.
Use the sample table as a starting point to determine your current incident management SLA:
Participants: IT Managers, Service Desk Manager, Project Team
| Response | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Priority | Response SLO | Resolution SLO | Escalation Time | |
| T1 | ||||
| Severity 1 | Critical | Within 10 minutes | 4 hours to resolve | Immediate |
| Severity 2 | High | Within 1 business hour | 8 business hours to resolve | 20 minutes |
| Severity 3 | Medium | Within 4 business hours | 24 business hours to resolve | After 20 minutes without progress |
| Severity 4 | Low | Same day (8 hours) | 72 business hours to resolve | After 1 hour without progress |
| SLO Response | Time it takes for service desk to respond to service request or incident. | Target response is 80% of SLO | ||
| SLO Resolution | Time it takes to resolve incident and return business services to normal. | Target resolution is 80% of SLO | ||
Download the Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template
Get a detailed plan from your selected vendor before signing a contract
Build a standard process to evaluate candidate vendors
Use section 5 of Info-Tech's Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template for commonly used questions and requirements for outsourcing the service desk. Ask the right questions to secure an agreement that meets your needs. If you are already in a contract with an MSP, tale the opportunity of contract renewal to improve the contract and service.

Download the Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template
Add your finalized assessment questions into Info-Tech's Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Scoring Tool to aggregate responses in one repository for comparison. Since the vendors are asked to respond in a standard format, it is easier to bring together all the responses to create a complete view of your options.
Download the Service Desk Vendor Proposal Scoring Tool
3.2.2 Score each vendor to mitigate the risk of failure
1-2 hours
Include the right requirements for your organization and analyze candidate vendors on their capability to satisfy them.
- Use section 5 of the RFP template to convert your determined requirements into questions to address in vendor briefings.
- Review the questions in the context of near- and long-term service desk outsourcing needs. In the template, we have separated requirements into 7 categories:
- Vendor Requirements (VR)
- Vendor Qualifications/Engagement/Administration Capabilities (VQ)
- Service Operations (SO)
- Service Support (SS)
- Service Level Agreement (SLA)
- Transition Processes (TP)
- Account Management (AM)
- Define the priority for each question:
- Required
- Desired
- Optional
- Leave the compliance and comments to when you brief with vendors.
Input
- Technical and functional requirements
Output
- Priority level for each requirement
- Completed list of requirement questions
Materials
- Whiteboard/flip charts
- Markers
- Laptops
Participants
- IT Director/CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
Download the Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template
3.2.3 Score RFP responses
2-3 hours
- Enter the requirements questions into the RFP Scoring Tool and use it during vendor briefings.
- Copy the Required and Desired priority requirements from the previous activity into the RFP Questions column.
- Evaluate each RFP response against the RFP criteria based on the scoring scale.
- The Results section in the tool shows the vendor ranking based on their overall scores.
- Compare potential outsourcing partners considering scores on individual requirements categories and based on overall scores.
Input
- Completed list of requirement questions
- Priority level for each requirement
Output
- List of top vendors for outsourcing the service desk
Materials
- Service Desk Vendor Proposal Scoring Tool
Participants
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
- Project Managers
- IT Director/CIO
Download the Service Desk Vendor Proposal Scoring Tool
3.2.3 Get referrals, conduct reference interviews, and evaluate responses for each vendor
- Outline a list of questions to conduct reference interviews with past/present clients of your candidate vendors.
- Use the reference interview template as a starting point. As a group review the questions and edit them to a list that will fulfill your requirements.
- Ask your candidate vendors to provide you with a list of three to five clients that have/had used their services. Make sure that vendors enforce the interview will be kept anonymous and names and results won't be disclosed.
- Ask vendors to book a 20-30 minute call with you and their client.
- Document your interview comments in your updated reference interview template.
- Update the RFP scoring tool accordingly.
Input
- List of top vendors for outsourcing the service desk
Output
- Updated list of top vendors for outsourcing the service desk
Materials
- Service Desk Outsourcing Reference Interview Template
- Service Desk Vendor Proposal Scoring Tool
Participants
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
- Project Managers
Download the Service Desk Vendor Proposal Scoring Tool
Compare pricing models of outsourcing services
It's a common sales tactic to use a low price as an easy solution. Carefully evaluate the vendors on your short-list and ensure that SLAs, culture, and price all match to your organization.
Research different pricing models and accurately assess which model fits your organization. Consider the following pricing models:
Pay per technician
In this model, a flat rate is allocated to agents tackling your service desk tickets. This is a good option for building long-term relationship with outsourcer's agents and efficient knowledge transfer to the external team; however, it's not ideal for small organizations that deal with few tickets. This is potentially an expensive model for small teams.
Pay per ticket
This model considers the number of tickets handled by the outsourcer. This model is ideal if you only want to pay for your requirement. Although the internal team needs to have a close monitoring strategy to make sure the outsourcer's efficiency in ticket resolution.
Pay per call
This is based on outbound and inbound calls. This model is proper for call centers and can be less expensive than the other models; however, tracking is not easy, as you should ensure service desk calls result in efficient resolution rather than unnecessary follow-up.
Pay per time (minutes or hours)
The time spent on tickets is considered in this model. With this model, you pay for the work done by agents, so that it may be a good and relatively cheap option. As quicker resolution SLA is usually set by the organization, customer satisfaction may drop, as agents will be driven to faster resolution, not necessarily quality of work.
Pay per user
This model is based on number of all users, or number of users for particular applications. In this model, correlation between number of users and number of tickets should be taken into account. This is an ideal model if you want to deal with impact of staffing changes on service price. Although you should first track metrics such as mean time to resolve and average number of tickets so you can prevent unnecessary payment based on number of users when most users are not submitting tickets.
Step 3.3
Manage the outsource relationship
Activities
3.3.1 Analyze your outsourced service desk for continual improvement
3.3.2 Make a case to either rehabilitate your outsourcing agreement or exit
3.3.3 Develop an exit strategy in case you need to end your contract early
Develop an RFP and make a long-term relationship
This step requires the following inputs:
- Service desk SLA
- List of impacted stakeholder groups
- List of impacts and benefits of the outsourced service desk
This step involves the following participants:
- CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
- Project Managers
Outcomes of this step
- Communication plan
- Vendor management strategy
Ensure formality of your vendor management practice
A service desk outsourcing project is an ongoing initiative. Build a relationship plan to make sure the outsourcer complies with the agreement.
Monitor Vendor Performance
Key Activity:
Measure performance levels with an agreed upon standard scorecard.
Manage Vendor Risk
Key Activity:
Periodical assessment of the vendors to ensure they are meeting compliance standards.
Manage Vendor Contracts and Relationships
Key Activity:
Manage the contracts and renewal dates, the level of demand for the services/products provided, and the costs accrued.
COMPLETE Identify and Evaluate Vendors
Key Activity:
Develop a plan with procurement and key internal stakeholders to define clear, consistent, and stable requirements.
COMPLETE Select a Vendor
Key Activity:
Develop a consistent and effective process for selecting the most appropriate vendor.
Manage Vendor Contracts and Relationships
Key Activity:
Contracts are consistently negotiated to ensure the vendor and the client have a documented and consistent understanding of mutual expectations.
Expect the vendor to manage processes according to your standards
You need this level of visibility into the service desk process, whether in-house or outsourced
Each of these steps requires documentation – either through standard operating procedures, SLAs, logs, or workflow diagrams.
- Define key operating procedures and workflows
- Record, classify, and prioritize tickets
- Verify, approve, and fulfill tickets
- Investigate, diagnose, and allocate tickets
- Resolve, recover, and close tickets
- Track and report
"Make sure what they've presented to you is exactly what's happening."
– Service Desk Manager, Financial Services
Manage the vendor relationship through regular communication
Regular contact with your MSP provides opportunities to address issues that emerge
Designate a relationship manager to act as a liaison at the business to be a conduit between the business and the MSP.
- The relationship manager will take feedback from the MSP and relate it back to you to bridge the technical and business gap between the two.
Who should be involved
- Routine review meetings should involve the MSP and your relationship manager.
- Technical knowledge may be needed to address specific issues, but business knowledge and relationship management skills are absolutely required.
- Other stakeholders and people who are deeply invested in the vendor relationship should be invited or at least asked to contribute questions and concerns.
What is involved
- Full review of the service desk statistics, escalations, staffing changes, process changes, and drivers of extra billing or cost.
- Updates to key documentation for the issues listed above and changes to the knowledgebase.
- Significant drivers of customer satisfaction and dissatisfaction.
- Changes that have/are being proposed that can impact any of the above.
Communicate changes to end users to avoid push back and get buy-in
Top-down processes for outsourcing will leave end users in the dark
- Your service desk staff has been involved in the outsourcing process the entire time, but end users are affected all the same.
- The service desk is the face of IT. A radical shift in service processes and points of contact can be detrimental to not only the service desk, but all of IT.
- Communicating the changes early to end users will both help them cope with the change and help the MSP achieve better results.
- An internal communication plan should be rolled out in order to inform and educate end users about the changes associated with outsourcing the service desk.
- Your relationship manager should be tasked with communicating the changes to end users. The focus should be on addressing questions or concerns about the transition while highlighting the value gained through outsourcing to an MSP.
- Service quality is a two-way street; the end user needs to be informed of proper protocols and points of contact so that the service desk technicians can fulfill their duties to the best of their ability.
"When my company decided to outsource, I performed the same role but for a different company. There was a huge disruption to the business flow and a lack of communication to manage the change. The transition took weeks before any end users figured out what the new processes were for submitting a ticket and who to ask for help, and from a personal side, it became difficult to maintain relationships with colleagues."
– IT Specialist for a financial institution
Info-Tech Insight
Educate the enterprise on expectations and processes that are handled by the MSP. Identify stakeholder groups affected by the outsourced processes then build a communication plan on what's been changed, what the benefits are, and how they will be impacted. Determine a timeline for communicating these initiatives and how these announcements will be made. Use InfoTech's Sample Communication Plan as a starting point.
Build a continual improvement plan to make sure your MSP is efficiently delivering services according to expectations
Ensure that your quality assurance program is repeatable and applicable to the outsourced services
- Design a QA scorecard that can help you assess steps the outsourcer agents should follow. Keep the questionnaire high level but specific to your environment. The scorecard should include questions that follow the steps to take considering your intake channels. For instance, if end users can reach the service desk via phone, chat, and email, build your QA around assessing customer service for call, chat, and ticket quality.
- Build a training program for agents: Develop an internal monitoring plan to relay detailed feedback to your MSP. Assess performance and utilize KBs as training materials for coaching agents on challenging transactions.
- Everything that goes to your service desk has to be documented; there will be no organic transfer of knowledge and experience.
- You need to let your MSP know how their efforts are impacting the performance of your organization. Measure your internal performance against the external performance of your service desk.
- Constant internal check-ins ensure that your MSP is meeting the SLAs outlined in the RFP.
- Routine reporting of metrics and ticket trends allow you to enact problem management. Otherwise, you risk your MSP operating your service desk with no internal feedback from its owner.
- Use metrics to determine the service desk functionality.
Consider the success story of your outsourced service desk
Build a feedback program for your outsourced services. Utilize transactional surveys to discover and tell outsourcing success to the impacted stakeholders.
Ensure you apply steps for providing feedback to make sure processes are handled as expected. Service desk is the face of IT. Customer satisfaction on ticket transactions reflects satisfaction with IT and the organization.
Build customer satisfaction surveys and conduct them for every transaction to get a better sense of outsourced service desk functionality. Collaborate with the vendor to make sure you build a proper strategy.
- Build a right list of questions. Multiple and lengthy questions may lead to survey taking fatigue. Make sure you ask the right questions and give an option to the customer to comment any additional notes.
- Give the option to users to rate the transaction. Make the whole process very seamless and doable in a few seconds.
- Ensure to follow-up on negative feedback. This will help you find gaps in services and provide training to improve customer service.
3.3.1 Analyze your outsourced service desk for continual improvement
1 hour
- In this project, you determined the KPIs based on your service desk objectives (activity 2.2.2).
- Refer to your list of metrics in section 7 of the Service Desk Outsourcing Project Charter.
- Think about what story you want to tell and determine what factors will help move the narrative.
- Discuss how often you would like to track these metrics. Determine the audience for each metric.
- Provide the list to the MSP to create reports with auto-distribution.
Input
- Determined CSFs and KPIs
Output
- List of metrics to track, including frequency to report and audience to report to
Materials
- Service Desk Outsourcing Project Charter
Participants
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
- Project Managers
Download the Project Charter Template
Reward the MSP for performance instead of "punishing" them for service failure
Turn your vendor into a true partner by including an "earn back" condition in the contract
MSPs often offer clients credit requests (service credits) for their service failures, which are applied to the previous month's monthly recurring charge. They are applied to the last month's MRC (monthly reoccurring charges) at the end of term and then the vendor pays out the residual.
However, while common, service credits are not always perceived to be a strong incentive for the provider to continually focus on improvement of mean-time-to-respond/mean-time-to-resolve.
- Engage the vendor as a true partner within a relationship only based upon Service Credits.
- Suggest the vendor include a minor change to the non-performance processes within the final agreement: the vendor implements an "earn back" condition in the agreement.
- Where a bank of service credits exists because of non-performance, if the provider exceeds the SLA performance metrics for a number of consecutive months (two is common), then an amount of any prior credits received by client is returned to the provider as an earn back for improved performance.
- This can be a useful mechanism to drive improved performance.
Measure the outsourced service desk ROI constantly to drive efficient decisions for continual improvement or an exit plan
Efficient outsourced service desk causes positive impacts on business satisfaction. To address the true value of the services outsourced, you should evaluate the return on investment (ROI) in these areas: Emotional ROI, Time ROI, Financial ROI
Emotional ROI
Service desk's main purpose should be to provide topnotch services to end users. Build a customer experience program and leverage transactional surveys and relationship surveys to constantly analyze customer feedback on service quality.
Ask yourself:
- How have the outsourced services improved customer satisfaction?
- How has the service desk impacted the business brand?
- Have these services improved agents' job satisfaction?
- What is the NPS score of the service desk?
- What should we do to reduce the detractor rate and improve satisfaction leveraging the outsourced service desk?
Time ROI
Besides customer satisfaction, SLA commitment is a big factor to consider when conducting ROI analysis.
Ask these questions:
- Have we had improvement in FCR?
- What are the mean time to resolve incidents and mean time to fulfill requests?
- Is the cost incurred to outsourced services worth improvement in such metrics?
Financial ROI
As already mentioned in Phase 1, the main motivation for outsourcing the service desk should not be around cost reduction, but to improve performance. Regardless, it's still important to understand the financial implications of your decision.
To evaluate the financial impact of your outsourced service desk, ask these questions:
- How much have the outsourced services impacted our business financially?
- How much are we paying compared to when it was done internally?
- Considering the emotional, time, and effort factors, is it worth bringing the services in house or changing the vendor?
3.3.2 Make a case to either rehabilitate your outsourcing agreement or exit
3-4 hours
- Refer to the results of activity 2.2.2. for the list of metrics and the metrics dashboard over the past quarter.
- Consider emotional and time ROI, assess end-user satisfaction and SLA, and run a report comparison with the baseline that you built prior to outsourcing the service desk.
- Estimate the organization's IT operating expenses over the next five years if you stay with the vendor.
- Estimate the organization's IT operating expenses over the next five years if you switch the vendor.
- Estimate the organization's IT operating expenses over the next five years if you repatriate the service desk.
- Estimate the non-recurring costs associated with the move, such as the penalty for early contract termination, data center moving costs, and cost of potential business downtime during the move. Sum them to determine the investment.
- Calculate the return on investment. Discuss and decide whether the organization should consider rehabilitating the vendor agreement or ending the partnership.
Input
- Outsourced service desk metrics
- Operating expenses
Output
- Return on investment
Materials
- List of metrics
- Laptop
- Markers
- Flip chart/whiteboard
Participants
- IT Director/CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
For more information on conducting this activity, refer to InfoTech's blueprint Terminate the IT Infrastructure Outsourcing Relationship
Define exit conditions to complete your contract with your MSP
The end of outsourcing is difficult. Your organization needs to maintain continuity of service during the transition. Your MSP needs to ensure that its resources can be effectively transitioned to the next deployment with minimal downtime. It is crucial to define your exit conditions so that both sides can prepare accordingly.
- Your exit conditions must be clearly laid out in the contract. Create a list of service desk functions and metrics that are important to your organization's success. If your MSP is not meeting those needs or performance levels, you should terminate your services.
- Most organizations accomplish this through a clear definition of hard and measurable KPIs and metrics that must be achieved and what will happen in the case these metrics are not being regularly met. If your vendor doesn't meet these requirements as defined in your contract, you then have a valid reason and the ability to leave the agreement.
Examples of exit conditions:
- Your MSP did not meet their SLAs on priority 1 or 2 tickets two times within a month.
- If they didn't meet the SLA twice in that 30 days, you could terminate the contract penalty-free.
Info-Tech Insight
If things start going south with your MSP, negotiate a "get well plan." Outline your problems to the MSP and have them come back to you with a list of how they're going to fix these problems to get well before you move forward with the contract.
Try to rehabilitate before you repatriate
Switching service providers or ending the contract can be expensive and may not solve your problems. Try to rehabilitate your vendor relationship before immediately ending it.
You may consider terminating your outsourcing agreement if you are dissatisfied with the current agreement or there has been a change in circumstances (either the vendor has changed, or your organization has changed).
Before doing so, consider the challenges:
- It can be very expensive to switch providers or end a contract.
- Switching vendors can be a large project involving transfer of knowledge, documentation, and data.
- It can be difficult to maintain service desk availability, functionality, and reliability during the transition.
Diagnose the cause of the problem before assuming it's the MSP's fault. The issue may lie with poorly defined requirements and processes, lack of communication, poor vendor management, or inappropriate SLAs. Re-assess your strategy and re-negotiate your contract if necessary.
Info-Tech Insight
There are many reasons why outsourcing relationships fail, but it's not always the vendor's fault.
Clients often think their MSP isn't doing a great job, but a lot of the time the reason comes back to the client. They may not have provided sufficient documentation on processes, were not communicating well, didn't have a regular point of contact, and weren't doing regular service reviews. Before exiting the relationship, evaluate why it's not working and try to fix things first.
Don't stop with an exit strategy, you also need to develop a transition plan
Plan out your transition timeline, taking into account current contract terms and key steps required. Be prepared to handle tickets immediately upon giving notice.
- Review your outsourcing contract with legal counsel to identify areas of concern for lock-in or breech.
- Complete a cost/benefit analysis.
- Bring intellectual property (including ticket data, knowledge base articles, and reports) back in-house (if you'd like to repatriate the service desk) or transfer to the next service desk vendor (if you're outsourcing to another MSP).
- Review and update service desk standard processes (escalation, service levels, ticket templates, etc.).
- Procure service desk software, licenses, and necessary hardware as needed.
- Train the staff (internal for repatriating the service desk, or external for the prospective MSP).
- Communicate the transition plan and be prepared to start responding to tickets immediately.
Info-Tech Insight
Develop a transition plan about six months before the contract notice date. Be proactive by constantly tracking the MSP, running ROI analyses and training staff before moving the services to the internal team or the next MSP. This will help you manage the transition smoothly and handle intake channels so that upon potential exit, users won't be disrupted.
3.3.3 Develop an exit strategy in case you need to end your contract early
3-4 hours
Create a plan to be prepared in case you need to end your contract with the MSP early.
Your exit strategy should encompass both the conditions under which you would need to end your contract with the MSP and the next steps you will take to transition your services.
- Define the exit conditions you plan to negotiate into your contract with the MSP:
- Identify the performance levels you will require your MSP to meet.
- Identify the actions you expect the MSP to take if they fail to meet these performance levels.
- Identify the conditions under which you would leave the contract early.
- Develop a strategy for transitioning services in the event you need to leave your contract with the MSP:
- Will you hand the responsibility to a new MSP or repatriate the service desk back in-house?
- How will you maintain services through the transition?
- Document your exit strategy in section 6 of the Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template.
Input
- Outsourced service desk metrics
- Operating expenses
Output
- Return on investment
Materials
- List of metrics
- Laptop
- Markers
- Flip chart/whiteboard
Participants
- IT Director/CIO
- Service Desk Manager
- IT Managers
Download the Service Desk Outsourcing RFP Template
Summary of Accomplishment
Problem Solved
You have now re-envisioned your service desk by building a solid strategy for outsourcing it to a vendor. You first analyzed your challenges with the current service desk and evaluated the benefits of outsourcing services. Then you went through requirements assessment to find out which processes should be outsourced. Thereafter, you developed an RFP to communicate your proposal and evaluate the best candidates.
You have also developed a continual improvement plan to ensure the outsourcer provides services according to your expectations. Through this plan, you're making sure to build a good relationship through incentivizing the vendor for accomplishments rather than punishing for service failures. However, you've also contemplated an exit plan in the RFP for potential consistent service failures.
Ideally, this blueprint has helped you go beyond requirements identification and served as a means to change your mindset and strategy for outsourcing the service desk efficiently to gain long-term benefits.
if you would like additional support, have our analysts guide you through other phases as part of an Info-Tech Workshop
Contact your account representative for more information
workshops@infotech.com
1-888-670-8889
Additional Support
If you would like additional support, have our analysts guide you through other phases as part of an Info-Tech Workshop
To accelerate this project, engage your IT team in an Info-Tech workshop with an Info-Tech analyst team.
Info-Tech analysts will join you and your team at your location or welcome you to Info-Tech's historic Toronto office to participate in an innovative onsite workshop.

Contact your account representative for more information.
workshops@infotech.com 1-888-670-8889
The following are sample activities that will be conducted by Info-Tech analysts with your team:

Identify Processes to Outsource
Identify service desk tasks that will provide the most value upon outsourcing.

Score Candidate Vendors
Evaluate vendors on their capabilities for satisfying your service desk requirements.
Related Info-Tech Research
- Improve customer service by driving consistency in your support approach and meeting SLAs.
Outsource IT Infrastructure to Improve System Availability, Reliability, and Recovery
- There are very few IT infrastructure components you should be housing internally – outsource everything else.
Terminate the IT Infrastructure Outsourcing Relationship
- There must be 50 ways to leave your vendor.
Research Contributors and Experts
Yev Khovrenkov; Enterprise Consultant, Solvera Solutions
Kamil Salagan; I&O Manager, Bartek Ingredients
Satish Mekerira; VP of IT, Coherus BioSciences
Kris Krishan; Head of IT and Business Systems, Waymo
Kris Arthur; Infra & Security Director, SEKO Logistics
Valance Howden; Principal Research Advisor, Info-Tech Research Group
Sandi Conrad; Principal Research Director, Info-Tech Research Group
Graham Price; Senior Director of Executive Services, Info-Tech Research Group
Barry Cousins; Practice Lead, Info-Tech Research Group
Mark Tauschek; VP of I&O Research, Info-Tech Research Group
Darin Stahl; Principal Research Advisor, Info-Tech Research Group
Scott Yong; Principal Research Advisor, Info-Tech Research Group
A special thank-you to five anonymous contributors
Bibliography
Allnutt, Charles. "The Ultimate List of Outsourcing Statistics." MicroSourcing, 2022. Accessed July 2022.
"Considerations for outsourcing the service desk. A guide to improving your service desk and service delivery performance through outsourcing." Giva. Accessed May 2022.
Hurley, Allison. "Service Desk Outsourcing | Statistics, Challenges, & Benefits." Forward BPO Inc., 2019. Accessed June 2022.
Mtsweni, Patricia, et al. "The impact of outsourcing information technology services on business operations." South African Journal of Information Management, 2021, Accessed May 2022.
"Offshore, Onshore or Hybrid–Choosing the Best IT Outsourcing Model." Calance, 2021. Accessed June 2022. Web.
"Service Integration and Management (SIAM) Foundation Body of Knowledge." Scopism, 2020. Accessed May 2022.
Shultz, Aaron. "IT Help Desk Outsourcing Pricing Models Comparison." Global Help Desk Services. Accessed June 2022. Web.
Shultz, Aaron. "4 Steps to Accurately Measure the ROI of Outsourced Help Desk Services" Global Help Desk Services, Accessed June 2022. Web.
Sunberg, John. "Great Expectations: What to Look for from Outsourced Service Providers Today." HDI. Accessed June 2022. Web.
Walters, Grover. "Pivotal Decisions in outsourcing." Muma Case Review, 2019. Accessed May 2022.
Wetherell, Steve. "Outsourced IT Support Services: 10 Steps to Better QA" Global Held Desk Services. Accessed May 2022. Web.

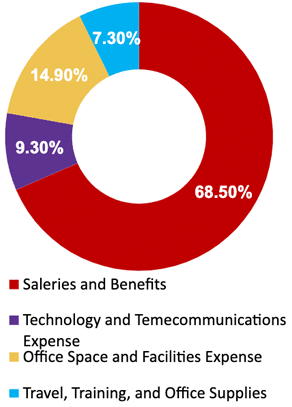
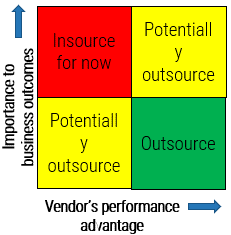



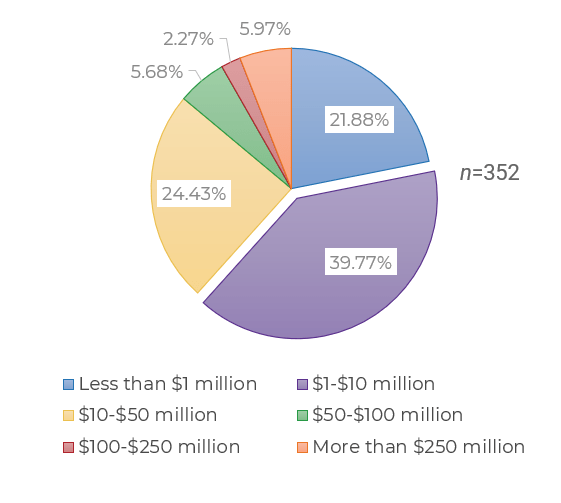

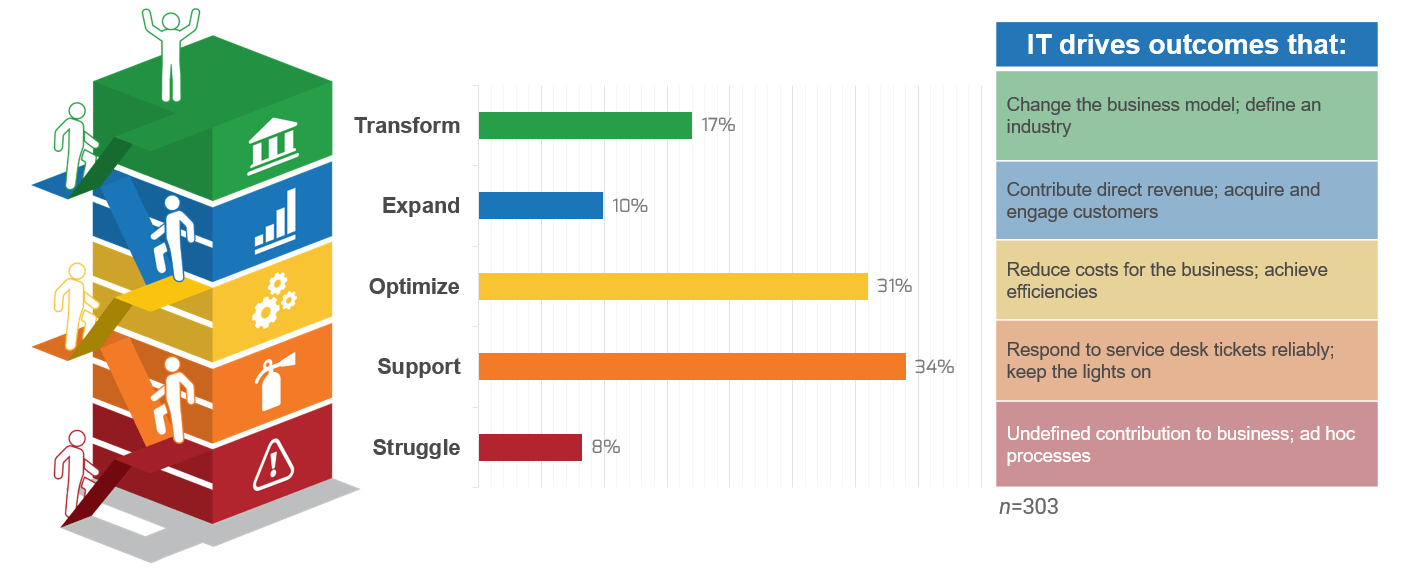
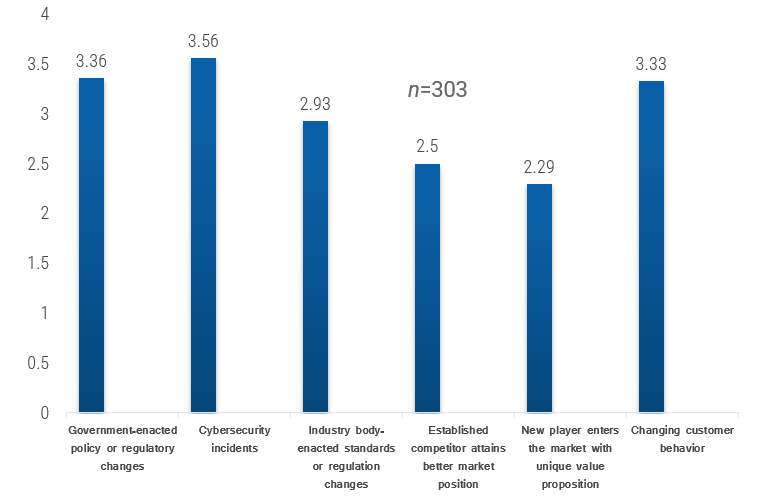
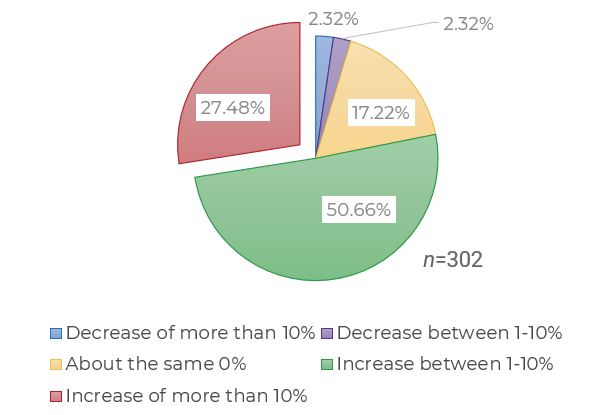
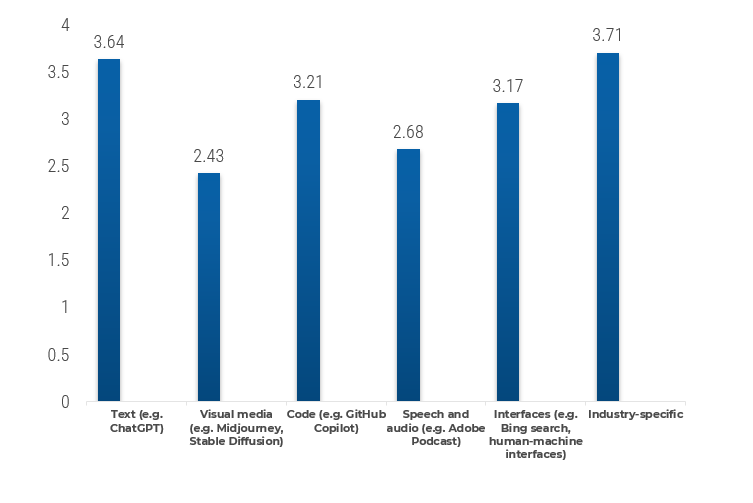
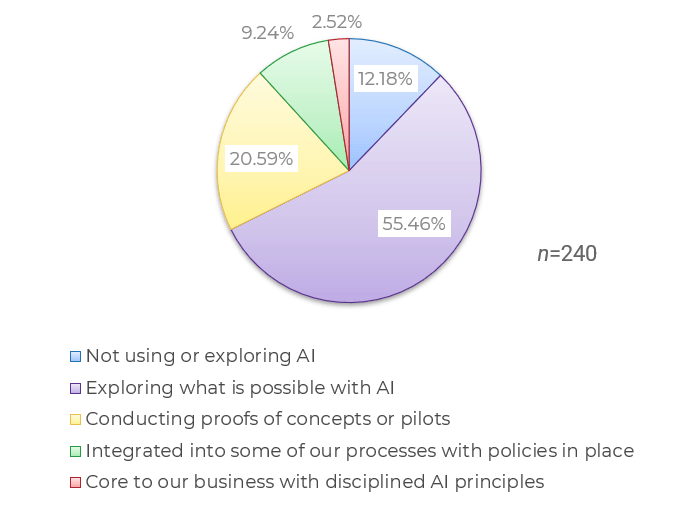
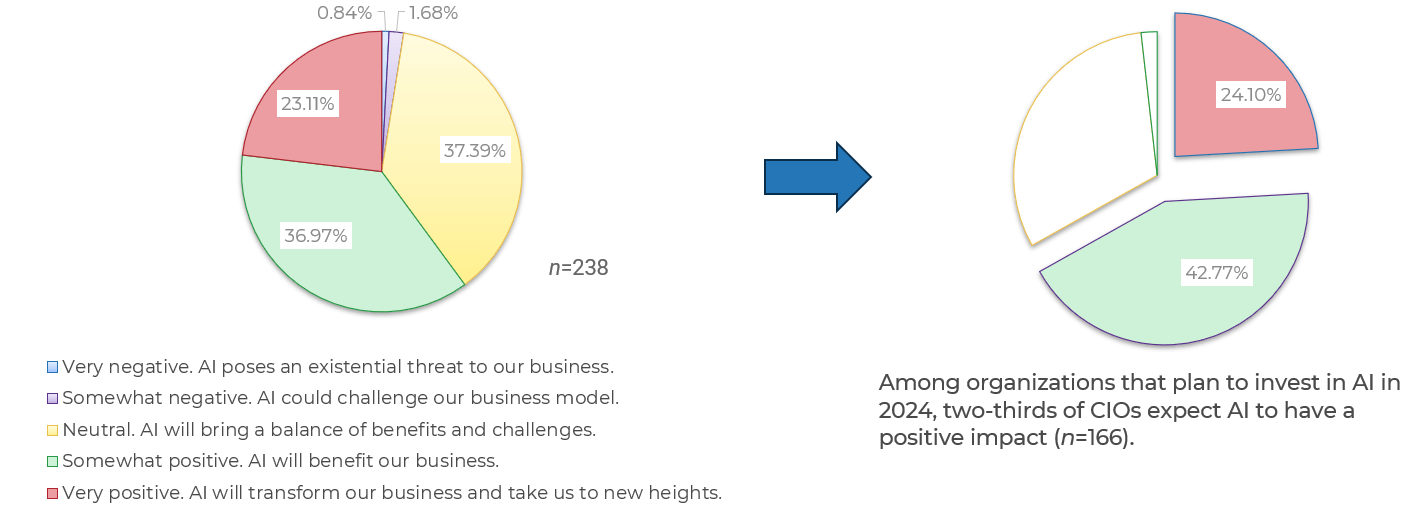
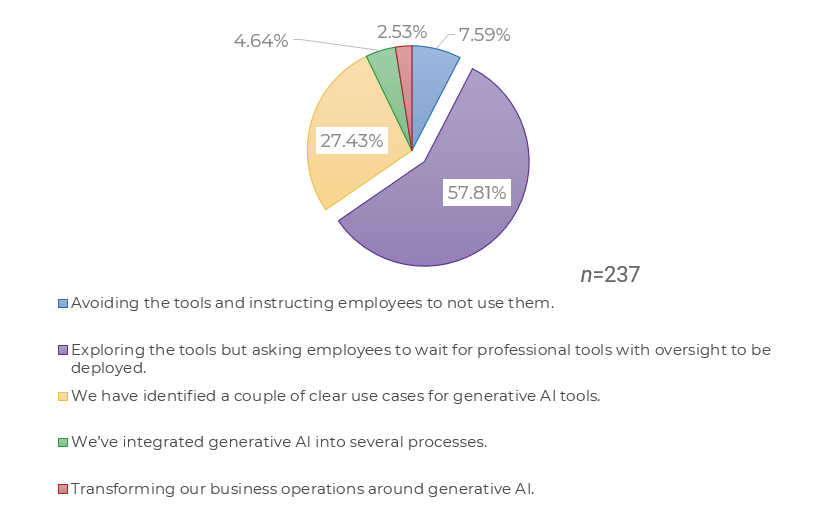
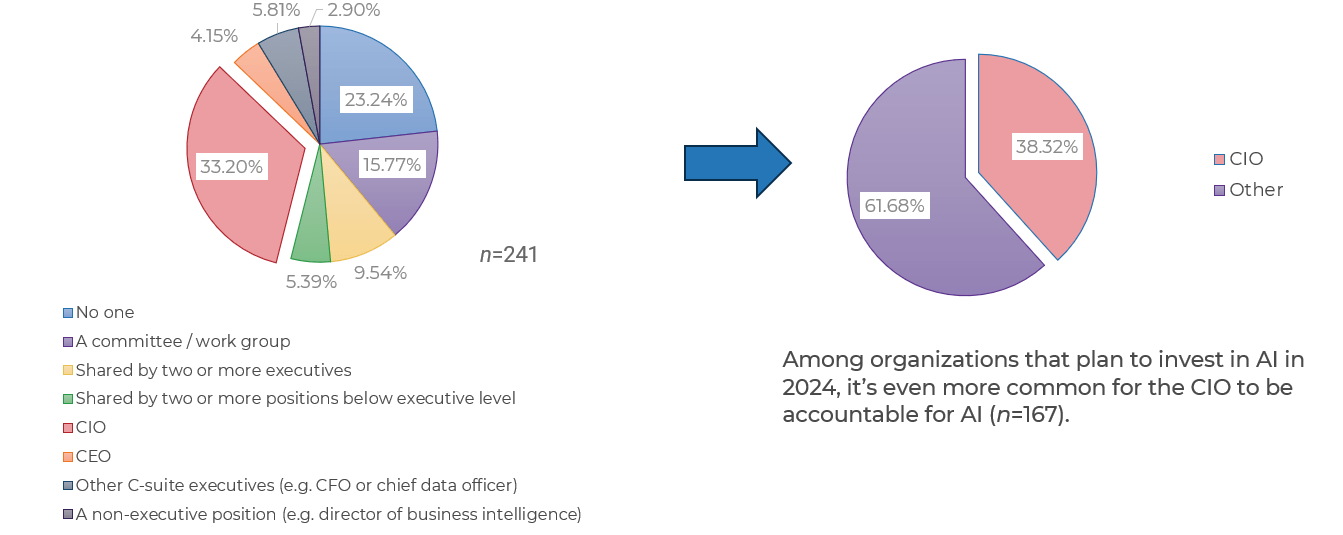
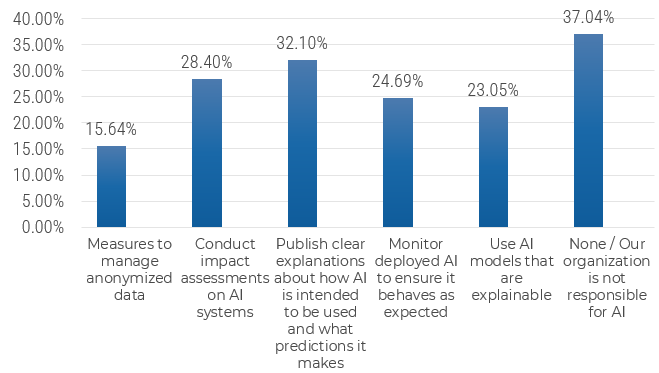
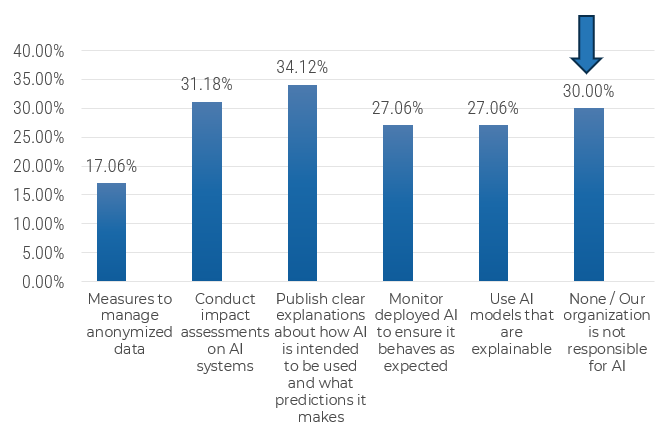





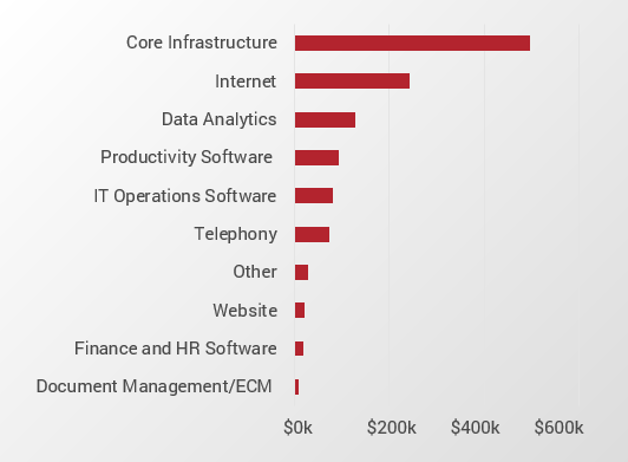
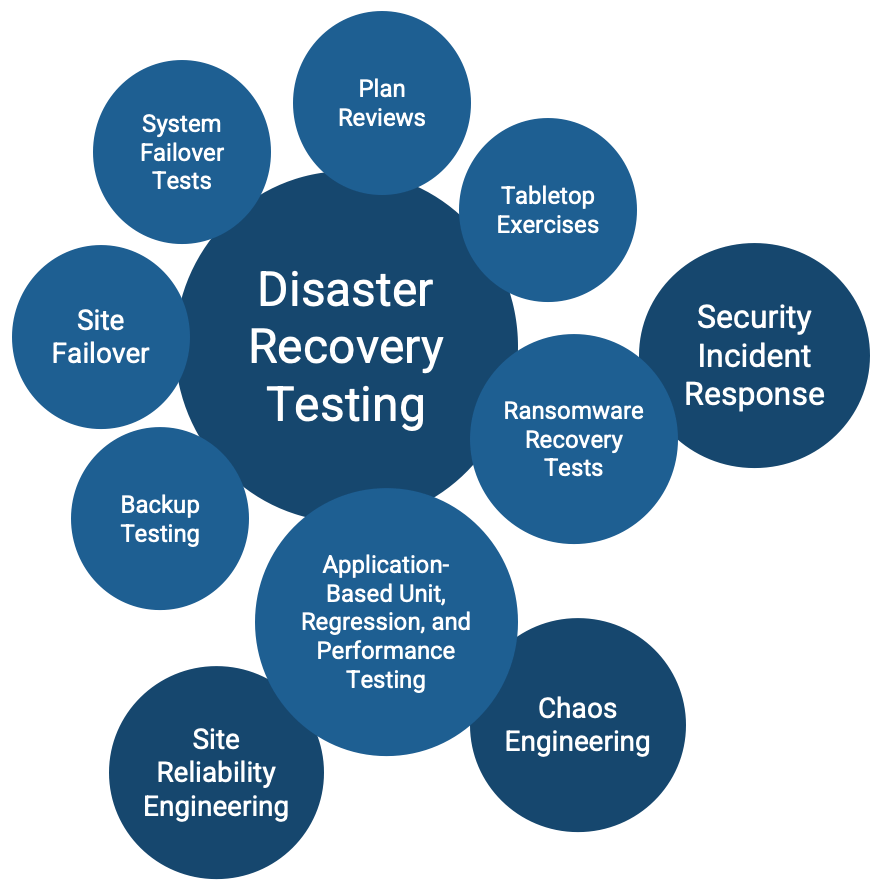

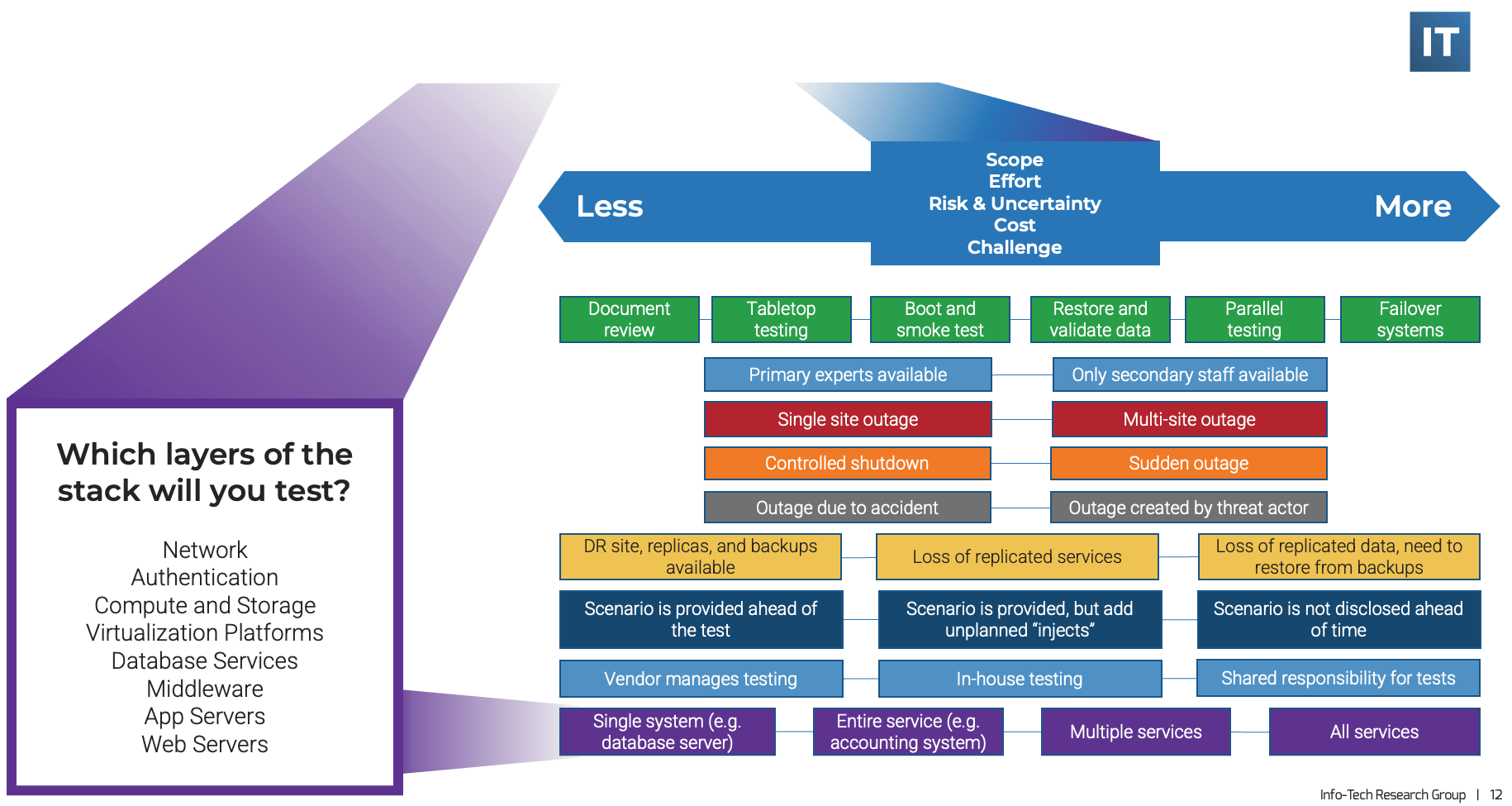
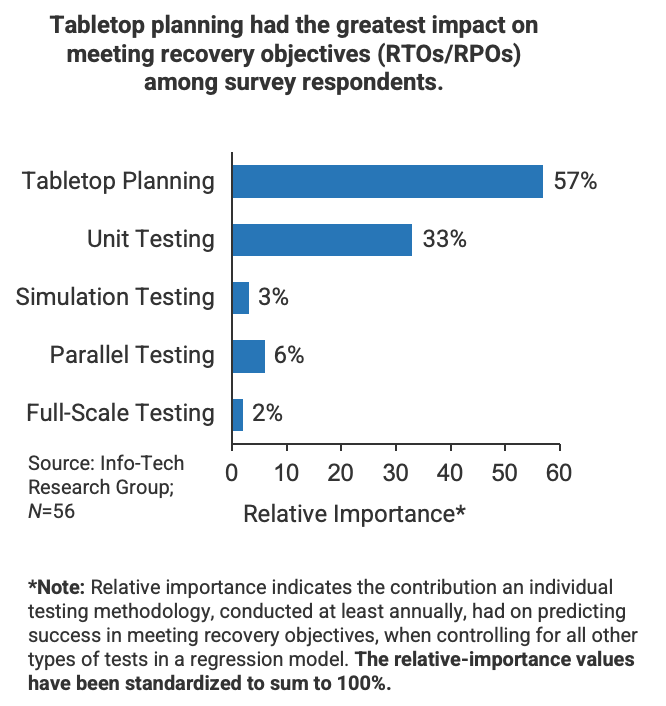
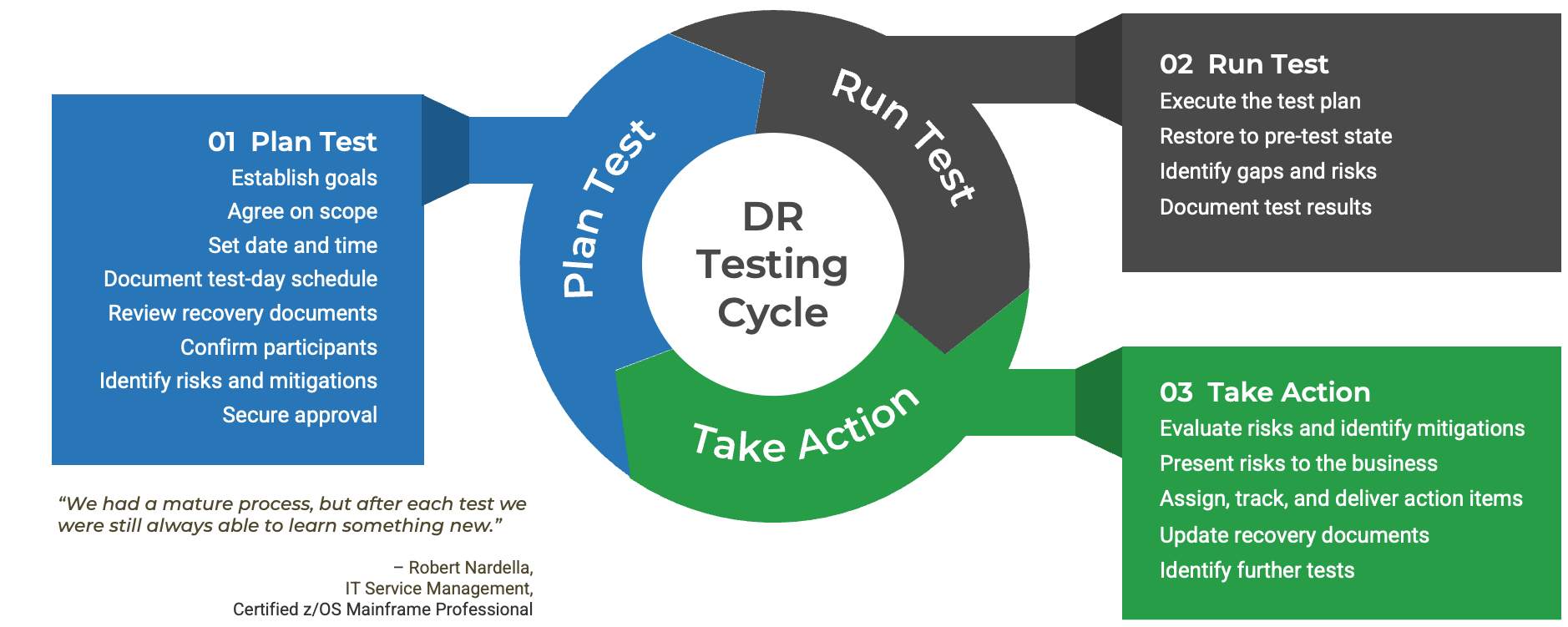


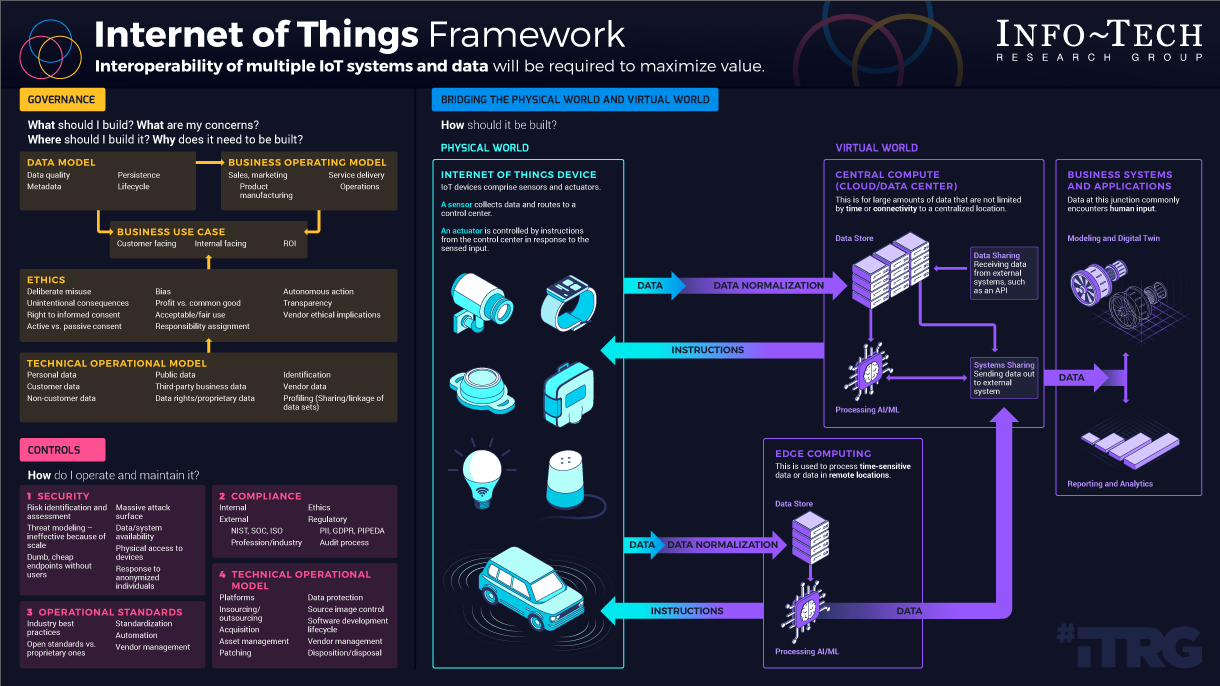

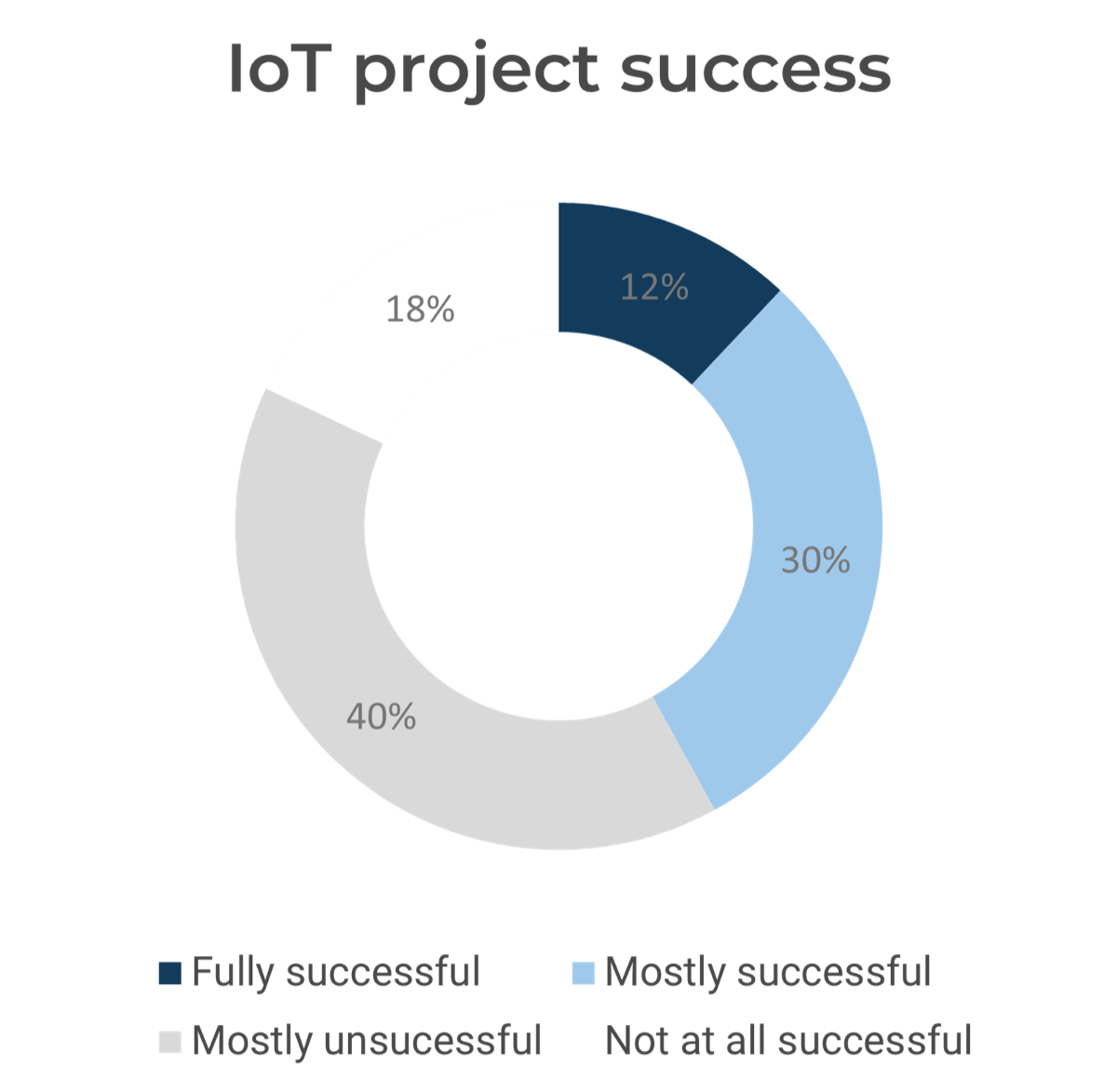
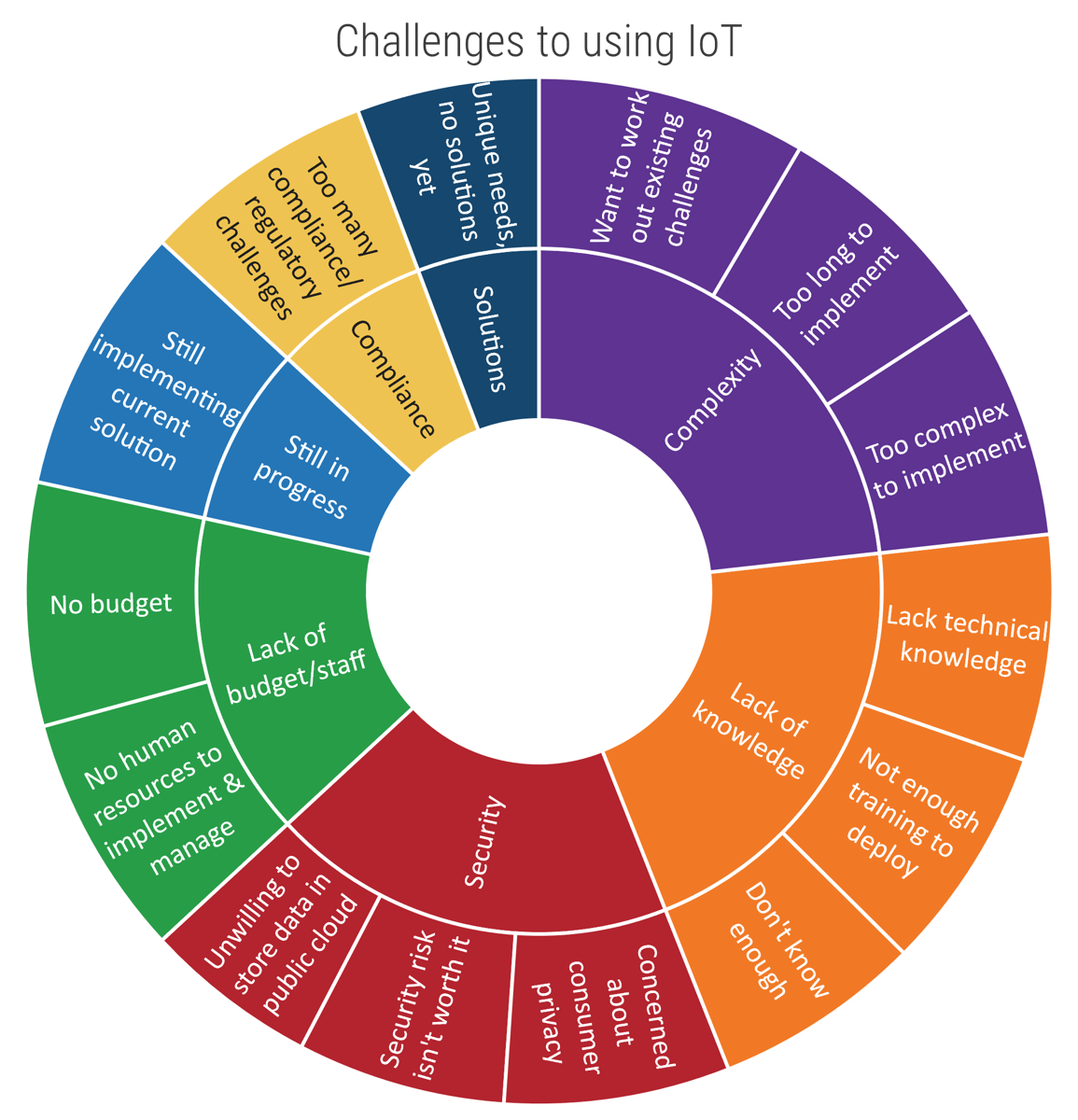
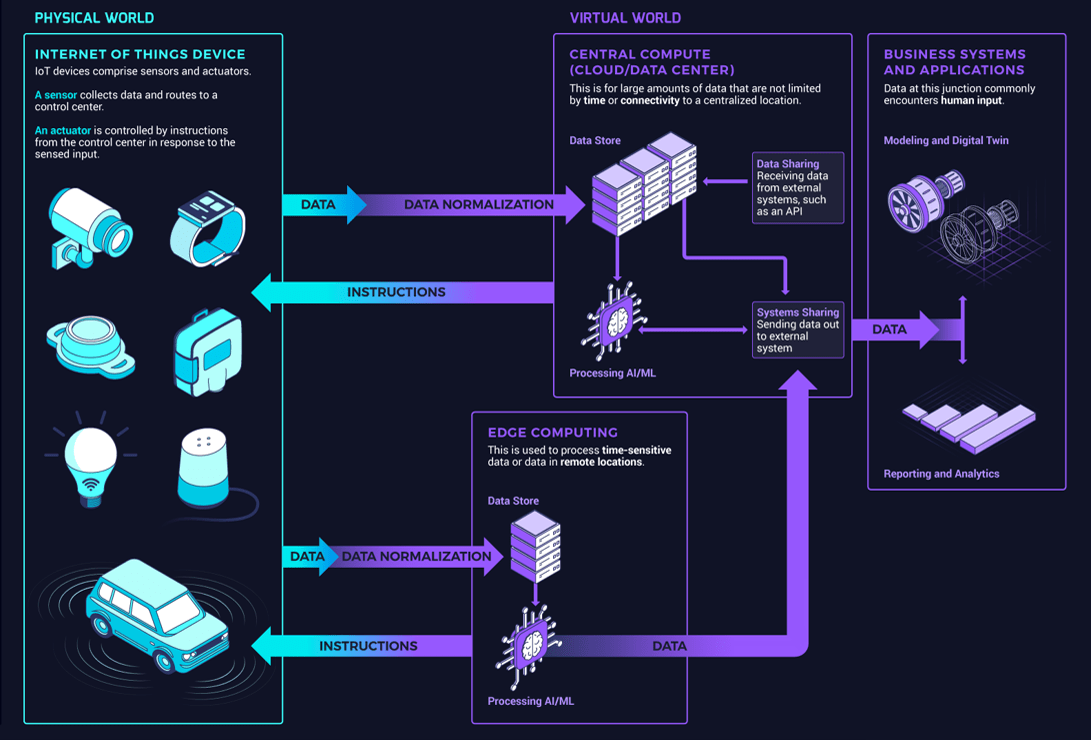 Data Normalization' from physical to virtual and 'Instructions' from virtual to physical.">
Data Normalization' from physical to virtual and 'Instructions' from virtual to physical.">


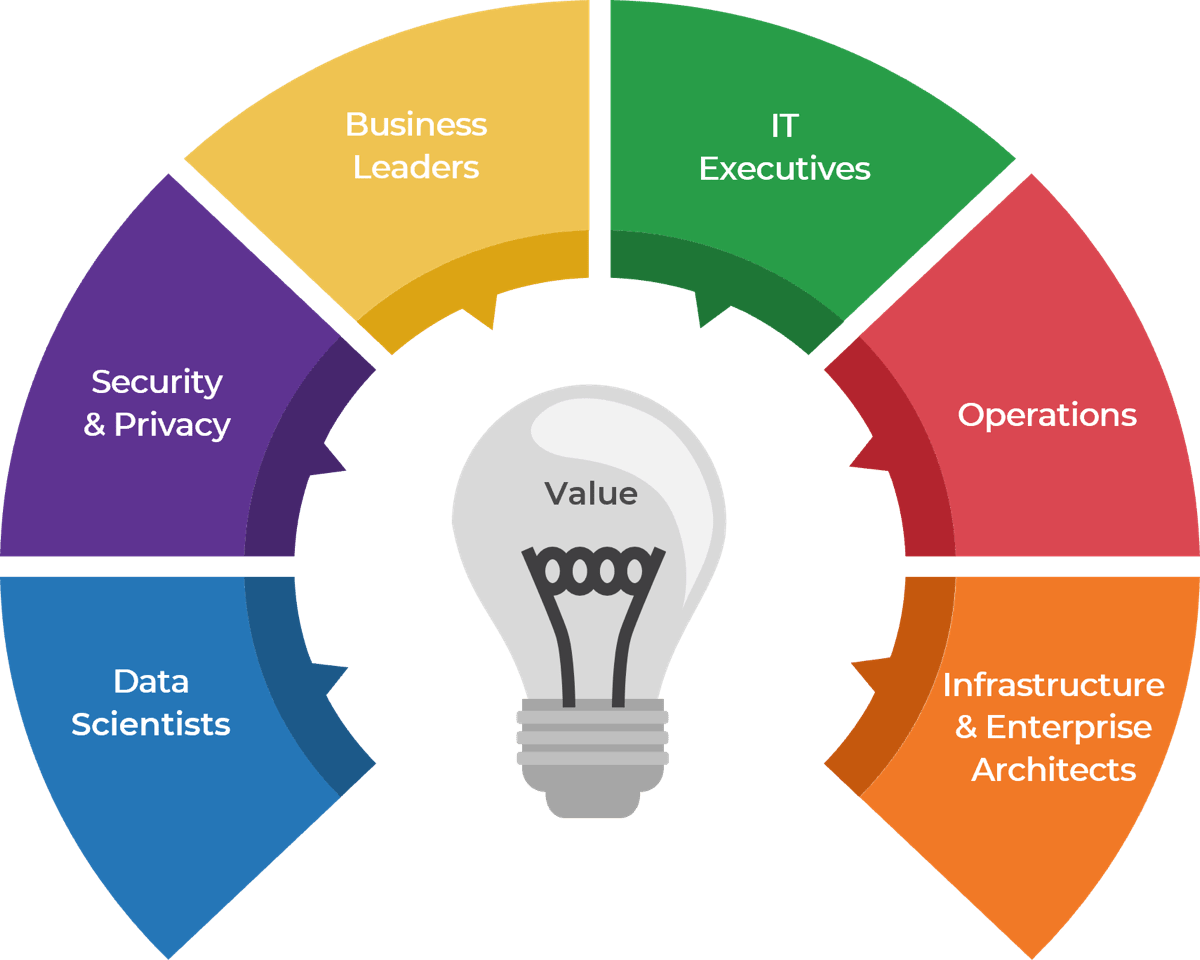





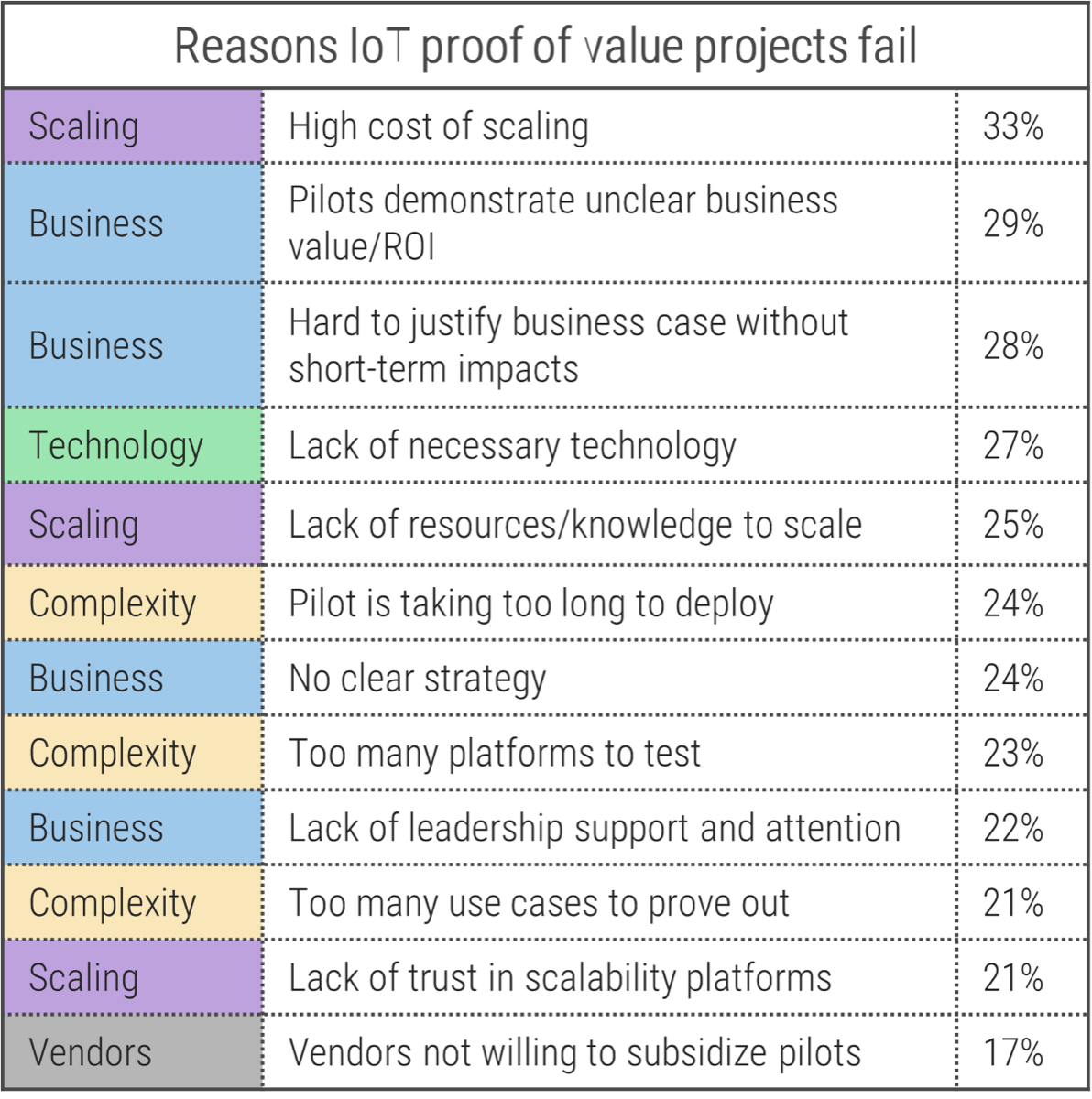















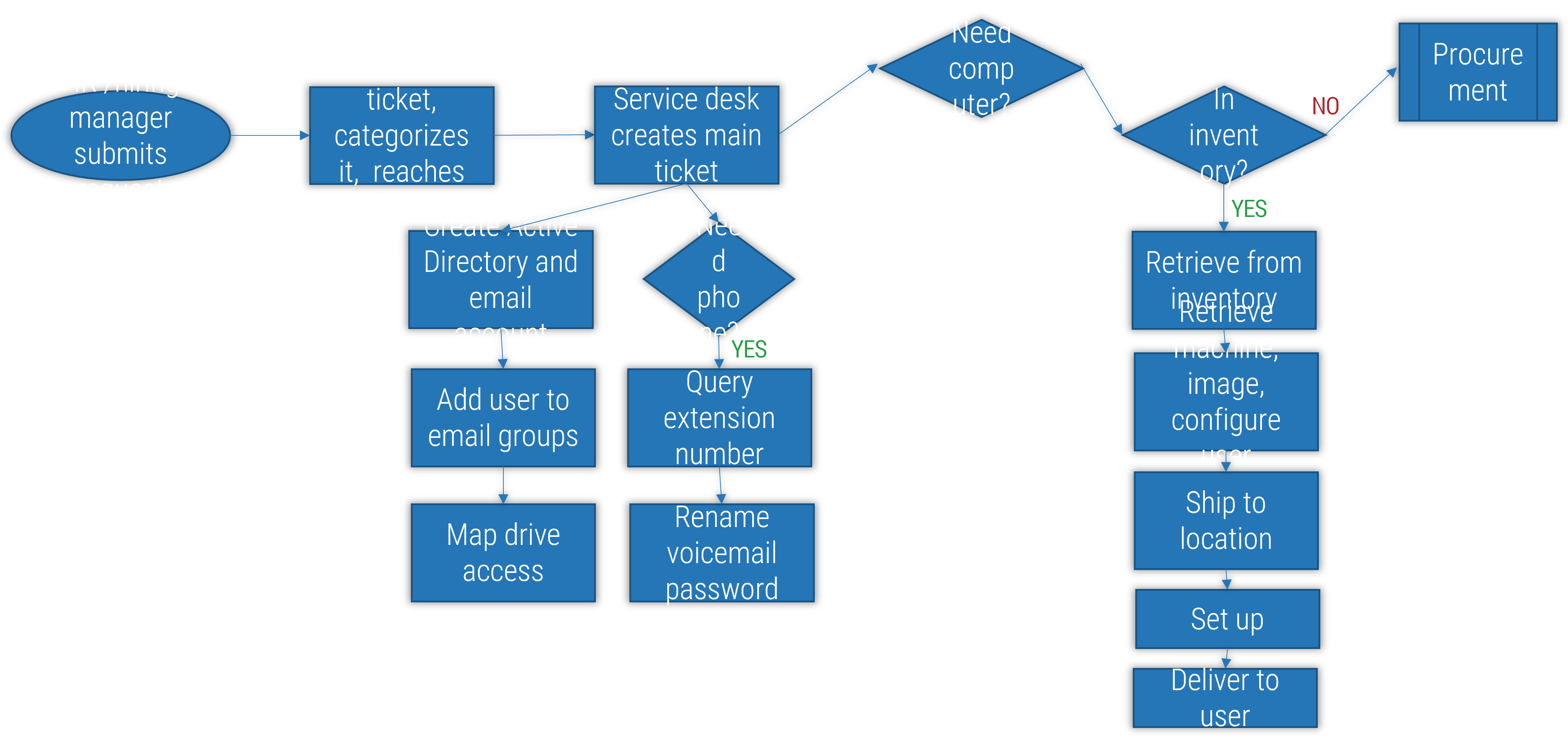




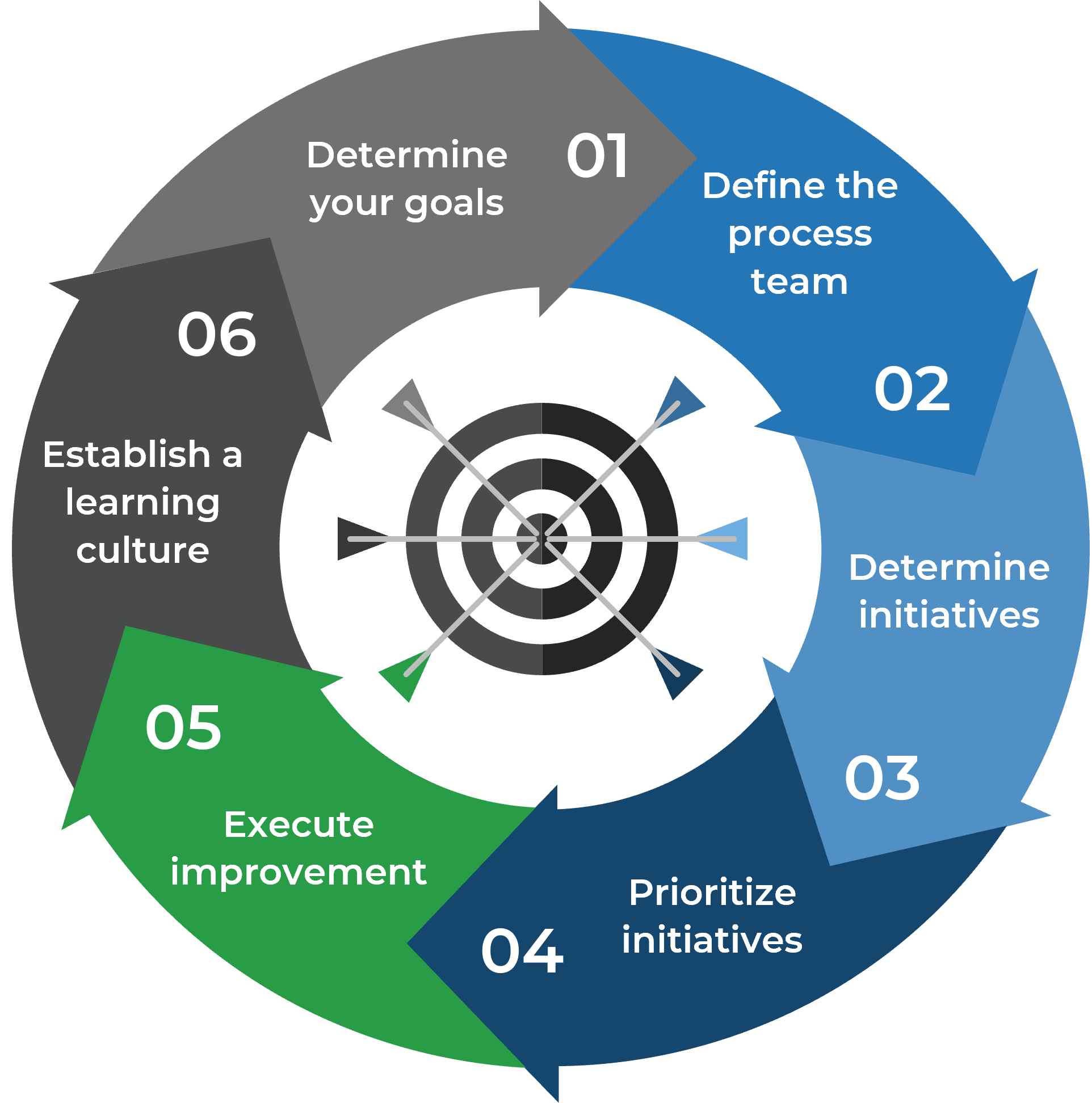


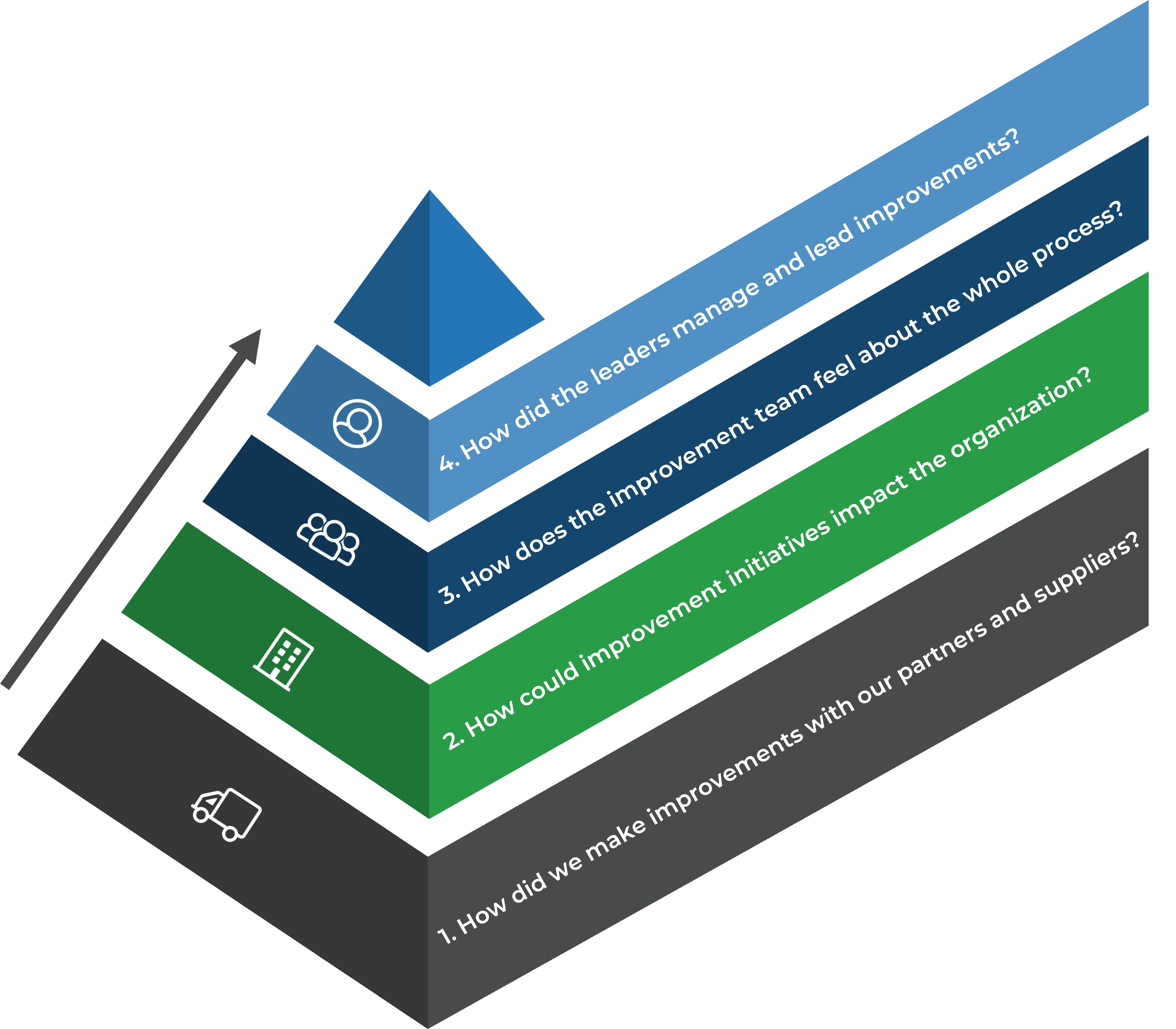
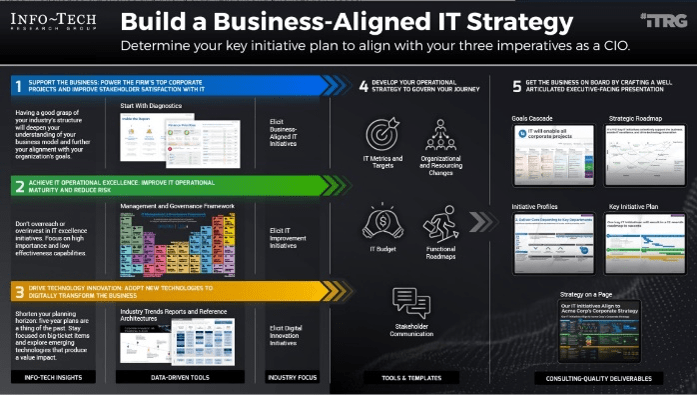
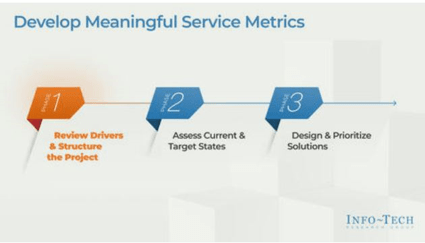







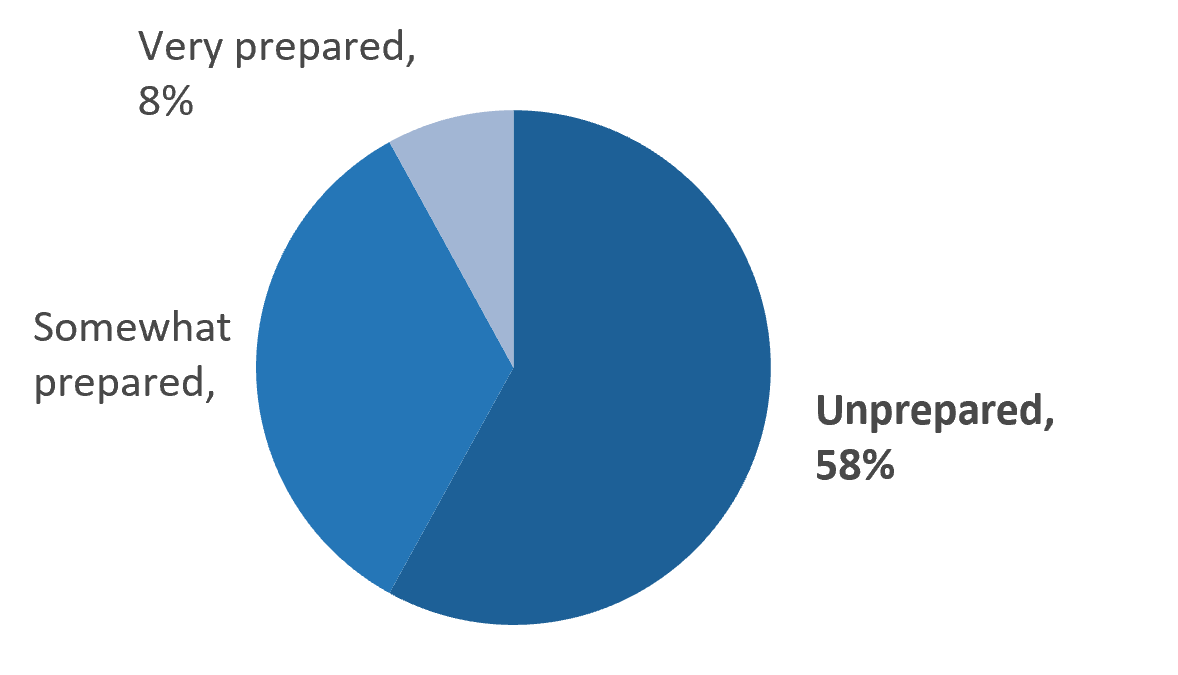
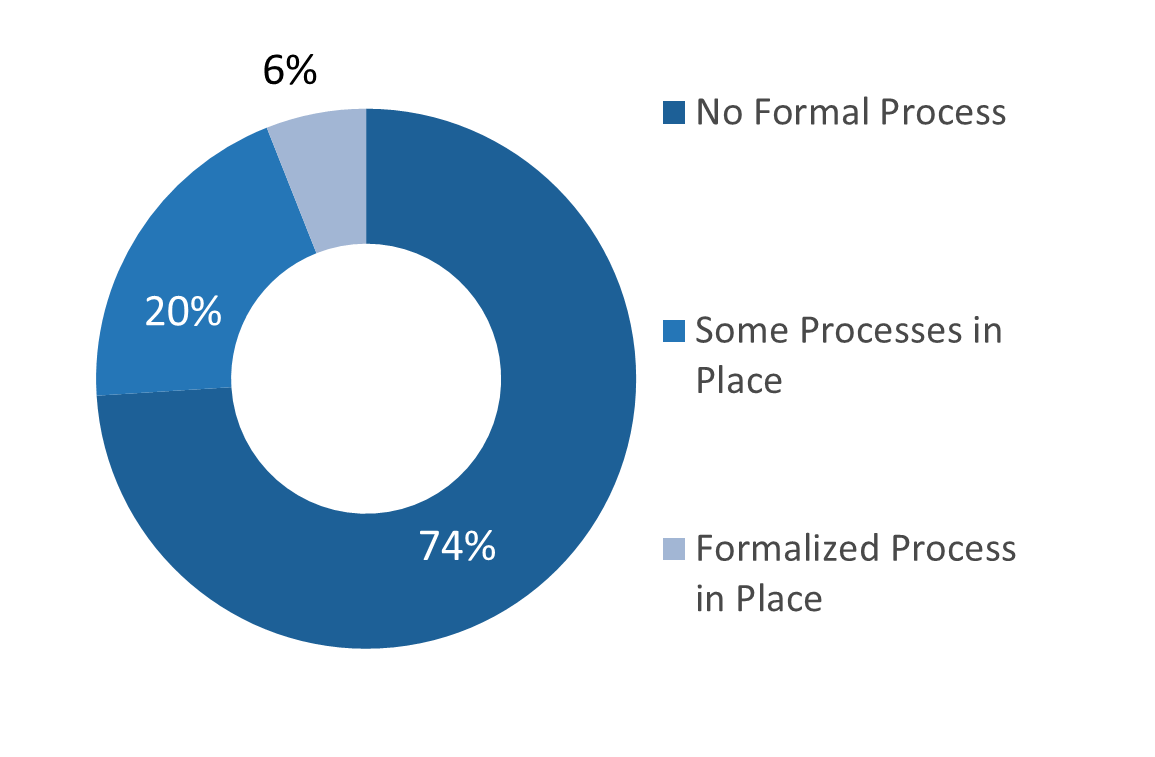
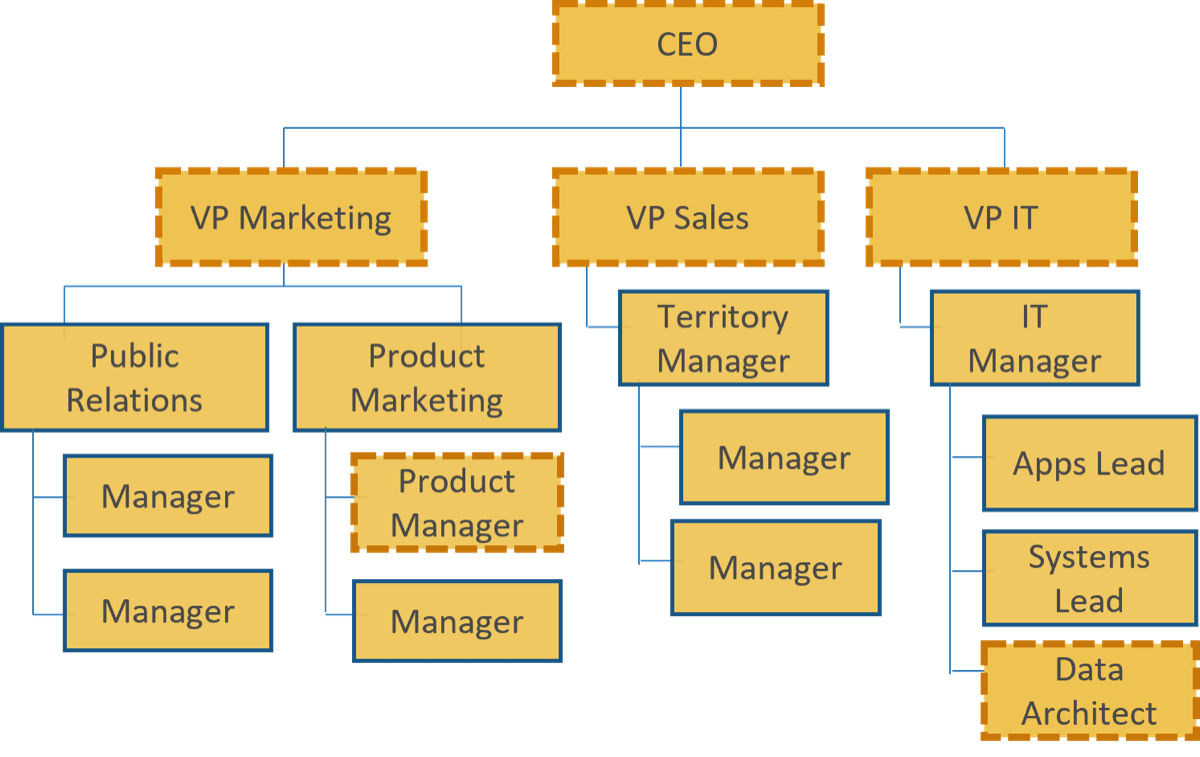


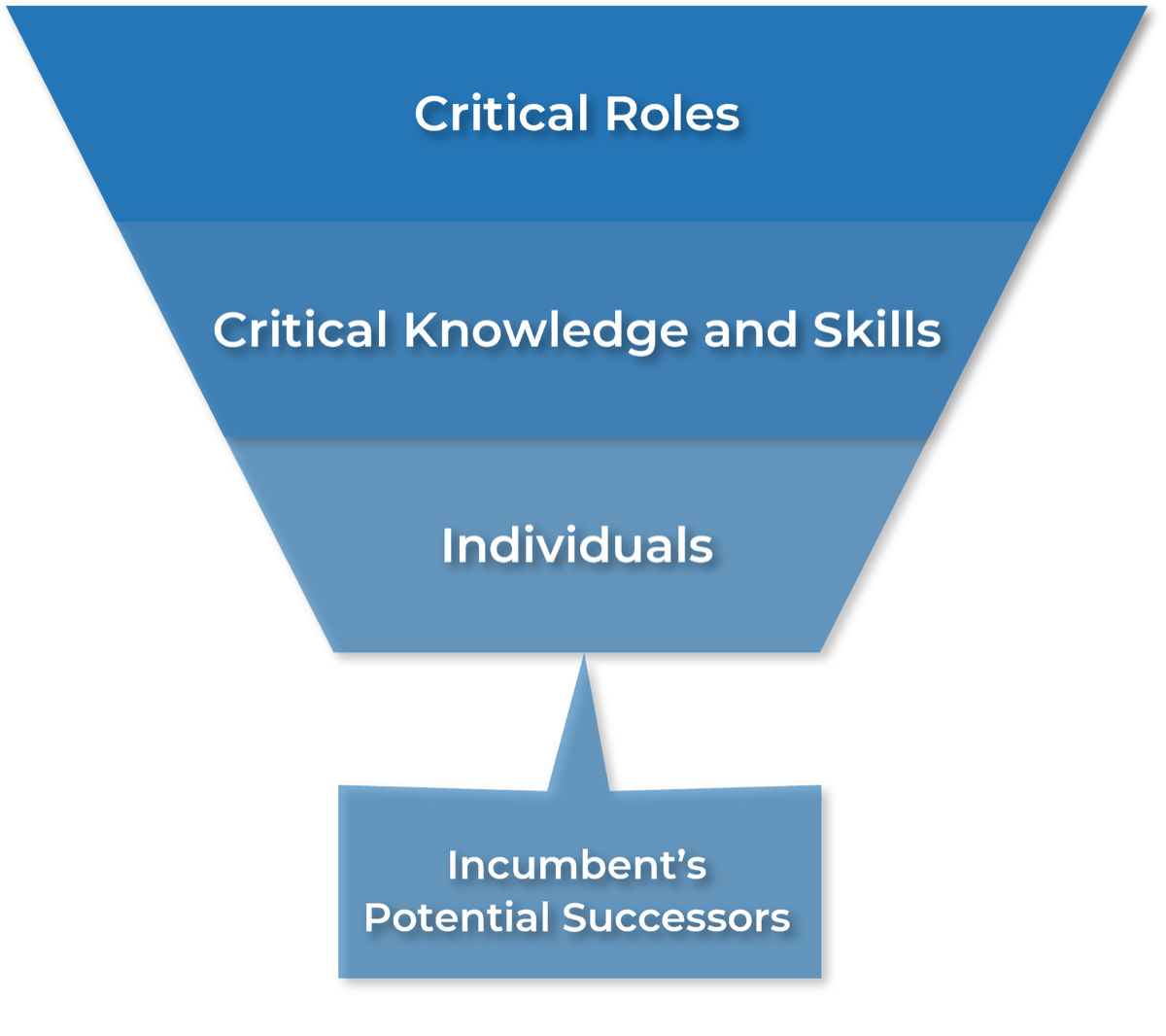

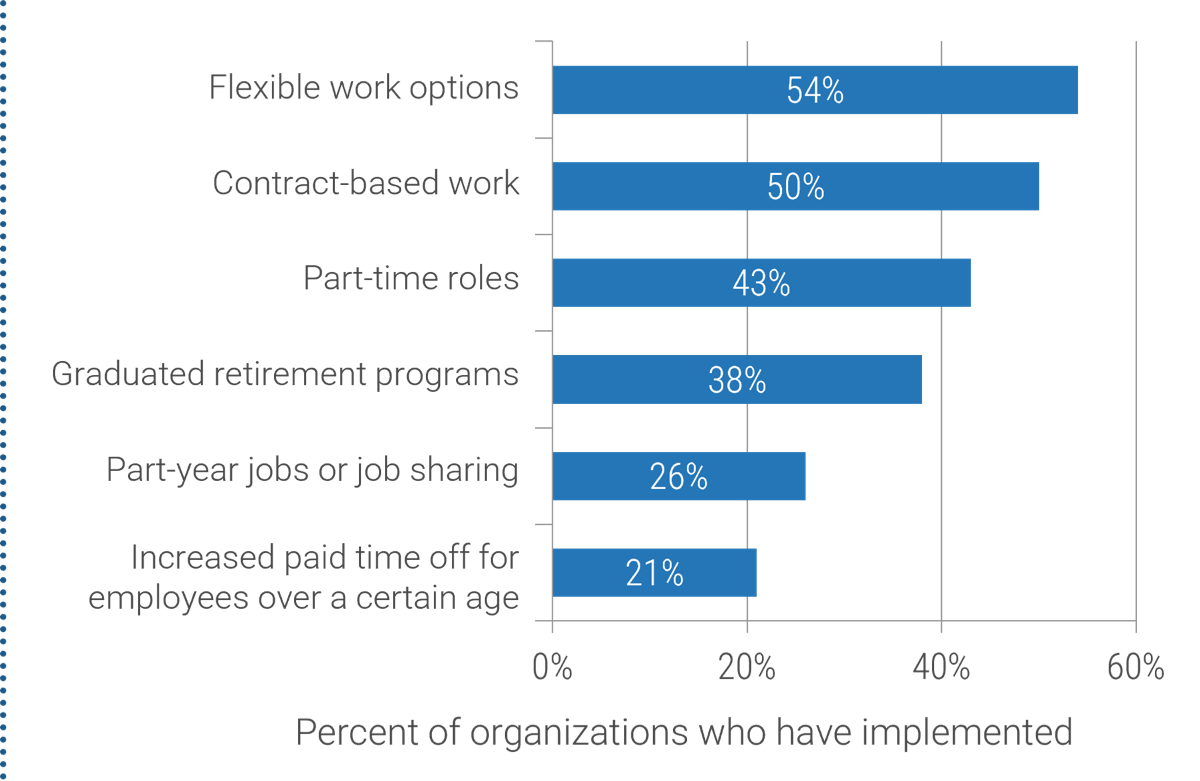





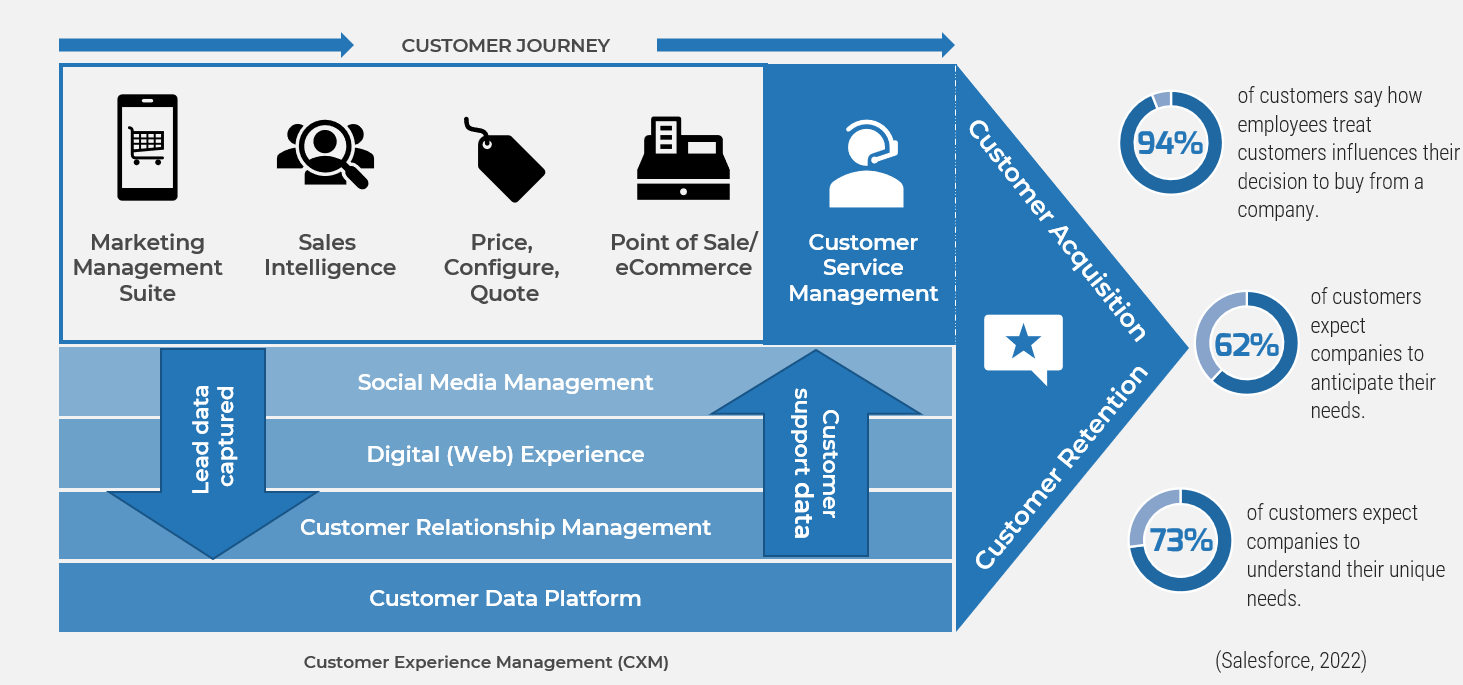



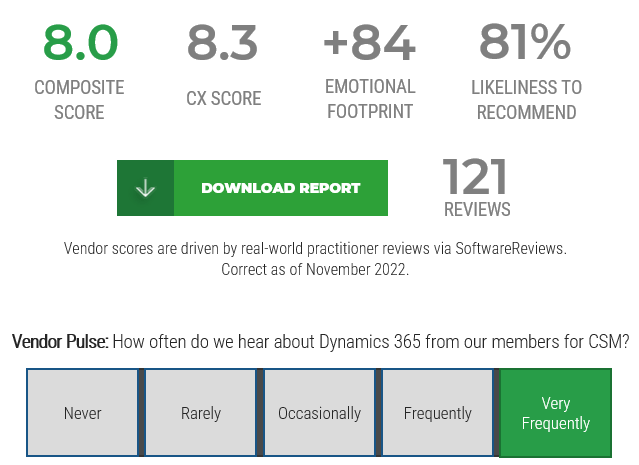




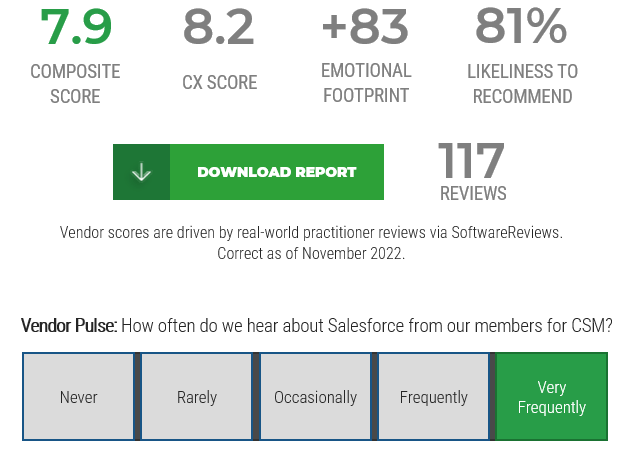




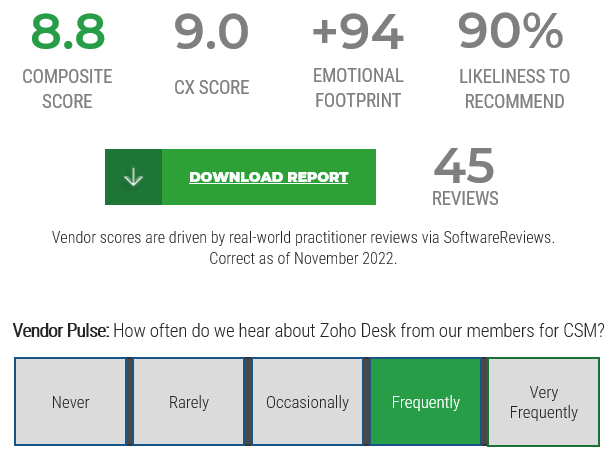




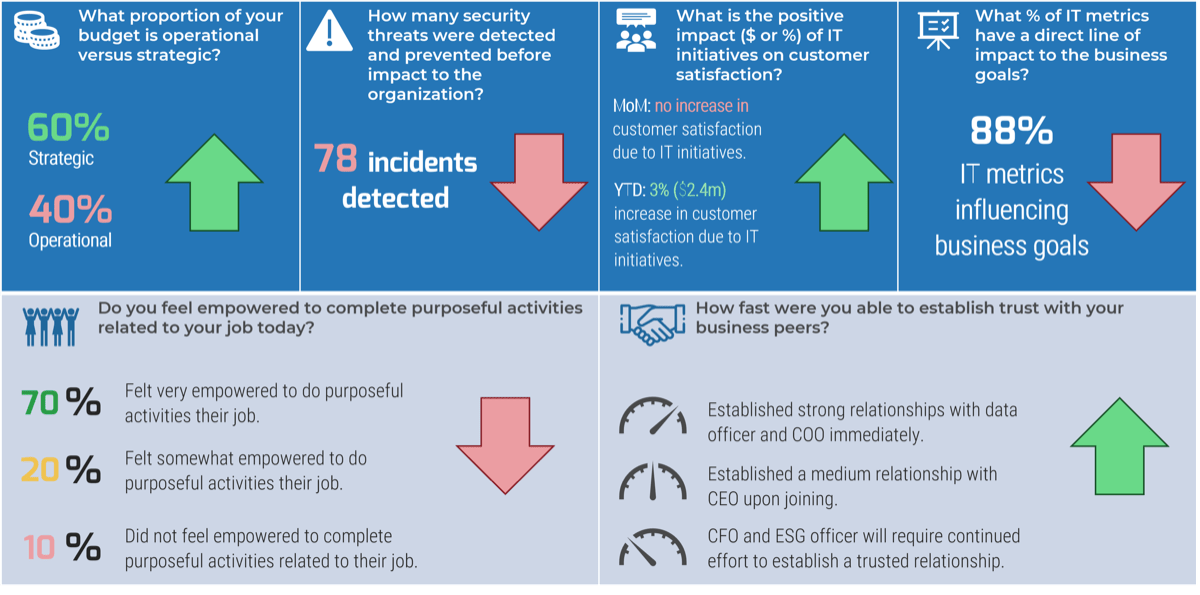













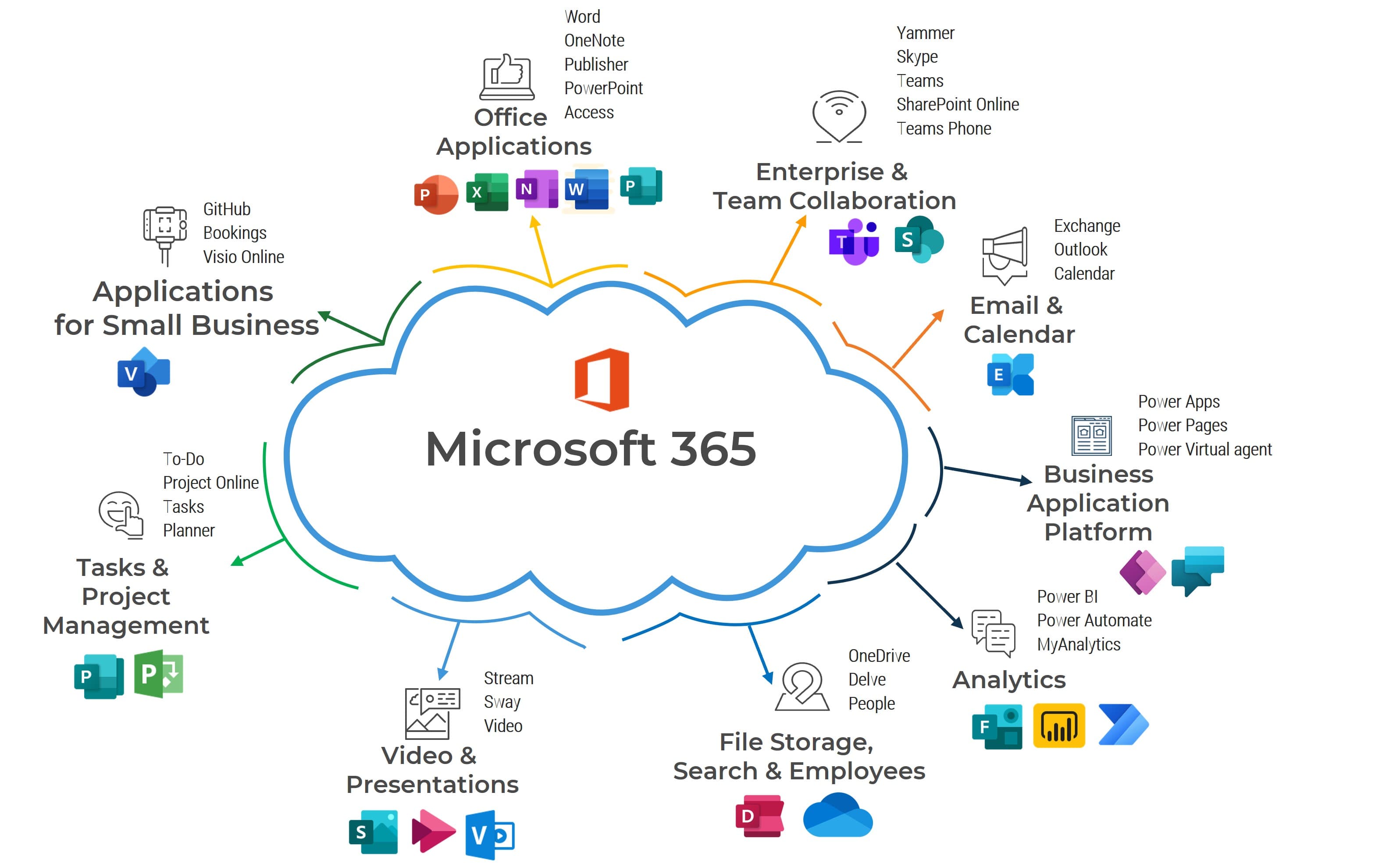

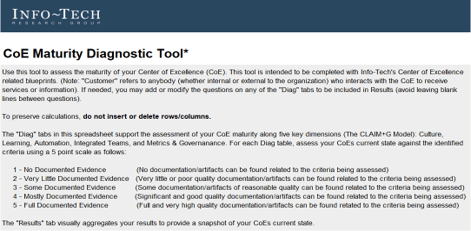


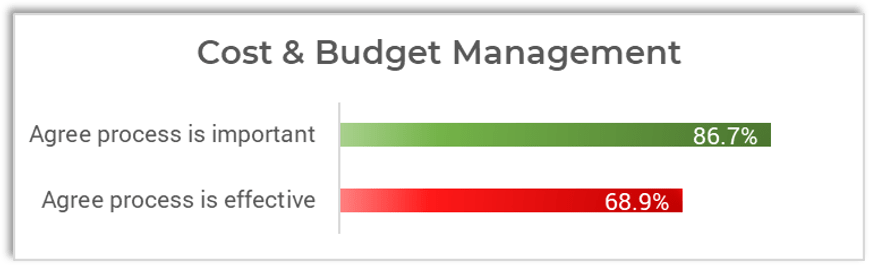
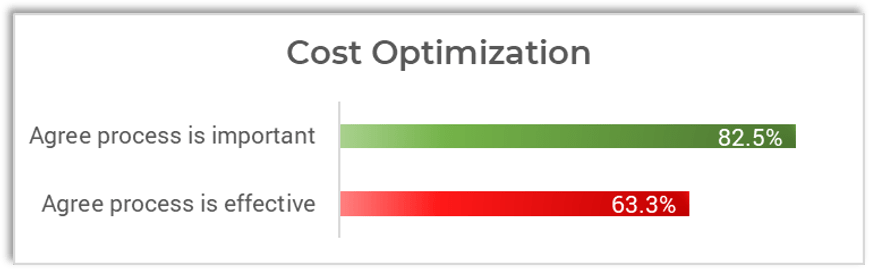
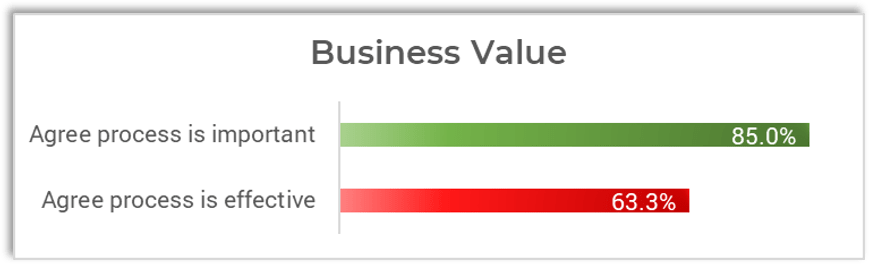
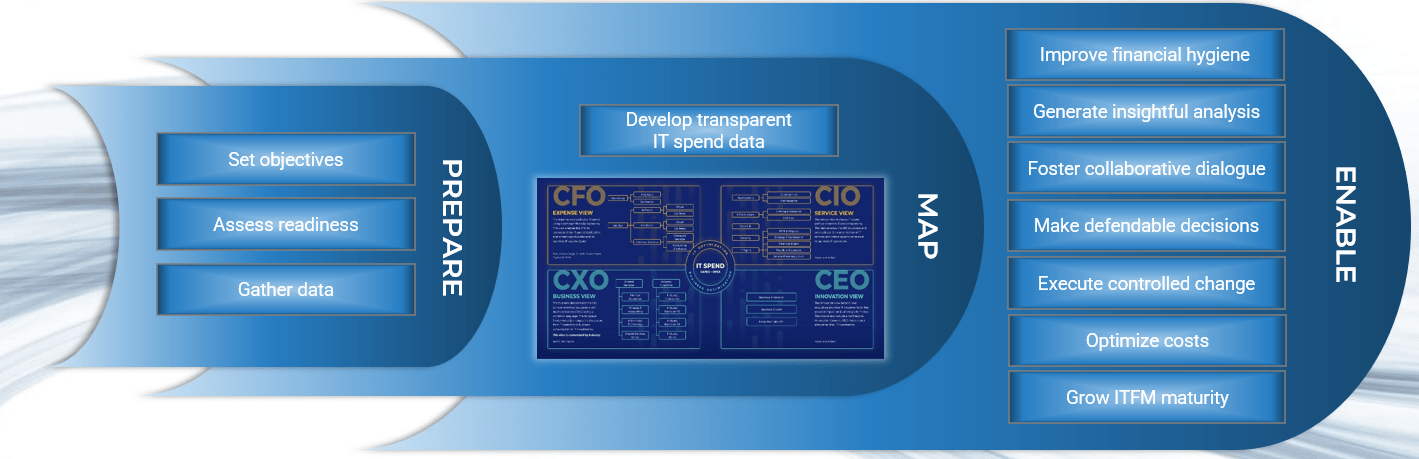
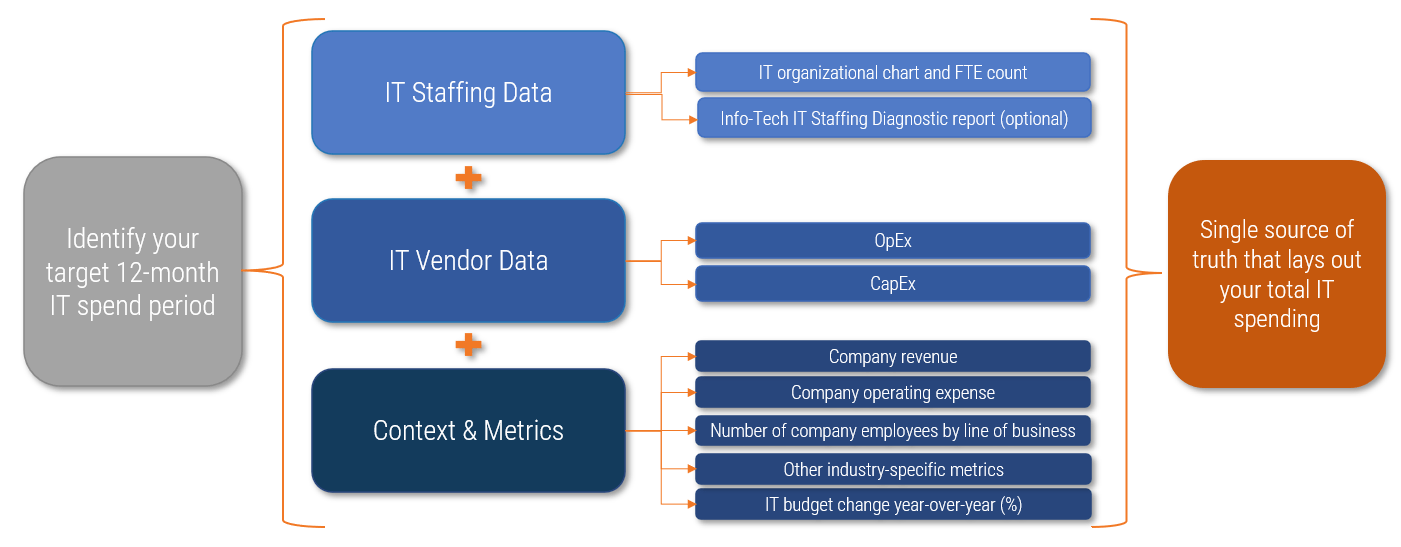
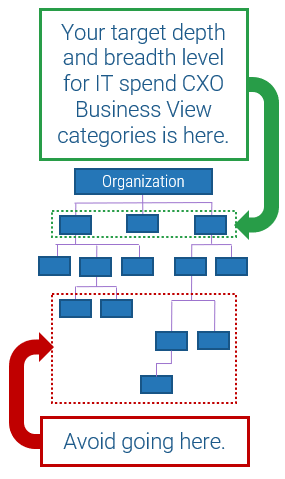
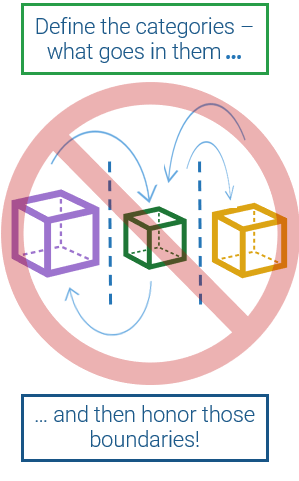
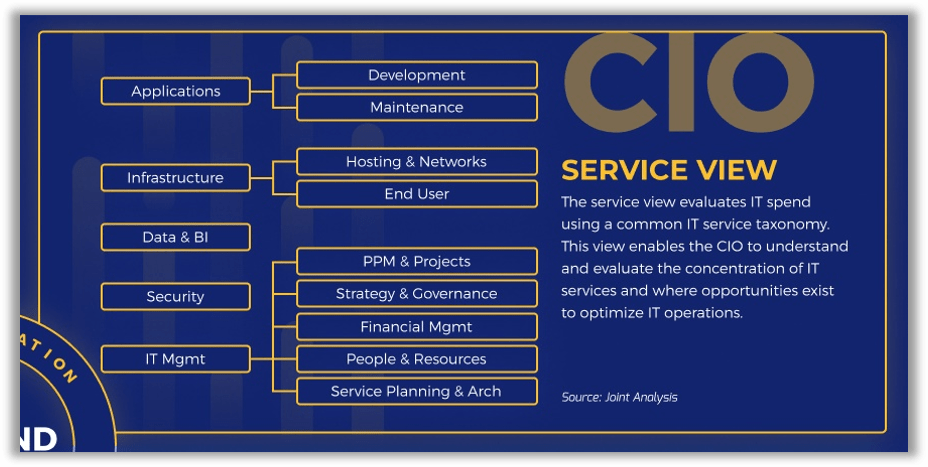
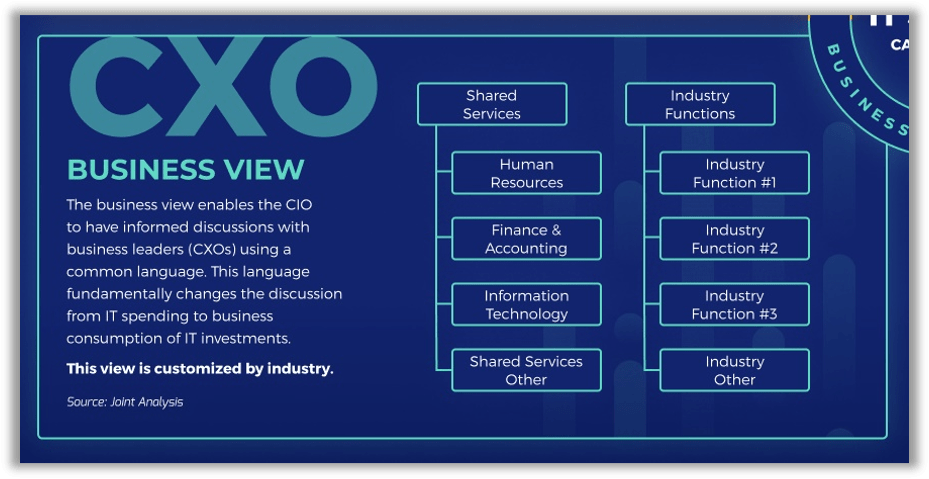

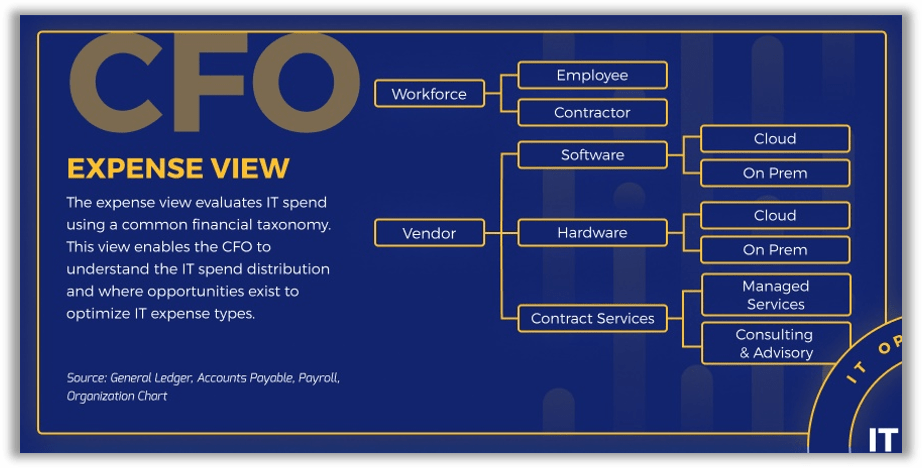
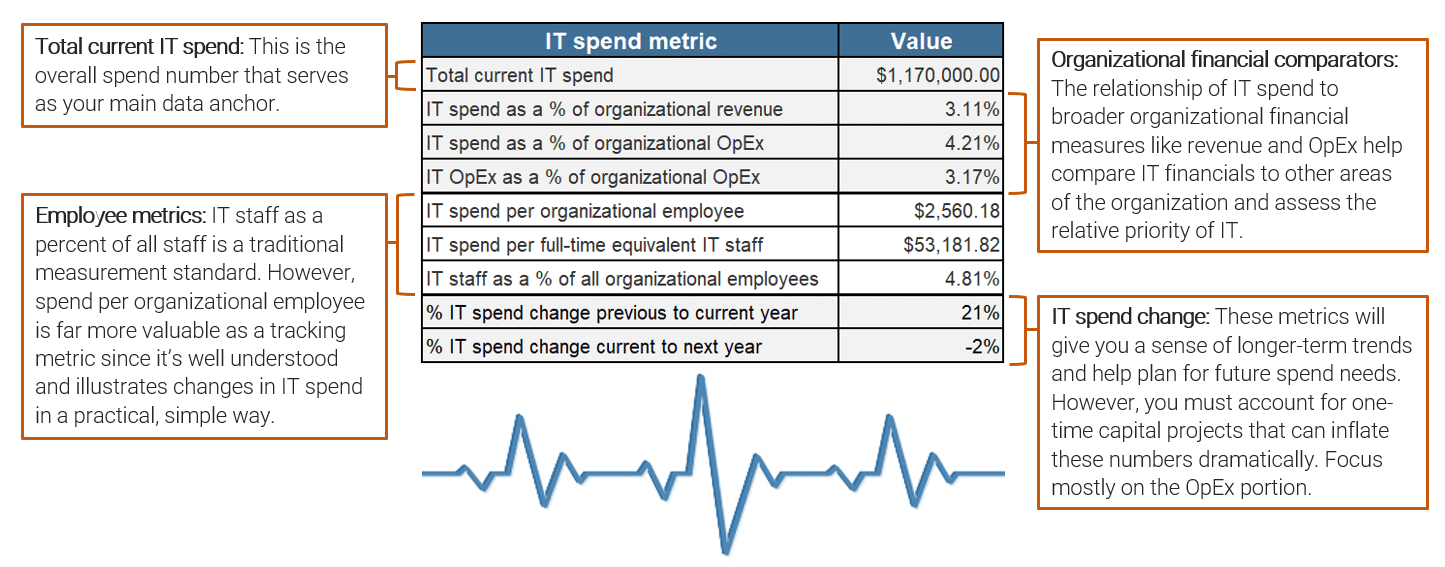
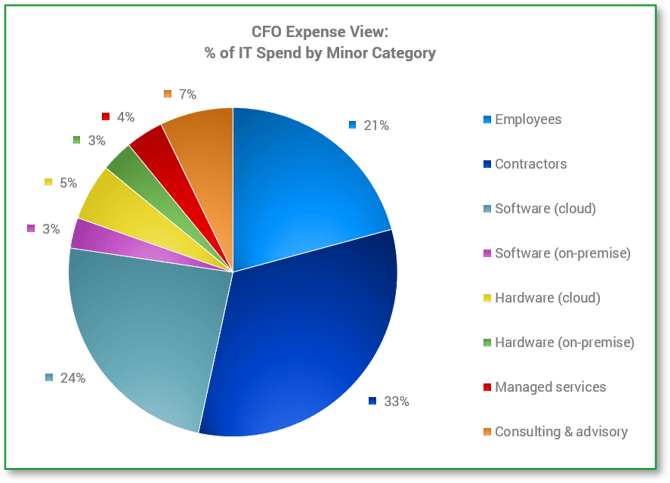
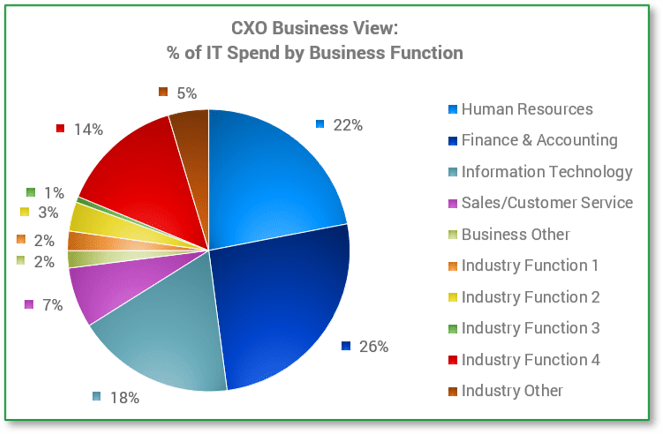
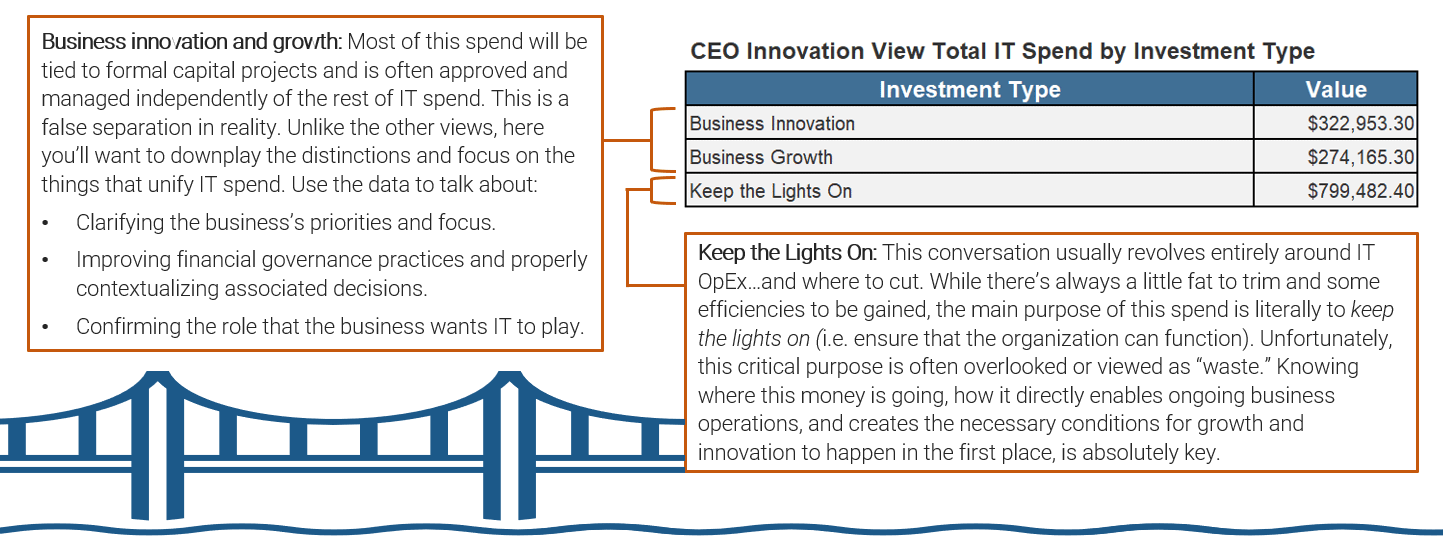









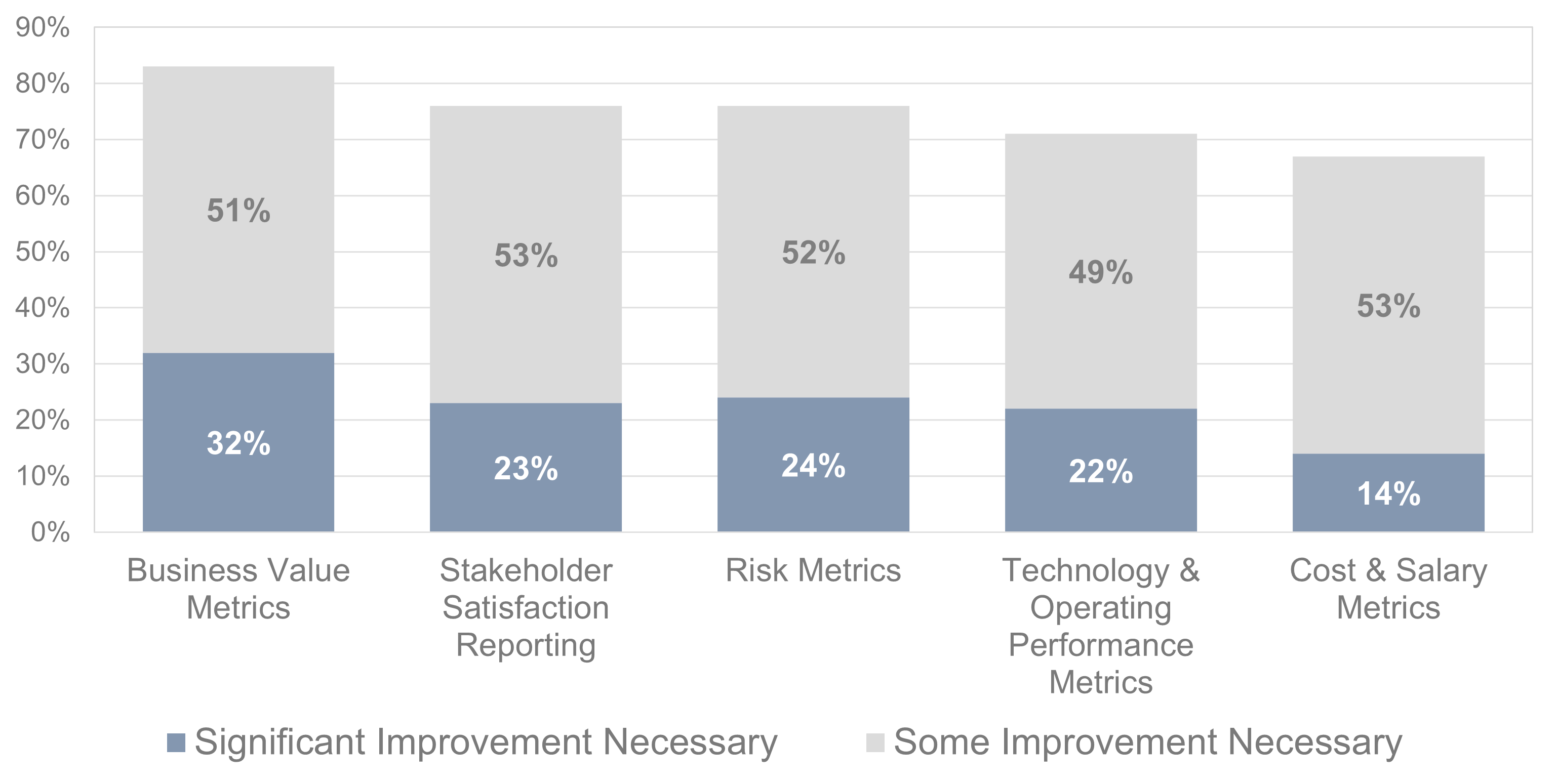
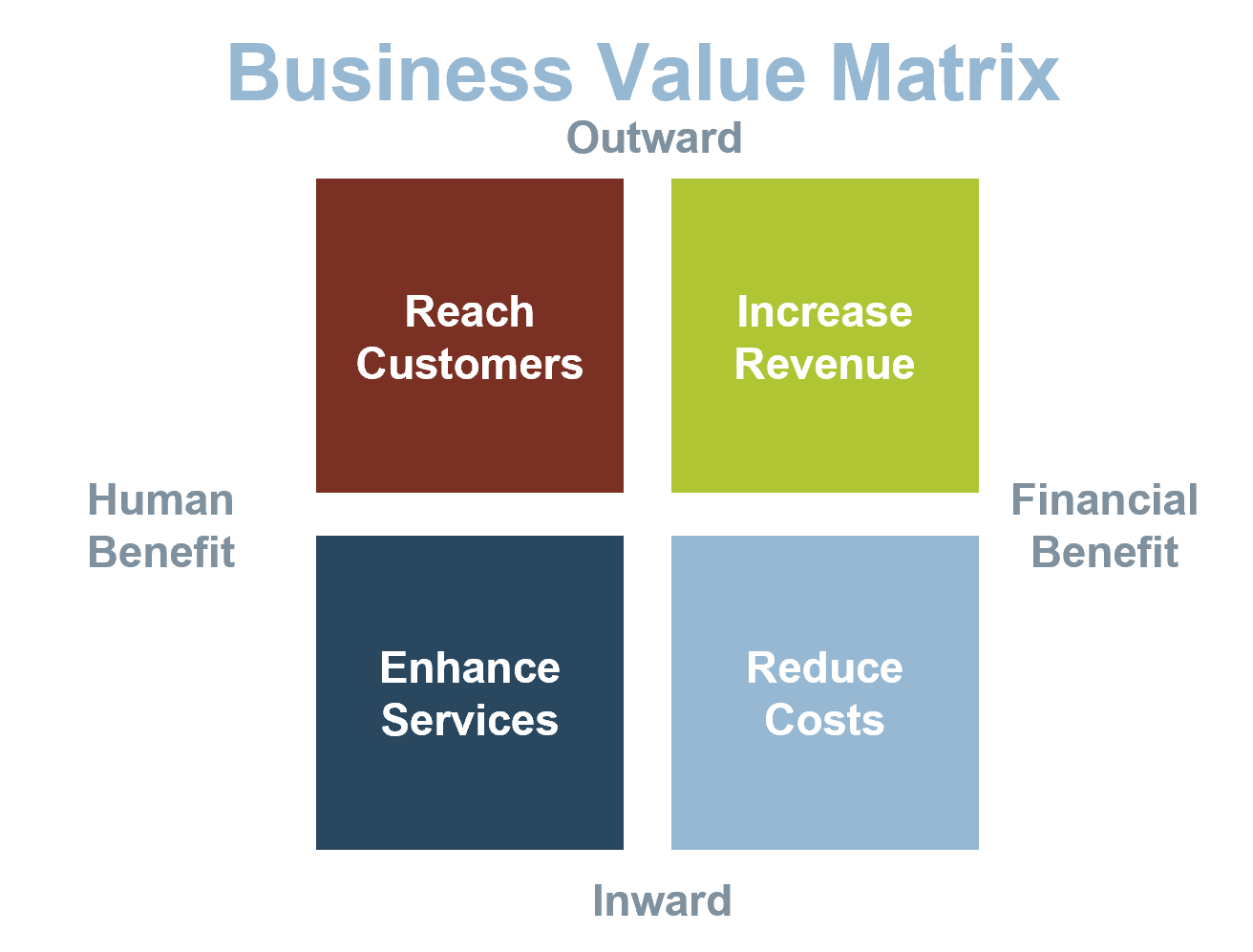
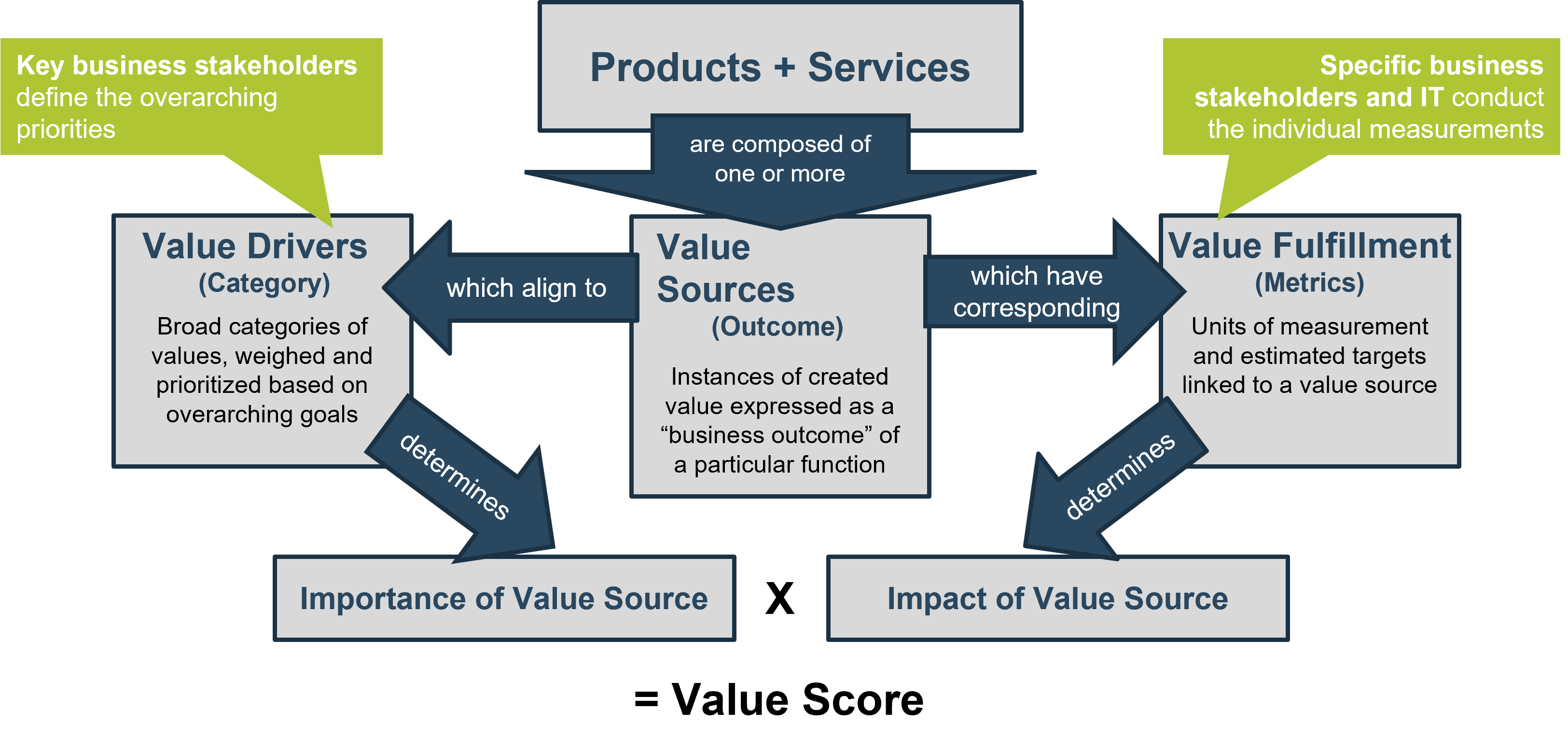

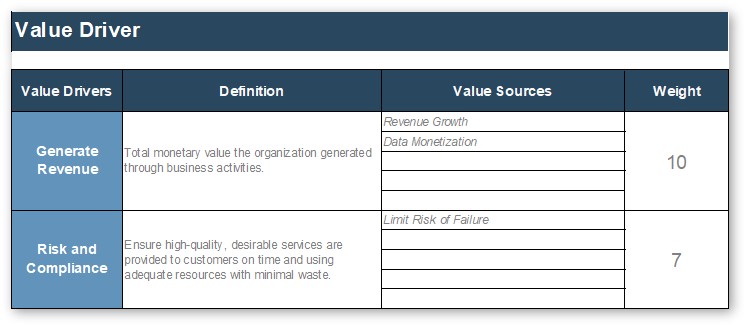
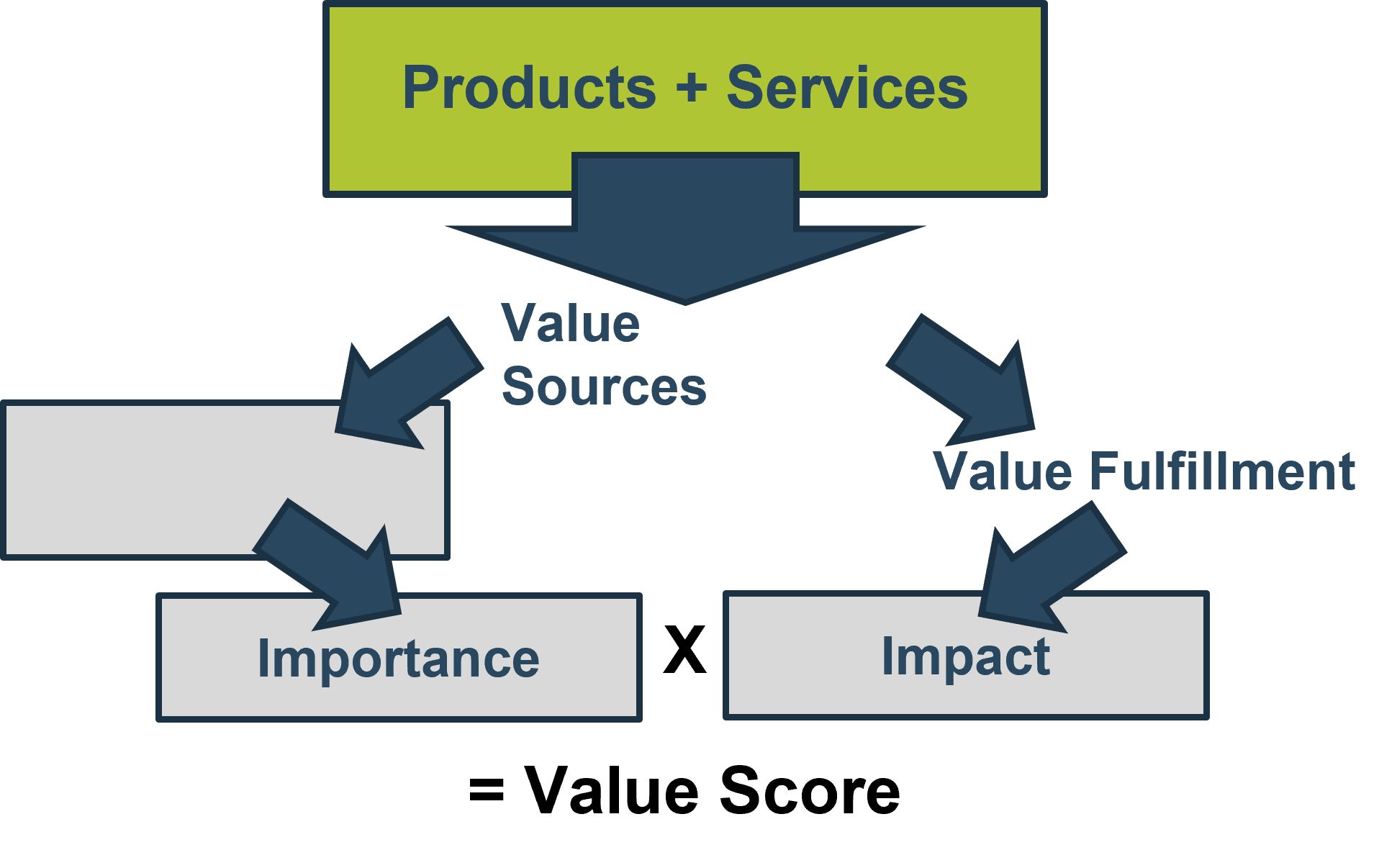
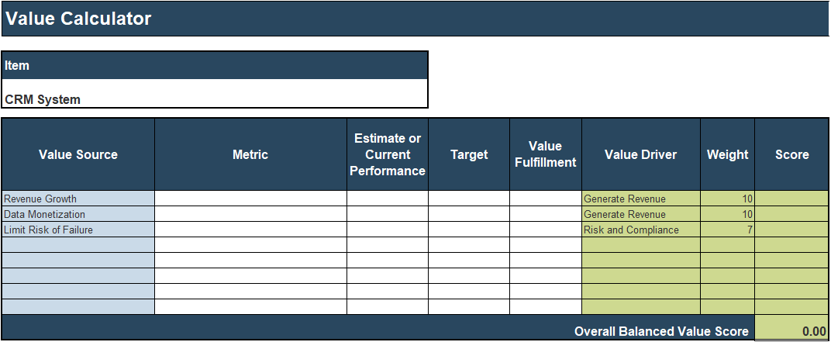
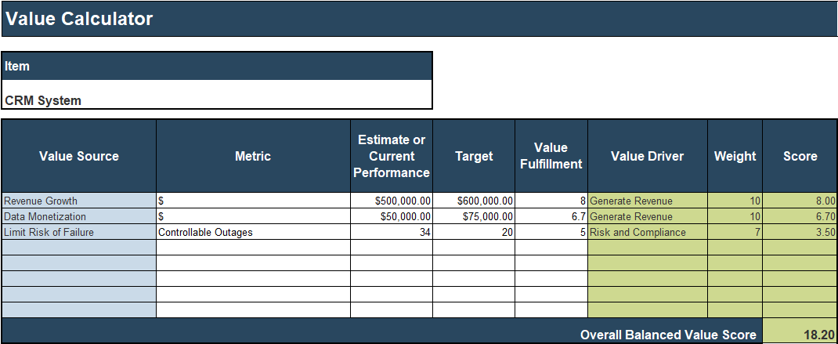


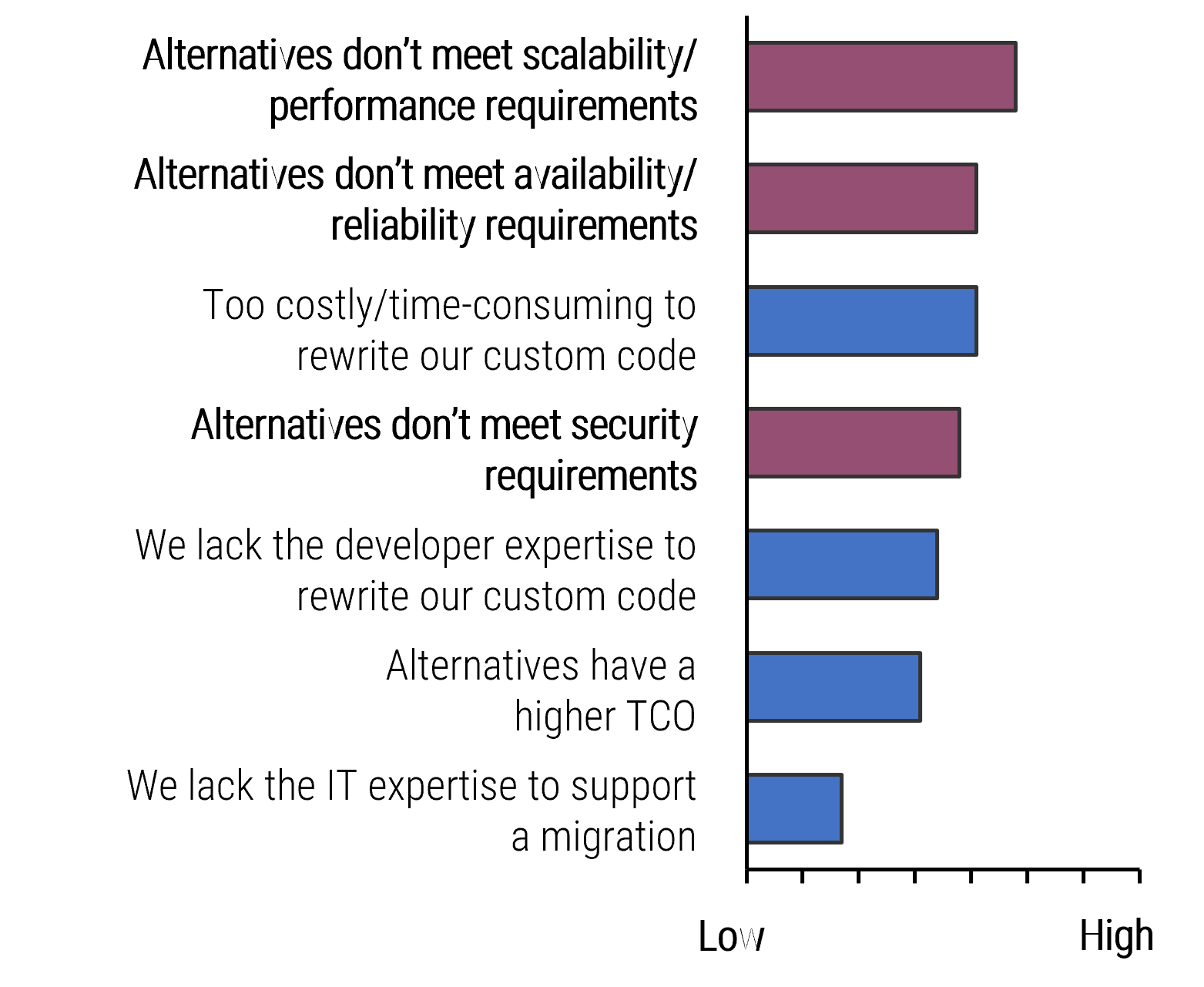



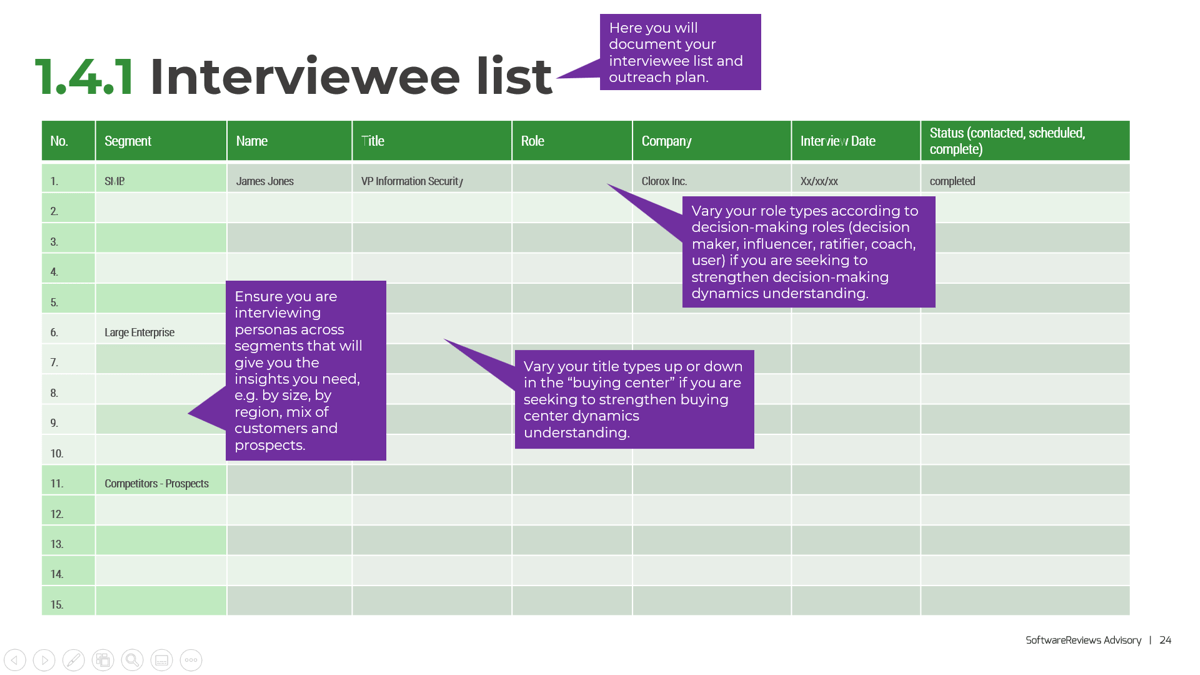


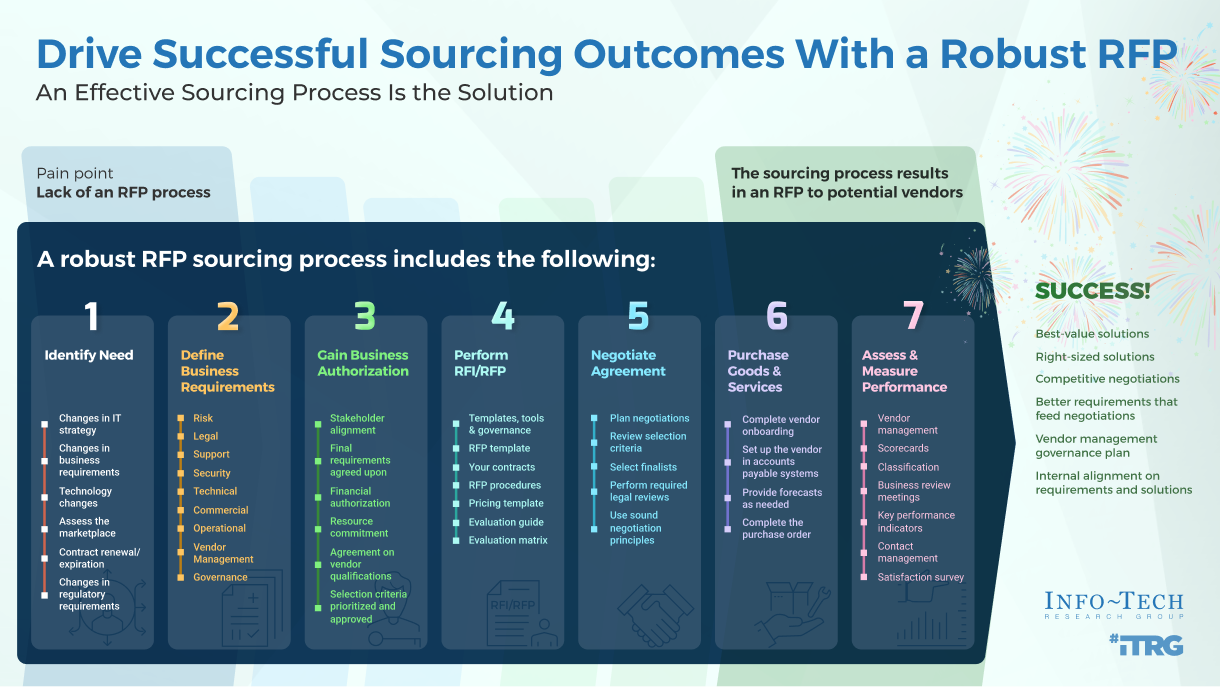
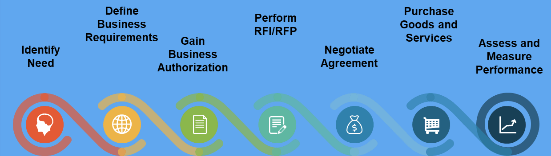

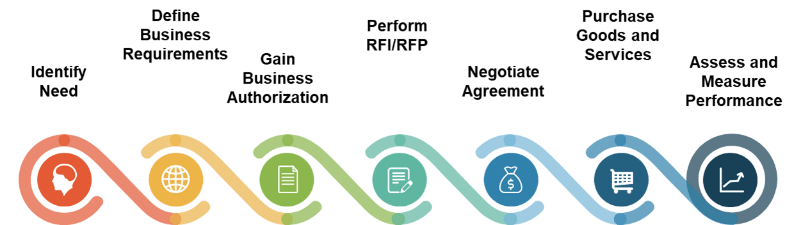









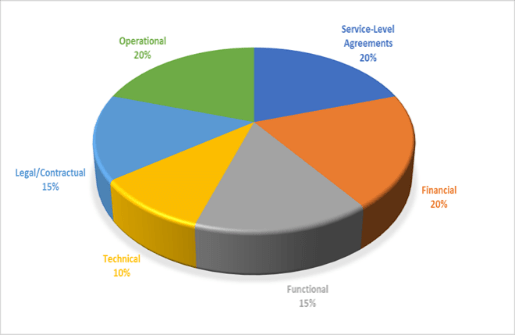









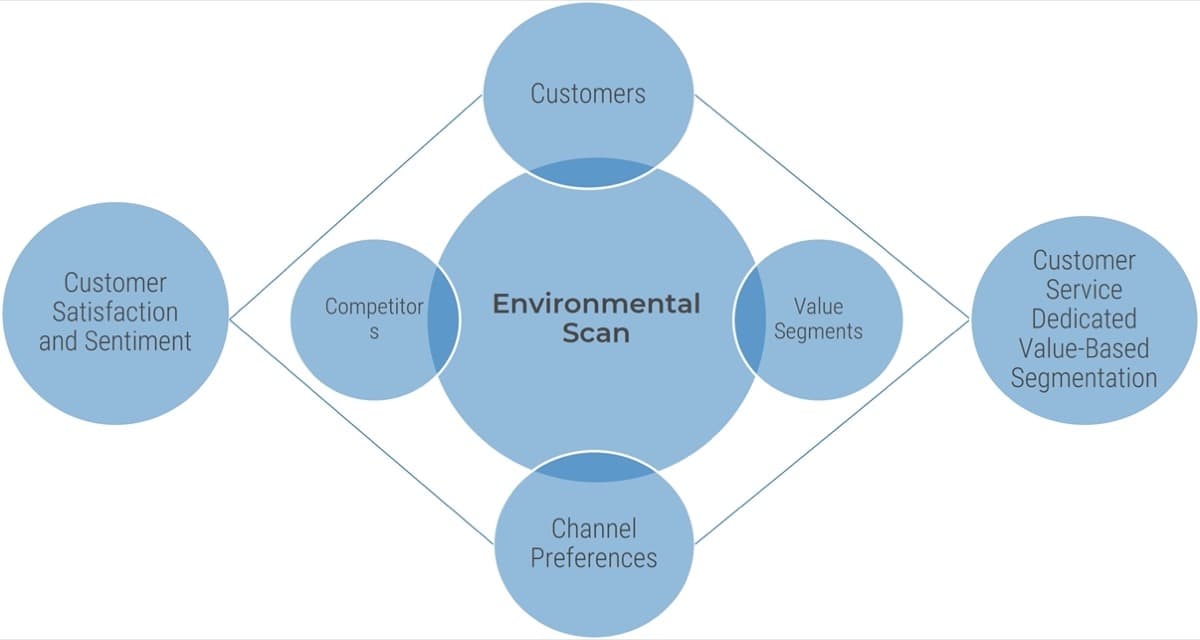
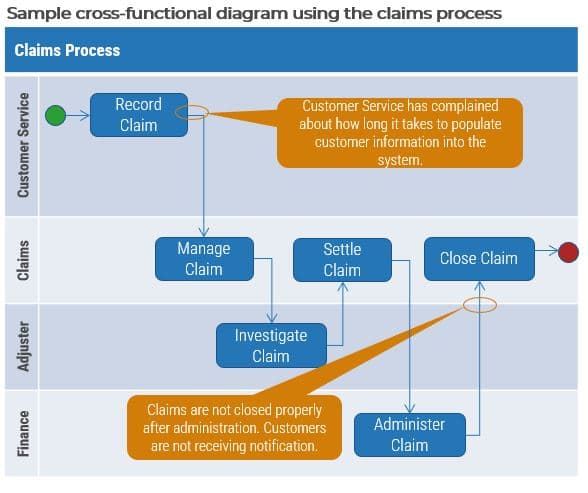
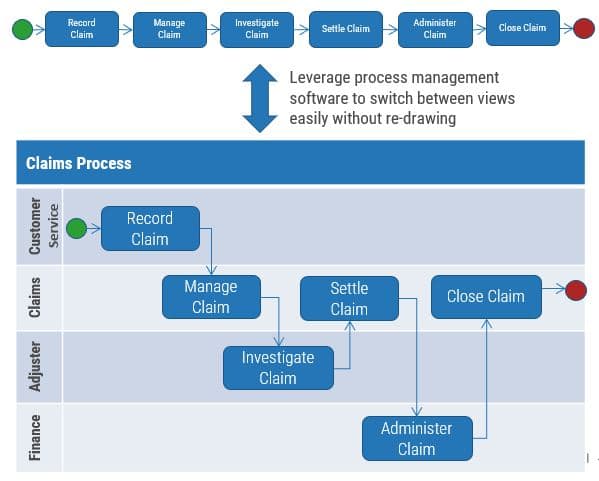


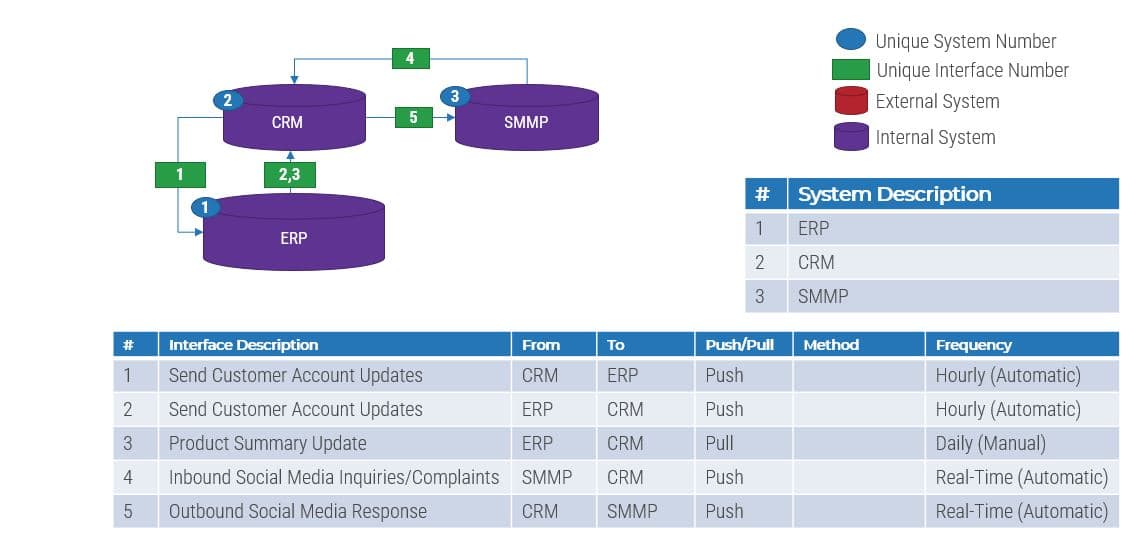
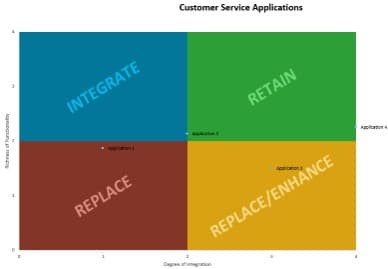
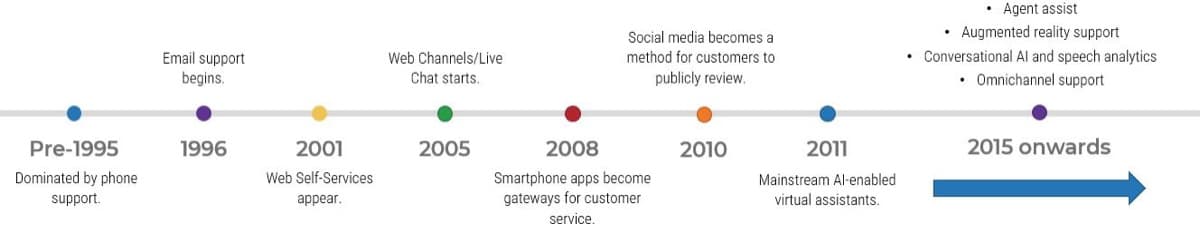
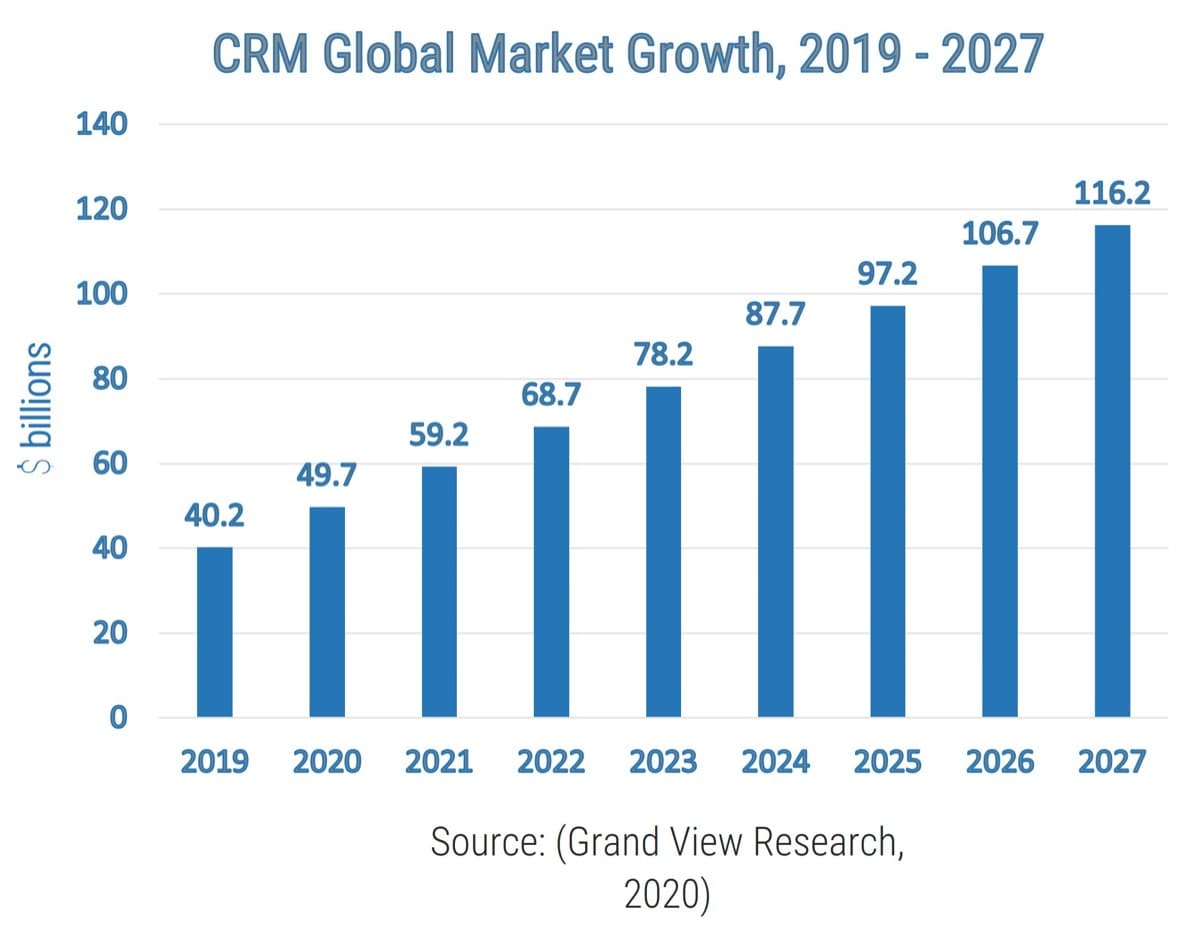





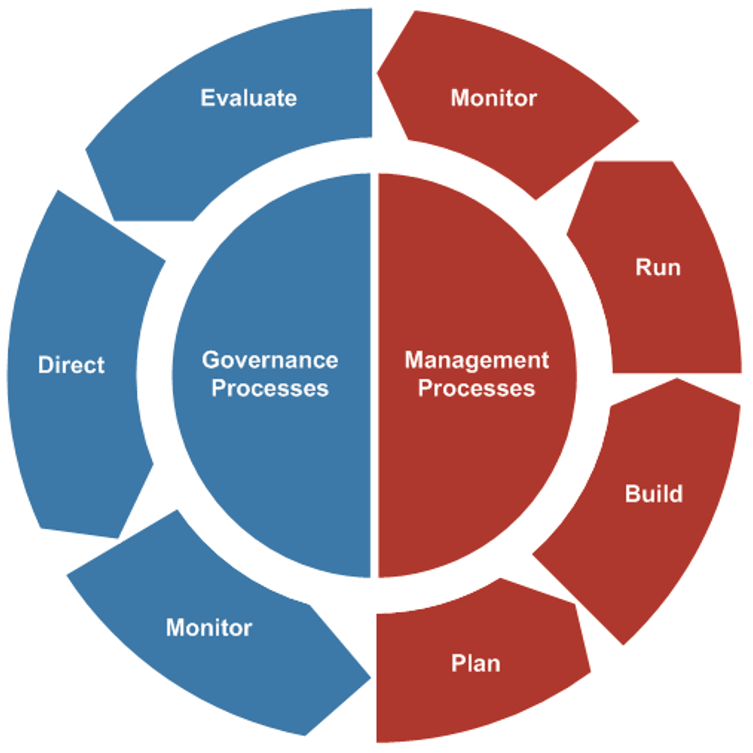
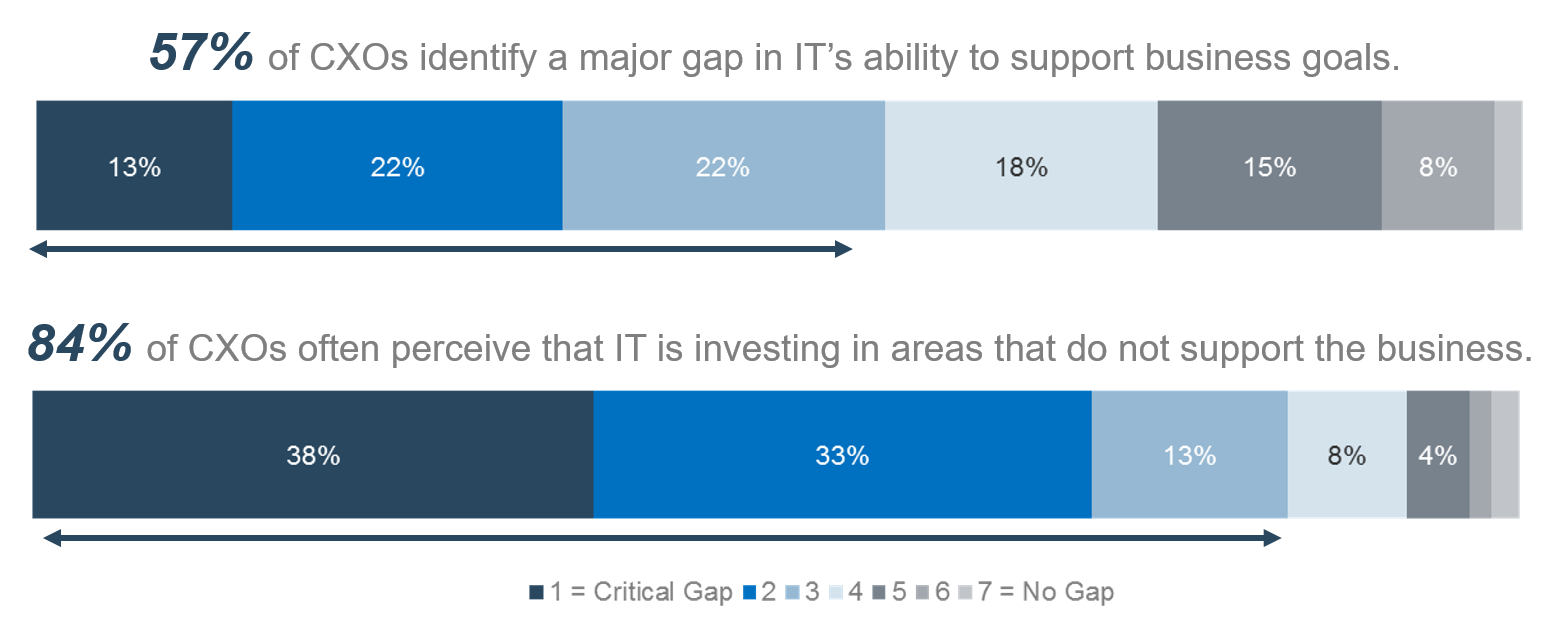




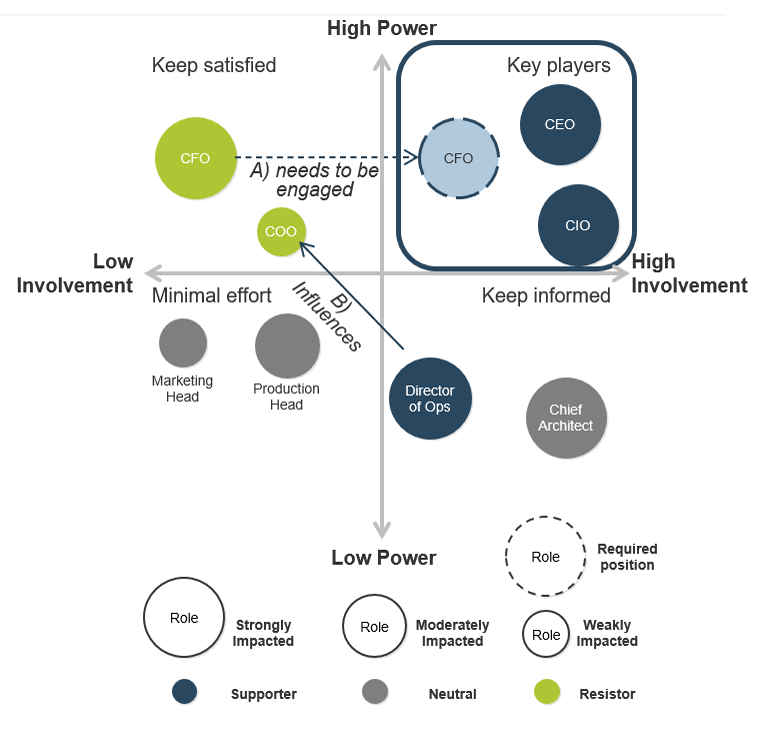




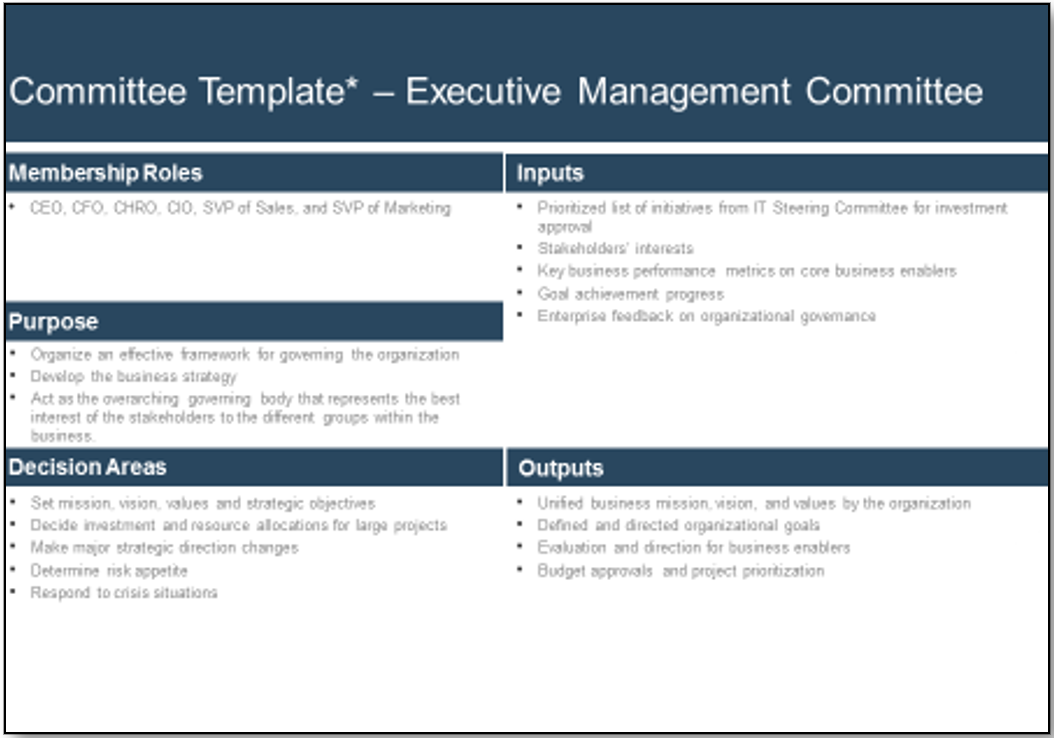
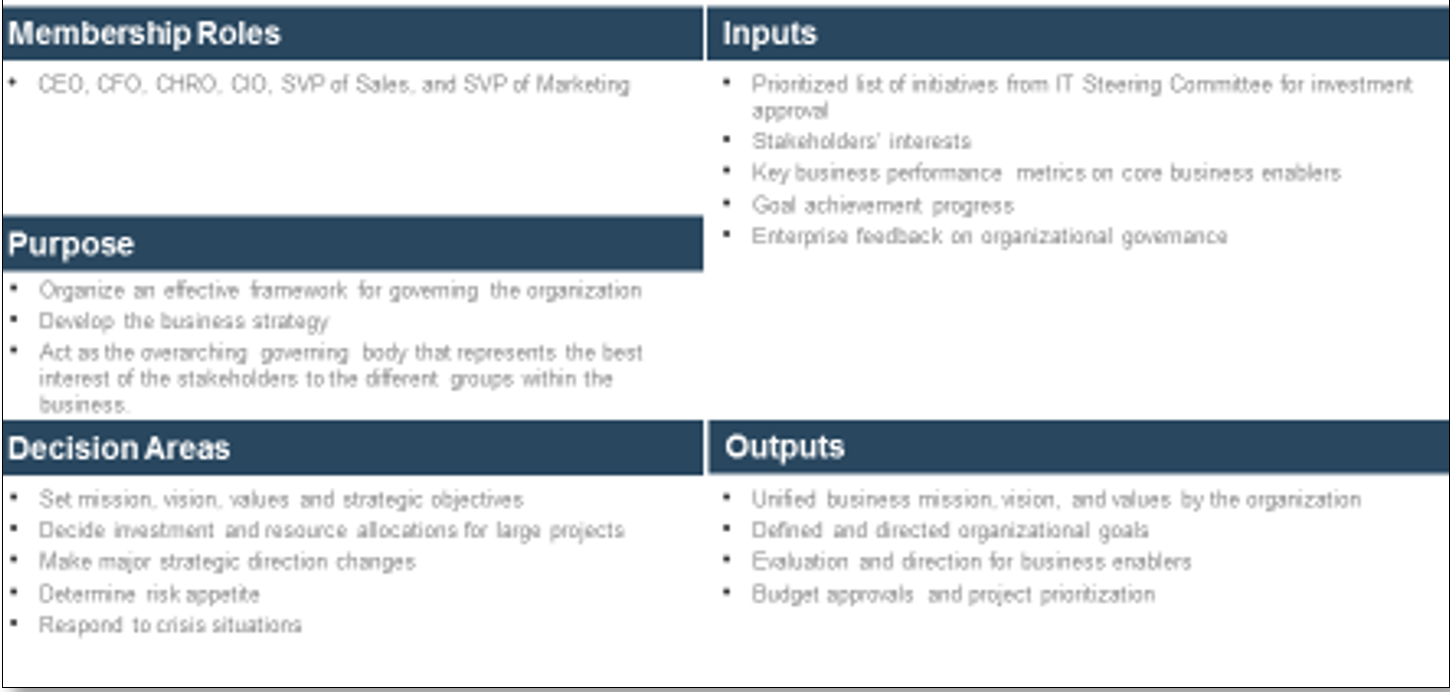
 Using the outline provided, create your own governance structure map to represent the way the governing bodies interact and feed into each other.
This is crucial to ensure that the governing structure is streamlined. It will ensure that communication occurs efficiently and that there are no barriers to making decisions swiftly.
Using the outline provided, create your own governance structure map to represent the way the governing bodies interact and feed into each other.
This is crucial to ensure that the governing structure is streamlined. It will ensure that communication occurs efficiently and that there are no barriers to making decisions swiftly.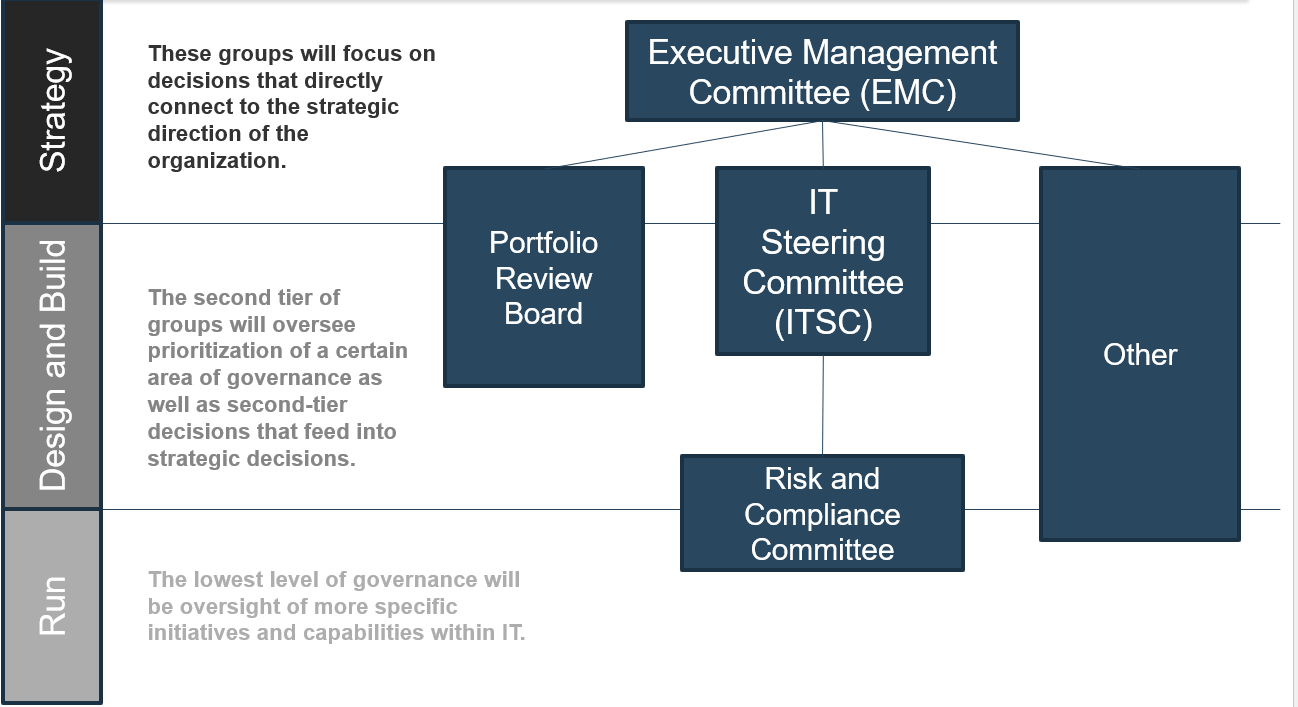
 Note: Refer to the example guidelines in the
Note: Refer to the example guidelines in the 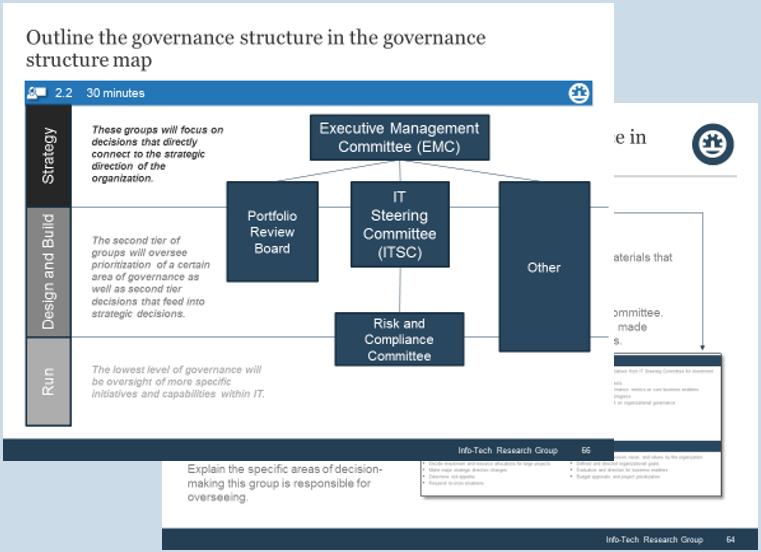

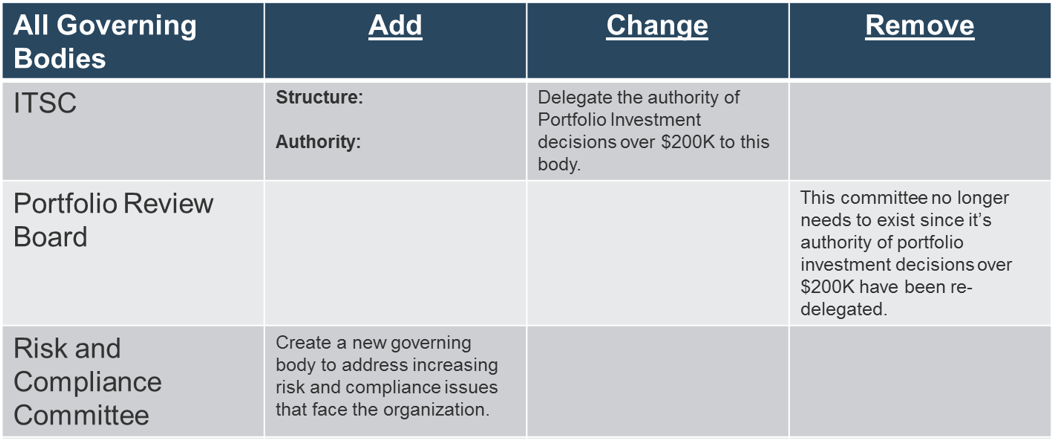
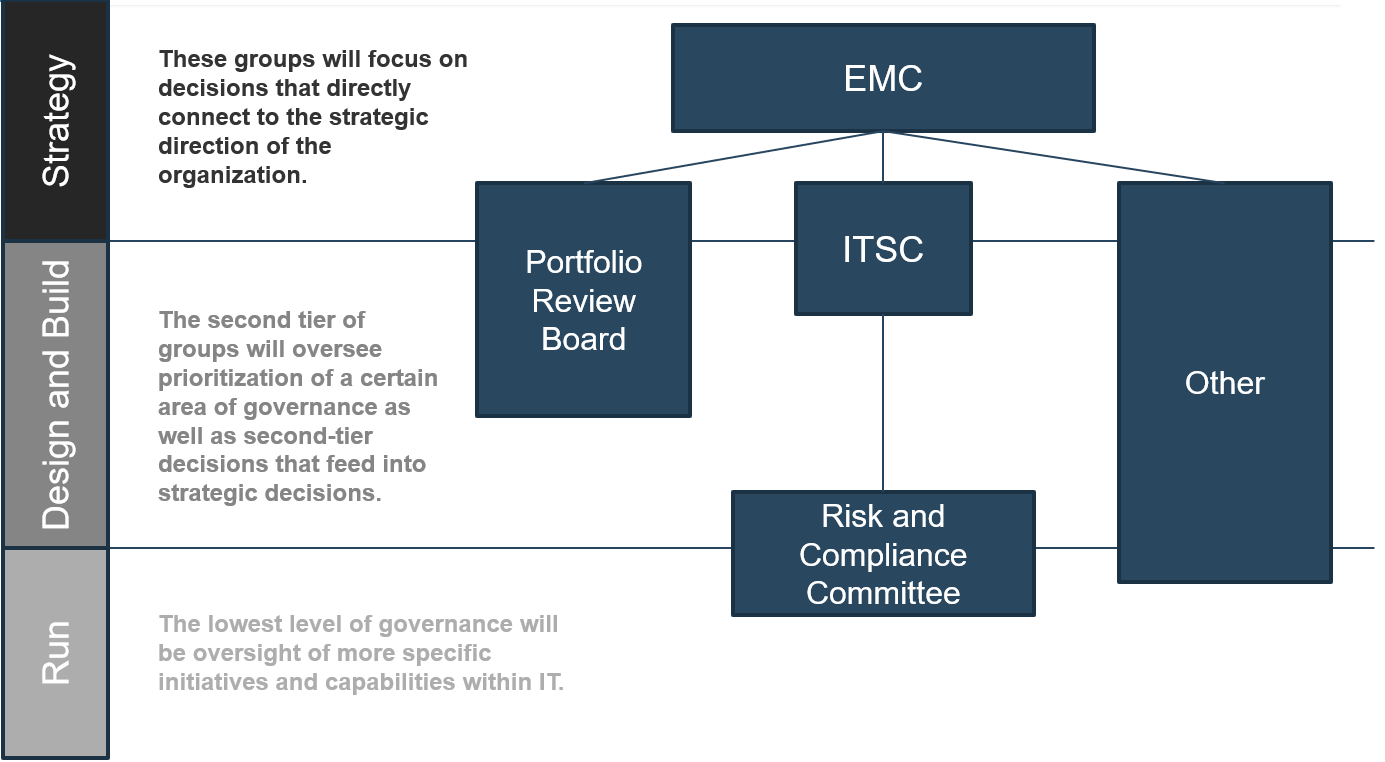
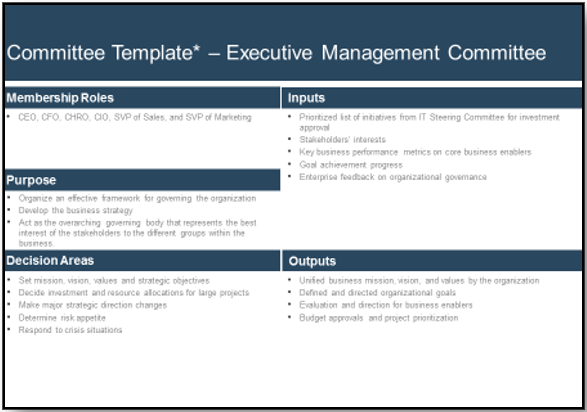




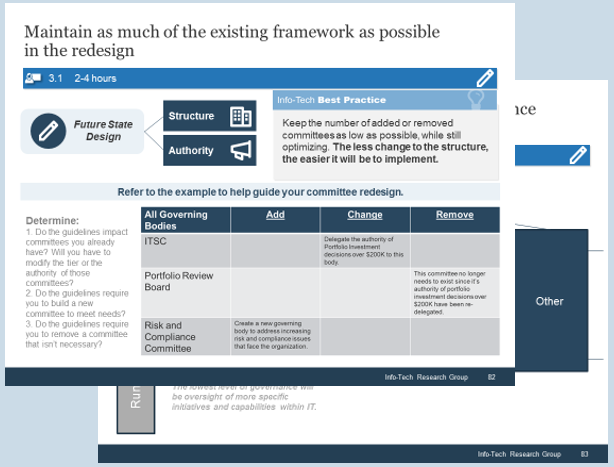
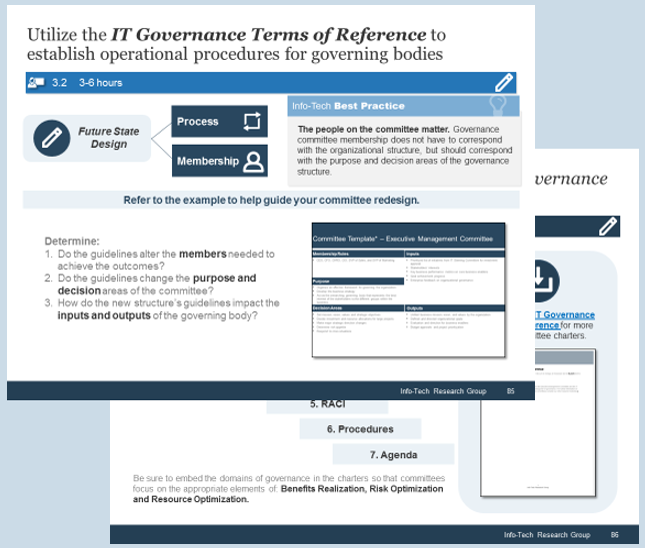
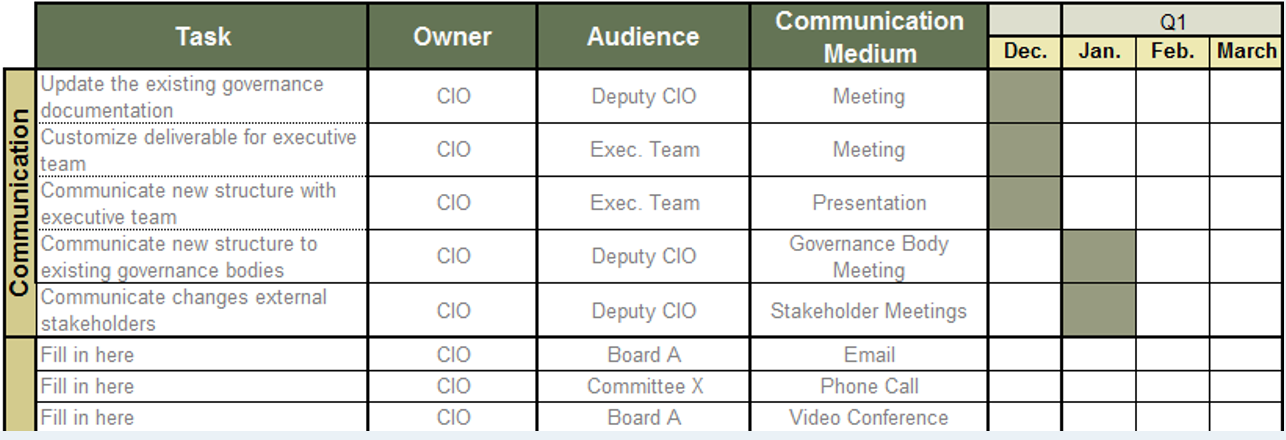

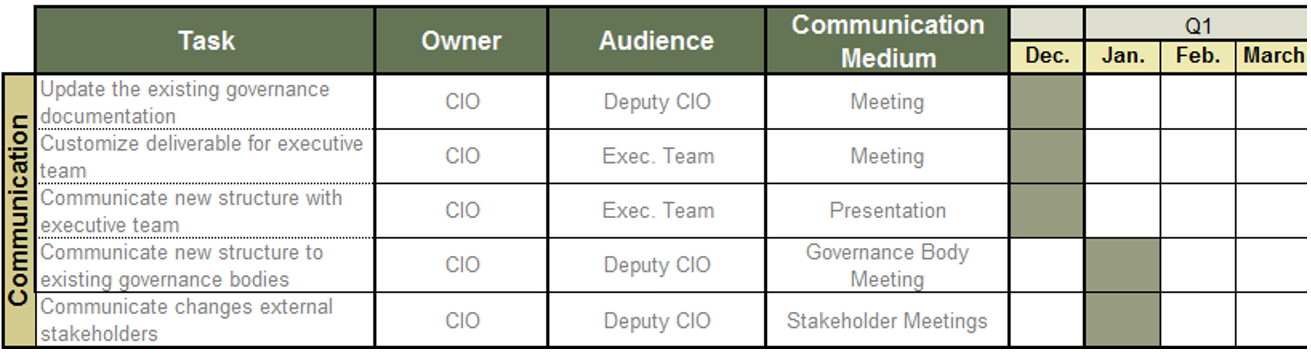



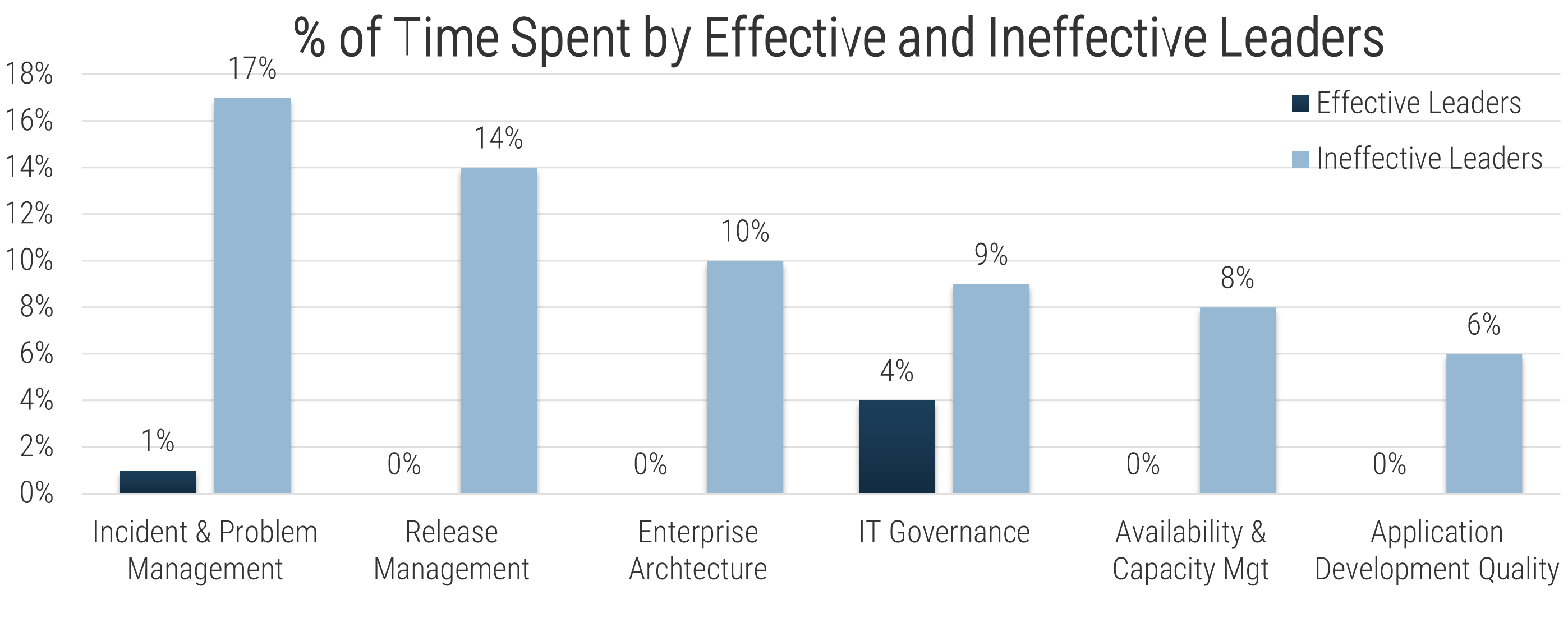






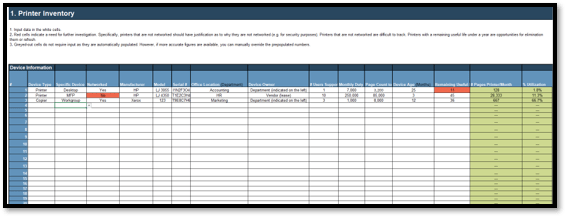
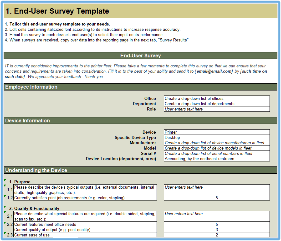

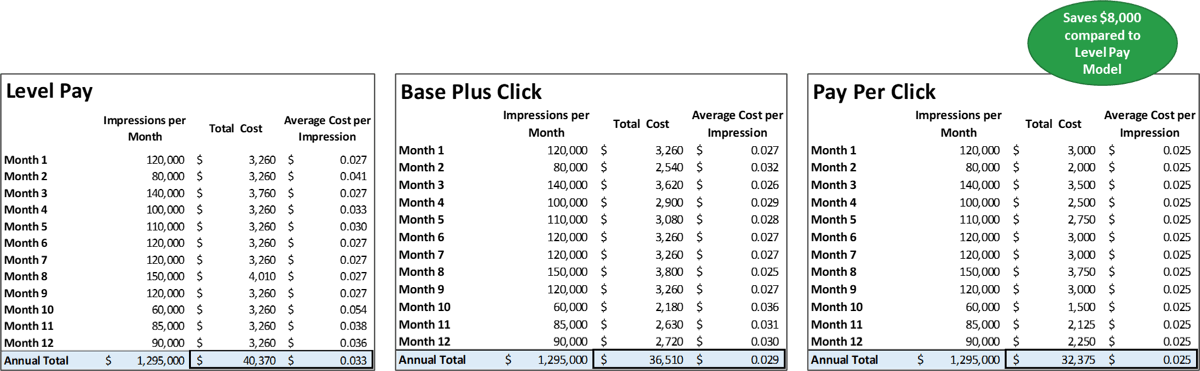
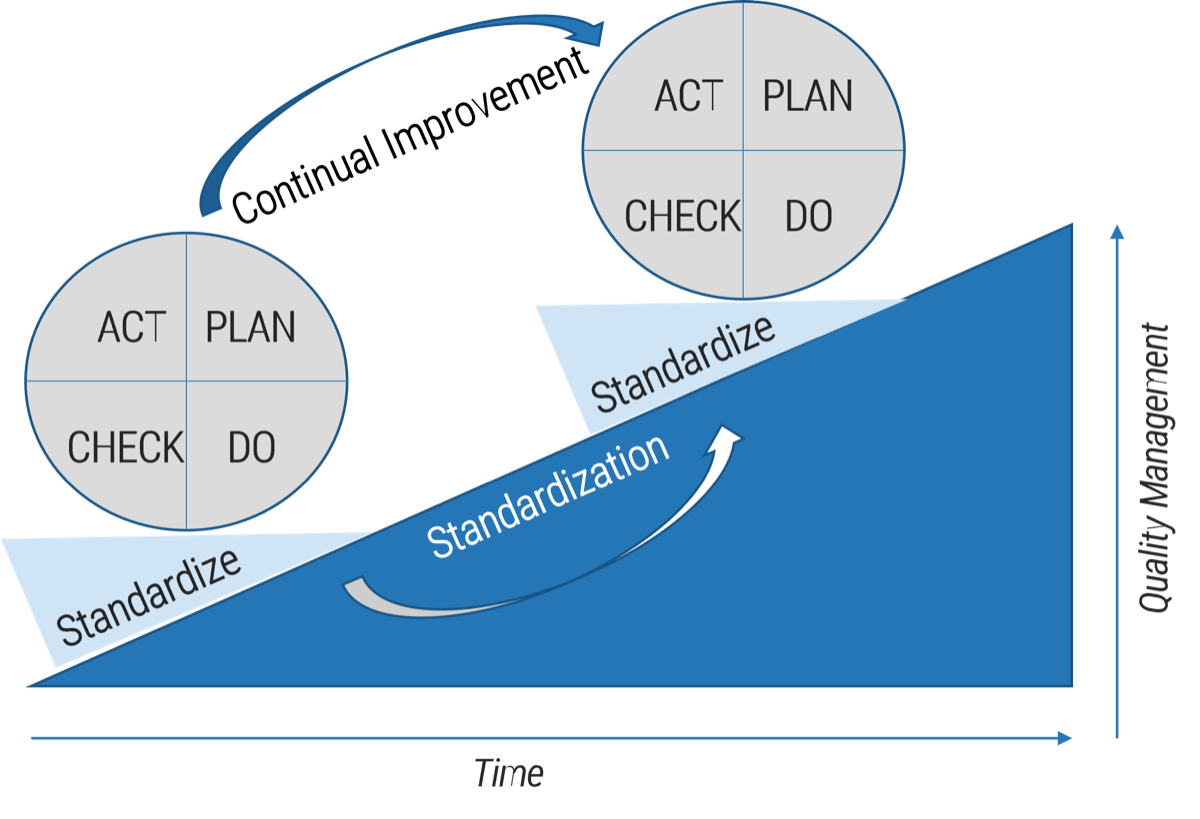







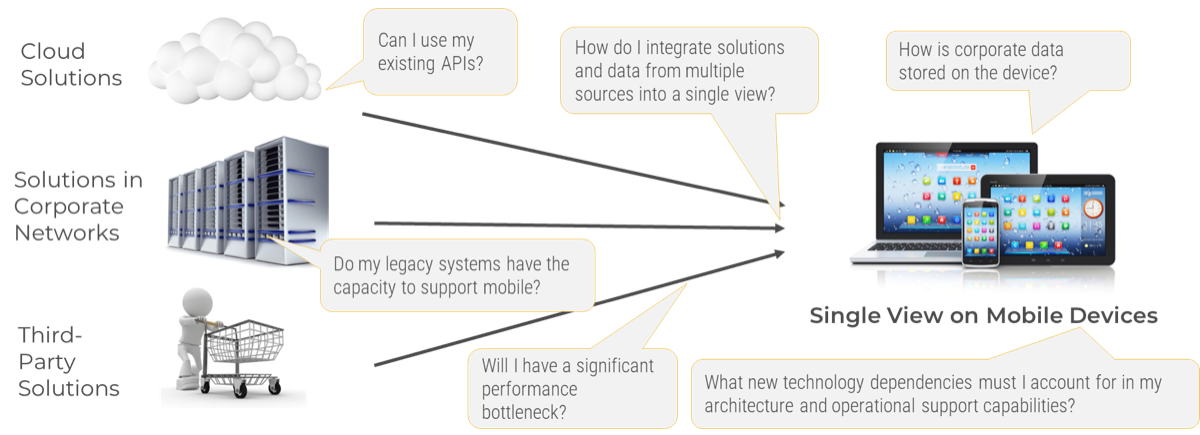
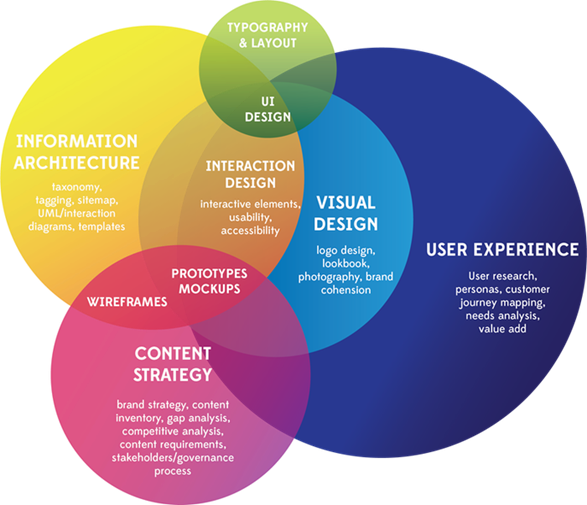

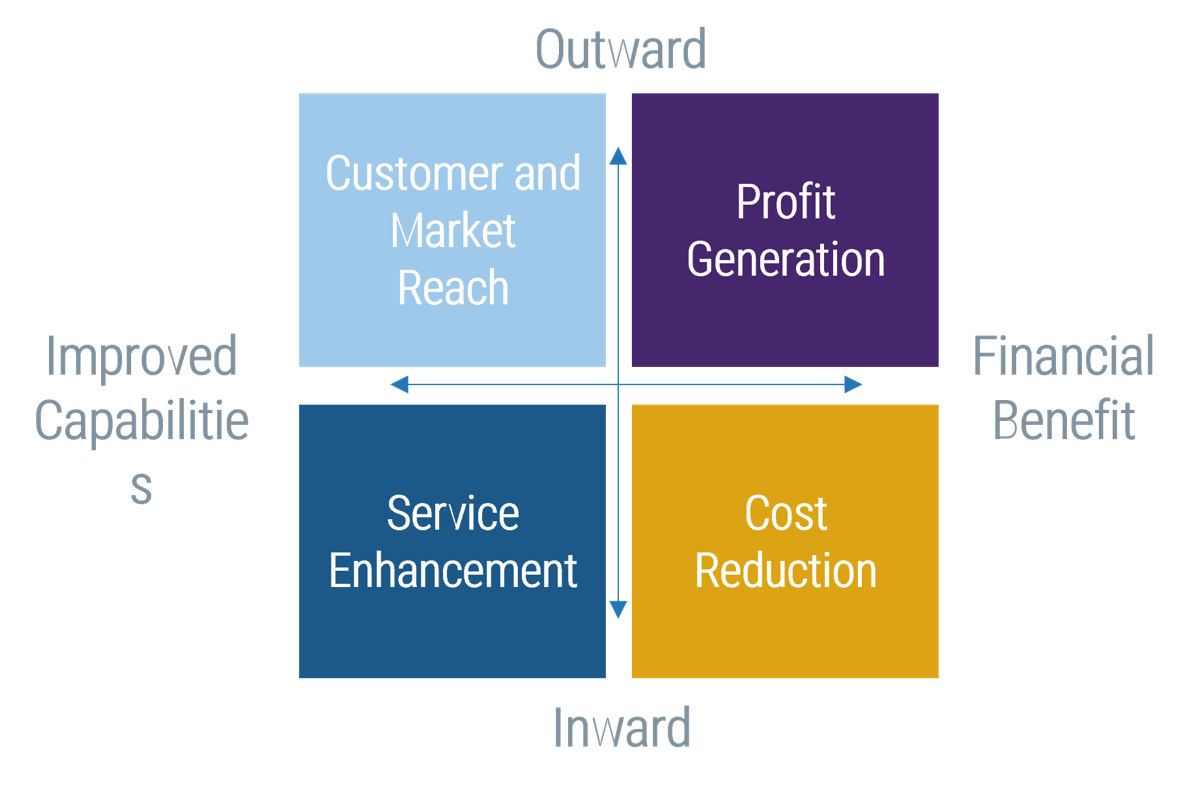
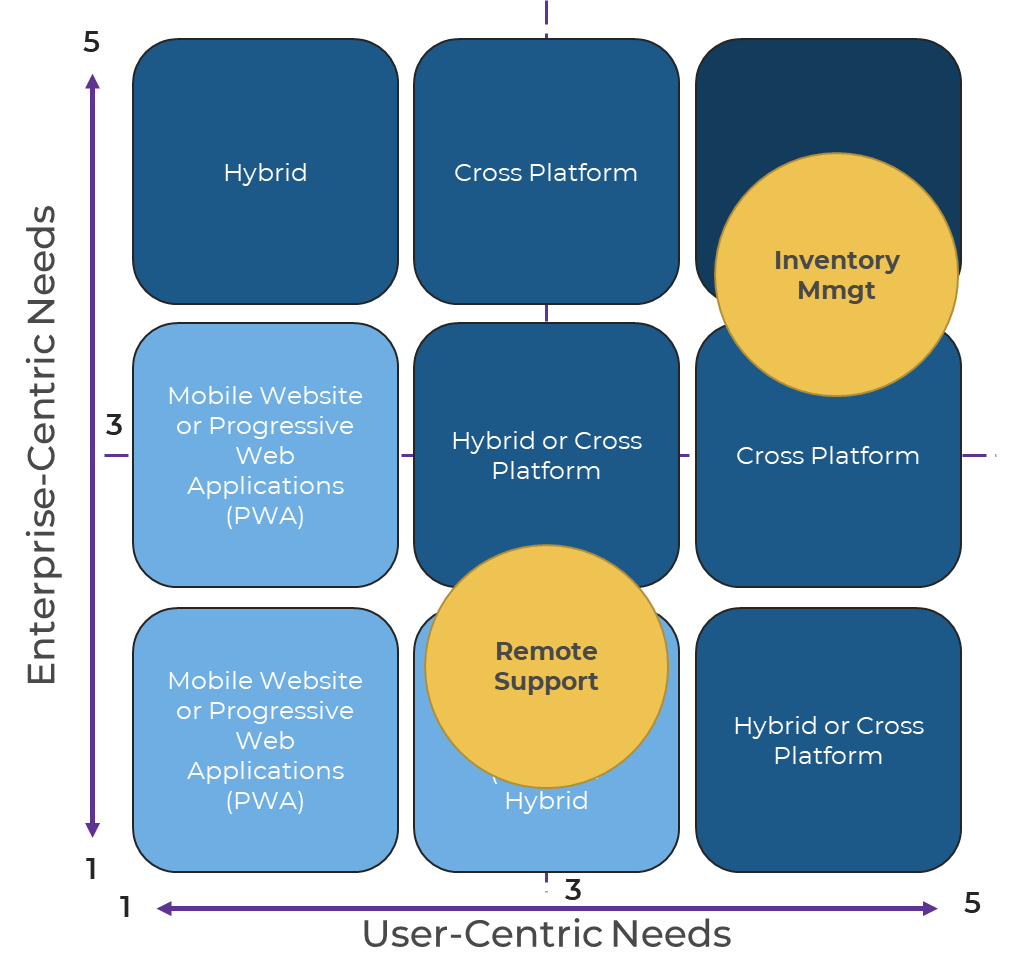
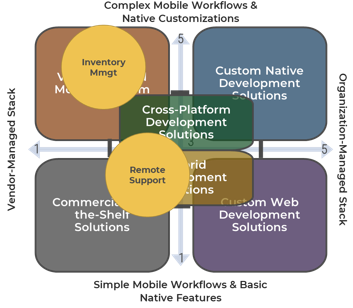
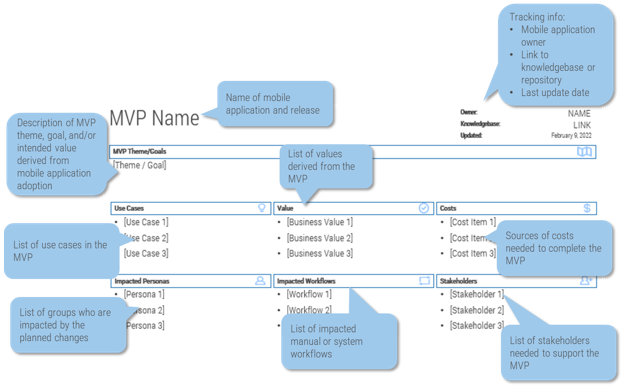
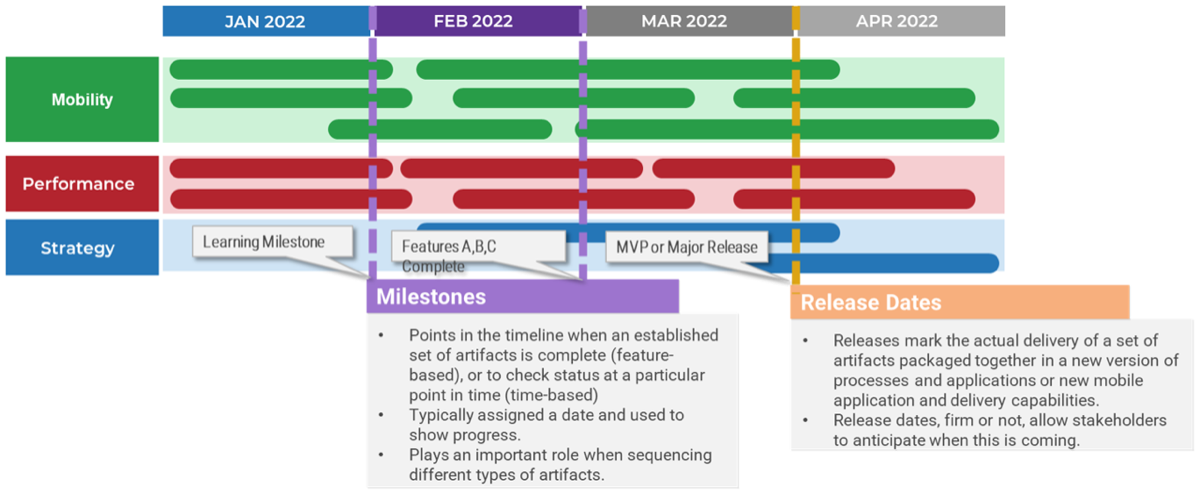
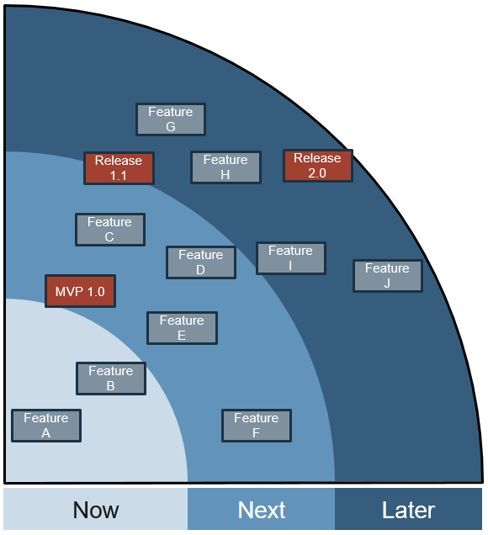

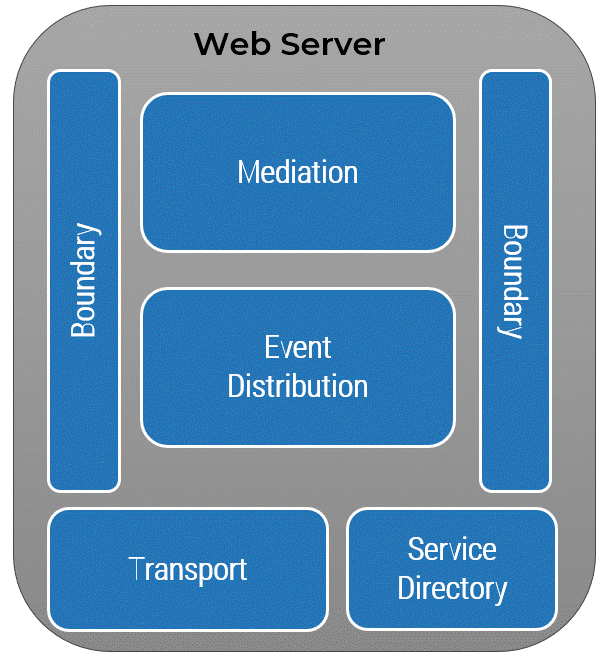




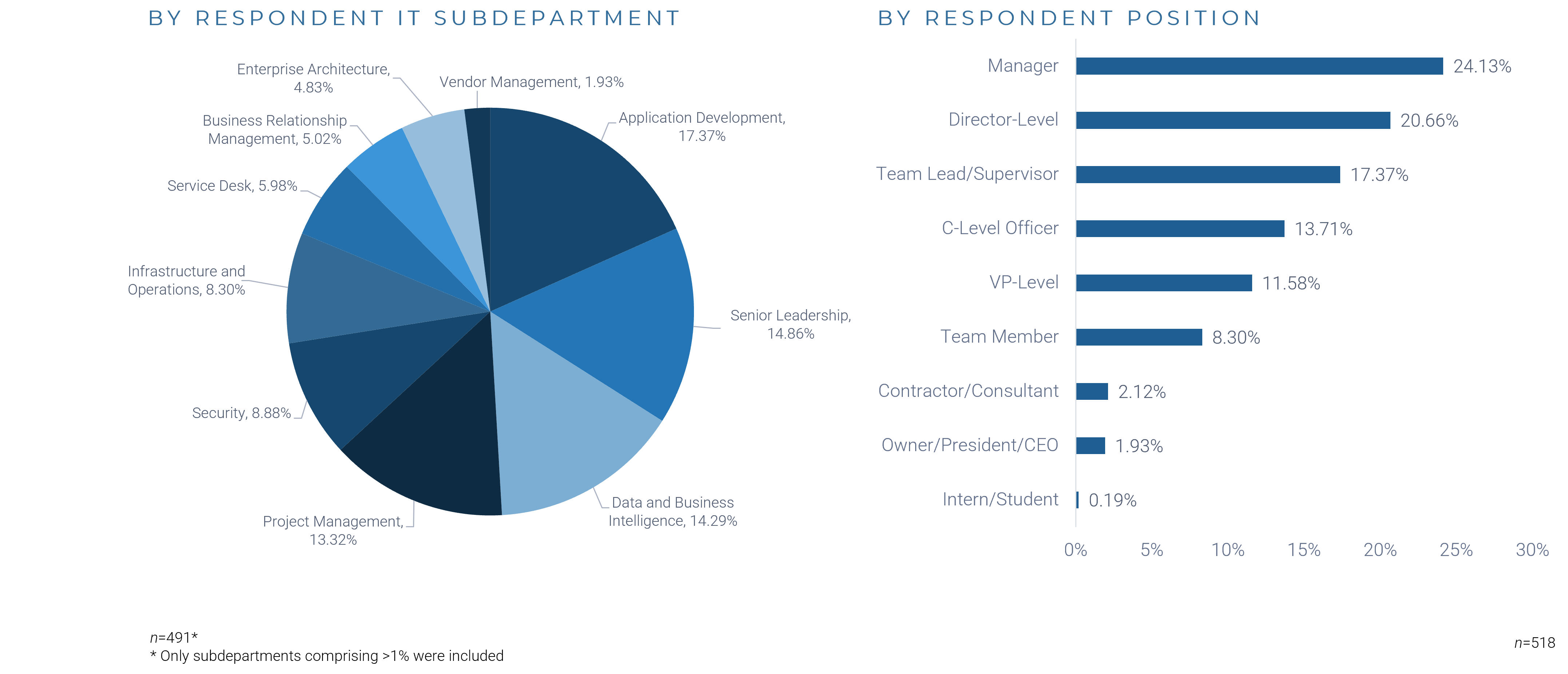

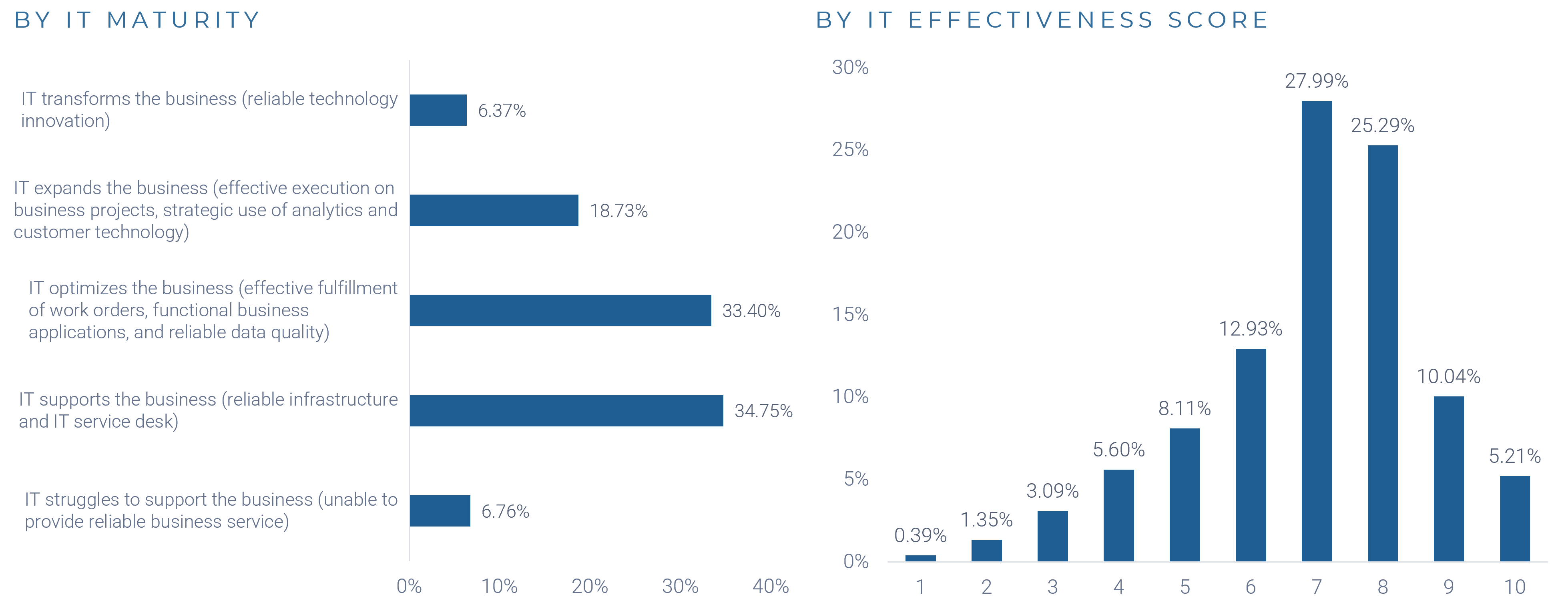
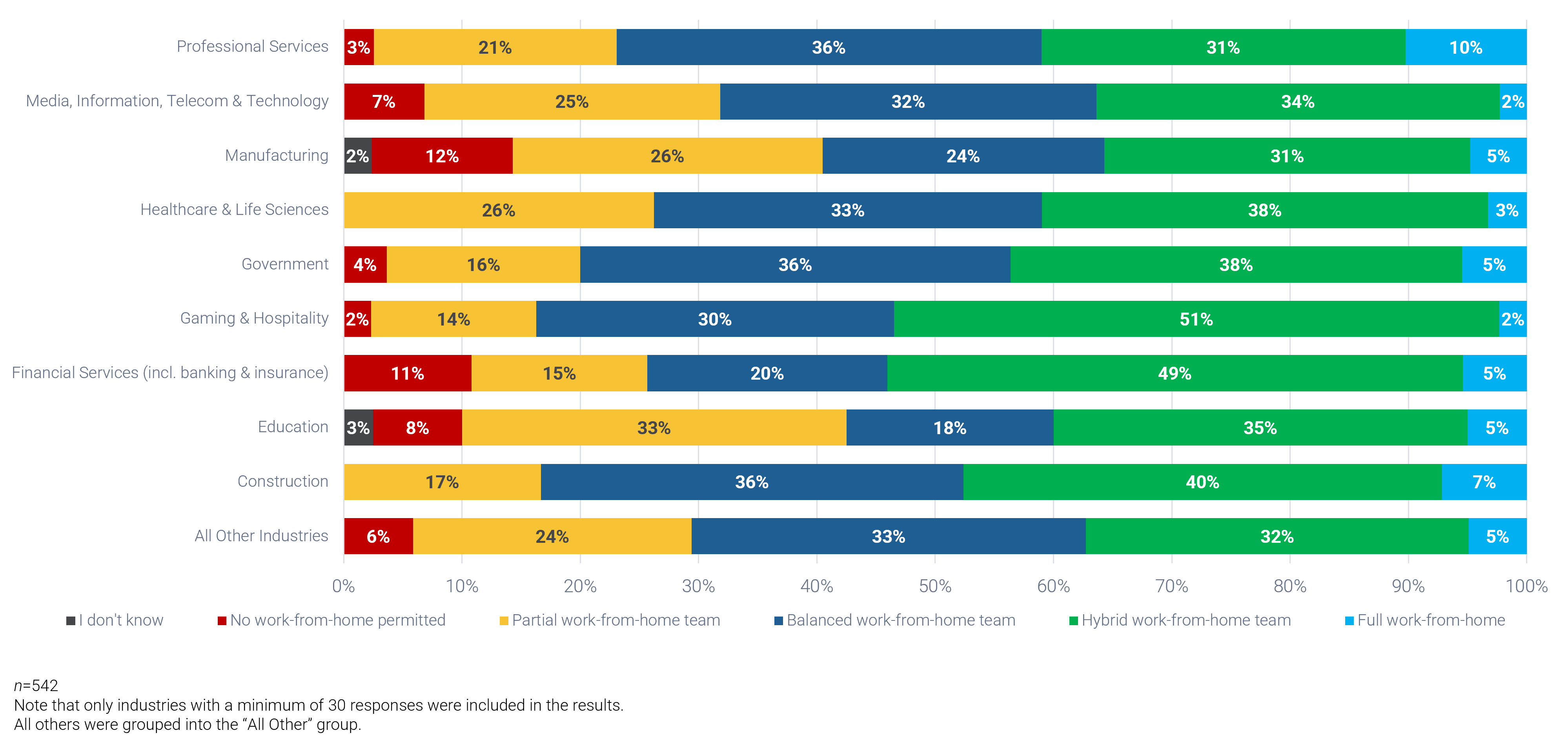


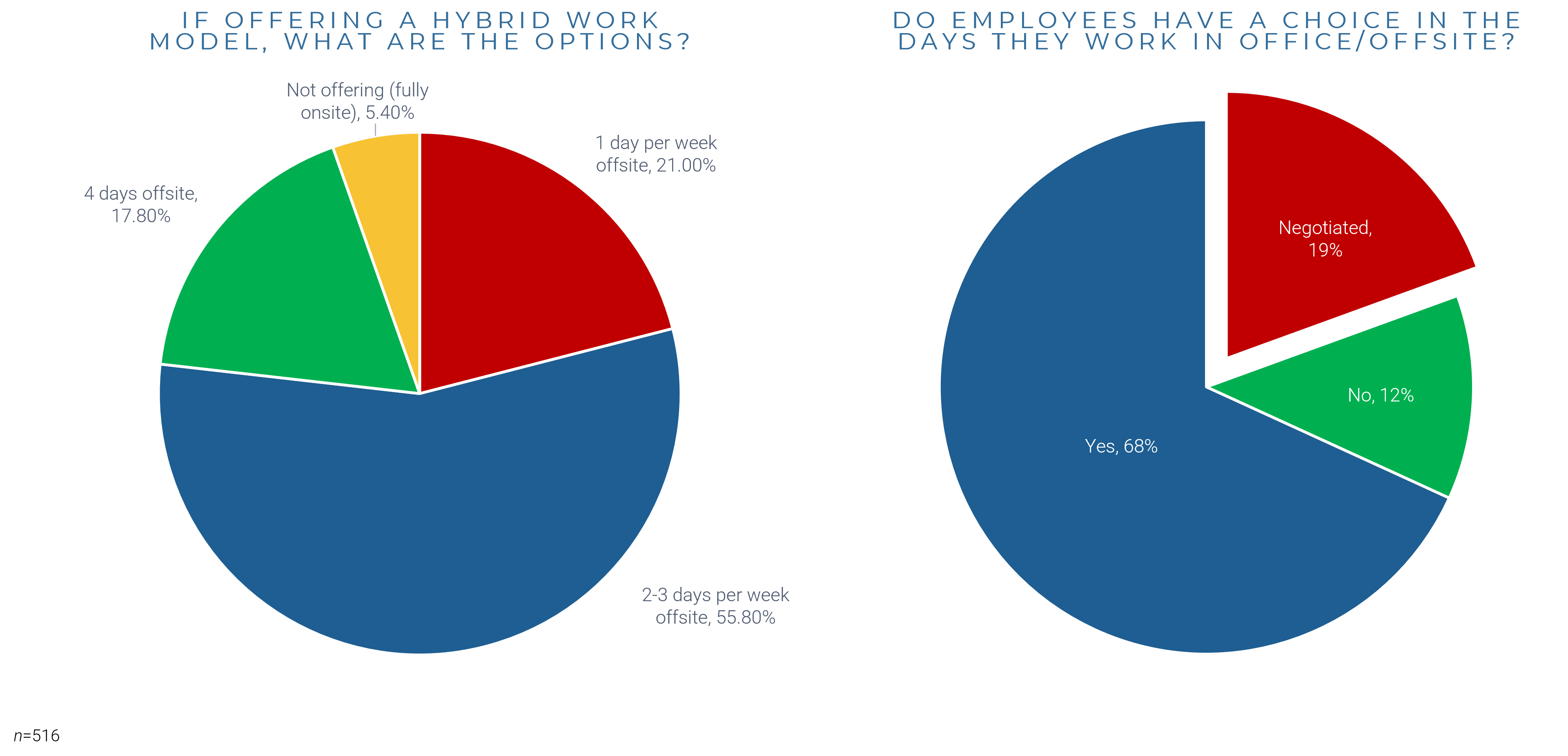
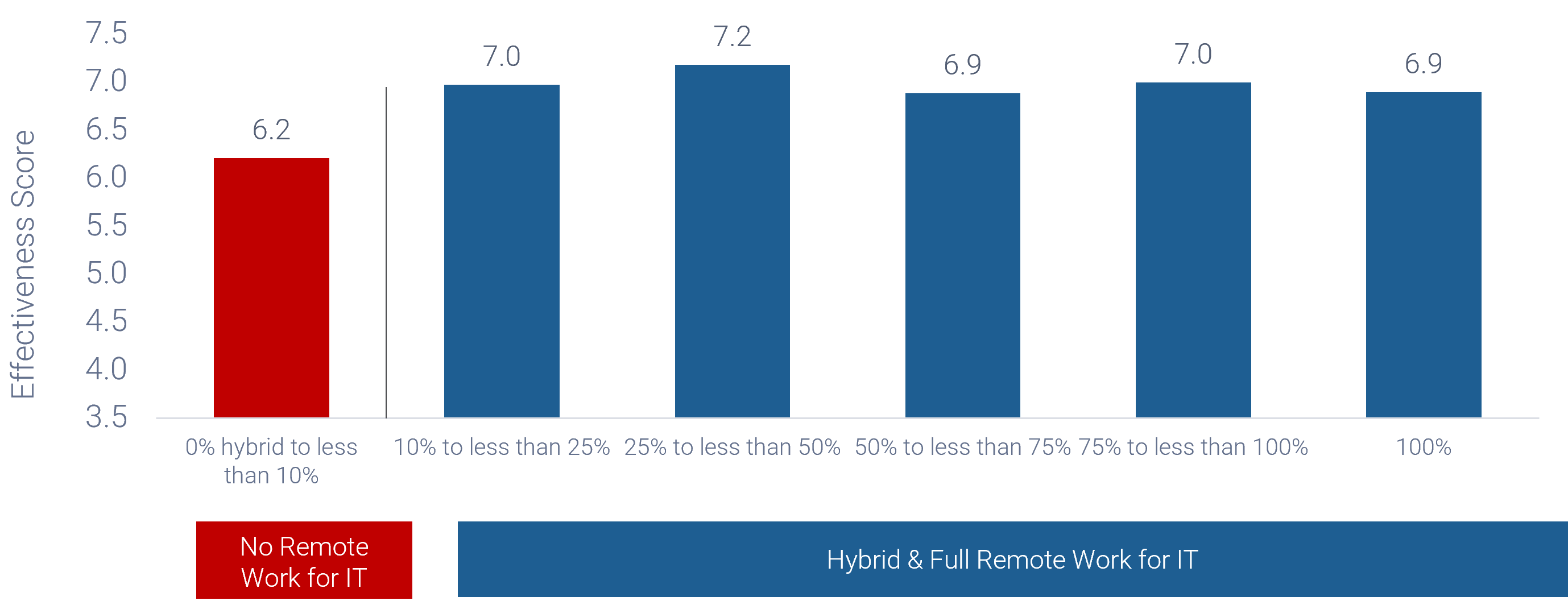
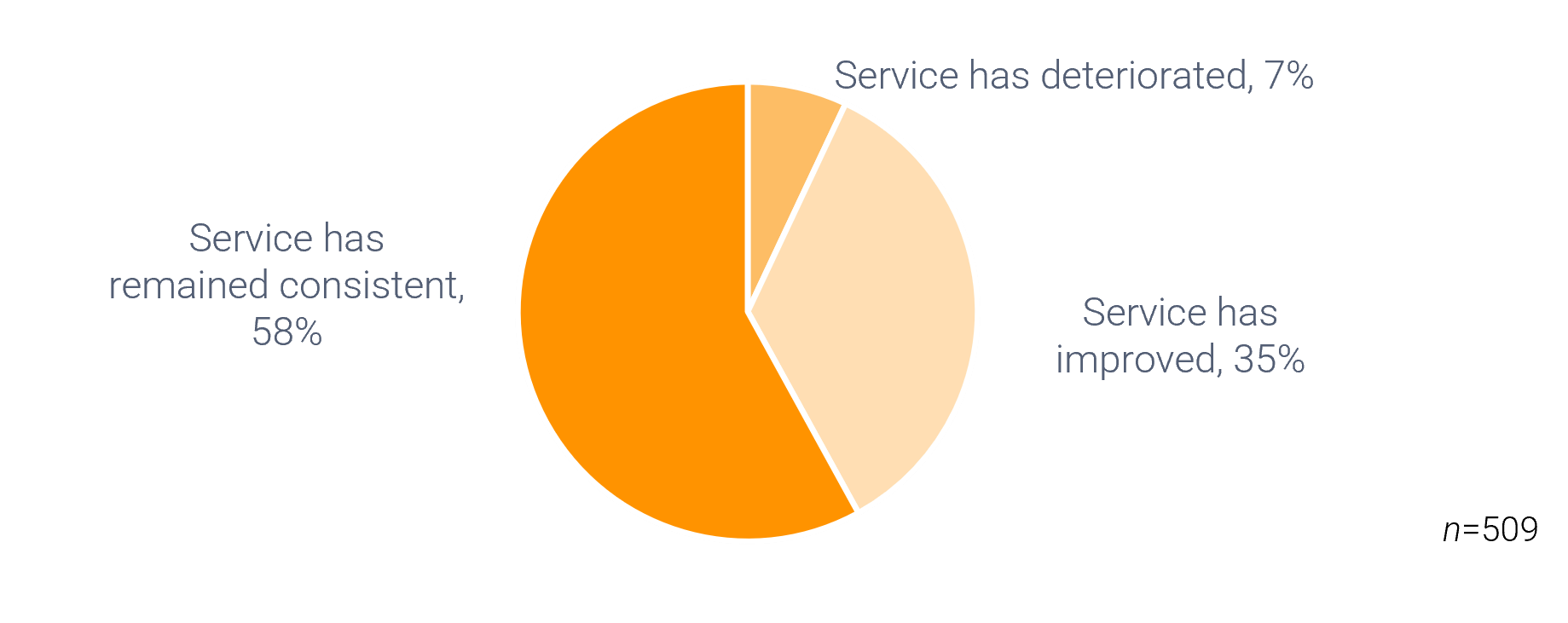
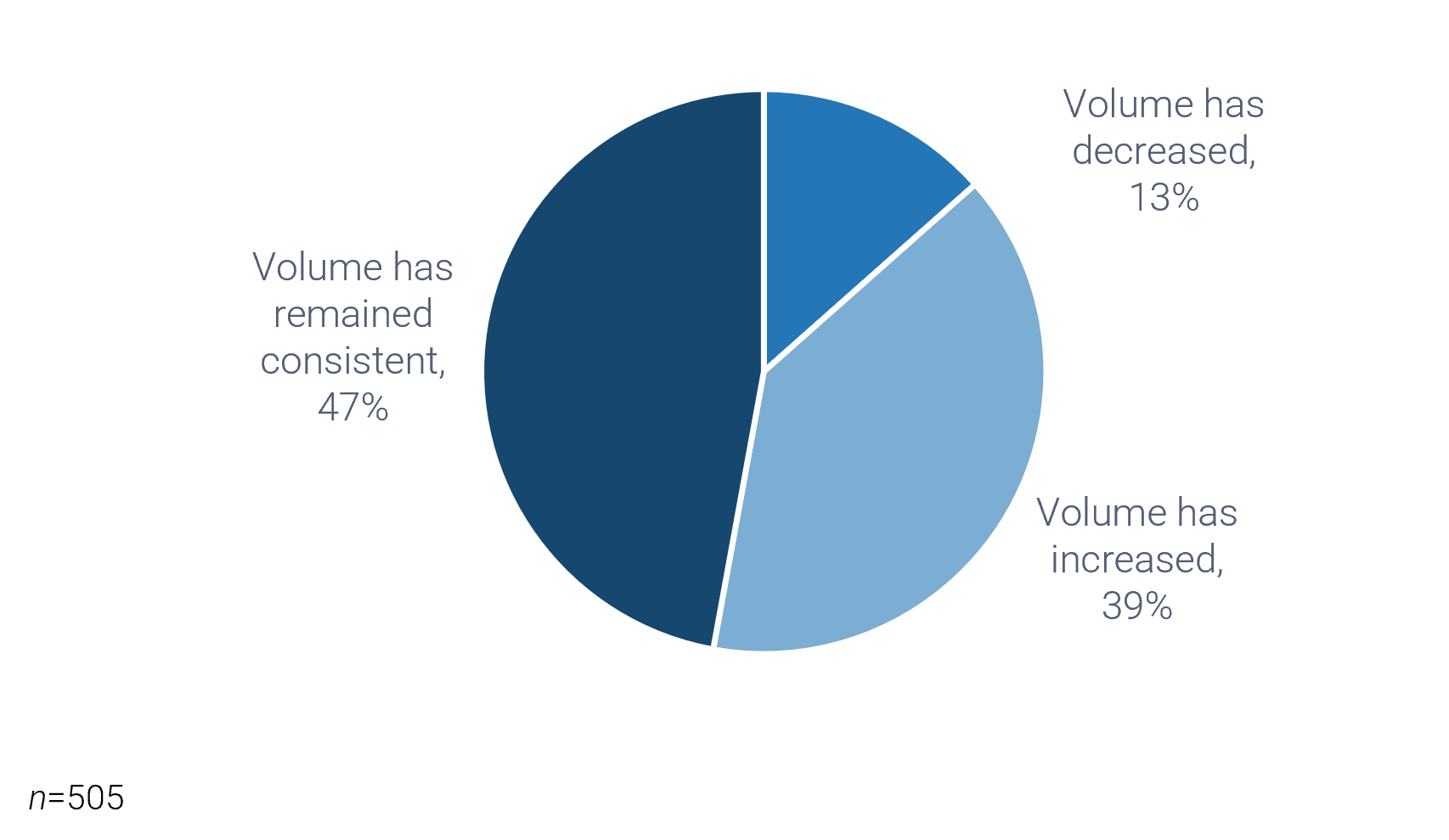
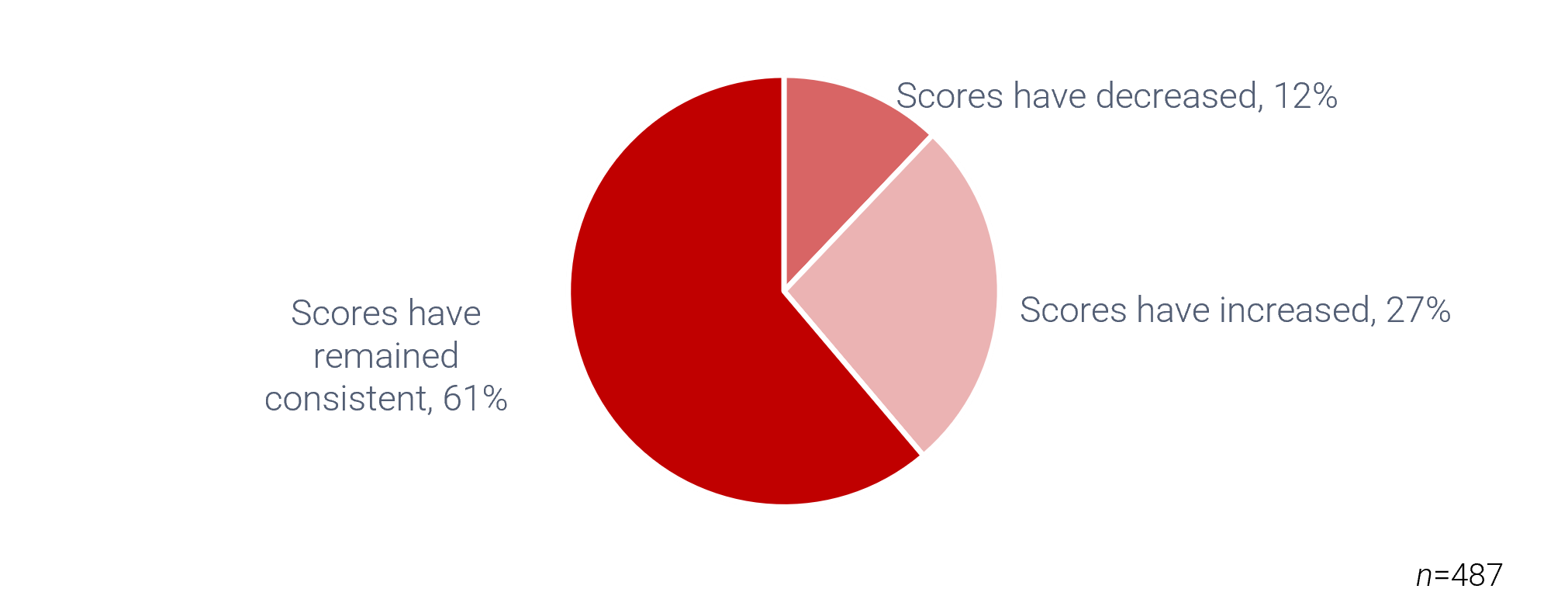
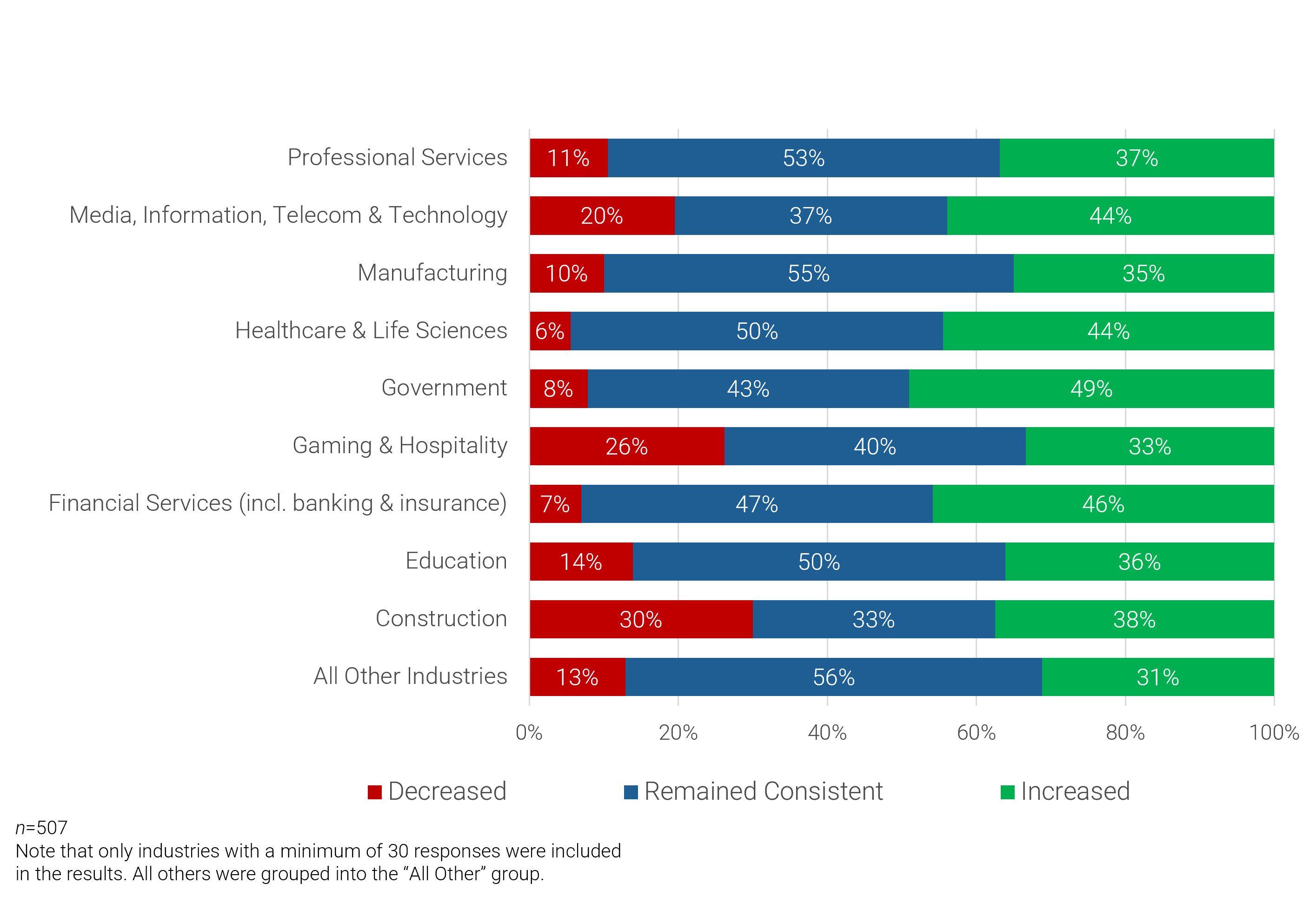
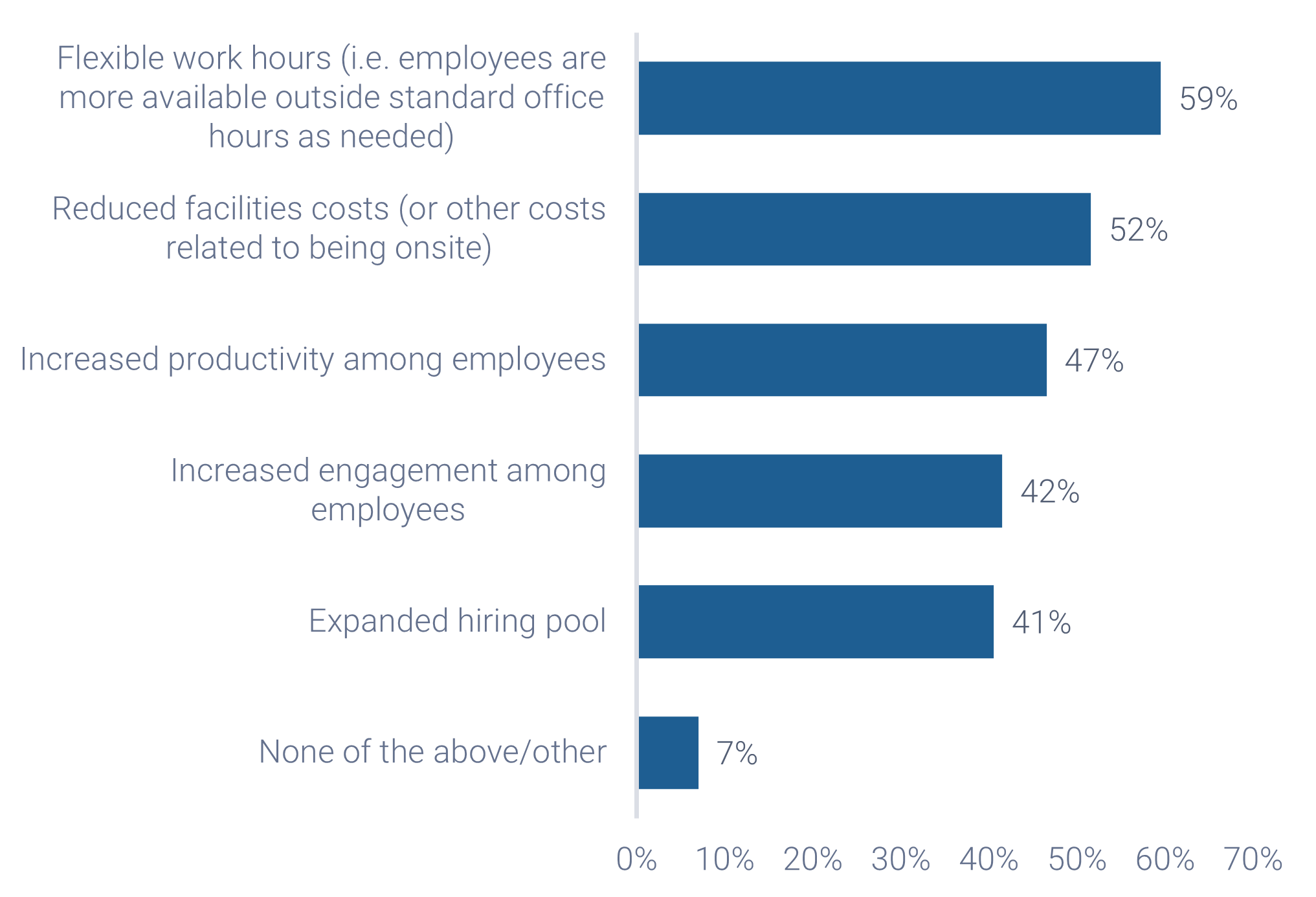
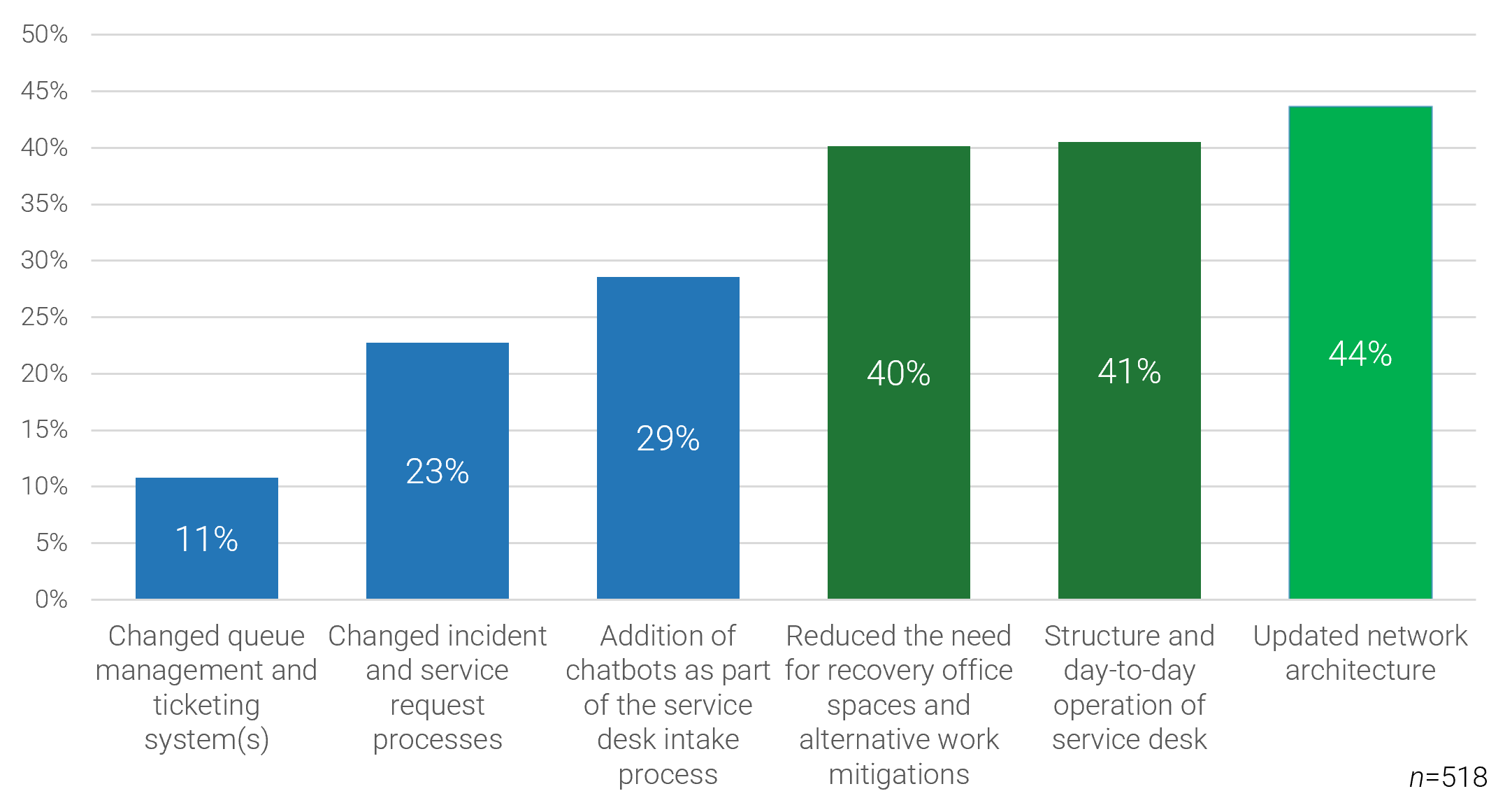
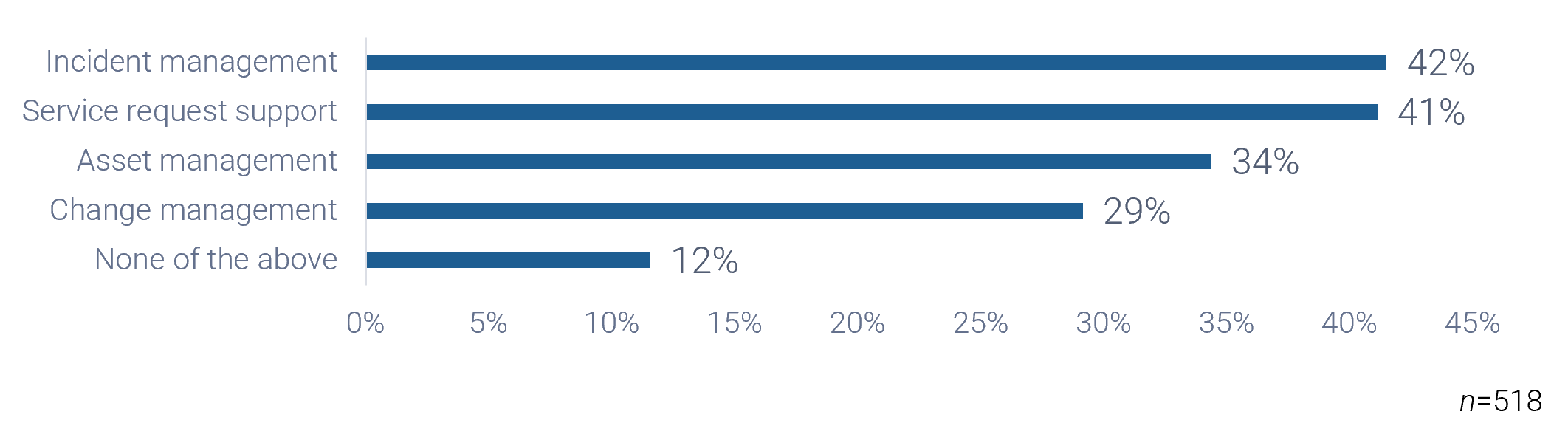
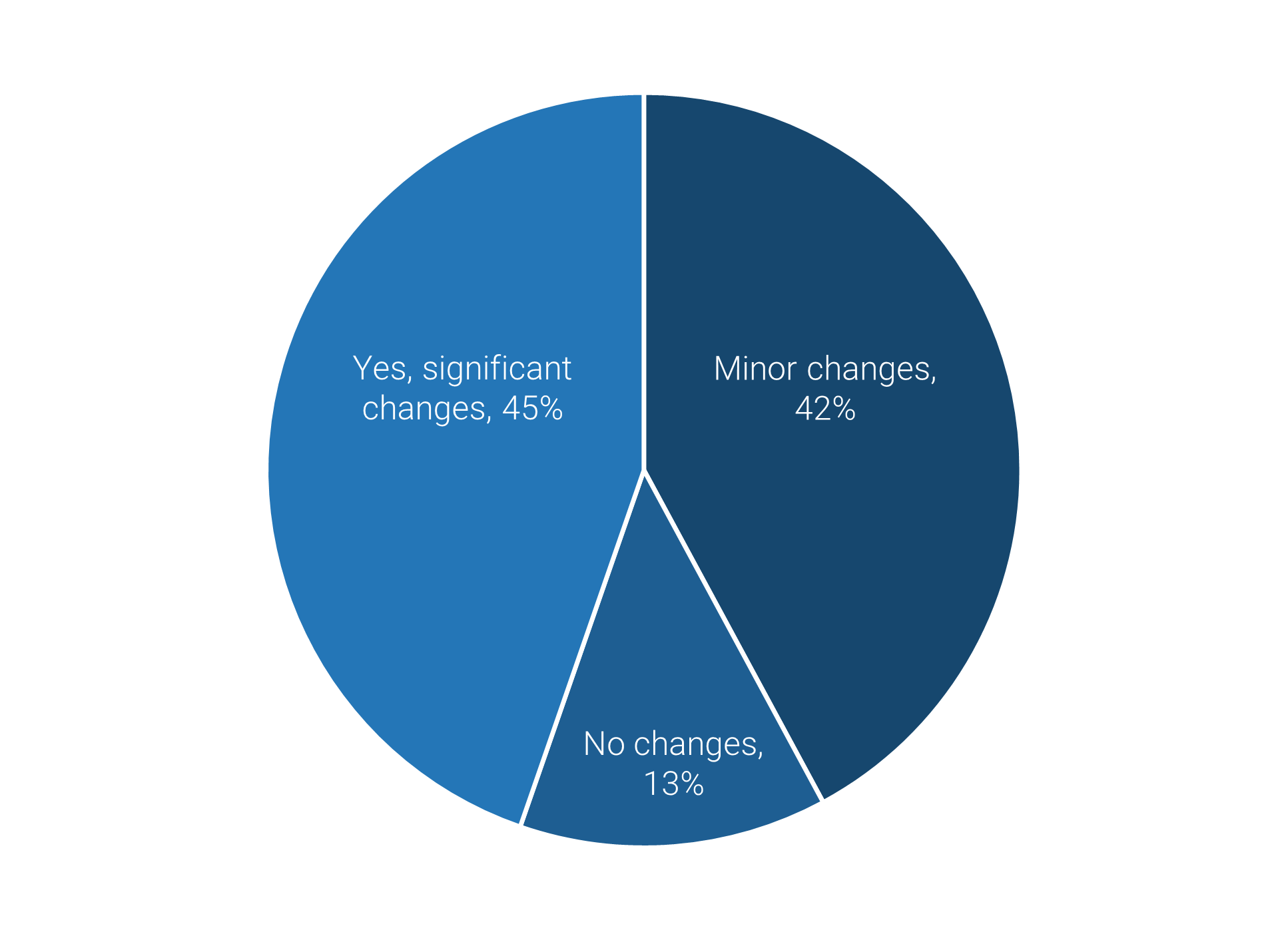
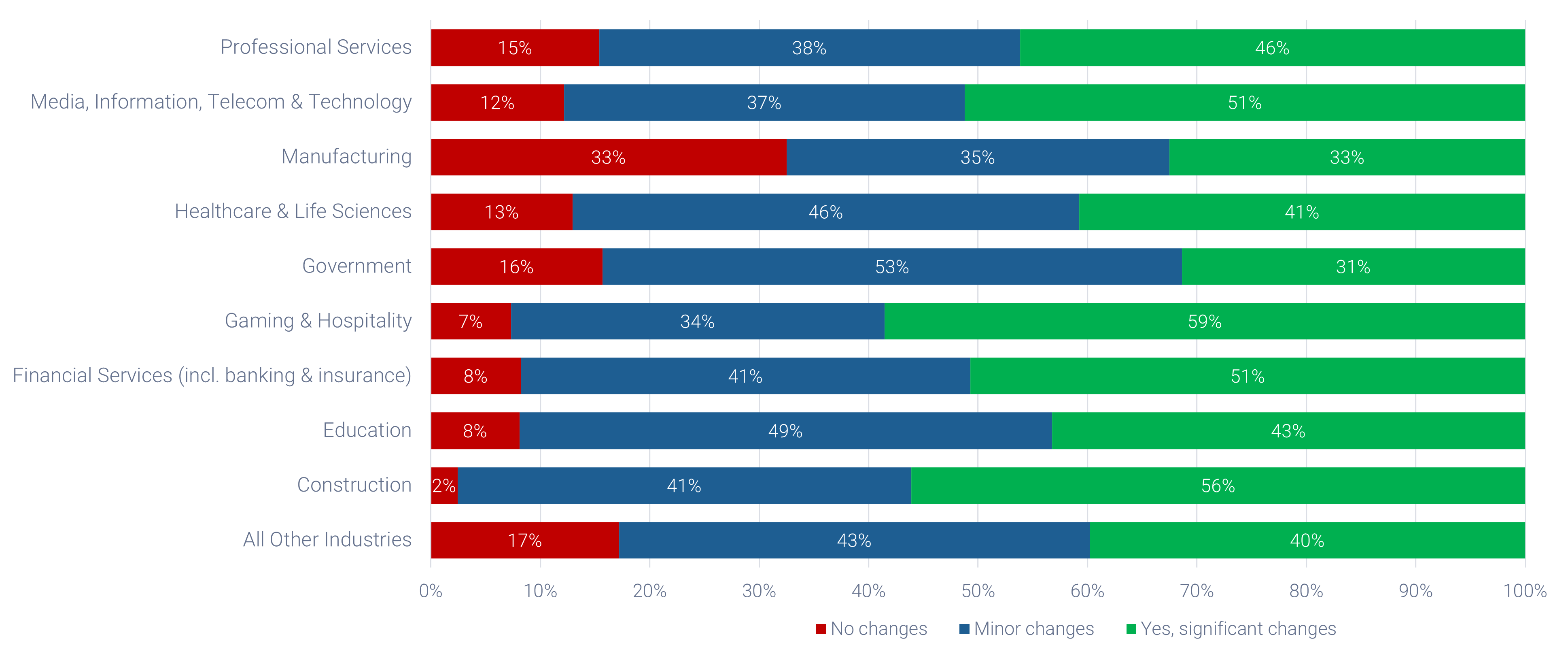
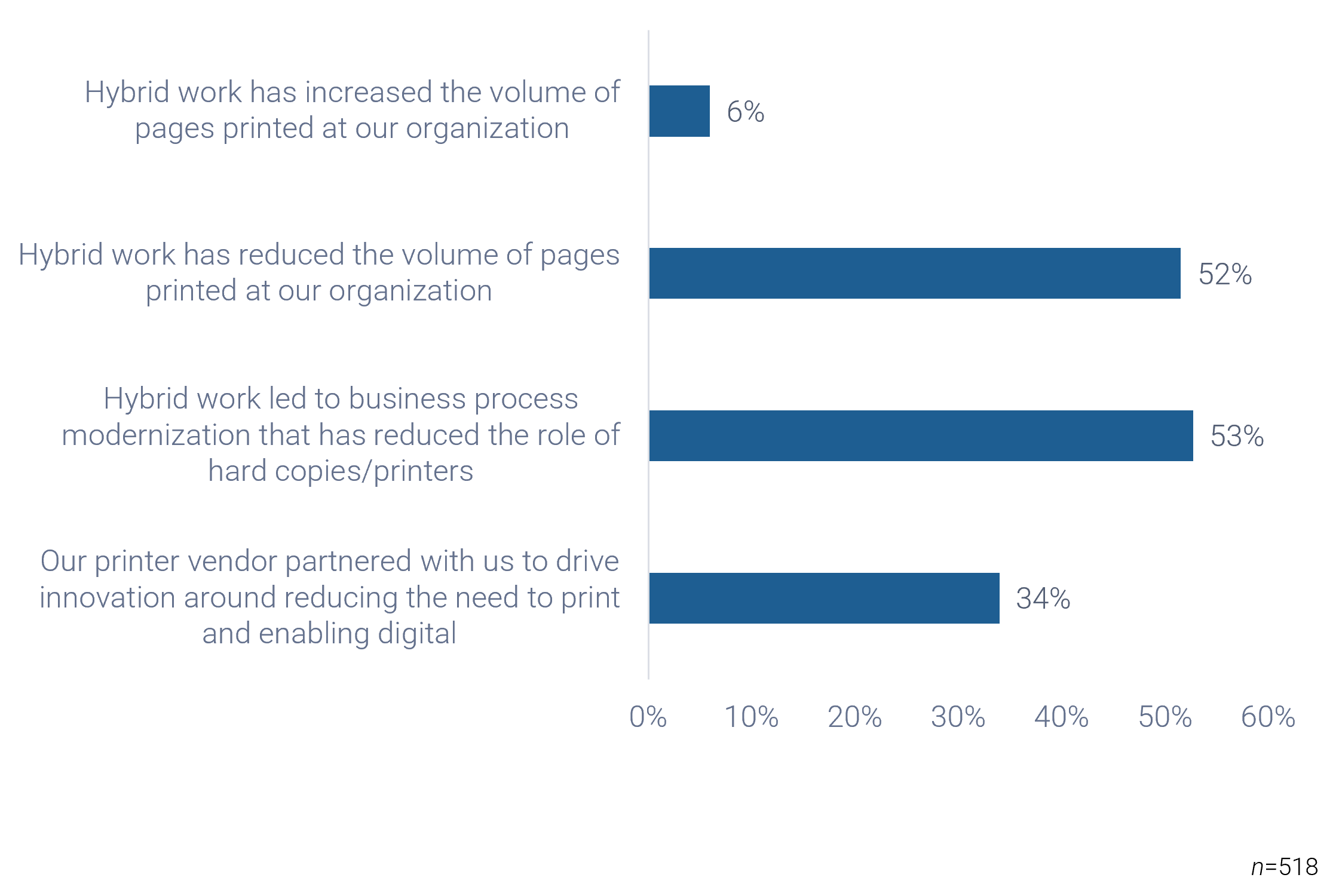
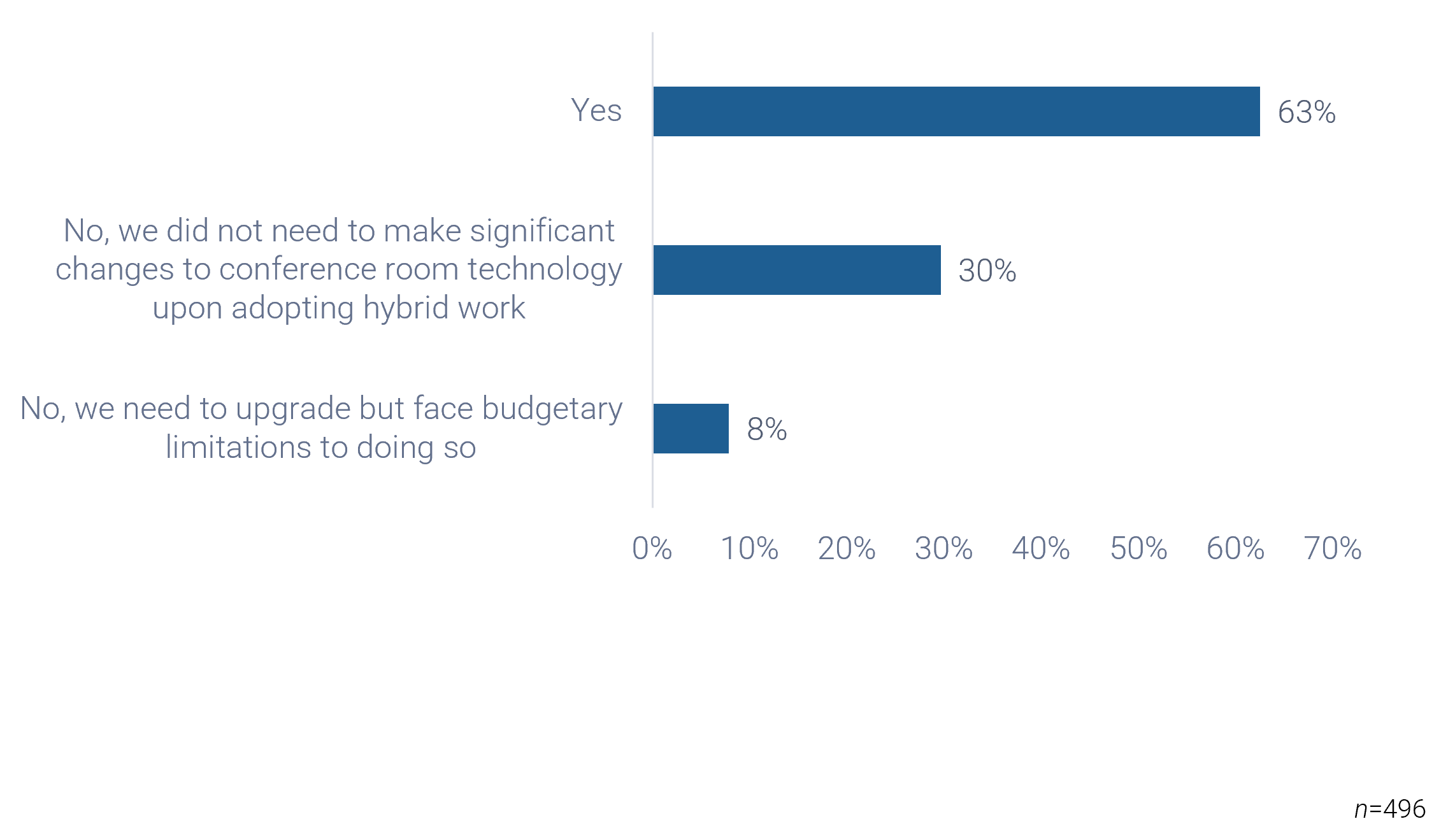
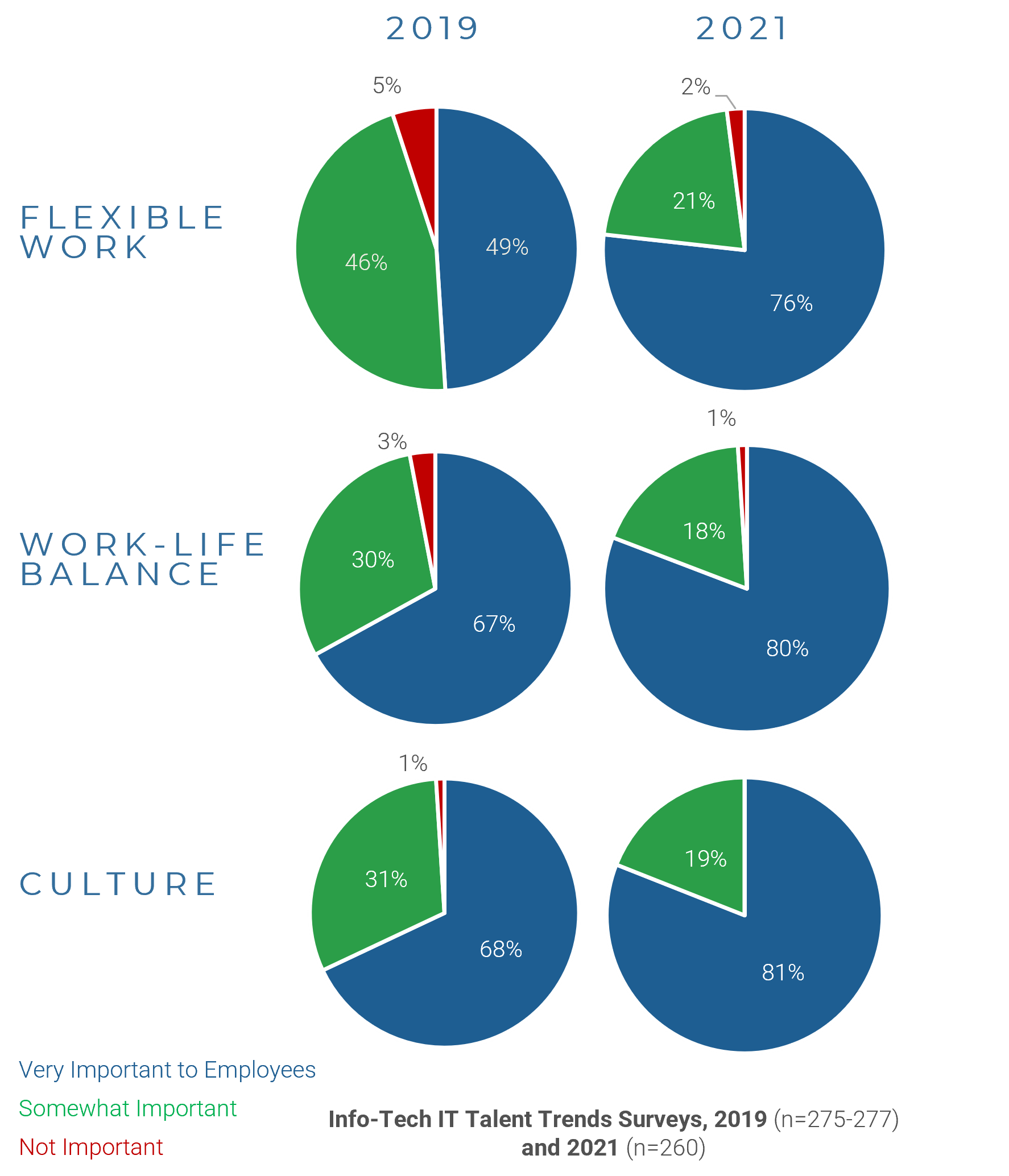
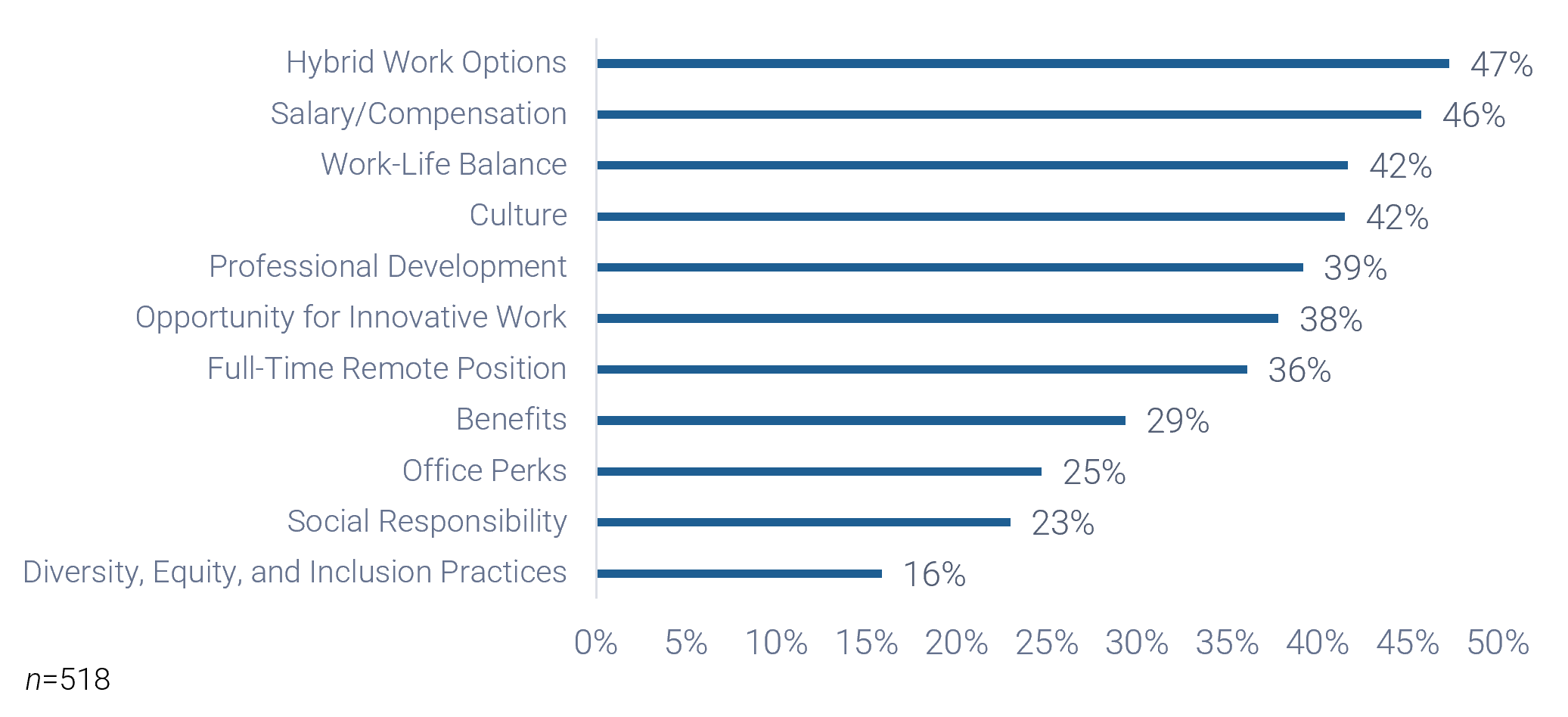
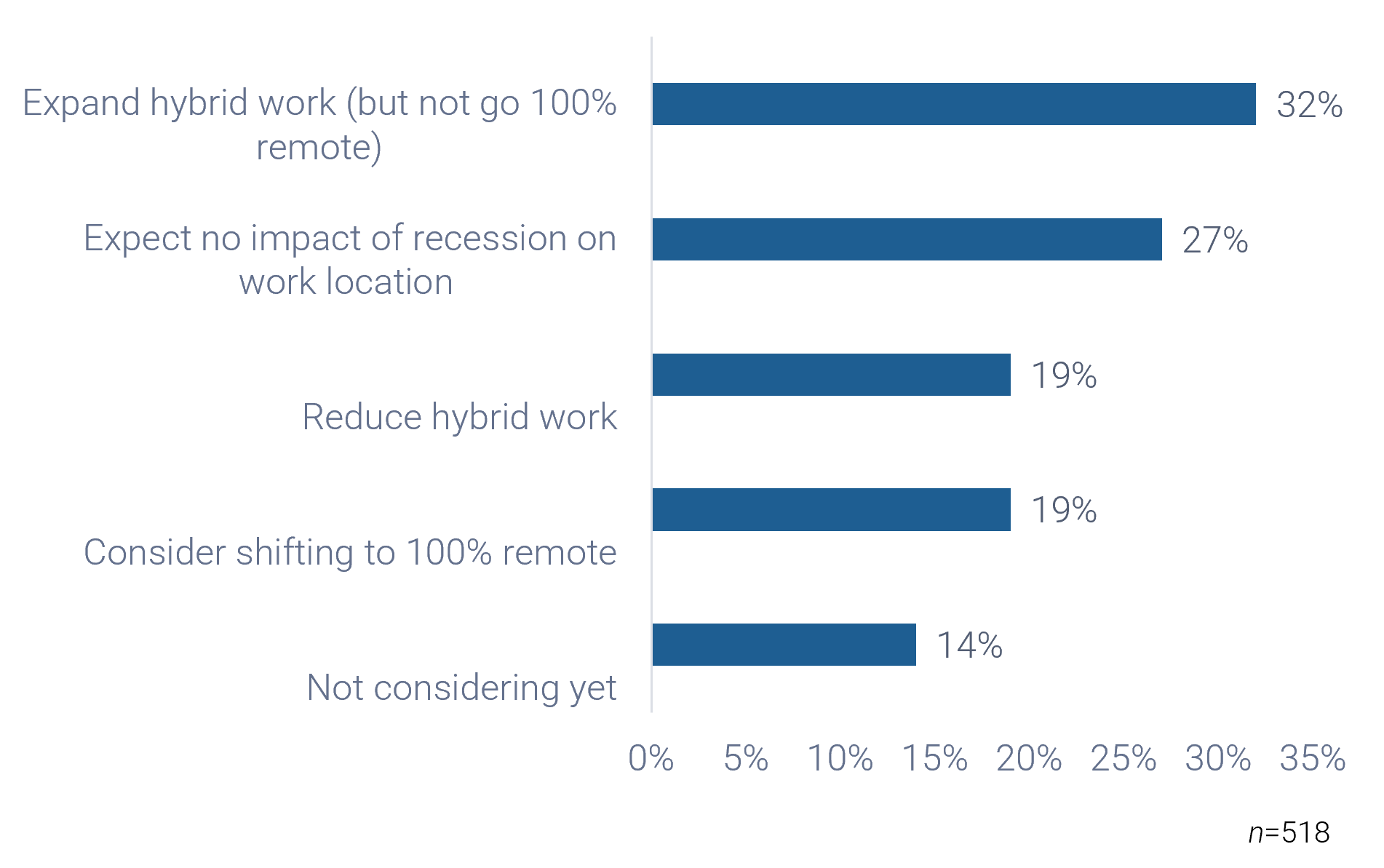
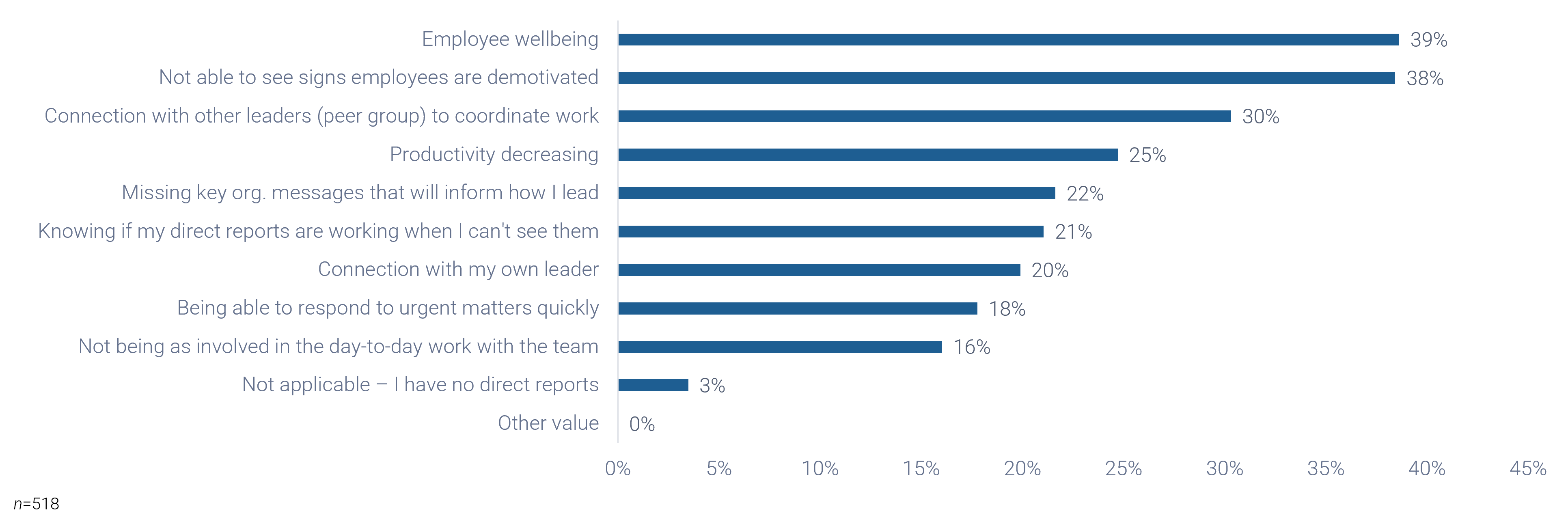
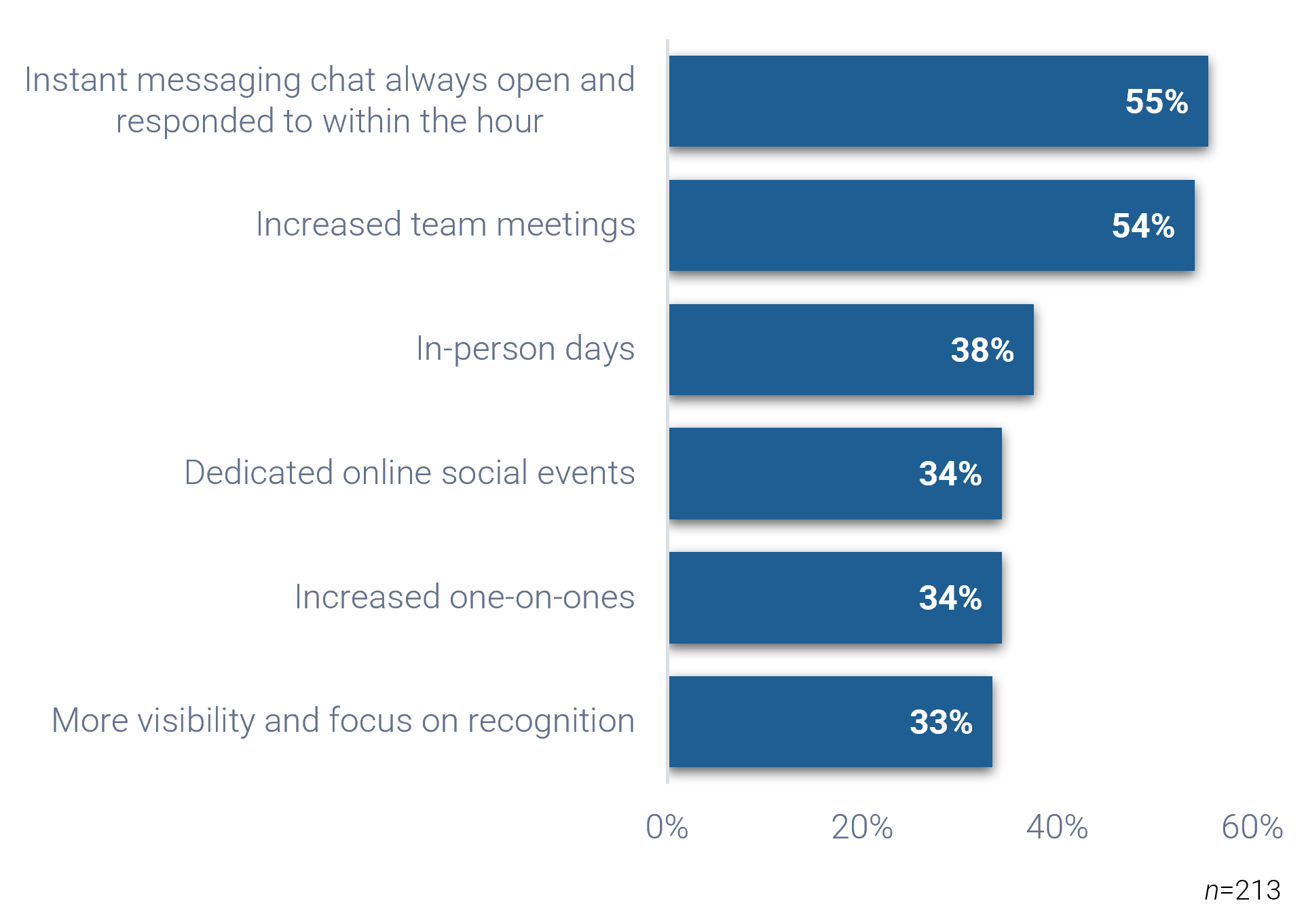
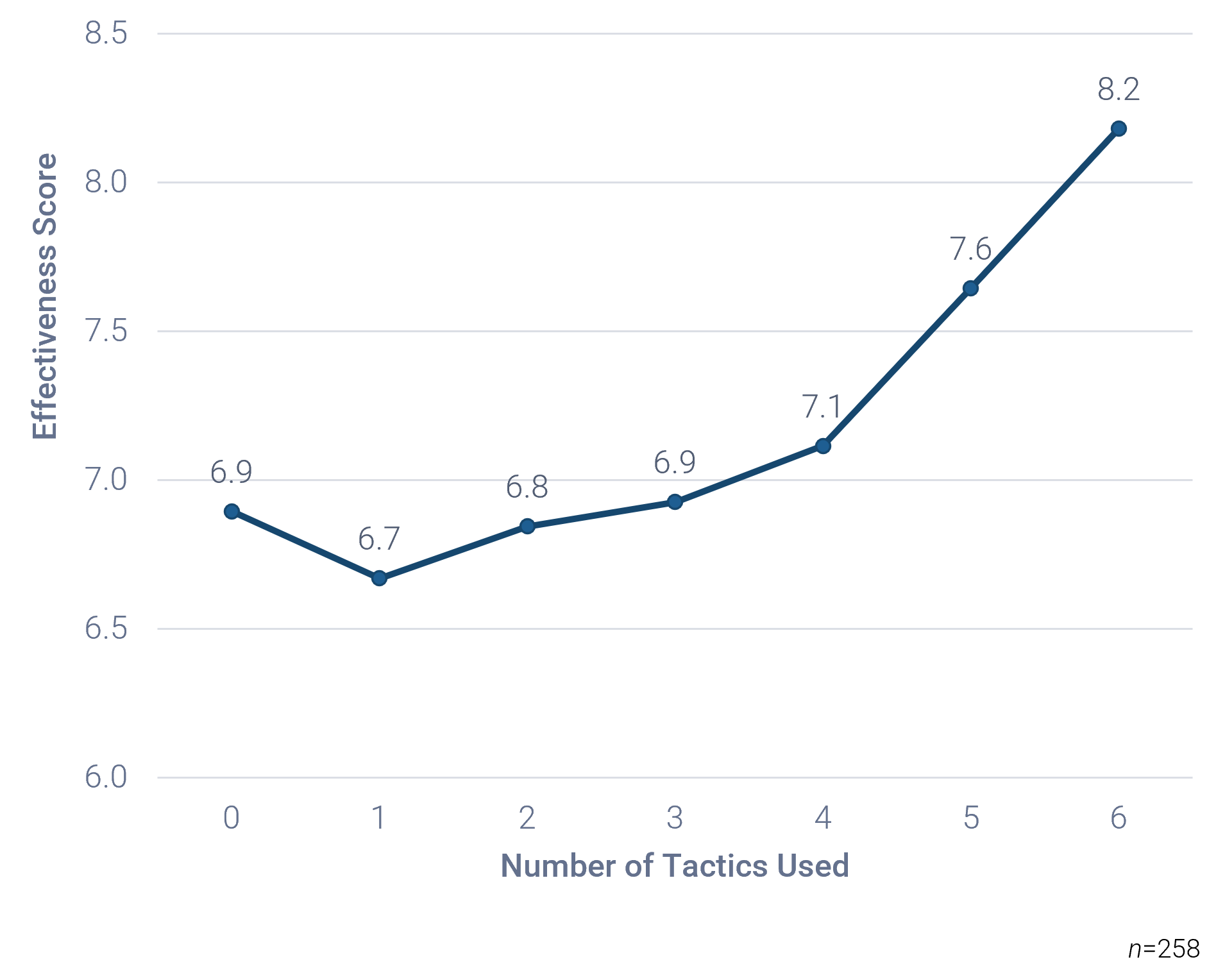
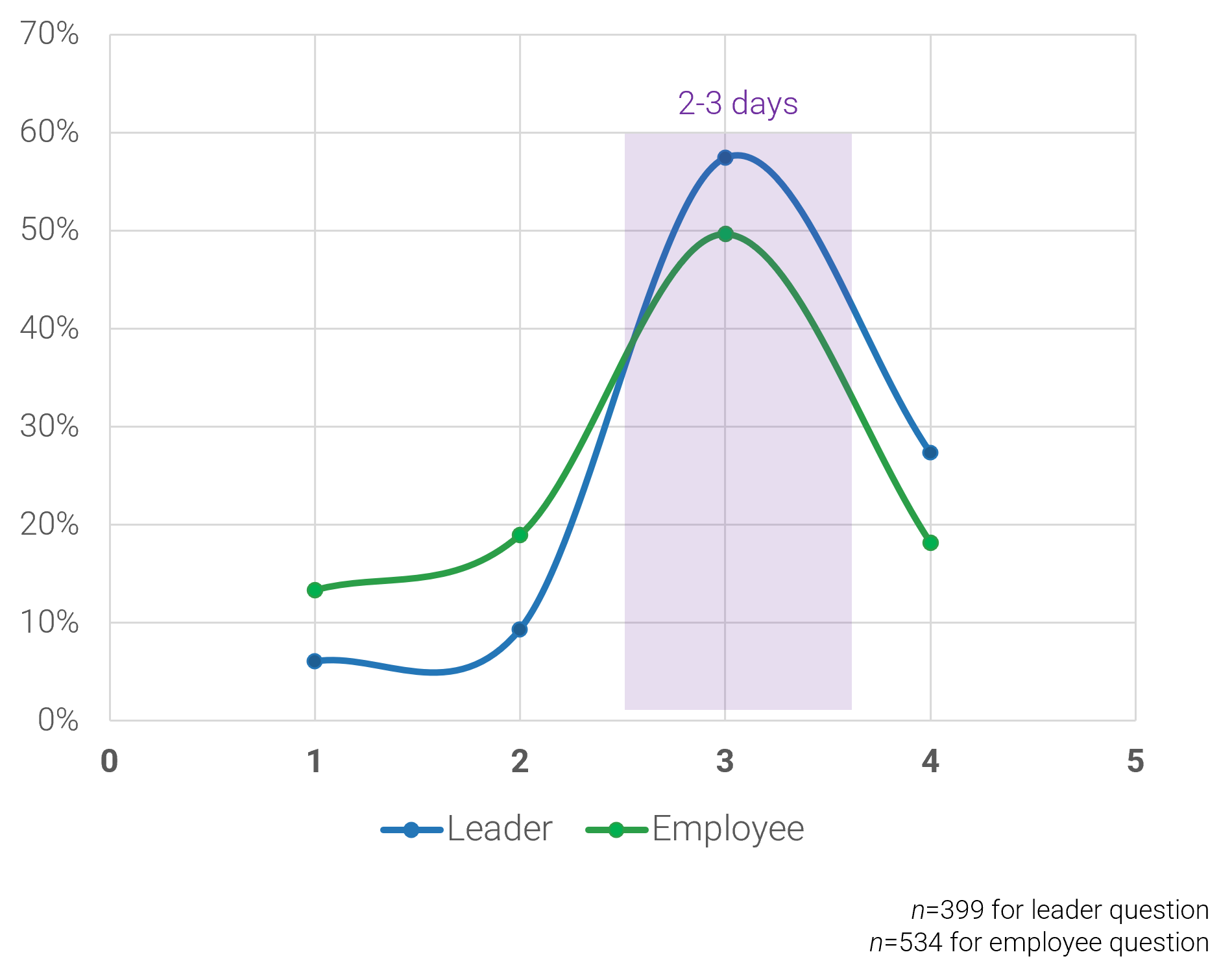
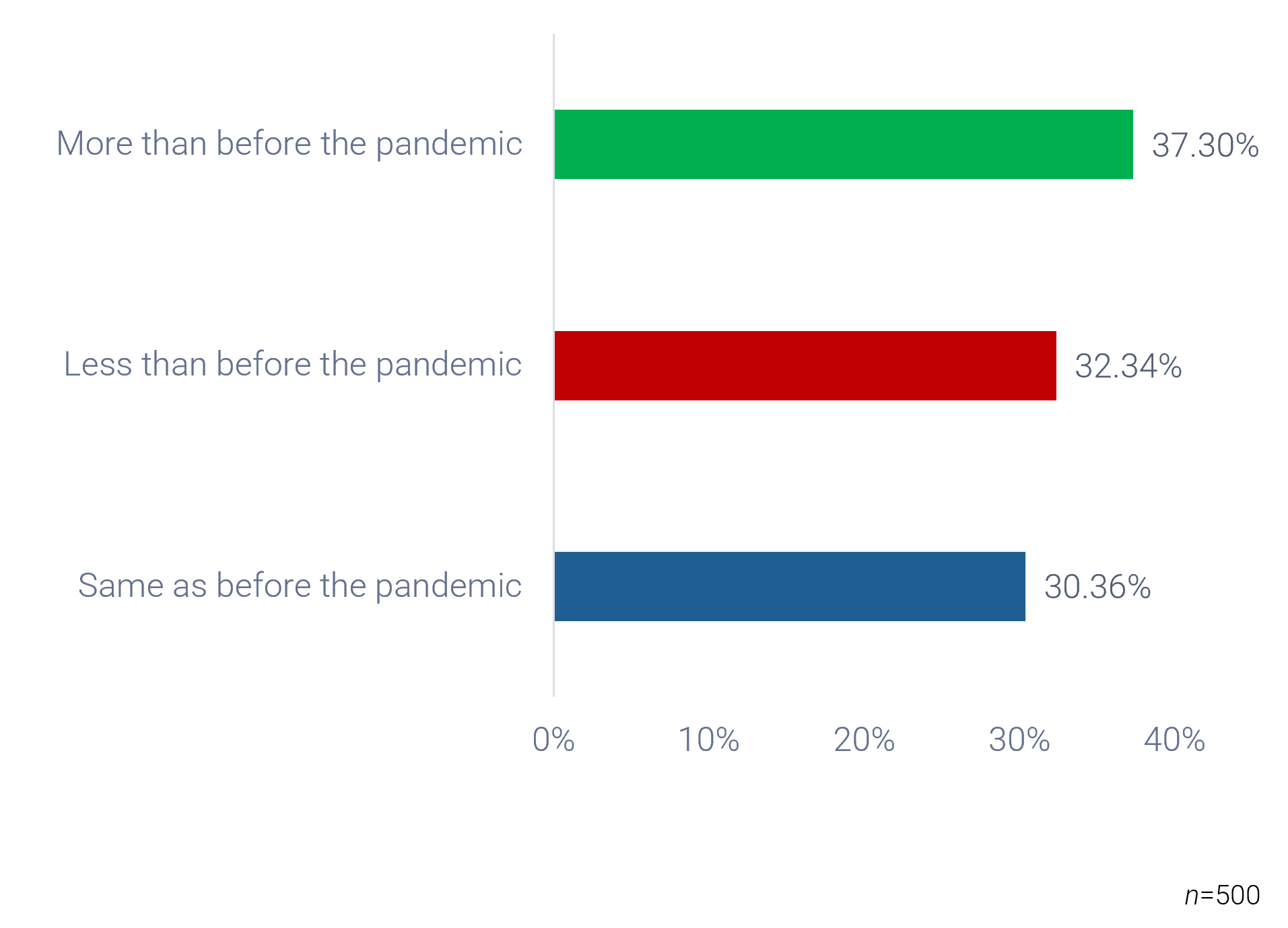




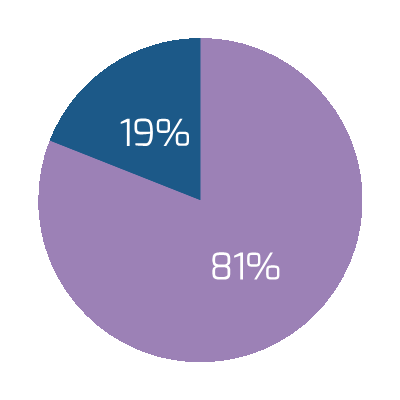


 (n=191)
(n=191)
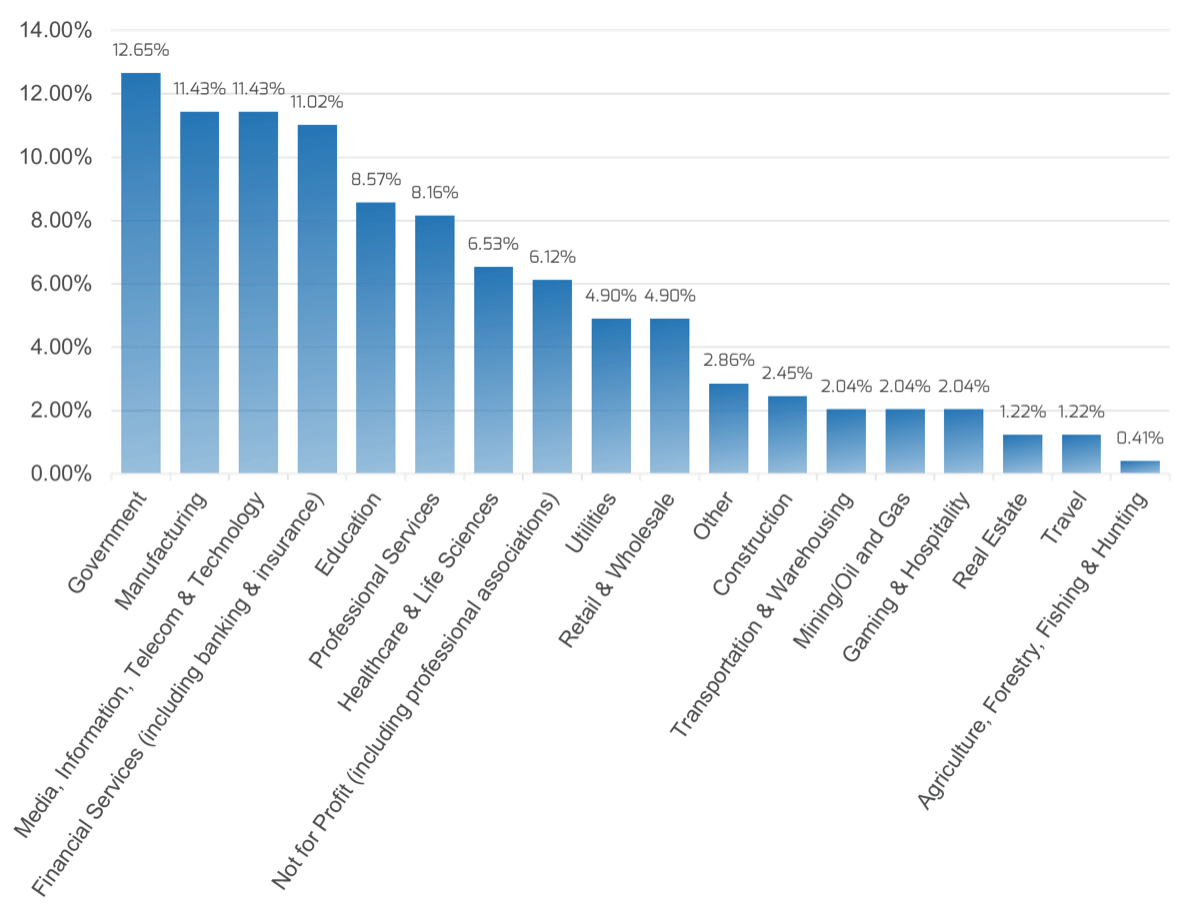
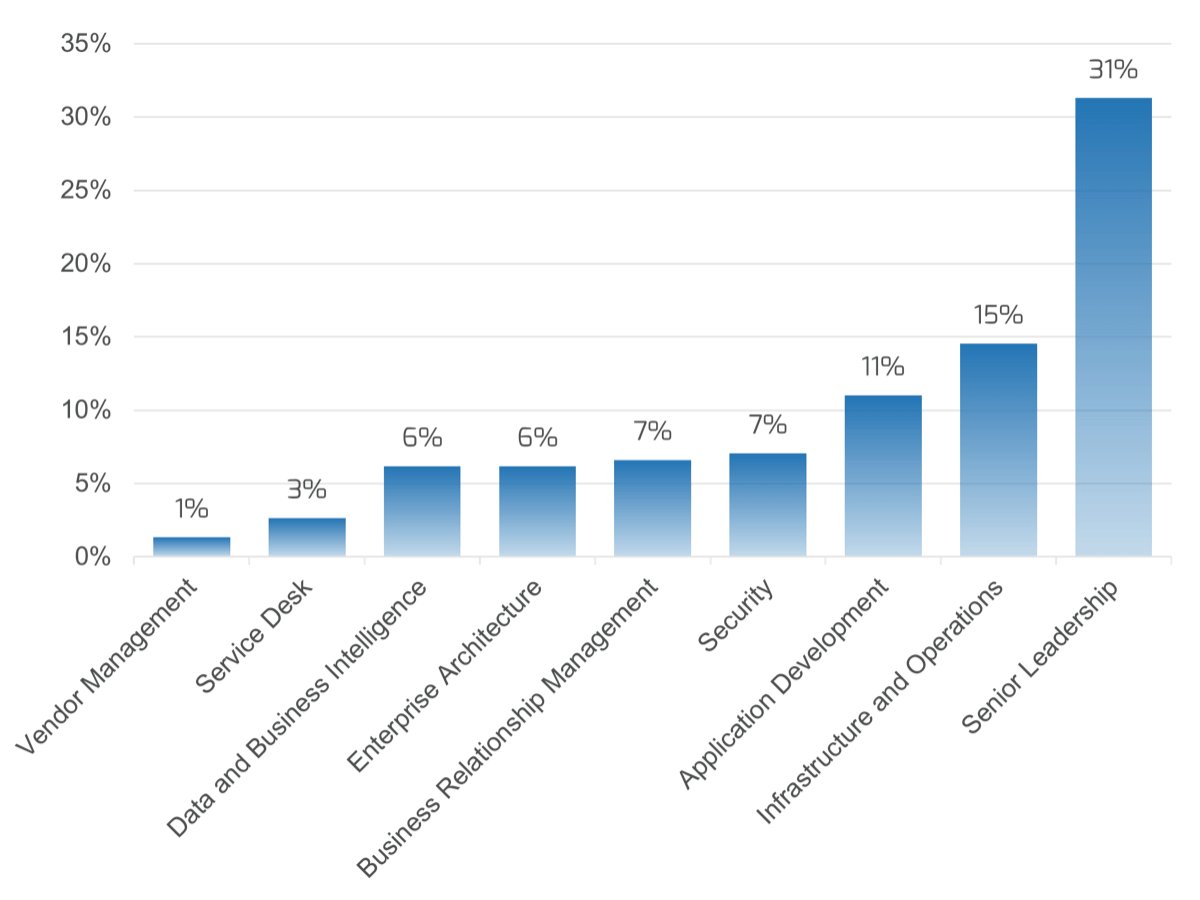
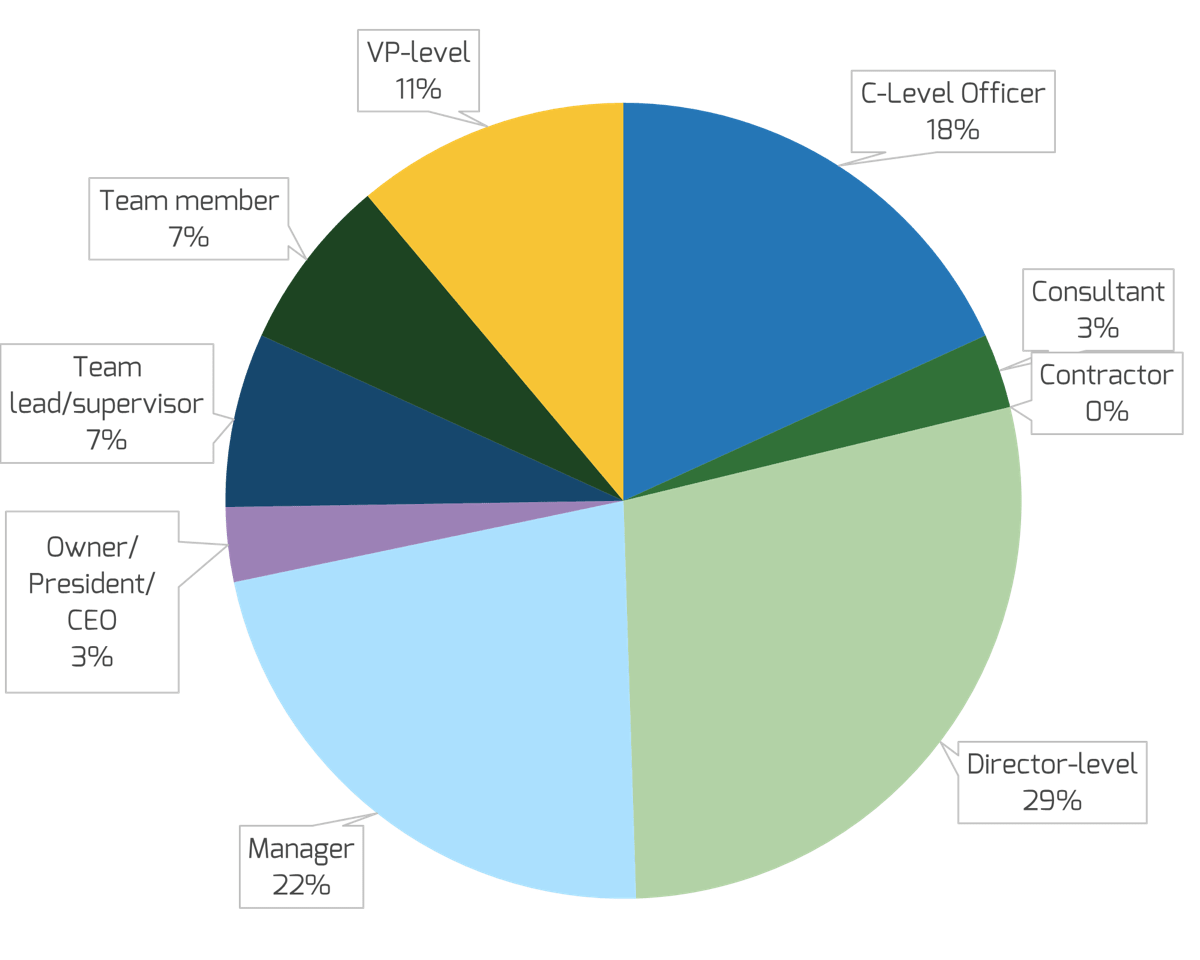

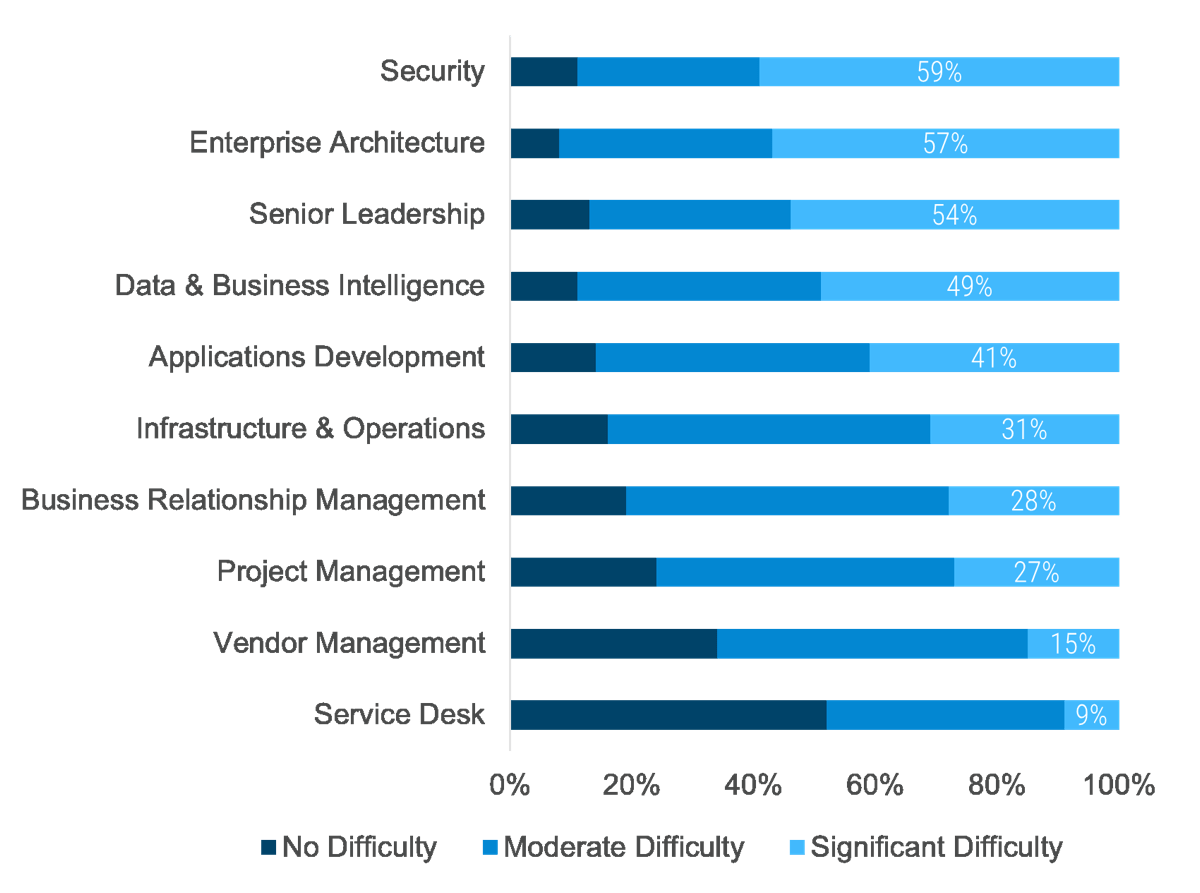 (Info-Tech Talent Trends 2022 Survey)
(Info-Tech Talent Trends 2022 Survey)


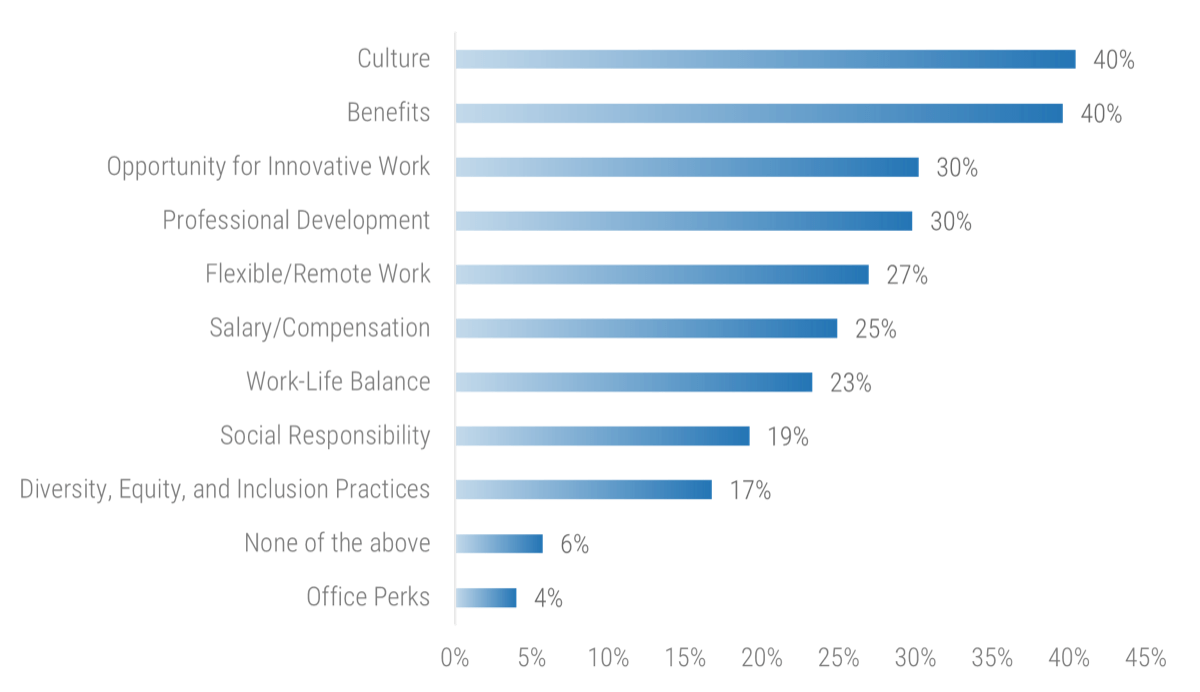 (Info-Tech IT Talent Trends 2022 Survey)
(Info-Tech IT Talent Trends 2022 Survey)


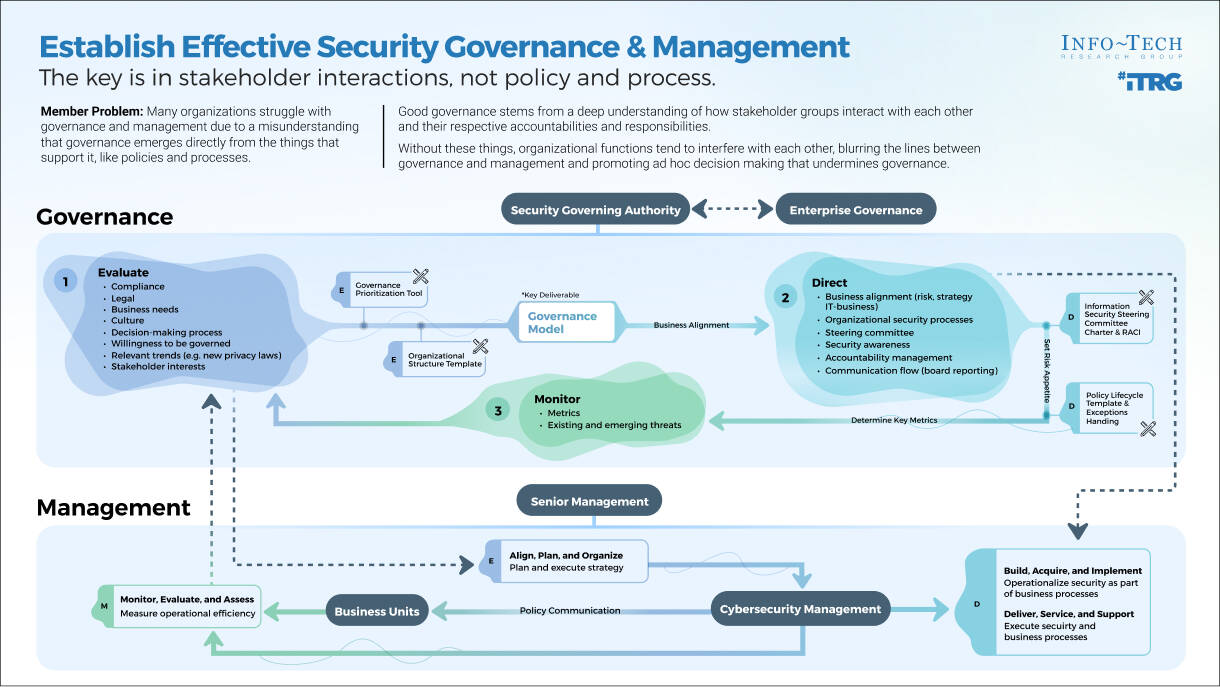

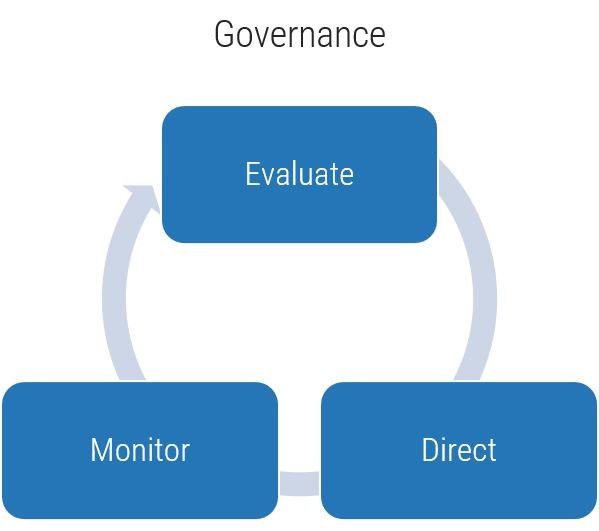
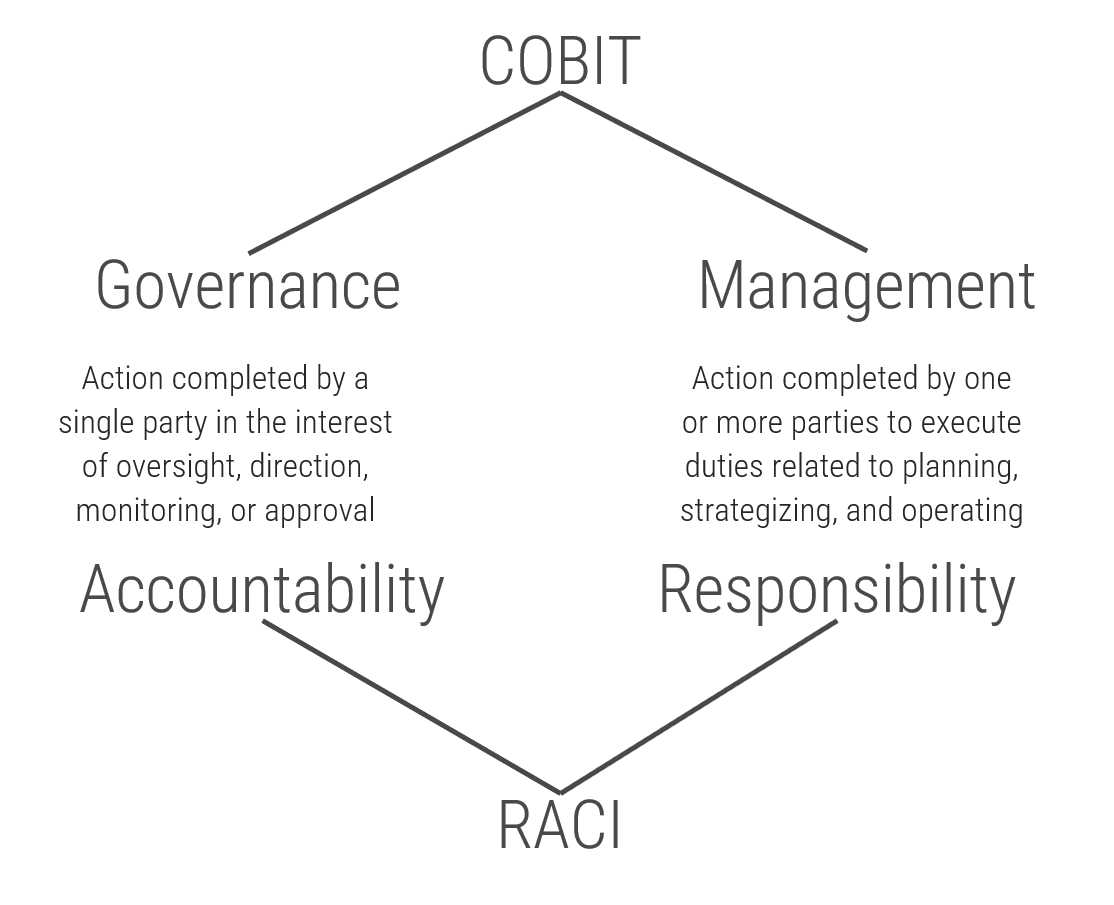
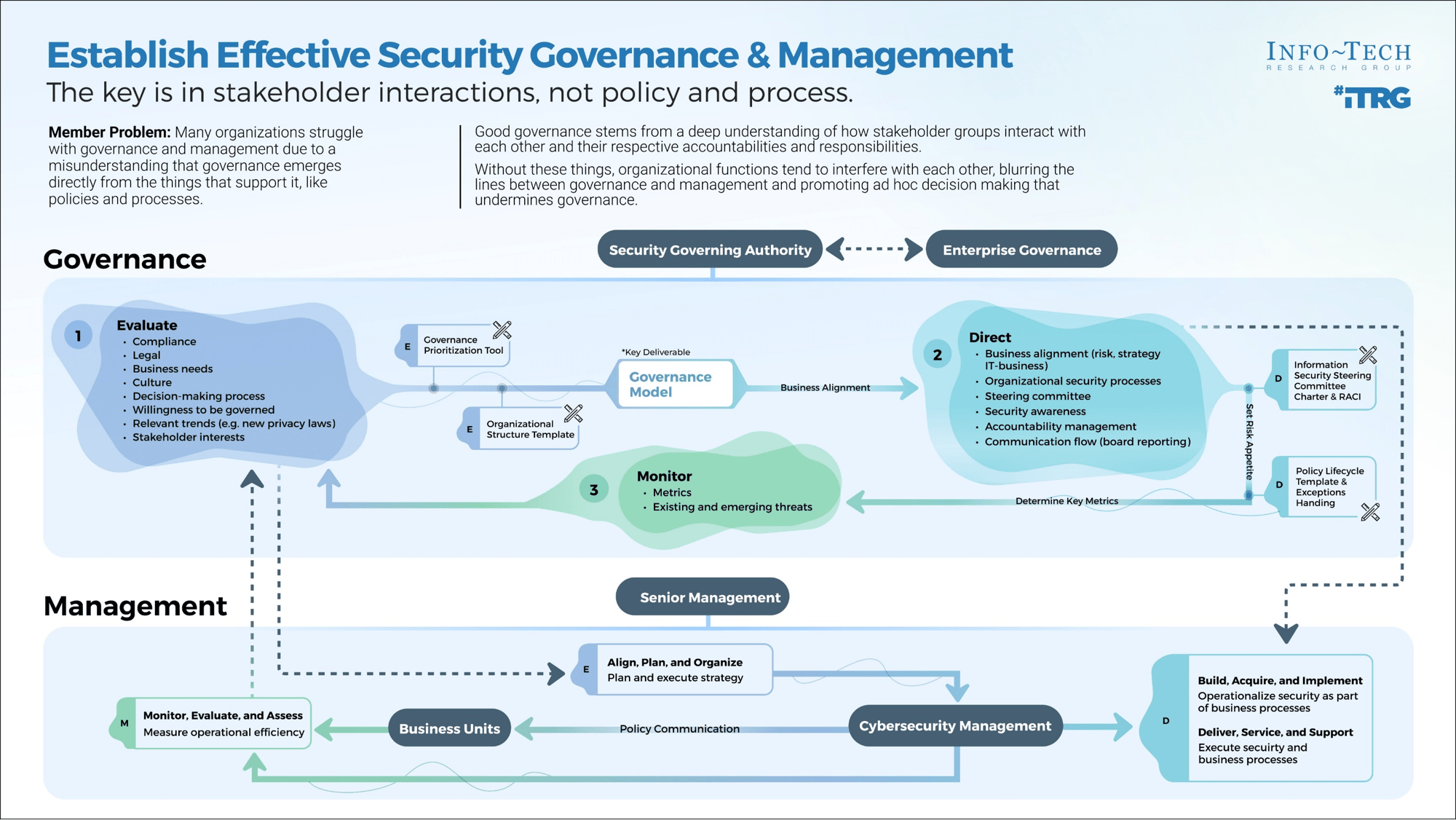
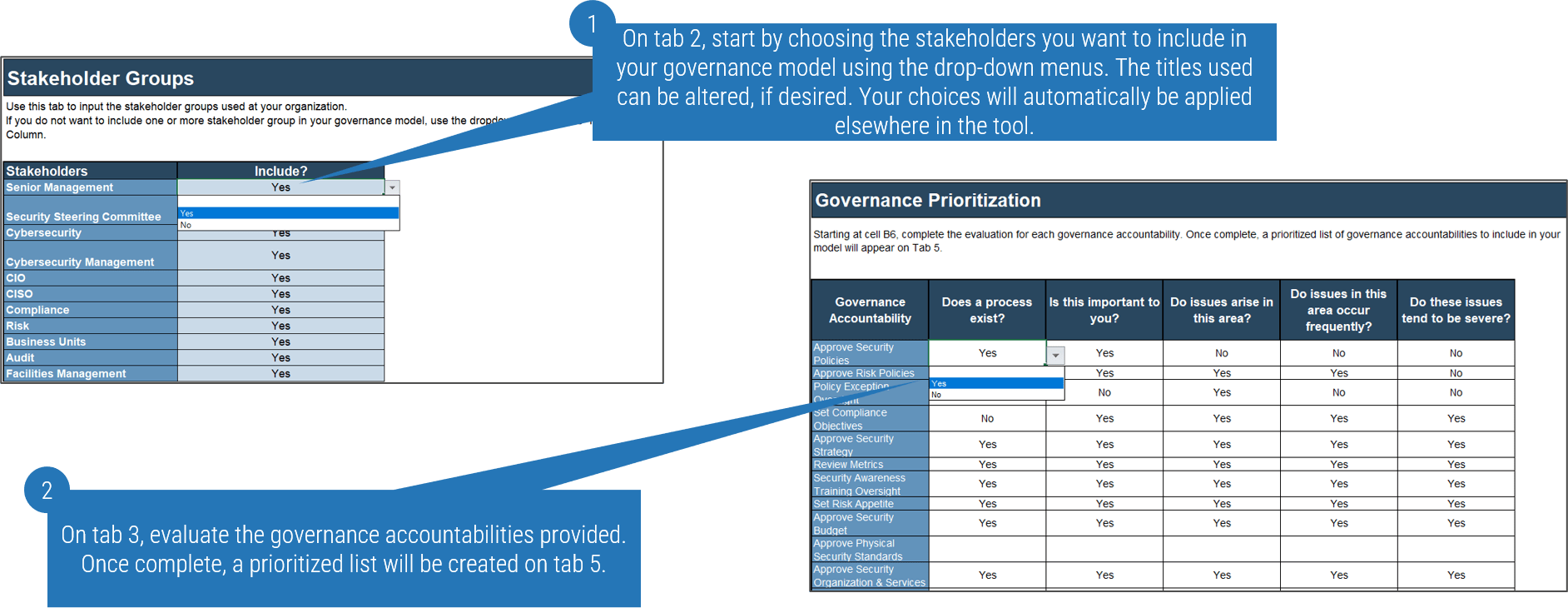
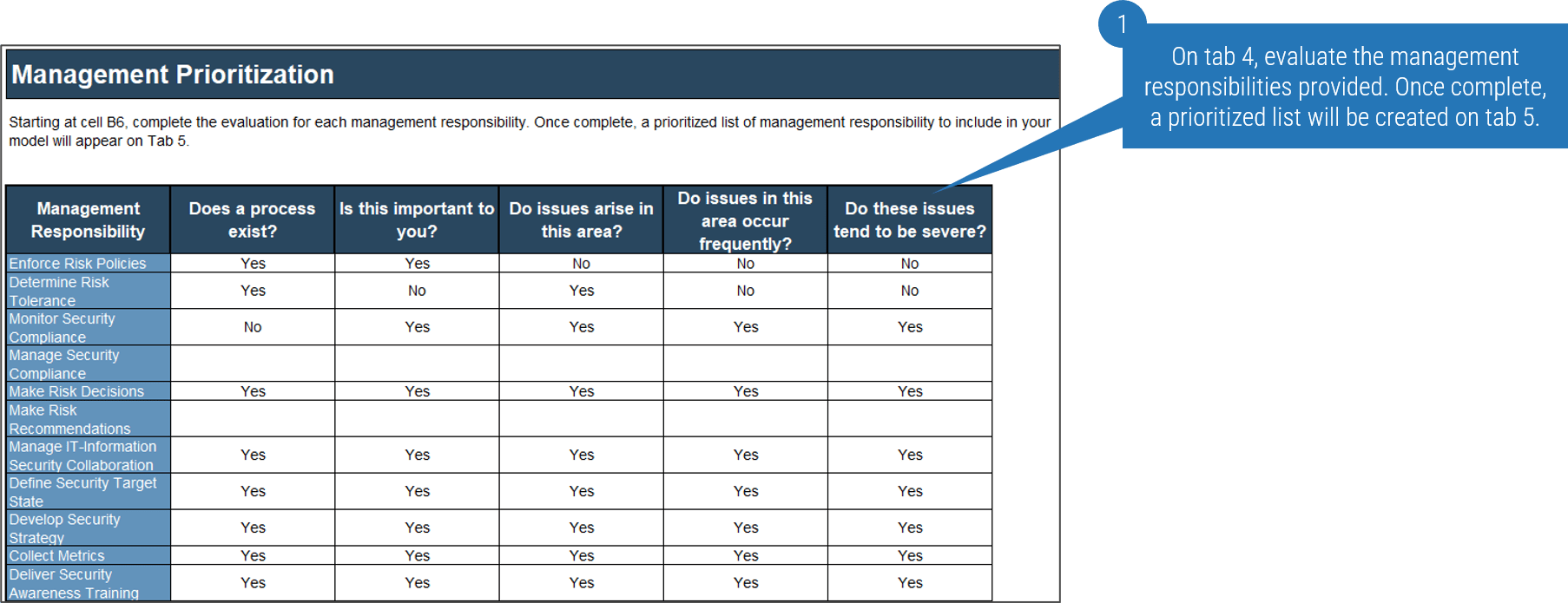
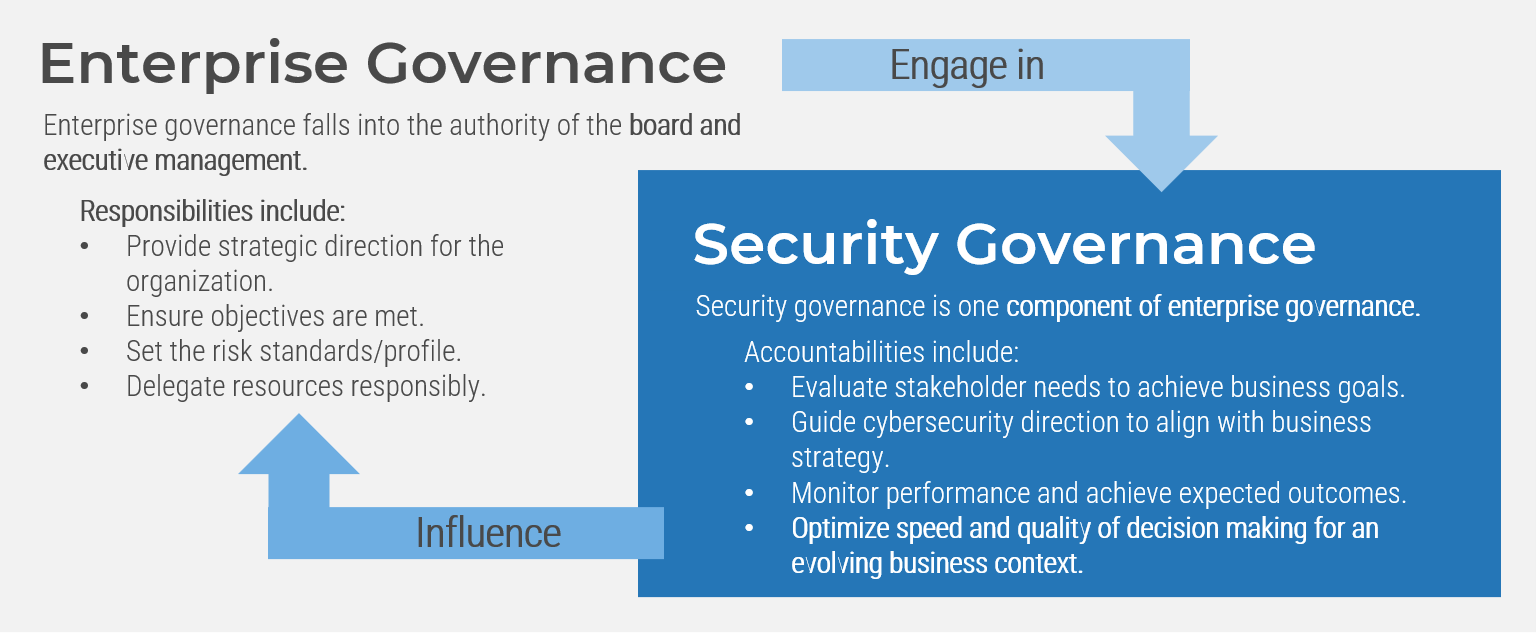
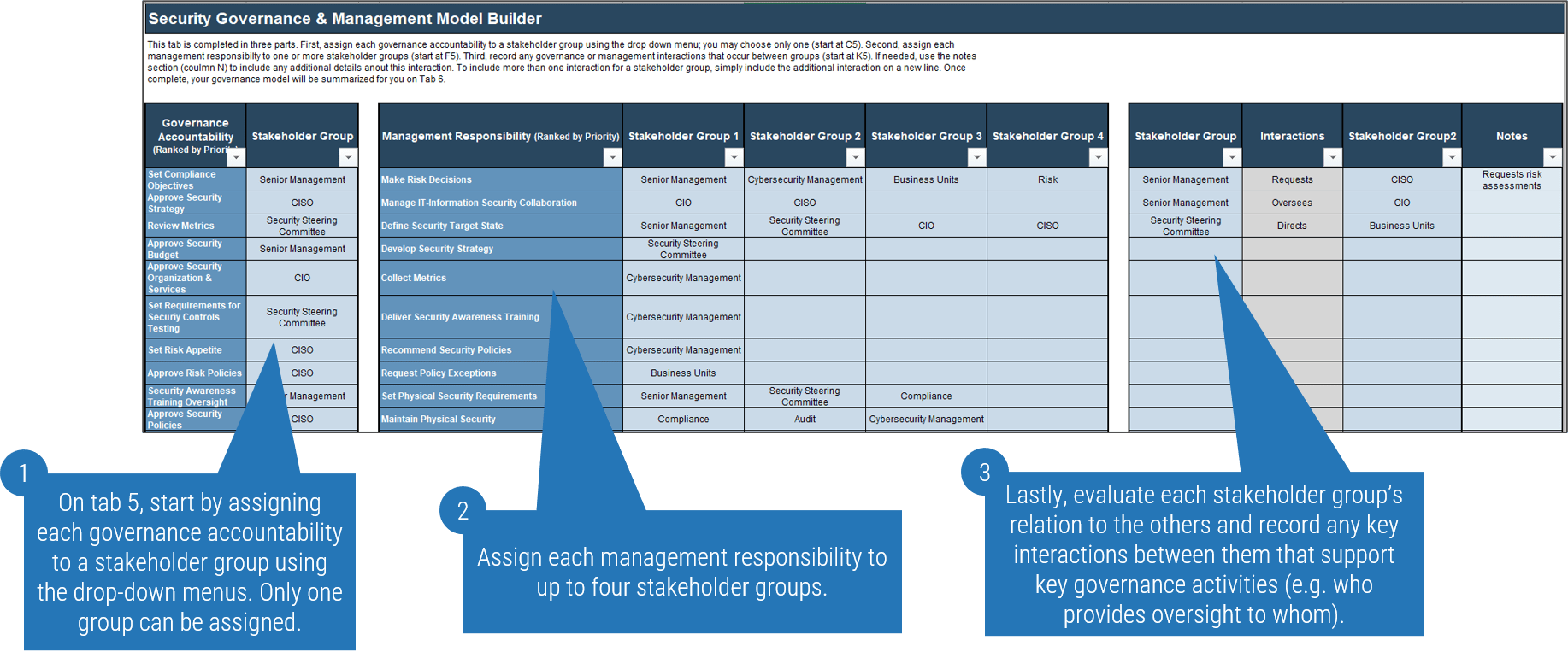
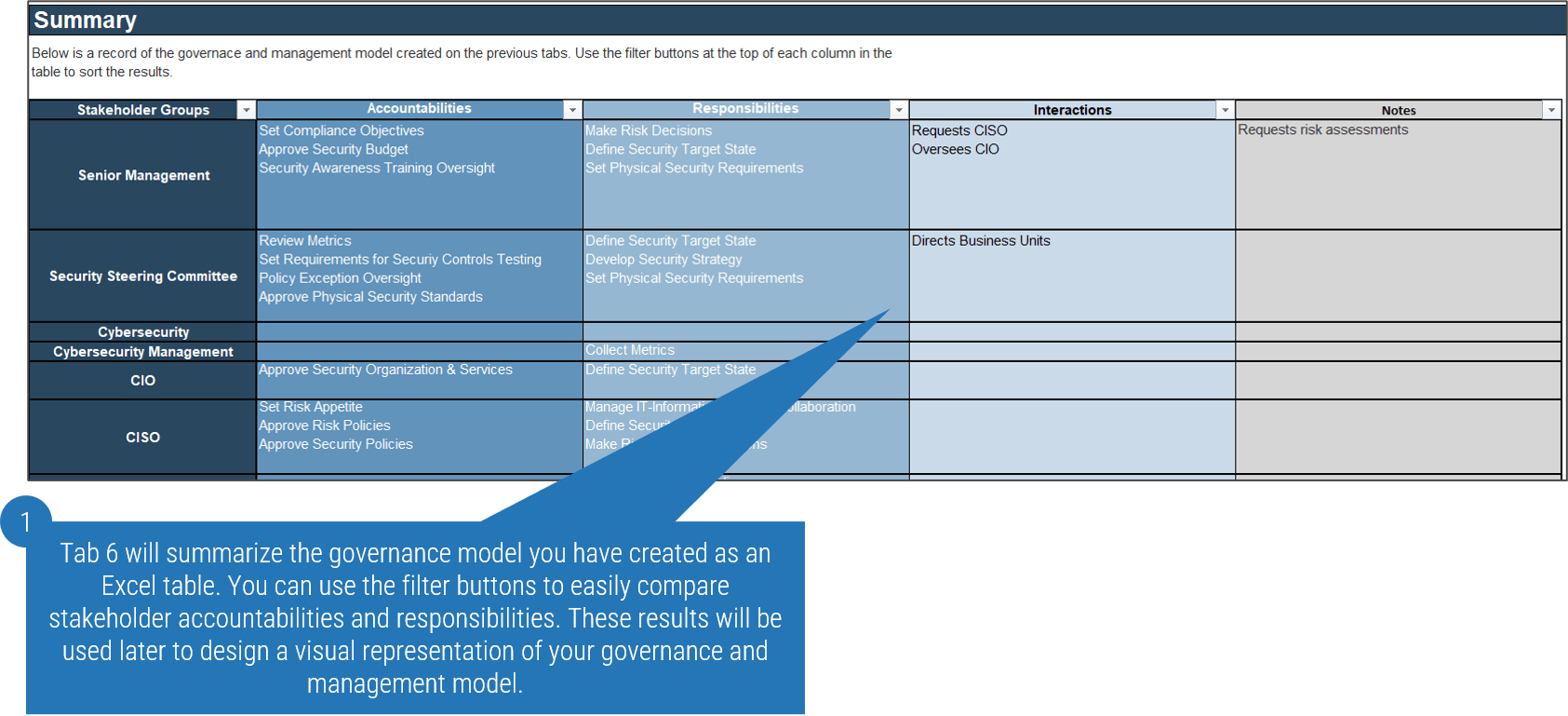
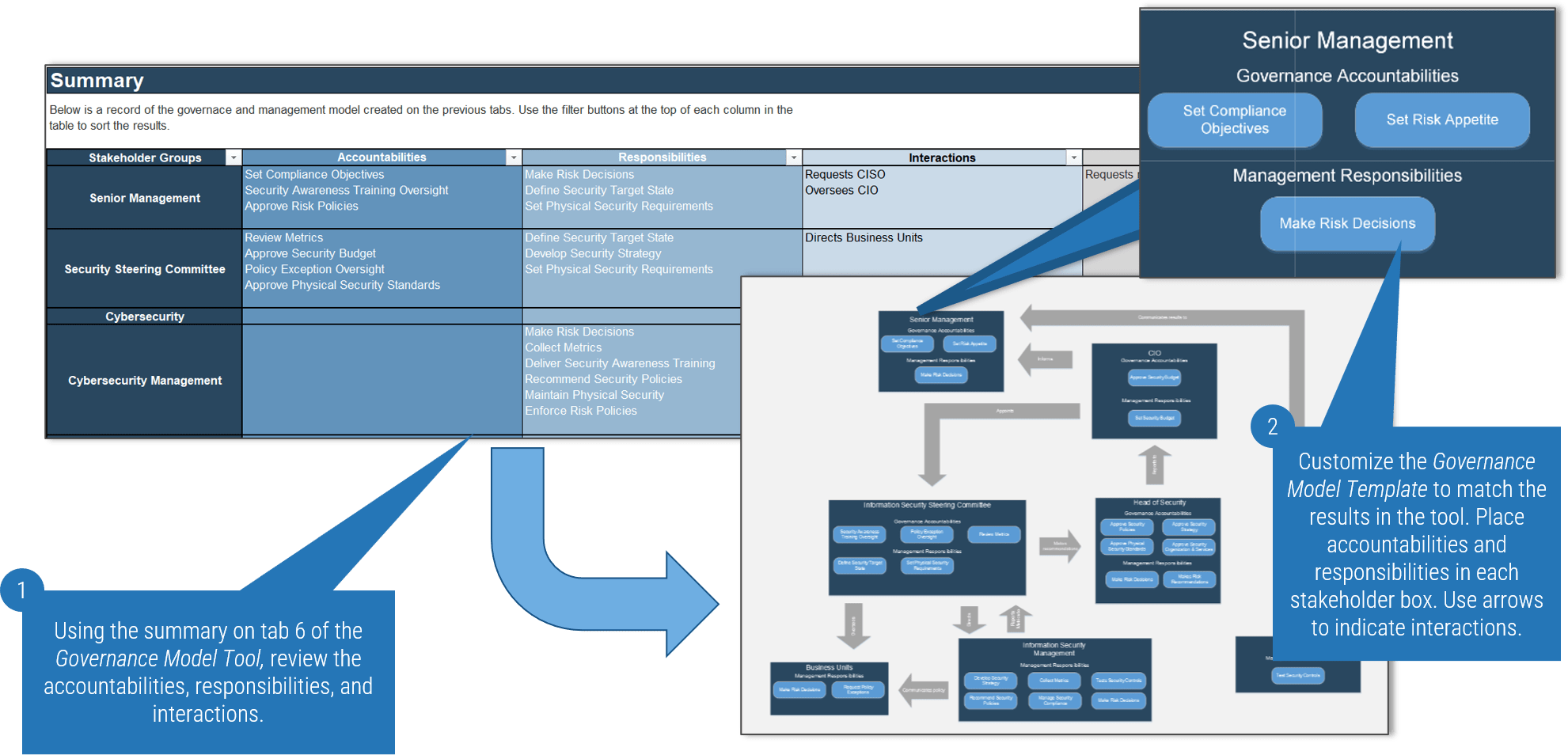
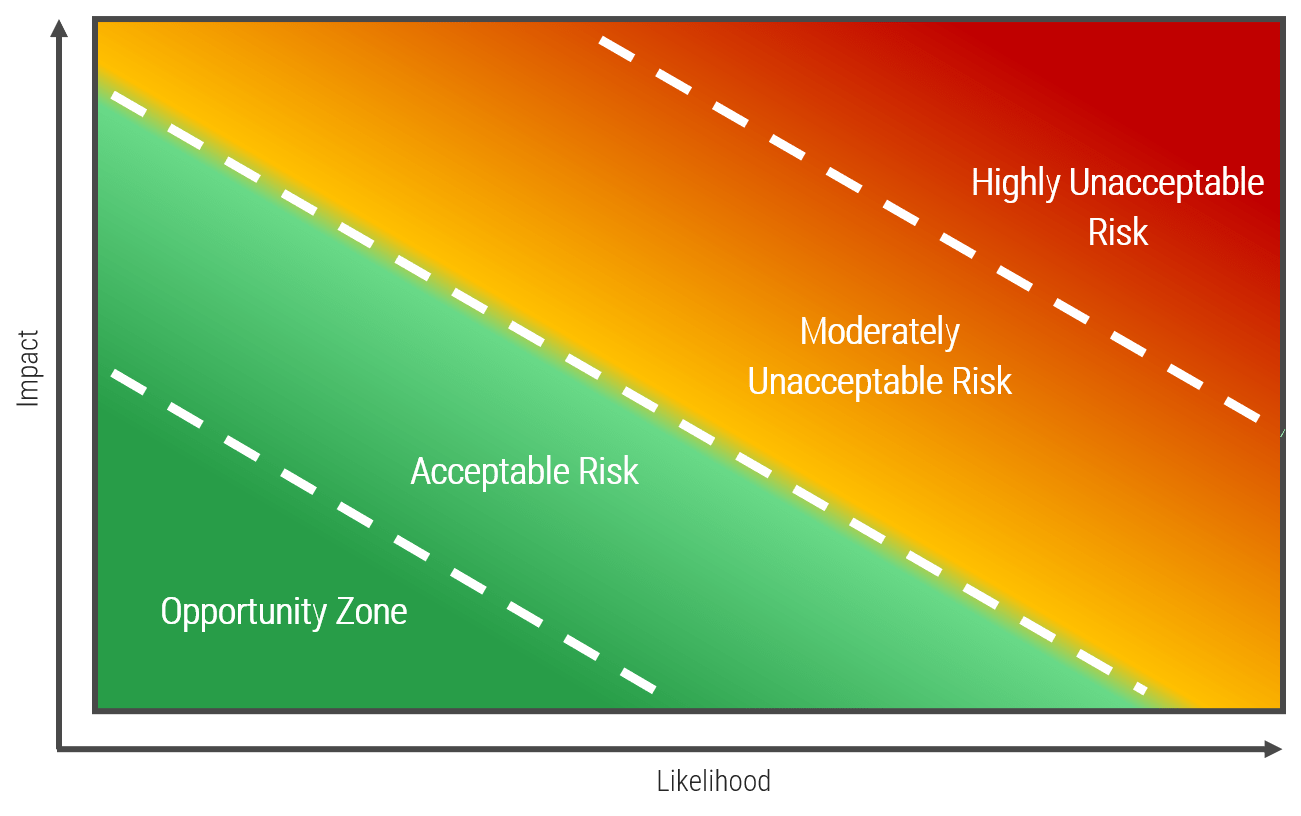
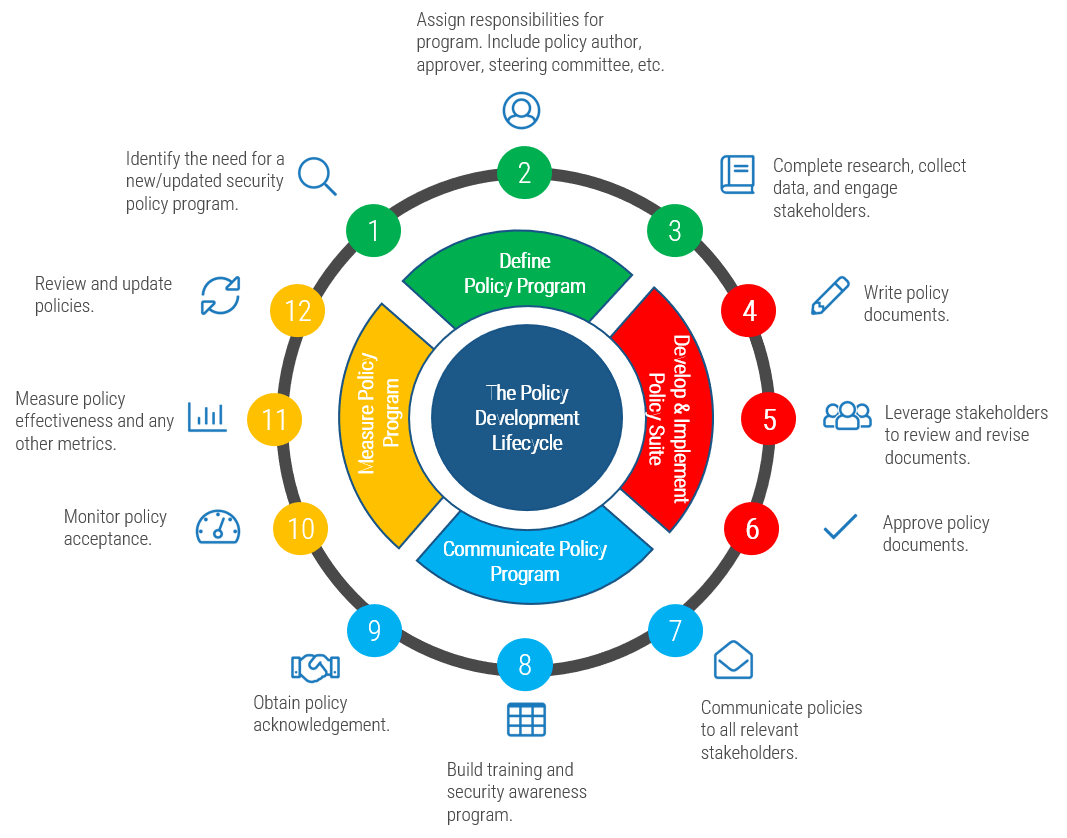






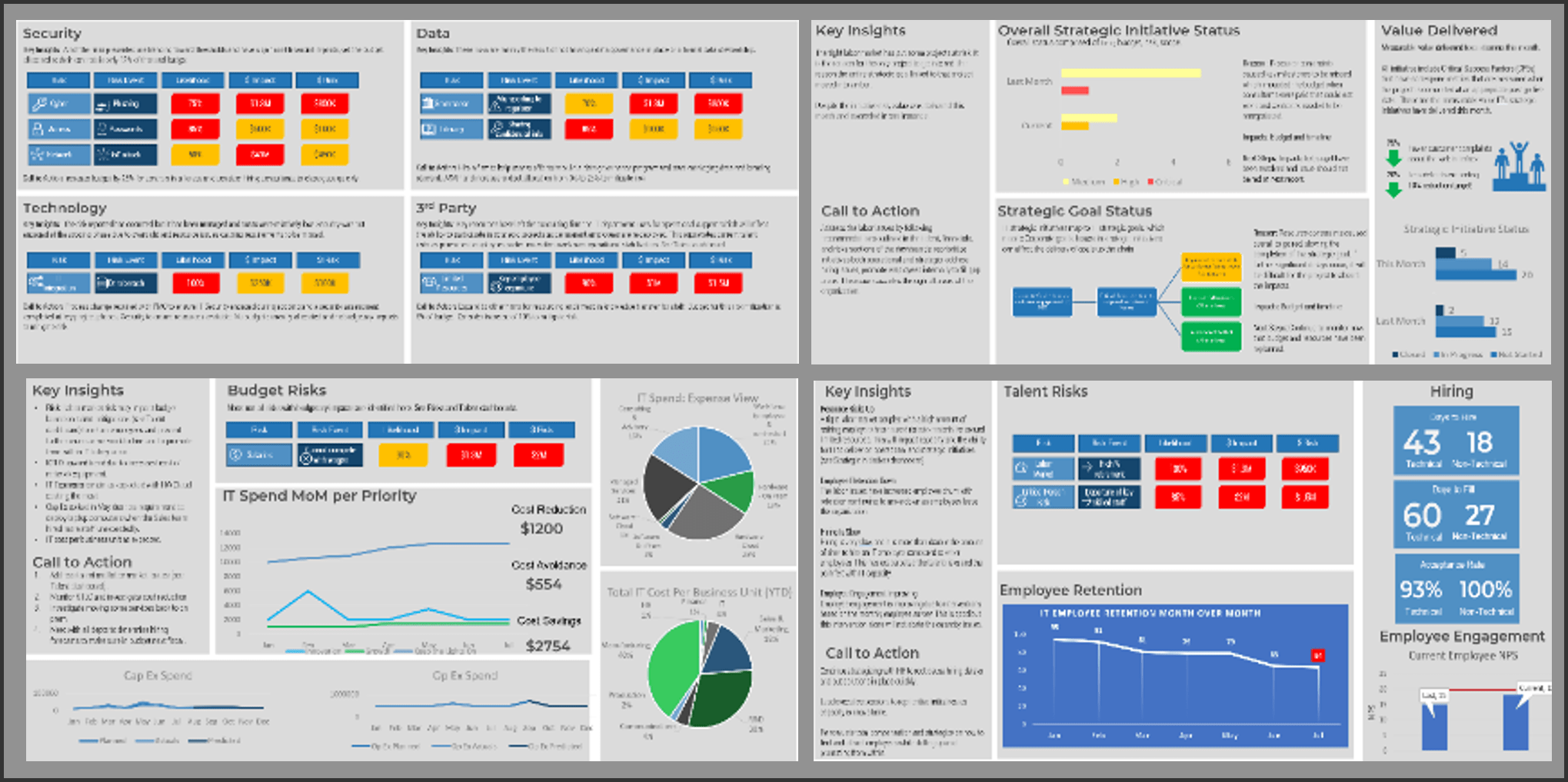

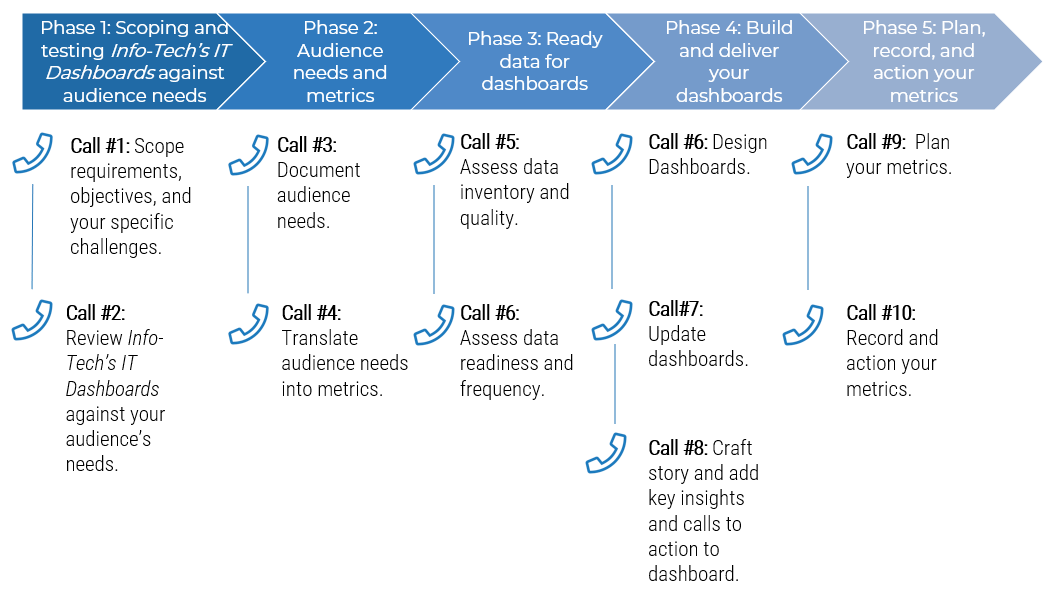
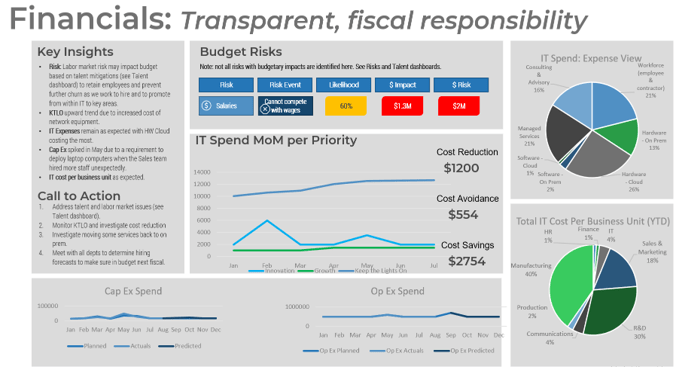
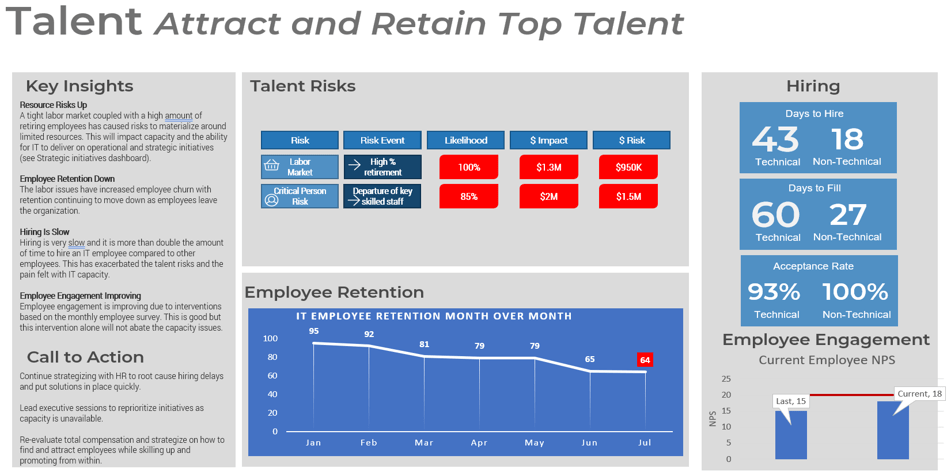
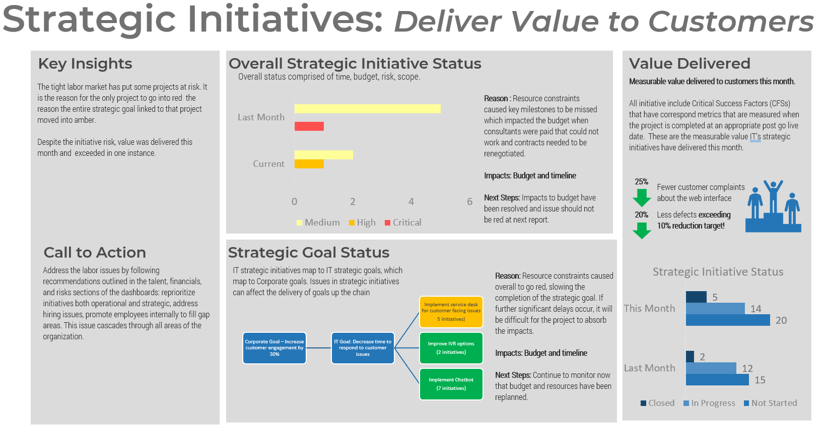
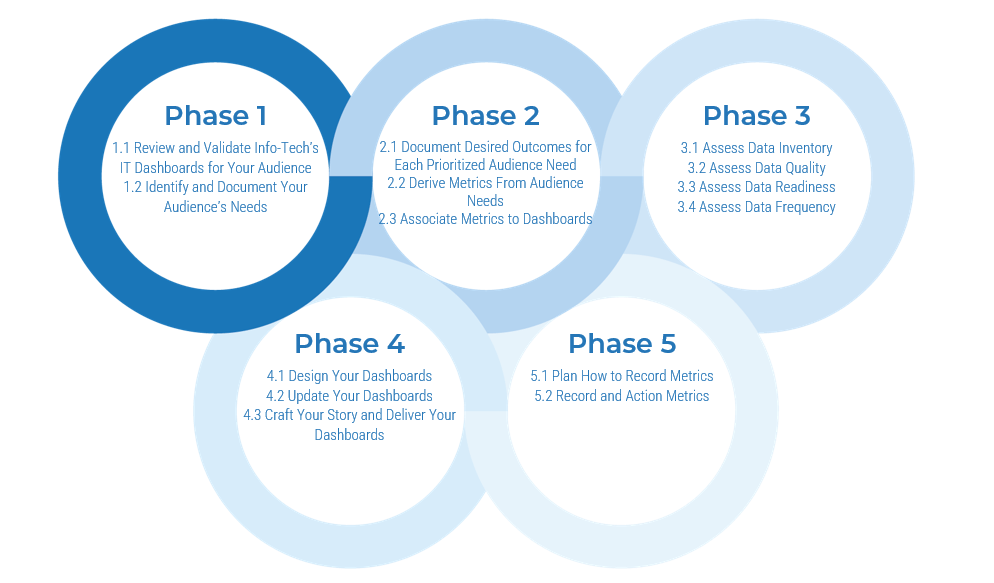


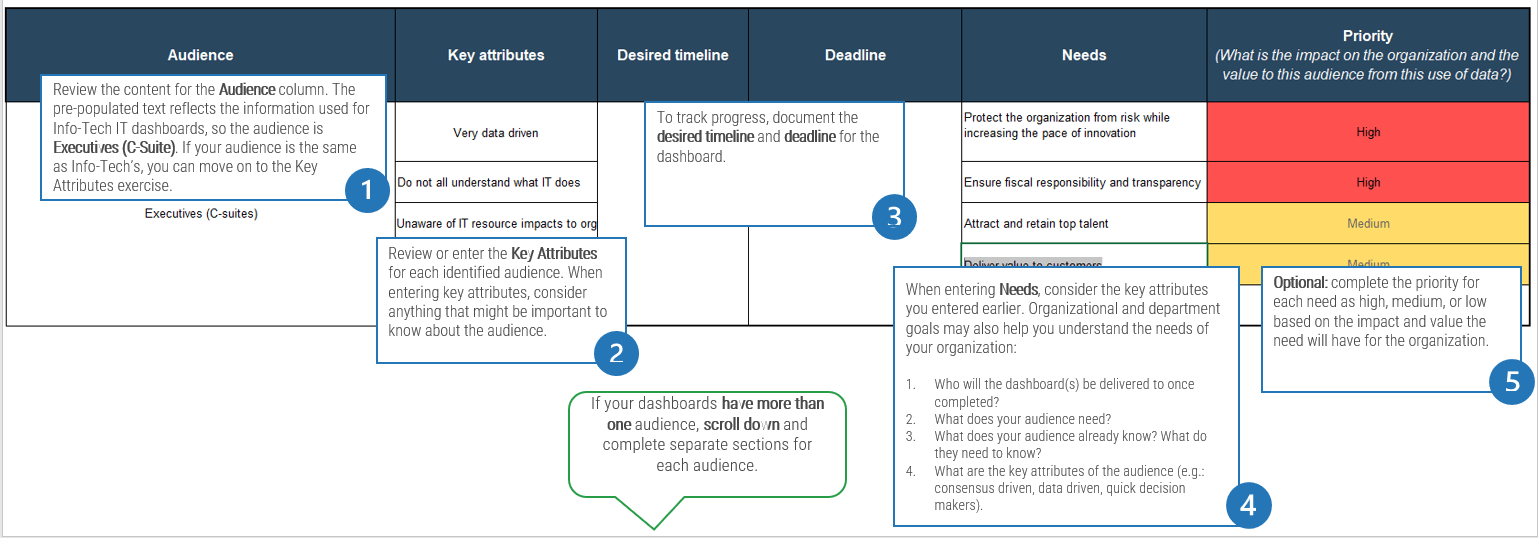
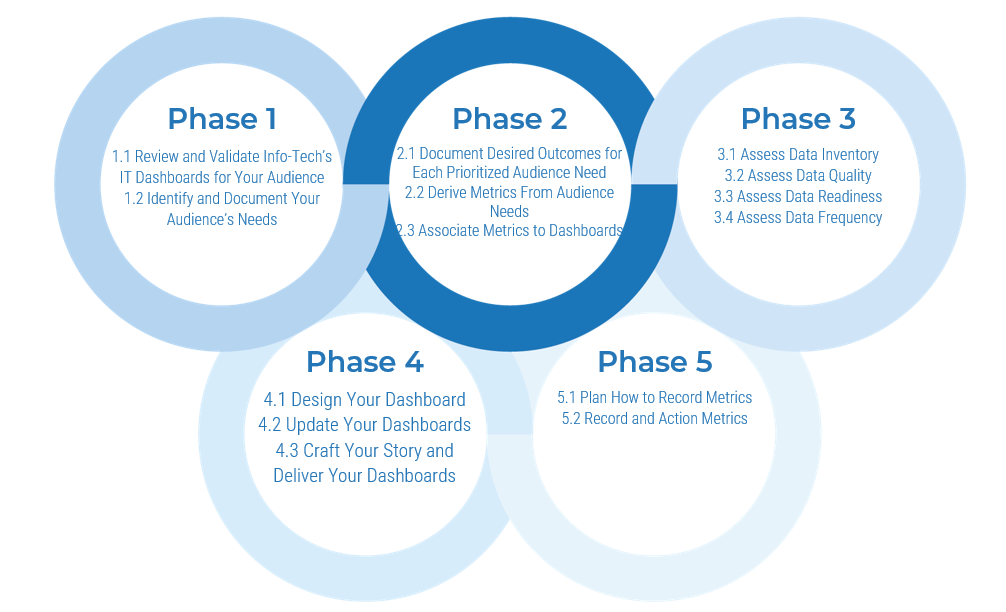

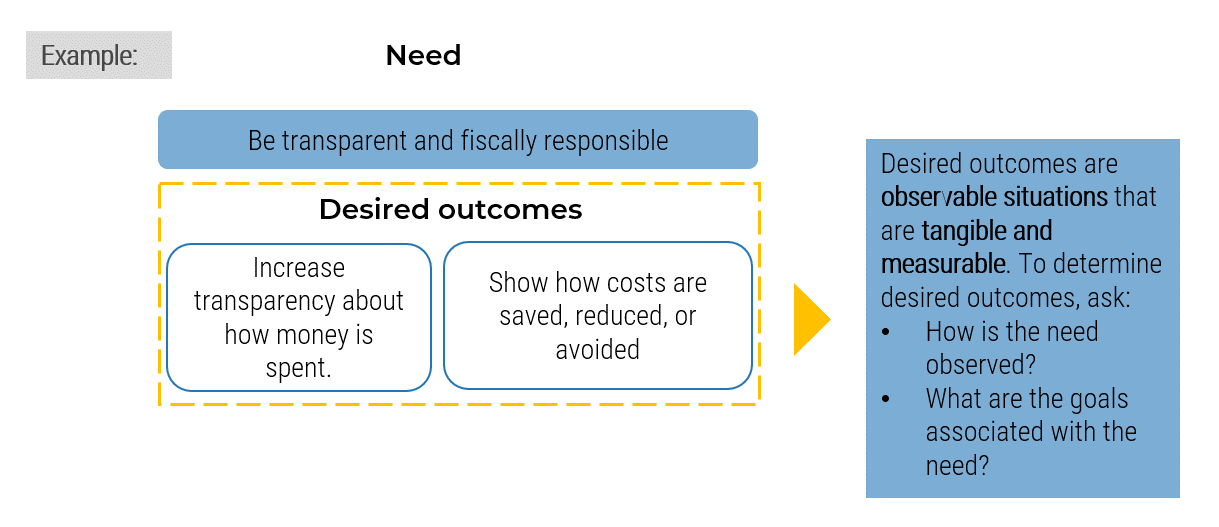
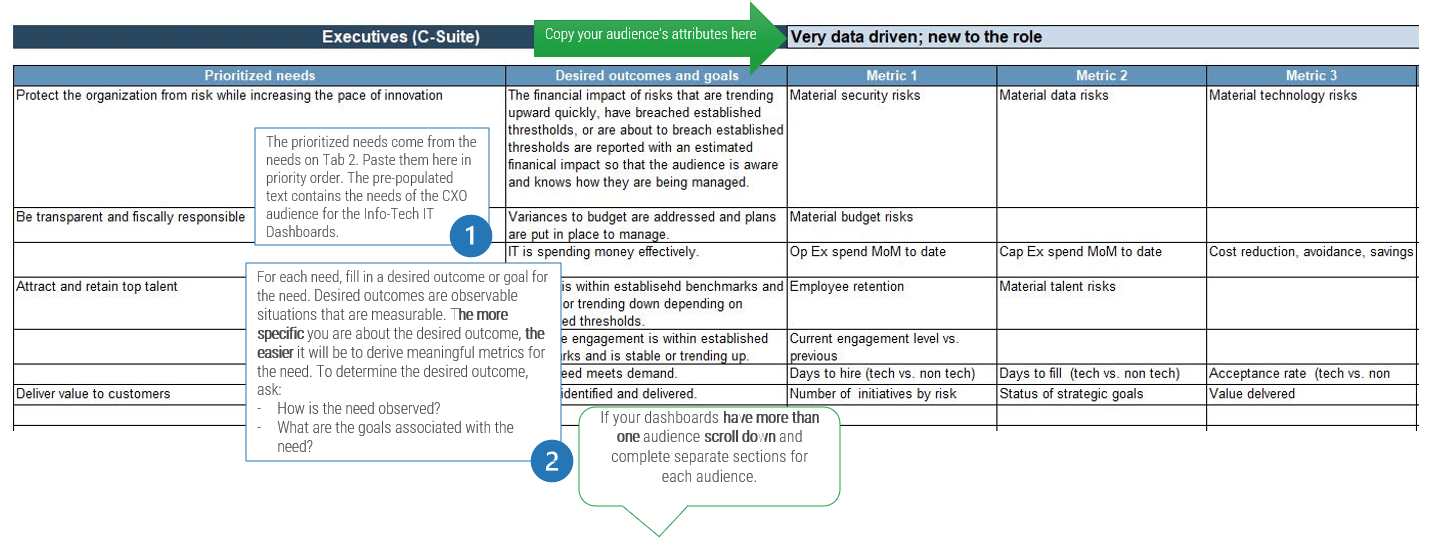
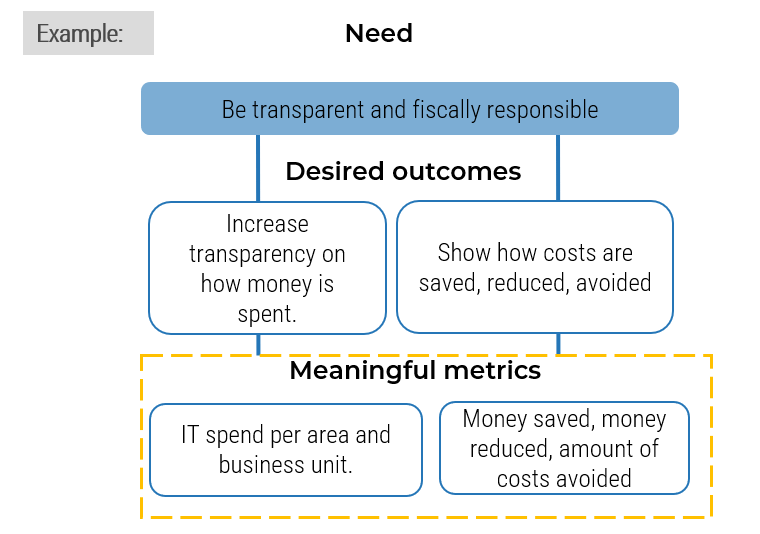
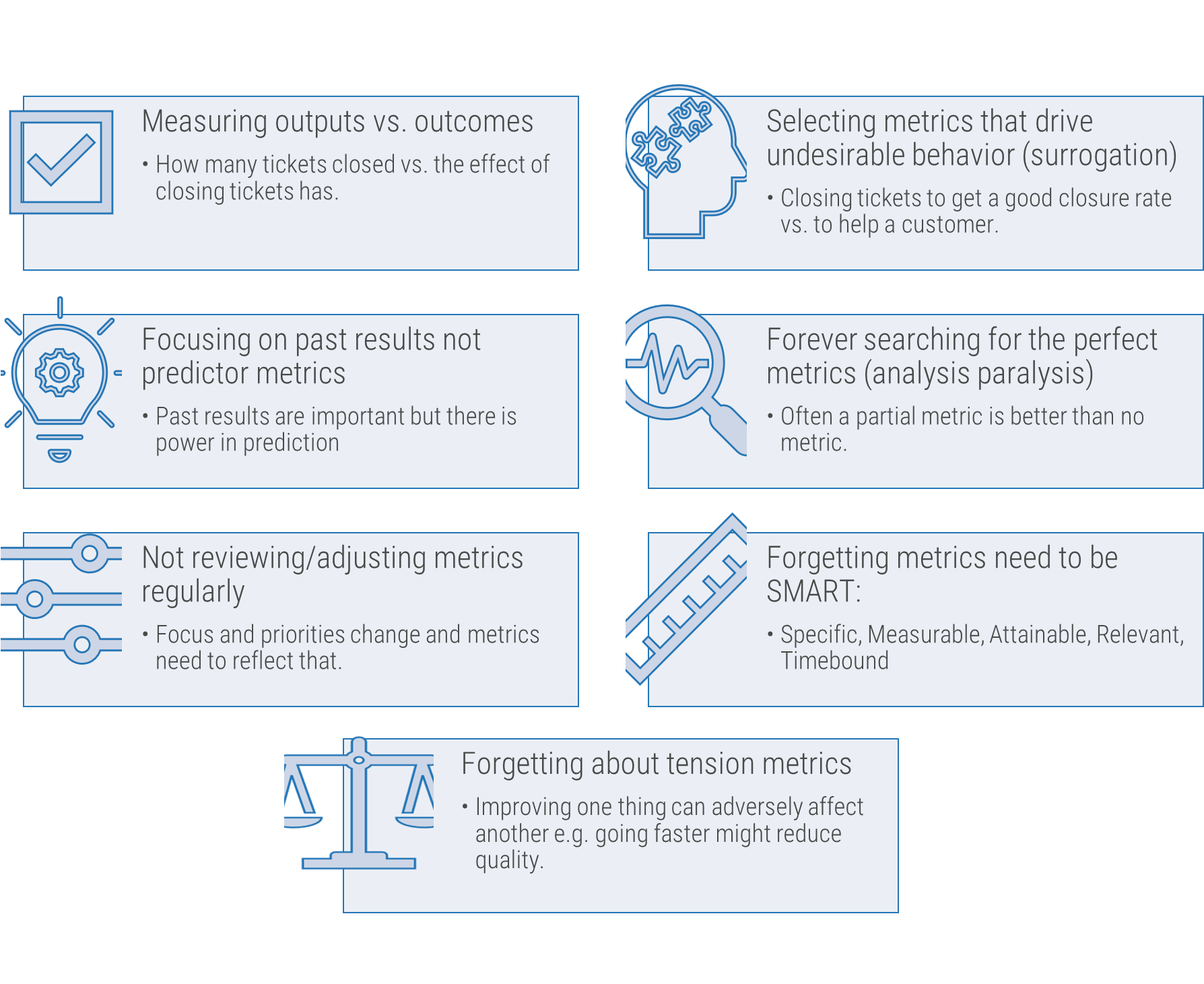

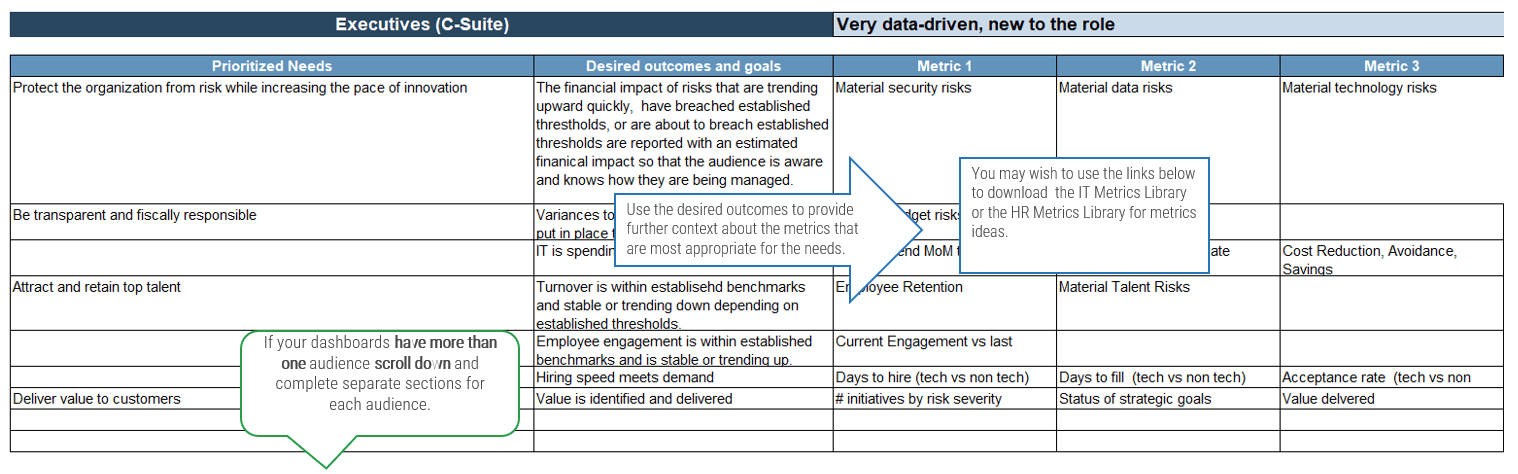

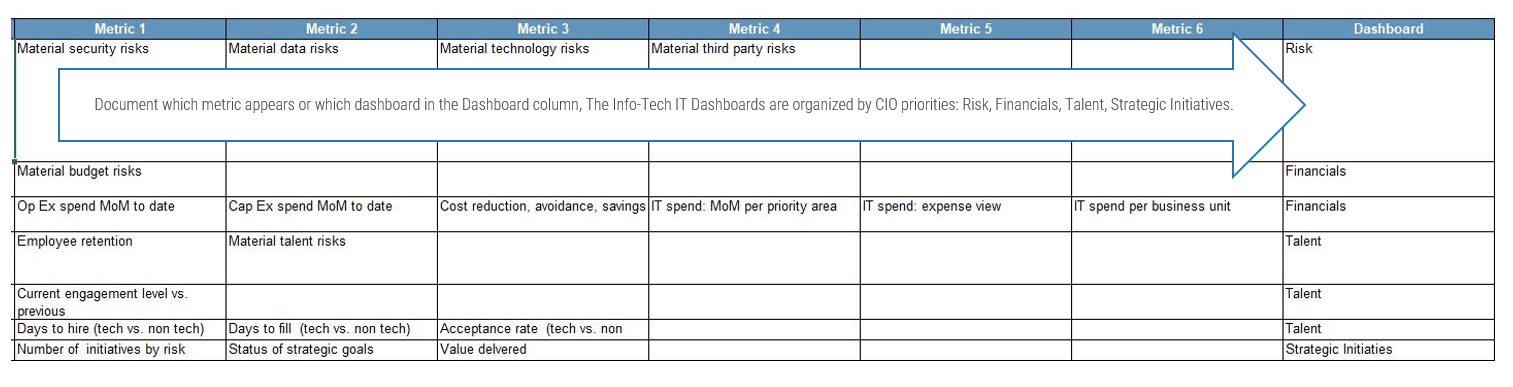
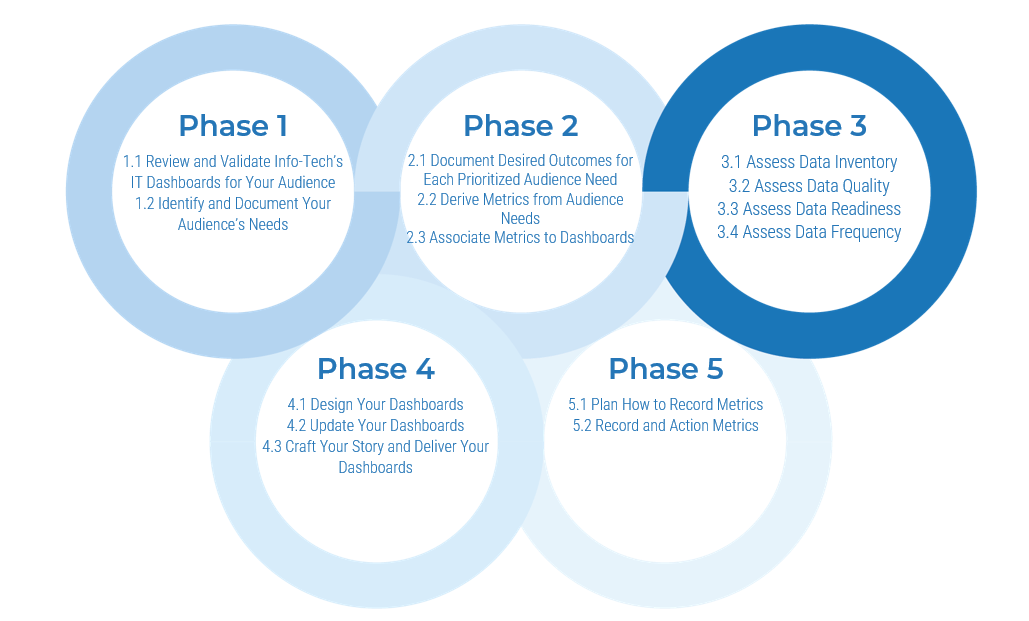




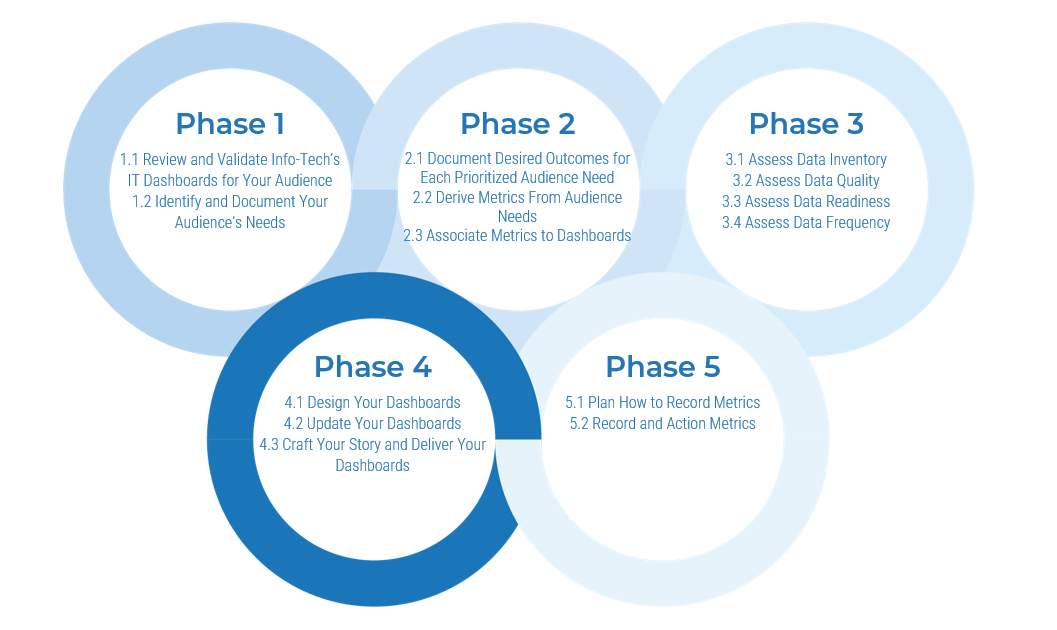

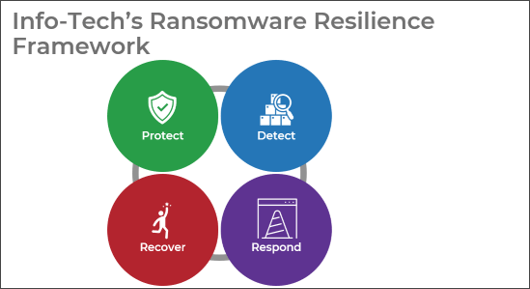
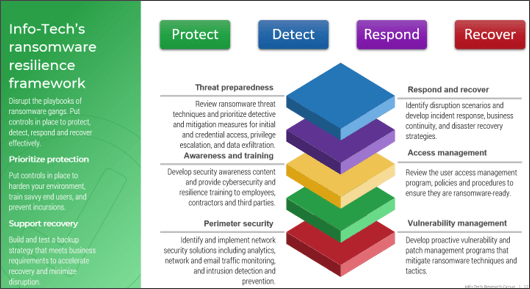





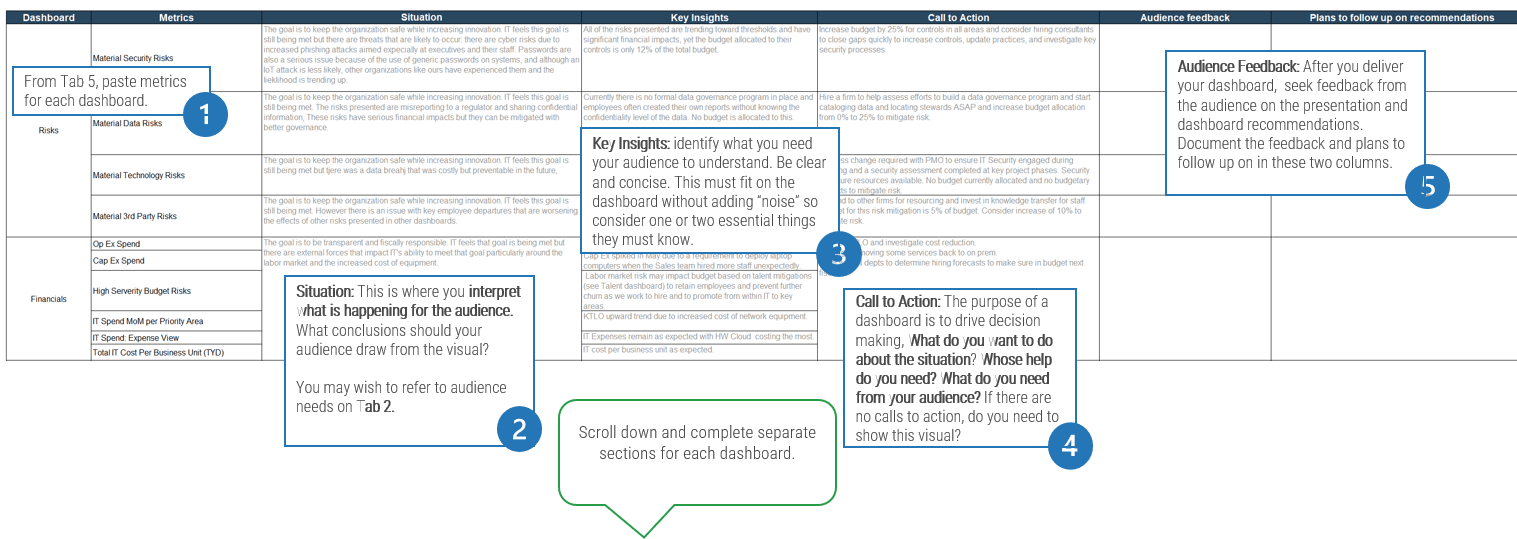
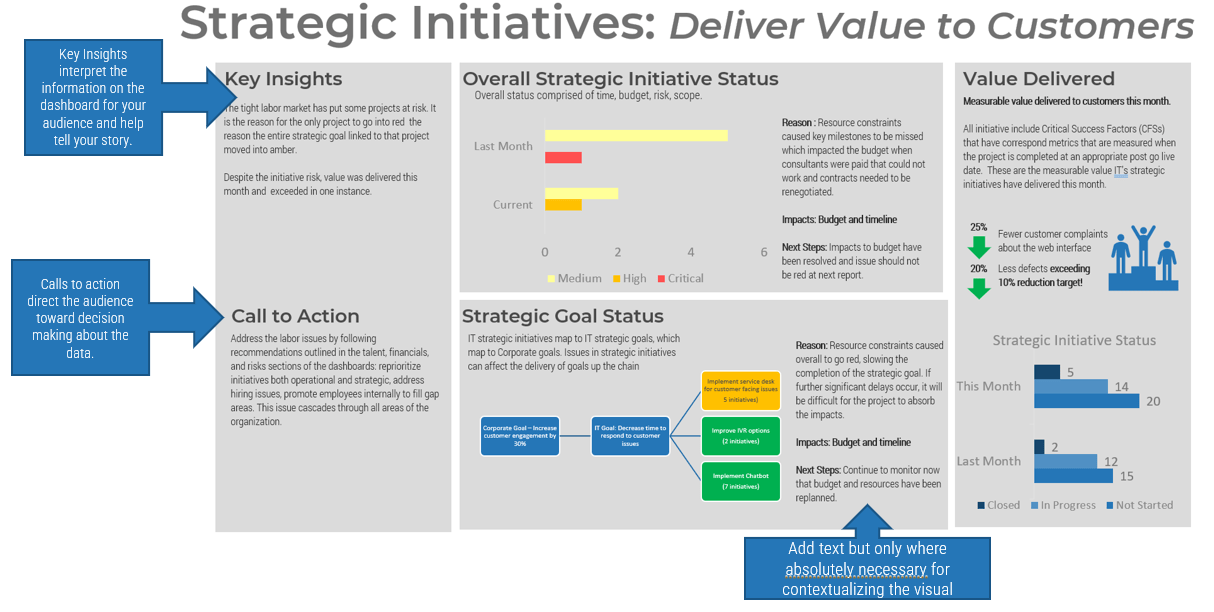
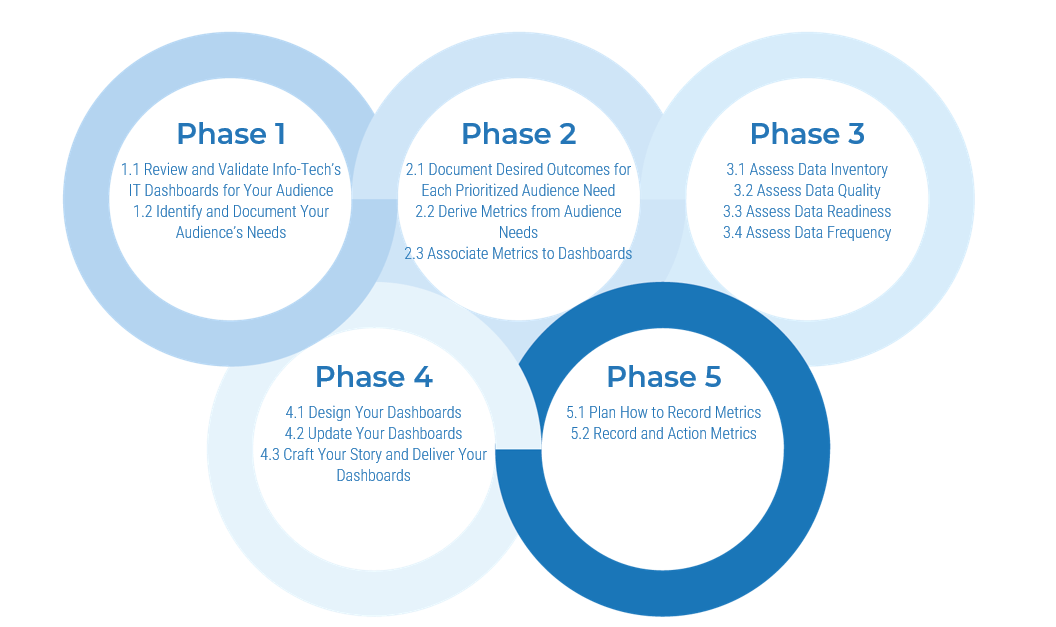

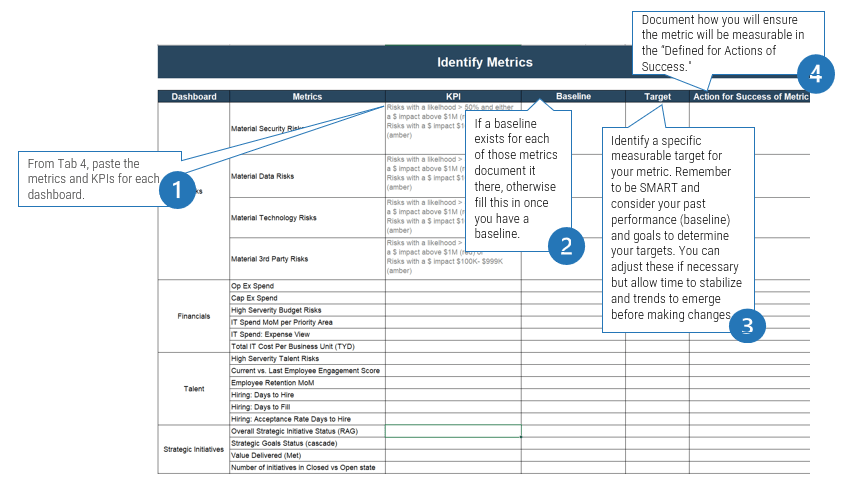
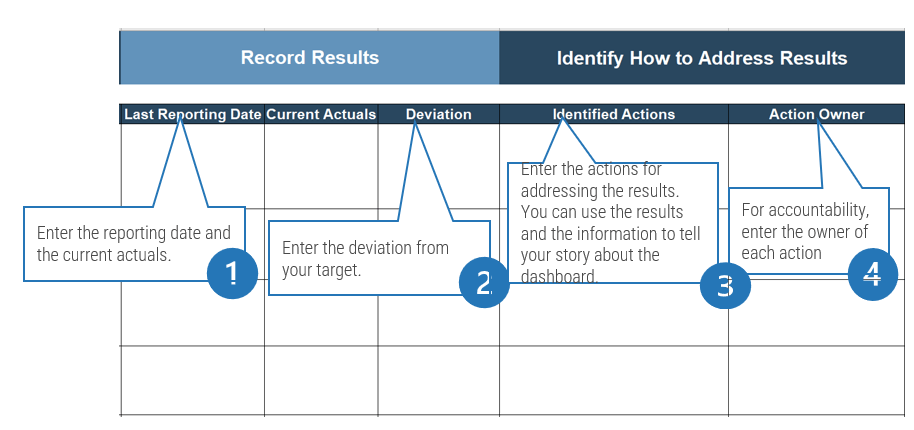












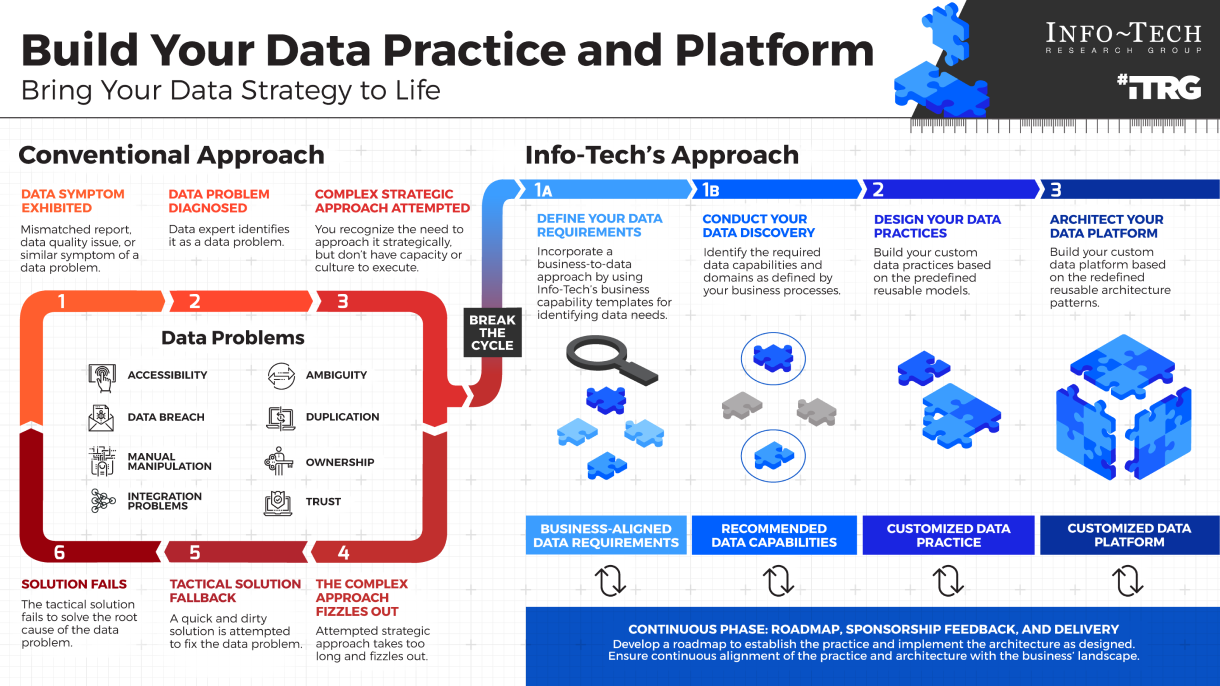




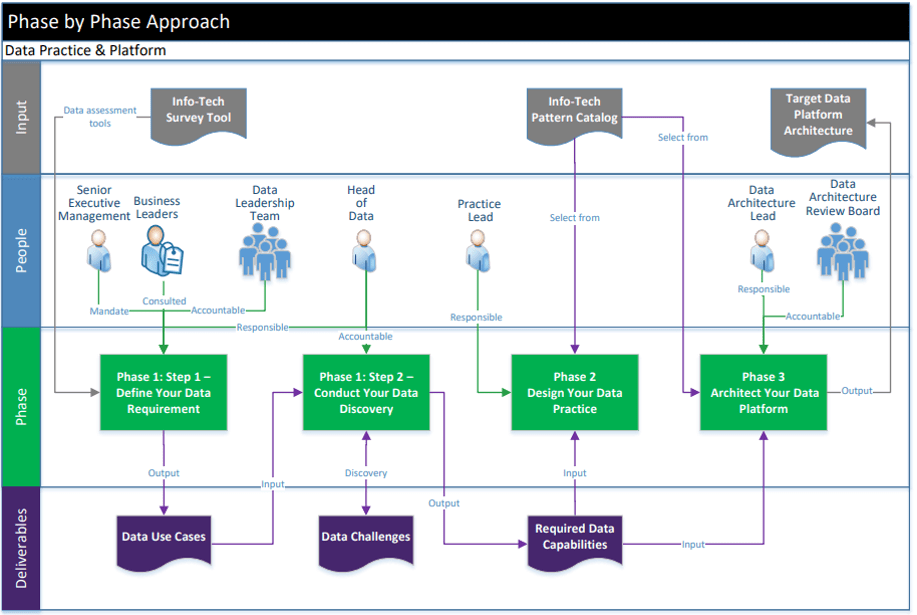


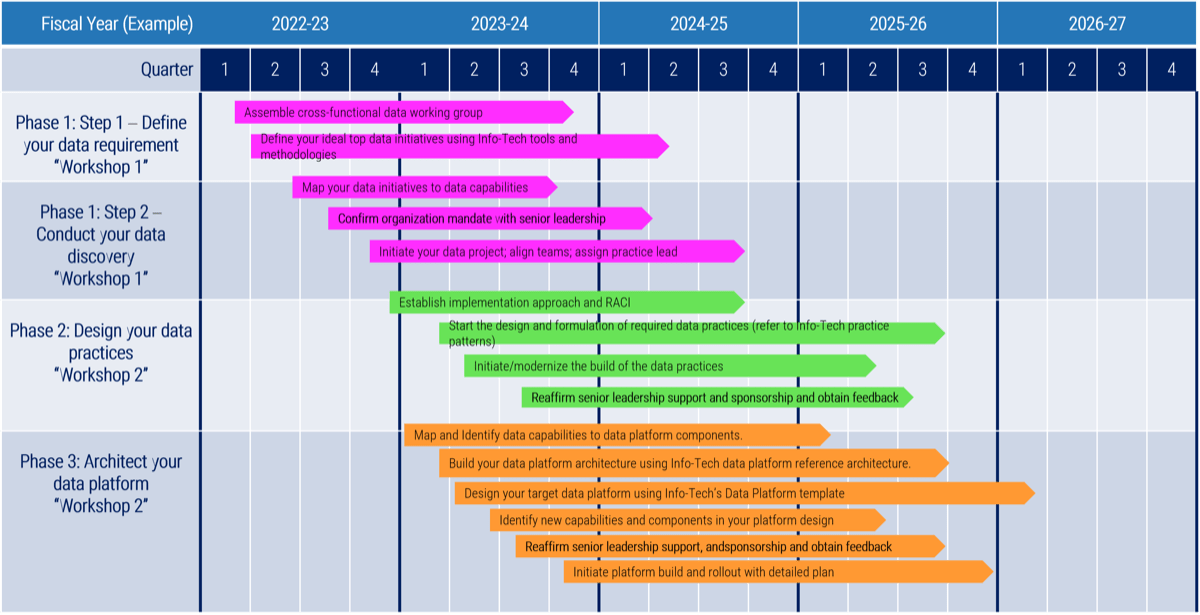
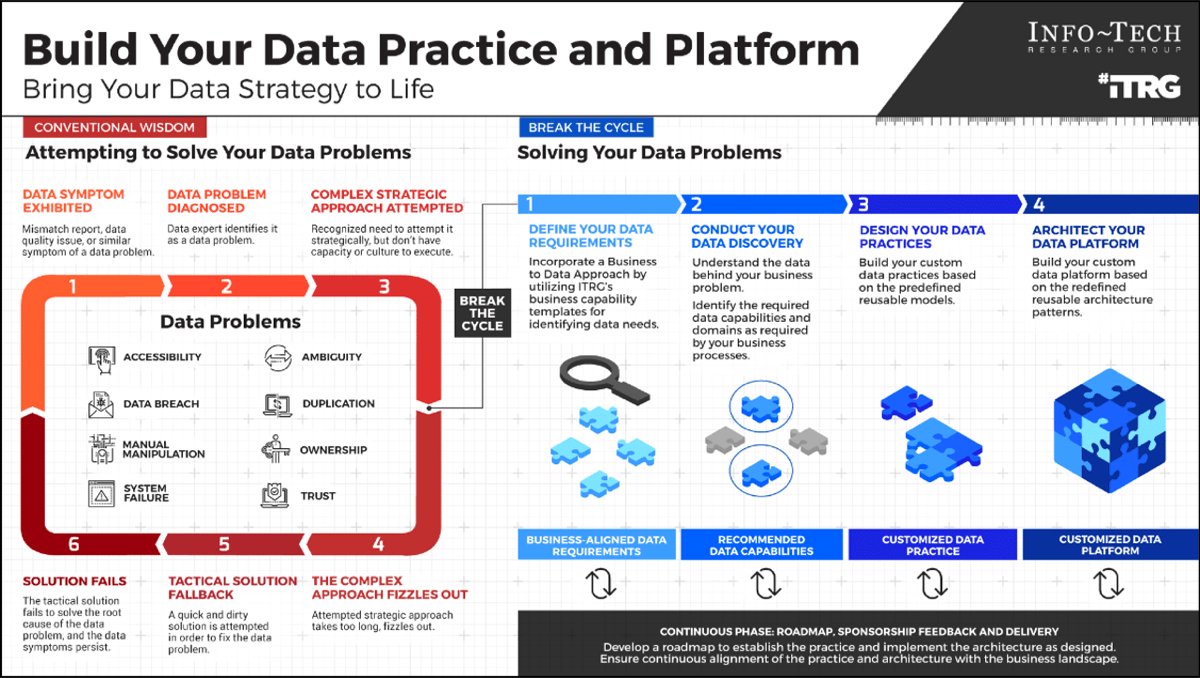



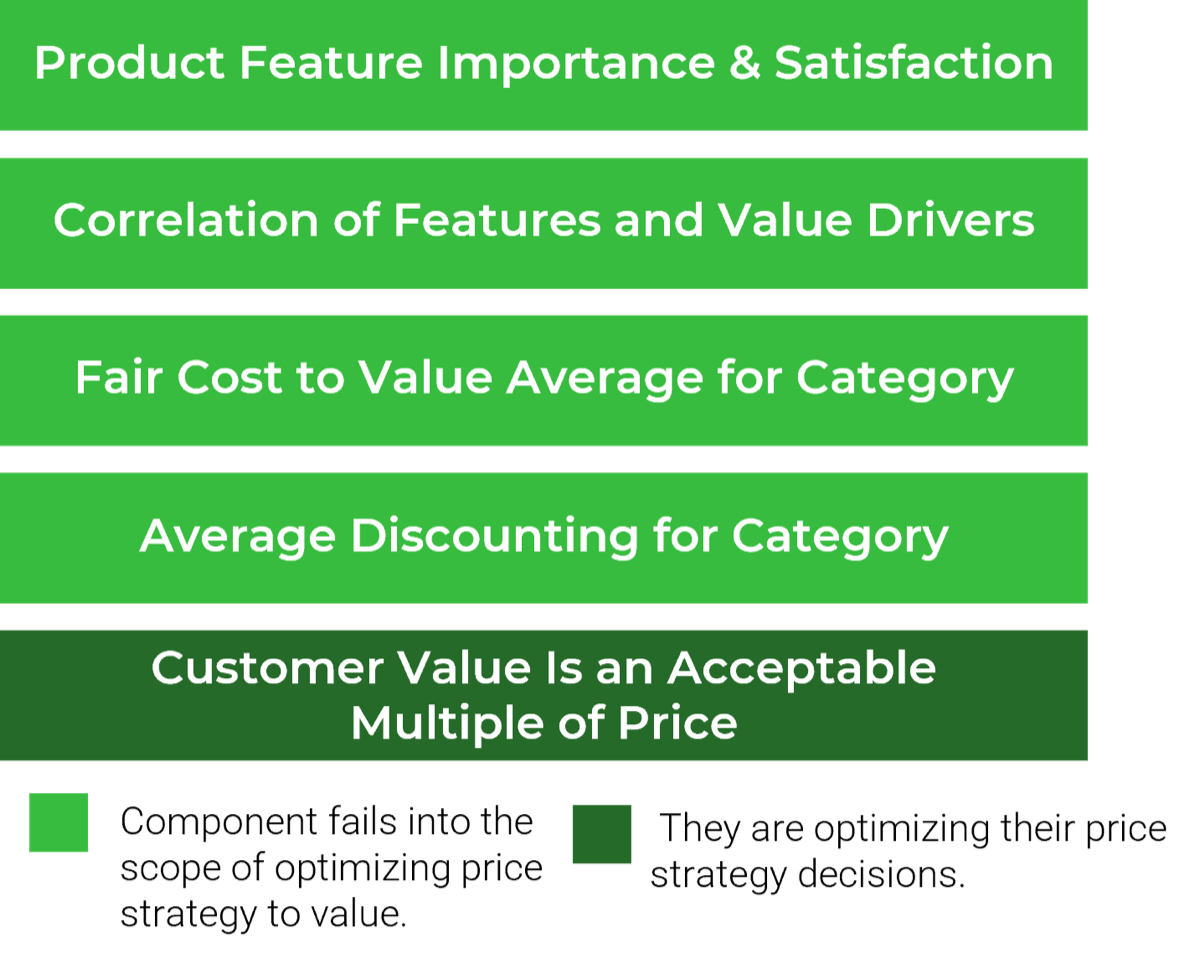





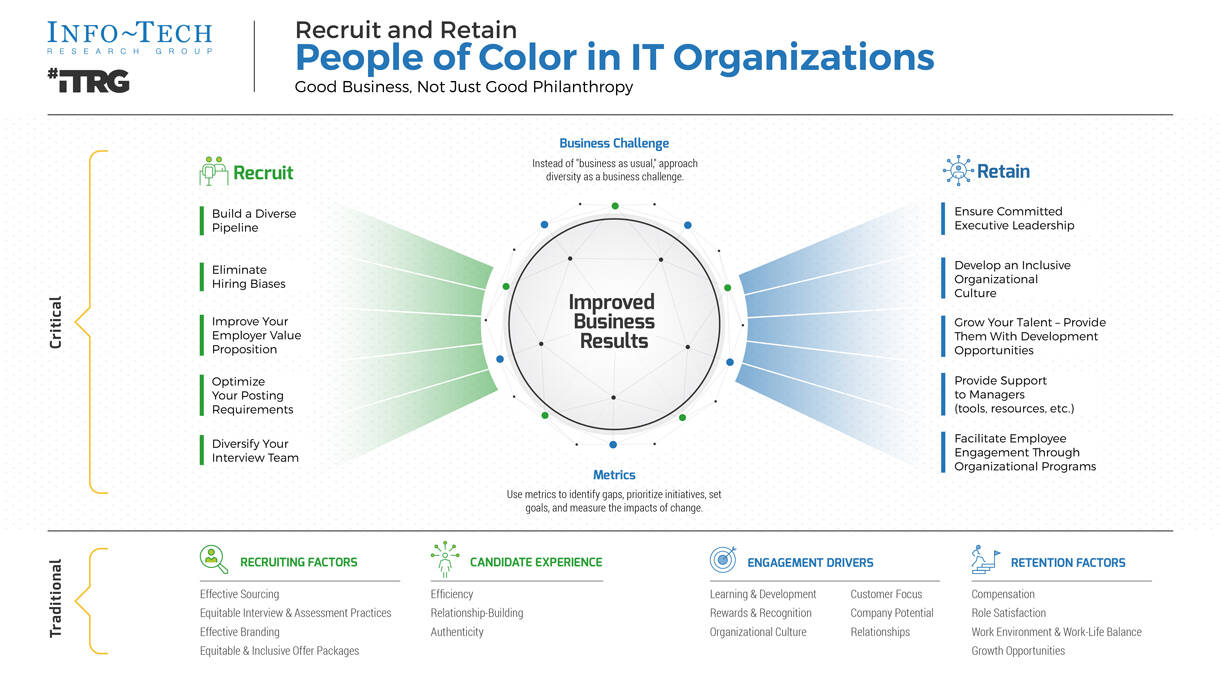









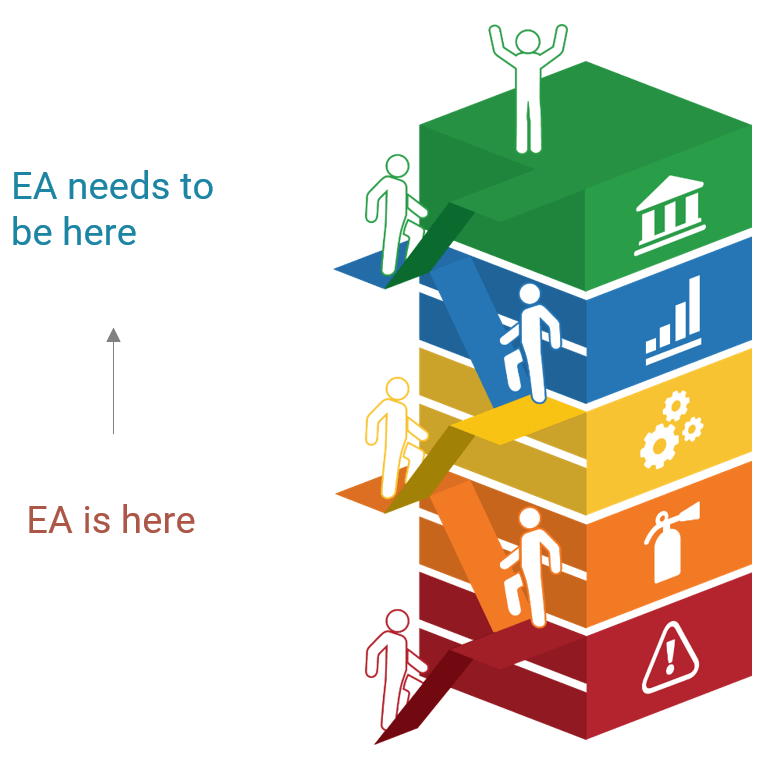
 (Source: The Center for Organizational Design)
(Source: The Center for Organizational Design)
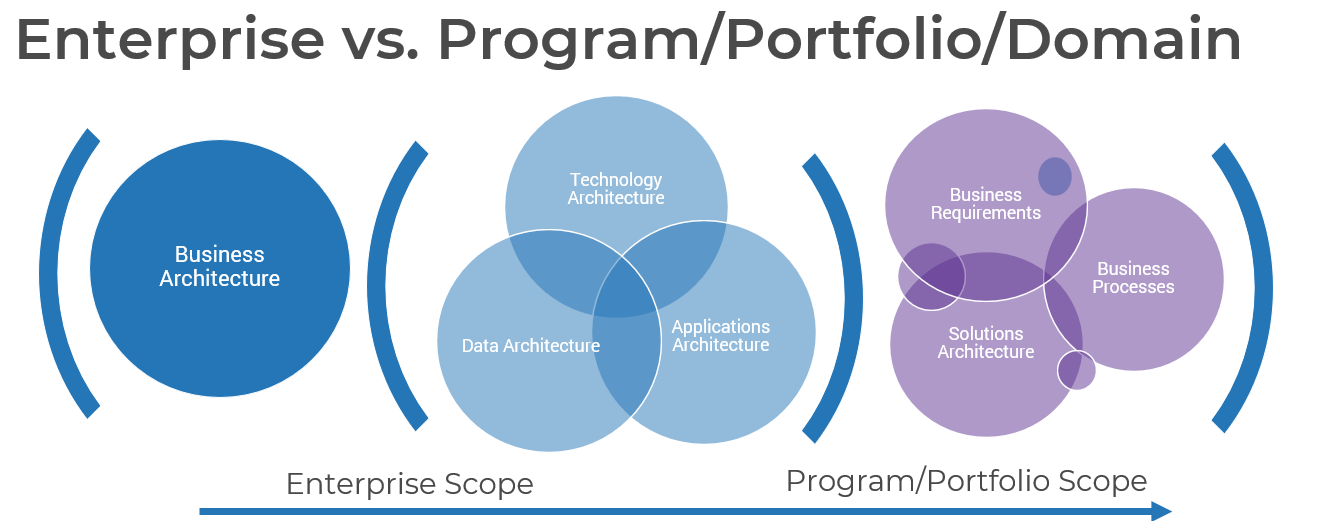
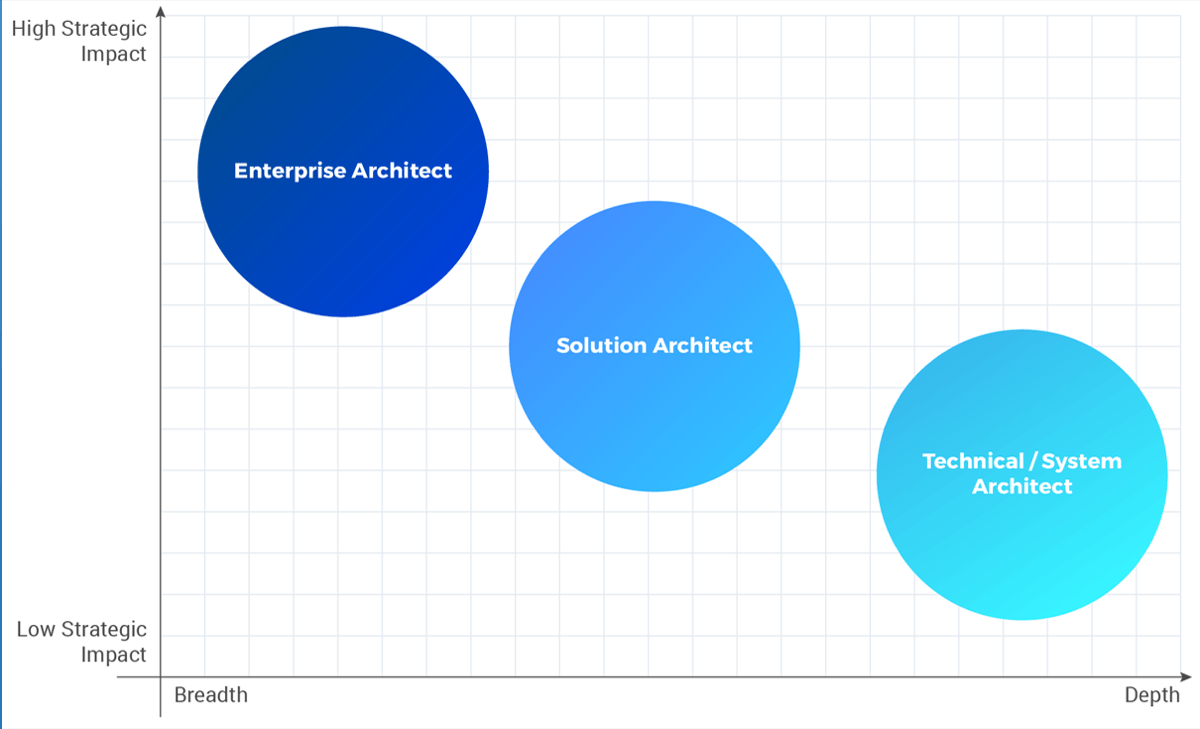
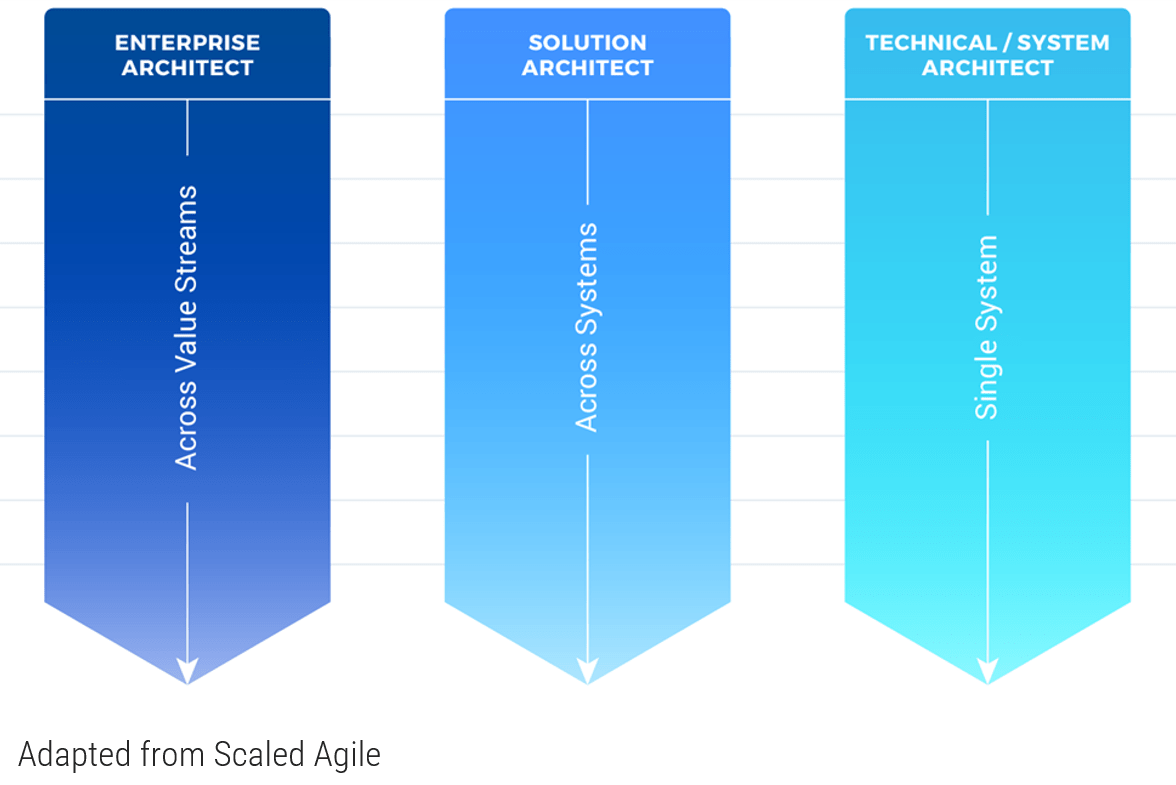
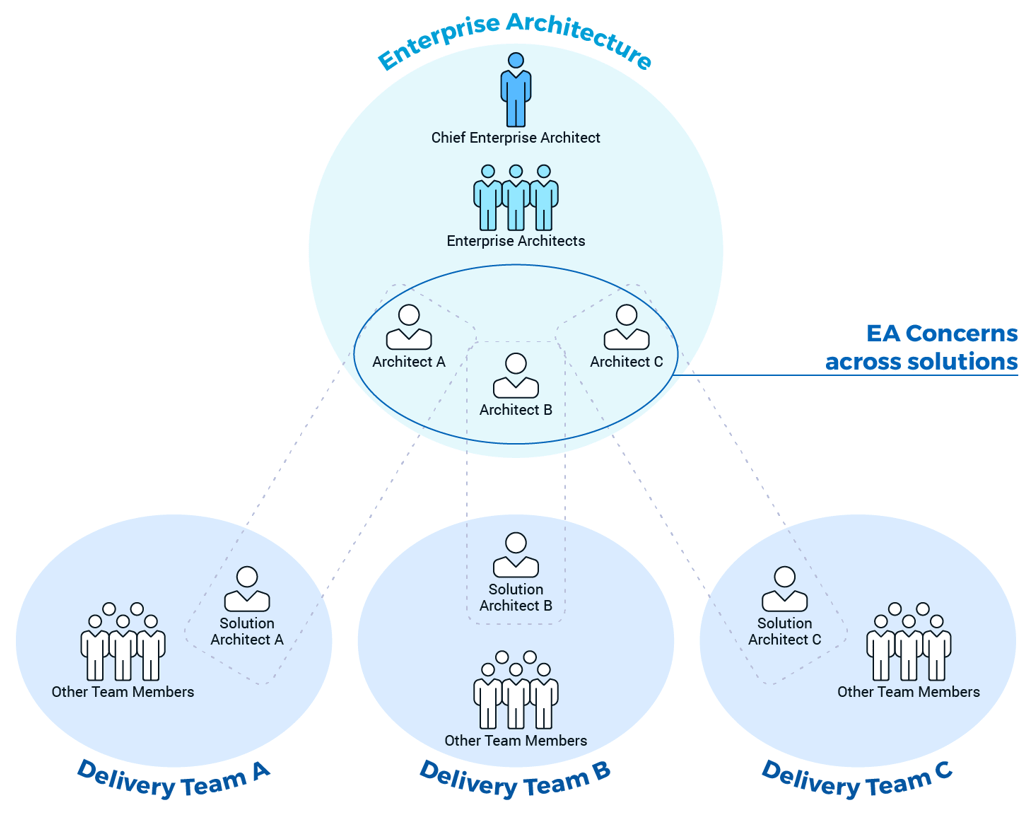 (Adapted from Disciplined Agile)
(Adapted from Disciplined Agile)












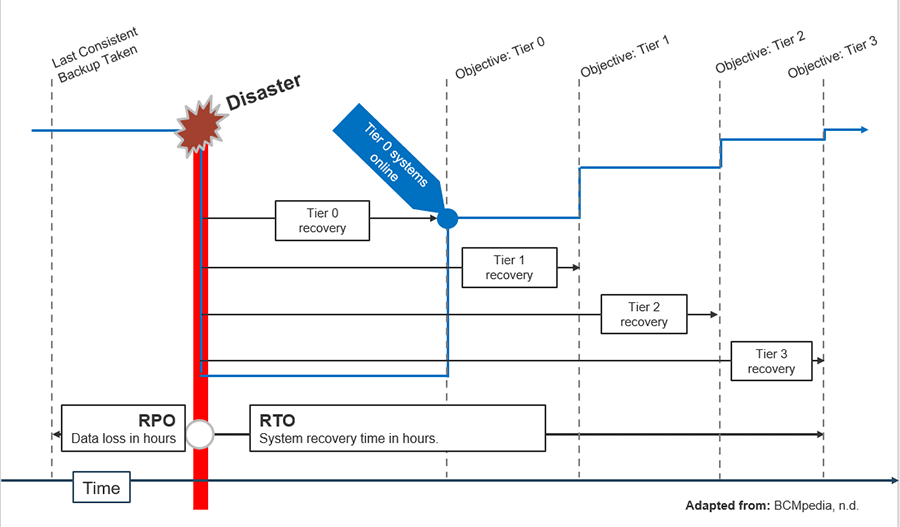
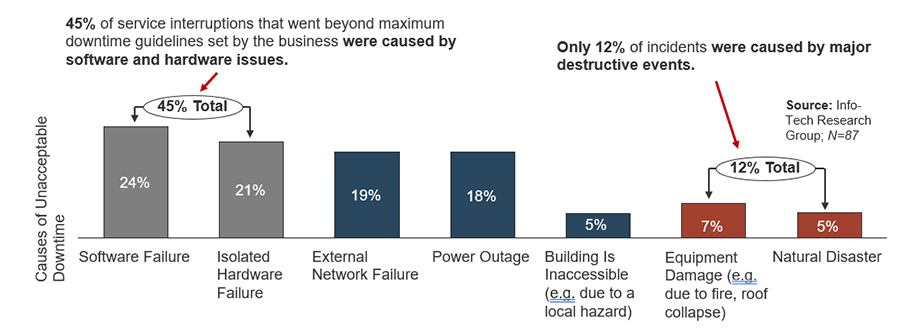
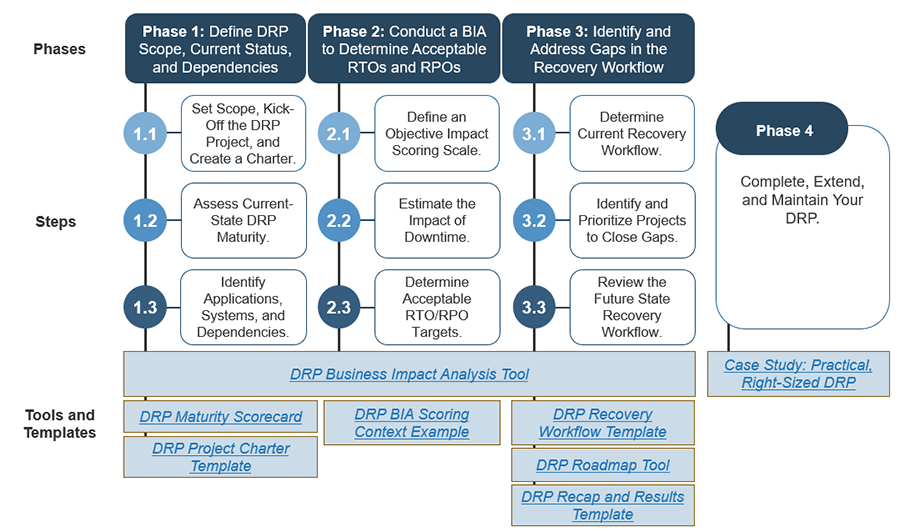
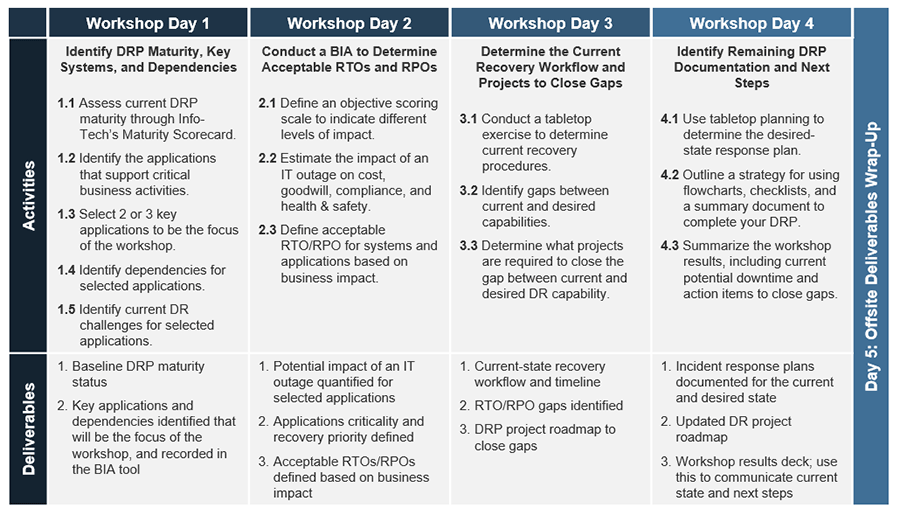
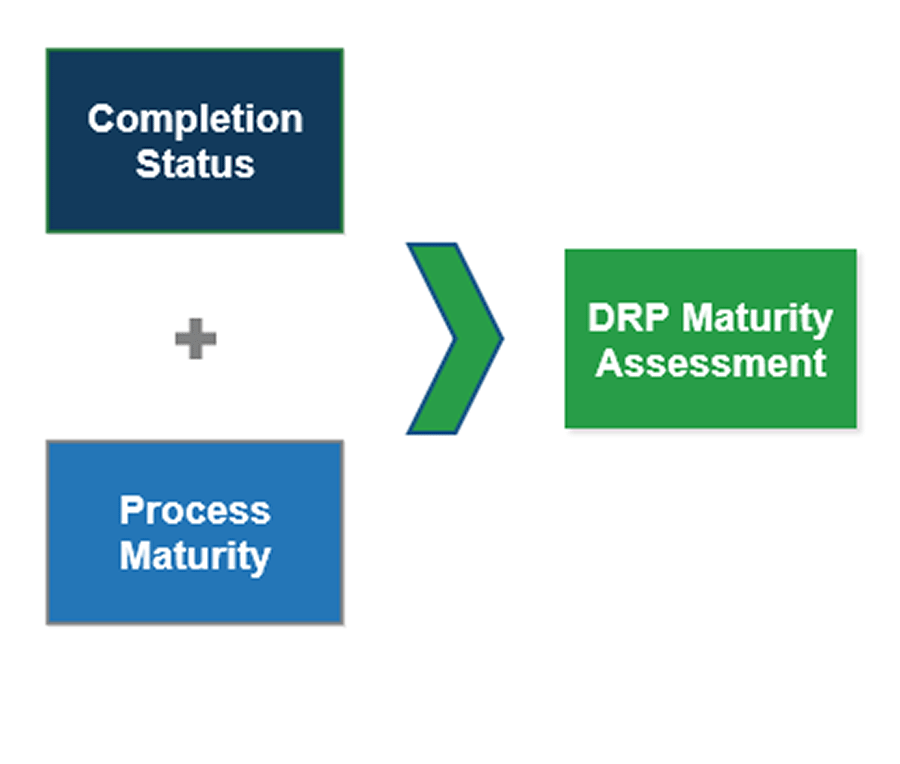
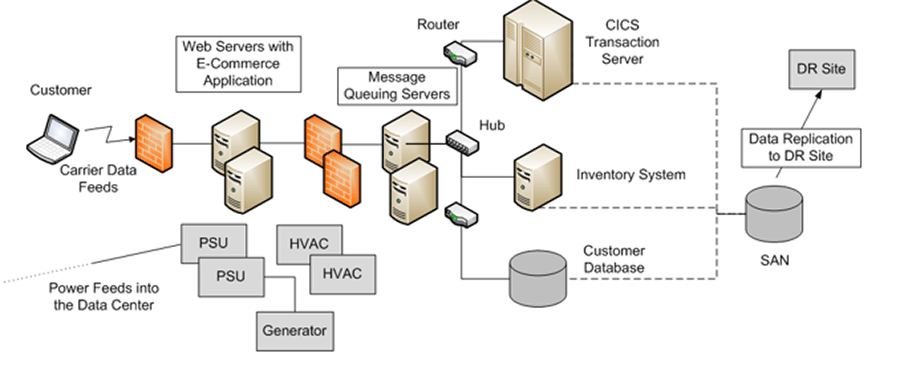
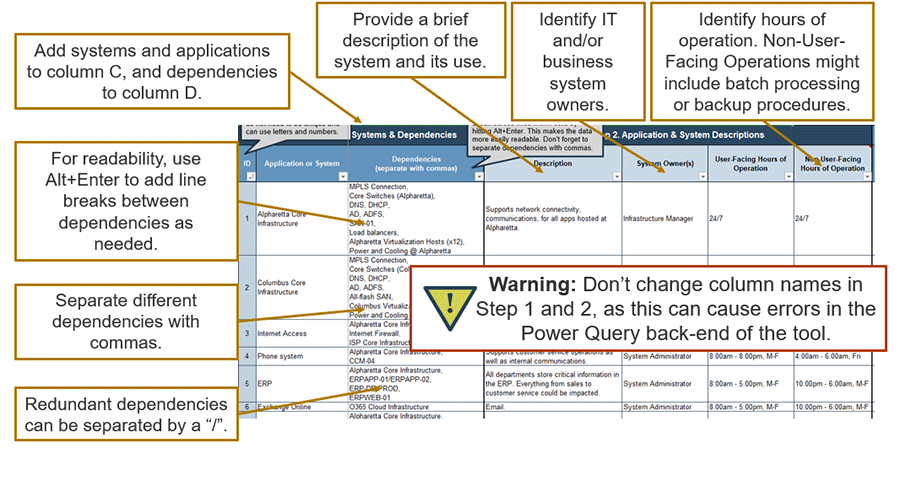
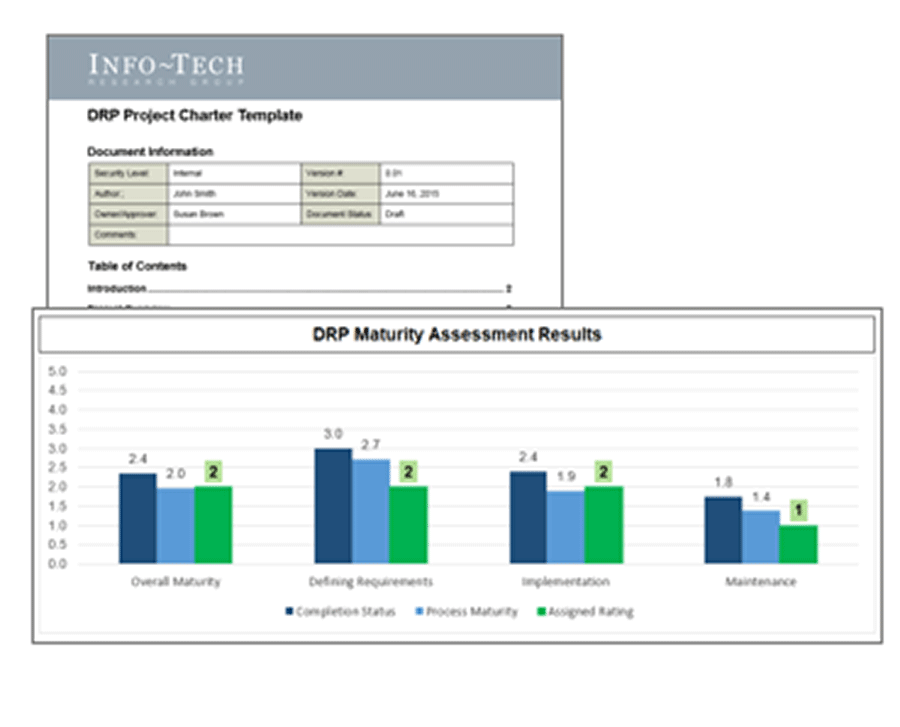
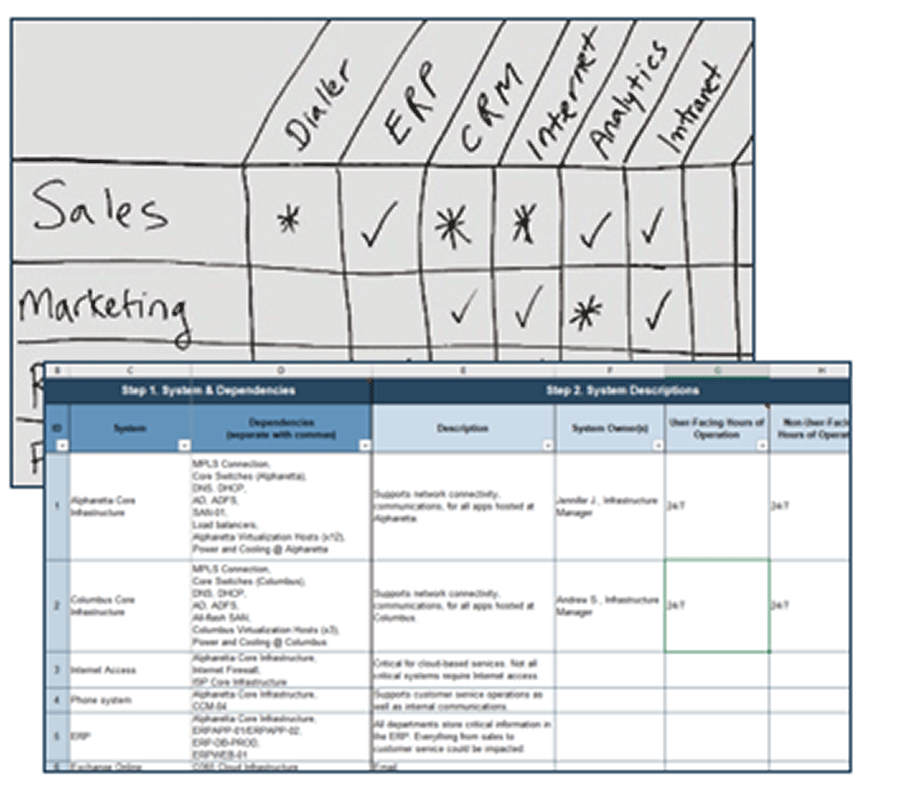
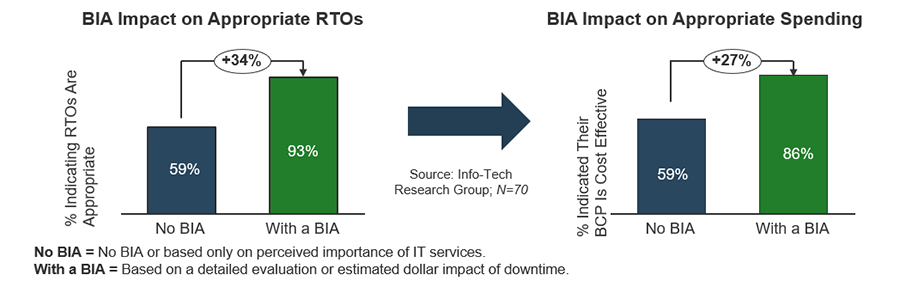
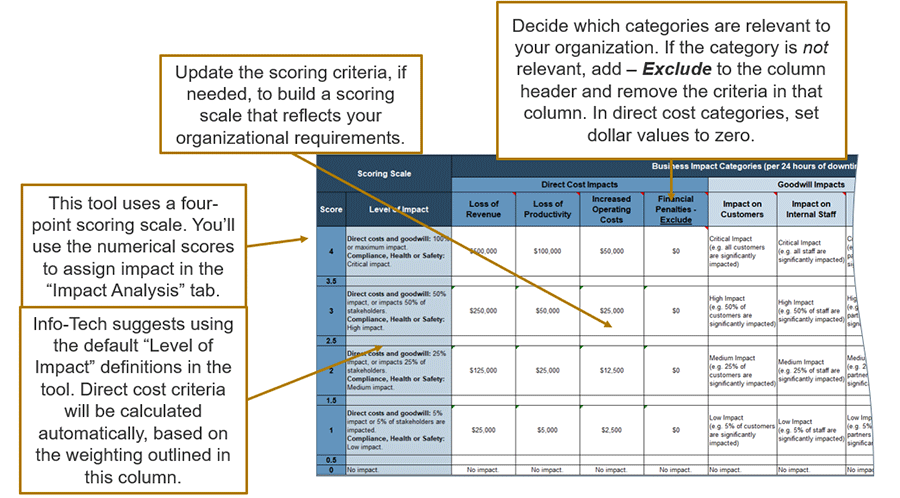
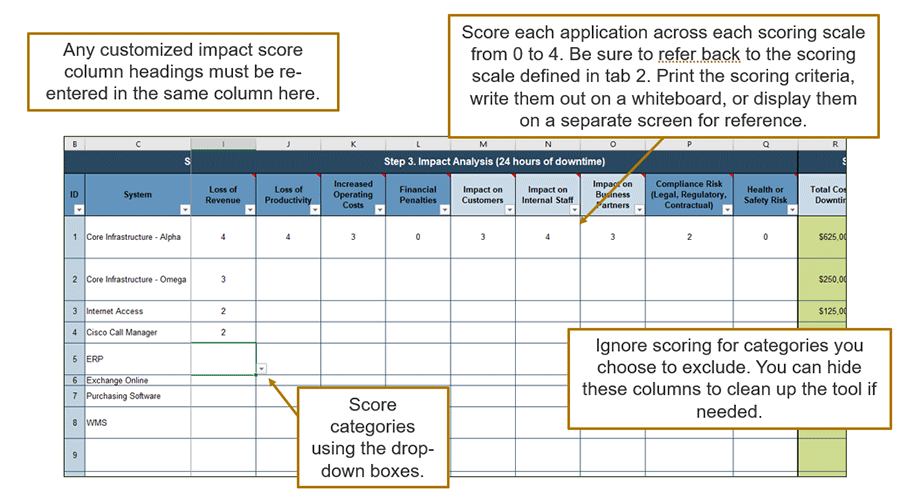

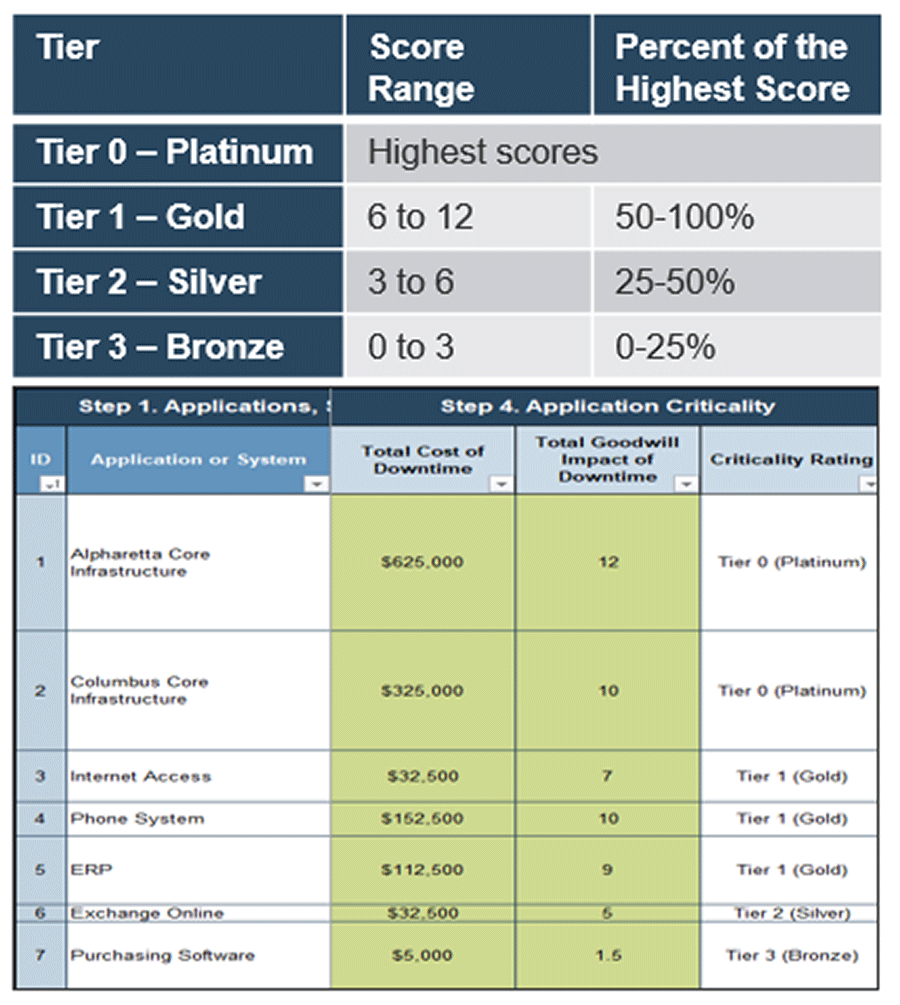
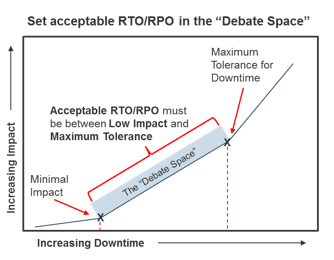
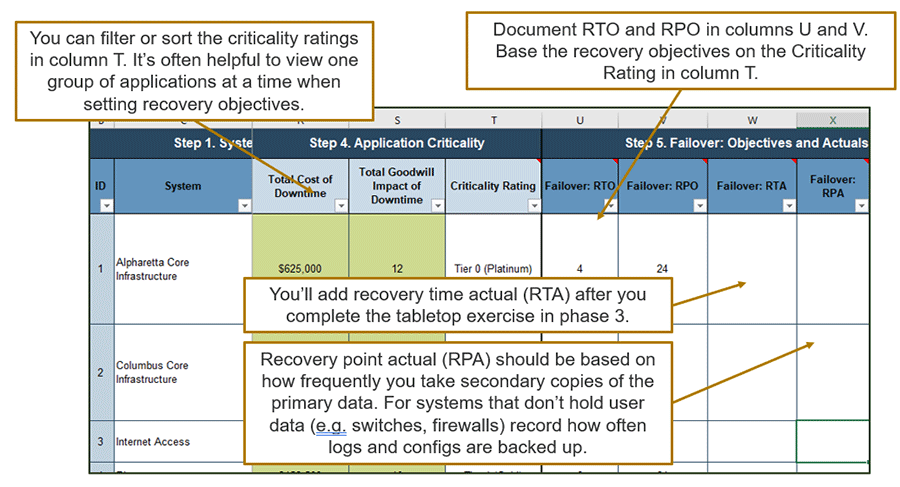
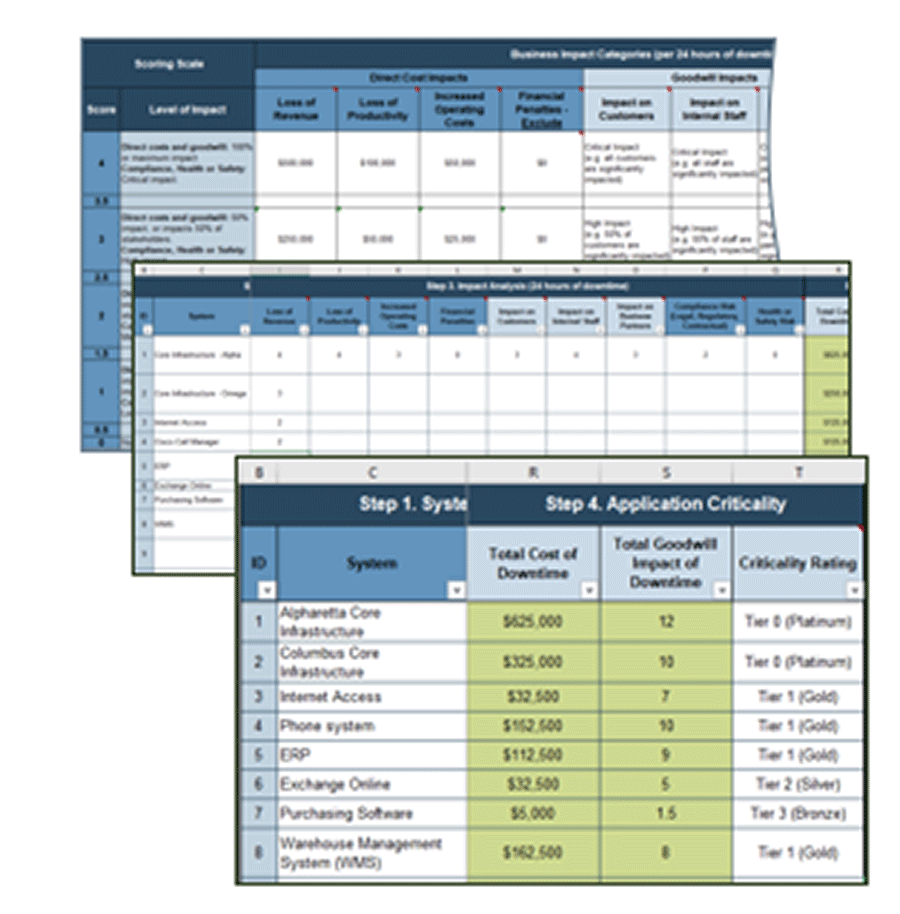
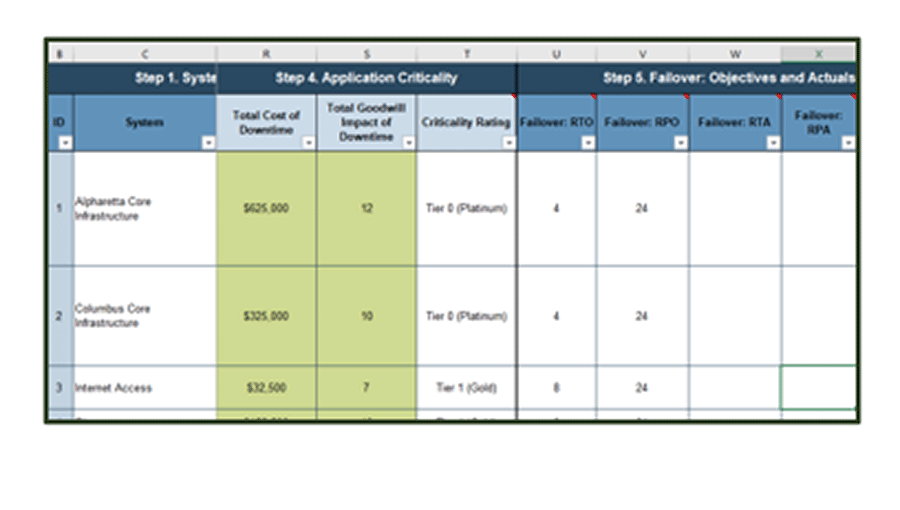
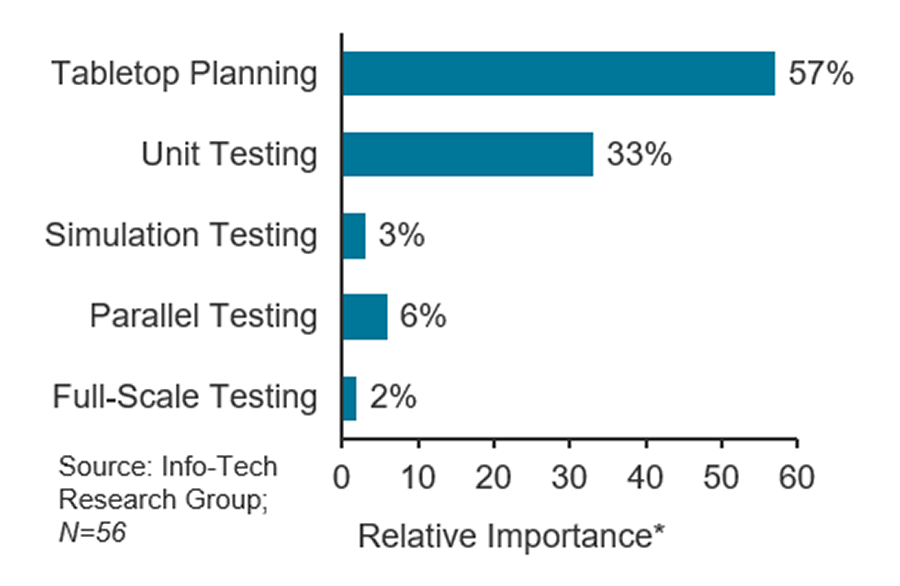
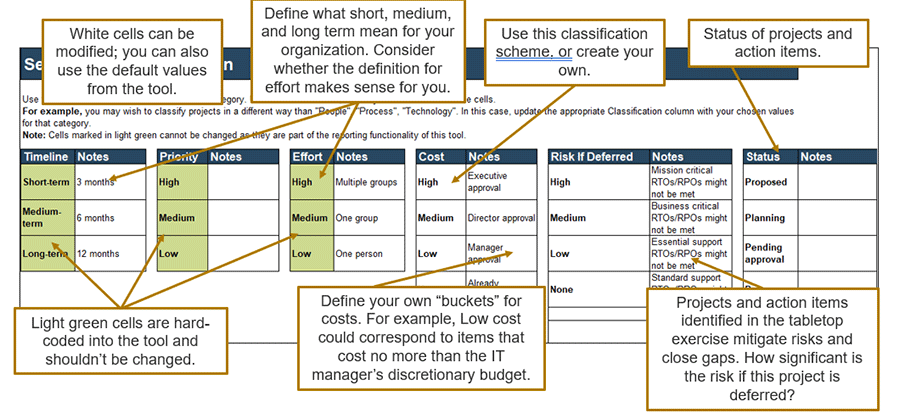
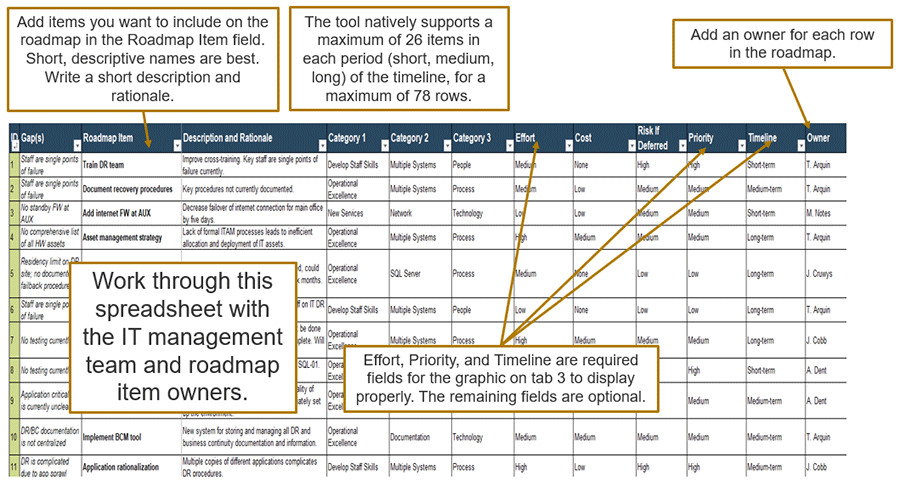
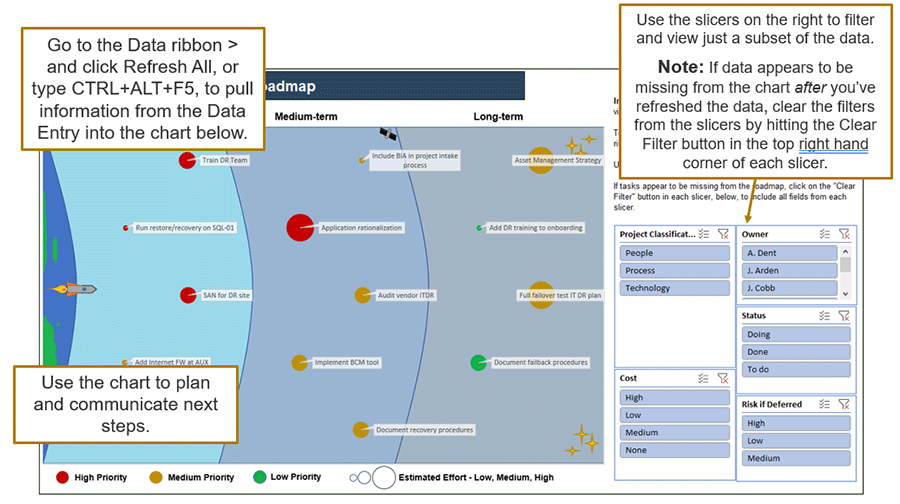

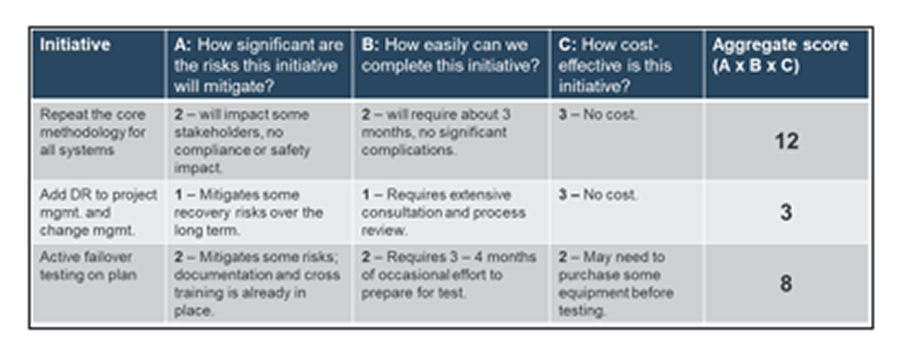


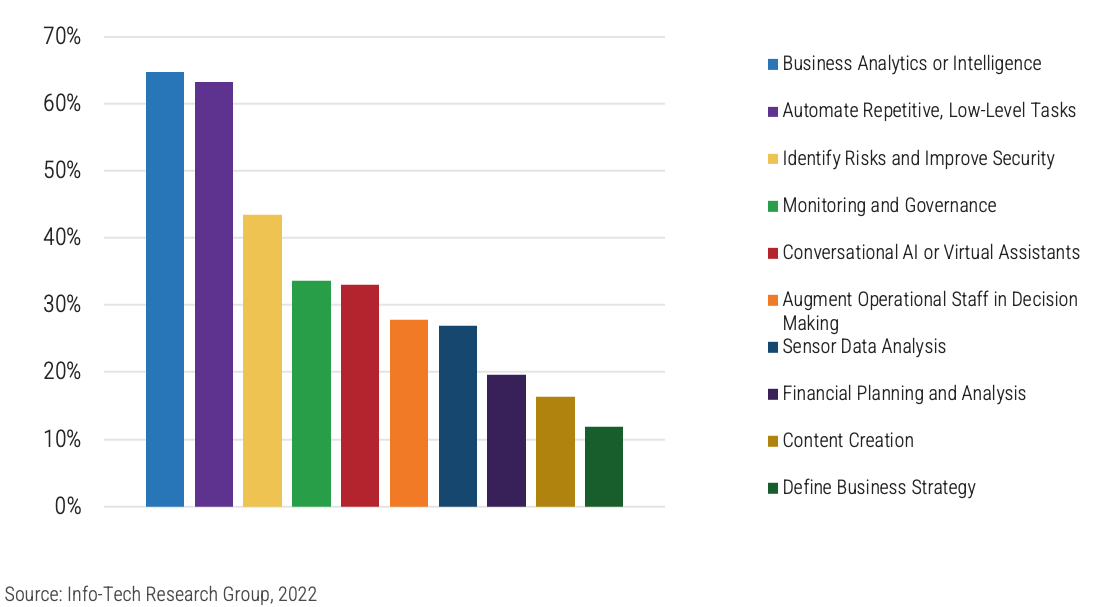






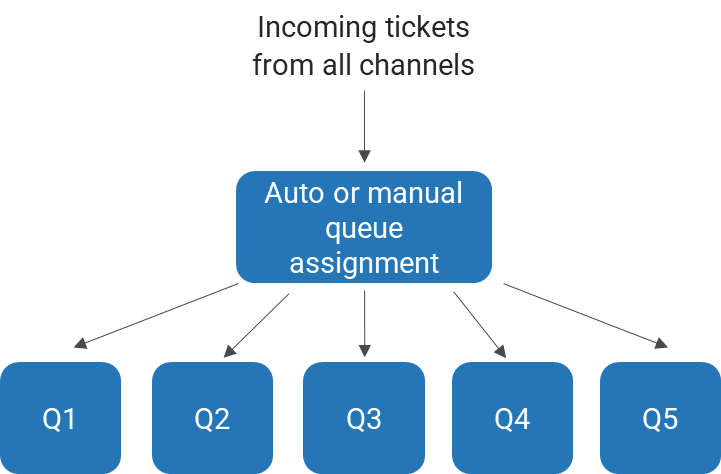
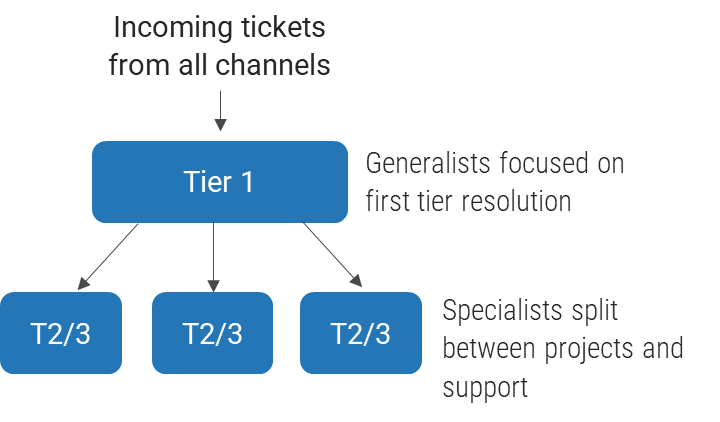
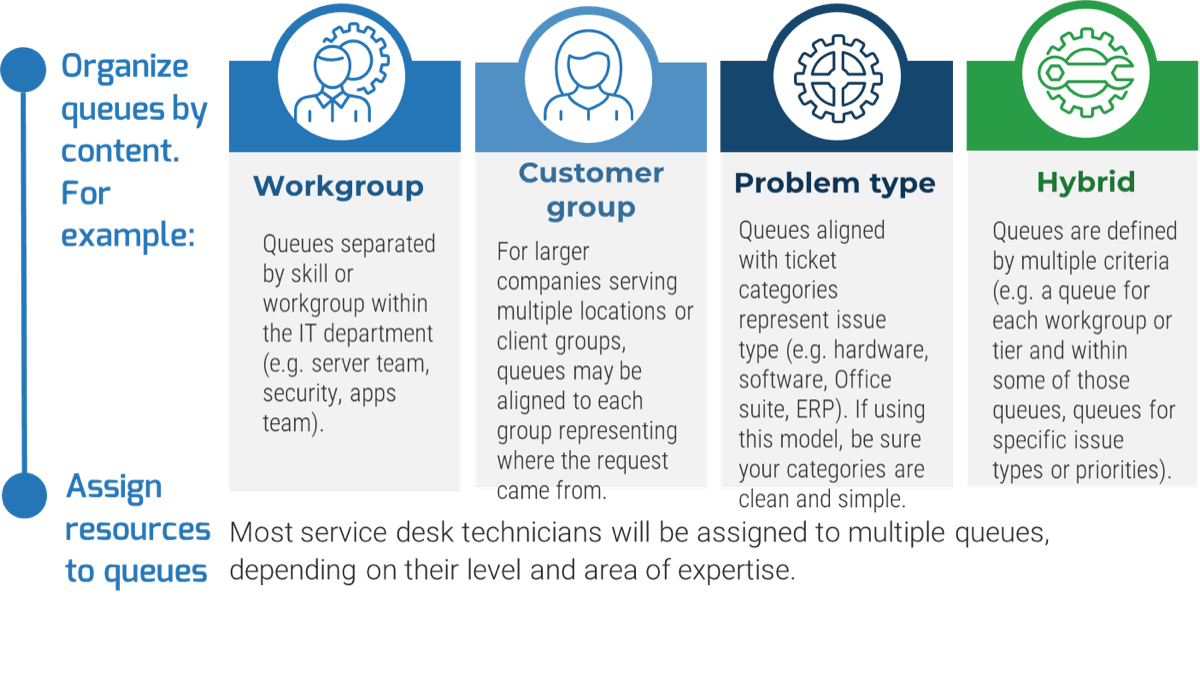
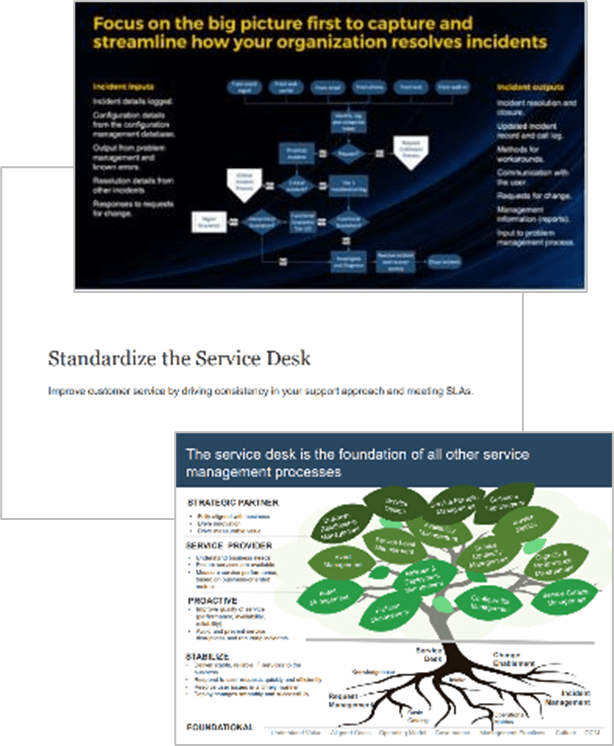









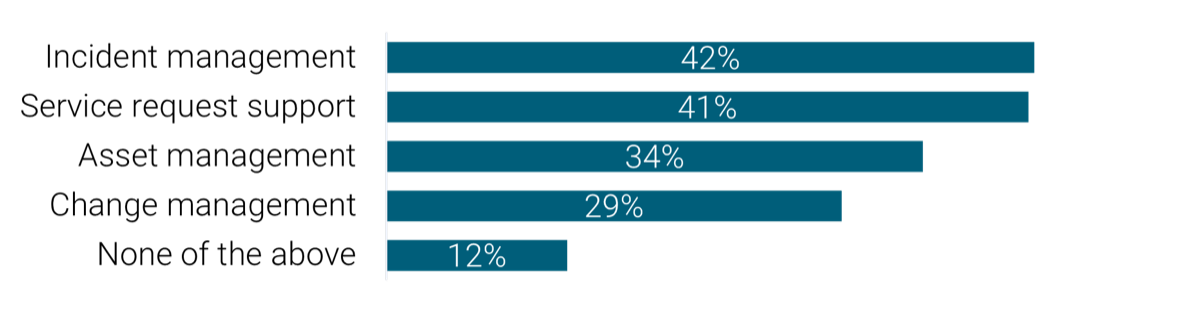
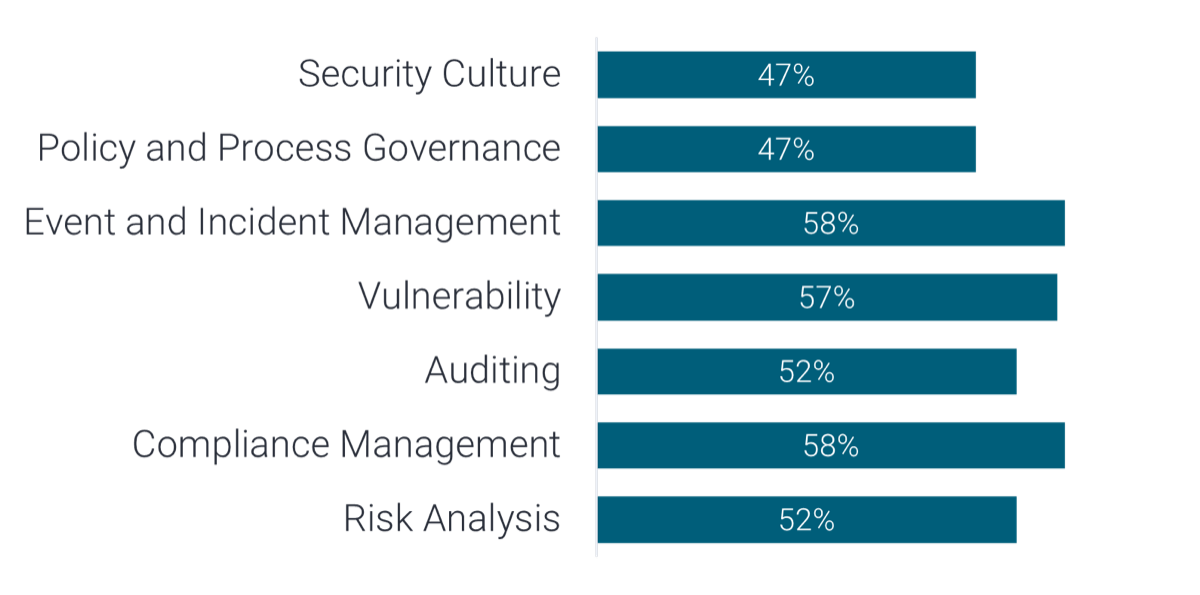
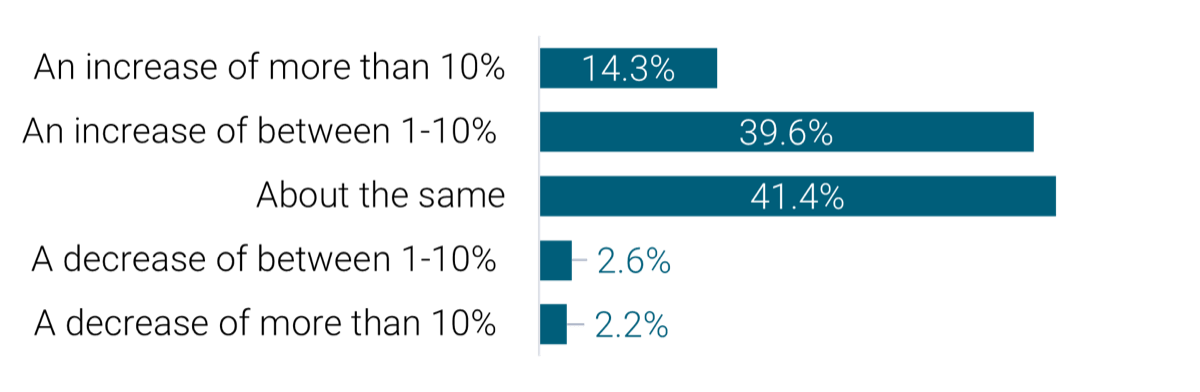
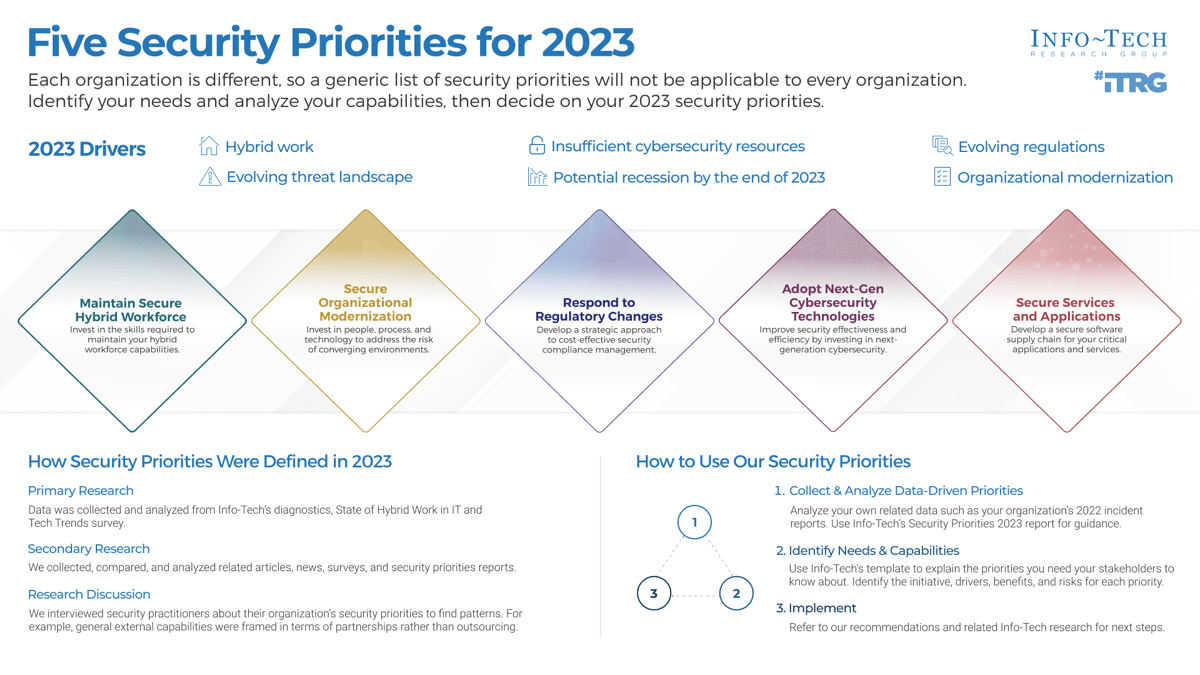
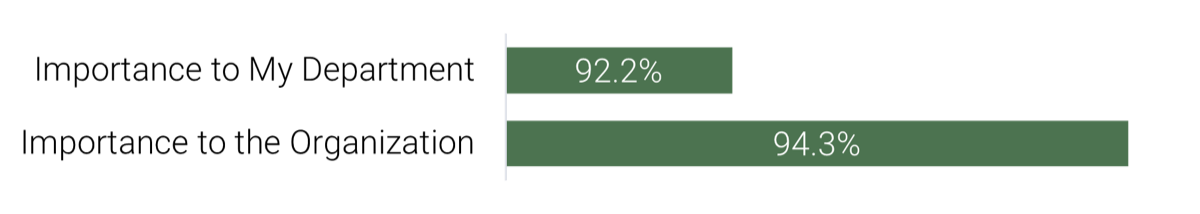
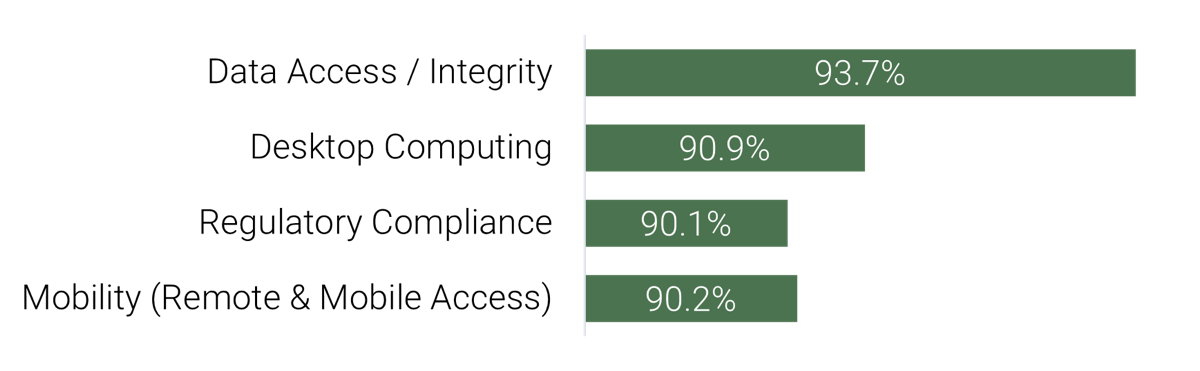
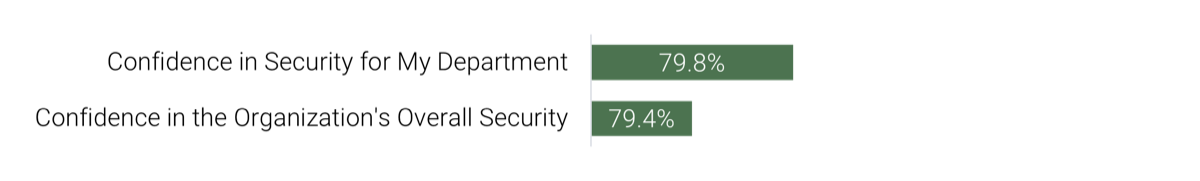
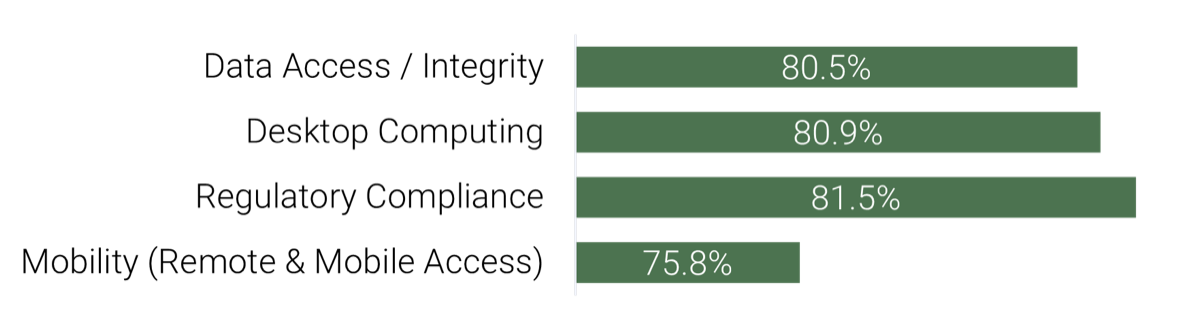







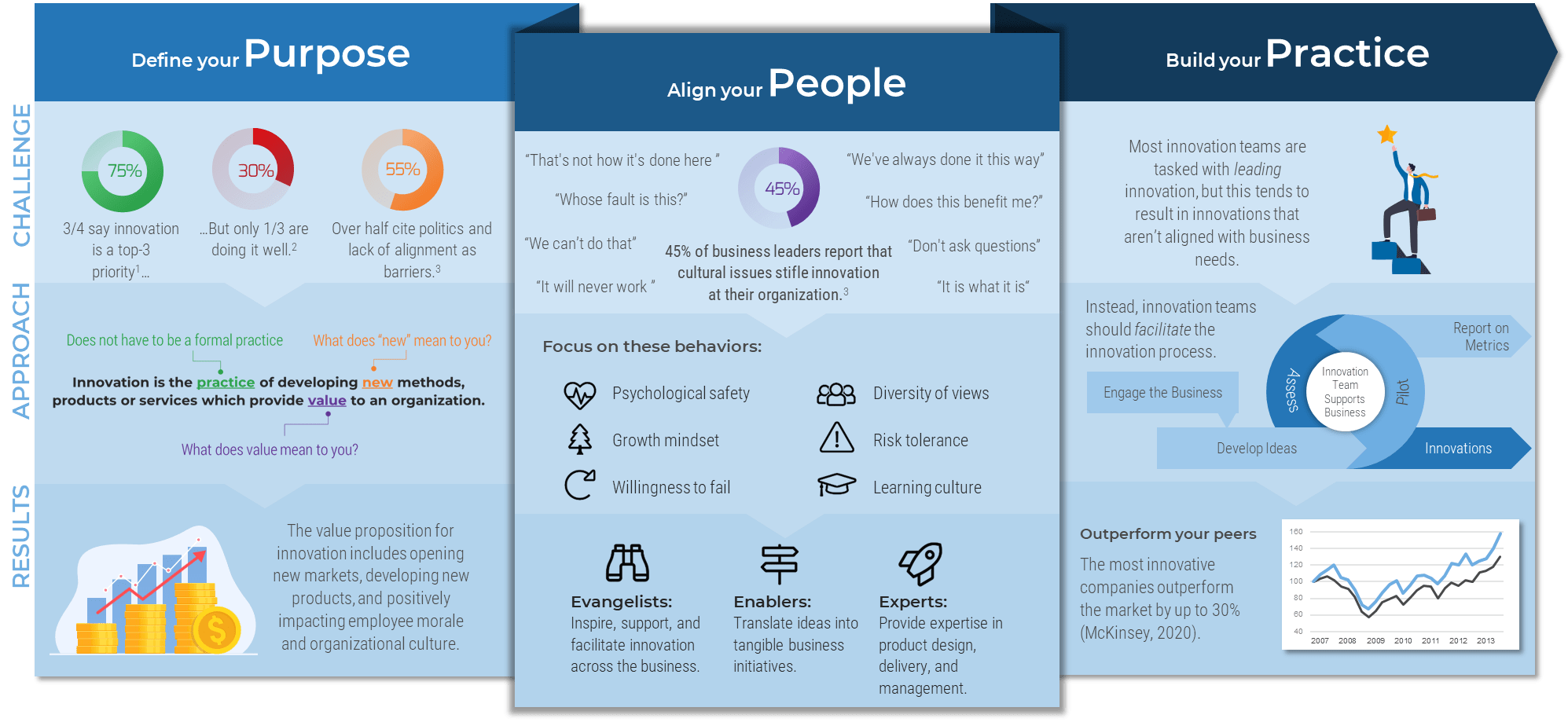







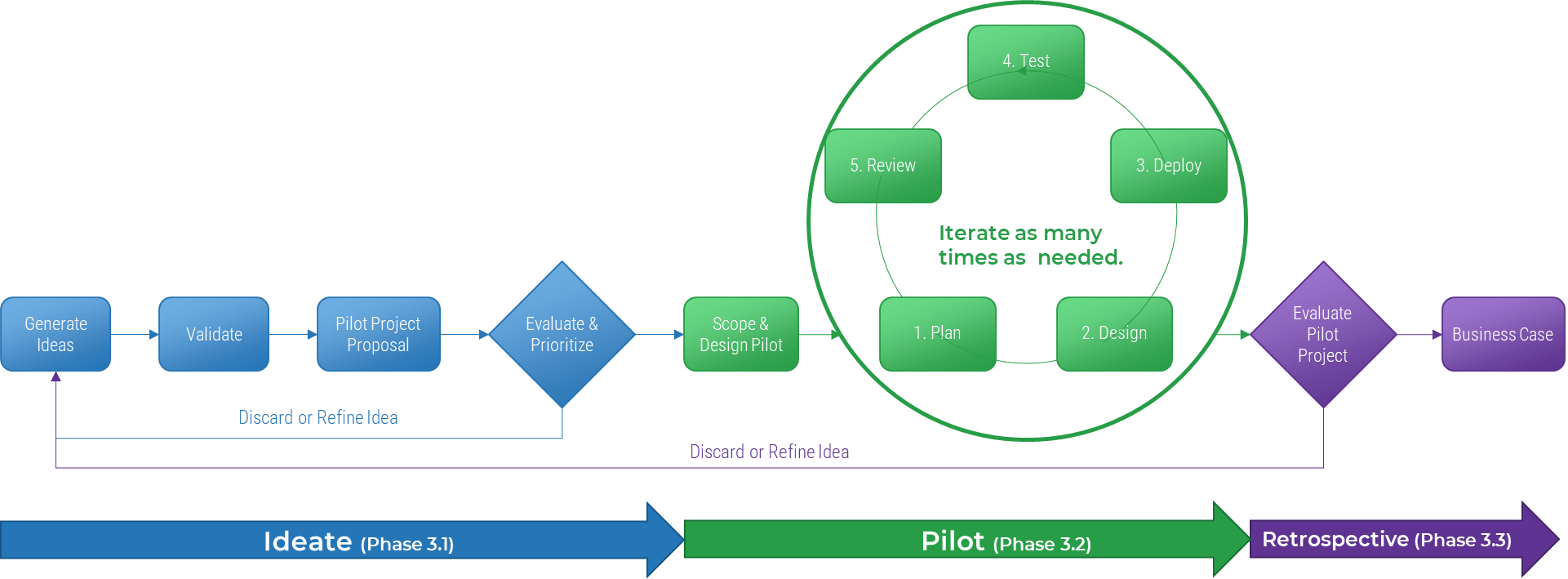





















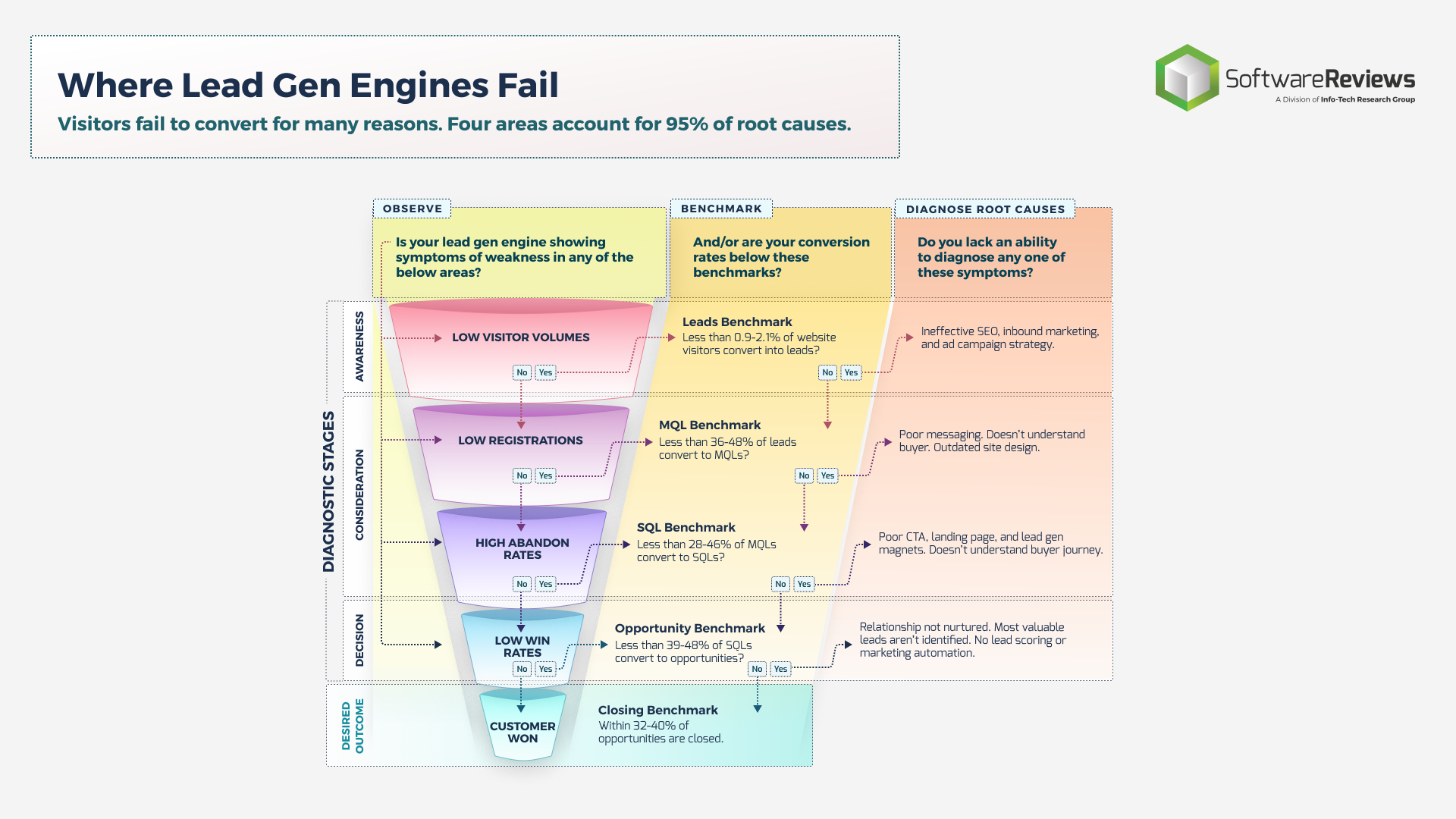
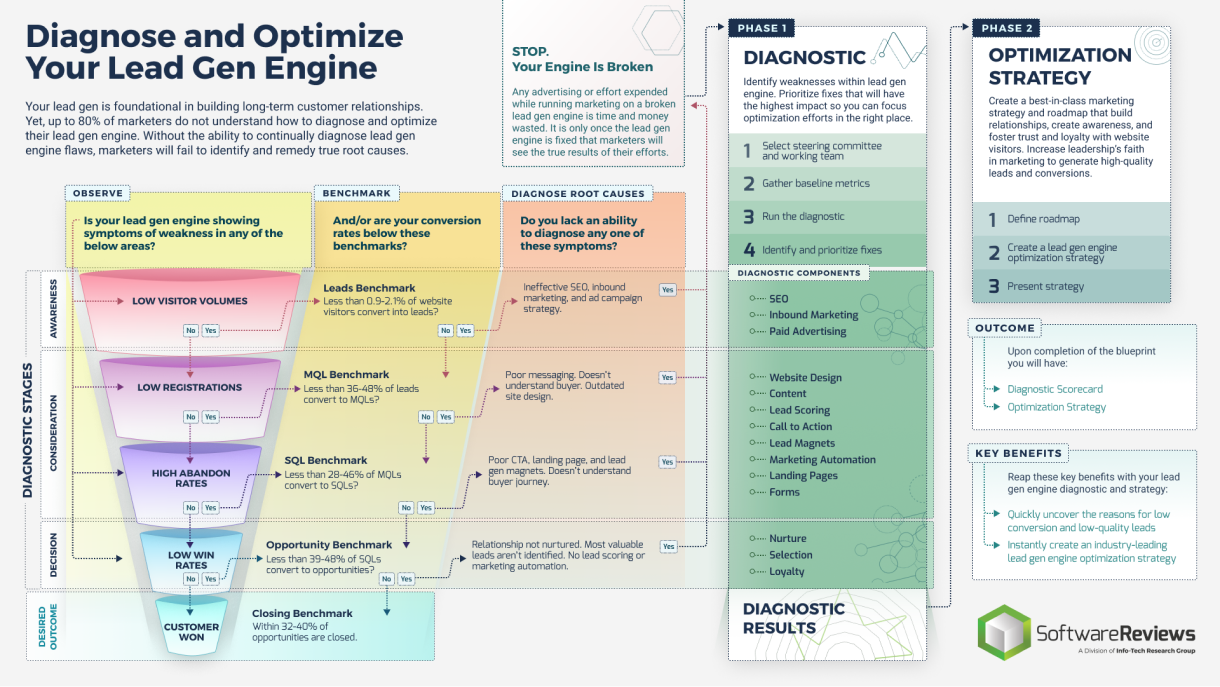
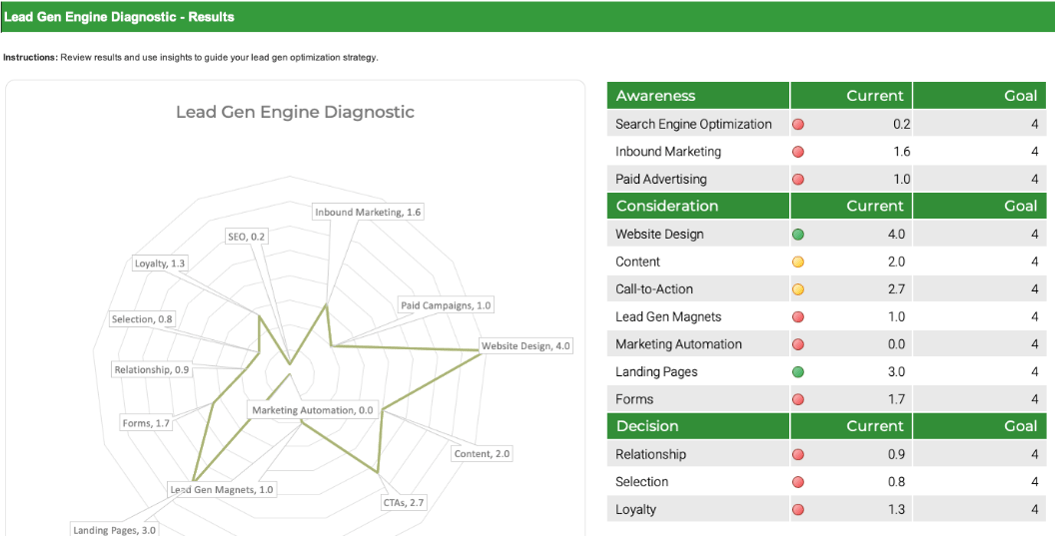
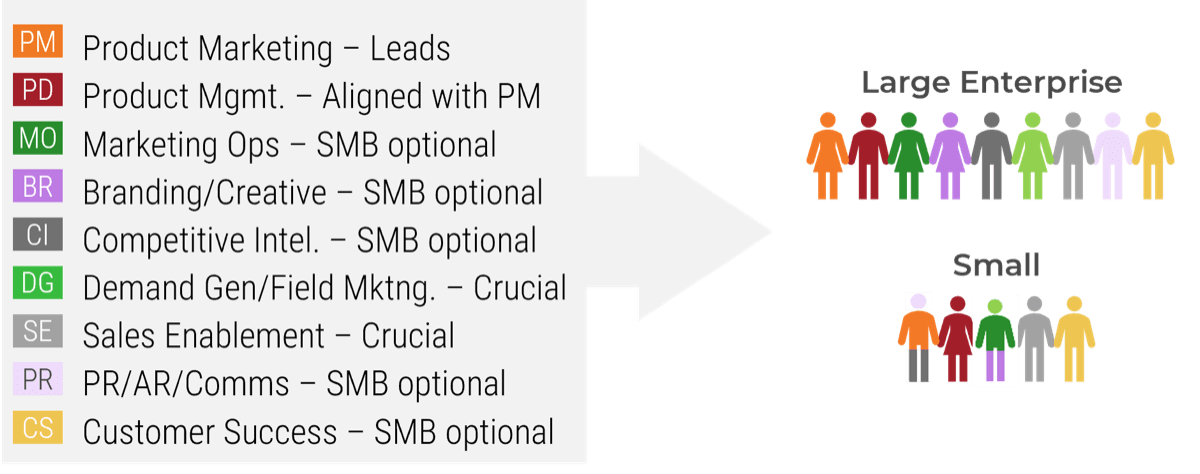

![Map different 'IBM i' scenarios with axes 'Importance to Business Outcomes - Low to High' and 'Vendor’s Performance Advantage - Low to High'. Quadrant labels are '[LI/LA] Potentially Outsource: Service management, Help desk, desk-side support, Asset management', '[LI/HA] Outsource: Application & Infra Support, Web Hosting, SAP Support, Email Services, Infrastructure', '[HI/LA] Insource (For Now): Application development tech support', and '[HI/HA] Potentially Outsource: Onshore or offshore application maintenance'.](/images/ITMGF/infra-and-operations/i-and-o-process-management/strategy-and-organizational-design/ibm-i-migration-considerations/04-ibmi-map-importance-advantage.png)